The Role of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms at the Arg399Gln Locus of the XRCC1 Gene in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Characteristics of Patients with NSCLC and Controls
4.2. DNA Isolation
4.3. Genotyping
- 2 μL of genomic DNA;
- 5 μL of PCR bubble (TaKaRa, Kyoto, Japan);
- 4 μL dNTPs (10 mM)(TaKaRa, Kyoto, Japan);
- 1 U Taq polymerase (TaKaRa, Kyoto, Japan);
- 0.5 μL of appropriately selected primers (10 mM) (Polgen, Łódź, Poland);
- H2O (UltraClean PCR Water, MO BIO Laboratories, Carlsbad, CA, USA).
4.4. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
4.5. Methods of Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Megyesfalvi, Z.; Gay, C.M.; Popper, H.; Pirker, R.; Ostoros, G.; Heeke, S.; Lang, C.; Hoetzenecker, K.; Schwendenwein, A.; Boettiger, K.; et al. Clinical insights into small cell lung cancer: Tumor heterogeneity, diagnosis, therapy, and future directions. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 620–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azar, I.; Austin, A.; Saha, B.K.; Kim, S.; Jang, H.; Al Sbihi, A.; Alkassis, S.; Yazpandanah, O.; Chi, J.; Dhillon, V.; et al. The Role of Surgery in Stage I Small Cell Lung Cancer: A National VA Database Analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 24, e179–e186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xu, S.; Pan, H.; Li, S.; He, J. Treatments for combined small cell lung cancer patients. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 1785–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.H.; Siraj, F.; Mehfooz, N.; Sofi, M.A.; Syed, N.A.; Dar, N.A.; Choh, N.A.; Qadri, S.K.; Bhat, G.M. Clinicopathological Profile of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and the Changing Trends in Its Histopathology: Experience from a Tertiary Care Cancer Center in Kashmir, India. Cureus 2023, 15, e34120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatabe, Y.; Dacic, S.; Borczuk, A.C.; Warth, A.; Russell, P.A.; Lantuejoul, S.; Beasley, M.B.; Thunnissen, E.; Pelosi, G.; Rekhtman, N.; et al. Best Practices Recommendations for Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry in Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 377–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brambilla, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Sage, J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuśnierczyk, P. Genetic differences between smokers and never-smokers with lung cancer. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1063716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hecht, S.S.; Hatsukami, D.K. Smokeless tobacco and cigarette smoking: Chemical mechanisms and cancer prevention. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2022, 22, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, S.M.; Kratzke, R.A.; Kelsey, K.T. Epigenetics of lung cancer. Transl. Res. 2015, 165, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Nath, S.K. Identification of Proteins Interacting with Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms (SNPs) by DNA Pull-Down Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1855, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Laczmanska, I.; Gil, J.; Karpinski, P.; Stembalska, A.; Kozlowska, J.; Busza, H.; Trusewicz, A.; Pesz, K.; Ramsey, D.; Schlade-Bartusiak, K.; et al. Influence of polymorphisms in xenobiotic-metabolizing genes and DNA-repair genes on diepoxybutane-induced SCE frequency. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2006, 47, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, B.J.; Willcox, B.J.; Donlon, T.A. Genetic and epigenetic regulation of human aging and longevity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 1718–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadet, J.; Davies, K.J.A. Oxidative DNA damage & repair: An introduction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 107, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, A.P.; Silva, S.N.; De Lima, J.P.; Reichert, A.; Lima, F.; Júnior, E.; Rueff, J. DNA repair genes polymorphisms and genetic susceptibility to Philadelphia-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms in a Portuguese population: The role of base excision repair genes polymorphisms. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 4641–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duell, E.J.; Wiencke, J.K.; Cheng, T.J.; Varkonyi, A.; Zuo, Z.F.; Ashok, T.D.; Mark, E.J.; Wain, J.C.; Christiani, D.C.; Kelsey, K.T. Polymorphisms in the DNA repair genes XRCC1 and ERCC2 and biomarkers of DNA damage in human blood mononuclear cells. Carcinogenesis 2000, 21, 965–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyohara, C.; Otsu, A.; Shirakawa, T.; Fukuda, S.; Hopkin, J.M. Genetic polymorphisms and lung cancer susceptibility: A review. Lung Cancer 2002, 37, 241–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minina, V.; Timofeeva, A.; Torgunakova, A.; Soboleva, O.; Bakanova, M.; Savchenko, Y.; Voronina, E.; Glushkov, A.; Prosekov, A.; Fucic, A. Polymorphisms in DNA Repair and Xenobiotic Biotransformation Enzyme Genes and Lung Cancer Risk in Coal Mine Workers. Life 2022, 12, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, H.; Gu, D.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Y.; Chen, S.; Tang, M.; Zhang, B.; Chen, H. Genetic polymorphisms and lung cancer risk: Evidence from meta-analyses and genome-wide association studies. Lung Cancer 2017, 113, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Xu, A.; Xia, W.; Li, P.; Zhang, B.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, S.; Wang, R. Association Between NAT2 Polymorphism and Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 567762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, R.E. XRCC1—Strategies for coordinating and assembling a versatile DNA damage response. DNA Repair. 2020, 93, 102917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldecott, K.W. XRCC1 protein; Form and function. DNA Repair. 2019, 81, 102664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.H.; West, M.G. XRCC1 keeps DNA from getting stranded. Mutat. Res. 2000, 459, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velmurugan, S.; Ganesan, K.; Rajendran, R.; Kumar Subbaraj, G. The X-ray repair cross-completing gene 1 (XRCC1) polymorphisms and lung cancer incidence—A confirmatory umbrella review of observational evidence. Eur. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2025, 23, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, A.; Anand, A.; Singh, A.; Roy, P.; Singh, N.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, S.; Baranwal, M. Machine learning-based ensemble approach in prediction of lung cancer predisposition using XRCC1 gene polymorphism. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 7828–7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.Y.; Shih, J.Y.; Chang, G.C.; Cheng, Y.K.; Yang, J.C.; Chen, Y.M.; Yu, C.J. Genetic polymorphism of XRCC1 Arg399Gln is associated with survival in non-small-cell lung cancer patients treated with gemcitabine/platinum. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permatasari, L.I.; Afifah, N.N.; Ishmatullah, M.H.; Intania, R.; Halimah, E.; Barliana, M.I. Genetic Navigation: A Narrative Review of XRCC1 Polymorphism Impact on Platinum-Based Chemotherapy Outcomes in NSCLC Patients. Cancer Manag. Res. 2025, 17, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortada, M.A.; Zidan, H.E.; Abdelsalam, N.A.; Mirvat, A. Eltoukhy Gene XRCC1Arg399Gln polymorphism and its genotype variations: Clinical associations in Egyptian systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Egypt. Rheumatol. Rehabil. 2020, 47, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanazia, M.; Pathana, A.A.K.; Ajajb, S.A.; Khana, W.; Shaik, J.P.; Tassanc, N.A.; Parinea, N.R. DNA Repair Genes XRCC1, XRCC3, XPD, and OGG1 Polymorphisms among the Central Region Population of Saudi Arabia. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cătană, A.; Pop, M.; Hincu, B.D.; Pop, I.V.; Petrişor, F.M.; Porojan, M.D.; Popp, R.A. The XRCC1 Arg194Trp polymorphism is significantly associated with lung adenocarcinoma: A case-control study in an Eastern European Caucasian group. Onco Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 3533–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tang, D.; Xue, K.; Xu, L.; Ma, G.; Hsu, Y.; Cho, S.S. DNA repair gene XRCC1 and XPD polymorphisms and risk of lung cancer in a Chinese population. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 1321–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, V.; Mehndiratta, M.; Mohapatra, D.; Grover, R.K.; Puri, D. XRCC-1 Gene Polymorphism (Arg399Gln) and Susceptibility to Development of Lung Cancer in Cohort of North Indian Population: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, CC17–CC20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.W.; Xu, Y.M.; Qin, S.H.; Chen, G.F.; Lau, A.T.Y. Epigenetic regulation of angiogenesis in lung cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2021, 236, 3194–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marschollek, K.; Brzecka, A.; Pokryszko-Dragan, A. New biochemical, immune and molecular markers in lung cancer: Diagnostic and prognostic opportunities. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 31, 1391–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramazi, S.; Dadzadi, M.; Sahafnejad, Z.; Allahverdi, A. Epigenetic regulation in lung cancer. Med. Commun. 2023, 4, e401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, R.; Tomuleasa, C.; Iuga, C.A.; Gulei, D.; Ciuleanu, T.E. Exploring Therapeutic Avenues in Lung Cancer: The Epigenetic Perspective. Cancers 2023, 15, 5394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didkowska, J.; Barańska, K.; Miklewska, M.J.; Wojciechowska, U. Cancer incidence and mortality in Poland in 2023 Nowotwory. J. Oncol. 2024, 74, 75–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks, L.E.L.; Remon, J.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Garassino, M.C.; Heymach, J.V.; Kerr, K.M.; Tan, D.S.W.; Veronesi, G.; Reck, M. Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2024, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torresan, S.; Costa, J.; Zanchetta, C.; De Marchi, L.; Rizzato, S.; Cortiula, F. Oligometastatic NSCLC: Current Perspectives and Future Challenges. Curr. Oncol. 2025, 32, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Jiang, W.; Inuzuka, H.; Simon, D.K.; Wei, W. Molecular Subtypes and Targeted Therapeutic Strategies in Small Cell Lung Cancer: Advances, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2025, 30, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Soler, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Sankar, K. Emerging Targets in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuorivia, V.; Attili, I.; Corvaja, C.; Asnaghi, R.; Carnevale Schianca, A.; Trillo Aliaga, P.; Del Signore, E.; Spitaleri, G.; Passaro, A.; de Marinis, F. Management of Non-Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) with Driver Gene Alterations: An Evolving Scenario. Curr. Oncol. 2024, 31, 5121–5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lei, S.; Ding, L.; Xu, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L. Global burden and trends of lung cancer incidence and mortality. Chin. Med. J. 2023, 136, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allemani, C.; Matsuda, T.; Di Carlo, V.; Harewood, R.; Matz, M.; Nikšić, M.; Bonaventure, A.; Valkov, M.; Johnson, C.J.; Estève, J.; et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): Analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet 2018, 391, 1023–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voigt, W.; Prosch, H.; Silva, M. Clinical Scores, Biomarkers and IT Tools in Lung Cancer Screening-Can an Integrated Approach Overcome Current Challenges? Cancers 2023, 15, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.; Bai, C.; Baldwin, D.R.; Chen, Y.; Connolly, C.; de Koning, H.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Hu, P.; Kazerooni, E.A.; Lancaster, H.L.; et al. Current and Future Perspectives on Computed Tomography Screening for Lung Cancer: A Roadmap From 2023 to 2027 From the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2024, 19, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tao, L.; Qiu, J.; Xu, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X.; Guan, X.; Cen, X.; Zhao, Y. Tumor biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Dey, M.K.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Biomarkers in Cancer Detection, Diagnosis, and Prognosis. Sensors 2023, 24, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.; Marks, L.; May, G.H.W.; Wilson, J.B. The genetic basis of disease. Essays Biochem. 2018, 62, 643–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Jia, D.; Ma, C.; Wei, D.; Zhang, X. Application of gene polymorphisms to predict the sensitivity of patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer undergoing chemoradiotherapy. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 7382–7387. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, S.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, H.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Yang, G.; Li, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhong, R.; et al. Associations of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons exposure and its interaction with XRCC1 genetic polymorphism with lung cancer: A case-control study. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.J.; Kong, X.M. No association of XRCC1 and CLPTM1L polymorphisms with non-small cell lung cancer in a non-smoking Han Chinese population. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 5171–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, M.P. Lung-Cancer Screening and the NELSON Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 2164–2165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Allehebi, A.; Al-Omair, A.; Mahboub, B.; Koegelenberg, C.F.; Mokhtar, M.; Madkour, A.M.; Al-Asad, K.; Selek, U.; Al-Shamsi, H.O. Recommended approaches for screening and early detection of lung cancer in the Middle East and Africa (MEA) region: A consensus statement. J. Thorac. Dis. 2024, 16, 2142–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Early Lung Cancer Action Program Investigators; Henschke, C.I.; Yankelevitz, D.F.; Libby, D.M.; Pasmantier, M.W.; Smith, J.P.; Miettinen, O.S. Survival of patients with stage I lung cancer detected on CT screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1763–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Lewandowska, A.; Lewandowski, T.; Zych, B.; Papp, K.; Zrubcová, D.; Ejder Apay, S.; Nagorska, M. Risk Factors for the Diagnosis of Lung Cancer in Poland: A Large-Scale, Population-Based Case-Control Study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2022, 23, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thun, M.J.; Carter, B.D.; Feskanich, D.; Freedman, N.D.; Prentice, R.; Lopez, A.D.; Hartge, P.; Gapstur, S.M. 50-year trends in smoking-related mortality in the United States. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 351–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Raptova, R.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Reactive oxygen species, toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: Chronic diseases and aging. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 2499–2574. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, Y.; Boiti, A.; Vallone, D.; Foulkes, N.S. Reactive Oxygen Species Signaling and Oxidative Stress: Transcriptional Regulation and Evolution. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shambhwani, D.; Pandey, S.; Singh, J.; Lalhlenmawia, H.; Kumarasamy, M.; Singh, S.K.; Chellappan, D.K.; Gupta, G.; Prasher, P.; et al. Advances in Lung Cancer Treatment Using Nanomedicines. ACS Omega 2022, 8, 10–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Zheng, C.C.; Huang, Y.N.; He, M.L.; Xu, W.W.; Li, B. Molecular mechanisms of chemo- and radiotherapy resistance and the potential implications for cancer treatment. Med. Commun. 2021, 2, 315–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Yuan, H.; Luo, Z. Genetic Polymorphisms and Platinum-Based Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicities in Patients with Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rina, A.; Maffeo, D.; Minnai, F.; Esposito, M.; Palmieri, M.; Serio, V.B.; Rosati, D.; Mari, F.; Frullanti, E.; Colombo, F. The Genetic Analysis and Clinical Therapy in Lung Cancer: Current Advances and Future Directions. Cancers 2024, 16, 2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Shao, F.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, Y.D. Updated assessment of the association of the XRCC1 Arg399Gln polymorphism with lung cancer risk in the Chinese population. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natukula, K.; Jamil, K.; Pingali, U.R.; Attili, V.S.; Madireddy, U.R. The codon 399 Arg/Gln XRCC1 polymorphism is associated with lung cancer in Indians. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 5275–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butkiewicz, D.; Rusin, M.; Sikora, B.; Lach, A.; Chorąży, M. An association between DNA repair gene polymorphisms and survival in patients with resected non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 5231–5241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesworo, B.; Budiarto, A.; Hidayat, A.A.; Pardamean, B. Cancer Risk Score Prediction Based on a Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Network. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2022, 28, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, S.E. Biochemistry of nicotine metabolism and its relevance to lung cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, U.; Nexø, B.A.; Wallin, H.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A.; Raaschou-Nielsen, O. No Association Between Base Excision Repair Gene Polymorphisms and Risk of Lung Cancer. Biochem. Genet. 2004, 42, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, X.; Gao, M.; Li, Y.; Song, B.; Niu, W. The relationship between XRCC1 and XRCC3 gene polymorphisms and lung cancer risk in northeastern Chinese. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikala, M.; Burzyńska, M.; Maniecka-Bryła, I. Changes in mortality and years of life lost due to lung cancer in Poland, 2000–2016. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosleh, B.; Sarova, P.; Zehetmayer, S.; Oberndorfer, F.; Widder, J.; Prosch, H.; Idzko, M.; Aigner, C.; Hoda, M.A.; Gompelmann, D. Sex-based differences in lung cancer susceptibility and molecular genetics in the 2020s. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alyafeai, E.; Qaed, E.; Al-Mashriqi, H.S.; Almaamari, A.; Almansory, A.H.; Futini, F.A.; Sultan, M.; Tang, Z. Molecular dynamics of DNA repair and carcinogen interaction: Implications for cancer initiation, progression, and therapeutic strategies. Mutat. Res. 2024, 829, 111883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Study Group (n = 118) | Control Group (n = 60) | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median | 25–75% | Median | 25–75% | |||
| Age | 66.5 | 62–70 | 60.5 | 41.5–69 | 0.0012 | |
| Category | Number | % | Number | % | ||
| Sex | woman | 46 | 38.98% | 32 | 53.33% | 0.0681 |
| man | 72 | 61.02% | 28 | 47.67% | ||
| Smoking | no | 11 | 9.02% | 19 | 33.93% | <0.0001 |
| yes | 71 | 58.20% | 37 | 66.07% | ||
| long quit | 40 | 32.79% | 0 | 0.00% | ||
| Feature | Number | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| side | left | 58 | 49.15 |
| right | 60 | 50.85 | |
| type | glandular | 64 | 54.24 |
| squamous cell | 44 | 37.29 | |
| mixed | 6 | 5.08 | |
| large cell | 4 | 3.39 | |
| treatment | upper lobectomy | 59 | 50.00 |
| lower lobectomy | 33 | 27.97 | |
| wedge resection | 6 | 5.08 | |
| middle lobectomy | 5 | 4.24 | |
| segmentectomy | 6 | 5.08 | |
| pneumonectomy | 6 | 5.08 | |
| lower bilobectomy | 3 | 2.54 | |
| TNM | I | 65 | 55.08 |
| II | 42 | 35.59 | |
| III | 11 | 9.32 | |
| metastases to nodes | yes | 24 | 21.05 |
| no | 90 | 76.27 | |
| grading | G1 | 4 | 3.57 |
| G2 | 95 | 84.82 | |
| G3 | 13 | 11.61 |
| Patients | Control | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype | N | % | N | % | p |
| Arg/Arg | 19 | 16.10% | 4 | 6.67% | 0.0182 |
| Arg/Gln | 32 | 27.12% | 28 | 46.67% | >0.05 |
| Gln/Gln | 67 | 58.78% | 28 | 46.67% | >0.05 |
| Adenocarcinoma |
Cancer Squamous Cell |
Cancer Glandular Squamous |
Cancer Large Cell | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arg/Arg | 12 | 6 | 1 | 0 |
| % | 63.16% | 31.58% | 5.26% | 0.00% |
| Arg/Gln | 19 | 12 | 0 | 1 |
| % | 59.38% | 37.50% | 0.00% | 3.13% |
| Gln/Gln | 33 | 26 | 5 | 3 |
| % | 49.25% | 38.81% | 7.46% | 4.48% |
| all | 64 | 44 | 6 | 4 |
| Tumor Stage I | Tumor Stage II | Tumor Stage III | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arg/Arg | 11 | 6 | 2 |
| % | 16.92% | 14.29% | 18.18% |
| Arg/Gln | 17 | 12 | 3 |
| % | 26.15% | 28.57% | 27.27% |
| Gln/Gln | 37 | 24 | 6 |
| % | 56.92% | 57.14% | 54.55% |
|
Tumor Grade G1 |
Tumor Grade G2 |
Tumor Grade G1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arg/Arg | 1 | 15 | 3 |
| % | 25.00% | 15.79% | 15.79% |
| Gln/Gln | 3 | 54 | 10 |
| % | 75.00% | 56.84% | 52.63% |
| Arg/Gln | 0 | 26 | 6 |
| % | 0.00% | 27.37% | 31.58% |
|
15 Pack/Year N = 17 |
15–30 Pack/Year N = 36 |
>30 Pack/Year N = 56 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arg/Arg | 5 | 9 | 18 |
| % | 29.41% | 25.00% | 32.14% |
| Arg/Gln | 7 | 12 | 16 |
| % | 41.17% | 33.33% | 28.57% |
| Gln/Gln | 5 | 15 | 22 |
| % | 29.41% | 41.67% | 39.28% |
| Unit/Level | Odds Ratio | 95%CI | p | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| age | 1 year | 1.06 | 1.03 | 1.10 | 0.0003 |
| sex | men | 1.60 | 0.77 | 3.34 | 0.2018 |
| Arg399Gln XRCC1 | allele Arg | 0.48 | 0.27 | 0.85 | 0.0114 |
| nicotine addiction | current or thrown | 3.803 | 1.42 | 10.19 | 0.0079 |
| Gene | XRCC1 |
|---|---|
| Polymorphism | Arg399Gln |
| Forward (5′→3′) | CAAGTACAGCCAGGTCCTAG |
| Reverse (5′→3′) | CCTTCCCTCATCTGGAGTAC |
| Thermal conditions of amplification | 1. 95 °C—5 min 2. 95 °C—30 s 3. 58 °C—30 s 4. 72 °C—30 s 5. 2 → 3 →4 × 35 cycles 6. 72 °C—3 min |
| Product Length (bp) | 248 |
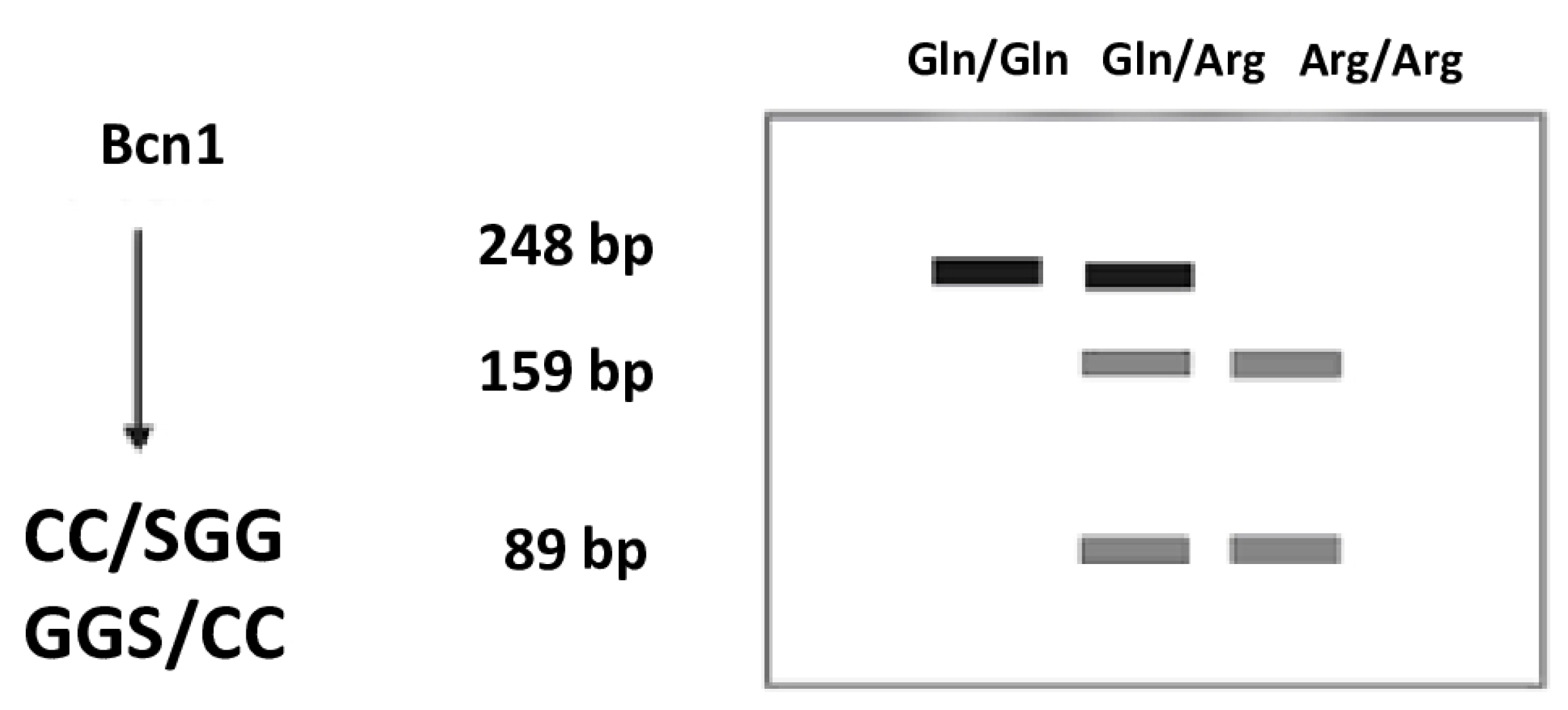
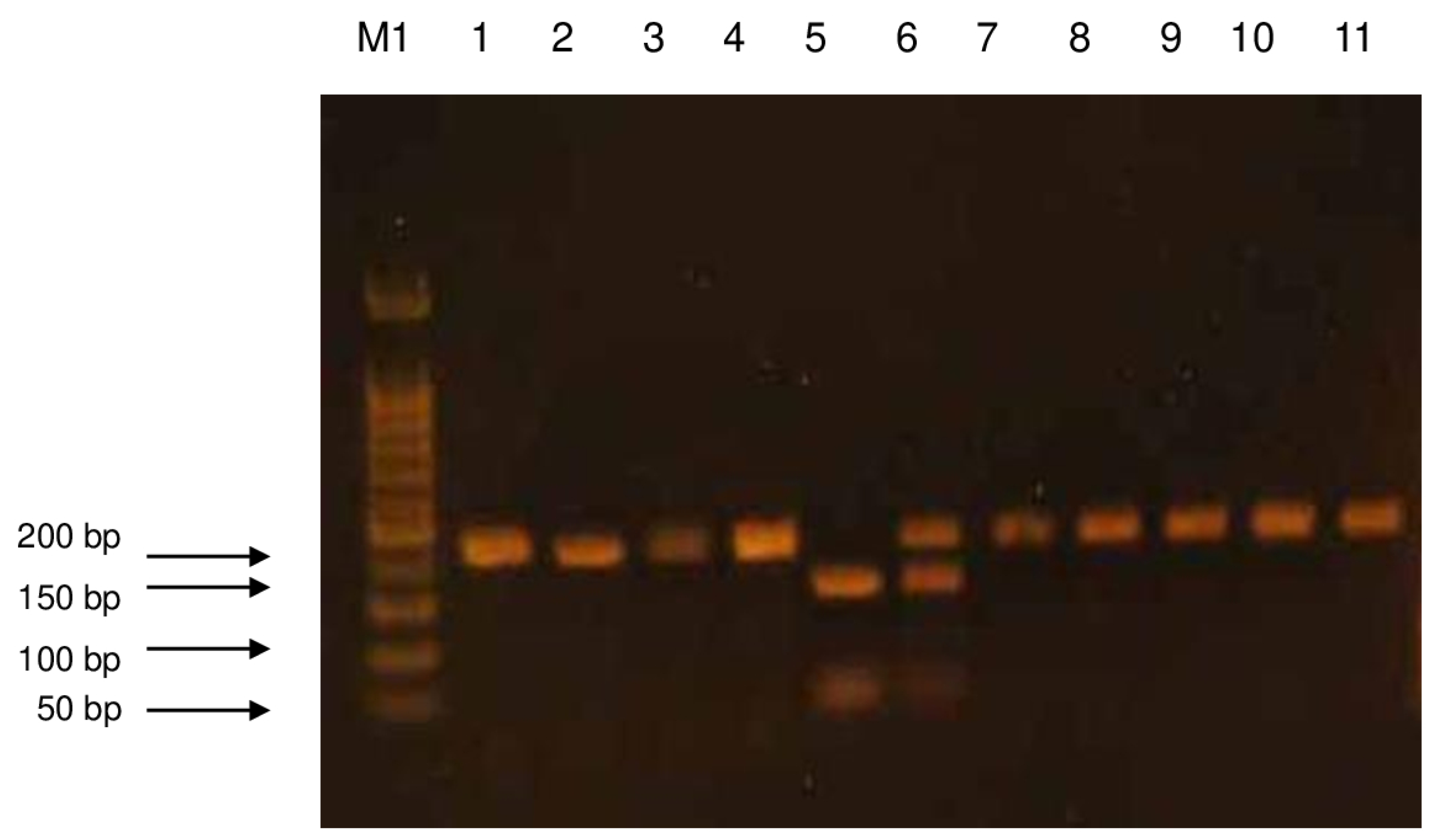
| Gene | Polymorphism | Enzyme | Fragments After Enzyme Digestion (bp) | Variant Recognized by the Enzyme |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XRCC1 | Arg399Gln | BcnI | 159, 89 | Arg |
| 248 | Gln | |||
| 248, 159, 89 | Arg/Gln |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smolarz, B.; Cieślik-Wolski, B.; Kozak, J.; Łukasiewicz, H.; Samulak, D.; Trzmielak, D.; Romanowicz, H.; Makowska, M. The Role of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms at the Arg399Gln Locus of the XRCC1 Gene in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136540
Smolarz B, Cieślik-Wolski B, Kozak J, Łukasiewicz H, Samulak D, Trzmielak D, Romanowicz H, Makowska M. The Role of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms at the Arg399Gln Locus of the XRCC1 Gene in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136540
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmolarz, Beata, Bartosz Cieślik-Wolski, Józef Kozak, Honorata Łukasiewicz, Dariusz Samulak, Dariusz Trzmielak, Hanna Romanowicz, and Marianna Makowska. 2025. "The Role of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms at the Arg399Gln Locus of the XRCC1 Gene in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136540
APA StyleSmolarz, B., Cieślik-Wolski, B., Kozak, J., Łukasiewicz, H., Samulak, D., Trzmielak, D., Romanowicz, H., & Makowska, M. (2025). The Role of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms at the Arg399Gln Locus of the XRCC1 Gene in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136540






