Rifaximin Attenuates Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocarcinogenesis in a Rat MASH Model by Suppressing the Gut–Liver Axis and Epiregulin–IL-8-Associated Angiogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
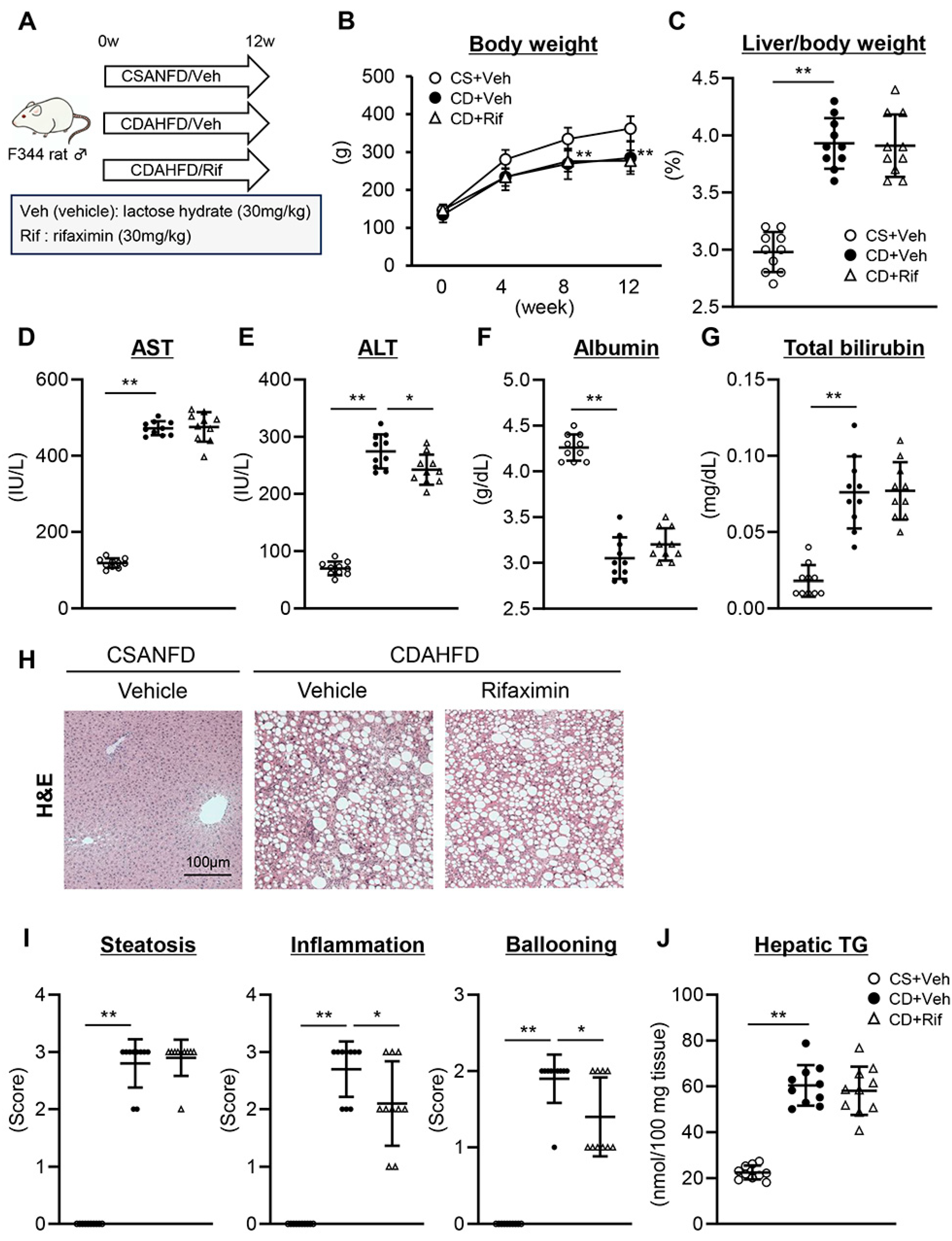
2.1. Rifaximin Attenuates Steatohepatitis in CDAHFD-Fed Rats
2.2. Rifaximin Suppresses Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocarcinogenesis in CDAHFD-Fed Rats
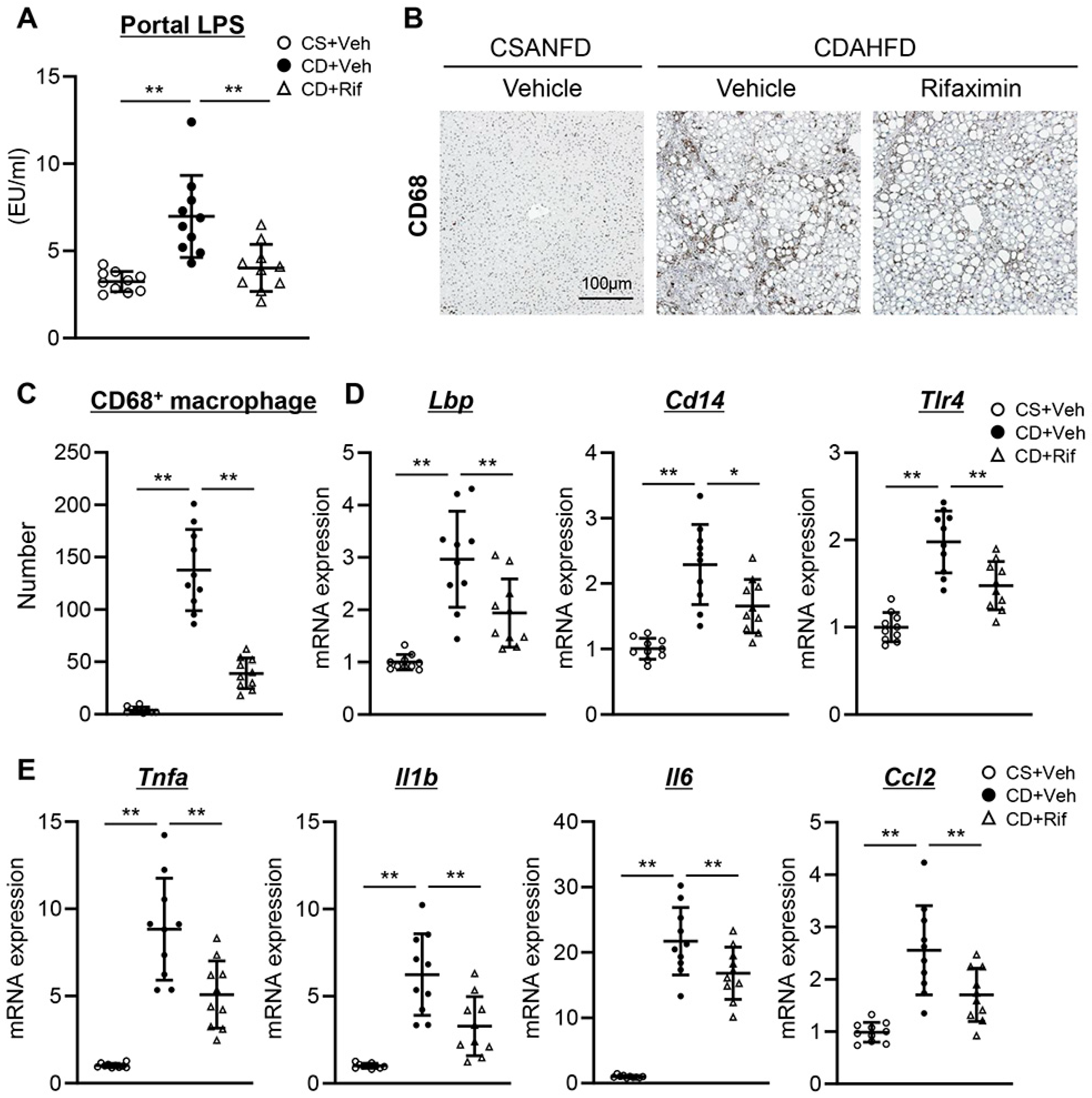
2.3. Rifaximin Reduces Portal LPS Levels and Ameliorates Hepatic LPS/TLR4-Mediated Kupffer Cell Activation
2.4. Rifaximin Reduces Epiregulin and Inhibits IL-8-Associated Neovascularization in the Liver of CDAHFD-Fed Rats
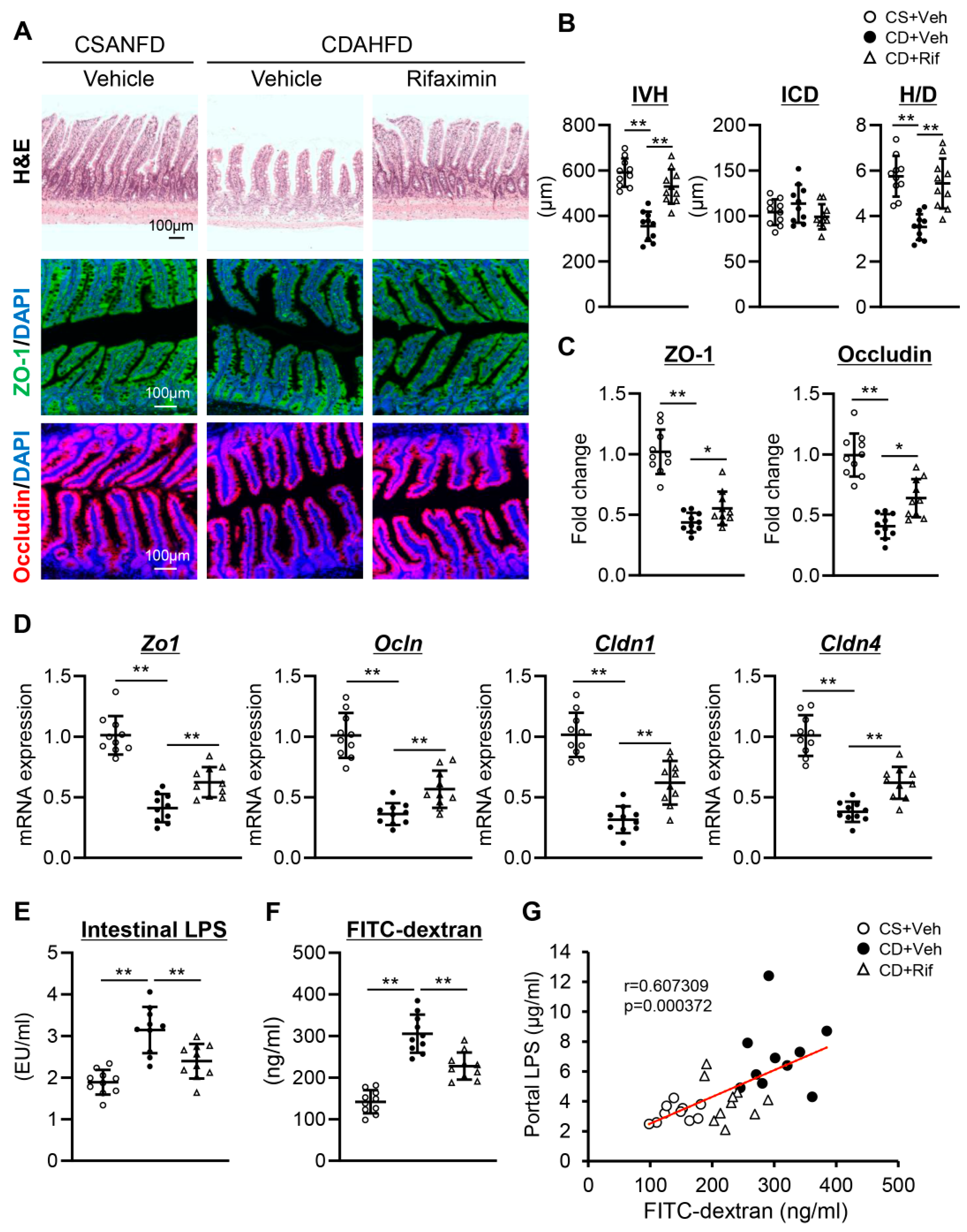
2.5. Rifaximin Reinforced Intestinal Barrier Function in CDAHFD-Fed Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Experiments
4.2. Histological Analyses
4.3. Immunohistochemical and Immunofluorescence Analyses
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.5. Measurement of LPS Levels in Portal Vein and Intestinal Tissue
4.6. Hepatic Triglyceride (TG) Measurement
4.7. Measurement of the Hepatic Epiregulin Level
4.8. Liver Hydroxyproline Content Measurement
4.9. Gut Permeability Assay
4.10. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sheka, A.C.; Adeyi, O.; Thompson, J.; Hameed, B.; Crawford, P.A.; Ikramuddin, S. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A review. JAMA 2020, 323, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Gong, W.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Trends in body mass index, overweight and obesity among adults in the USA, the NHANES from 2003 to 2018: A repeat cross-sectional survey. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e065425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Q.; El-Serag, H.B.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Willoughby, C.E.; Singal, A.G.; Greten, T.F.; Heikenwälder, M.; El-Serag, H.B.; Finn, R.S.; Friedman, S.L. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.S.; Taylor, R.J.; Bayliss, S.; Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Ishigami, M.; Toyoda, H.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Peleg, N.; et al. Association Between Fibrosis Stage and Outcomes of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1611–1625.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, H.; Jin, X.; Sun, J.; Li, Y. The multifaceted roles of macrophages in the transition from hepatitis to hepatocellular carcinoma: From mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Basis. Dis. 2025, 1871, 167676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasopoulos, N.A.; Charchanti, A.V.; Barbouti, A.; Mastoridou, E.M.; Goussia, A.C.; Karampa, A.D.; Christodoulou, D.; Glantzounis, G.K. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Cellular Senescence in the Pathogenesis of Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinyol, R.; Torrecilla, S.; Wang, H.; Montironi, C.; Piqué-Gili, M.; Torres-Martin, M.; Wei-Qiang, L.; Willoughby, C.E.; Ramadori, P.; Andreu-Oller, C.; et al. Molecular characterisation of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 865–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfar, H.; Javed, N.; Qasim, A.; Zacharia, G.S.; Ghazanfar, A.; Jyala, A.; Shehi, E.; Patel, H. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis and Progression to Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Literature Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Ma, S.; Huang, J.; Si, X.; Yang, M.; Song, W.; Lv, G.; Wang, G. Trojan-Horse Strategy Targeting the Gut-Liver Axis Modulates Gut Microbiome and Reshapes Microenvironment for Orthotopic Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2310002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Pan, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Qiu, J.; Wang, X.; Tang, N. Lipopolysaccharide facilitates immune escape of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via m6A modification of lncRNA MIR155HG to upregulate PD-L1 expression. Cell. Biol. Toxicol. 2022, 38, 1159–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, A.; Tang, L.; Zeng, S.; Lei, Y.; Yang, S.; Tang, B. Gut microbiota: A new piece in understanding hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer. Lett. 2020, 474, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.T.; Jing, Y.Y.; Gao, L.; Li, R.; Yang, X.; Pan, X.R.; Yang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Hou, X.J.; Zhao, Q.D.; et al. Lipopolysaccharide induces the differentiation of hepatic progenitor cells into myofibroblasts constitutes the hepatocarcinogenesis-associated microenvironment. Cell. Death. Differ. 2020, 27, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.X.; Yan, H.X.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W.; Wu, H.P.; Dong, W.; Tang, L.; Lin, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Zou, S.S.; et al. Endotoxin accumulation prevents carcinogen-induced apoptosis and promotes liver tumorigenesis in rodents. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasinariu, O.E.; Ceccarelli, S.; Alisi, A.; Moraru, E.; Nobili, V. Gut-liver axis and fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: An input for novel therapies. Dig. Liver Dis. 2013, 45, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, G.L. Lipopolysaccharides in liver injury: Molecular mechanisms of Kupffer cell activation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G256–G265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zou, L.; Jagavelu, K.; Simonetto, D.A.; Huebert, R.C.; Jiang, Z.D.; DuPont, H.L.; Shah, V.H. Intestinal decontamination inhibits TLR4 dependent fibronectin-mediated cross-talk between stellate cells and endothelial cells in liver fibrosis in mice. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; De Minicis, S.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Kluwe, J.; Osawa, Y.; Brenner, D.A.; Schwabe, R.F. TLR4 enhances TGF-beta signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1324–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yan, M.; Li, J.; Long, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H. Dual functions of STAT3 in LPS-induced angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell. Res. 2019, 1866, 566–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, N. Lipopolysaccharide promotes angiogenesis in mice model of HCC by stimulating hepatic stellate cell activation via TLR4 pathway. Acta. Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Caraceni, P.; Vargas, V.; Solà, E.; Alessandria, C.; de Wit, K.; Trebicka, J.; Angeli, P.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Durand, F.; Pose, E.; et al. The Use of Rifaximin in Patients with Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Zhu, X.; Wu, J.; Hong, W.; Hu, W.; Fang, T. Mechanisms of rifaximin inhibition of hepatic fibrosis in mice with metabolic dysfunction associated steatohepatitis through the TLR4/NFkappaB pathway. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, M.; Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Fujimoto, Y.; Murata, K.; Takeda, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Fujinaga, Y.; Takaya, H.; Kawaratani, H.; et al. Rifaximin and lubiprostone mitigate liver fibrosis development by repairing gut barrier function in diet-induced rat steatohepatitis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2022, 54, 1392–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Razik, A.; Mousa, N.; Shabana, W.; Refaey, M.; Elzehery, R.; Elhelaly, R.; Zalata, K.; Abdelsalam, M.; Eldeeb, A.A.; Awad, M.; et al. Rifaximin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Hit multiple targets with a single shot. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, T.; Nishimura, N.; Kaji, K.; Tomooka, F.; Shibamoto, A.; Iwai, S.; Suzuki, J.; Kawaratani, H.; Namisaki, T.; Akahane, T.; et al. Role of Epiregulin on Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Hepatocarcinogenesis as a Mediator via EGFR Signaling in the Cancer Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnaud, M.; Faivre, J.; Moniaux, N. Targeting gut flora to prevent progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 385–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapito, D.H.; Mencin, A.; Gwak, G.Y.; Pradere, J.P.; Jang, M.K.; Mederacke, I.; Caviglia, J.M.; Khiabanian, H.; Adeyemi, A.; Bataller, R.; et al. Promotion of hepatocellular carcinoma by the intestinal microbiota and TLR4. Cancer. Cell 2012, 21, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, T.; Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Asada, S.; Koizumi, A.; Tanaka, M.; Yorioka, N.; Tsuji, Y.; Kitagawa, K.; Sato, S.; et al. Cabozantinib prevents the progression of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis by inhibiting the activation of hepatic stellate cell and macrophage and attenuating angiogenic activity. Heliyon 2024, 10, e38647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagire, H.S.; Pagire, S.H.; Jeong, B.K.; Choi, W.I.; Oh, C.J.; Lim, C.W.; Kim, M.; Yoon, J.; Kim, S.S.; Bae, M.A.; et al. Discovery of a peripheral 5HT2A antagonist as a clinical candidate for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazanave, S.C.; Warren, A.D.; Pacula, M.; Touti, F.; Zagorska, A.; Gural, N.; Huang, E.K.; Sherman, S.; Cheema, M.; Ibarra, S.; et al. Peptide-based urinary monitoring of fibrotic nonalcoholic steatohepatitis by mass-barcoded activity-based sensors. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021, 13, eabe8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.K.; Chaudhari, S.N.; Lee, Y.; Sojoodi, M.; Adhikari, A.A.; Zukerberg, L.; Shroff, S.; Barrett, S.C.; Tanabe, K.; Chung, R.T.; et al. Inhibition of microbial deconjugation of micellar bile acids protects against intestinal permeability and liver injury. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo2794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K.; Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Enomoto, M.; Fujimoto, Y.; Takeda, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Fujinaga, Y.; Takaya, H.; Kawaratani, H.; et al. Rifaximin enhances the L-carnitine-mediated preventive effects on skeletal muscle atrophy in cirrhotic rats by modulating the gut-liver-muscle axis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 50, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, B.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, Z. MicroRNA-146a-5p attenuates irradiation-induced and LPS-induced hepatic stellate cell activation and hepatocyte apoptosis through inhibition of TLR4 pathway. Cell. Death Dis. 2018, 9, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Gao, J.; Gillilland, M., 3rd; Wu, X.; Song, I.; Kao, J.Y.; Owyang, C. Rifaximin alters intestinal bacteria and prevents stress-induced gut inflammation and visceral hyperalgesia in rats. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 484–496.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riese, D.J., 2nd; Cullum, R.L. Epiregulin: Roles in normal physiology and cancer. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2014, 28, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.J.; Mill, C.; Lambert, S.; Buchman, J.; Wilson, T.R.; Hernandez-Gordillo, V.; Gallo, R.M.; Ades, L.M.; Settleman, J.; Riese, D.J., 2nd. EGFR ligands exhibit functional differences in models of paracrine and autocrine signaling. Growth Factors 2012, 30, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.L.; Feng, P.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Chen, K.Y.; Sun, W.L.; Van Hiep, N.; Luo, C.S.; Wu, S.M. The Role of EREG/EGFR Pathway in Tumor Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.W.; Yang, L.Q.; Zhao, F.; Chen, C.W.; Xu, L.H.; Fu, J.; Li, S.L.; Ge, X.Y. Epiregulin Promotes Lung Metastasis of Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3700–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Duda, D.G.; Sahani, D.V.; Jain, R.K. HCC and angiogenesis: Possible targets and future directions. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, J.; Shirabe, K.; Sugimachi, K.; Maehara, Y. Review of angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, 12310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Gigli, S.; Seguella, L.; Nobile, N.; D’Alessandro, A.; Pesce, M.; Capoccia, E.; Steardo, L.; Cirillo, C.; Cuomo, R.; et al. Rifaximin, a non-absorbable antibiotic, inhibits the release of pro-angiogenic mediators in colon cancer cells through a pregnane X receptor-dependent pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaoki, S.; Suzuki, H.; Okada, M.; Fukui, N.; Isobe, M.; Saito, T. Development of an experimental rat model of hyperammonemic encephalopathy and evaluation of the effects of rifaximin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 779, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. HGF Aggravated Periodontitis-Associated Gut Barrier and Microbial Dysfunction: Implications for Oral-Gut Axis Regulation. Biology 2025, 14, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.H.; Wen, S.L.; Tong, H.; Wang, C.H.; Yang, W.J.; Tang, S.H.; Yan, Z.P.; Tai, Y.; Ye, C.; Liu, R.; et al. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 alleviates liver cirrhosis via improvement of the dysfunctional gut-liver axis in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G962–G972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishimura, N.; Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Hanatani, J.; Nakatani, T.; Oyama, M.; Shibamoto, A.; Tsuji, Y.; Kitagawa, K.; Sato, S.; et al. Rifaximin Attenuates Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocarcinogenesis in a Rat MASH Model by Suppressing the Gut–Liver Axis and Epiregulin–IL-8-Associated Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146710
Nishimura N, Kaji K, Nishimura N, Hanatani J, Nakatani T, Oyama M, Shibamoto A, Tsuji Y, Kitagawa K, Sato S, et al. Rifaximin Attenuates Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocarcinogenesis in a Rat MASH Model by Suppressing the Gut–Liver Axis and Epiregulin–IL-8-Associated Angiogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146710
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishimura, Naoki, Kosuke Kaji, Norihisa Nishimura, Junichi Hanatani, Tatsuya Nakatani, Masafumi Oyama, Akihiko Shibamoto, Yuki Tsuji, Koh Kitagawa, Shinya Sato, and et al. 2025. "Rifaximin Attenuates Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocarcinogenesis in a Rat MASH Model by Suppressing the Gut–Liver Axis and Epiregulin–IL-8-Associated Angiogenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146710
APA StyleNishimura, N., Kaji, K., Nishimura, N., Hanatani, J., Nakatani, T., Oyama, M., Shibamoto, A., Tsuji, Y., Kitagawa, K., Sato, S., Namisaki, T., Tamaoki, S., & Yoshiji, H. (2025). Rifaximin Attenuates Liver Fibrosis and Hepatocarcinogenesis in a Rat MASH Model by Suppressing the Gut–Liver Axis and Epiregulin–IL-8-Associated Angiogenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6710. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146710





