Piezo-Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 (PIEZO1) as a Potential Prognostic Marker in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PIEZO1 Expression Patterns in ccRCC and Adjacent Non-Tumor Tissues
2.2. Association with the Clinicopathological Characteristics
2.3. Association with the Clinical Outcome
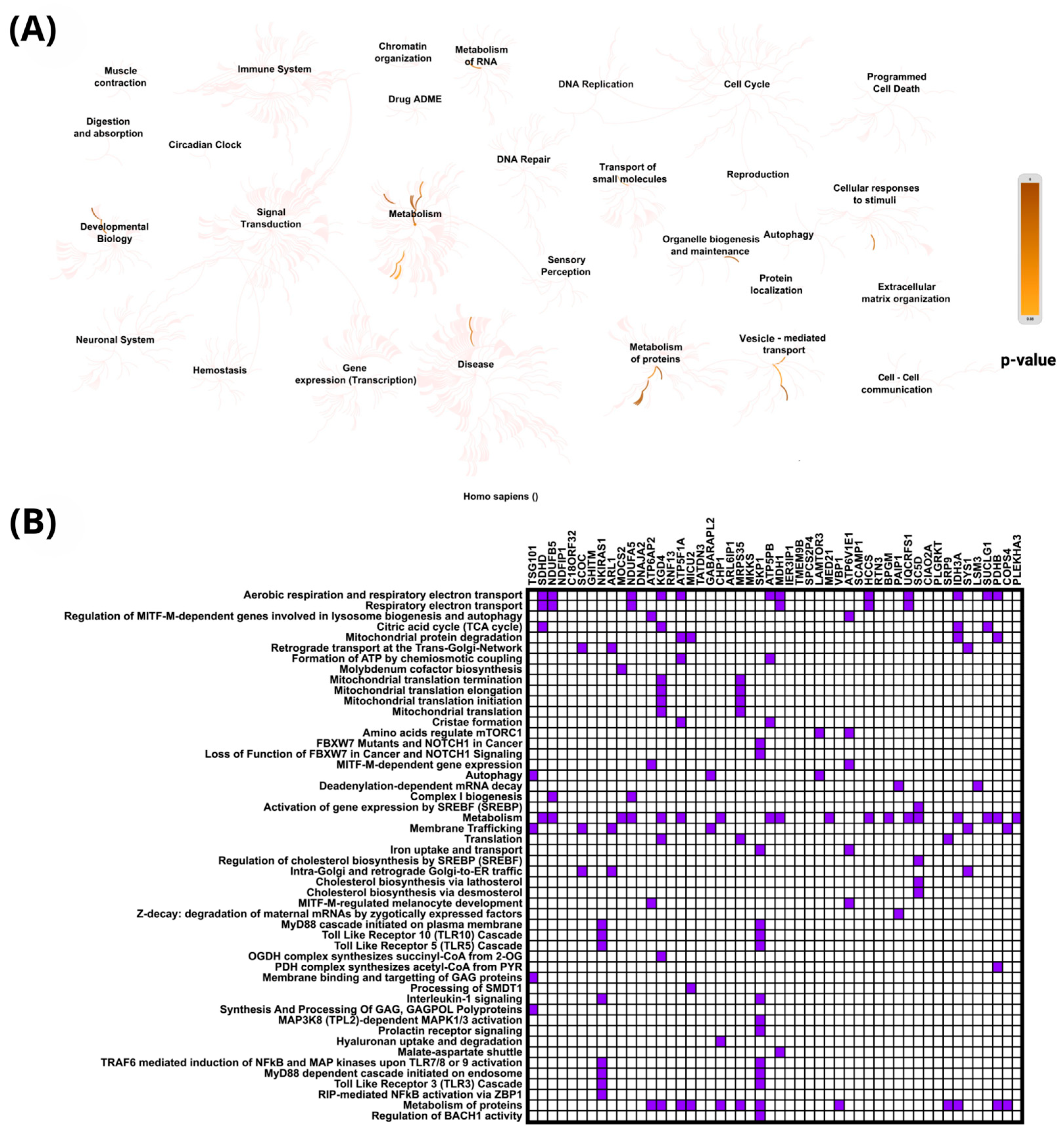
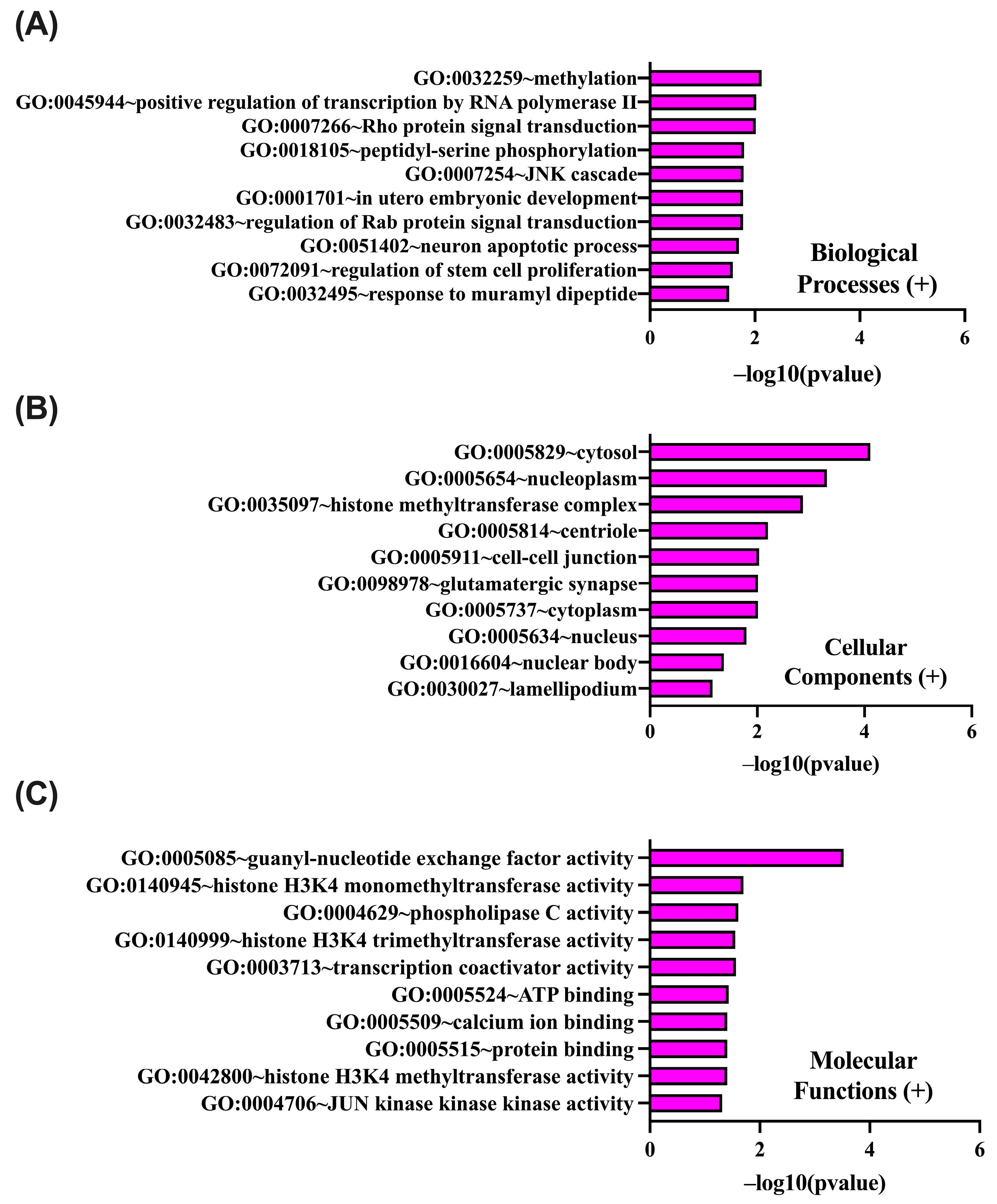
2.4. In Silico Analysis of Functional Pathways Linked to PIEZO1-Correlated Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, B.; Albiges, L.; Abu-Ghanem, Y.; Bedke, J.; Capitanio, U.; Dabestani, S.; Fernández-Pello, S.; Giles, R.H.; Hofmann, F.; Hora, M.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Renal Cell Carcinoma: The 2022 Update. Eur. Urol. 2022, 82, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitanio, U.; Bensalah, K.; Bex, A.; Boorjian, S.A.; Bray, F.; Coleman, J.; Gore, J.L.; Sun, M.; Wood, C.; Russo, P. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.; Ma, J.; Zou, Z.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, J.J.; Purdue, M.P.; Signoretti, S.; Swanton, C.; Albiges, L.; Schmidinger, M.; Heng, D.Y.; Larkin, J.; Ficarra, V. Renal Cell Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popławski, P.; Bogusławska, J.; Hanusek, K.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. Nucleolar Proteins and Non-Coding Rnas: Roles in Renal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Hu, J.; Zheng, Q.; Feng, X.; Zhan, F.; Wang, X.; Xu, G.; Hua, F. Piezo1 Channels as Force Sensors in Mechanical Force-Related Chronic Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 816149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coste, B.; Mathur, J.; Schmidt, M.; Earley, T.J.; Ranade, S.; Petrus, M.J.; Dubin, A.E.; Patapoutian, A. Piezo1 and Piezo2 Are Essential Components of Distinct Mechanically Activated Cation Channels. Science 2010, 330, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PIEZO1 Piezo Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 (Er Blood Group) [Homo Sapiens (Human)]—Gene—NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/9780 (accessed on 9 June 2024).
- Saotome, K.; Murthy, S.E.; Kefauver, J.M.; Whitwam, T.; Patapoutian, A.; Ward, A.B. Structure of the Mechanically Activated Ion Channel. Nature 2018, 554, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bera, K.; Kiepas, A.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.X.; Konstantopoulos, K. The Interplay between Physical Cues and Mechanosensitive Ion Channels in Cancer Metastasis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 954099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Han, L.; Nookaew, I.; Mannen, E.; Silva, M.J.; Almeida, M.; Xiong, J. Stimulation of Piezo1 by Mechanical Signals Promotes Bone Anabolism. Elife 2019, 8, e49631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Dubin, A.E.; Zhang, Y.; Mousavi, S.A.R.; Wang, Y.; Coombs, A.M.; Loud, M.; Andolfo, I.; Patapoutian, A. A Role of PIEZO1 in Iron Metabolism in Mice and Humans. Cell 2021, 184, 969–982.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahalan, S.M.; Lukacs, V.; Ranade, S.S.; Chien, S.; Bandell, M.; Patapoutian, A. Piezo1 Links Mechanical Forces to Red Blood Cell Volume. Elife 2015, 4, e07370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, M.M.; Nourse, J.L.; Tran, T.; Hwe, J.; Arulmoli, J.; Le, D.T.T.; Bernardis, E.; Flanagan, L.A.; Tombola, F. Stretch-Activated Ion Channel Piezo1 Directs Lineage Choice in Human Neural Stem Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16148–16153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, W.C.; Yang, J.R.; Yankaskas, C.L.; Wong, B.S.; Wu, P.H.; Pardo-Pastor, C.; Serra, S.A.; Chiang, M.J.; Gu, Z.; Wirtz, D.; et al. Confinement Sensing and Signal Optimization via Piezo1/PKA and Myosin II Pathways. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 1430–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, S.S.; Qiu, Z.; Woo, S.H.; Hur, S.S.; Murthy, S.E.; Cahalan, S.M.; Xu, J.; Mathur, J.; Bandell, M.; Coste, B.; et al. Piezo1, a Mechanically Activated Ion Channel, Is Required for Vascular Development in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10347–10352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.L.; Liao, H.Y. Piezo-Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 (Piezo1) in Human Cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 140, 111692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poole, R.A.; Wang, Q.; Ray, A.; Takabe, K.; Opyrchal, M.; Katsuta, E. Increased PIEZO1 Expression Is Associated with Worse Clinical Outcomes in Hormone-Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer Patients. Cancers 2024, 16, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, D.; Men, H.; Huo, L.; Geng, Q.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 Promotes Prostate Cancer Development through the Activation of the Akt/MTOR Pathway and Acceleration of Cell Cycle. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 629–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, K.; Fujii, S.; Matsumoto, S.; Tajiri, Y.; Kikuchi, A.; Kiyoshima, T. YAP Signaling Induces PIEZO1 to Promote Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Proliferation. J. Pathol. 2021, 253, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Muraki, Y.; Hatano, N.; Suzuki, H.; Muraki, K. PIEZO1 Channel Is a Potential Regulator of Synovial Sarcoma Cell-Viability. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, S.; Li, S.; Hu, Z. Upregulation of Piezo1 Is a Novel Prognostic Indicator in Glioma Patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 3527–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zhao, Y.D.; Chen, W.X. The Function of the Novel Mechanical Activated Ion Channel Piezo1 in the Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 5070–5082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Li, M.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Zhi, L.; Zhao, J.; Wang, G. The Function of Piezo1 in Colon Cancer Metastasis and Its Potential Regulatory Mechanism. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 1139–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, G.; Miao, Y.; Qiu, F.; Bai, L.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Dong, L.; Niu, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Piezo Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 Facilitates Gastric Cancer Omentum Metastasis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 2238–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Wei, M.; Duan, W.; Wu, S.; Kasim, V. Mechanosensitive Ion Channel PIEZO1 Signaling in the Hall-Marks of Cancer: Structure and Functions. Cancers 2022, 14, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, S.; Gong, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Yue, Y.; Qian, W.; Ma, Q.; et al. Mechanically Activated Ion Channel Piezo1 Contributes to Melanoma Malignant Progression through AKT/MTOR Signaling. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.; Niu, K.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Loss of Stretch-Activated Channels, PIEZOs, Accelerates Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Progression and Cell Migration. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Li, F.; Yu, J.; Liang, Z.; Ke, X.; Wang, Y.; Song, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, G.; Guo, Y. PIEZO1 Mediates Matrix Stiffness-Induced Tumor Progression in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma by Activating the Ca2+/Calpain/YAP Pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2025, 1872, 119871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hou, C.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M.; Yao, X. A Pancancer Study of PIEZO1 as a Prognosis and Immune Biomarker of Human Tumors. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 6725570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombroski, J.A.; Hope, J.M.; Sarna, N.S.; King, M.R. Channeling the Force: Piezo1 Mechanotransduction in Cancer Metastasis. Cells 2021, 10, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, J.; He, B.; Luo, S.; Tan, Q.; Yao, Y.; Wan, R.; Xu, H.; Liu, S.; Pan, X.; et al. Piezo1 Aggravates Ischemia/Reperfusion—Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Ca2+—Dependent Calpain/HIF-1α/Notch Signaling. Ren. Fail. 2025, 47, 2447801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, R. Comprehensive Analysis of MRNA Expression of Piezo1 and Piezo2 in Tumor Samples and Their Prognostic Implications in Gastric Cancer. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Rezania, S.; Kammerer, S.; Sokolowski, A.; Devaney, T.; Gorischek, A.; Jahn, S.; Hackl, H.; Groschner, K.; Windpassinger, C.; et al. Piezo1 Forms Mechanosensitive Ion Channels in the Human MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Line. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, L.; Zhao, M.; Wei, H.; Dong, W.; Bi, X.; Ang, L.; Zhang, S. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Association between MiR-942-5p-Induced Downregulation of PIEZO-Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 and Poor Prognosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Mediated by the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Transl. Med. 2024, 10, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caolo, V.; Debant, M.; Endesh, N.; Futers, T.S.; Lichtenstein, L.; Parsonage, G.; Jones, E.A.; Beech, D.J. Piezo1 Channel Activates ADAM10 Sheddase to Regulate Notch1 and Gene Expression. bioRxiv 2019. bioRxiv:732370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antosik, P.; Durślewicz, J.; Smolińska-Świtała, M.; Podemski, J.; Podemska, E.; Neska-Długosz, I.; Jóźwicki, J.; Grzanka, D. KIF11 and KIF14 Are a Novel Potential Prognostic Biomarker in Patients with Endometrioid Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

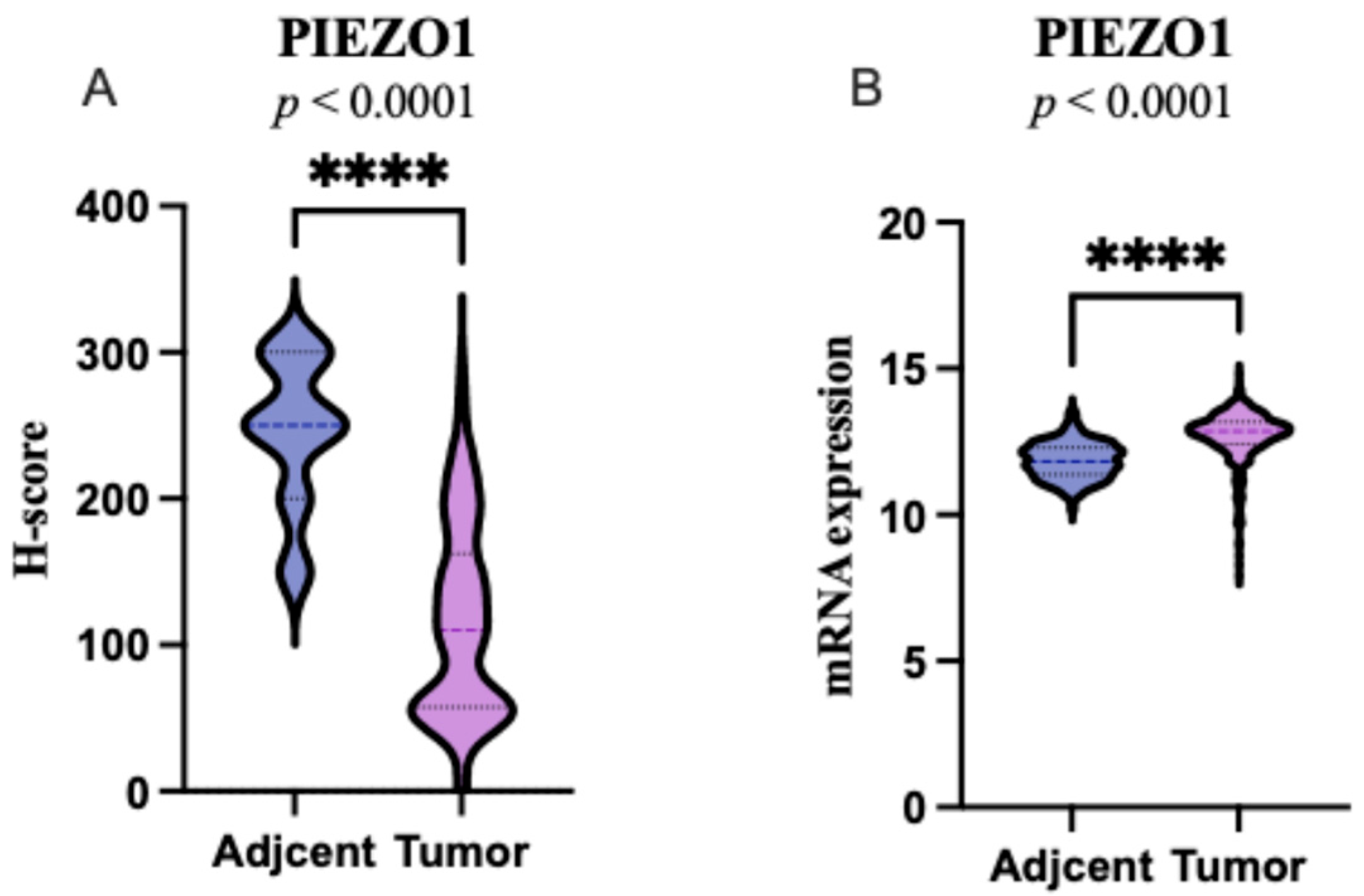
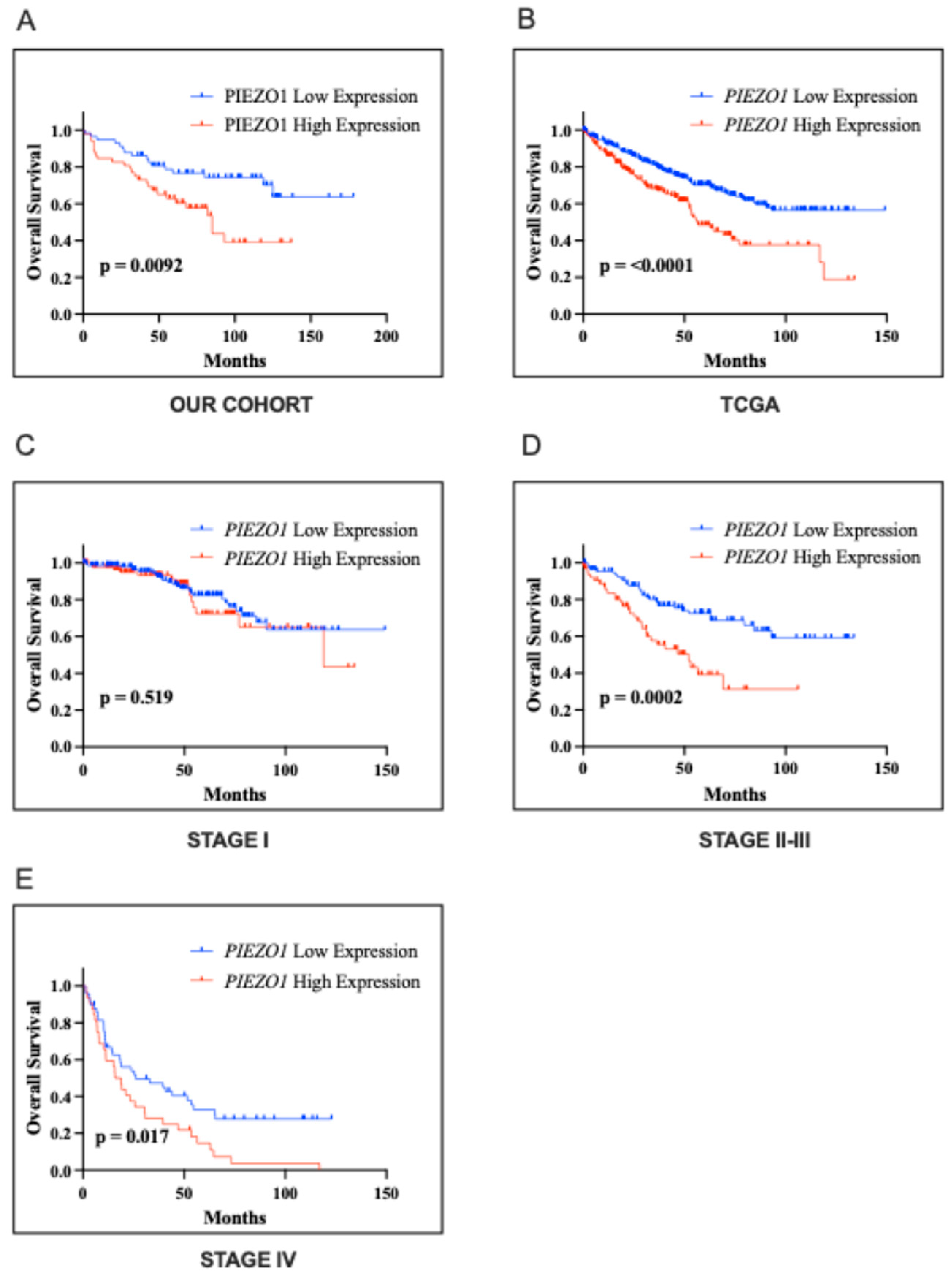
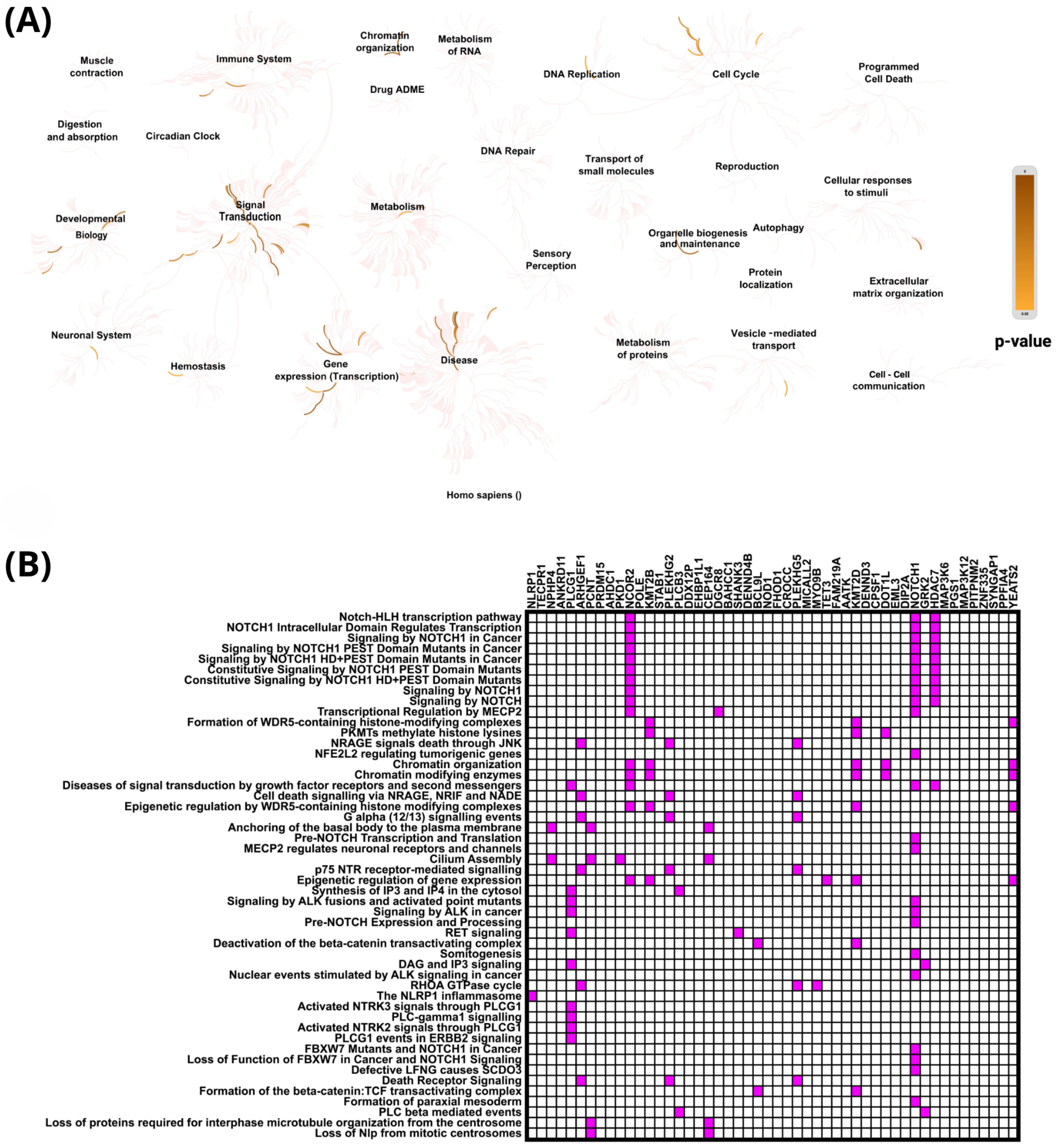
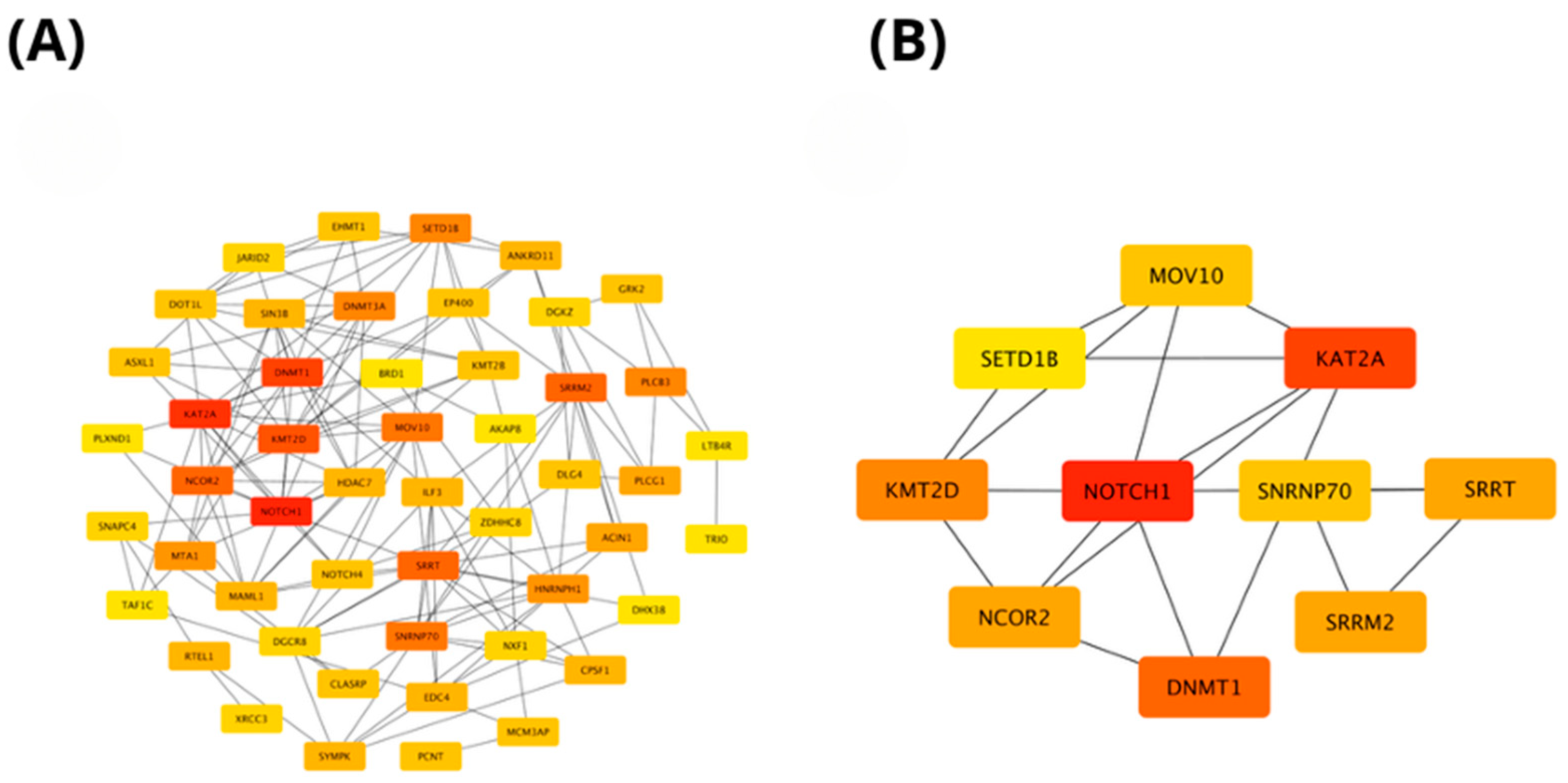


| PIEZO1 Our Cohort | PIEZO1 TCGA Cohort | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Number | Low | High | p Value | Variables | Number | Low | High | p Value |
| n = 59 | n = 52 | n = 319 | n = 185 | ||||||
| Age | Age | ||||||||
| ≤60 | 36 | 21 | 15 | 0.5432 | ≤60 | 252 | 155 | 97 | 0.4598 |
| >60 | 75 | 38 | 37 | >60 | 252 | 164 | 88 | ||
| Sex | Sex | ||||||||
| Male | 66 | 31 | 35 | 0.1257 | Male | 324 | 206 | 118 | 0.9232 |
| Female | 45 | 28 | 17 | Female | 180 | 113 | 67 | ||
| Histologic grade | Histologic grade | ||||||||
| G1–G2 | 95 | 55 | 40 | 0.0147 | G1–G2 | 225 | 145 | 80 | 0.5732 |
| G3–G4 | 16 | 4 | 12 | G3–G4 | 271 | 168 | 103 | ||
| Gx | 8 | - | - | ||||||
| pT status | pT status | ||||||||
| T1 | 74 | 40 | 34 | 0.3127 | T1 | 251 | 158 | 93 | 0.9184 |
| T2 | 17 | 11 | 6 | T2 | 65 | 43 | 22 | ||
| T3 | 20 | 8 | 12 | T3 | 178 | 111 | 67 | ||
| T4 | 10 | 7 | 3 | ||||||
| pN | pN | ||||||||
| N0 | 109 | 58 | 51 | >0.9999 | N0 | 228 | 150 | 78 | 0.7801 |
| N1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | N1 | 15 | 9 | 6 | ||
| Nx | 261 | - | - | ||||||
| Lymphovascular invasion | (LVI) | ||||||||
| Present | 5 | 3 | 2 | >0.9999 | |||||
| Absent | 106 | 56 | 50 | ||||||
| Stage | Stage | ||||||||
| I | 74 | 40 | 34 | 0.3127 | I | 246 | 155 | 91 | 0.8984 |
| II | 17 | 11 | 6 | II | 53 | 36 | 17 | ||
| III | 20 | 8 | 12 | III | 124 | 78 | 46 | ||
| IV | - | - | - | IV | 81 | 50 | 31 | ||
| Variable | Univariate Analysis of Own Cohort | Multivariate Analysis of Own Cohort | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value | |||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||
| PIEZO1 | 2.13 | 1.14 | 3.98 | 0.0182 | 2.08 | 1.08 | 4.01 | 0.0300 |
| sex | 2.66 | 1.31 | 5.43 | 0.0070 | 2.37 | 1.14 | 4.89 | 0.0200 |
| grade | 2.88 | 1.44 | 5.75 | 0.0027 | 3.22 | 1.58 | 6.56 | 0.0010 |
| pT | 3.59 | 1.84 | 7.00 | 0.0002 | - | - | - | - |
| pN | 17.17 | 3.72 | 79.14 | 0.0003 | - | - | - | - |
| LVI | 6.35 | 2.23 | 18.08 | 0.0005 | 7.60 | 2.51 | 23.06 | <0.001 |
| PIEZO1 (+) Correlated Gene | Cytoband | Spearman’s Correlation | p-Value | PIEZO1 (+) Correlated Gene | Cytoband | Spearman’s Correlation | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NLRP1 | 17p13 | 0.590 | 3.05 × 10−49 | FHOD1 | 16q22.1 | 0.528 | 6.32 × 10−38 |
| TECPR1 | 7q21.3 | 0.582 | 1.47 × 10−47 | CROCC | 1p36.13 | 0.527 | 9.59 × 10−38 |
| NPHP4 | 1p36.31 | 0.575 | 2.95 × 10−46 | PLEKHG5 | 1p36.31 | 0.525 | 1.89 × 10−37 |
| ANKRD11 | 16q24.3 | 0.574 | 6.20 × 10−46 | MICALL2 | 7p22.3 | 0.521 | 7.30 × 10−37 |
| PLCG1 | 20q12 | 0.570 | 2.79 × 10−45 | MYO9B | 19p13.11 | 0.519 | 1.49 × 10−36 |
| ARHGEF1 | 19q13.2 | 0.561 | 1.19 × 10−43 | TET3 | 2p13.1 | 0.518 | 2.71 × 10−36 |
| PCNT | 21q22.3 | 0.559 | 2.77 × 10−43 | FAM219A | 9p13.3 | 0.517 | 3.97 × 10−36 |
| PRDM15 | 21q22.3 | 0.558 | 3.93 × 10−43 | AATK | 17q25.3 | 0.516 | 5.59 × 10−36 |
| AHDC1 | 1p36.11-p35.3 | 0.556 | 1.04 × 10−42 | KMT2D | 12q13.12 | 0.514 | 9.09 × 10−36 |
| PKD1 | 16p13.3 | 0.556 | 1.24 × 10−42 | DENND3 | 8q24.3 | 0.514 | 1.00 × 10−35 |
| NCOR2 | 12q24.31 | 0.551 | 9.19 × 10−42 | CPSF1 | 8q24.3 | 0.514 | 1.15 × 10−35 |
| POLE | 12q24.33 | 0.546 | 5.78 × 10−41 | DOT1L | 19p13.3 | 0.513 | 1.62 × 10−35 |
| KMT2B | 19q13.12 | 0.544 | 1.42 × 10−40 | EML3 | 11q12.3 | 0.512 | 1.85 × 10−35 |
| STAB1 | 3p21.1 | 0.543 | 2.09 × 10−40 | DIP2A | 21q22.3 | 0.510 | 3.53 × 10−35 |
| PLEKHG2 | 19q13.2 | 0.541 | 3.60 × 10−40 | NOTCH1 | 9q34.3 | 0.510 | 3.60 × 10−35 |
| PLCB3 | 11q13.1 | 0.541 | 4.51 × 10−40 | GRK2 | 11q13.2 | 0.510 | 4.24 × 10−35 |
| DDX12P | 12p13.31 | 0.538 | 1.56 × 10−39 | HDAC7 | 12q13.11 | 0.509 | 5.34 × 10−35 |
| EHBP1L1 | 11q13.1 | 0.537 | 2.04 × 10−39 | MAP3K6 | 1p36.11 | 0.509 | 5.80 × 10−35 |
| CEP164 | 11q23.3 | 0.537 | 2.28 × 10−39 | PGS1 | 17q25.3 | 0.509 | 5.96 × 10−35 |
| DGCR8 | 22q11.21 | 0.536 | 2.59 × 10−39 | MAP3K12 | 12q13.13 | 0.508 | 7.84 × 10−35 |
| BAHCC1 | 17q25.3 | 0.535 | 4.73 × 10−39 | PITPNM2 | 12q24.31 | 0.508 | 8.52 × 10−35 |
| SHANK3 | 22q13.33 | 0.534 | 5.11 × 10−39 | ZNF335 | 20q13.12 | 0.507 | 9.95 × 10−35 |
| DENND4B | 1q21.3 | 0.532 | 1.34 × 10−38 | SYNGAP1 | 6p21.32 | 0.507 | 1.14 × 10−34 |
| BCL9L | 11q23.3 | 0.531 | 1.80 × 10−38 | PPFIA4 | 1q32.1 | 0.505 | 2.12 × 10−34 |
| NOD1 | 7p14.3 | 0.531 | 1.93 × 10−38 | YEATS2 | 3q27.1 | 0.505 | 2.34 × 10−34 |
| PIEZO1 (-) correlated Gene | Cytoband | Spearman’s Correlation | p-Value | PIEZO1 (−) Correlated Gene | Cytoband | Spearman’s Correlation | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSG101 | 11p15.1 | −0.553 | 3.23 × 10−42 | MDH1 | 2p15 | −0.468 | 3.86 × 10−29 |
| SDHD | 11q23.1 | −0.536 | 2.66 × 10−39 | IER3IP1 | 18q21.1 | −0.468 | 4.23 × 10−29 |
| NDUFB5 | 3q26.33 | −0.526 | 1.16 × 10−37 | TMEM9B | 11p15.4 | −0.465 | 9.92 × 10−29 |
| NDFIP1 | 5q31.3 | −0.518 | 2.37 × 10−36 | SPCS2P4 | 1p35.3 | −0.464 | 1.29 × 10−28 |
| C18ORF32 | 18q21.1 | −0.516 | 4.34 × 10−36 | LAMTOR3 | 4q23 | −0.462 | 2.39 × 10−28 |
| SCOC | 4q31.1 | −0.513 | 1.33 × 10−35 | MED21 | 12p11.23 | −0.461 | 2.99 × 10−28 |
| GHITM | 10q23.1 | −0.512 | 1.79 × 10−35 | VBP1 | Xq28 | −0.460 | 4.37 × 10−28 |
| NKIRAS1 | 3p24.2 | −0.511 | 2.80 × 10−35 | ATP6V1E1 | 22q11.21 | −0.459 | 5.83 × 10−28 |
| ARL1 | 12q23.2 | −0.504 | 3.75 × 10−34 | SCAMP1 | 5q14.1 | −0.458 | 7.79 × 10−28 |
| MOCS2 | 5q11.2 | −0.501 | 8.15 × 10−34 | HCCS | Xp22.2 | −0.456 | 1.44 × 10−27 |
| NDUFA5 | 7q31.32 | −0.493 | 1.18 × 10−32 | RTN3 | 11q13 | −0.456 | 1.60 × 10−27 |
| DNAJA2 | 16q11.2 | −0.491 | 2.54 × 10−32 | BPGM | 7q33 | −0.455 | 1.80 × 10−27 |
| ATP6AP2 | Xp11.4 | −0.486 | 1.29 × 10−31 | PAIP1 | 5p12 | −0.455 | 2.20 × 10−27 |
| KGD4 | 5q13.2 | −0.485 | 1.99 × 10−31 | UQCRFS1 | 19q12 | −0.454 | 2.41 × 10−27 |
| RNF13 | 3q25.1 | −0.484 | 2.89 × 10−31 | SC5D | 11q23.3-q24.1 | −0.454 | 2.44 × 10−27 |
| ATP5F1A | 18q21.1 | −0.484 | 2.96 × 10−31 | CIAO2A | 15q22.31 | −0.451 | 6.20 × 10−27 |
| MICU2 | 13q12.11 | −0.480 | 9.28 × 10−31 | PLGRKT | 9p24.1 | −0.450 | 9.63 × 10−27 |
| TATDN3 | 1q32.3 | −0.478 | 1.64 × 10−30 | SRP9 | 1q42.12 | −0.446 | 2.40 × 10−26 |
| GABARAPL2 | 16q23.1 | −0.476 | 2.92 × 10−30 | IDH3A | 15q25.1 | −0.445 | 3.29 × 10−26 |
| CHP1 | 15q15.1 | −0.475 | 5.32 × 10−30 | SYS1 | 20q13.12 | −0.444 | 4.95 × 10−26 |
| ARL6IP1 | 16p12.3 | −0.473 | 9.97 × 10−30 | LSM3 | 3p25.1 | −0.444 | 4.97 × 10−26 |
| MRPS35 | 12p11.22 | −0.472 | 1.09 × 10−29 | SUCLG1 | 2p11.2 | −0.443 | 6.48 × 10−26 |
| MKKS | 20p12.2 | −0.472 | 1.30 × 10−29 | PDHB | 3p14.3 | −0.434 | 7.79 × 10−25 |
| SKP1 | 5q31.1 | −0.470 | 2.04 × 10−29 | COPS4 | 4q21.22 | −0.434 | 8.47 × 10−25 |
| ATP5PB | 1p13.2 | −0.470 | 2.54 × 10−29 | PLEKHA3 | 2q31.2 | −0.433 | 9.35 × 10−25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antosik, P.; Szachniewicz, M.; Baran, M.; Bonowicz, K.; Jerka, D.; Motylewska, E.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Gagat, M.; Grzanka, D. Piezo-Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 (PIEZO1) as a Potential Prognostic Marker in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146598
Antosik P, Szachniewicz M, Baran M, Bonowicz K, Jerka D, Motylewska E, Kwiatkowski M, Gagat M, Grzanka D. Piezo-Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 (PIEZO1) as a Potential Prognostic Marker in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146598
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntosik, Paulina, Martyna Szachniewicz, Michał Baran, Klaudia Bonowicz, Dominika Jerka, Ewelina Motylewska, Maciej Kwiatkowski, Maciej Gagat, and Dariusz Grzanka. 2025. "Piezo-Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 (PIEZO1) as a Potential Prognostic Marker in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146598
APA StyleAntosik, P., Szachniewicz, M., Baran, M., Bonowicz, K., Jerka, D., Motylewska, E., Kwiatkowski, M., Gagat, M., & Grzanka, D. (2025). Piezo-Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 (PIEZO1) as a Potential Prognostic Marker in Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6598. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146598






