CSPG4.CAR-T Cells Modulate Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in DMD Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
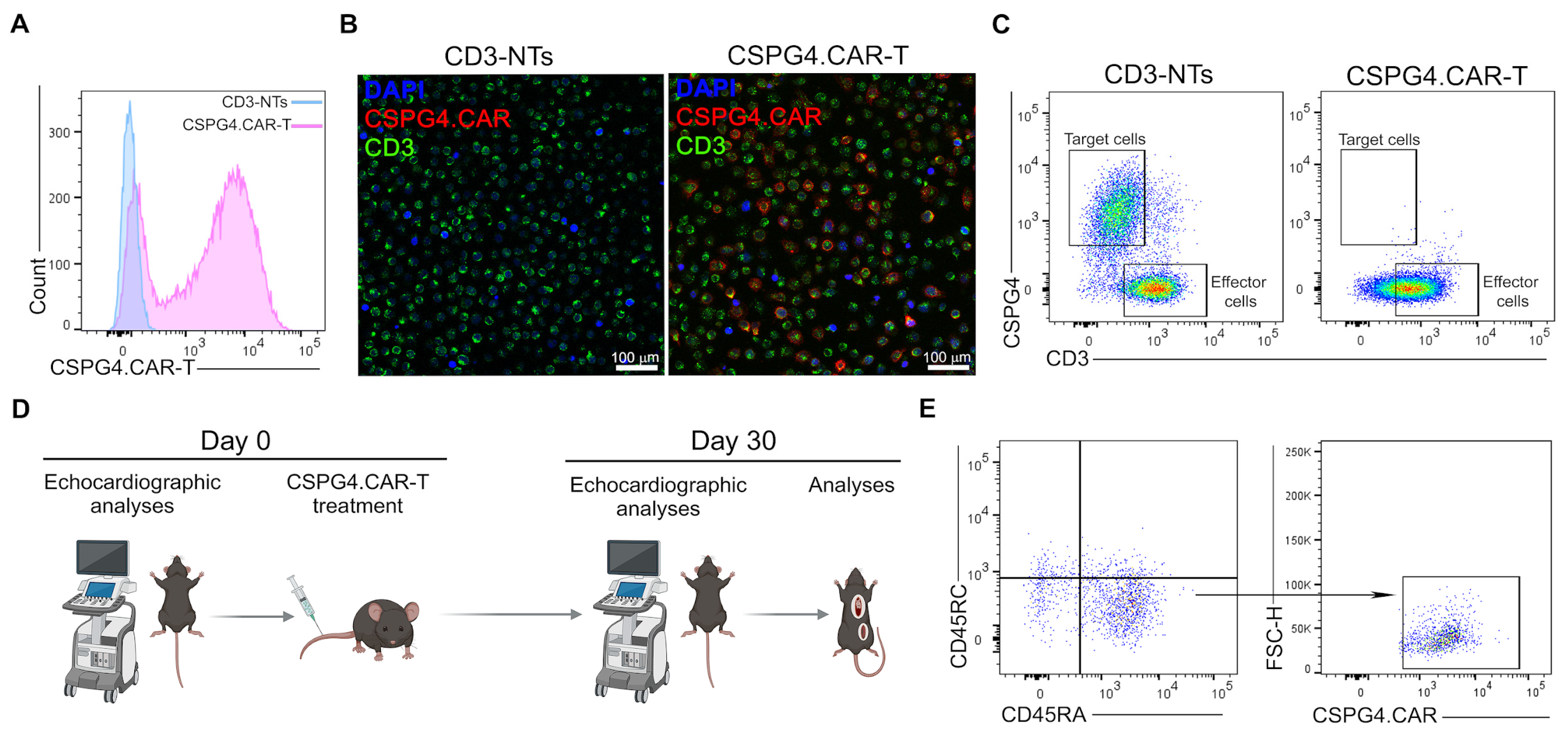
2.1. CSPG4.CAR-T Generation and In Vivo Experiments
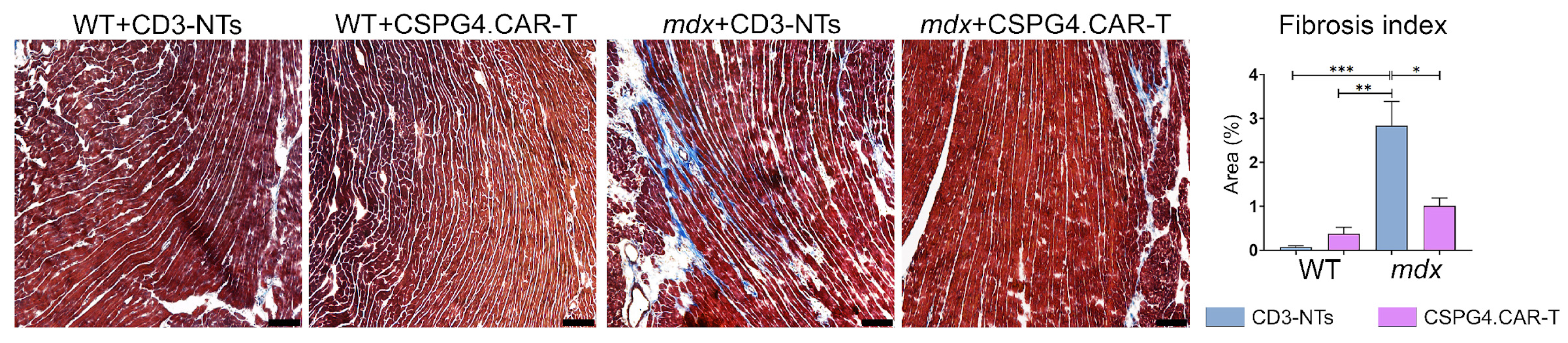
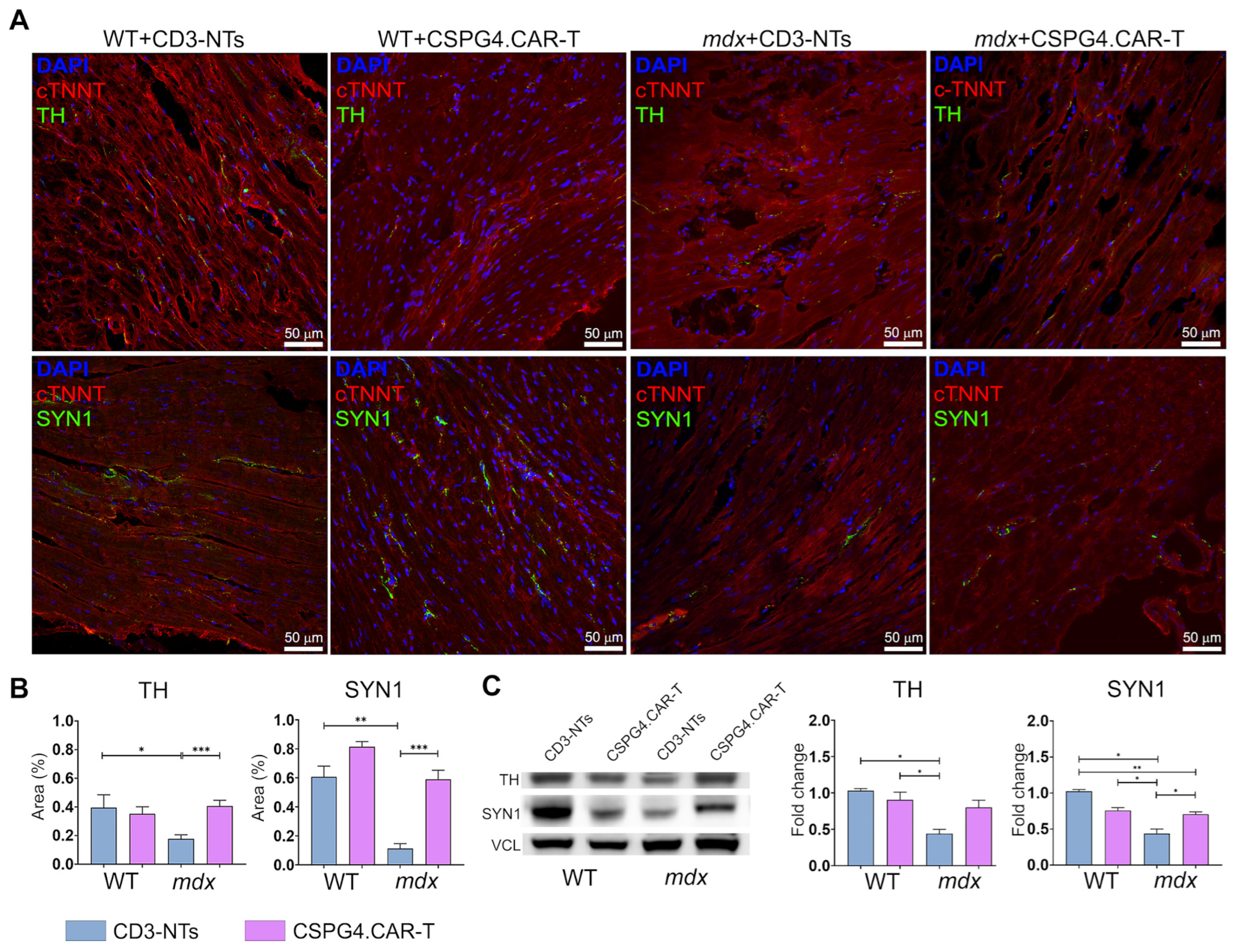
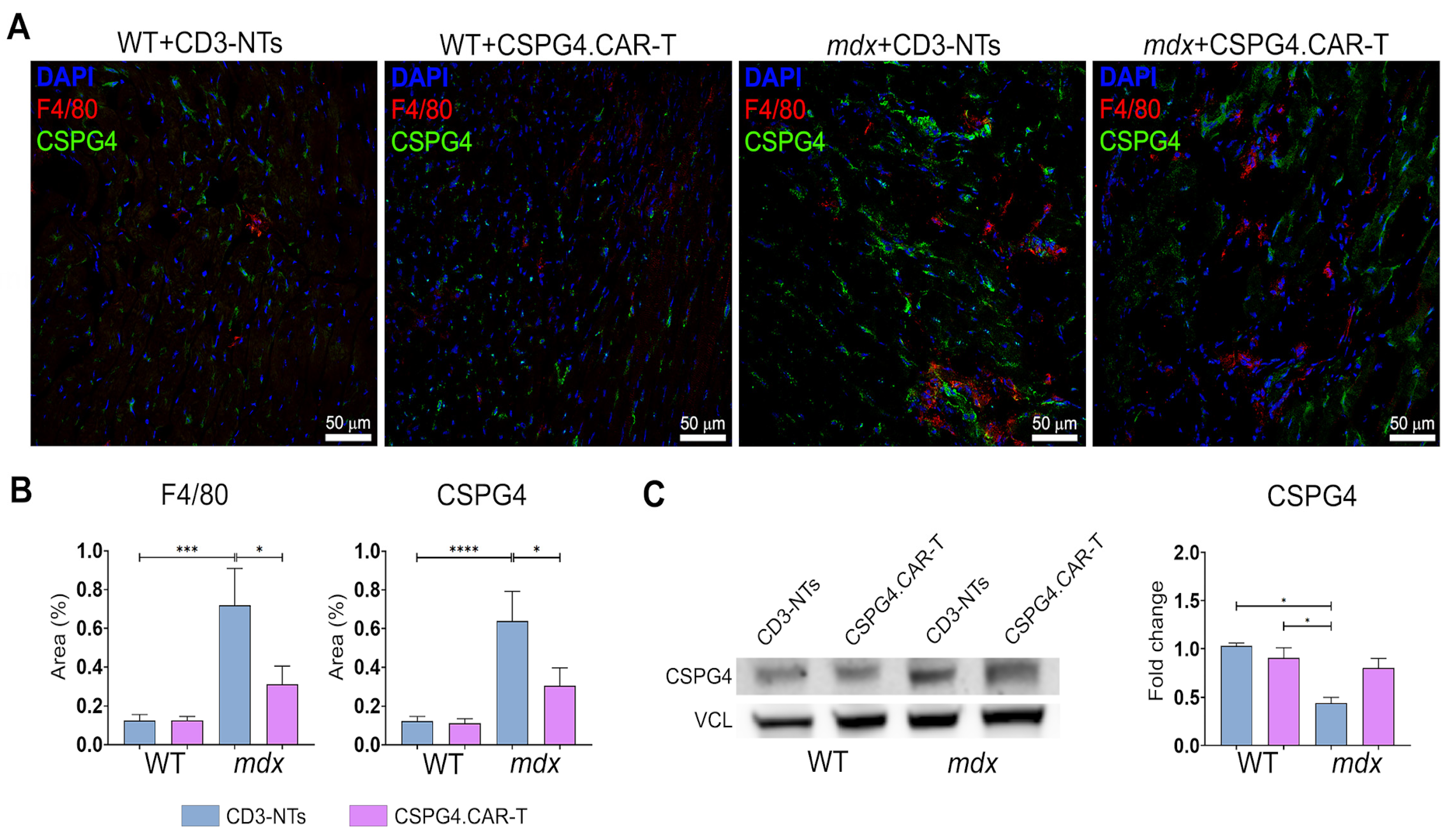
2.2. CSPG4.CAR-T Cells Reduce Fibrosis and Enhance Innervation Recovery in mdx Mice
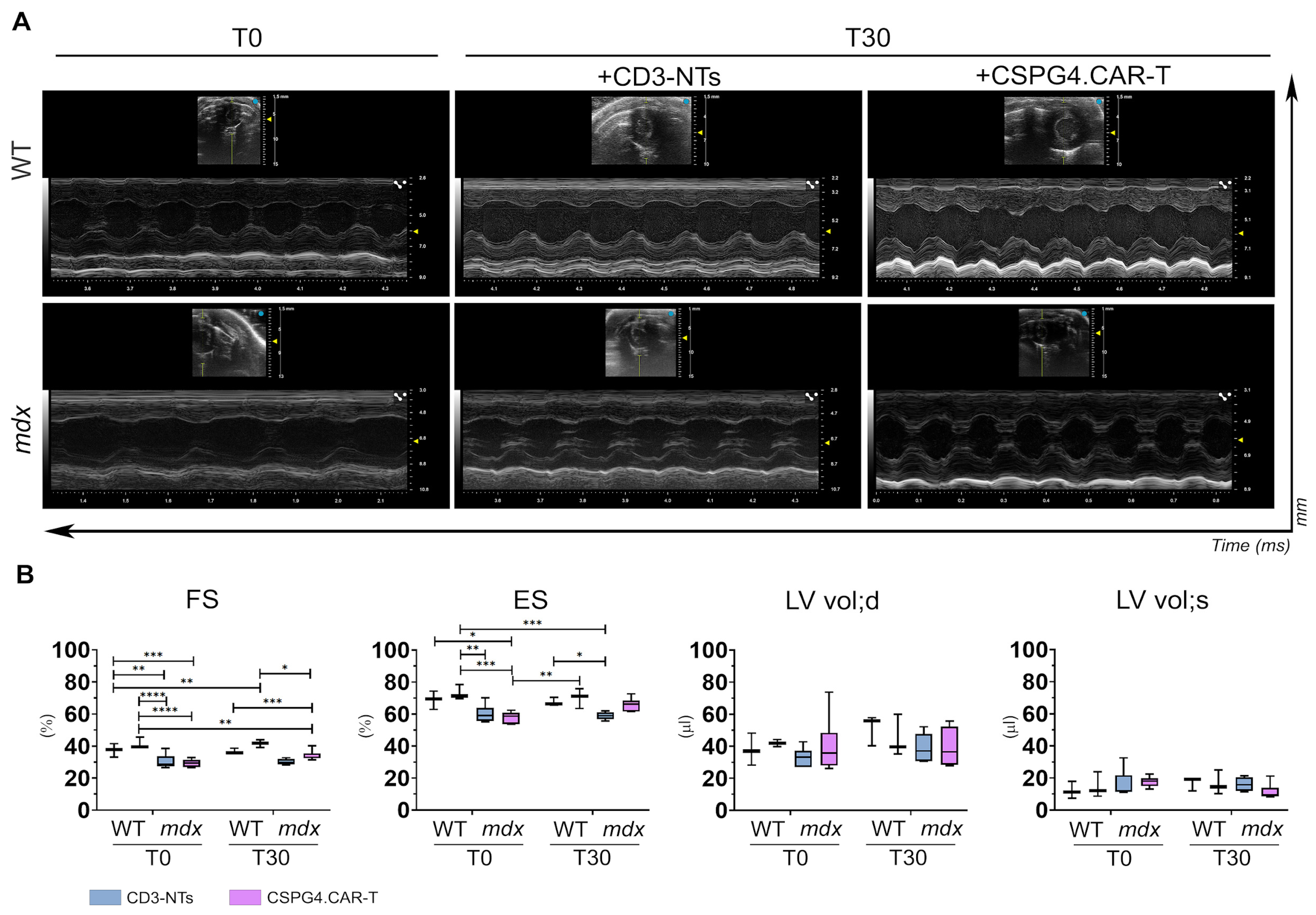
2.3. CSPG4.CAR-T Cells Improve Cardiac Function in mdx Mice
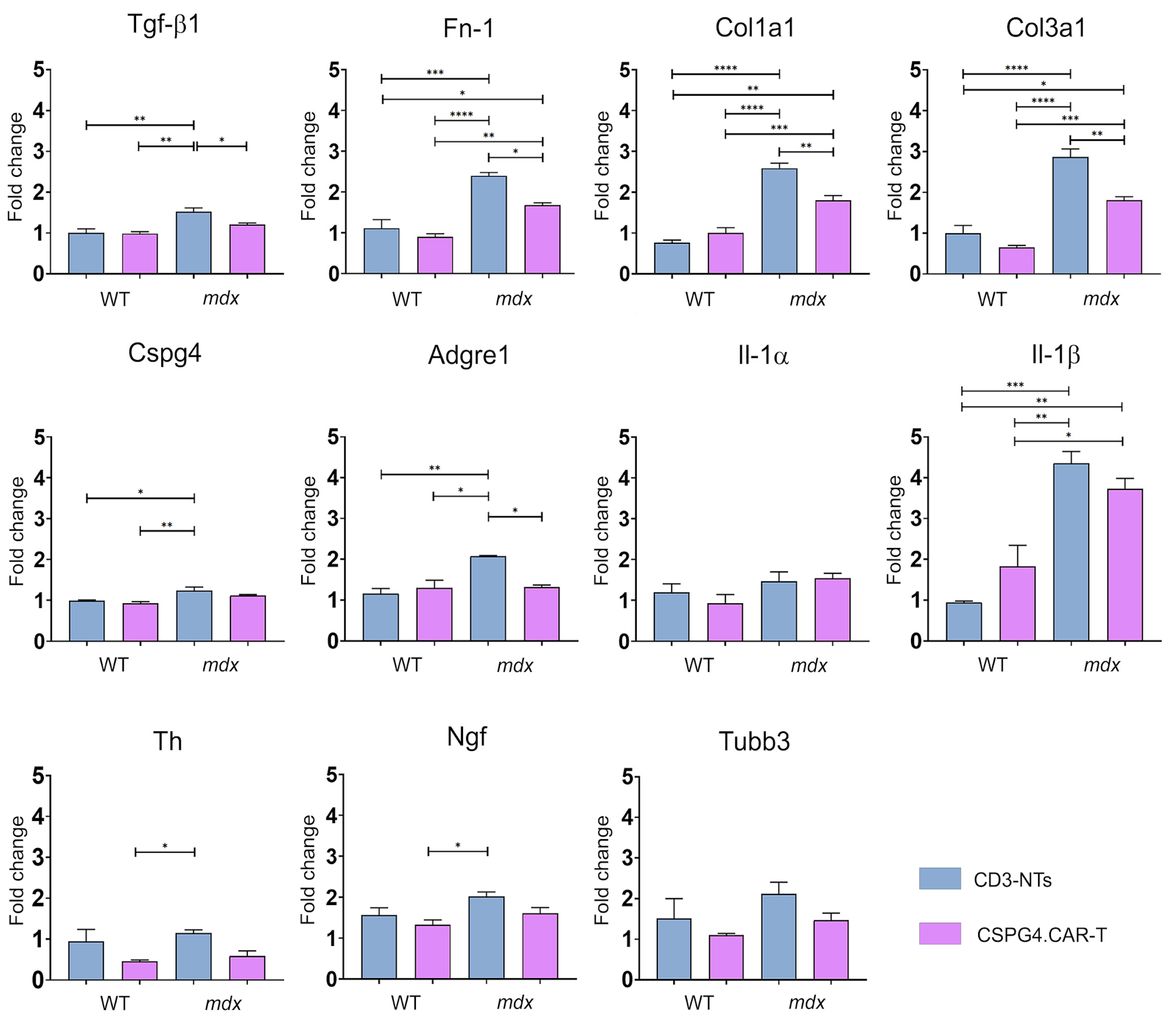
2.4. CSPG4.CAR-T Effects on Gene and Cytokine Profiles
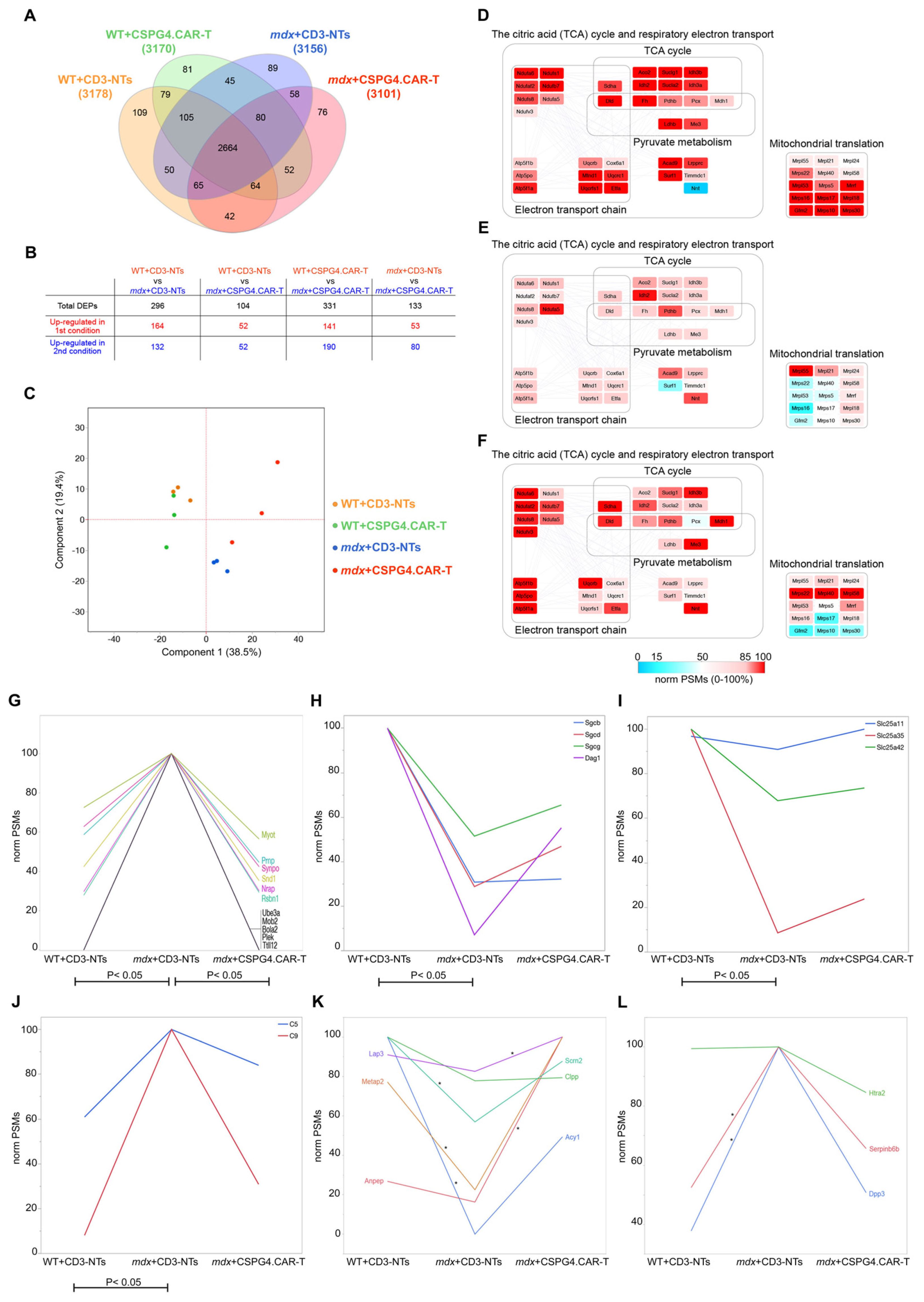
2.5. CSPG4.CAR-T Therapy Effect on Cardiac Proteome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of CAR-T Cells from Human PBMC Characterization
4.2. CAR-T Cells’ Characterization
4.3. Echocardiogram
4.4. Mice Treatment
4.5. Spleen Processing
4.6. Histological Analysis
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Gene Expression Analysis
4.9. Cytokine Assay
4.10. Proteomic Analysis
4.11. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAR | Chimeric Antigen Receptor |
| CSPG4 | Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan 4 |
| cTNNT | Cardiac Troponin T |
| DMD | Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| EF | Ejection Fraction |
| FS | Fractional Shortening |
| NCJ | Neurocardiac Junction |
| SYN1 | Synapsin 1 |
| TH | Tyrosine Hydroxylase |
References
- Lombardi, L.; De Stefano, M.E.; Paggi, P. Components of the NGF Signaling Complex Are Altered in Mdx Mouse Superior Cervical Ganglion and Its Target Organs. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 32, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, L.; Persiconi, I.; Gallo, A.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; De Stefano, M.E. NGF-Dependent Axon Growth and Regeneration Are Altered in Sympathetic Neurons of Dystrophic Mdx Mice. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 80, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, J.G.; Hahn, H.S.; Wong, B.L.; Lorenz, J.N.; Wenisch, A.S.; Levin, L.S. Evolution of the Mdx Mouse Cardiomyopathy: Physiological and Morphological Findings. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2004, 14, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirm, M.; Fonteyne, L.M.; Shashikadze, B.; Lindner, M.; Chirivi, M.; Lange, A.; Kaufhold, C.; Mayer, C.; Medugorac, I.; Kessler, B.; et al. A Scalable, Clinically Severe Pig Model for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Dis. Models Mech. 2021, 14, dmm049285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.T.; Ripplinger, C.M.; Myles, R.C.; Habecker, B.A. Molecular Mechanisms of Sympathetic Remodeling and Arrhythmias. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2016, 9, e001359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingler, W.; Jurkat-Rott, K.; Lehmann-Horn, F.; Schleip, R. The Role of Fibrosis in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Acta Myol. 2012, 31, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haddad, C.N.; Ali, S.; Stephanou, D.; Assakura, M.S.; Sahagian, L.; Trogkanis, E. Pharmacological Management of Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Systematic Review. Hell. J. Cardiol. 2023, 74, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adorisio, R.; Mencarelli, E.; Cantarutti, N.; Calvieri, C.; Amato, L.; Cicenia, M.; Silvetti, M.; D’Amico, A.; Grandinetti, M.; Drago, F.; et al. Duchenne Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Cardiac Management from Prevention to Advanced Cardiovascular Therapies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.N.A.; Yokota, T. Cardiac Therapies for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Ther. Adv. Neurol. Disord. 2023, 16, 17562864231182934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, M.; Pace, V.; Maiullari, F.; Chirivì, M.; Baci, D.; Maiullari, S.; Madaro, L.; Maccari, S.; Stati, T.; Marano, G.; et al. Givinostat Reduces Adverse Cardiac Remodeling through Regulating Fibroblasts Activation. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, M.; Maiullari, F.; Chirivì, M.; Ceraolo, M.G.; Zigiotto, R.; Soluri, A.; Maiullari, S.; Landoni, E.; Silvestre, D.D.; Brambilla, F.; et al. Macrophages Producing Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan-4 Induce Neuro-Cardiac Junction Impairment in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Pathol. 2025, 265, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consalvi, S.; Saccone, V.; Mozzetta, C. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors: A Potential Epigenetic Treatment for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Epigenomics 2014, 6, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Vilchez, J.J.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O.; Zaidman, C.M.; Mah, J.K.; Goemans, N.; Müller-Felber, W.; Niks, E.H.; Schara-Schmidt, U.; Bertini, E.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Givinostat in Boys with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (EPIDYS): A Multicentre, Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Neurol. 2024, 23, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New Treatment Against Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy|European Medicines Agency (EMA). Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/new-treatment-against-duchenne-muscular-dystrophy (accessed on 16 May 2025).
- Canonico, F.; Chirivi, M.; Maiullari, F.; Milan, M.; Rizzi, R.; Arcudi, A.; Galli, M.; Pane, M.; Gowran, A.; Pompilio, G.; et al. Focus on the Road to Modelling Cardiomyopathy in Muscular Dystrophy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 1872–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirivì, M.; Maiullari, F.; Milan, M.; Ceraolo, M.G.; Fratini, N.; Fasciani, A.; Bousselmi, S.; Stirm, M.; Scalera, F.; Gervaso, F.; et al. Mimicking the Dystrophic Cardiac Extracellular Environment through DystroGel. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2025, 14, e2404251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackensen, A.; Müller, F.; Mougiakakos, D.; Böltz, S.; Wilhelm, A.; Aigner, M.; Völkl, S.; Simon, D.; Kleyer, A.; Munoz, L.; et al. Anti-CD19 CAR T Cell Therapy for Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mougiakakos, D.; Krönke, G.; Völkl, S.; Kretschmann, S.; Aigner, M.; Kharboutli, S.; Böltz, S.; Manger, B.; Mackensen, A.; Schett, G. CD19-Targeted CAR T Cells in Refractory Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 567–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Lyu, J.; Jing, D.; Liu, L.; Fu, Y.; Niu, W.; Jin, L.; Zhang, C. The Expanded Application of CAR-T Cell Therapy for the Treatment of Multiple Non-Tumoral Diseases. Protein Cell 2024, 15, 633–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Tan, A.T. HBV as a Target for CAR or TCR-T Cell Therapy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2020, 66, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, H.; Theobald, S.J.; Slabik, C.; Gerasch, L.; Schneider, A.; Mach, M.; Shum, T.; Mamonkin, M.; Stripecke, R. Adult and Cord Blood-Derived High-Affinity gB-CAR-T Cells Effectively React Against Human Cytomegalovirus Infections. Hum. Gene Ther. 2020, 31, 423–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnozzi, R.J.; Johansen, A.K.Z.; Molkentin, J.D. CARdiac Immunotherapy: T Cells Engineered to Treat the Fibrotic Heart. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1869–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crunkhorn, S. CAR T Cells Combat Cardiac Fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, A.M.E.; Miao, Y.; Ahmed, A.I.M.; Meng, N.; Ouyang, C. CAR-T Cell Therapeutic Avenue for Fighting Cardiac Fibrosis: Roadblocks and Perspectives. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2024, 42, e3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajanian, H.; Kimura, T.; Rurik, J.G.; Hancock, A.S.; Leibowitz, M.S.; Li, L.; Scholler, J.; Monslow, J.; Lo, A.; Han, W.; et al. Targeting Cardiac Fibrosis with Engineered T Cells. Nature 2019, 573, 430–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rurik, J.G.; Tombácz, I.; Yadegari, A.; Méndez Fernández, P.O.; Shewale, S.V.; Li, L.; Kimura, T.; Soliman, O.Y.; Papp, T.E.; Tam, Y.K.; et al. CAR T Cells Produced in Vivo to Treat Cardiac Injury. Science 2022, 375, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, R.T.; Habecker, B.A. Infarct-Derived Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycans Prevent Sympathetic Reinnervation after Cardiac Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 7175–7183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmen, L.; Maria, V.; Morales-Medina, J.C.; Vallelunga, A.; Palmieri, B.; Iannitti, T. Role of Proteoglycans and Glycosaminoglycans in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraudo, L.; Cattaneo, G.; Gammaitoni, L.; Iaia, I.; Donini, C.; Massa, A.; Centomo, M.L.; Basiricò, M.; Vigna, E.; Pisacane, A.; et al. CSPG4 CAR-Redirected Cytokine Induced Killer Lymphocytes (CIK) as Effective Cellular Immunotherapy for HLA Class I Defective Melanoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, D.; Xue, Q.; Waddell, T.Q.; Kurudza, E.; Chaudhary, P.; Belote, R.L.; Dotti, G.; Judson-Torres, R.L.; Reeves, M.Q.; Cheshier, S.H.; et al. Human CSPG4-targeting CAR-macrophages inhibit melanoma growth. Oncogene 2025, 44, 1665–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pellegatta, S.; Savoldo, B.; Di Ianni, N.; Corbetta, C.; Chen, Y.; Patané, M.; Sun, C.; Pollo, B.; Ferrone, S.; DiMeco, F.; et al. Constitutive and TNFα-Inducible Expression of Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan 4 in Glioblastoma and Neurospheres: Implications for CAR-T Cell Therapy. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaao2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Chi, X.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, N. Expression Features of Targets for Anti-Glioma CAR-T Cell Immunotherapy. J. Neurooncol. 2025, 171, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrer, D.C.; Schuler, G.; Dörrie, J.; Schaft, N. CSPG4-Specific CAR T Cells for High-Risk Childhood B Cell Precursor Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrer, D.C.; Dörrie, J.; Schaft, N. CSPG4 as Target for CAR-T-Cell Therapy of Various Tumor Entities-Merits and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldres, C.; Savoldo, B.; Hoyos, V.; Caruana, I.; Zhang, M.; Yvon, E.; Del Vecchio, M.; Creighton, C.J.; Ittmann, M.; Ferrone, S.; et al. T Lymphocytes Redirected against the Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan-4 Control the Growth of Multiple Solid Tumors Both in Vitro and In Vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theret, M.; Saclier, M.; Messina, G.; Rossi, F.M.V. Macrophages in Skeletal Muscle Dystrophies, An Entangled Partner. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2022, 9, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, D.O.; Hildyard, J.C.W.; Harron, R.C.M.; Hornby, N.L.; Wells, D.J.; Piercy, R.J. Serum inflammatory cytokines as disease biomarkers in the DE50-MD dog model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Dis. Models Mech. 2022, 15, dmm049394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xue, L.; Chen, E.; Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Gao, M.; Li, Y.; Ren, J.; Sathiyanadan, K.; et al. IL-10 Expressing CD19 CAR-T Cells Induce Complete Remission and Improve Long-Term Protection in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Hematological Malignancies. Blood 2024, 144, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, Q.; Yu, T.; Zhang, Y. Identifying the Hub Genes for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Becker Muscular Dystrophy by Weighted Correlation Network Analysis. BMC Genom. Data 2021, 22, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Lin, Z.-J.; Fan, L.-L.; Xu, J.-M.; Yu, R. A Novel Mutation of Myotilin Is Associated with Muscular Dystrophy and Postoperative Respiratory Failure. QJM 2023, 116, 859–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetorou, K.; Aghaeipour, A.; Singh, S.; Morgan, J.E.; Muntoni, F. The Role of Dystrophin Isoforms and Interactors in the Brain. Brain 2025, 148, 1081–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, P.; Brandes, G.; Hemeling, H.; Huang, Z.; Wrede, C.; Hegermann, J.; Vlachos, A.; Lenz, M. Synaptopodin Regulates Denervation-Induced Plasticity at Hippocampal Mossy Fiber Synapses. Cells 2024, 13, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiferling, D.; Szczepanowska, K.; Becker, C.; Senft, K.; Hermans, S.; Maiti, P.; König, T.; Kukat, A.; Trifunovic, A. Loss of CLPP Alleviates Mitochondrial Cardiomyopathy without Affecting the Mammalian UPRmt. EMBO Rep. 2016, 17, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deniau, B.; Rehfeld, L.; Santos, K.; Dienelt, A.; Azibani, F.; Sadoune, M.; Kounde, P.R.; Samuel, J.L.; Tolpannen, H.; Lassus, J.; et al. Circulating Dipeptidyl Peptidase 3 Is a Myocardial Depressant Factor: Dipeptidyl Peptidase 3 Inhibition Rapidly and Sustainably Improves Haemodynamics. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, P.; Duan, W.; Leng, Y.-Q.; Wang, Y.-K.; Tan, X.; Wang, W.-Z. DPP3: From Biomarker to Therapeutic Target of Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 974035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranowska, K.; Samadaei, M.; Kalic, T.; Pinter, M.; Breiteneder, H.; Hafner, C. A chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4-specific monoclonal antibody inhibits melanoma cell invasion in a spheroid model. Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- de Souza Costa, Á.D.; Vermeulen-Serpa, K.M.; Batista Marinho, K.M.; de Medeiros, C.A.C.X.; Antunes de Araújo, A.; Teixeira Dourado-Junior, M.E.; Brandão-Neto, J.; Lima Maciel, B.L.; Helena de Lima Vale, S. Persistent inflammation and nutritional status in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 61, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera, J.; Savoldo, B.; Vigouroux, S.; Biagi, E.; Pule, M.; Rossig, C.; Wu, J.; Heslop, H.E.; Rooney, C.M.; Brenner, M.K.; et al. T Lymphocytes Redirected against the Kappa Light Chain of Human Immunoglobulin Efficiently Kill Mature B Lymphocyte-Derived Malignant Cells. Blood 2006, 108, 3890–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulè, M.A.; Straathof, K.C.; Dotti, G.; Heslop, H.E.; Rooney, C.M.; Brenner, M.K. A Chimeric T Cell Antigen Receptor That Augments Cytokine Release and Supports Clonal Expansion of Primary Human T Cells. Mol. Ther. 2005, 12, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegoli, G.; Milan, M.; Manti, P.G.; Bianchi, A.; Lucini, F.; Santarelli, P.; Bearzi, C.; Rizzi, R.; Lanzuolo, C. Role of Cdkn2a in the Emery–Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy Cardiac Phenotype. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612, Erratum in Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 10800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoot, M.; Ono, K.; Ideker, T.; Maere, S. PiNGO: A Cytoscape plugin to find candidate genes in biological networks. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1030–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Gene Symbol | Sense-Forward Primer | Antisense-Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Col1a1 | CCTCAGGGTATTGCTGGACA | GAAGGACCTTGTTTGCCAGG |
| Col3a1 | CCCAACCCAGAGATCCCATT | GGTCACCATTTCTCCCAGGA |
| Fibronectin | CATGCCTCGGGAATGGAAAG | TGCTTCATGGGGATCACACT |
| Tgf-β1 | CAACCCAGGTCCTTCCTAAA | GGAGAGCCCTGGATACCAAC |
| Adgre1 | CGTGTTGTTGGTGGCACTGTGA | CCACATCAGTGTTCCAGGAGAC |
| Cspg4 | AAGGAAGTGCAGAGGAGGTC | TGAGGACAGTAGGAGACCGA |
| Th | CAATACAAGCAGGGTGAGCC | TAGCATAGAGGCCCTTCAGC |
| Ngf | ATACTGCACCACGACTCACA | GGCTGTGTCTATCCGGATGA |
| Il-1α | ACGGCTGAGTTTCAGTGAGACC | CACTCTGGTAGGTGTAAGGTGC |
| Il-1β | TGGACCTTCCAGGATGAGGACA | GTTCATCTCGGAGCCTGTAGTG |
| Tubb3 | AACCTGGAACCATGGACAGT | AGCACCACTCTGACCAAAGA |
| Eef1a2 | CAAGATTGGGGGCATTGGGA | TCGCTAAGTGCCTCATGGTG |
| Exploris 240 Parameter | |
|---|---|
| Full scan | |
| Resolution MS1 | 120,000 |
| Scan range lower limit, m/z | 375 |
| Scan range upper limit, m/z | 1200 |
| AGC target custom, normalized % | 300 |
| Maximum injection time mode | auto |
| RF lens % | 80 |
| Filters | |
| MIPS | |
| Monoisotopic peak det. | peptide |
| Intensity | |
| Intensity threshold | 8.0 × 103 |
| Charge state | |
| Include charge state | 2–6 |
| Dynamic Exclusion custom | |
| Exclude after n times | 1 |
| Exclusion duration (s) | 15 |
| Mass tolerance ppm | 10 |
| ddMS2 (top 20 scans) | |
| Resolution MS2 | 15,000 |
| AGC target custom, normalized % | 100 |
| Maximum injection time, ms | auto |
| Scan range lower limit, m/z | 120 |
| Scan range upper limit, m/z | 1200 |
| Isolation window, m/z | 2 |
| HCD collision energy, % | 30 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ceraolo, M.G.; Milan, M.; Fratini, N.; Viganò, R.; Bousselmi, S.; Soluri, A.; Pesce, E.; Mauri, P.L.; Ciuffreda, G.; Landoni, E.; et al. CSPG4.CAR-T Cells Modulate Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in DMD Cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146590
Ceraolo MG, Milan M, Fratini N, Viganò R, Bousselmi S, Soluri A, Pesce E, Mauri PL, Ciuffreda G, Landoni E, et al. CSPG4.CAR-T Cells Modulate Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in DMD Cardiomyopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(14):6590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146590
Chicago/Turabian StyleCeraolo, Maria Grazia, Marika Milan, Nicole Fratini, Raffaello Viganò, Salma Bousselmi, Andrea Soluri, Elisa Pesce, Pier Luigi Mauri, Giusy Ciuffreda, Elisa Landoni, and et al. 2025. "CSPG4.CAR-T Cells Modulate Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in DMD Cardiomyopathy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 14: 6590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146590
APA StyleCeraolo, M. G., Milan, M., Fratini, N., Viganò, R., Bousselmi, S., Soluri, A., Pesce, E., Mauri, P. L., Ciuffreda, G., Landoni, E., Brambilla, F., Dotti, G., Di Silvestre, D., Maiullari, F., Bearzi, C., & Rizzi, R. (2025). CSPG4.CAR-T Cells Modulate Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in DMD Cardiomyopathy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(14), 6590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26146590










