A Case of Salt-Wasting Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Caused by a Rare Intronic Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Presentation
2.1. Clinical Evaluation
2.2. Methodology
2.2.1. Amplicon and Sanger Sequencing
2.2.2. Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.3. Molecular Findings
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAH | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
| HC | Hydrocortisone |
| FLC | Fludrocortisone |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| IGV | Integrative Genomics Viewer |
| MPS | Massive parallel sequencing |
| MLPA | Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification |
References
- Parsa, A.A.; New, M.I. Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Genet. Steroid Disord. 2017, 165, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merke, D.P.; Bornstein, S.R. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Lancet 2005, 365, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, S.; Röhl, F.-W.; Bonfig, W.; Brämswig, J.; Richter-Unruh, A.; Fricke-Otto, S.; Bettendorf, M.; Riepe, F.; Kriegshäuser, G.; Schönau, E.; et al. Genotype/Phenotype Correlations in 538 Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Patients from Germany and Austria: Discordances in Milder Genotypes and in Screened Versus Prescreening Patients. Endocr. Connect. 2019, 8, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrysheva, N.G.; Melnichenko, G.A.; Adamyan, L.V.; Troshina, E.A.; Molashenko, N.V.; Sazonova, A.I.; Uvarova, E.V.; Esayan, R.M.; Andreeva, E.N.; Uzhegova, Z.A.; et al. Russian clinical practice guidelines «congenital adrenal hyperplasia». Obes. Metab. 2021, 18, 345–382. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelkers, W.K. Effects of Estrogens and Progestogens on the Renin-Aldosterone System and Blood Pressure. XVII Meet. Int. Study Group Steroid Horm. 1996, 61, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, G.-H.; Yoo, H.-W.; Choi, J.-H. Molecular Basis and Genetic Testing Strategies for Diagnosing 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency, Including CAH-X Syndrome. Ann. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 28, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchong, C.A.; Zhou, B.; Rupert, K.L.; Chung, E.K.; Jones, K.N.; Sotos, J.F.; Zipf, W.B.; Rennebohm, R.M.; Yu, C.Y. Deficiencies of Human Complement Component C4a and C4b and Heterozygosity in Length Variants of RP-C4-CYP21-TNX (RCCX) Modules in Caucasians: The Load of Rccx Genetic Diversity on Major Histocompatibility Complex–Associated Disease. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 2183–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsamo, A.; Baldazzi, L.; Menabò, S.; Cicognani, A. Impact of Molecular Genetics on Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Management. Sex. Dev. 2010, 4, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-H. Mutational Analysis of CYP21A2 Gene and CYP21A1P Pseudogene: Long-Range PCR on Genomic DNA. In Pseudogenes: Functions and Protocols; Poliseno, L., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S. Ultrafast One-Pass FASTQ Data Preprocessing, Quality Control, and Deduplication Using Fastp. iMeta 2023, 2, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasimuddin, M.; Misra, S.; Li, H.; Aluru, S. Efficient Architecture-Aware Acceleration of BWA-MEM for Multicore Systems. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium (IPDPS), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 20–24 May 2019; pp. 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poplin, R.; Chang, P.-C.; Alexander, D.; Schwartz, S.; Colthurst, T.; Ku, A.; Newburger, D.; Dijamco, J.; Nguyen, N.; Afshar, P.T.; et al. A Universal SNP and Small-Indel Variant Caller Using Deep Neural Networks. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 983–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genomics in the Cloud. Available online: https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/genomics-in-the/9781491975183/ (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Martin, M.; Patterson, M.; Garg, S.; O Fischer, S.; Pisanti, N.; Klau, G.W.; Schöenhuth, A.; Marschall, T. WhatsHap: Fast and Accurate Read-Based Phasing. bioRxiv 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaganathan, K.; Panagiotopoulou, S.K.; McRae, J.F.; Darbandi, S.F.; Knowles, D.; Li, Y.I.; Kosmicki, J.A.; Arbelaez, J.; Cui, W.; Schwartz, G.B.; et al. Predicting Splicing from Primary Sequence with Deep Learning. Cell 2019, 176, 535–548.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, N.; Çelik, M.H.; Hölzlwimmer, F.R.; Mertes, C.; Prokisch, H.; Yépez, V.A.; Gagneur, J. Aberrant Splicing Prediction across Human Tissues. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leman, R.; Parfait, B.; Vidaud, D.; Girodon, E.; Pacot, L.; Le Gac, G.; Ka, C.; Ferec, C.; Fichou, Y.; Quesnelle, C.; et al. SPiP: Splicing Prediction Pipeline, a Machine Learning Tool for Massive Detection of Exonic and Intronic Variant Effects on mRNA Splicing. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 2308–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Wenger, A.M.; Zehir, A.; Mesirov, J.P. Variant Review with the Integrative Genomics Viewer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e31–e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Francioli, L.C.; Goodrich, J.K.; Collins, R.L.; Kanai, M.; Wang, Q.; Alföldi, J.; Watts, N.A.; Vittal, C.; Gauthier, L.D.; et al. A Genomic Mutational Constraint Map Using Variation in 76,156 Human Genomes. Nature 2024, 625, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and Guidelines for the Interpretation of Sequence Variants: A Joint Consensus Recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Carss, K.J.; Halldorsson, B.V.; Cortes, A.; UK Biobank Whole-Genome Sequencing Consortium. Whole-Genome Sequencing of Half-a-Million UK Biobank Participants. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VCV000800630.4-ClinVar-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/variation/800630/ (accessed on 8 April 2025).
- Ellingford, J.M.; Ahn, J.W.; Bagnall, R.D.; Baralle, D.; Barton, S.; Campbell, C.; Downes, K.; Ellard, S.; Duff-Farrier, C.; FitzPatrick, D.R.; et al. Recommendations for Clinical Interpretation of Variants Found in Non-Coding Regions of the Genome. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner-Parzer, S.; Witsch-Baumgartner, M.; Hoeppner, W. EMQN Best Practice Guidelines for Molecular Genetic Testing and Reporting of 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 28, 1341–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiryagin, V.V.; Devyatkin, A.A.; Fateev, O.D.; Petriaikina, E.S.; Bogdanov, V.P.; Antysheva, Z.G.; Volchkov, P.Y.; Yudin, S.M.; Woroncow, M.; Skvortsova, V.I. Genomic Complexity and Clinical Significance of the RCCX Locus. PeerJ 2024, 12, e18243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangodkar, P.; Khadilkar, V.; Raghupathy, P.; Kumar, R.; Dayal, A.A.; Dayal, D.; Ayyavoo, A.; Godbole, T.; Jahagirdar, R.; Bhat, K.; et al. Clinical Application of a Novel next Generation Sequencing Assay for CYP21A2 Gene in 310 Cases of 21- Hydroxylase Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia from India. Endocrine 2020, 71, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Mao, A.; Li, J.; Bao, S.; Li, J. Long-read sequencing: An Effective Method for Genetic Analysis of CYP21A2 Variation in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 547, 117419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, P.W.; Azziz, R.; Baskin, L.S.; Ghizzoni, L.; Hensle, T.W.; Merke, D.P.; Meyer-Bahlburg, H.F.L.; Miller, W.L.; Montori, V.M.; Oberfield, S.E.; et al. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4133–4160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Concolino, P.; Rizza, R.; Costella, A.; Carrozza, C.; Zuppi, C.; Capoluongo, E. CYP21A2 Intronic Variants Causing 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2017, 71, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsumata, N.; Shinagawa, T.; Horikawa, R.; Fujikura, K. Novel Intronic CYP21A2 Mutation in a Japanese Patient with Classic salt-Wasting Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2010, 59, 1628–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubtsov, P.M.; Igudin, E.L.; Pichugina, M.Y.; Spirin, P.V.; Prassolov, V.S.; Tyul’pakov, A.N. Characterization of a New Splicing Mutation in the Steroid 21-Hydroxylase Gene. Russ. J. Bioorg. Chem. 2011, 37, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocova, M.; Concolino, P.; Falhammar, H. Characteristics of In2G Variant in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 12, 788812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agathe, J.-M.d.S.; Filser, M.; Isidor, B.; Besnard, T.; Gueguen, P.; Perrin, A.; Van Goethem, C.; Verebi, C.; Masingue, M.; Rendu, J.; et al. SpliceAI-visual: A Free Online Tool to Improve SpliceAI Splicing Variant Interpretation. Hum. Genom. 2023, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
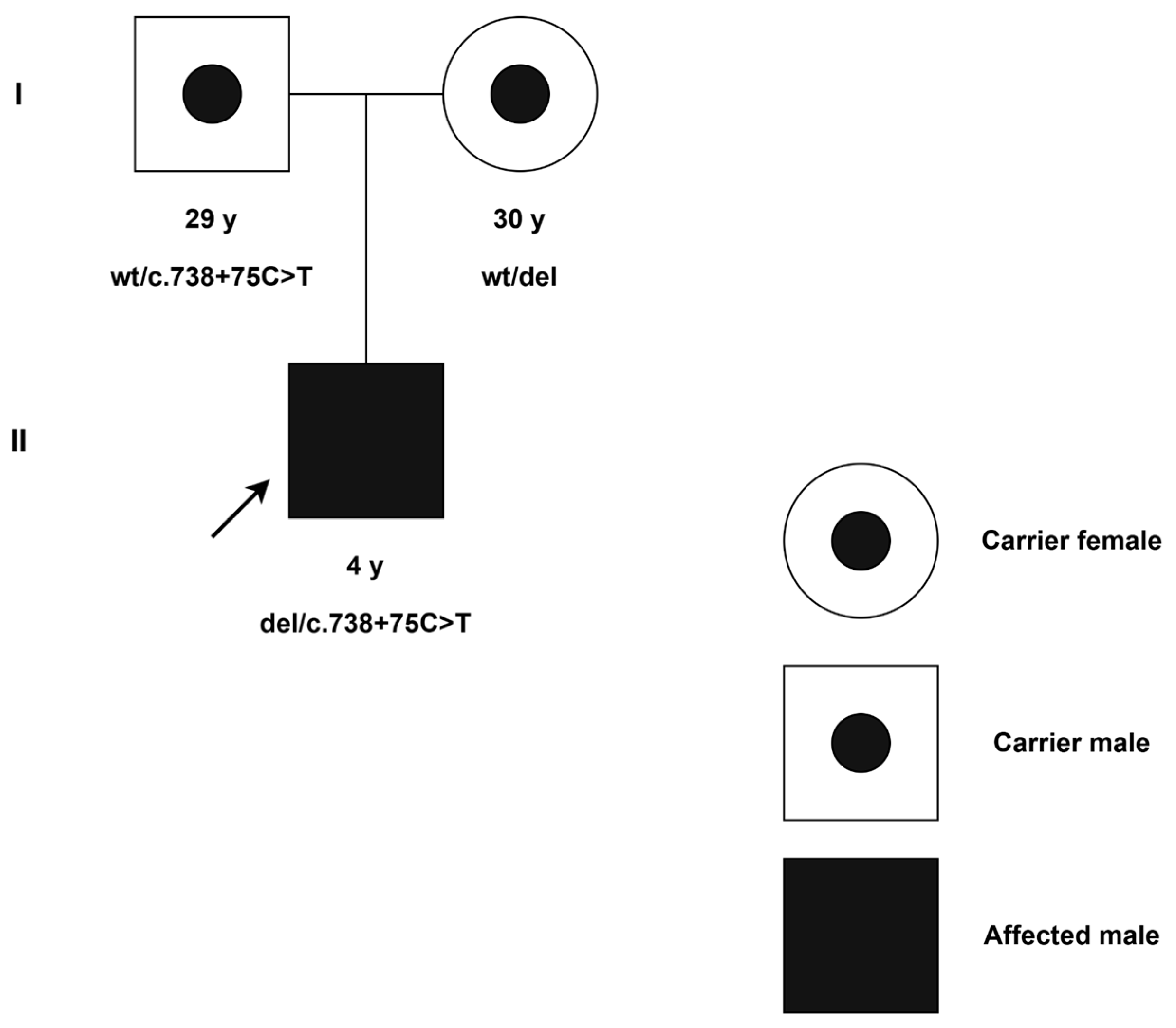
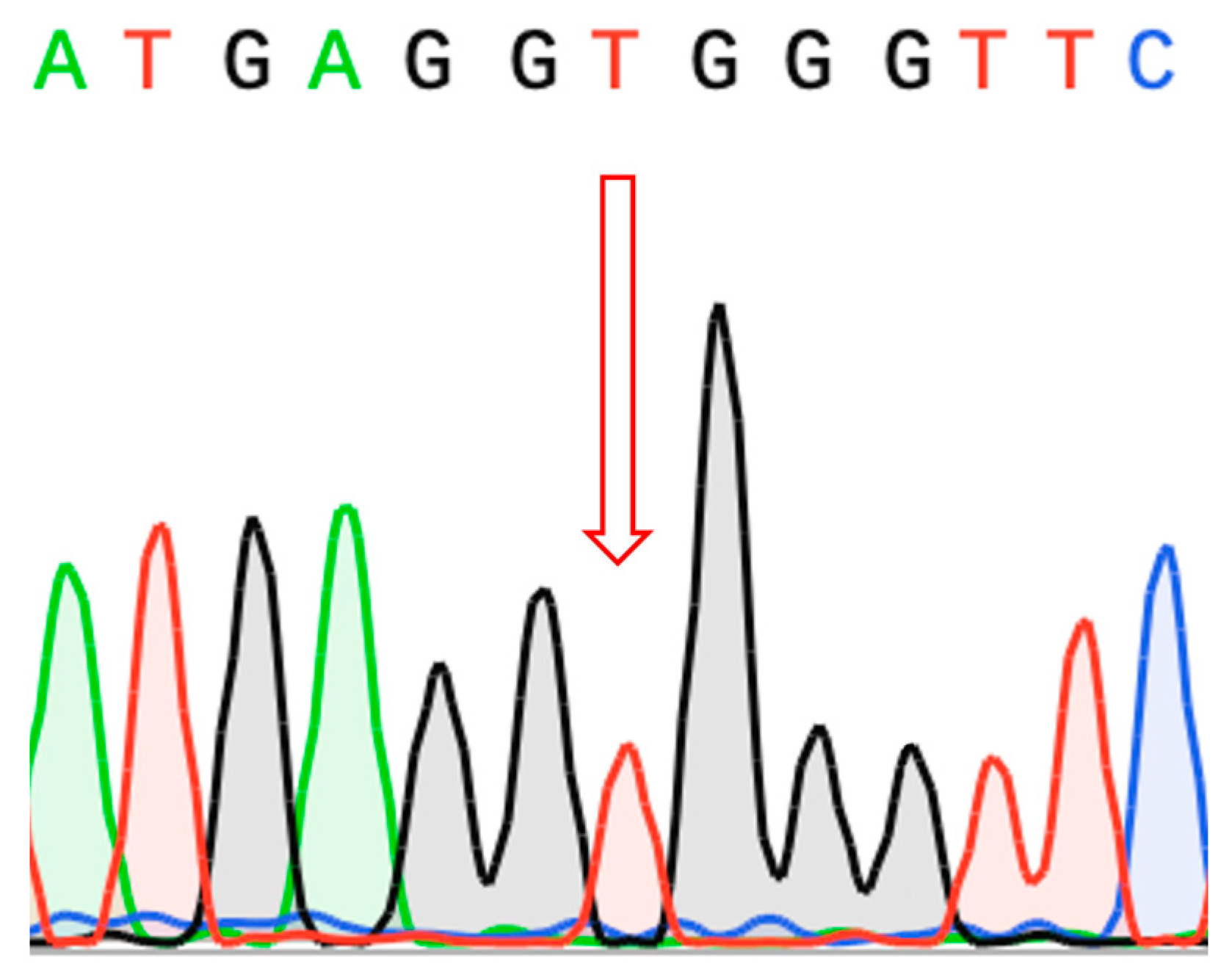
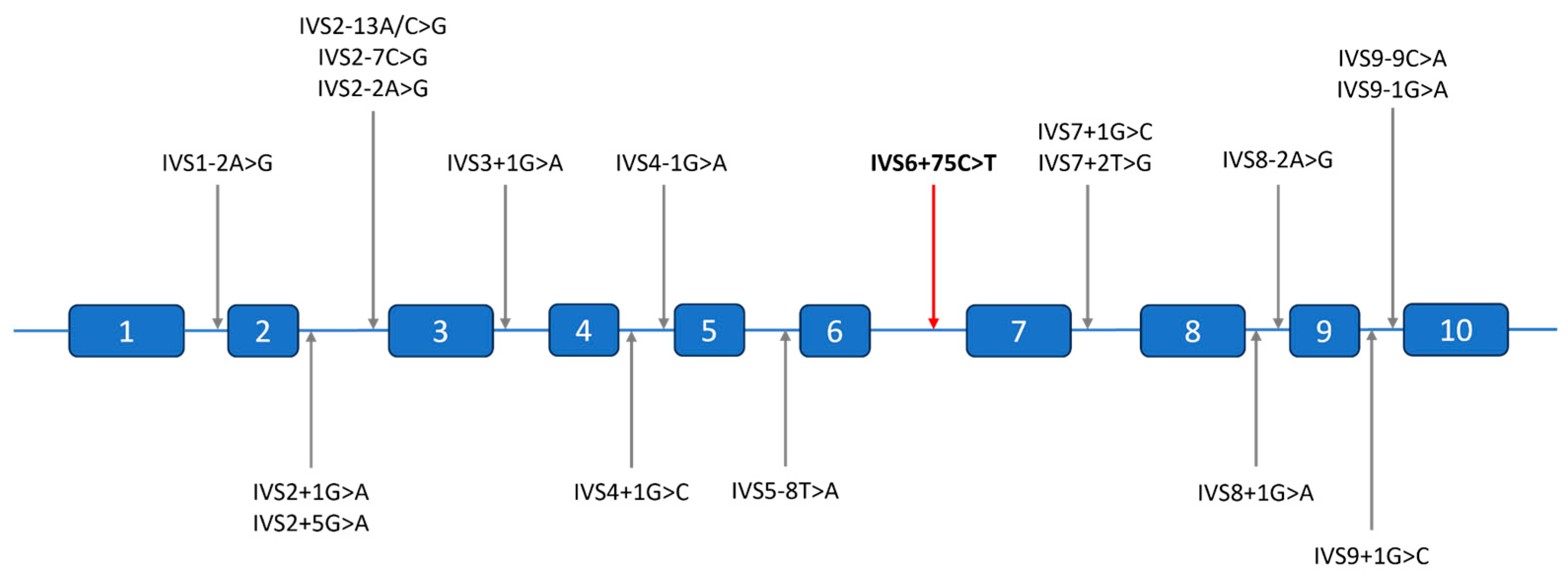

| Laboratory Values | Normal Range | 2020 June (Diagnosis) | 2021 July | 2022 June | 2022 October | 2023 April | 2023 August | 2023 September | 2024 September (Last Follow-Up) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ongoing treatment at the moment of presentation (mg/day) | – | – | HC—5 FLC—0.1 | HC—5 FLC—0.83 | HC—3.75 FLC—0.066 | HC—3.75 FLC—0.066 | HC—3.75 FLC—0.066 | HC—7.5 FLC—0.066 | HC—7.5 FLC—0.066 |
| Na+ (mmol/L) | 132–147 | 120 | 138 | – | 138 | – | – | 138 | 139 |
| K+ (mmol/L) | 3.6–6.1 | 9 | 4.4 | – | 3.9 | – | – | 3.8 | 4.5 |
| 17-hydroxyprogesterone (ng/mL) | 0.2–0.8 | 462 | 0.08 | 0.1 | 0.53 | 4.74 | 41.5 | 2.36 | 0.15 |
| Glucose (mmol/L) | 3.3–5.5 | 2.5 | 5 | – | 4.35 | – | – | 3.7 | 5 |
| Height (cm) | age dependent | 50 | 73 (−1.26 SDS) | – | 89 (−0.24 SDS) | – | – | 98 (−0.1 SDS) | 107 (+0.36 SDS) |
| Weight (kg) | age dependent | 3310 | 8.9 | – | 13.6 | – | – | 13.6 | 19.3 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | age dependent | 12.7 | 16.5 | – | 17.2 | – | – | 14.2 | 16.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antysheva, Z.; Esibov, A.; Avsievich, E.; Petriaikina, E.; Yudin, V.; Keskinov, A.; Yudin, S.; Svetlichnyy, D.; Krupinova, J.; Ivashechkin, A.; et al. A Case of Salt-Wasting Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Caused by a Rare Intronic Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6648. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146648
Antysheva Z, Esibov A, Avsievich E, Petriaikina E, Yudin V, Keskinov A, Yudin S, Svetlichnyy D, Krupinova J, Ivashechkin A, et al. A Case of Salt-Wasting Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Caused by a Rare Intronic Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6648. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146648
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntysheva, Zoia, Anton Esibov, Ekaterina Avsievich, Ekaterina Petriaikina, Vladimir Yudin, Anton Keskinov, Sergey Yudin, Dmitry Svetlichnyy, Julia Krupinova, Aleksey Ivashechkin, and et al. 2025. "A Case of Salt-Wasting Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Caused by a Rare Intronic Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6648. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146648
APA StyleAntysheva, Z., Esibov, A., Avsievich, E., Petriaikina, E., Yudin, V., Keskinov, A., Yudin, S., Svetlichnyy, D., Krupinova, J., Ivashechkin, A., Katsaran, Y., Woroncow, M., Skvortsova, V., Bogdanov, V., & Volchkov, P. (2025). A Case of Salt-Wasting Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Caused by a Rare Intronic Variant in the CYP21A2 Gene. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6648. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146648





