Crebanine Induces Cell Death and Alters the Mitotic Process in Renal Cell Carcinoma In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
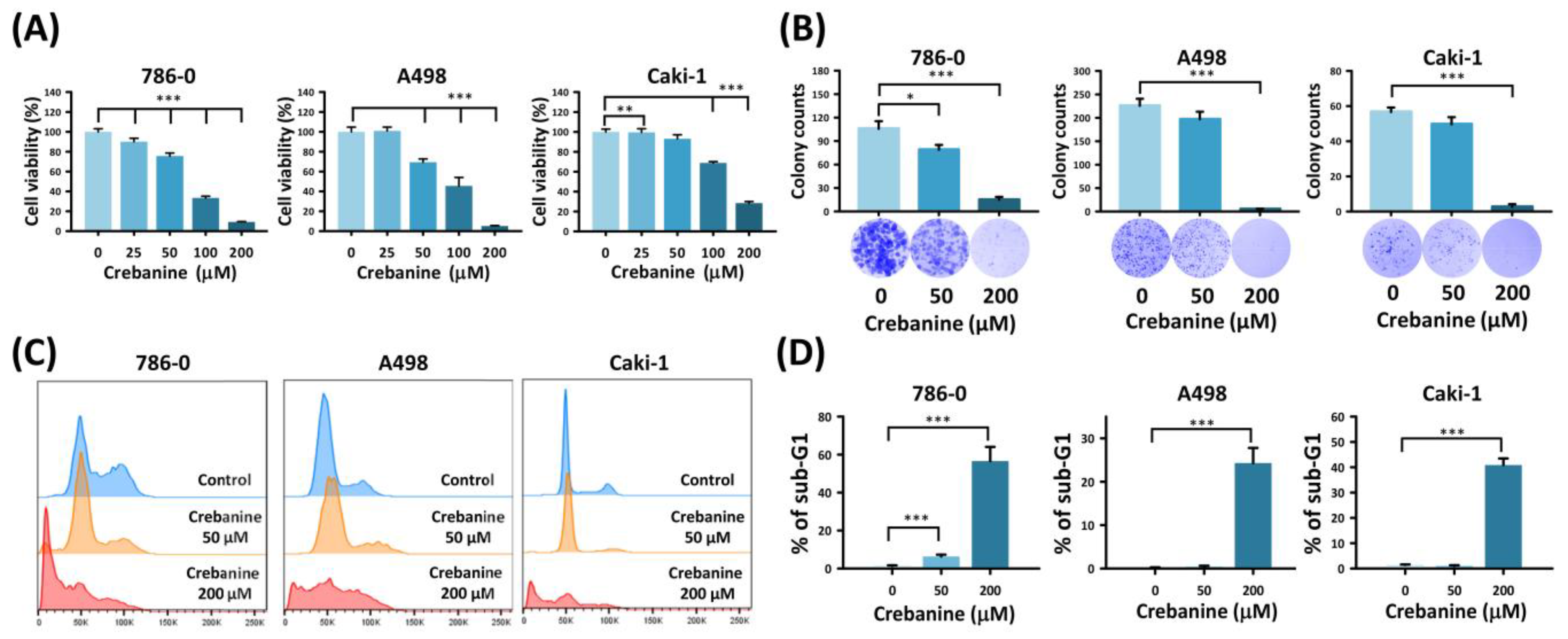
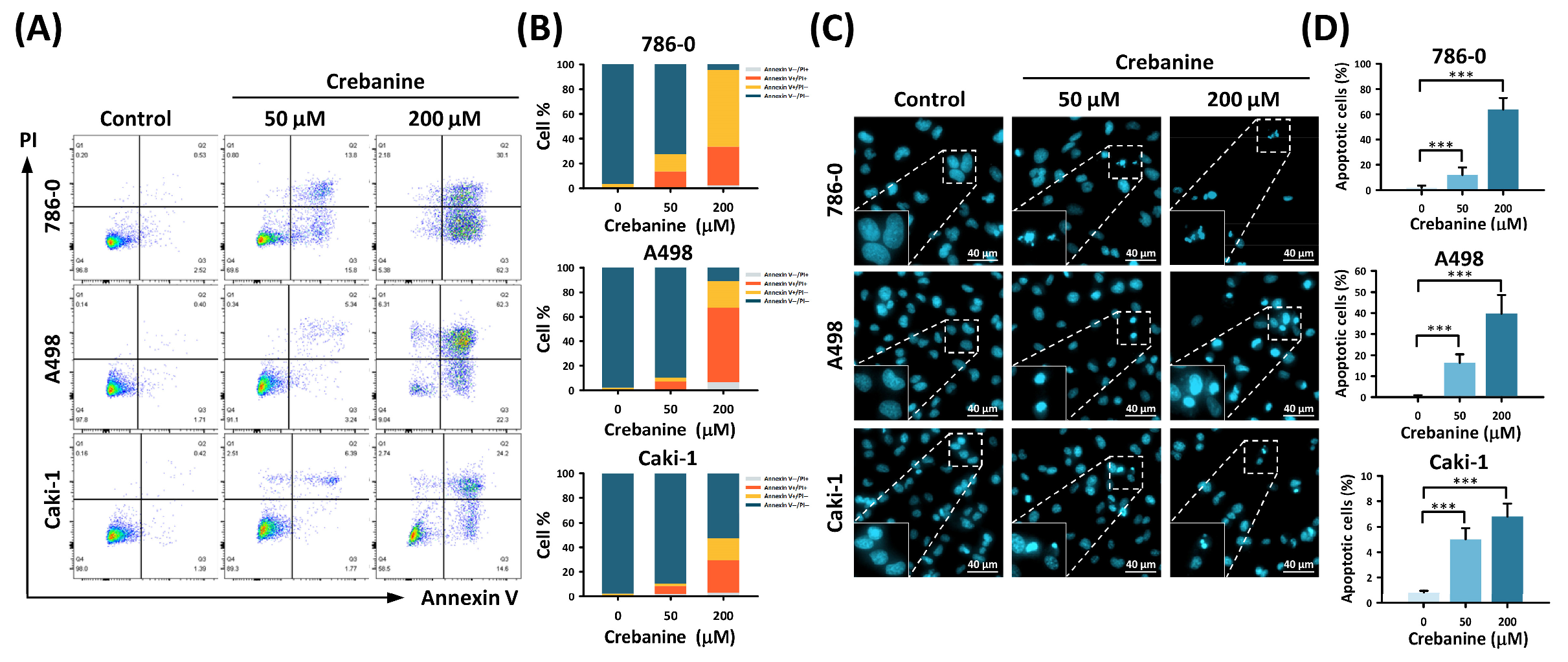
2.1. Crebanine Prohibits Cell Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis in 786-0, A498, and Caki-1 Cells In Vitro
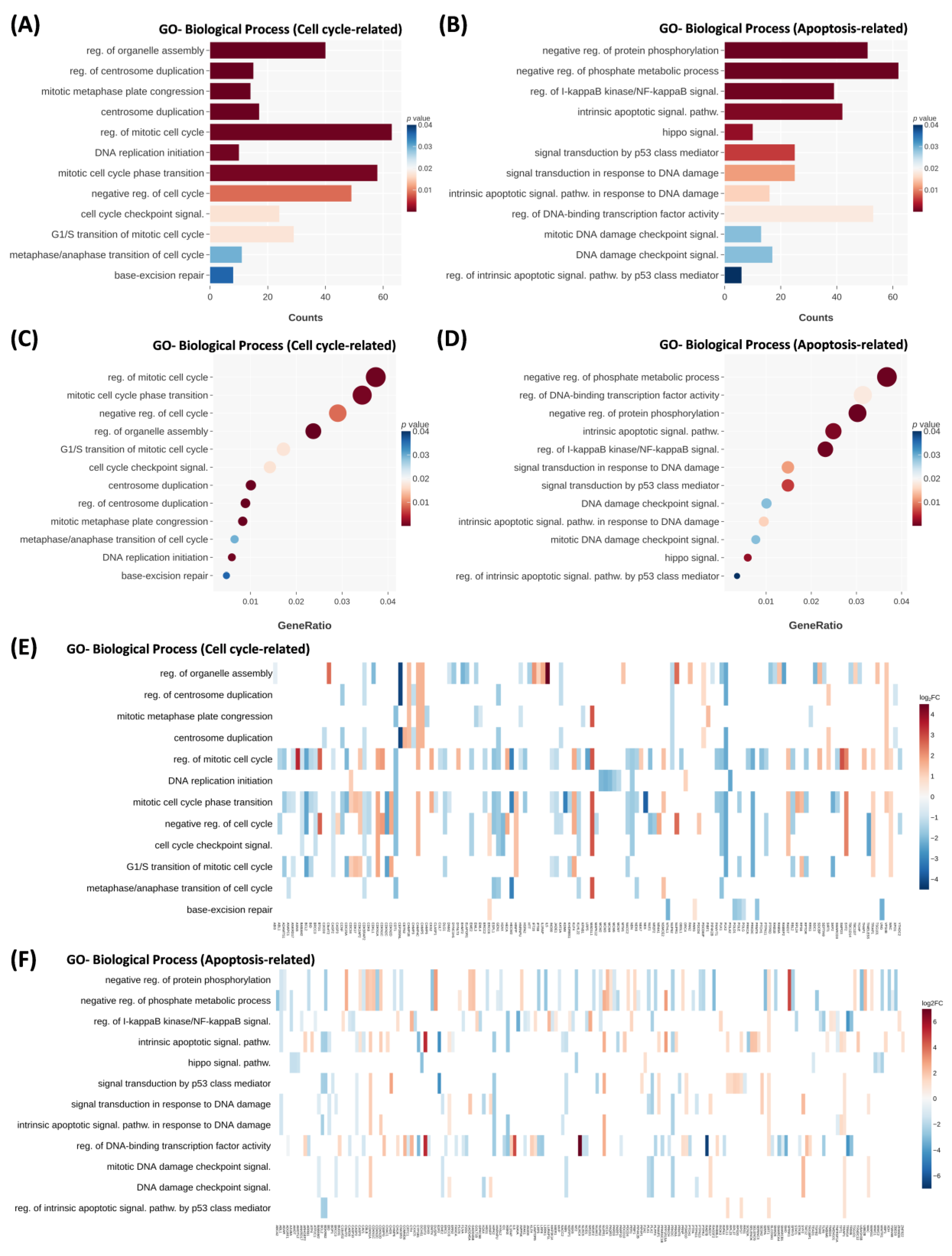
2.2. Crebanine Alters the Mitotic Process and the IκB Kinase/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Differential Gene Analysis
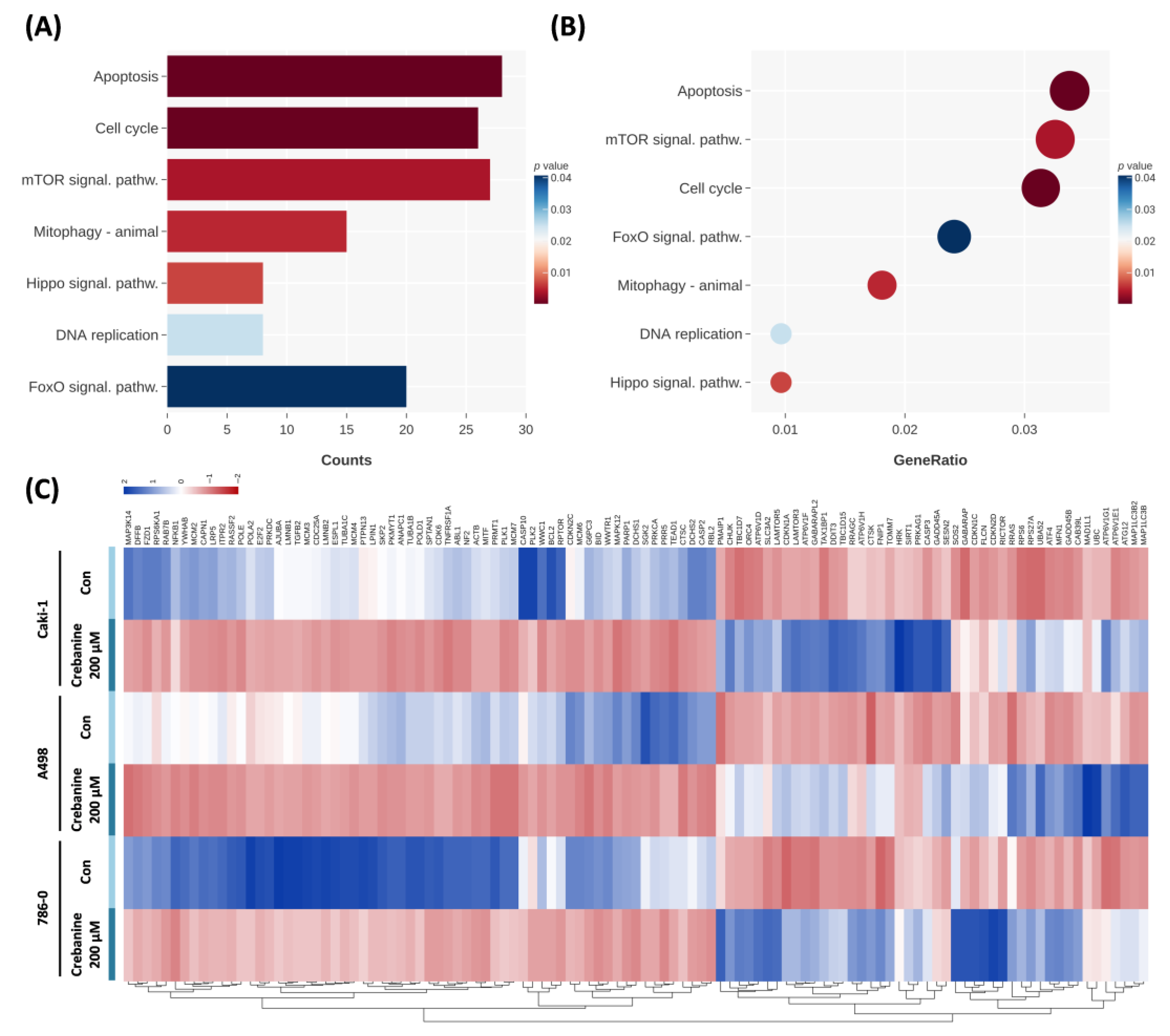
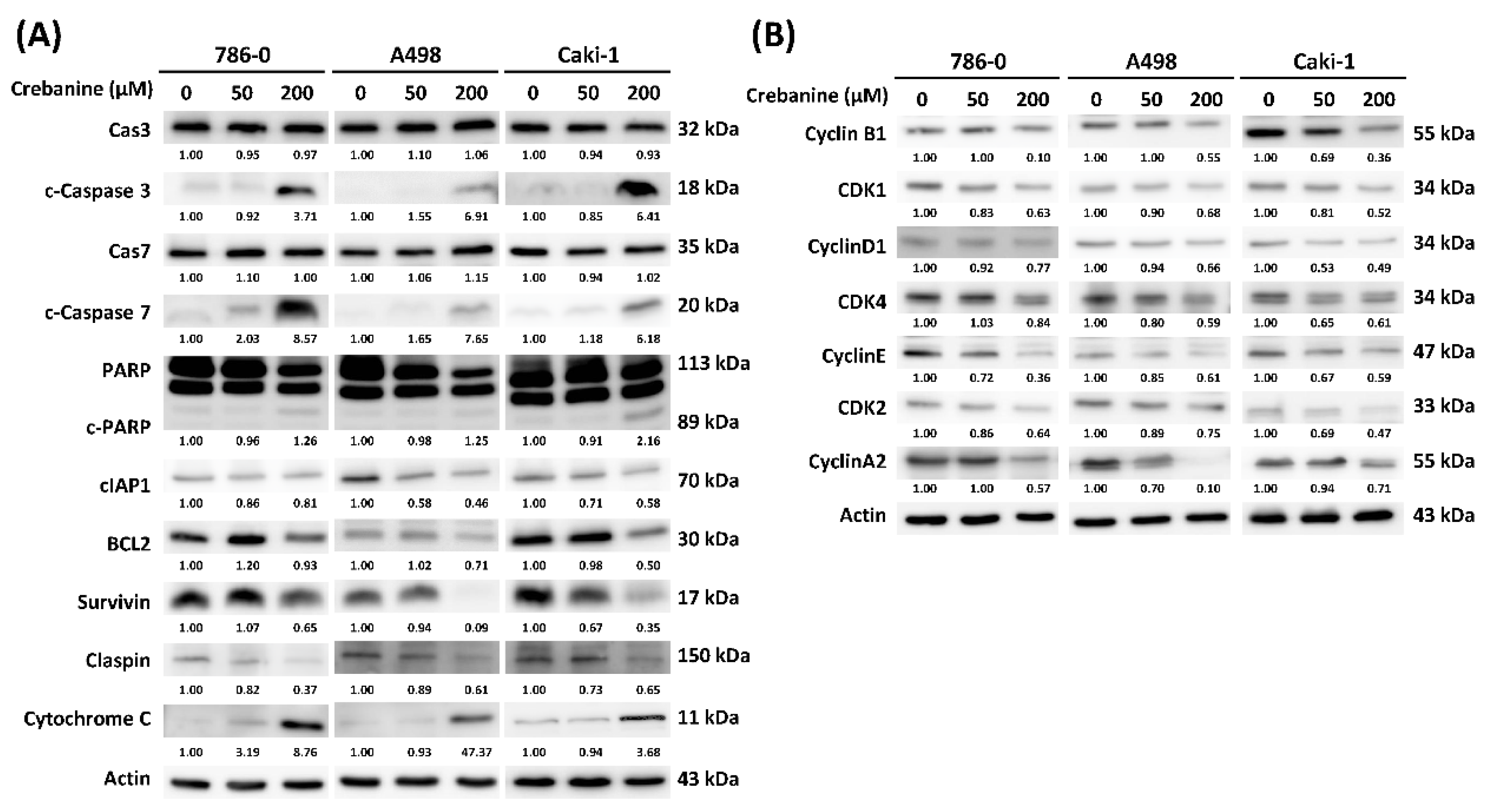
2.3. Crebanine Exerts Its Anticancer Effects Through the Promotion of Apoptosis and Regulation of the G1/S Phase Transition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. The MTT Assay
4.3. The Colony Formation Assay
4.4. Cell Cycle and Apoptosis Analysis
4.5. Nuclear Morphology Analysis Using Hoechst Staining
4.6. RNA Extraction and Next-Generation Sequencing
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| BAP1 | BRCA1-associated protein 1 |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BID | BH3-interacting domain death agonist |
| BIM | B-cell lymphoma 2-like protein 11 |
| CDK | cyclin-dependent kinases |
| cIAP1 | cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 1 |
| CTLA-4 | cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| G1 phase | gap1 phase |
| GLOBOCAN | Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today |
| GO | gene ontology |
| HIF | hypoxia-inducible factor |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| MCL1 | myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 |
| MCRS1 | microspherule protein 1 |
| MET | MET proto-oncogene, receptor tyrosine kinase |
| MLL3 | mixed lineage leukemia 3 |
| MOMP | mitochondrial outer membrane permeability |
| mRCC | metastatic renal cell carcinoma |
| MST1 | mammalian sterile 20-like protein kinase 1 |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| MTT assay | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide assay |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| NSAIDs | non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| PARP | poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| PBRM1 | polybromo 1 |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| PD-1 | programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | programmed cell death ligand 1 |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| pRB | retinoblastoma protein |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| PUMA | p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SEER | Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results |
| SETD2 | SET domain containing 2, histone lysine methyltransferase |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| S phase | synthesis phase |
| TEAD | transcriptional enhanced associated domain |
| TP53 | tumor protein p53 |
| UGTs | uridine diphosphate glycosyltransferases |
| YAP | yes-associated protein |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muglia, V.F.; Prando, A. Renal cell carcinoma: Histological classification and correlation with imaging findings. Radiol. Bras. 2015, 48, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, R.E.; Harris, G.T. Renal Cell Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 99, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zerdes, I.; Tolia, M.; Tsoukalas, N.; Mitsis, M.; Kardamakis, D.; Pistevou-Gombaki, K.; Tsekeris, P.; Kyrgias, G. Systemic therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: Review of the current literature. Urologia 2019, 86, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, E.A.; Rumble, R.B.; Van Veldhuizen, P.J. Management of Metastatic Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline Q&A. JCO Oncol. Pract. 2023, 19, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratigos, A.J.; Garbe, C.; Dessinioti, C.; Lebbe, C.; van Akkooi, A.; Bataille, V.; Bastholt, L.; Dreno, B.; Dummer, R.; Fargnoli, M.C.; et al. European consensus-based interdisciplinary guideline for invasive cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma: Part 2. Treatment-Update 2023. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 193, 113252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer InstituteSurveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program. SEER*Explorer. 2023. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statistics-network/explorer/ (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Schwab, M.; Hofmann, R.; Heers, H.; Hegele, A. mRCC Outcome in the Treatment of Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma—A German Single-center Real-world Experience. In Vivo 2018, 32, 1617–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, I.D.; Xie, W.; Pezaro, C.; Donskov, F.; Wells, J.C.; Agarwal, N.; Srinivas, S.; Yuasa, T.; Beuselinck, B.; Wood, L.A.; et al. Efficacy of Second-line Targeted Therapy for Renal Cell Carcinoma According to Change from Baseline in International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium Prognostic Category. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldin, A.; Besiroglu, B.; Adams, A.; Monsef, I.; Piechotta, V.; Tomlinson, E.; Hornbach, C.; Dressen, N.; Goldkuhle, M.; Maisch, P.; et al. First-line therapy for adults with advanced renal cell carcinoma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 5, Cd013798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangthongyou, T.; Makarasen, A.; Techasakul, S.; Chimnoi, N.; Siripaisarnpipat, S. (-)-crebanine. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Struct. Rep. Online 2011, 67 Pt 2, o402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Xiang, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, B.; Zhang, H. Crebanine induces ROS-dependent apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the AKT/FoxO3a signaling pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1069093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mon, M.T.; Yodkeeree, S.; Punfa, W.; Pompimon, W.; Limtrakul, P. Alkaloids from Stephania venosa as Chemo-Sensitizers in SKOV3 Ovarian Cancer Cells via Akt/NF-κB Signaling. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 66, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yodkeeree, S.; Pompimon, W.; Limtrakul, P. Crebanine, an aporphine alkaloid, sensitizes TNF-α-induced apoptosis and suppressed invasion of human lung adenocarcinoma cells A549 by blocking NF-κB-regulated gene products. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 8615–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongsirisin, P.; Yodkeeree, S.; Pompimon, W.; Limtrakul, P. Induction of G1 Arrest and Apoptosis in Human Cancer Cells by Crebanine, an Alkaloid from Stephania venosa. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahari, A.; Ablat, A.; Omer, N.; Nafiah, M.A.; Sivasothy, Y.; Mohamad, J.; Khan, M.N.; Awang, K. Ultraviolet-visible study on acid-base equilibria of aporphine alkaloids with antiplasmodial and antioxidant activities from Alseodaphne corneri and Dehaasia longipedicellata. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhan, X.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, H.; Deng, J.; Yang, H. Natural aporphine alkaloids: A comprehensive review of phytochemistry, pharmacokinetics, anticancer activities, and clinical application. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 63, 231–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krabbe, L.M.; Margulis, V.; Lotan, Y. Prognostic Role of Cell Cycle and Proliferative Markers in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 43, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Terekhanova, N.V.; Caravan, W.; Naser Al Deen, N.; Lal, P.; Chen, S.; Mo, C.K.; Cao, S.; Li, Y.; Karpova, A.; et al. Epigenetic and transcriptomic characterization reveals progression markers and essential pathways in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.J.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Petralia, F.; Pan, J.; Song, X.; Hu, Y.; da Veiga Leprevost, F.; Reva, B.; Lih, T.M.; Chang, H.Y.; et al. Integrated Proteogenomic Characterization of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell 2019, 179, 964–983.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonasch, E.; Walker, C.L.; Rathmell, W.K. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma ontogeny and mechanisms of lethality. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Lei, H.; Ma, F.; Shi, M.; Shi, W.; Xie, X.; Di, C. Aberrant Cyclin D1 splicing in cancer: From molecular mechanism to therapeutic modulation. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistritto, G.; Trisciuoglio, D.; Ceci, C.; Garufi, A.; D’Orazi, G. Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: Function and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic strategies. Aging 2016, 8, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, B.A.; El-Deiry, W.S. Targeting apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 395–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.W.; Oh, J.S.; Seok, S.H.; An, H.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Lee, N.Y.; Ha, T.; Kim, H.A.; Yoon, G.M.; Kim, S.E.; et al. Combined inhibition of Bcl-2 family members and YAP induces synthetic lethality in metastatic gastric cancer with RASA1 and NF2 deficiency. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, D.D.; Virumbrales-Muñoz, M.; Beebe, D.J.; Abel, E.J. Models of Renal Cell Carcinoma Used to Investigate Molecular Mechanisms and Develop New Therapeutics. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 871252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupo, B.; Trusolino, L. Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in cancer: Old and new paradigms revisited. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1846, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpova, Y.; Guo, D.; Makhov, P.; Haines, A.M.; Markov, D.A.; Kolenko, V.; Tulin, A.V. Poly(ADP)-Ribosylation Inhibition: A Promising Approach for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pletcher, J.P.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Doan, J.P.; Wynn, R.; Sindhwani, P.; Nadiminty, N.; Petros, F.G. The Emerging Role of Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors as Effective Therapeutic Agents in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 681441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slee, E.A.; Adrain, C.; Martin, S.J. Executioner caspase-3, -6, and -7 perform distinct, non-redundant roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7320–7326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri, T.K.; Kaelin, W.G., Jr. Targeting the HIF2-VEGF axis in renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Q. Von Hippel-Lindau protein signalling in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2024, 21, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milella, M.; Rutigliano, M.; Pandolfo, S.D.; Aveta, A.; Crocetto, F.; Ferro, M.; d’Amati, A.; Ditonno, P.; Lucarelli, G.; Lasorsa, F. The Metabolic Landscape of Cancer Stem Cells: Insights and Implications for Therapy. Cells 2025, 14, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Komine, K.; Taniguchi, S.; Yamada, H.; Sasaki, K.; Umegaki, S.; Kawamura, Y.; Kasahara, Y.; Ouchi, K.; et al. Correlation between Efficacy and Cardiovascular Adverse Events in Patients with Advanced Solid Cancer Who Received VEGF Pathway Inhibitors: Hypertension within the First Eight Weeks Is Associated with Favorable Outcomes of Patients Treated with VEGF Pathway Inhibitors. Intern. Med. 2025, 64, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.-S.; Wang, J.-Q.; Dai, S.-J.; He, W.-f.; Li, S.-Y.; Ashby, C.R.; Chen, Z.-S.; He, Q. Sunitinib resistance in renal cell carcinoma: From molecular mechanisms to predictive biomarkers. Drug Resist. Updates 2023, 67, 100929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powles, T.; Tomczak, P.; Park, S.H.; Venugopal, B.; Ferguson, T.; Symeonides, S.N.; Hajek, J.; Gurney, H.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lee, J.L.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus placebo as post-nephrectomy adjuvant therapy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-564): 30-month follow-up analysis of a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choueiri Toni, K.; Tomczak, P.; Park Se, H.; Venugopal, B.; Ferguson, T.; Symeonides Stefan, N.; Hajek, J.; Chang, Y.-H.; Lee, J.-L.; Sarwar, N.; et al. Overall Survival with Adjuvant Pembrolizumab in Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; An, T.; Huang, Z.; Chong, T. A network meta-analysis evaluating the efficacy and safety of adjuvant therapy after nephrectomy in renal cell carcinoma. BMC Urol. 2024, 24, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.; Alekseev, B.; Rha, S.Y.; Porta, C.; Eto, M.; Powles, T.; Grünwald, V.; Hutson, T.E.; Kopyltsov, E.; Méndez-Vidal, M.J.; et al. Lenvatinib plus Pembrolizumab or Everolimus for Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Porta, C.; Eto, M.; Powles, T.; Grünwald, V.; Hutson, T.E.; Alekseev, B.; Rha, S.Y.; Merchan, J.; Goh, J.C.; et al. Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab Versus Sunitinib in First-Line Treatment of Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma: Final Prespecified Overall Survival Analysis of CLEAR, a Phase III Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzer, R.J.; Bex, A.; Russo, P.; Tomita, Y.; Cutuli, H.J.; Rojas, C.; Gross-Goupil, M.; Schinzari, G.; Melichar, B.; Barthélémy, P.; et al. Adjuvant Nivolumab for Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma at High Risk of Recurrence After Nephrectomy: Part B of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Phase III CheckMate 914 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 43, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofano, G.; Saitta, C.; Musso, G.; Meagher, M.F.; Capitanio, U.; Dabbas, M.; Birouty, N.; Karamcheti, S.; Kim, B.; Yuen, K.L.; et al. Positive Surgical Margins in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Prognostic Impact and Implications for Risk Stratification and Adjuvant Therapy. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantapap, S.; Loetchutinat, C.; Meepowpan, P.; Nuntasaen, N.; Pompimon, W. Antiproliferative Effects of Alkaloids Isolated from the Tuber of Stephania venosa via the Induction of Cell Cycle Arrest in Mammalian Cancer Cell Lines. Am. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 7, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.L.; Kim, W.Y. Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Review. Jama 2024, 332, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Jin, Y.; Chen, X.; Ye, X.; Shen, X.; Lin, M.; Zeng, C.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. NF-κB in biology and targeted therapy: New insights and translational implications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Arkan, M.C.; Bollrath, J.; Hsu, L.C.; Goode, J.; Miething, C.; Göktuna, S.I.; Neuenhahn, M.; Fierer, J.; Paxian, S.; et al. NF-kappaB is a negative regulator of IL-1beta secretion as revealed by genetic and pharmacological inhibition of IKKbeta. Cell 2007, 130, 918–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Jiang, B.; Guo, J. The roles of curcumin in regulating the tumor immunosuppressive microenvironment. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 3059–3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, N.; Abdulwahid, A.R.R.; Mansouri, A.; Karimi, N.; Bostani, R.J.; Beiranvand, S.; Adelian, S.; Khorram, R.; Vafadar, R.; Hamblin, M.R.; et al. Targeting the NF-κB pathway as a potential regulator of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2024, 81, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Su, Z.; Han, S.; Huang, J.; Lin, L.; Shuai, X. Dual pH-sensitive nanodrug blocks PD-1 immune checkpoint and uses T cells to deliver NF-κB inhibitor for antitumor immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Ruiz, E.; Minute, L.; Otano, I.; Alvarez, M.; Ochoa, M.C.; Belsue, V.; de Andrea, C.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Marquez-Rodas, I.; et al. Prophylactic TNF blockade uncouples efficacy and toxicity in dual CTLA-4 and PD-1 immunotherapy. Nature 2019, 569, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Ding, D.; Yan, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Ma, L.; Ye, Z.; Ma, T.; Wu, Q.; Rodrigues, D.N.; et al. Phosphorylated RB Promotes Cancer Immunity by Inhibiting NF-κB Activation and PD-L1 Expression. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 22–35.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.; Hu, Y.; Lan, T.; Guan, K.L.; Luo, T.; Luo, M. The Hippo signalling pathway and its implications in human health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Zhou, X. Targeting Hippo signaling in cancer: Novel perspectives and therapeutic potential. MedComm 2023, 4, e375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Zhu, L.; Xiao, S.; Cui, Z.; Tang, J.; Yu, J.; Xie, M. MST1 inhibits the progression of breast cancer by regulating the Hippo signaling pathway and may serve as a prognostic biomarker. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Hao, T.; Yao, X.; Che, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Chai, H.; Li, N.; et al. Crebanine ameliorates ischemia-reperfusion brain damage by inhibiting oxidative stress and neuroinflammation mediated by NADPH oxidase 2 in microglia. Phytomedicine 2023, 120, 155044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Ge, J.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Song, W.; Li, Z.; Sun, S. Crebanine mitigates glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by restoring bone remodelling homeostasis via attenuating oxidative stress. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e70044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Peng, C.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Fan, X.; Li, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y. The anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of 2Br-Crebanine and Stephanine from Stephania yunnanenses H. S.Lo. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1092583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shih, H.-J.; Hsu, H.-C.; Liu, C.-T.; Chang, Y.-C.; Yu, C.-Y.; Sung, W.-W. Crebanine Induces Cell Death and Alters the Mitotic Process in Renal Cell Carcinoma In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146896
Shih H-J, Hsu H-C, Liu C-T, Chang Y-C, Yu C-Y, Sung W-W. Crebanine Induces Cell Death and Alters the Mitotic Process in Renal Cell Carcinoma In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146896
Chicago/Turabian StyleShih, Hung-Jen, Hsuan-Chih Hsu, Chien-Te Liu, Ya-Chuan Chang, Chia-Ying Yu, and Wen-Wei Sung. 2025. "Crebanine Induces Cell Death and Alters the Mitotic Process in Renal Cell Carcinoma In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146896
APA StyleShih, H.-J., Hsu, H.-C., Liu, C.-T., Chang, Y.-C., Yu, C.-Y., & Sung, W.-W. (2025). Crebanine Induces Cell Death and Alters the Mitotic Process in Renal Cell Carcinoma In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6896. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146896







