Lead Induces Mitochondrial Dysregulation in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells via a lncRNA/circRNA–miRNA–mRNA Interdependent Networks
Abstract
1. Background
2. Results
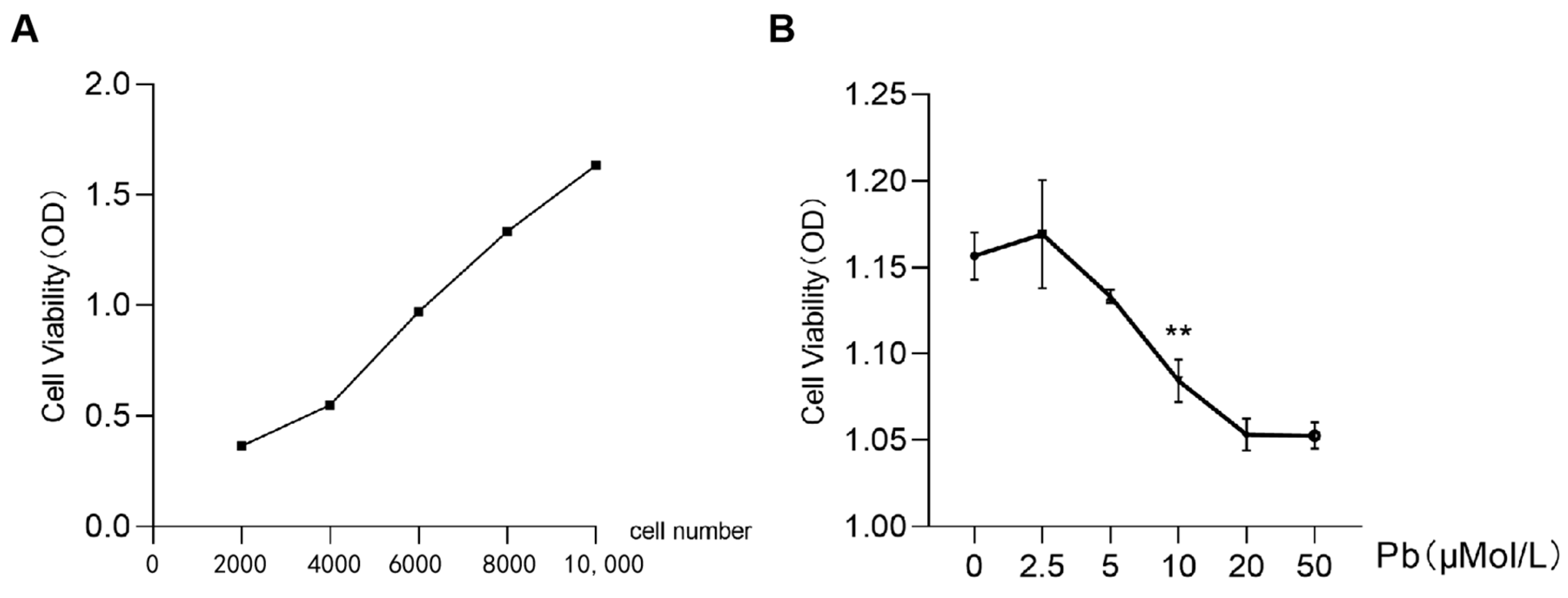
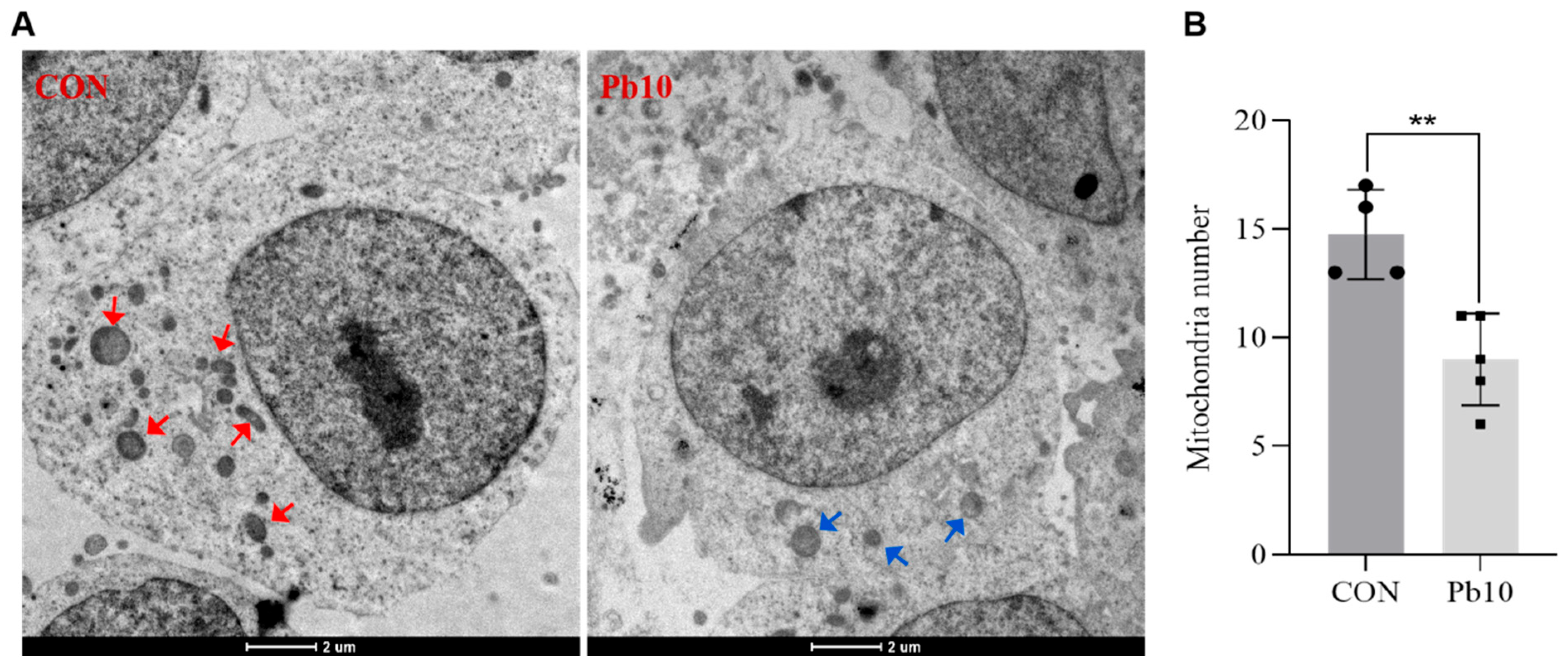
2.1. Effects of Lead Acetate on SY5Y Cell Viability and the Number of Mitochondrial
2.2. Effects of Lead Acetate on Mitochondrial Dynamics-Related Protein Expression
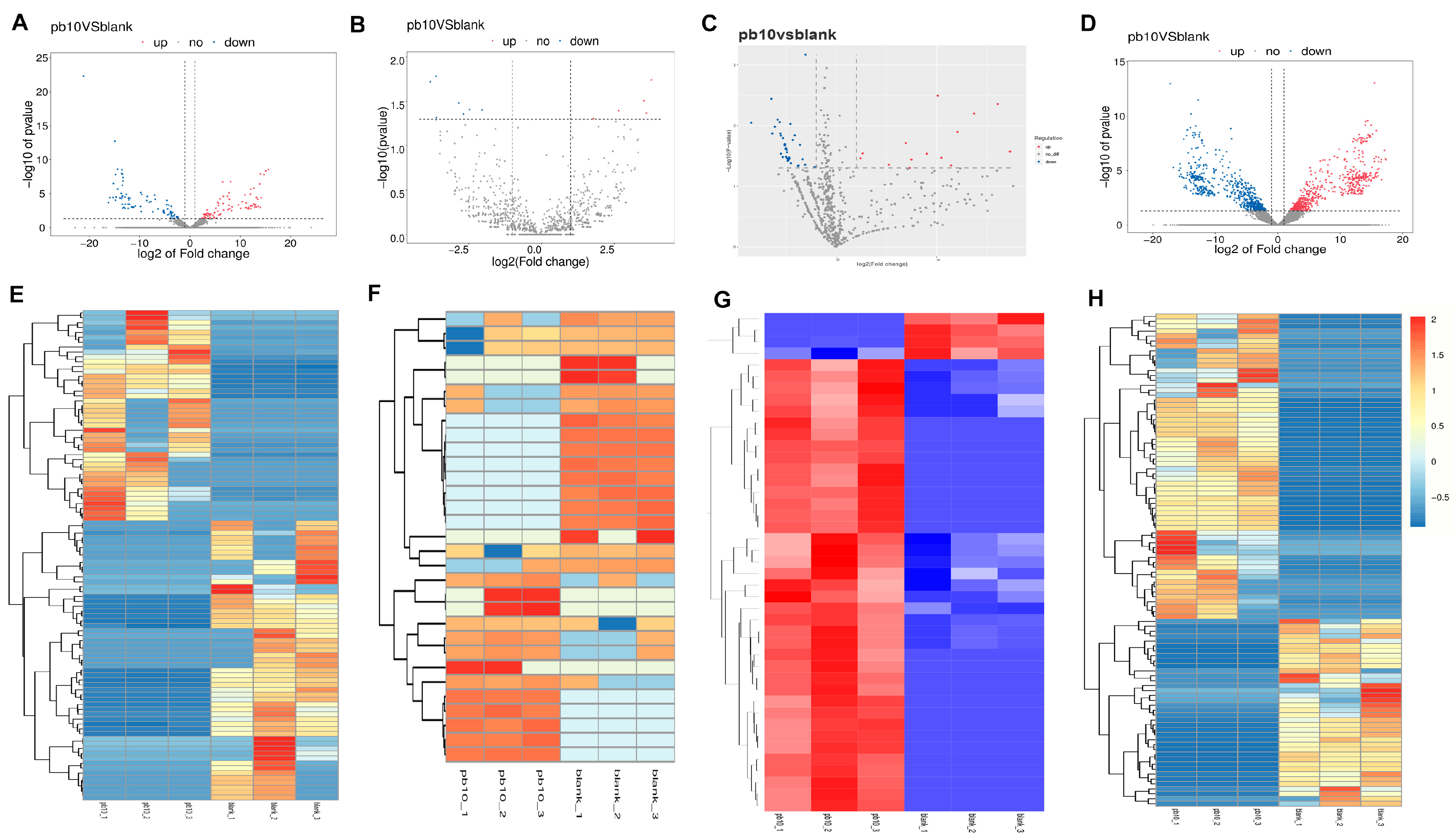
2.3. Differential Expression Analysis of ceRNAs
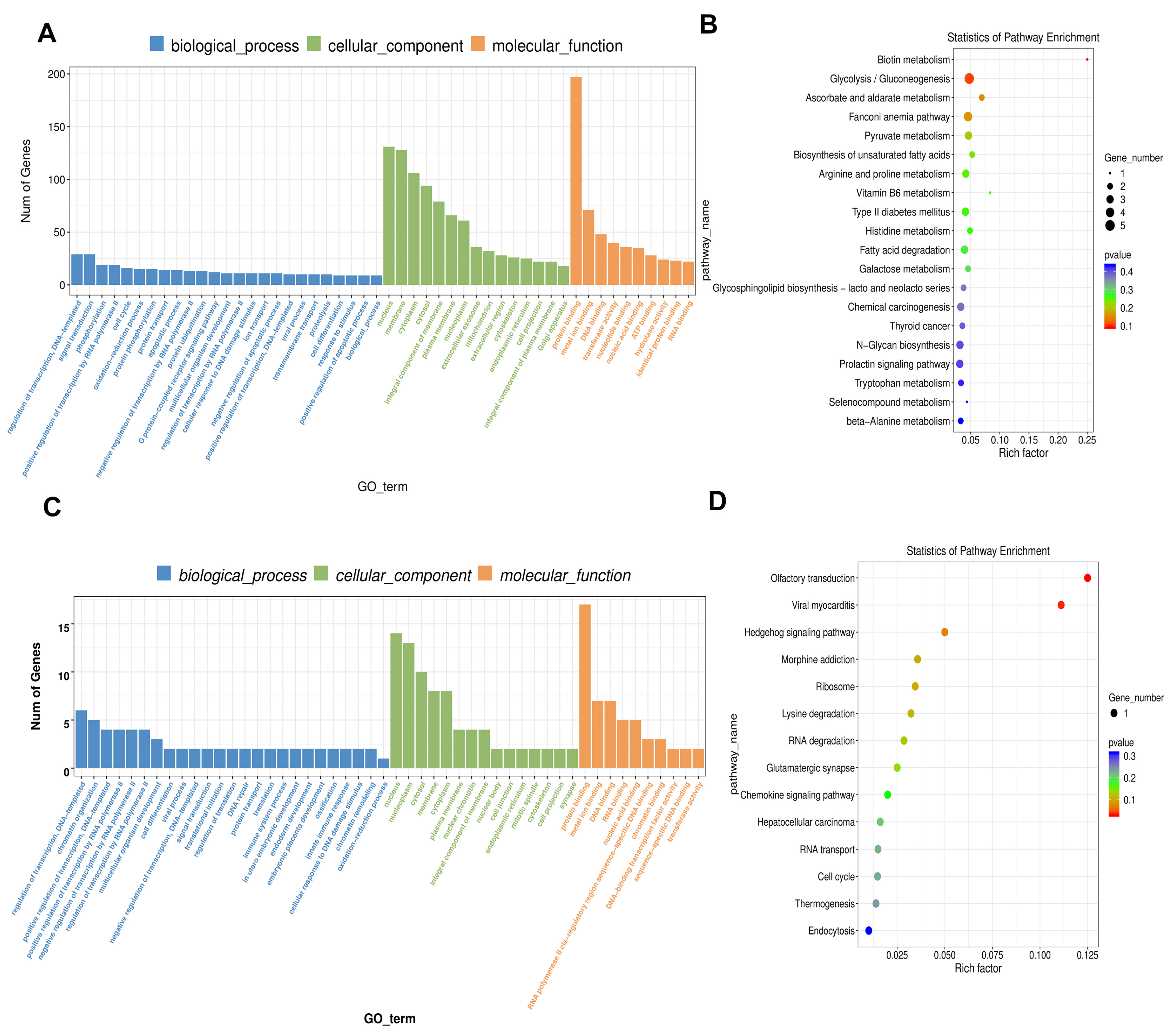
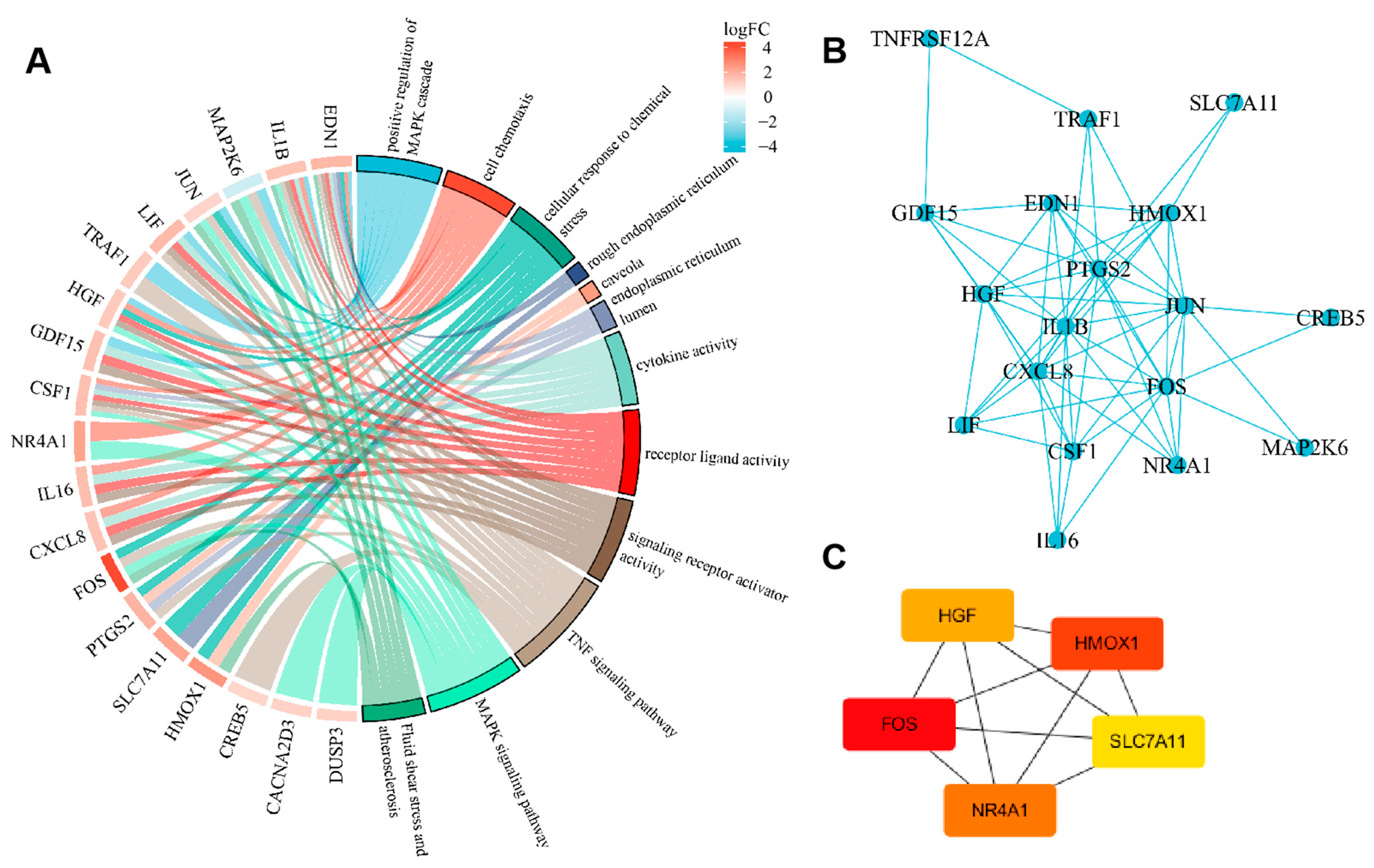
2.4. GO Analysis of Differentially Expressed ceRNAs
2.5. KEGG Enrichment Analysis
2.6. PPI (Protein–Protein Interaction, PPI) Network Construction
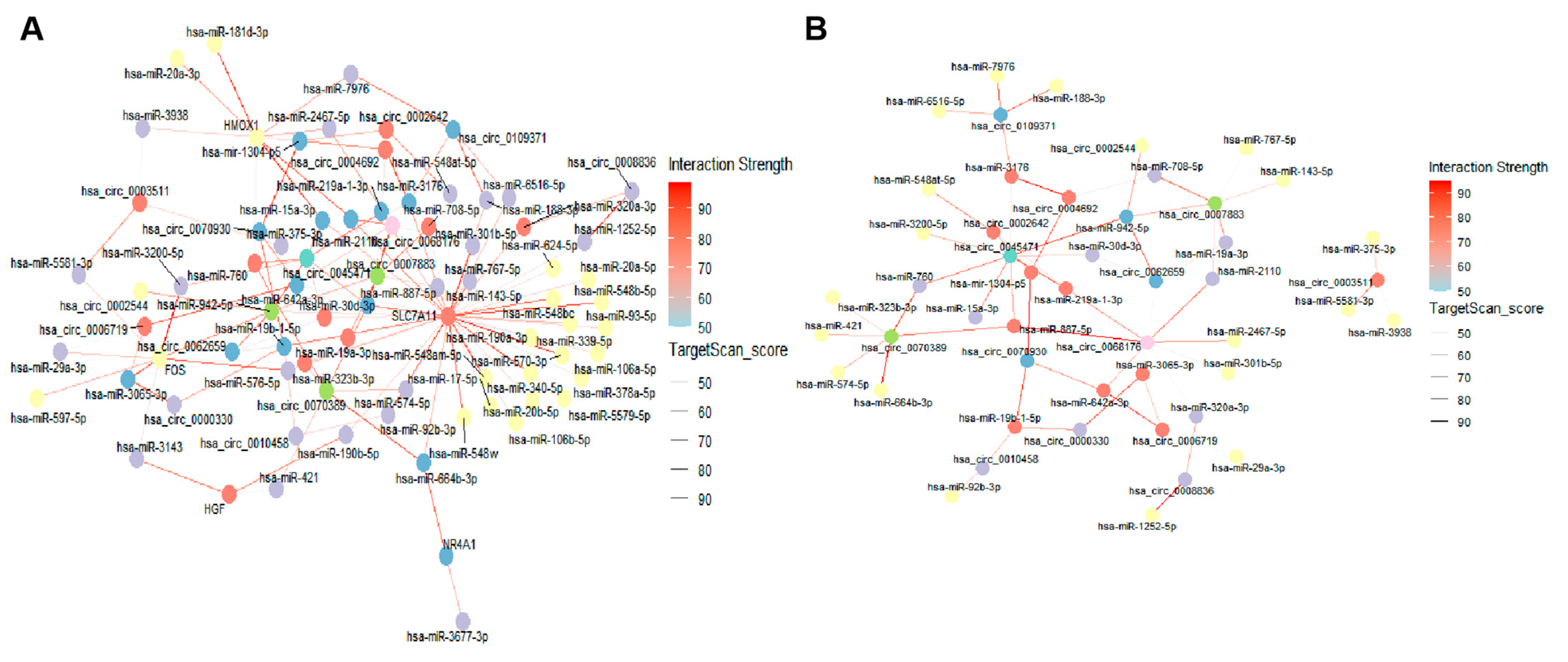
2.7. DE lncRNA/DE circRNA–DE miRNA–DE mRNA Network Construction
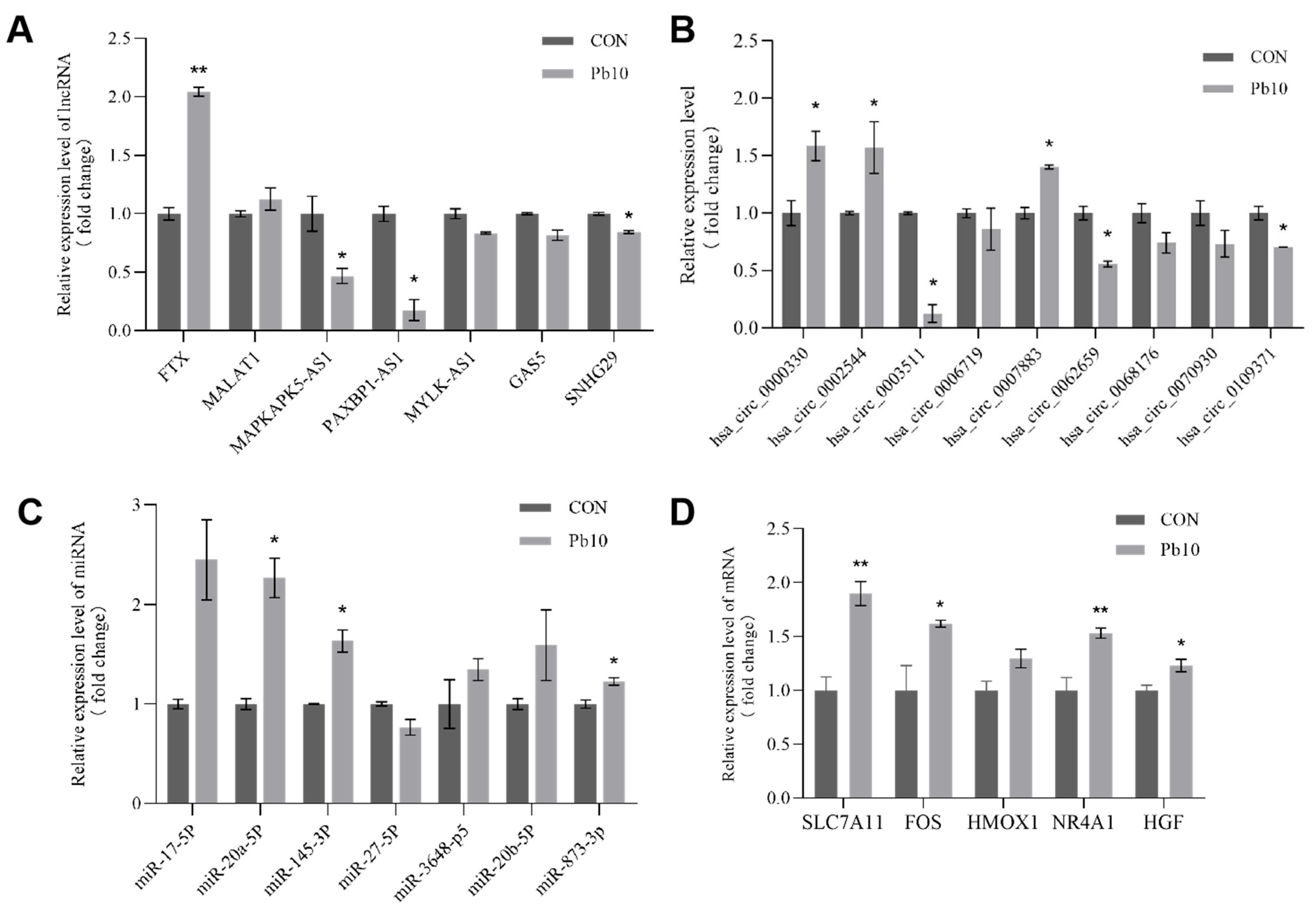
2.8. Validation of Key Genes
3. Discussion
4. Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Lead Treatment
4.2. Cell Counting Kit-8
4.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.4. Western Blotting Assay
4.5. RNA Extraction and Sequencing
4.6. Data Analysis
4.7. Functional Enrichment Analysis
4.8. PPI and ceRNA Network Construction
4.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| GTPases | Guanosine triphosphatases |
| DRP1 | Dynamin-related protein 1 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LC3B | Microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3 beta |
| ceRNA | Competing endogenous RNA |
| SH-SY5Y | Human neuroblastoma cell line |
| DE lncRNAs | Differentially expressed lncRNAs |
| ncRNAs | Non-coding RNAs |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative real-time PCR |
| PPI | Protein–Protein Interaction |
References
- Ngole-Jeme, V.M.; Fantke, P. Ecological and human health risks associated with abandoned gold mine tailings contaminated soil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alriksson, S.; Voxberg, E.; Karlsson, H.; Ljunggren, S.; Augustsson, A. Temporal risk assessment-20th century Pb emissions to air and exposure via inhalation in the Swedish glass district. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Xu, X.; Cao, L.; Xiang, Q.; Gao, Q.; Duan, H.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Yang, X. Single and joint exposure of Pb, Cd, Hg, Se, Cu, and Zn were associated with cognitive function of older adults. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 28567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunnari, J.; Suomalainen, A. Mitochondria: In sickness and in health. Cell 2012, 148, 1145–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhao, F.; Ma, X.; Perry, G.; Zhu, X. Mitochondria dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Recent advances. Mol. Neurodegener. 2020, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizama, B.N.; Chu, C.T. Neuronal autophagy and mitophagy in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2021, 82, 100972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemmensen, M.M.; Borrowman, S.H.; Pearce, C.; Pyles, B.; Chandra, B. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. Neurother. 2024, 21, e00292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.C. Mitochondrial Dynamics and Its Involvement in Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2020, 15, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliuso, A.; Cossart, P.; Stavru, F. The ever-growing complexity of the mitochondrial fission machinery. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 355–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Chen, M.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; Hou, Y. Mdivi-1 alleviates nicotine-induced human periodontal ligament cells injury by inhibiting mitochondrial fission and dysfunction through the JNK/Drp1 pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 288, 117338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Zhao, Y. Acetaldehyde induces phosphorylation of dynamin-related protein 1 and mitochondrial dysfunction via elevating intracellular ROS and Ca(2+) levels. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chun, H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, Y.; Park, U.; Chu, J.; Bhalla, M.; Choi, S.H.; Yousefian-Jazi, A.; Kim, S.; et al. Astrocytic autophagy plasticity modulates Aβ clearance and cognitive function in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Su, L.Y.; Li, G.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; Yang, L.X.; Zhang, D.F.; Zhou, H.; Xu, M.; Fan, Y.; et al. Activation of PPARA-mediated autophagy reduces Alzheimer disease-like pathology and cognitive decline in a murine model. Autophagy 2020, 16, 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandhok, G.; Lazarou, M.; Neumann, B. Structure, function, and regulation of mitofusin-2 in health and disease. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2018, 93, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.H.; Oliver, D.M. Amyloid Beta and Phosphorylated Tau-Induced Defective Autophagy and Mitophagy in Alzheimer’s Disease. Cells 2019, 8, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlubek, M.; Baranowska-Bosiacka, I. Selected Functions and Disorders of Mitochondrial Metabolism under Lead Exposure. Cells 2024, 13, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, X.; Jiang, A.; Li, X.; Chang, W.; Chen, J.; Ye, F. Metformin alleviates lead-induced mitochondrial fragmentation via AMPK/Nrf2 activation in SH-SY5Y cells. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Sun, Z.; Liu, E.; Wei, N.; Liu, X.; Shu, J.; Zhao, N.; Sun, M. Long Non-Coding RNAs: Crucial Regulators in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis and Prospects for Precision Medicine. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 7525–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.; Chen, J.; Tao, Z.; Ren, J. Non-coding RNAs: New players in mitophagy and neurodegeneration. Neurochem. Int. 2022, 152, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.S.; Peng, S.I.; Leong, L.I.; Gall-Duncan, T.; Wong, N.S.J.; Li, T.H.; Lin, X.; Wei, Y.; Koon, A.C.; Huang, J.; et al. Mutant huntingtin induces neuronal apoptosis via derepressing the non-canonical poly(A) polymerase PAPD5. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, H.X.; Qin, S.J.; Andersson, J.; Li, S.P.; Zeng, Q.G.; Li, J.H.; Wu, Q.Z.; Meng, W.J.; Oudin, A.; Kanninen, K.M.; et al. The emerging roles of particulate matter-changed non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: A comprehensive in silico analysis and review. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 366, 125440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickerson, J.A.; Momen-Heravi, F. Long non-coding RNAs: Roles in cellular stress responses and epigenetic mechanisms regulating chromatin. Nucleus 2024, 15, 2350180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejadi Orang, F.; Abdoli Shadbad, M. Competing endogenous RNA networks and ferroptosis in cancer: Novel therapeutic targets. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Gaetano, C.; Martelli, F. Long Noncoding Competing Endogenous RNA Networks in Age-Associated Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Xu, K.; Sun, J.K.; Liu, S.; Zhao, B.; Shi, J.; Herrup, K.; Chow, H.M.; Lu, L.; Li, J. The mitochondrial long non-coding RNA lncMtloop regulates mitochondrial transcription and suppresses Alzheimer’s disease. Embo J. 2024, 43, 6001–6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murumulla, L.; Bandaru, L.J.M.; Challa, S. Heavy Metal Mediated Progressive Degeneration and Its Noxious Effects on Brain Microenvironment. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2024, 202, 1411–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cao, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, G.; Ma, Y.; Hao, X.; Fan, H. Mitigation of honokiol on fluoride-induced mitochondrial oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and cognitive deficits through activating AMPK/PGC-1α/Sirt3. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 437, 129381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasertsuksri, P.; Kraokaew, P.; Pranweerapaiboon, K.; Sobhon, P.; Chaithirayanon, K. Neuroprotection of Andrographolide against Neurotoxin MPP(+)-Induced Apoptosis in SH-SY5Y Cells via Activating Mitophagy, Autophagy, and Antioxidant Activities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Suarez, L.; Awabdh, S.A.; Coumoul, X.; Chauvet, C. The SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line, a relevant in vitro cell model for investigating neurotoxicology in human: Focus on organic pollutants. Neurotoxicology 2022, 92, 131–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyalasomayajula, N.; Bandaru, L.J.M.; Chetty, C.S.; Dixit, P.K.; Challa, S. Mitochondria-Mediated Moderation of Apoptosis by EGCG in Cytotoxic Neuronal Cells Induced by Lead (Pb) and Amyloid Peptides. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2022, 200, 3582–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Zeng, H.; Cai, C.; Hu, Q.; Cai, S.; Xu, L.; Meng, X.; Zou, F. Role of the mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter in Pb2+-induced oxidative stress in human neuroblastoma cells. Brain Res. 2014, 1575, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Li, X.; Li, F.; Li, J.; Chang, W.; Yuan, J.; Chen, J. Cyclosporin A protects against Lead neurotoxicity through inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening in nerve cells. Neurotoxicology 2016, 57, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y. LncRNA FTX Inhibits Ferroptosis of Hippocampal Neurons Displaying Epileptiform Discharges In Vitro Through the miR-142-5p/GABPB1 Axis. Neuroscience 2023, 526, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Sun, H.; Song, L.; Hu, Y.; Guo, F. LncRNA FTX Involves in the Nogo-66-Induced Inhibition of Neurite Outgrowth Through Regulating PDK1/PKB/GSK-3β Pathway. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 40, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Yi, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, T.; Yang, S. LncRNA MALAT1 aggravates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis via the miR-195a-5p/HMGA1 axis. Biol. Res. 2021, 54, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zheng, B.; Pang, L.; Che, Y.; Qi, X. Suppression of MALAT1 alleviates neurocyte apoptosis and reactive oxygen species production through the miR-499-5p/SOX6 axis in subarachnoid hemorrhage. J. Mol. Histol. 2022, 53, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Perkins, G.A.; Poblenz, A.T.; Harris, J.B.; Hung, M.; Ellisman, M.H.; Fox, D.A. Bcl-xL overexpression blocks bax-mediated mitochondrial contact site formation and apoptosis in rod photoreceptors of lead-exposed mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1022–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Dai, S.; Yin, Z.; Lu, H.; Jia, R.; Xu, J.; Song, X.; Li, L.; Shu, Y.; Zhao, X.; et al. Sub-chronic lead and cadmium co-induce apoptosis protein expression in liver and kidney of rats. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 2905–2914. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Mei, L.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Gao, K.; Song, J.; Jiang, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Pang, B.; et al. Ferroptosis contributes to lead-induced cochlear spiral ganglion neurons injury. Toxicology 2024, 509, 153938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, C.; Jin, J.; Li, W.; Liang, J.; Zhou, S.; Weng, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, X.; Gu, A. Early-life exposure to lead changes cardiac development and compromises long-term cardiac function. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. FTX Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via miR-186-5p/MDM4 Pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, J.; Liu, J.; Wan, L.; Jiang, H.; Xin, L.; Sun, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. m(6)A-mediated lncRNA MAPKAPK5-AS1 induces apoptosis and suppresses inflammation via regulating miR-146a-3p/SIRT1/NF-κB axis in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Cycle 2023, 22, 2602–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Yang, L.; Liu, X.; Liu, M.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Luo, J. Long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 29 drives chronic myeloid leukemia progression via microRNA-483-3p/Casitas B-lineage Lymphoma axis-mediated activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. Med. Oncol. 2024, 41, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Zhang, Q. The transcription factor ZEB1 mediates the progression of epithelial ovarian cancer by promoting the transcription of CircANKRD17. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; An, P.; Xie, E.; Wu, Q.; Fang, X.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; et al. Characterization of ferroptosis in murine models of hemochromatosis. Hepatology 2017, 66, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitti, M.; Piras, S.; Brondolo, L.; Marinari, U.M.; Pronzato, M.A.; Furfaro, A.L. Heme Oxygenase 1 in the Nervous System: Does It Favor Neuronal Cell Survival or Induce Neurodegeneration? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, H.M.; Song, W.; Tavitian, A.; Cressatti, M. The sinister face of heme oxygenase-1 in brain aging and disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 172, 40–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Guan, R.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, W.; Du, K. Lead Induces Mitochondrial Dysregulation in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells via a lncRNA/circRNA–miRNA–mRNA Interdependent Networks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146851
Wang Y, Shen X, Guan R, Zhao Z, Wang T, Zhou Y, Chen X, Zhang J, Luo W, Du K. Lead Induces Mitochondrial Dysregulation in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells via a lncRNA/circRNA–miRNA–mRNA Interdependent Networks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146851
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Xuefeng Shen, Ruili Guan, Zaihua Zhao, Tao Wang, Yang Zhou, Xiaoming Chen, Jianbin Zhang, Wenjing Luo, and Kejun Du. 2025. "Lead Induces Mitochondrial Dysregulation in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells via a lncRNA/circRNA–miRNA–mRNA Interdependent Networks" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146851
APA StyleWang, Y., Shen, X., Guan, R., Zhao, Z., Wang, T., Zhou, Y., Chen, X., Zhang, J., Luo, W., & Du, K. (2025). Lead Induces Mitochondrial Dysregulation in SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells via a lncRNA/circRNA–miRNA–mRNA Interdependent Networks. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6851. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146851





