Vitamin D Reshapes Genomic Hierarchies in Skin Cells: lncRNA-Driven Responses in Carcinoma Versus Transcription Factor-Based Regulation in Healthy Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
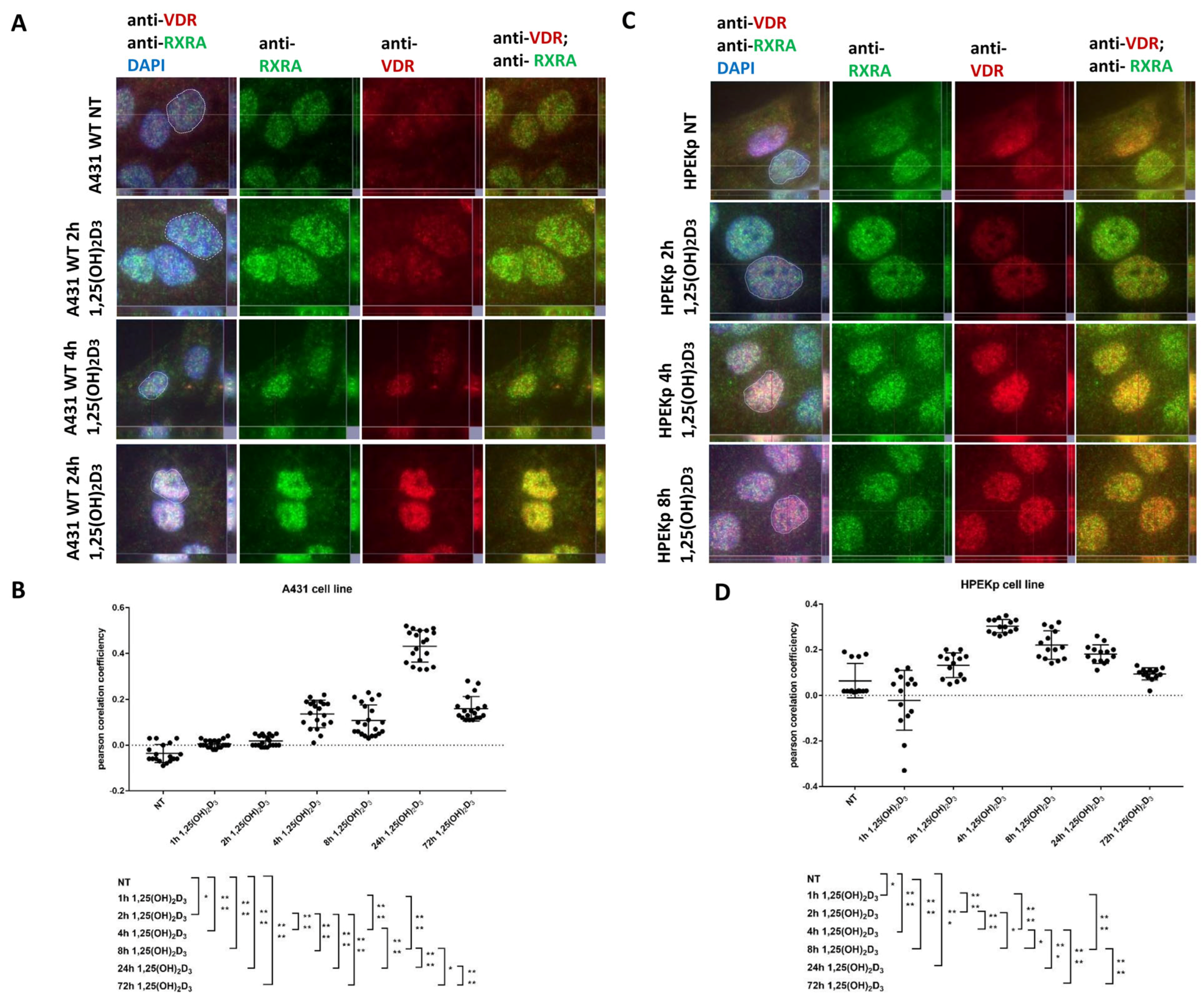
2.1. VDR-RXRA Nuclear Colocalization Occurs in Both Cell Types but Follows Distinct Dynamics in Carcinoma Versus Normal Keratinocytes
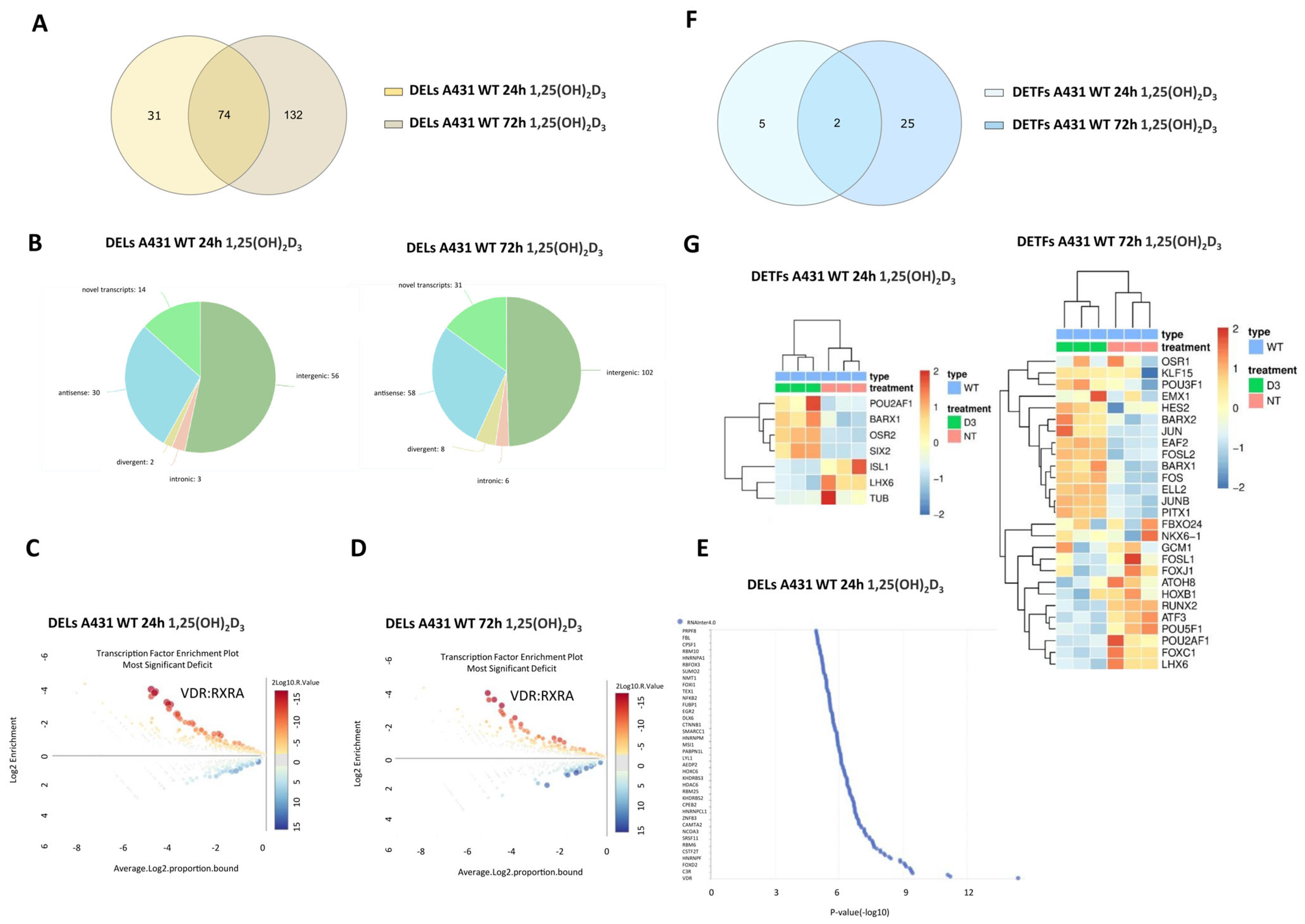
2.2. 1,25(OH)2D3 Treatment of Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells (A431) Leads to a Time-Dependent Increase in DELs and a Decrease in DETFs
2.3. 1,25(OH)2D3 Treatment of Normal Keratinocytes (HPEKp) Leads to a Time-Dependent Decrease in DELs and an Increase in DETFs
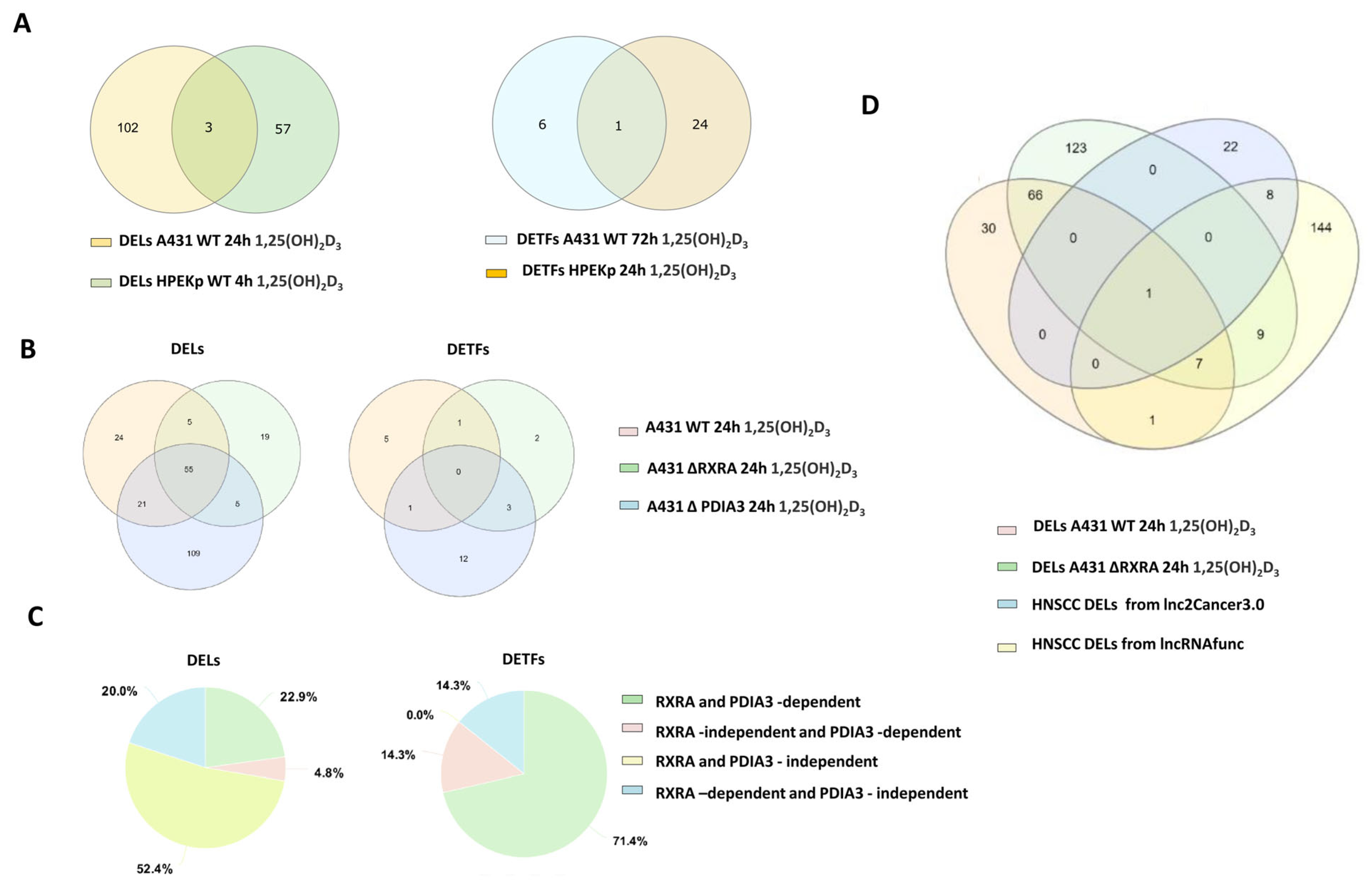
2.4. VDR-Dependent DEL and DET Responses to 1,25(OH)2D3 in A431 Cells Are Abolished by VDR Knockout and Diverge from Typical HNSCC Patterns
| Gene ID | Expression Level in A431 Treated with 1,25(OH)2D3/PDIA3-Dependency | Role in Different Cancers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| LINC00973 | Upregulated only at 24 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | Promotes the Warburg effect by enhancing LDHA enzyme activity in breast cancer | [43] |
| Knockdown of LINC0973 decreases p21 levels, activates the cellular proliferation of cancer cells, and suppresses the apoptosis of drug-treated colorectal cancer | [44] | ||
| Involved in cancer immune suppression through positive regulation of Siglec-15 (sialic acid binding Ig like lectin) in renal cell carcinoma | [45] | ||
| The expression of LINC00973 is consistently increased upon treatment of colon cancer cells | [46] | ||
| TONSL-AS1 | Upregulated only at 24 h treatment (PDIA3-dependent) | TONSL-AS1 regulates the progression of gastric cancer by activating TONSL | [47] |
| Overexpression of TONSL-AS1 resulted in the upregulation of CDK1 and poor prognosis (ovarian cancer) | [48] | ||
| MicroRNA-135a expression is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and targets long non-coding RNA TONSL-AS1 to suppress cell proliferation | [49] | ||
| LINC01764 | Upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | Low expression of LINC01764 was associated with poor prognoses in bladder cancer patients | [50] |
| LINC01764, based on RNA interactions, regulates UCA1 expression in the prevention of colorectal cancer | [51] | ||
| LINC00880 | Upregulated only at 24 h treatment (PDIA3-dependent) | Higher expression of LINC02086 and LINC00880 predicted worse overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma | [52] |
| LINC01559 | Upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | Promotes progression of gastric cancer via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | [53] |
| LINC01559 promotes colorectal cancer via sponging miR-1343-3p to modulate PARP1/PTEN/AKT pathway | [54] | ||
| LINC01559 accelerates pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration through the YAP-mediated pathway | [55] | ||
| Promotes resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma to oxaliplatin by directly sponging miR-6783-3p | [56] | ||
| Indicates lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis Promotes lung cancer cell proliferation and migration in vitro, by enhancing the autophagy signal pathway via sponging has-miR-1343-3p | [57] | ||
| Knockdown of LINC01559 inhibited breast cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion | [52] | ||
| Promotes pancreatic cancer progression by acting as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-1343-3p to upregulate RAF1 expression | [58] | ||
| CALML3-AS1 | Upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-dependent) | Suppresses papillary thyroid cancer progression via sponging miR-20a-5p/RBM38 axis Promotes the tumorigenesis of bladder cancer via regulating ZBTB2 by suppression of microRNA-4316 Upregulation of CALML3-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in cervical cancer via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway | [59] |
| [60] | |||
| [61] | |||
| LINC01193 | Downregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | Overexpression predicts the tumor stage and patient survival rate in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma | [62] |
| ITGB2-AS1 | Downregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | Promotes the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by modulating the miR-328-5p/HMGA1 axis | [63] |
| Promotes the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells through upregulating ITGB2 | [64] | ||
| Promotes cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting ferroptosis via activating the FOSL2/NAMPT axis | [65] | ||
| Downregulation of ITGB2-AS1 inhibits osteosarcoma proliferation and metastasis by repressing Wnt/β-catenin signalling | [66] |
| Gene ID | Expression Level in A431 Treated with 1,25(OH)2D3/PDIA3-Dependency | Role in Different Cancers | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPSR1-AS1 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | promotes the proliferation and glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating the MAPK/ERK pathway | [67] |
| activates the MAPK pathway to facilitate thyroid cancer cell malignant behaviors via recruiting ELAVL1 to stabilize NPSR1 mRNA | [68] | ||
| expressions of NPSR1-AS1 were negatively associated with CD8 T cells in lung adenocarcinoma | [69] | ||
| UCA1 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | UCA1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances chemoresistance in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma cells | [70] |
| promotes proliferation and cisplatin resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma by suppressing miR-184 expression | [71] | ||
| promotes cell proliferation, invasion, and migration of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | [72] | ||
| regulates CCR7 expression to promote tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression by sponging miR-138-5p | [73] | ||
| inhibits esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma growth by regulating the Wnt signaling pathway | [74] | ||
| AATBC | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | promotes the proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells through the miR-1245b-5p/CASK Axis | [75] |
| facilitates the cell growth and metastasis of cervical cancer as a sponge of miR-1245b-5p | [76] | ||
| promotes breast cancer migration and invasion by interacting with YBX1 and activating the YAP1/Hippo signaling pathway | [77] | ||
| suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in bladder cancer | [78] | ||
| LINC01748 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | cancerogenic role in lung cancer via the microRNA-520a-5p/HMGA1 axis regulation | [79] |
| LINC02474 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | upregulation of LINC02474 promotes migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells | [80] |
| TRIM31-AS1 | upregulated only at 24 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | highly expressed in colon organoids | [81] |
| LINC00649 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | promotes the development of bladder cancer by regulating the miR-15a-5p/HMGA1 axis | [82] |
| promotes the development of breast cancer via the stabilization of HIF-1α through the NF90/NF45 complex | [83] | ||
| promotes the development of lung squamous cell carcinoma via activating the MAPK signaling pathway | [84] | ||
| FLG-AS1 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | downregulated in oral SCC | [85] |
| LINC02428 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | overexpressed LINC02428 suppressed the proliferation and metastasis of HCC | [86] |
| CASC9 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through upregulating LAMC2 expression | [87] |
| promotes tumor progression by suppressing autophagy-mediated cell apoptosis via the AKT/mTOR pathway | [88] | ||
| promotes tumorigenesis by affecting epithelial-mesenchymal transition | [89] | ||
| LINC00491 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis | [90] |
| LINC01605 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | promotes the proliferation of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma | [91] |
| promotes tumor growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via regulation of the NF-κB pathway | [92] | ||
| BBOX1-AS1 | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | BBOX1-AS1 silencing inhibits esophageal squamous cell cancer progression | [93] |
| promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the HOXB7/β-catenin axis | [94] | ||
| promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by activation of the Hedgehog signaling pathway | [95] | ||
| MIR4713HG | upregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | aggravates malignant behaviors in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma via binding with microRNA let-7c-5p | [96] |
| LINC00243 | downregulated at 24 h and 72 h treatment (PDIA3-independent) | promotes proliferation and glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells | [97] |
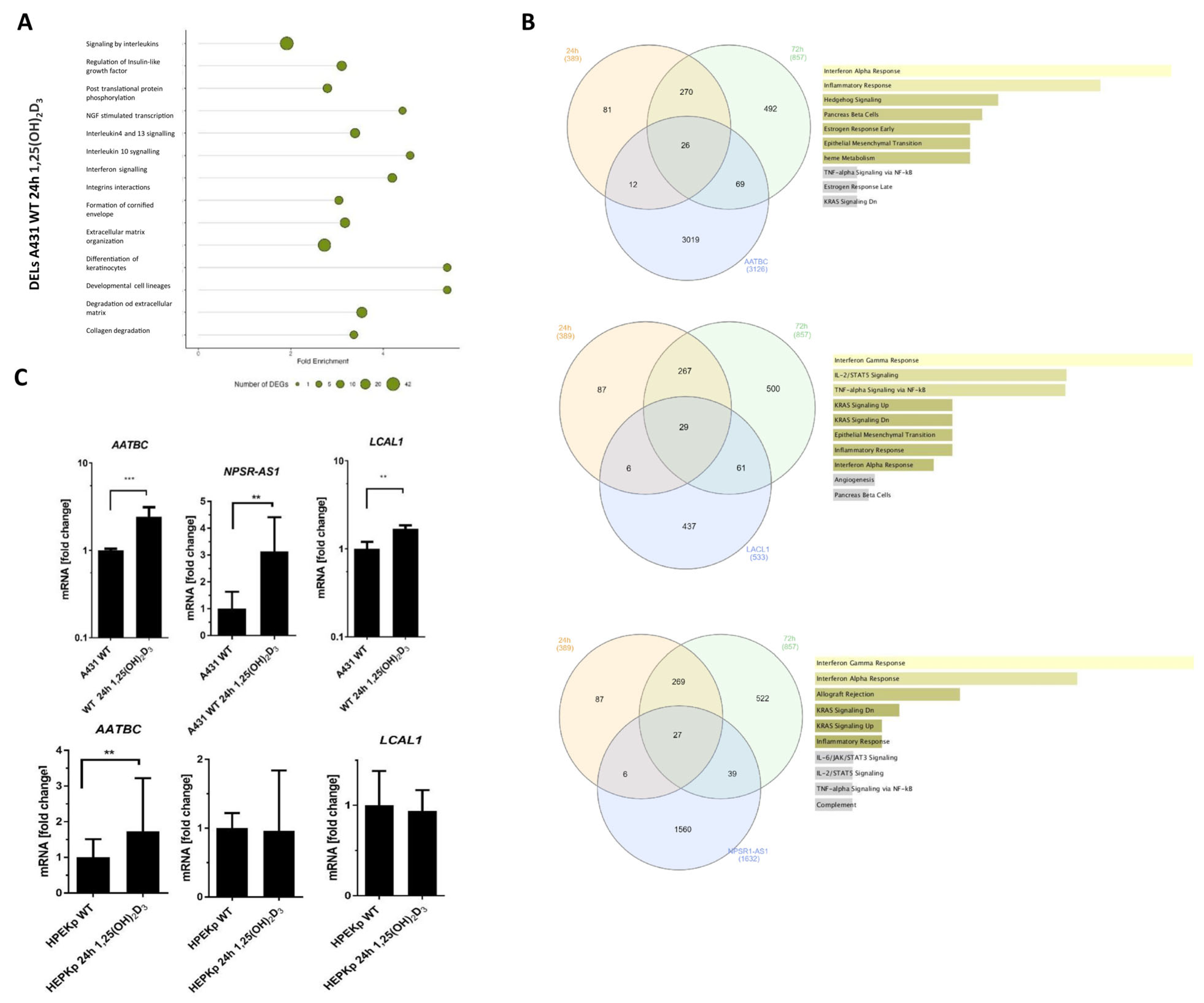
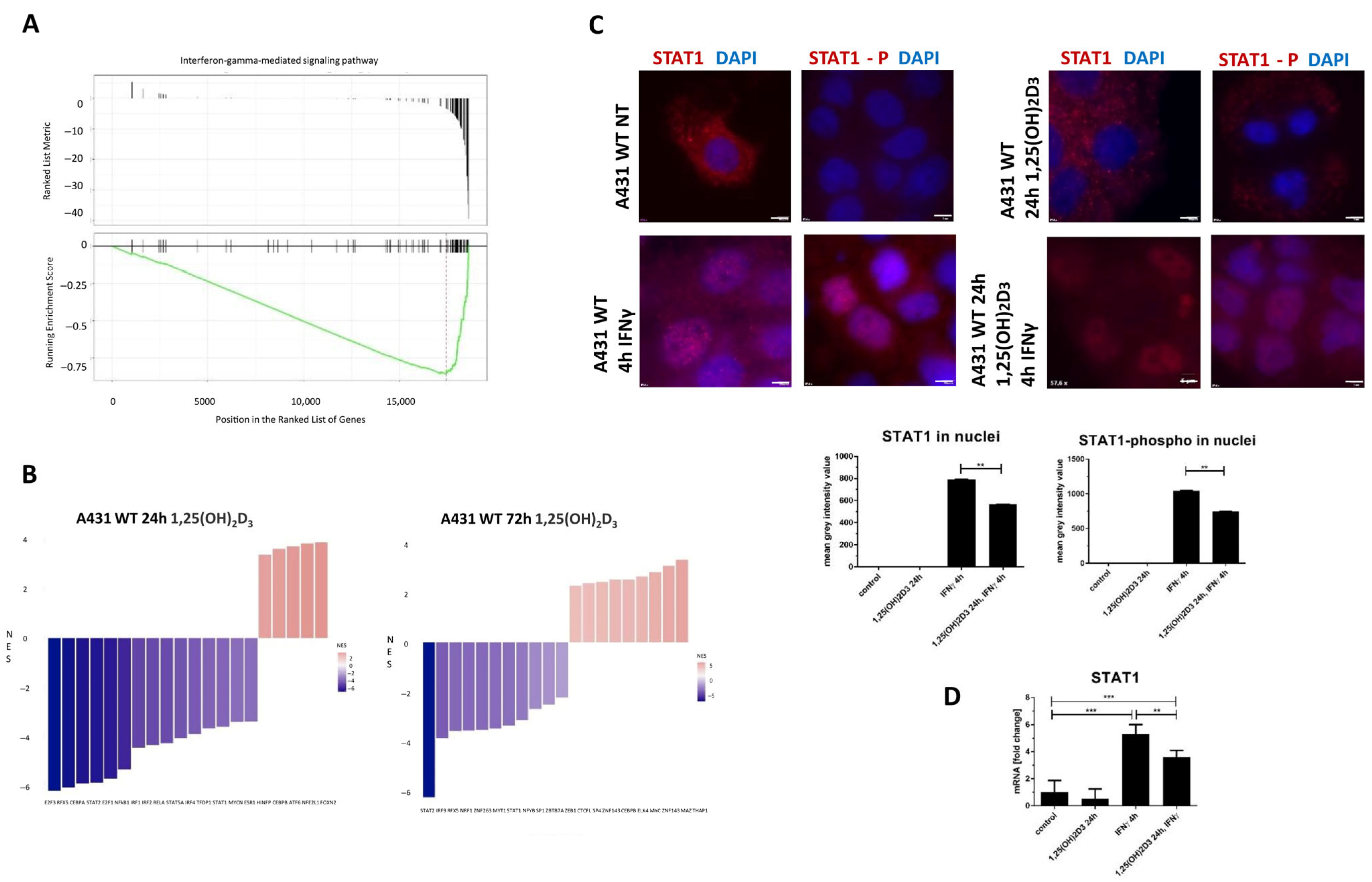
2.5. Deregulated lncRNAs Following 1,25(OH)2D3 Treatment Can Be Potentially Involved in Modulating Interferon-Gamma Signaling Pathways
2.6. Gene Ontology and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis of All 1,25(OH)2D3–Deregulated Genes in A431 Cells Revealed a Significant Enrichment in Pathways Related to the Interferon-Gamma Response
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines, 1,25(OH)2D3 and IFNγ Treatment
4.2. RNA Sequencing (RNAseq)
4.3. Bioinformatics Analyses
4.4. Analysis of the Transcription Factor Binding Sites and Their Enrichment Analysis
4.5. Real-Time qPCRs
4.6. Immunofluorescence Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BARX1 | BARX Homeobox 1 |
| BCL6 | B-Cell CLL/Lymphoma 6 |
| BNIP3P1 | BCL2/Adenovirus E1B 19kDa Interacting Protein 3 Pseudogene 1 |
| CALML3 | Calmodulin Like 3 |
| COLCA1 | Colorectal Cancer Associated 1 |
| CYP2B7P | Cytochrome P450 Family 2 Subfamily B Member 7 Pseudogene |
| DE | Differentially Expressed |
| DUXAP10 | Double Homeobox A Pseudogene 10 |
| EGFR | Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor |
| ELF4 | E74-Like ETS Transcription Factor 4 |
| EP300 | E1A Binding Protein P300 |
| FAM30A | Family With Sequence Similarity 30 Member A |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| FC | Fold Change |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FTH1P3 | Ferritin Heavy Chain 1 Pseudogene 3 |
| GAS5 | Growth Arrest Specific 5 |
| HDAC1 | Histone Deacetylase 1 |
| HMGN2P46 | High Mobility Group Nucleosomal Binding Domain 2 Pseudogene 46 |
| HNSCC | Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| HOTAIR | HOX Transcript Antisense RNA |
| JUN | Jun Proto-Oncogene |
| LHX6 | LIM Homeobox 6 |
| lncRNAs | Long Non-Coding RNAs |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis-Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| MAPK/ERK | Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase/Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| NFE2 | Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2 |
| NR2F2 | Proteins Nuclear Receptor Subfamily 2 Group F Member 2 |
| OSR2 | Odd-Skipped Related Transcription Factor 2 |
| PDIA3 | Protein Disulfide Isomerase A3 |
| PDIA3P | Protein Disulfide Isomerase Family A Member 3 Pseudogene 1 |
| PHBP1 | PHB1 Pseudogene 1 |
| PI3K-AKT | Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Protein Kinase B |
| PICSAR | P38 Inhibited Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma-Associated lncRNA |
| POU2AF1 | POU Class 2 Homeobox Associating Factor 1 |
| POU4F2 | POU Class 4 Homeobox 2 |
| PRAF2 | PRA1 Domain Family Member 2 Protein |
| PTENP1 | Phosphatase And Tensin Homolog Pseudogene 1 |
| PTTG3P | Pseudogenes Pituitary Tumor-Transforming 3 |
| RNA28S5 | 28S Ribosomal 5 |
| RXRA | Retinoid X Receptor Alpha |
| SCC | Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| SLC25A47P1 | Solute Carrier Family 25 Member 47 Pseudogene 1 |
| TFs | Transcription Factors |
| TINCR | TINCR Ubiquitin Domain Containing |
| TUSC2P | Tumor Suppressor Candidate 2 Pseudogene 1 |
| VDR | Vitamin D Receptor |
| VDREs | VDR Binding Sites |
| WT | Wild-Type Cells |
| ZNF136 | Zinc Finger Protein 136 |
References
- Geidel, G.; Heidrich, I.; Kött, J.; Schneider, S.W.; Pantel, K.; Gebhardt, C. Emerging precision diagnostics in advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Lou, Q.Y.; Yang, W.Y.; Wang, Y.R.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, T.; Zhang, L. The role of non-coding RNAs in drug resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma and therapeutic potential. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 981–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, B.; Wen, X.; Hao, D.; Du, D.; He, G.; Jiang, X. The Roles of lncRNA in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Fang, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Z. Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Biological Function and Clinical Application. Cancers 2021, 13, 5944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, D.W.; Zhang, P. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR functions as a competitive endogenous RNA to regulate PRAF2 expression by sponging miR-326 in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Liang, L.; Ouyang, K.; Li, Z.; Yi, X. MALAT1 induces tongue cancer cells’ EMT and inhibits apoptosis through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piipponen, M.; Heino, J.; Kähäri, V.M.; Nissinen, L. Long non-coding RNA PICSAR decreases adhesion and promotes migration of squamous carcinoma cells by downregulating α2β1 and α5β1 integrin expression. Biol. Open 2018, 7, bio037044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretz, M.; Siprashvili, Z.; Chu, C.; Webster, D.E.; Zehnder, A.; Qu, K.; Lee, C.S.; Flockhart, R.J.; Groff, A.F.; Chow, J.; et al. Control of somatic tissue differentiation by the long non-coding RNA TINCR. Nature 2013, 493, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.L.; Zhong, S. Long noncoding RNA LINC00520 prevents the progression of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma through the inactivation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by downregulating EGFR. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 454–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.H.; Chan, C.W.; Fang, J.Y.; Shih, Y.M.; Liu, Y.W.; Wang, T.V.; Chen, C.Y. 2-O-Methylmagnolol upregulates the long non-coding RNA, GAS5, and enhances apoptosis in skin cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, K.; Bayraktar, R.; Ferracin, M.; Calin, G.A. Non-coding RNAs in disease: From mechanisms to therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2024, 25, 211–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Liang, Y.; Xie, H.; Yang, X.; Zheng, G. Long non-coding RNAs in cutaneous biology and proliferative skin diseases: Advances and perspectives. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.C.; Wang, K.C. Long noncoding RNA: Significance and potential in skin biology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a015404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guglas, K.; Kolenda, T.; Teresiak, A.; Kopczyńska, M.; Łasińska, I.; Mackiewicz, J.; Mackiewicz, A.; Lamperska, K. lncRNA Expression after Irradiation and Chemoexposure of HNSCC Cell Lines. Non-Coding RNA 2018, 4, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña-Flores, J.A.; Bermúdez, M.; Ramos-Payán, R.; Villegas-Mercado, C.E.; Soto-Barreras, U.; Muela-Campos, D.; Álvarez-Ramírez, A.; Pérez-Aguirre, B.; Larrinua-Pacheco, A.D.; López-Camarillo, C.; et al. Emerging role of lncRNAs in drug resistance mechanisms in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 965628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, M.; Shoorei, H.; Tondro Anamag, F.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Dinger, M.E. LncRNAs and miRNAs participate in determination of sensitivity of cancer cells to cisplatin. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 123, 104602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu El Maaty, M.A.; Wölfl, S. Effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on Cancer Cells and Potential Applications in Combination with Established and Putative Anti-Cancer Agents. Nutrients 2017, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chalmers, M.J.; Stayrook, K.R.; Burris, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Busby, S.A.; Pascal, B.D.; Garcia-Ordonez, R.D.; Bruning, J.B.; Istrate, M.A.; et al. DNA binding alters coactivator interaction surfaces of the intact VDR-RXR complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, A.; Nowak, J.I.; Wierzbicka, J.M.; Domżalski, P.; Górska-Arcisz, M.; Sądej, R.; Popiel, D.; Wieczorek, M.; Żmijewski, M.A. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors Decrease Proliferation of Melanoma Cell Lines and Their Activity Is Modulated by Vitamin D. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domżalski, P.; Piotrowska, A.; Tuckey, R.C.; Zmijewski, M.A. Anticancer Activity of Vitamin D, Lumisterol and Selected Derivatives against Human Malignant Melanoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, J.I.; Olszewska, A.M.; Piotrowska, A.; Myszczyński, K.; Domżalski, P.; Żmijewski, M.A. PDIA3 modulates genomic response to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) in squamous cell carcinoma of the skin. Steroids 2023, 199, 109288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowak, J.I.; Olszewska, A.M.; Król, O.; Zmijewski, M.A. PDIA3 knockout abrogate effects of 1,25(OH)2D3 on cellular respiration and glycolysis in squamous cell carcinoma. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warwick, T.; Schulz, M.H.; Günther, S.; Gilsbach, R.; Neme, A.; Carlberg, C.; Brandes, R.P.; Seuter, S. A hierarchical regulatory network analysis of the vitamin D induced transcriptome reveals novel regulators and complete VDR dependency in monocytes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuter, S.; Neme, A.; Carlberg, C. Characterization of genomic vitamin D receptor binding sites through chromatin looping and opening. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D.; Elalieh, H.; Welsh, J.; Oh, D.; Cleaver, J.; Teichert, A. Protective role of vitamin D signaling in skin cancer formation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 136, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasiak, J.; Chojnacki, J.; Pawlowska, E.; Jablkowska, A.; Chojnacki, C. Vitamin D May Protect against Breast Cancer through the Regulation of Long Noncoding RNAs by VDR Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Bikle, D.D. LncRNA profiling reveals new mechanism for VDR protection against skin cancer formation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144 Pt A, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, P.; Jiang, F.; Yu, J.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Z.; Pei, H.; Li, B. A Newly Identified lncBCAS1-4_1 Associated With Vitamin D Signaling and EMT in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 691500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, S.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, X. Long Non-coding RNA MEG3 Activated by Vitamin D Suppresses Glycolysis in Colorectal Cancer via Promoting c-Myc Degradation. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholghi Oskooei, V.; Geranpayeh, L.; Omrani, M.D.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Assessment of functional variants and expression of long noncoding RNAs in vitamin D receptor signaling in breast cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 3451–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheliji, T.; Oskooei, V.K.; Ashrafi Hafez, A.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Evaluation of expression of vitamin D receptor related lncRNAs in lung cancer. Noncoding RNA Res. 2020, 5, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Song, H.; Gao, J.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y. Vitamin D (1,25-(OH)(2)D(3)) regulates the gene expression through competing endogenous RNAs networks in high glucose-treated endothelial progenitor cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 193, 105425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska, A.M.; Nowak, J.I.; Myszczynski, K.; Słominski, A.; Żmijewski, M.A. Dissection of an impact of VDR and RXRA on the genomic activity of 1,25(OH)(2)D(3) in A431 squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2024, 582, 112124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.L.; Reshmi, S.C.; Ried, T.; Gottberg, W.; Wilson, J.W.; Reddy, J.K.; Khanna, P.; Johnson, J.T.; Myers, E.N.; Gollin, S.M. Chromosomal imbalances in oral squamous cell carcinoma: Examination of 31 cell lines and review of the literature. Oral. Oncol. 2008, 44, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, D.; Krishnan, A.V.; Swami, S.; Giovannucci, E.; Feldman, B.J. The role of vitamin D in reducing cancer risk and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segovia-Mendoza, M.; García-Quiroz, J.; Díaz, L.; García-Becerra, R. Combinations of Calcitriol with Anticancer Treatments for Breast Cancer: An Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.C.; Tung, S.L.; Chen, Y.L.; Chen, P.M.; Chu, P.Y. IFI44L is a novel tumor suppressor in human hepatocellular carcinoma affecting cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance via regulating met/Src signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oak, A.S.W.; Bocheva, G.; Kim, T.K.; Brożyna, A.A.; Janjetovic, Z.; Athar, M.; Tuckey, R.C.; Slominski, A.T. Noncalcemic Vitamin D Hydroxyderivatives Inhibit Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Down-regulate Hedgehog and WNT/β-Catenin Pathways. Anticancer Res. 2020, 40, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, A.; Beserra, F.P.; Wierzbicka, J.M.; Nowak, J.I.; Żmijewski, M.A. Vitamin D Enhances Anticancer Properties of Cediranib, a VEGFR Inhibitor, by Modulation of VEGFR2 Expression in Melanoma Cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 763895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.L.; Carpenter, E.L.; Slominski, A.T.; Indra, A.K. The Role of the Vitamin D Receptor in the Pathogenesis, Prognosis, and Treatment of Cutaneous Melanoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 743667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slominski, A.T.; Brożyna, A.A.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Jóźwicki, W.; Jetten, A.M.; Mason, R.S.; Tuckey, R.C.; Elmets, C.A. Vitamin D signaling and melanoma: Role of vitamin D and its receptors in melanoma progression and management. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 706–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Shen, X.; Shi, L.; Liu, W. Dysregulation and implications of lncRNAs and miRNAs in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma: In reply with emphasis on the role of ceRNAs. Oral. Oncol. 2023, 136, 106277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lin, K.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; et al. Oncogenic lncRNA LINC00973 promotes Warburg effect by enhancing LDHA enzyme activity. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1330–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, D.S.; Spirin, P.V.; Zheltukhin, A.O.; Tutyaeva, V.V.; Zinovieva, O.L.; Grineva, E.N.; Matrosova, V.A.; Krasnov, G.S.; Snezhkina, A.V.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; et al. LINC00973 Induces Proliferation Arrest of Drug-Treated Cancer Cells by Preventing p21 Degradation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y. LINC00973 is involved in cancer immune suppression through positive regulation of Siglec-15 in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 3693–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinovieva, O.L.; Grineva, E.N.; Prokofjeva, M.M.; Karpov, D.S.; Zheltukhin, A.O.; Krasnov, G.S.; Snezhkina, A.V.; Kudryavtseva, A.V.; Chumakov, P.M.; Mashkova, T.D.; et al. Expression of long non-coding RNA LINC00973 is consistently increased upon treatment of colon cancer cells with different chemotherapeutic drugs. Biochimie 2018, 151, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, J.; Ding, Y. A novel long non-coding RNA TONSL-AS1 regulates progression of gastric cancer via activating TONSL. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 382, 111453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z. LncRNA TONSL-AS1 regulates miR-490-3p/CDK1 to affect ovarian epithelial carcinoma cell proliferation. J. Ovarian Res. 2020, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Cheng, J.; Zhan, N.; Chen, J.; Zhan, Y.; Ni, Y.; Liao, C. MicroRNA-135a expression is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and targets long non-coding RNA TONSL-AS1 to suppress cell proliferation. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Wan, E.; Zhang, E.; Sun, L. Construction of an lncRNA model for prognostic prediction of bladder cancer. BMC Med. Genom. 2022, 15, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, C.; Brex, D.; Caponnetto, A.; Cirnigliaro, M.; Scalia, M.; Magnano, A.; Caltabiano, R.; Barbagallo, D.; Biondi, A.; Cappellani, A.; et al. LncRNA UCA1, Upregulated in CRC Biopsies and Downregulated in Serum Exosomes, Controls mRNA Expression by RNA-RNA Interactions. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 12, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Qian, X.; Xu, X.; Lv, P. Long non-coding RNA LINC01559 serves as a competing endogenous RNA accelerating triple-negative breast cancer progression. Biomed. J. 2022, 45, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bo, X.; Yi, X.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, L.; Li, B. Exosome-transferred LINC01559 promotes the progression of gastric cancer via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Lai, Y.; Huang, S.; Zheng, L.; Fan, N. LINC01559 promotes colorectal cancer via sponging miR-1343-3p to modulate PARP1/PTEN/AKT pathway. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2021, 224, 153521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, C.; Zhao, J.; Gu, Y.; Li, Q.; Tang, S.; Wu, Y.; Tang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y. LINC01559 accelerates pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration through YAP-mediated pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 3928–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Fu, Y.; Yang, K.; Zhang, X.; Miao, R.; Long, Y.; Liu, C. Linc01559 Served as a Potential Oncogene and Promoted Resistance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma to Oxaliplatin by Directly Sponging miR-6783-3p. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2021, 21, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wan, J.; Guo, M.; Yang, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ming, L. Long non-coding RNA LINC01559 exerts oncogenic role via enhancing autophagy in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, F.; Mou, T.; Zhong, P.; Hua, H.; Liu, P.; Yang, Q. Long noncoding RNA LINC01559 promotes pancreatic cancer progression by acting as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-1343-3p to upregulate RAF1 expression. Aging 2020, 12, 14452–14466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jia, Q.; Li, H.; Ma, R.; Yang, G.; Yin, F.; Jiang, N.; Yin, D. LncRNA CALML3-AS1 suppresses papillary thyroid cancer progression via sponging miR-20a-5p/RBM38 axis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zu, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, H.; Xie, H.; Yang, Y. LncRNA CALML3-AS1 promotes tumorigenesis of bladder cancer via regulating ZBTB2 by suppression of microRNA-4316. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.N.; Zhang, H.Y.; Liu, C.L.; Wang, C.C. Upregulation of lncRNA CALML3-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in cervical cancer via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5611–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, K.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Q. Bioinformatics identification of lncRNA biomarkers associated with the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 5309–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, Y.; Shi, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, X.; Yang, Y.; Wan, B. LncRNA ITGB2-AS1 promotes the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by modulating miR-328-5p/HMGA1 axis. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 1545–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Gou, L.; Xia, J.; Wan, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, S.; Tang, M.; He, T.; Zhang, Y. LncRNA ITGB2-AS1 Could Promote the Migration and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cells through Up-Regulating ITGB2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wan, Z.; Zhou, L.; Liao, H.; Wan, R. LncRNA ITGB2-AS1 promotes cisplatin resistance of non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting ferroptosis via activating the FOSL2/NAMPT axis. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2023, 24, 2223377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xu, L.J.; Han, G.D.; Jiang, H.T.; Sun, H.L.; Zhu, G.T.; Tang, X.M. Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA ITGB2-AS1 inhibits osteosarcoma proliferation and metastasis by repressing Wnt/β-catenin signalling and predicts favourable prognosis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, S783–S790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Chen, T.; Mo, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, Q.; Guo, C. Hypoxia-inducible long noncoding RNA NPSR1-AS1 promotes the proliferation and glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating the MAPK/ERK pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 533, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, T.; Guo, D.; Tan, L.; Xiao, Z.; Shi, Y. NPSR1-AS1 activates the MAPK pathway to facilitate thyroid cancer cell malignant behaviors via recruiting ELAVL1 to stabilize NPSR1 mRNA. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, J.; Xiang, Y.; Liu, Y. Comprehensive Analysis of NPSR1-AS1 as a Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker Involved in Immune Infiltrates in Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 2099327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Fang, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, M. Exosomal lncRNA UCA1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts enhances chemoresistance in vulvar squamous cell carcinoma cells. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2021, 47, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Xie, W.; Sun, Q.; Wang, H.; Qiao, B. LncRNA UCA1 promotes proliferation and cisplatin resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma by sunppressing miR-184 expression. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2897–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Gong, C.; Yuan, K. LncRNA UCA1 promotes cell proliferation, invasion and migration of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.T.; Li, R.; Zhao, L. Long noncoding RNA UCA1 regulates CCR7 expression to promote tongue squamous cell carcinoma progression by sponging miR-138-5p. Neoplasma 2020, 67, 1256–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gao, Z.; Liao, J.; Shang, M.; Li, X.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y.; Liu, R. lncRNA UCA1 inhibits esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma growth by regulating the Wnt signaling pathway. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2016, 79, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, J. Long Noncoding RNA AATBC Promotes the Proliferation and Migration of Prostate Cancer Cell Through miR-1245b-5p/CASK Axis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 5091–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Q.; Liu, C.; Bai, Y.; Gao, J. LncRNA AATBC indicates development and facilitates cell growth and metastasis of cervical cancer as a sponge of miR-1245b-5p. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dai, M.; Wang, D.; Tang, T.; Xiong, F.; Xiang, B.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Xiong, W.; et al. The long noncoding RNA AATBC promotes breast cancer migration and invasion by interacting with YBX1 and activating the YAP1/Hippo signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2021, 512, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Lin, T.; He, W.; Han, J.; Zhu, D.; Hu, K.; Li, W.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, J.; Xie, W. Knockdown of a novel lincRNA AATBC suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in bladder cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1064–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Xu, F.; Xu, L.; Cui, J. Long non-coding RNA LINC01748 exerts carcinogenic effects in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines by regulating the microRNA-520a-5p/HMGA1 axis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Wang, C. Long Non-coding RNA LINC02474 Affects Metastasis and Apoptosis of Colorectal Cancer by Inhibiting the Expression of GZMB. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 651796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devall, M.A.; Eaton, S.; Ali, M.W.; Dampier, C.H.; Weisenberger, D.; Powell, S.M.; Li, L.; Casey, G. DNA methylation analysis of normal colon organoids from familial adenomatous polyposis patients reveals novel insight into colon cancer development. Clin. Epigenetics 2022, 14, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, S. LINC00649 promotes bladder cancer malignant progression by regulating the miR-15a-5p/HMGA1 axis. Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Du, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. LncRNA LINC00649 promotes the growth and metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer by maintaining the stability of HIF-1α through the NF90/NF45 complex. Cell Cycle 2022, 21, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, Q.; Yang, X.; Ding, C.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, Y. LncRNA LINC00649 recruits TAF15 and enhances MAPK6 expression to promote the development of lung squamous cell carcinoma via activating MAPK signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Houck, J.R.; Lohavanichbutr, P.; Chen, C. Transcriptome analysis reveals differentially expressed lncRNAs between oral squamous cell carcinoma and healthy oral mucosa. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31521–31531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, H.; Peng, H.; Mao, X.; Liu, S.; Xu, W.; Feng, K.; Zhang, Y. Downregulated liver-elevated long intergenic noncoding RNA (LINC02428) is a tumor suppressor that blocks KDM5B/IGF2BP1 positive feedback loop in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K.; Guan, X.; Yang, K.; Bai, Y. LncRNA CASC9 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through upregulating LAMC2 expression by interacting with the CREB-binding protein. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1980–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, H.; Yang, K. Increased expression of lncRNA CASC9 promotes tumor progression by suppressing autophagy-mediated cell apoptosis via the AKT/mTOR pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.D.; Liu, X.Y.; Lin, Y.; Liu, H.F.; Zhang, G.J. LncRNA CASC9 promotes tumorigenesis by affecting EMT and predicts poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Mulmi Shrestha, S.; Zhu, J.; Ding, Y.; Shi, R. Long non-coding RNA LINC00491 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, P.C.; Huang, F.J.; Jian, X.; Wei, Z.C.; Chen, Y.Q. LINC01605 promotes the proliferation of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma through targeting miR-493-3p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 10379–10386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Xin, L.; Tang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, R. A positive feedback loop between LINC01605 and NF-κB pathway promotes tumor growth in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. RNA Biol. 2022, 19, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Chen, G.; Zhao, X.; Xu, X.; Liu, J. lncRNA BBOX1-AS1 silencing inhibits esophageal squamous cell cancer progression by promoting ferroptosis via miR-513a-3p/SLC7A11 axis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 934, 175317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, C.; Jia, J.; Chu, J.; Ju, C.; Wan, J.; He, J.; He, F. Long non-coding RNA BBOX1-AS1 exacerbates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development by regulating HOXB7/β-catenin axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 415, 113117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Cao, H.; Zheng, L.; Li, R. BBOX1-AS1 Activates Hedgehog Signaling Pathway to Facilitate the Proliferation and Stemness of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells via miR-506-5p/EIF5A/PTCH1 Axis. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2023, 16, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Zheng, X.; Qiu, X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, J.; Huang, Z.; Xiang, S.; Chen, G.; Zhao, J. Long non-coding RNA MIR4713HG aggravates malignant behaviors in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma via binding with microRNA let-7c-5p. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 47, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Yang, S. Long non-coding RNA LINC00243 promotes proliferation and glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by positively regulating PDK4 through sponging miR-507. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 463, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D. The vitamin D receptor: A tumor suppressor in skin. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 810, 282–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamis, A.; Gül, D.; Wandrey, M.; Lu, Q.; Knauer, S.K.; Reinhardt, C.; Strieth, S.; Hagemann, J.; Stauber, R.H. The Vitamin D Receptor-BIM Axis Overcomes Cisplatin Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurminen, V.; Neme, A.; Ryynänen, J.; Heikkinen, S.; Seuter, S.; Carlberg, C. The transcriptional regulator BCL6 participates in the secondary gene regulatory response to vitamin D. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.; Zhou, M. Immune-related eight-lncRNA signature for improving prognosis prediction of lung adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e24018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastjerdi, S.; Valizadeh, M.; Nemati, R.; Honardoost, M.A.; Dolatabadi, N.F.; Zamani, A.; Tabatabaeian, H. Highly expressed TLX1NB and NPSR1-AS1 lncRNAs could serve as diagnostic tools in colorectal cancer. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giroud, M.; Kotschi, S.; Kwon, Y.; Le Thuc, O.; Hoffmann, A.; Gil-Lozano, M.; Karbiener, M.; Higareda-Almaraz, J.C.; Khani, S.; Tews, D.; et al. The obesity-linked human lncRNA AATBC stimulates mitochondrial function in adipocytes. EMBO Rep. 2023, 24, e57600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Yang, L.; Cao, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Gong, Z.; Xiong, F.; He, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liao, Q.; et al. LncRNA AATBC regulates Pinin to promote metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 2251–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, N.A.; Ebied, S.A.; Belal, A.A.M.; Ahmad, M.A.; Weheida, E.S.A. Expression profiling of circulating lncRNA GIAT4RA, lncRNA AATBC, lncRNA Sirt1-AS, and SMARCB1 in lung cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Y.; Feng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cai, L. Senescence-Related lncRNA Signature Predicts Prognosis, Response to Immunotherapy and Chemotherapy in Skin Cutaneous Melanoma. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorostgoo, Z.; Fattahi, A.S.; Moosavi, S.S.; Ghafouri-Fard, S.; Oskooei, V.K. Down-regulation of SLC16A-AS1 and LINC00900 lncRNAs in Iranian patients with breast cancer. Breast Dis. 2022, 41, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Xiao, T. Gene Instability-Related lncRNA Prognostic Model of Melanoma Patients via Machine Learning Strategy. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 5582920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Luo, Z.Q. LCAL1 enhances lung cancer survival via inhibiting AMPK-related antitumor functions. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 457, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, N.M.; Cabanski, C.R.; Silva-Fisher, J.M.; Dang, H.X.; Govindan, R.; Maher, C.A. Transcriptome sequencing reveals altered long intergenic non-coding RNAs in lung cancer. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liu, X.; Pan, S.; Ke, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H. A Novel Autophagy-Related Long Non-Coding RNA Signature to Predict Prognosis and Therapeutic Response in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 8325–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, S.; Krueger, F.; Seconds-Pichon, A.; Biggins, F.; Wingett, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenfuhrer, J. topGO:Enrichment Analysis for Gene Ontology. Bioconductor. 2013. Available online: http://bioconductor.jp/packages/3.12/bioc/html/topGO.html (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Team RC. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. Available online: www.r-project.org (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Gearing, L.J.; Cumming, H.E.; Chapman, R.; Finkel, A.M.; Woodhouse, I.B.; Luu, K.; Gould, J.A.; Forster, S.C.; Hertzog, P.J. CiiiDER: A tool for predicting and analysing transcription factor binding sites. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0215495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewska, A.M.; Nowak, J.I.; Król, O.; Flis, D.; Żmijewski, M.A. Different impact of vitamin D on mitochondrial activity and morphology in normal and malignant keratinocytes, the role of genomic pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 210, 286–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olszewska, A.M.; Nowak, J.I.; Domżalski, P.; Myszczyński, K.; Żmijewski, M.A. Vitamin D Reshapes Genomic Hierarchies in Skin Cells: lncRNA-Driven Responses in Carcinoma Versus Transcription Factor-Based Regulation in Healthy Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146632
Olszewska AM, Nowak JI, Domżalski P, Myszczyński K, Żmijewski MA. Vitamin D Reshapes Genomic Hierarchies in Skin Cells: lncRNA-Driven Responses in Carcinoma Versus Transcription Factor-Based Regulation in Healthy Skin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146632
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlszewska, Anna M., Joanna I. Nowak, Paweł Domżalski, Kamil Myszczyński, and Michał A. Żmijewski. 2025. "Vitamin D Reshapes Genomic Hierarchies in Skin Cells: lncRNA-Driven Responses in Carcinoma Versus Transcription Factor-Based Regulation in Healthy Skin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146632
APA StyleOlszewska, A. M., Nowak, J. I., Domżalski, P., Myszczyński, K., & Żmijewski, M. A. (2025). Vitamin D Reshapes Genomic Hierarchies in Skin Cells: lncRNA-Driven Responses in Carcinoma Versus Transcription Factor-Based Regulation in Healthy Skin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6632. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146632






