Safety Evaluation and Biodistribution of Fetal Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Sprague Dawley Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
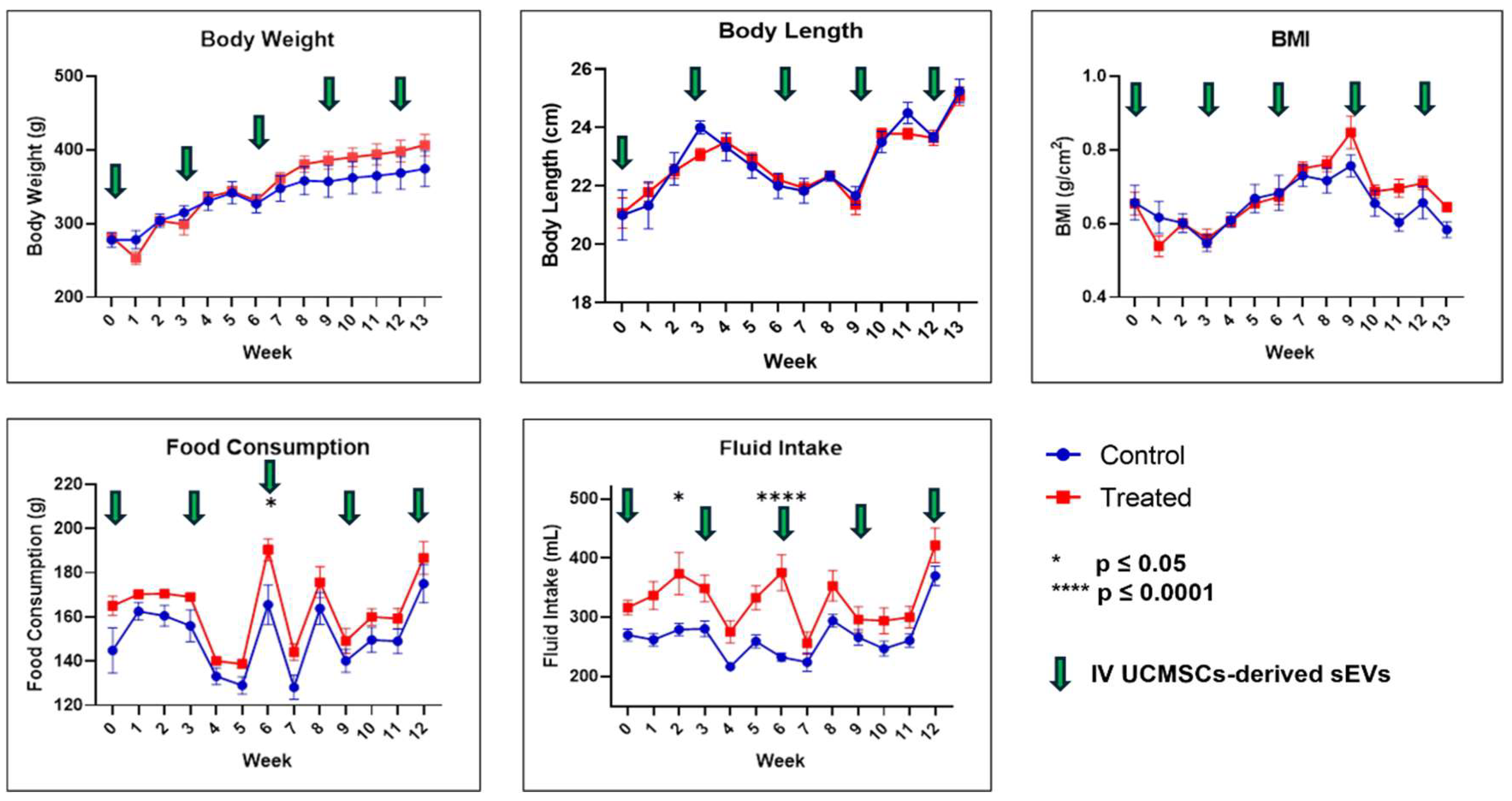
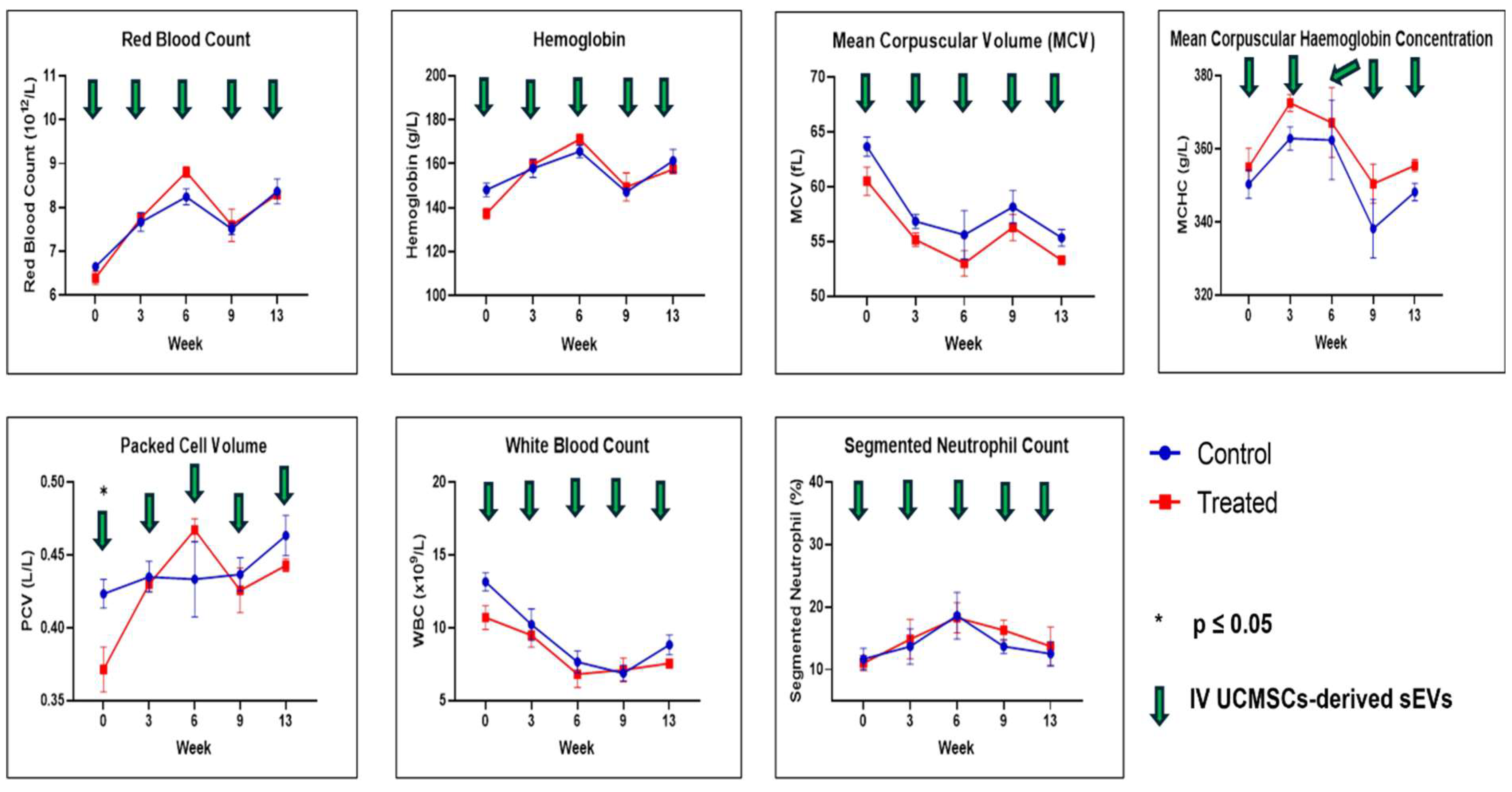
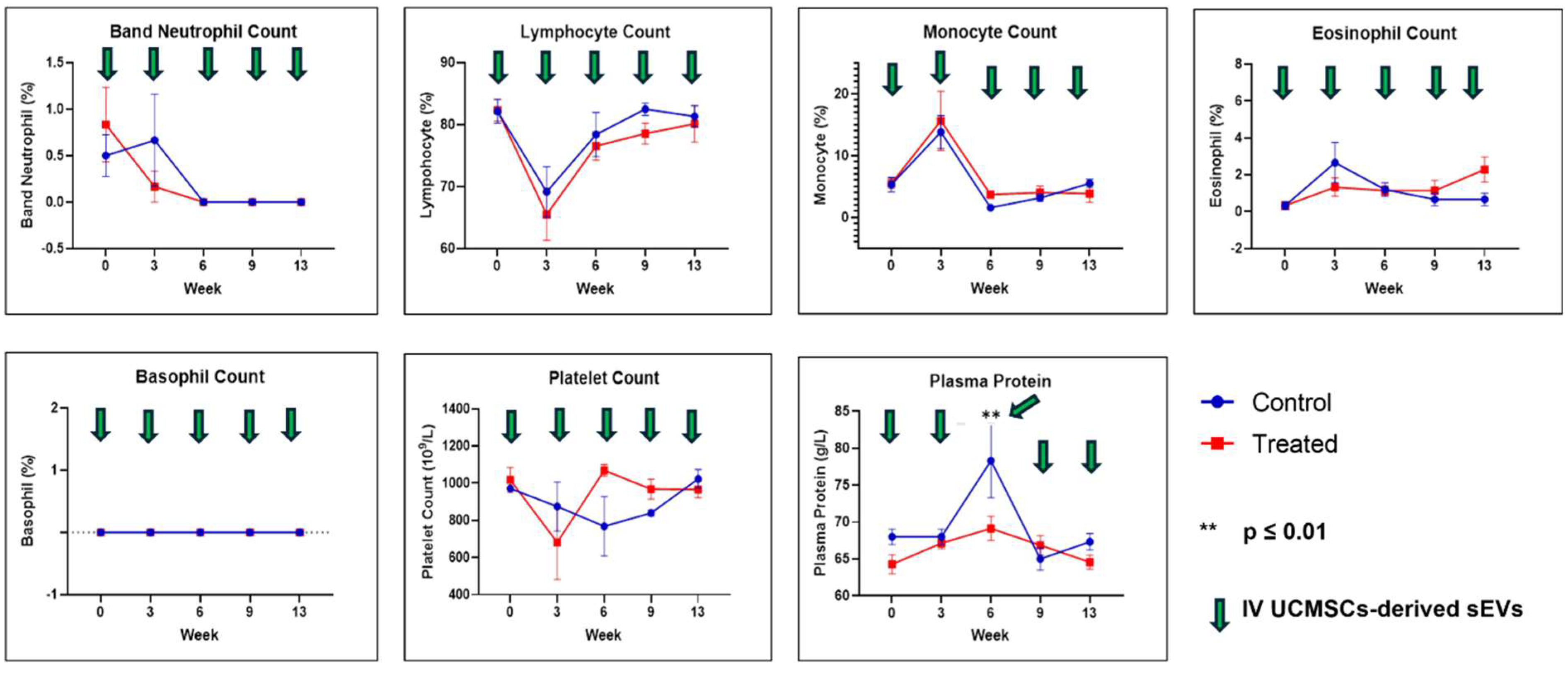
2.1. Physical Measurements, Observation, Selected Serum Biochemistry, and Full Blood Count
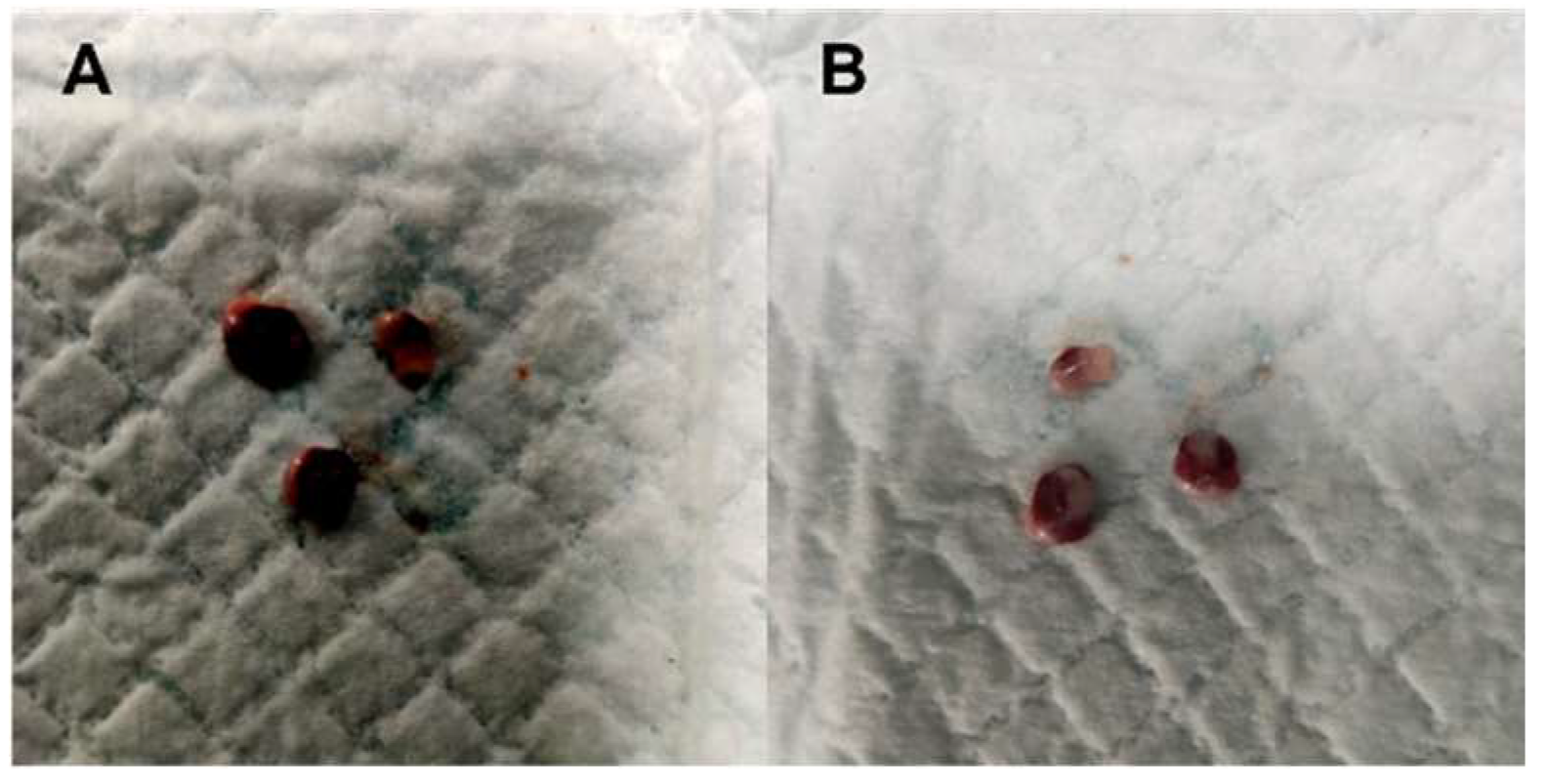
2.2. Gross Necropsy Evaluation, Relative Organ Weight, and Histopathology Assessment
2.3. Biodistribution Study
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Research and Animal Ethics
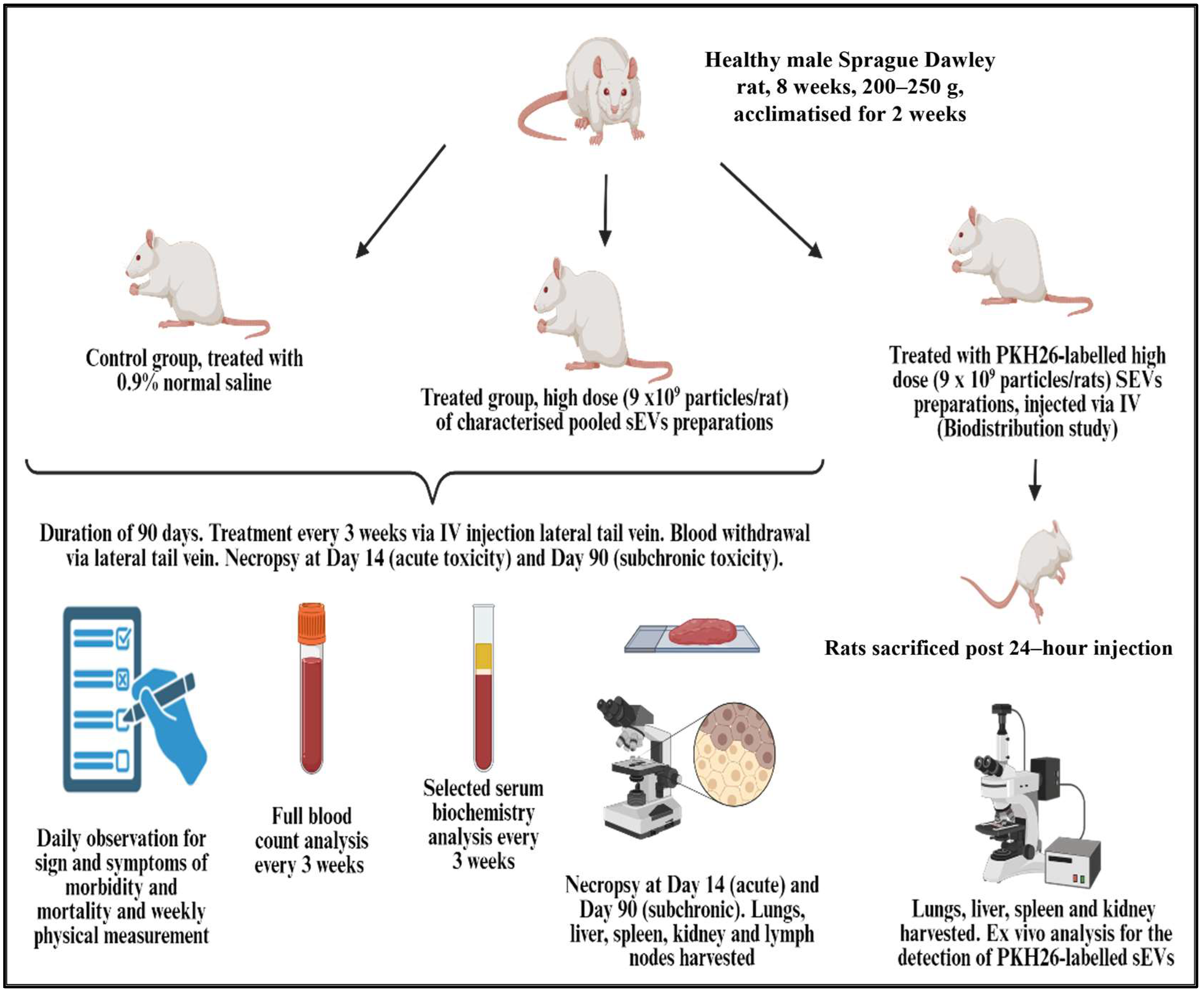
4.2. Safety Study Design
4.3. Animals
4.4. Animal Treatment
4.5. Fetal Umbilical Cord Protocol and Isolation of Small Extracellular Vesicles
4.6. Safety Study Monitoring Parameters
4.6.1. Physical Measurement and Observation
4.6.2. Blood Analysis
4.6.3. Necropsy
4.6.4. Histopathological Assessment
4.7. Biodistribution Study
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, A.M.L.; Ng, A.M.H.; Mohd Yunus, M.H.; Hj Idrus, R.B.; Law, J.X.; Yazid, M.D.; Chin, K.-Y.; Shamsuddin, S.A.; Mohd Yusof, M.R.; Razali, R.A.; et al. Safety study of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cell therapy in animal model. Regen. Ther. 2022, 19, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galipeau, J.; Sensébé, L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnoub, A.E.; Dash, A.B.; Vo, A.P.; Sullivan, A.; Brooks, M.W.; Bell, G.W.; Richardson, A.L.; Polyak, K.; Tubo, R.; Weinberg, R.A. Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2007, 449, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, H.; Yang, F.; Jiang, M.; Hu, L.; Feng, K.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, B.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; et al. The correlation between cotransplantation of mesenchymal stem cells and higher recurrence rate in hematologic malignancy patients: Outcome of a pilot clinical study. Leukemia 2008, 22, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukomska, B.; Stanaszek, L.; Zuba-Surma, E.; Legosz, P.; Sarzynska, S.; Drela, K. Challenges and Controversies in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 9628536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Ryan, A.E.; Griffin, M.D.; Ritter, T. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: Toward cell-free therapeutic applications. Mol. Ther. 2015, 23, 812–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelek, J.; Zuba-Surma, E.K. Perspectives for Future Use of Extracellular Vesicles from Umbilical Cord- and Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Regenerative Therapies—Synthetic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kwon, S.; Um, W.; Shin, S.; Kim, C.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, B.-S. Functional Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Medicine. Small 2022, 18, 2106569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Ruan, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cui, W.; Chen, H.; Shen, H. Advances in extracellular vesicle functionalization strategies for tissue regeneration. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 25, 500–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Masawa, M.E.; Alshawsh, M.A.; Ng, C.Y.; Ng, A.M.H.; Foo, J.B.; Vijakumaran, U.; Subramaniam, R.; Ghani, N.A.A.; Witwer, K.W.; Law, J.X. Efficacy and safety of small extracellular vesicle interventions in wound healing and skin regeneration: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies. Theranostics 2022, 12, 6455–6508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, B.; Ocansey, D.K.W.; Xu, W.; Qian, H. Extracellular vesicles: A bright star of nanomedicine. Biomaterials 2021, 269, 120467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Zhou, O.; Liu, J.; Zou, W.; Zhang, L.; Tian, D.; Dai, J.; Luo, Z.; Liu, E.; Fu, Z.; et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Alleviate Lung Injury in Rat Model of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia by Affecting Cell Survival and Angiogenesis. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 1520–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Gao, Z.; Zhao, L.; Du, B.; Ma, B.; Nian, H.; Wei, R. MSC-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Attenuate Autoimmune Dacryoadenitis by Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization and Inducing Tregs via miR-100-5p. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 888949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Ma, D.; Zhang, G.; Gao, J.; Su, Y.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Han, J.; Tian, M.; Wei, C.; et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis via immunomodulatory T lymphocytes. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 135, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, L.; Maqsood, M.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Diabetic Wound Healing via Promoting M2 Macrophage Polarization, Angiogenesis, and Collagen Deposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Kong, Y. Exosomes Derived From Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modulate miR-126 to Ameliorate Hyperglycemia-Induced Retinal Inflammation Via Targeting HMGB1. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, R.; Yoshioka, Y.; Furukawa, Y.; Naruse, M.; Kuwagata, M.; Ochiya, T.; Kitajima, S.; Hirabayashi, Y. Novel hepatotoxicity biomarkers of extracellular vesicle (EV)-associated miRNAs induced by CCl4. Toxicol. Rep. 2020, 7, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.M.; Wang, C.C.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.R.; Jiang, P.; Wang, Y.K.; Lin, Y.J.; Li, L.C.; Qi, Z.Q. Non-Clinical Safety Evaluation of Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Cynomolgus Monkeys. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 4923–4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendt, M.; Kamerkar, S.; Sugimoto, H.; McAndrews, K.M.; Wu, C.C.; Gagea, M.; Yang, S.; Blanko, E.V.R.; Peng, Q.; Ma, X.; et al. Generation and testing of clinical-grade exosomes for pancreatic cancer. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e99263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Xu, R.; Sun, X.; Duan, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qian, H.; Zhu, W.; Xu, W. Safety Evaluation of Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stromal Cell. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, A.F.; Lázaro-Ibáñez, E.; Forsgard, M.A.; Shatnyeva, O.; Osteikoetxea, X.; Karlsson, F.; Heath, N.; Ingelsten, M.; Rose, J.; Harris, J.; et al. Extracellular vesicles induce minimal hepatotoxicity and immunogenicity. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 6990–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Badawi, M.; Pomeroy, S.; Sutaria, D.S.; Xie, Z.; Baek, A.; Jiang, J.; Elgamal, O.A.; Mo, X.; Perle, K.; et al. Comprehensive toxicity and immunogenicity studies reveal minimal effects in mice following sustained dosing of extracellular vesicles derived from HEK293T cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2017, 6, 1324730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.H.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, J.; Kwon, H.H.; Park, G.H.; Yang, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Park, S.R.; Youn, J.; et al. Toxicological evaluation of exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem/stromal cells. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 115, 104686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, C.; Kiaie, S.H.; Zolbanin, N.M.; Lotfinejad, P.; Ramezani, R.; Kashanchi, F.; Jafari, R. Exosomes for mRNA delivery: A novel biotherapeutic strategy with hurdles and hope. BMC Biotechnol. 2021, 21, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhou, Y.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y. Exosomes Derived from Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Tumor Growth Through Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2242–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Su, X.; Xu, M.; Xiao, X.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Keating, A.; Zhao, R.C. Exosomes secreted by mesenchymal stromal/stem cell-derived adipocytes promote breast cancer cell growth via activation of Hippo signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.L.; Xie, H. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: A possible therapeutic strategy for orthopaedic diseases: A narrative review. Biomater. Transl. 2022, 3, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemian, S.O. Application of Exosomes-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Treatment of Fungal Diseases: From Basic to Clinical Sciences. Front. Fungal Biol. 2021, 2, 736093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowen, A.; Shahjin, F.; Chand, S.; Odegaard, K.E.; Yelamanchili, S.V. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Challenges in Clinical Applications. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, J.D.; Nuttall, J.P. Preclinical safety evaluation. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 383, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Percie du Sert, N.; Vollert, J.; Rice, A.S.C. General Principles of Preclinical Study Design. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2020, 257, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.-H.; Ryu, S.-W.; Choi, H.; You, S.; Park, J.; Choi, C. Manufacturing Therapeutic Exosomes: From Bench to Industry. Mol. Cells 2022, 45, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannelli, L.; Bari, E.; Jommi, C.; Tartara, F.; Armocida, D.; Garbossa, D.; Cofano, F.; Torre, M.L.; Segale, L. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome and extracellular vesicles for neurodegenerative diseases: Risk-benefit profile and next steps for the market access. Bioact. Mater. 2023, 29, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Consumer Alert on Regenerative Medicine Products Including Stem Cells and Exosomes. 2020. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/consumers-biologics/consumer-alert-regenerative-medicine-products-including-stem-cells-and-exosomes (accessed on 16 June 2024).
- Krishnan, I.; Chan, A.M.L.; Law, J.X.; Ng, M.H.; Jayapalan, J.J.; Lokanathan, Y. Proteomic Analysis of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Takakura, Y. Possibility of Exosome-Based Therapeutics and Challenges in Production of Exosomes Eligible for Therapeutic Application. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 835–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, C.; Tapparo, M.; Bruno, S.; Chatterjee, D.; Quesenberry, P.J.; Tetta, C.; Camussi, G. Biodistribution of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in a model of acute kidney injury monitored by optical imaging. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.W.; Sceneay, J.; Lima, L.G.; Wong, C.S.F.; Becker, M.; Krumeich, S.; Lobb, R.J.; Castillo, V.; Wong, K.N.; Ellis, S.; et al. The Biodistribution and Immune Suppressive Effects of Breast Cancer–Derived Exosomes. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6816–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Dong, B.; Zeng, E.; Wang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, D. In Vivo Tracking of Multiple Tumor Exosomes Labeled by Phospholipid-Based Bioorthogonal Conjugation. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11273–11279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Jordan, V.; Blenkiron, C.; Chamley, L.W. Biodistribution of extracellular vesicles following administration into animals: A systematic review. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, R.; Zou, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Ran, R.; Chen, Q. Comparison of the Biological Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived from the Human Placenta and Umbilical Cord. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.; Razi, Z.R.; Law, J.; Nawi, A.M.; Idrus, R.B.; Ng, M.H. MSCs can be differentially isolated from maternal, middle and fetal segments of the human umbilical cord. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 1493–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelen, D.L.; van der Mast, B.J.; in’t Anker, P.S.; Kleijburg, C.; Eikmans, M.; van Beelen, E.; de Groot-Swings, G.M.; Fibbe, W.E.; Kanhai, H.H.; Scherjon, S.A.; et al. Differential immunomodulatory effects of fetal versus maternal multipotent stromal cells. Hum. Immunol. 2009, 70, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Teoh, S.H.; Chong, M.S.; Schantz, J.T.; Fisk, N.M.; Choolani, M.A.; Chan, J. Superior osteogenic capacity for bone tissue engineering of fetal compared with perinatal and adult mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Götherström, C.; Ringdén, O.; Tammik, C.; Zetterberg, E.; Westgren, M.; Le Blanc, K. Immunologic properties of human fetal mesenchymal stem cells. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 190, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, R.; Walther-Jallow, L.; David, A.L.; Götherström, C.; Westgren, M. Fetal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: An Opportunity for Prenatal Cellular Therapy. Curr. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halamoda-Kenzaoui, B.; Baconnier, S.; Bastogne, T.; Bazile, D.; Boisseau, P.; Borchard, G.; Borgos, S.E.; Calzolai, L.; Cederbrant, K.; Di Felice, G.; et al. Bridging communities in the field of nanomedicine. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 106, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Tan, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhao, T.; Mao, F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Yan, Z.; Qian, H.; Yan, Y. Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl(4)-Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 6079642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomi, G.; Surbek, D.; Haesler, V.; Joerger-Messerli, M.; Schoeberlein, A. Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells reduce microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in perinatal brain injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Yao, Y.; Liao, W. Exosomal cargoes in OSCC: Current findings and potential functions. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börger, V.; Weiss, D.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Borràs, F.E.; Bussolati, B.; Carter, D.R.F.; Dominici, M.; Falcón-Pérez, J.M.; Gimona, M.; Hill, A.F.; et al. International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and International Society for Cell and Gene Therapy statement on extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stromal cells and other cells: Considerations for potential therapeutic agents to suppress coronavirus disease-19. Cytotherapy 2020, 22, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lener, T.; Gimona, M.; Aigner, L.; Börger, V.; Buzas, E.; Camussi, G.; Chaput, N.; Chatterjee, D.; Court, F.A.; Del Portillo, H.A.; et al. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials—An ISEV position paper. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 30087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.T.; Lai, R.C.; Padmanabhan, J.; Sim, W.K.; Choo, A.B.; Lim, S.K. Assessment of Tumorigenic Potential in Mesenchymal-Stem/Stromal-Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles (MSC-sEV). Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, E.; Pachler, K.; Gimona, M. Manufacturing and characterization of extracellular vesicles from umbilical cord–derived mesenchymal stromal cells for clinical testing. Cytotherapy 2019, 21, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.H.; Lee, A.R.; Moon, K.-S. Characteristics of Extracellular Vesicles and Preclinical Testing Considerations Prior to Clinical Applications. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allioux, C.; Achaintre, L.; Cheataini, F.; Balança, B.; Marinesco, S. Animal welfare assessment after severe traumatic brain injury in rats. Lab. Anim. 2022, 56, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.H.; Rose, F.R.A.J.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Modo, M.; White, L.J. Translational considerations in injectable cell-based therapeutics for neurological applications: Concepts, progress and challenges. Npj Regen. Med. 2017, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, G.; Rasmusson-Duprez, I.; von Bahr, L.; Connolly-Andersen, A.-M.; Elgue, G.; Funke, L.; Hamad, O.A.; Lönnies, H.; Magnusson, P.U.; Sanchez, J.; et al. Are Therapeutic Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Compatible with Human Blood? Stem Cells 2012, 30, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, N.; Matsushita, T.; Matsuo, S.; Hiranuma, M.; Azabu, H.; Saito, R.; Komatsu, S.I.; Kato, A.; Toyota, N.; Taketo, J.; et al. Effects of two weeks of food restriction on toxicological parameters in cynomolgus monkeys. Exp. Anim. 2024, 73, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, T.; Tsujioka, S.; Ohira, T.; Nonaka, S.; Ikeda, H.; Sugiura, H.; Tomohiro, M.; Samura, K.; Nishikibe, M. Effects of reduced food intake on toxicity study parameters in rats. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 33, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, T.; Kornadt-Beck, N.; Oskamp, A.; Elmenhorst, D.; Touma, C.; Palme, R.; Bauer, A. Additional Assessment of Fecal Corticosterone Metabolites Improves Visual Rating in the Evaluation of Stress Responses of Laboratory Rats. Animals 2021, 11, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, J.M.; Ward, J.M.; Treuting, P.M. Cause-of-Death Analysis in Rodent Aging Studies. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 53, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotariu, D.; Babes, E.E.; Tit, D.M.; Moisi, M.; Bustea, C.; Stoicescu, M.; Radu, A.-F.; Vesa, C.M.; Behl, T.; Bungau, A.F.; et al. Oxidative stress—Complex pathological issues concerning the hallmark of cardiovascular and metabolic disorders. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powanda, M.C.; Moyer, E.D. A brief, highly selective history of acute phase proteins as indicators of infection, inflammation and injury. Inflammopharmacology 2021, 29, 897–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, M.; Fang, H.; Li, T.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Xiao, P.; Hu, M. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Various Chronic Liver Diseases: Hype or Hope? J. Inflamm. Res. 2024, 17, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, I.; Ling, M.T.M.; Ng, M.H.; Law, J.X.; Yusof, M.R.M.; Thangarajah, T.; Mahmood, Z.; Uda Zahli, N.I.; Rajamanickam, S.; Subramani, B.; et al. Efficacy of Fetal Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Metabolic Syndrome. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krampera, M.; Le Blanc, K. Mesenchymal stromal cells: Putative microenvironmental modulators become cell therapy. Cell Stem Cell 2021, 28, 1708–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, M.; Cesari, N.; Murgia, A.; Puccini, P.; Riccardi, B.; Dominici, M. Dissecting the Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics of MSCs to Overcome Limitations in Their Clinical Translation. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2019, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driedonks, T.; Jiang, L.; Carlson, B.; Han, Z.; Liu, G.; Queen, S.E.; Shirk, E.N.; Gololobova, O.; Liao, Z.; Nyberg, L.H.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of extracellular vesicles administered intravenously and intranasally to Macaca nemestrina. J. Extracell. Biol. 2022, 1, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Tieu, A.; Slobodian, M.; Shorr, R.; Burger, D.; Lalu, M.M.; Allan, D.S. Preclinical Studies of MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles to Treat or Prevent Graft Versus Host Disease: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 17, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Deun, J.; Mestdagh, P.; Agostinis, P.; Akay, Ö.; Anand, S.; Anckaert, J.; Martinez, Z.A.; Baetens, T.; Beghein, E.; Bertier, L.; et al. EV-TRACK: Transparent reporting and centralizing knowledge in extracellular vesicle research. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krenkel, O.; Tacke, F. Liver macrophages in tissue homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklander, O.P.; Nordin, J.Z.; O’Loughlin, A.; Gustafsson, Y.; Corso, G.; Mäger, I.; Vader, P.; Lee, Y.; Sork, H.; Seow, Y.; et al. Extracellular vesicle in vivo biodistribution is determined by cell source, route of administration and targeting. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, T.; Kullberg, M.; Malik, N.; Smith-Jones, P.; Graner, M.W.; Anchordoquy, T.J. Biodistribution and delivery efficiency of unmodified tumor-derived exosomes. J. Control. Release 2015, 199, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Ferro, Z.; Rocha, G.; Silva, K.; Paredes, B.; Loiola, E.; Santos, J.; Dias, R.; Figueira, C.; Oliveira, C.; Moura, L.; et al. Product characterization and preclinical evaluation of the biodistribution and safety of umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Res. Sq. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Kato, K.; Morishita, M.; Yamashita, T.; Matsumoto, A.; Charoenviriyakul, C.; Takakura, Y. Macrophage-dependent clearance of systemically administered B16BL6-derived exosomes from the blood circulation in mice. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 26238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, J.; Stewart, T.; Banks, W.A.; Zhang, J. The Transport Mechanism of Extracellular Vesicles at the Blood-Brain Barrier. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 6206–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.K.A.; Morille, M.; Piffoux, M.; Arumugam, S.; Mauduit, P.; Larghero, J.; Bianchi, A.; Aubertin, K.; Blanc-Brude, O.; Noël, D.; et al. Development of extracellular vesicle-based medicinal products: A position paper of the group “Extracellular Vesicle translatiOn to clinicaL perspectiVEs—EVOLVE France”. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 179, 114001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, I.; Yong, N.C.; Ting, K.L.; Hwei, N.M.; Xian, L.J.; Thavachelvi, T.; Amelia, Z.A.; Zalina, M.; Shathiya, R.; Baskar, S.; et al. Quality Control of Fetal Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 1807–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuda, T.; Tsuchiya, R.; Kosaka, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takagaki, K.; Oki, K.; Takeshita, F.; Sakai, Y.; Kuroda, M.; Ochiya, T. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells secrete functional neprilysin-bound exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, R.; Uemoto, S.; Tabata, Y. Immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes on a concanavalin A-induced liver injury model. Inflamm. Regen. 2016, 36, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


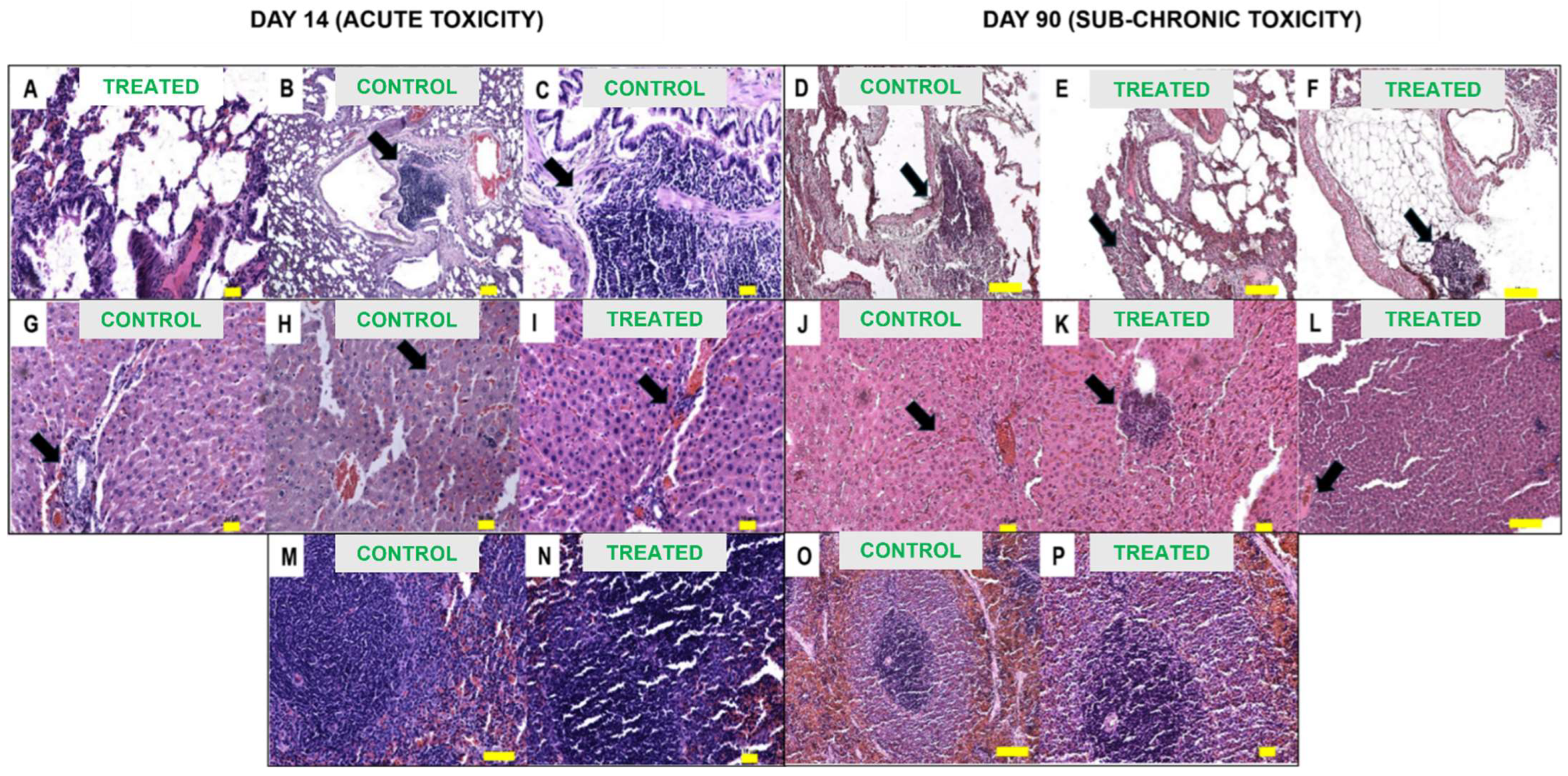

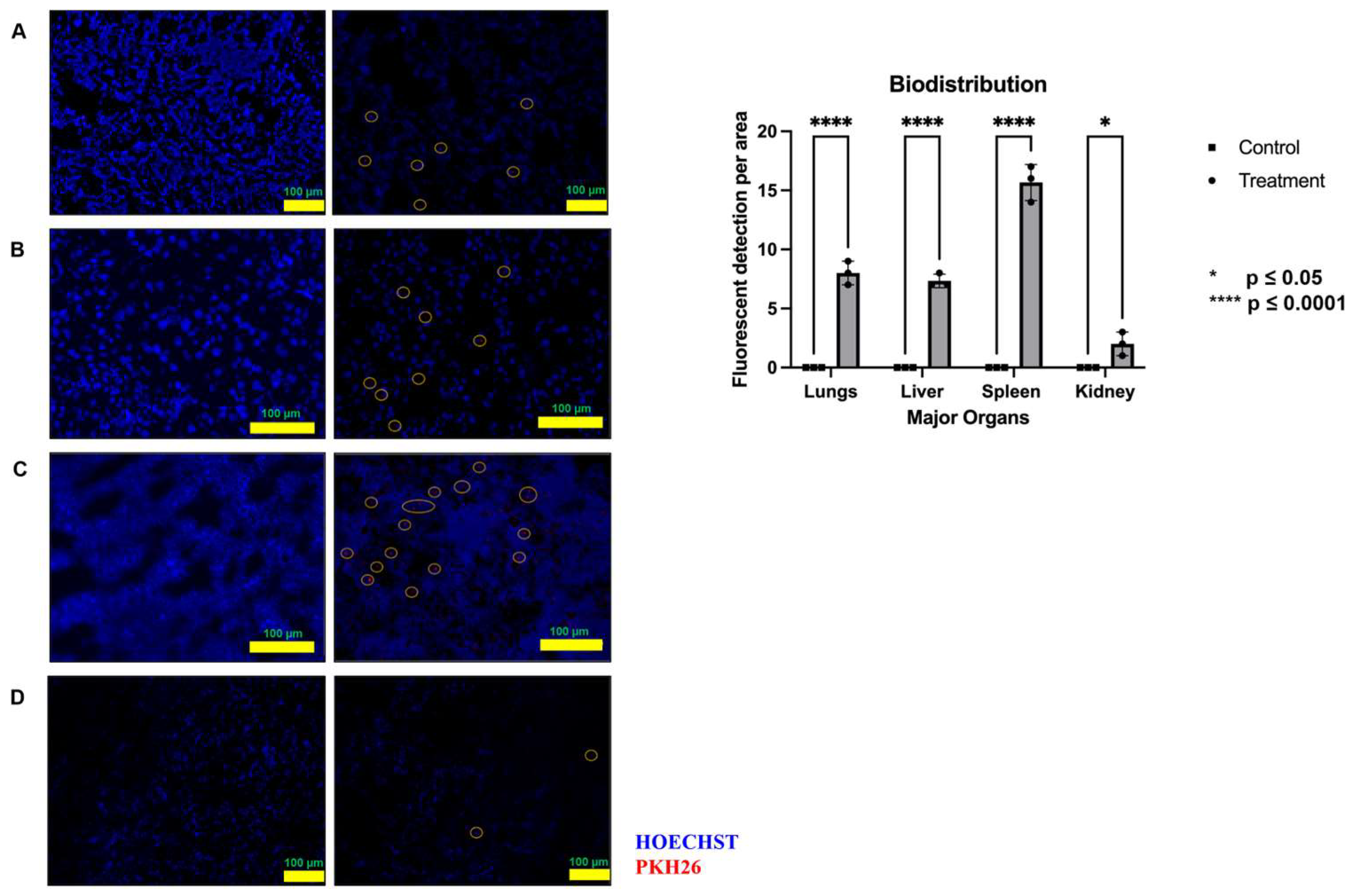
| Organ | Day 14 (Acute Toxicity) | Day 90 (Sub-Chronic Toxicity) |
|---|---|---|
| Lungs | Normal | Normal |
| Liver | Normal | Mottled edge appearance control (n = 3) and treated (n = 3) |
| Spleen | Normal | Blunt edge appearance control (n = 1) and treated (n = 1) |
| Kidney | Normal | Normal |
| Lymph nodes | NP | Reddish appearance treated (n = 3) |
| Assessment Parameter | Acute (D14) Toxicity | Sub-Chronic (D90) Toxicity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treated | Control | Treated | |
| Necrosis | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Pulmonary oedema | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Inflammation (lymphoplasmacytic) | Severe (focal) | NIL | Severe (focal) | Severe (focal) |
| Inflammation (neutrophils) | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Haemorrhage | NIL | NIL | Mild | NIL |
| Assessment Parameter | Acute (D14) Toxicity | Sub-Chronic (D90) Toxicity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treated | Control | Treated | |
| Necrosis | Mild | Mild | NIL | NIL |
| Apoptosis | NIL | Mild | NIL | NIL |
| Inflammation (lymphoplasmacytic) | Mild | Mild to moderate | Mild | Mild |
| Inflammation (neutrophils) | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Vascular congestion | Mild | Moderate | Moderate | Mild |
| Haemorrhage | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Assessment Parameter | Acute (D14) Toxicity | Sub-Chronic (D90) Toxicity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treated | Control | Treated | |
| Necrosis | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Apoptosis | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Largest size of lymphoid follicles (mm) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 1.5 |
| Giant cells | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Assessment Parameter | Acute (D14) Toxicity | Sub-Chronic (D90) Toxicity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treated | Control | Treated | |
| Necrosis | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Apoptosis | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Inflammation (lymphoplasmacytic) | NIL | NIL | NIL | Moderate (focal) |
| Inflammation (neutrophils) | NIL | NIL | NIL | NIL |
| Tubular changes (dilation) | NIL | Mild | Mild | Mild |
| Assessment Parameter | Sub-Chronic (D90) Toxicity | |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Treated | |
| Necrosis | NIL | NIL |
| Apoptosis | NIL | NIL |
| Lymphovacular dilatation | Mild | Mild |
| Lymphoid follicles diameter (mm) | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Giant cells | NIL | NIL |
| Granuloma | NIL | NIL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishnan, I.; Vijakumaran, U.; Hwei, N.M.; Xian, L.J.; Mohd Yusof, M.R.; Thangarajah, T.; Chin, T.G.; Wong, Y.P.; Kalyanasundaram, A.; Mahmood, Z.; et al. Safety Evaluation and Biodistribution of Fetal Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Sprague Dawley Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146806
Krishnan I, Vijakumaran U, Hwei NM, Xian LJ, Mohd Yusof MR, Thangarajah T, Chin TG, Wong YP, Kalyanasundaram A, Mahmood Z, et al. Safety Evaluation and Biodistribution of Fetal Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Sprague Dawley Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146806
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishnan, Illayaraja, Ubashini Vijakumaran, Ng Min Hwei, Law Jia Xian, Mohd Rafizul Mohd Yusof, Thavachelvi Thangarajah, Tan Geok Chin, Yin Ping Wong, Anusha Kalyanasundaram, Zalina Mahmood, and et al. 2025. "Safety Evaluation and Biodistribution of Fetal Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Sprague Dawley Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146806
APA StyleKrishnan, I., Vijakumaran, U., Hwei, N. M., Xian, L. J., Mohd Yusof, M. R., Thangarajah, T., Chin, T. G., Wong, Y. P., Kalyanasundaram, A., Mahmood, Z., Rajamanickam, S., Subramani, B., & Lokanathan, Y. (2025). Safety Evaluation and Biodistribution of Fetal Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Sprague Dawley Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146806








