Comparative Transcriptome and Hormonal Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Salt Tolerance in Rice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
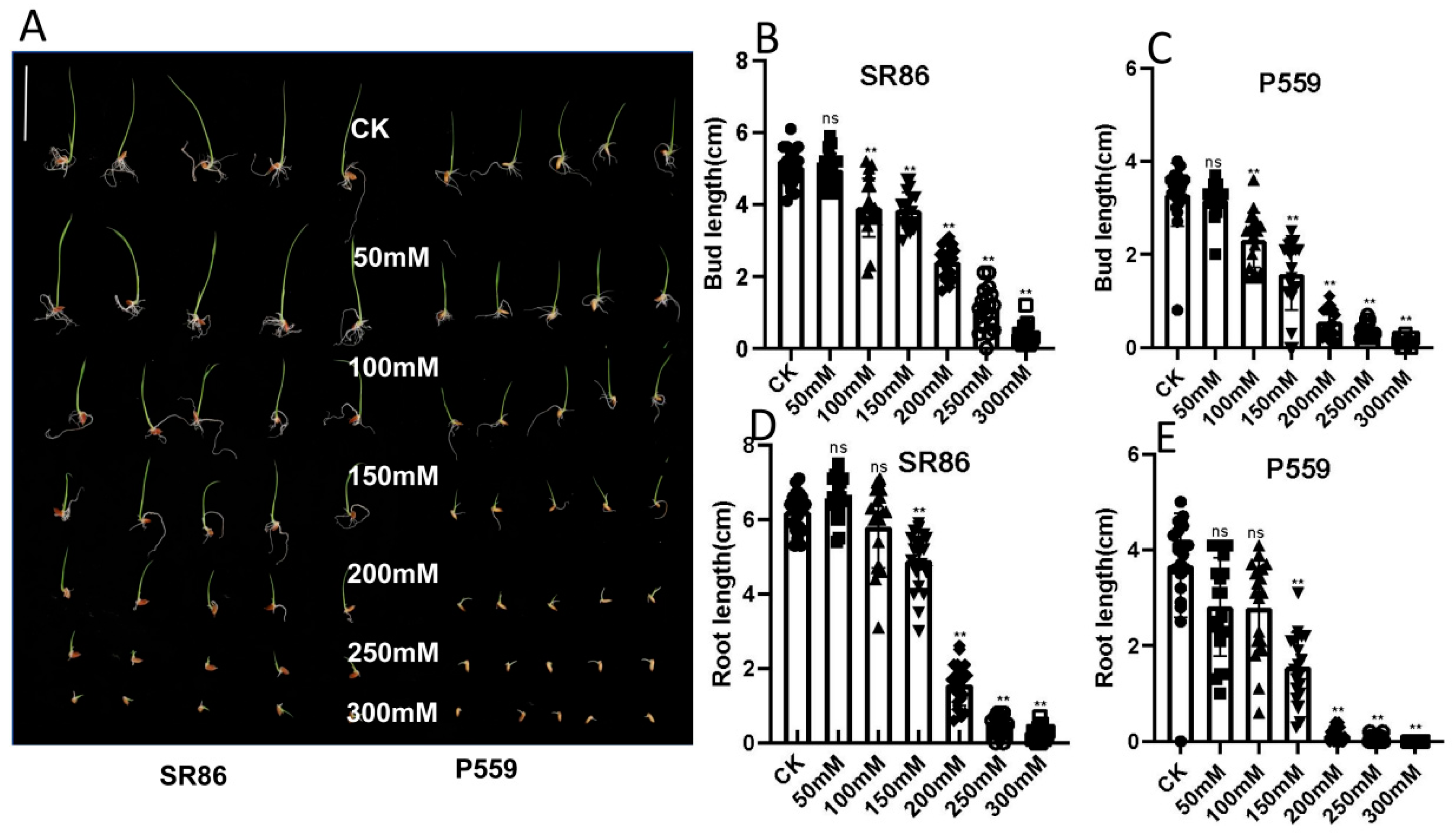
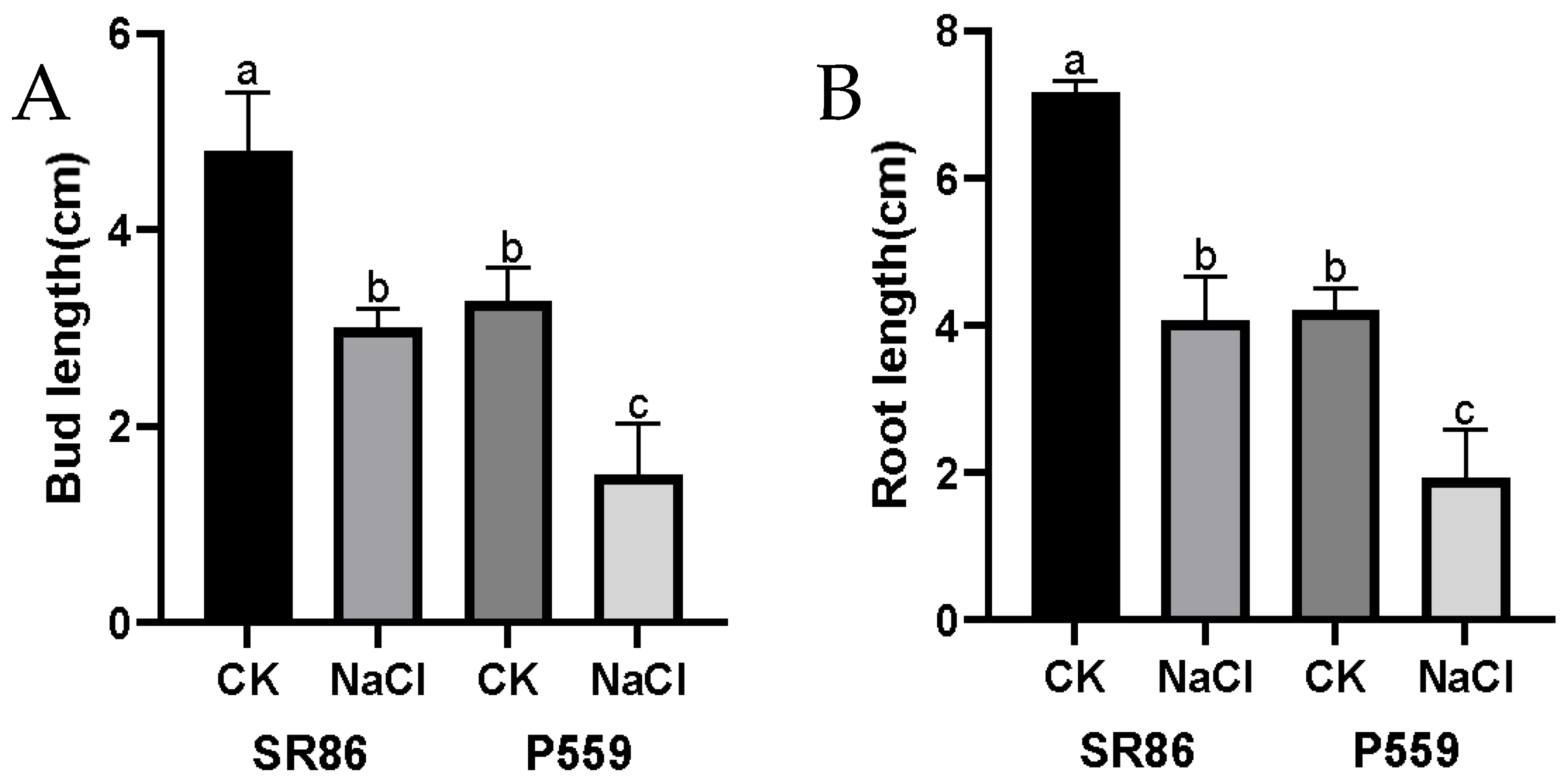
2.1. Phenotypic Response of Rice to Salt Stress
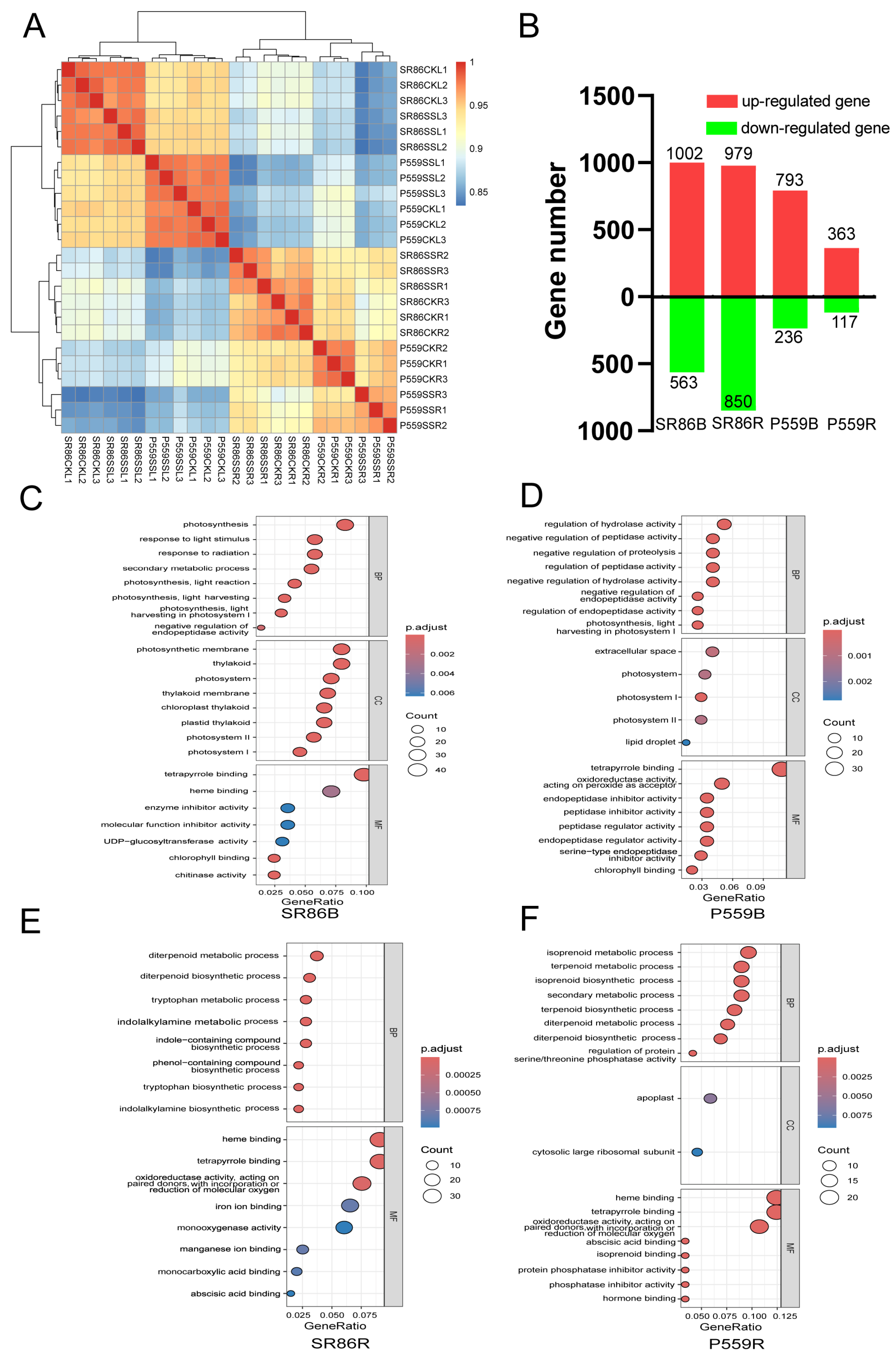
2.2. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of Two Rice Genotypes with Contrasting Salt Tolerance
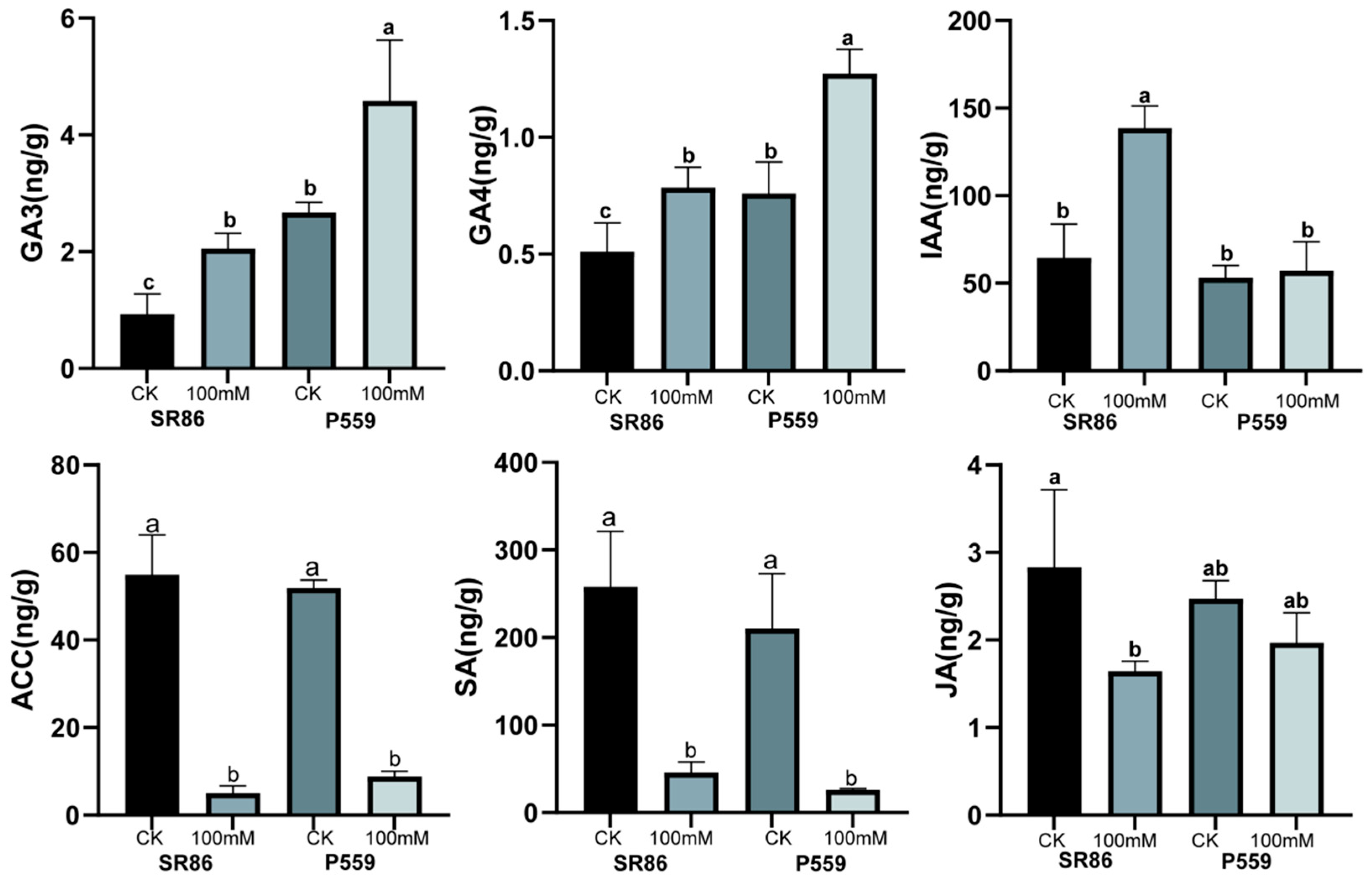
2.3. Changes in Endogenous Hormones Exposed to Salt Stress
3. Discussion
3.1. Changes in Gene Transcription of Rice Under Salt Stress
3.2. Buds and Roots Synergistically Regulate Antioxidant Pathways to Cope with Salt Stress
3.3. Regulation of Hormone Metabolic Pathway Exposed to Salt Stress
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Measurement of Hormones
4.3. RNA Sequencing and Analysis
4.4. Transcriptome Data Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, Z.; Xiong, L.; Shi, H.; Yang, S.; Herrera-Estrella, L.R.; Xu, G.; Chao, D.Y.; Li, J.; Wang, P.Y.; Qin, F.; et al. Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci. China Life Sci. 2020, 63, 635–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morton, M.J.L.; Awlia, M.; Al-Tamimi, N.; Saade, S.; Pailles, Y.; Negrao, S.; Tester, M. Salt stress under the scalpel—Dissecting the genetics of salt tolerance. Plant J. 2019, 97, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munns, R.; Tester, M. Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 651–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, H.; Yang, Y.; Feng, X.; Chen, X.; Xiao, F.; Lin, H.; Guo, Y. Insights into plant salt stress signaling and tolerance. J. Genet. Genom. 2024, 51, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epron, D.; Toussaint, M.L.; Badot, P.M. Effects of sodium chloride salinity on root growth and respiration in oak seedlings. Ann. Sci. For. 1999, 56, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zelm, E.; Zhang, Y.; Testerink, C. Salt Tolerance Mechanisms of Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2020, 71, 403–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; He, B.; Han, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, Z. A global examination of the response of ecosystem water-use efficiency to drought based on MODIS data. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Liang, J.Z. Initiation and regulation of water deficit-induced abscisic acid accumulation in maize leaves and roots: Cellular volume and water relations. J. Exp. Bot. 2001, 52, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, M.M.; Flexas, J.; Pinheiro, C. Photosynthesis under drought and salt stress: Regulation mechanisms from whole plant to cell. Ann. Bot. 2009, 103, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-StPaul, N.; Delzon, S.; Cochard, H. Plant resistance to drought depends on timely stomatal closure. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 1437–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauline, A.; Essah, R.D.; Tester, M. Sodium Influx and Accumulation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2003, 133, 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Keisham, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhatla, S.C. Mechanisms of Sodium Transport in Plants—Progresses and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartels, D.; Sunkar, R. Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2005, 24, 23–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Rebecca Njeri, D.; Chen, X.; Lin, Z. Molecular mechanisms underlying the signal perception and transduction during seed germination. Mol. Breed 2024, 44, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.A.; Ma, W.; Shen, S.; Gu, A. Underlying Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms for Seed Germination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, K.; Liu, X.D.; Xie, Q.; He, Z.H. Two Faces of One Seed: Hormonal Regulation of Dormancy and Germination. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Chen, M.; Zhan, C.; Liu, K.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, T.; Zhu, P.; He, Y.; Zeng, P.; Tang, H.; et al. Identification of OsPK5 involved in rice glycolytic metabolism and GA/ABA balance for improving seed germination via genome-wide association study. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 3446–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, K.; Linkies, A.; Steinbrecher, T.; Mummenhoff, K.; Tarkowska, D.; Tureckova, V.; Ignatz, M.; Sperber, K.; Voegele, A.; de Jong, H.; et al. DELAY OF GERMINATION 1 mediates a conserved coat-dormancy mechanism for the temperature- and gibberellin-dependent control of seed germination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3571–E3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Htwe, Y.M.; Li, J.; Shi, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Ihase, L.O. Integrative omics analysis on phytohormones involved in oil palm seed germination. BMC Plant Biol 2019, 19, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-K. Salt and Drought Stress Signal Transduction in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2002, 53, 247–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ma, B.; He, S.-J.; Xiong, Q.; Duan, K.-X.; Yin, C.-C.; Chen, H.; Lu, X.; Chen, S.-Y.; Zhang, J.-S. MAOHUZI6/ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-LIKE1 and ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE3-LIKE2 Regulate Ethylene Response of Roots and Coleoptiles and Negatively Affect Salt Tolerance in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, M.; Datta, K.; Roychoudhury, A.; Gayen, D.; Sengupta, D.N.; Datta, S.K. Overexpression of Rab16A gene in indica rice variety for generating enhanced salt tolerance. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Chen, S.; Cheng, S.; Li, C.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Zha, W.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.; Li, P.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis Revealed the Dynamic and Rapid Transcriptional Reprogramming Involved in Cold Stress and Related Core Genes in the Rice Seedling Stage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, P.; Jing, W.; Cao, C.; Sun, M.; Chi, W.; Zhao, S.; Dai, J.; Shi, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, B.; et al. Transcriptional repressor RST1 controls salt tolerance and grain yield in rice by regulating gene expression of asparagine synthetase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2210338119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Mo, J.; Zhou, H.; Shen, X.; Xie, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, S. Comparative transcriptome analysis of gene responses of salt-tolerant and salt-sensitive rice cultivars to salt stress. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.A.; Sharma, N.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Colmer, T.D.; Sutton, T.; Baumann, U. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals molecular regulation of salt tolerance in two contrasting chickpea genotypes. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Magwanga, R.O.; Jin, D.; Cai, X.; Hou, Y.; Juyun, Z.; Agong, S.G.; Wang, K.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Z. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals evolutionary divergence and shared network of cold and salt stress response in diploid D-genome cotton. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, T.; Gao, M.; Ye, M.; Lin, M.; Wu, D.; Guo, J.; Guan, W.; Wang, J.; Yang, K.; et al. Transcriptome and Metabolome Profiling Reveal the Resistance Mechanisms of Rice against Brown Planthopper. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Du, B.; Hao, F.; Lei, H.; Wan, Q.; He, G.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. Dynamic metabolic responses of brown planthoppers towards susceptible and resistant rice plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 1346–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, L.; Li, M.; Ma, B.; Yan, C.; Chen, J. Omics-Based Comparative Transcriptional Profiling of Two Contrasting Rice Genotypes during Early Infestation by Small Brown Planthopper. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 28746–28764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Z.; Fang, C.; Liu, K. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveal the responses of brown planthoppers to RH resistant rice cultivar. Front Physiol. 2022, 13, 1018470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Tzin, V.; Romeis, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y. Combined transcriptome and metabolome analyses to understand the dynamic responses of rice plants to attack by the rice stem borer Chilo suppressalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S.; Chen, L.; Tu, W.; Scossa, F.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Fernie, A.R.; Song, B.; Xie, C. The arginine decarboxylase gene ADC1, associated to the putrescine pathway, plays an important role in potato cold-acclimated freezing tolerance as revealed by transcriptome and metabolome analyses. Plant J. 2018, 96, 1283–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, N.; Uzair, M.; Zaid, I.U.; Attia, K.A.; Inam, S.; Fiaz, S.; Abdallah, R.M.; Naeem, M.K.; Farooq, U.; Rehman, N.; et al. The comparative transcriptome analysis of two green super rice genotypes with varying tolerance to salt stress. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 51, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, F.; Li, W.; Wang, F.; Zhong, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, J. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals molecular response to salinity stress of salt-tolerant and sensitive genotypes of indica rice at seedling stage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, A.L.S.; Passaia, G.; Lobo, A.K.M.; Jardim-Messeder, D.; Silveira, J.A.; Margis-Pinheiro, M. Mitochondrial glutathione peroxidase (OsGPX3) has a crucial role in rice protection against salt stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 158, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhen, Z.; Peng, J.; Chang, L.; Gong, Q.; Wang, N.N. Loss of ACS7 confers abiotic stress tolerance by modulating ABA sensitivity and accumulation in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4875–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Ren, D. Activation of MAPK kinase 9 induces ethylene and camalexin biosynthesis and enhances sensitivity to salt stress in Arabidopsis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 26996–27006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, J.; Xing, D. Low concentrations of salicylic acid delay methyl jasmonate-induced leaf senescence by up-regulating nitric oxide synthase activity. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 5233–5245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Lin, H.H. Role of salicylic acid in plant abiotic stress. Z. Naturforschung C J. Biosci. 2008, 63, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albaseer, S.S.; Rao, R.N.; Swamy, Y.V.; Mukkanti, K. An overview of sample preparation and extraction of synthetic pyrethroids from water, sediment and soil. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 5537–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcke, G.U.; Handrick, V.; Bergau, N.; Fichtner, M. An UPLC-MS/MS method for highly sensitive high-throughput analysis of phytohormones in plant tissues. Plant Methods 2012, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Cai, W.J.; Yu, L.; Ding, J.; Feng, Y.Q. Comprehensive Profiling of Phytohormones in Honey by Sequential Liquid-Liquid Extraction Coupled with Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 65, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, D.; Xu, Y.; Iqbal, A.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Tang, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Huang, M.; et al. Comparative Transcriptome and Hormonal Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Salt Tolerance in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146660
Jin D, Xu Y, Iqbal A, Liu Y, Zhang Y, Lin Y, Tang L, Wang X, Wang J, Huang M, et al. Comparative Transcriptome and Hormonal Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Salt Tolerance in Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146660
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Dingsha, Yanchao Xu, Asif Iqbal, Yuqing Liu, Yage Zhang, Youzhen Lin, Liqiong Tang, Xinhua Wang, Junjie Wang, Mengshu Huang, and et al. 2025. "Comparative Transcriptome and Hormonal Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Salt Tolerance in Rice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146660
APA StyleJin, D., Xu, Y., Iqbal, A., Liu, Y., Zhang, Y., Lin, Y., Tang, L., Wang, X., Wang, J., Huang, M., Xu, P., & Wang, X. (2025). Comparative Transcriptome and Hormonal Analysis Reveals the Mechanisms of Salt Tolerance in Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146660







