bFGF-Mediated Inhibition of Astrocytes’ Optogenetic Activation Impairs Neuronal Repair in Female Rats After Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
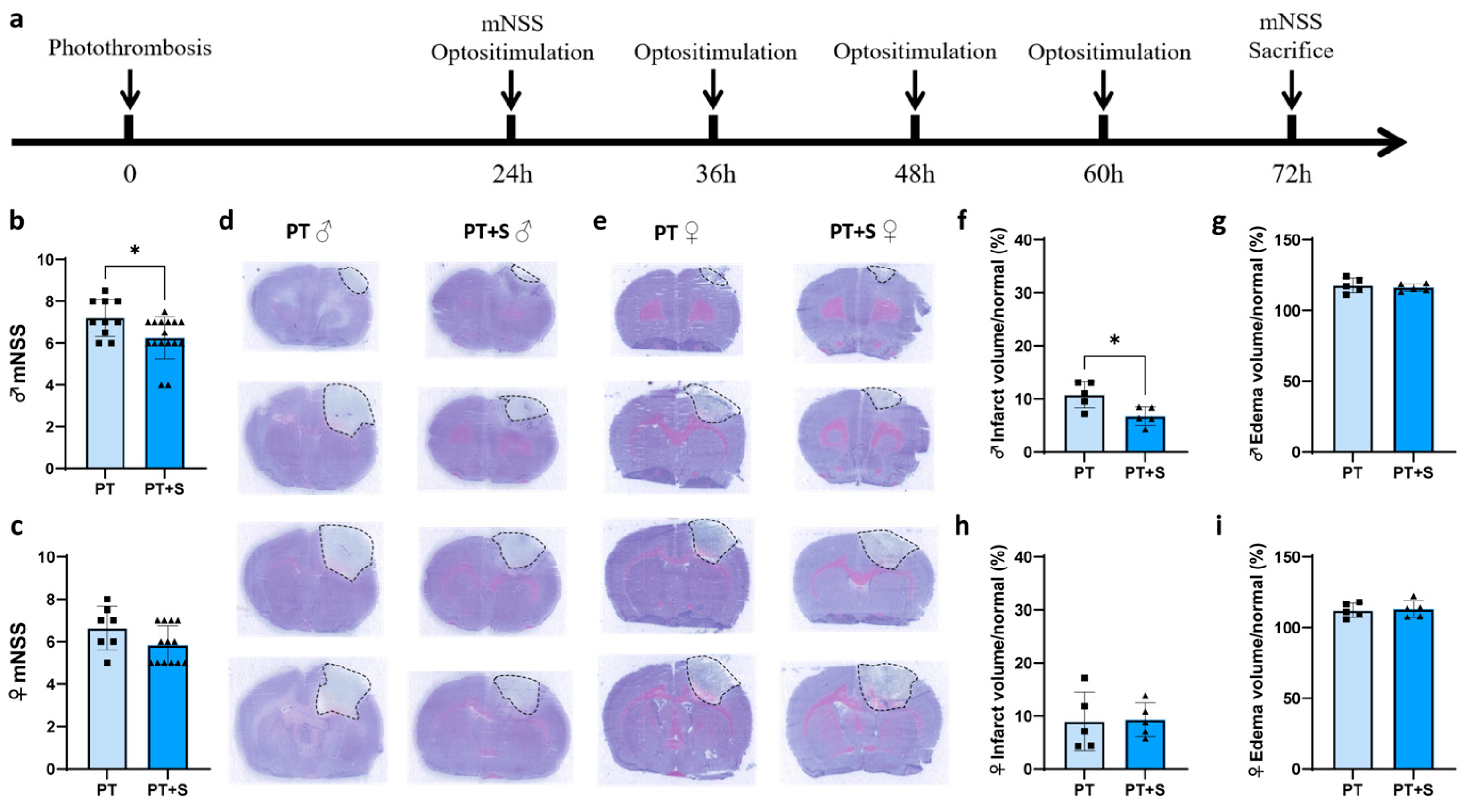
2.1. Astrocytic Optogenetic Stimulation Has No Effect on Neurobehavioral Outcomes in Female Rats During Acute Phase of Stroke
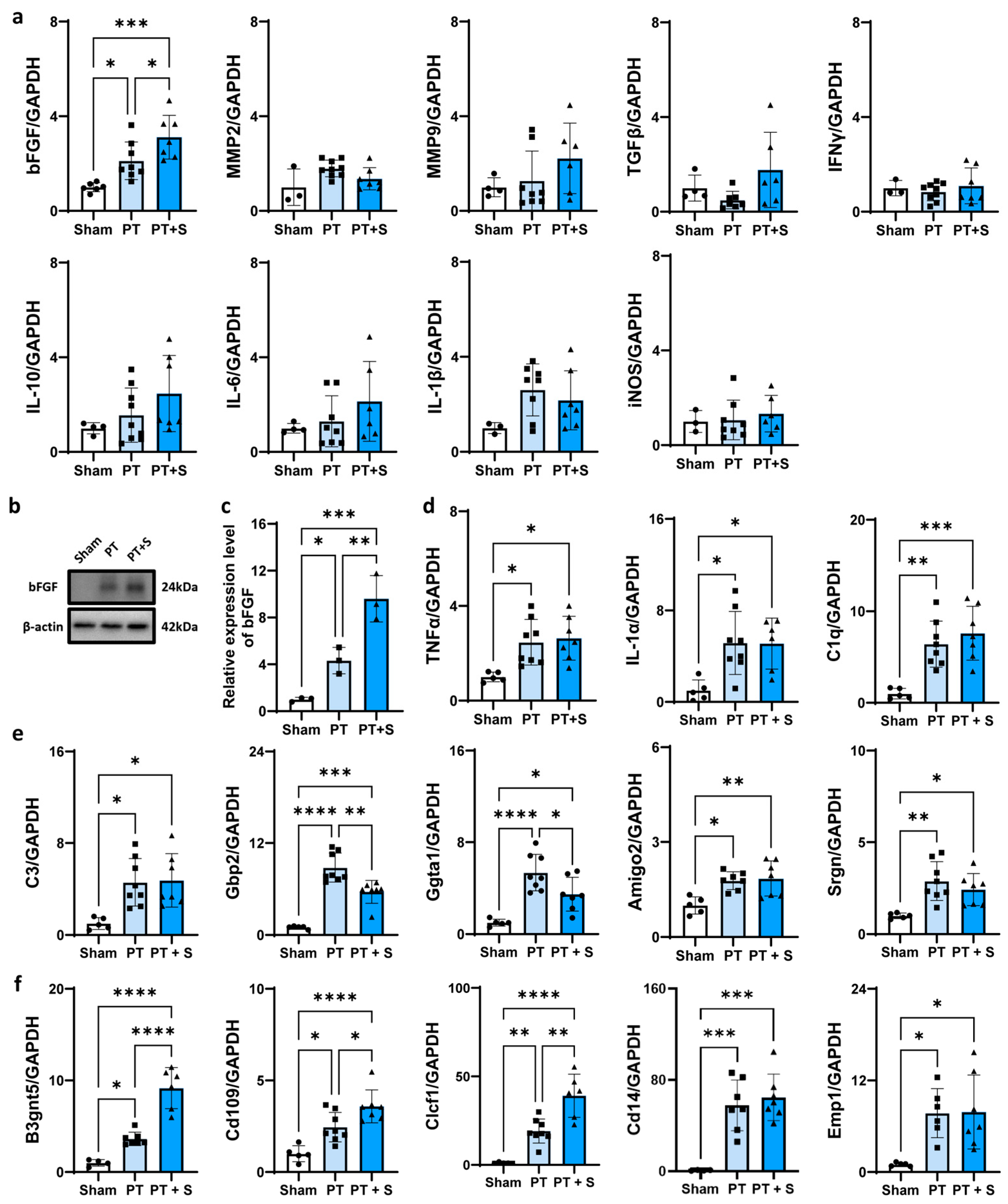
2.2. bFGF Expression Upregulated in Female Photothrombotic Rats After Astrocytic Photogenetic Stimulation
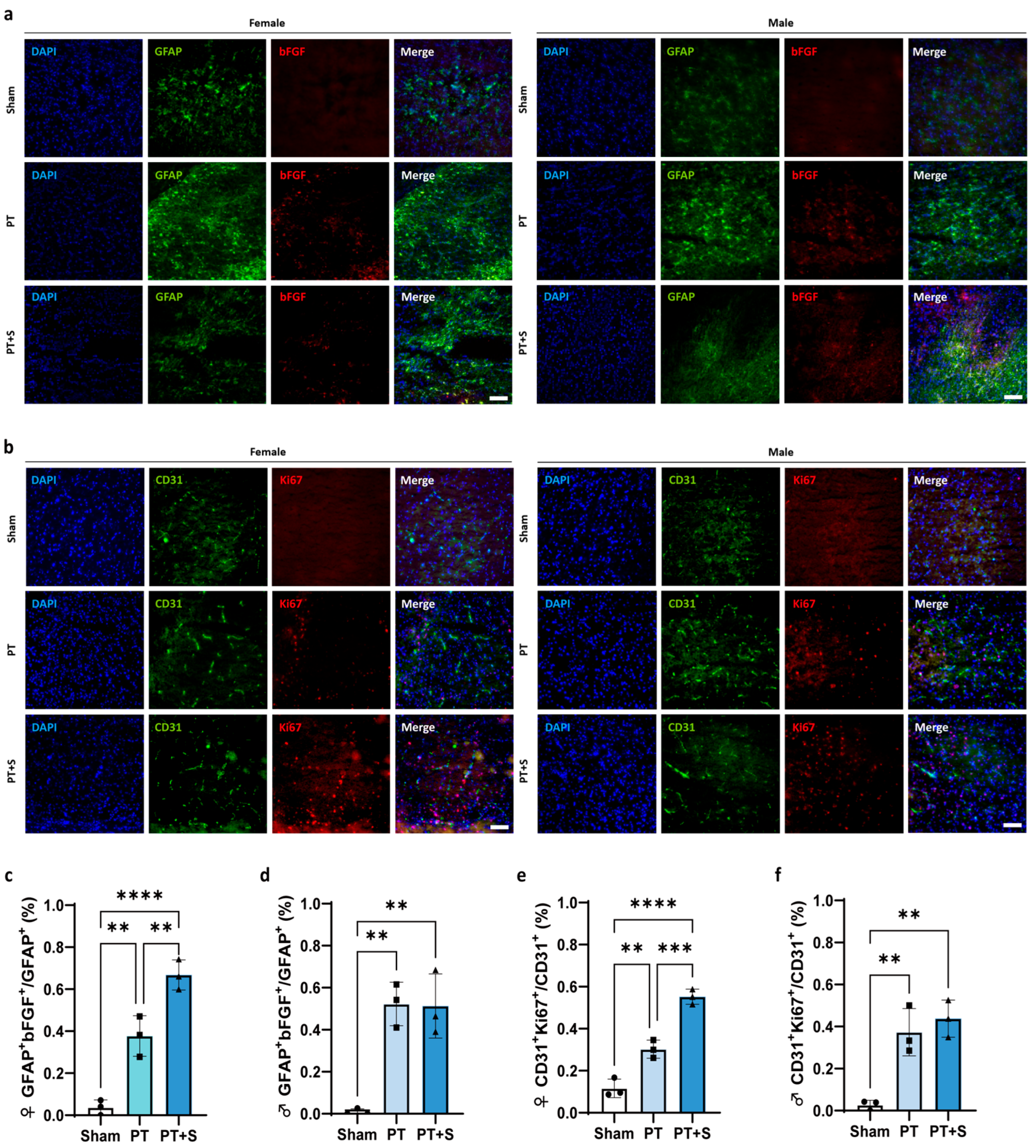
2.3. Upregulation of bFGF Promotes Endothelial Cell Proliferation in Female Photothrombotic Rats
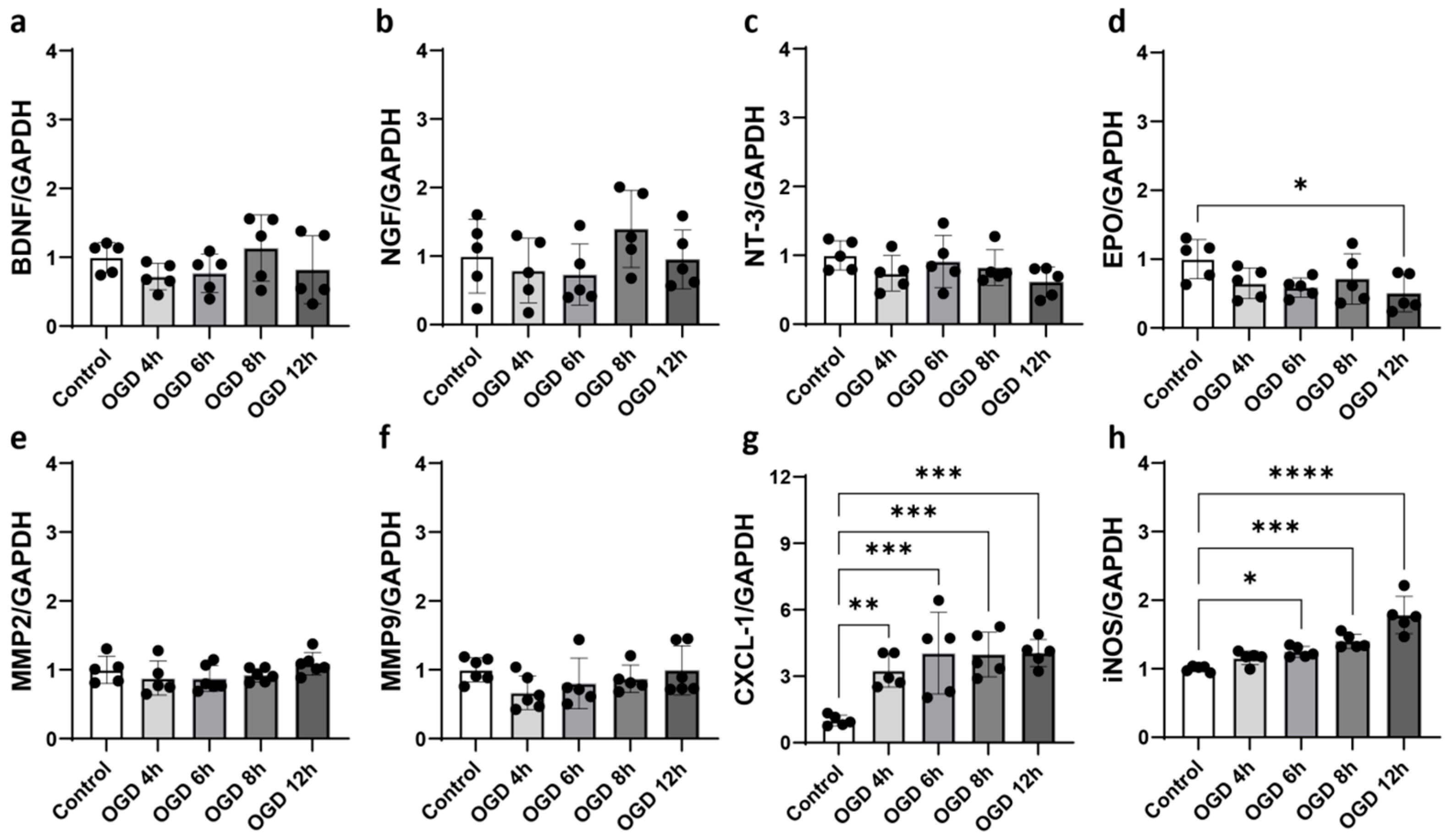
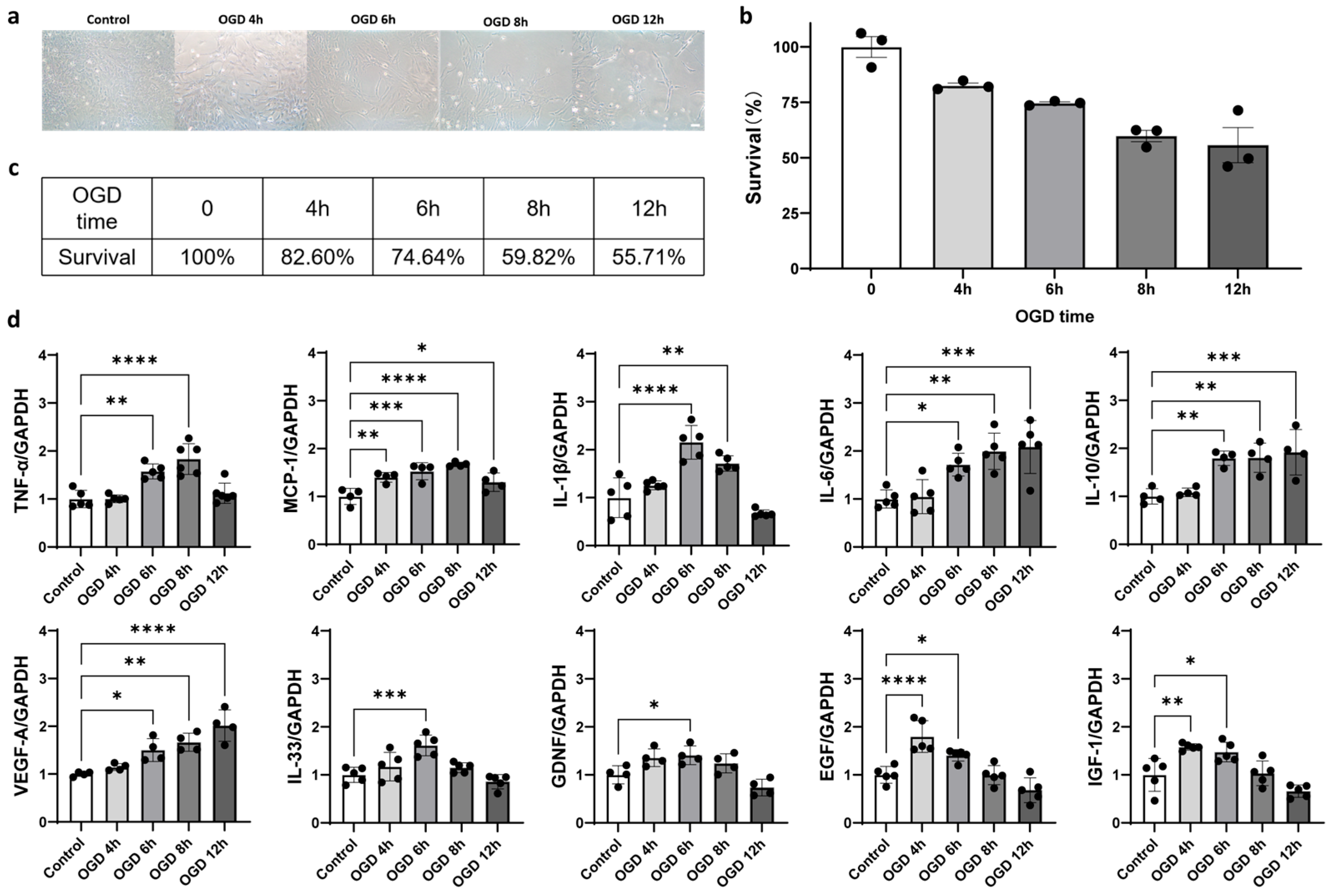
2.4. Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation (OGD) Induced Astrocyte Activation In Vitro
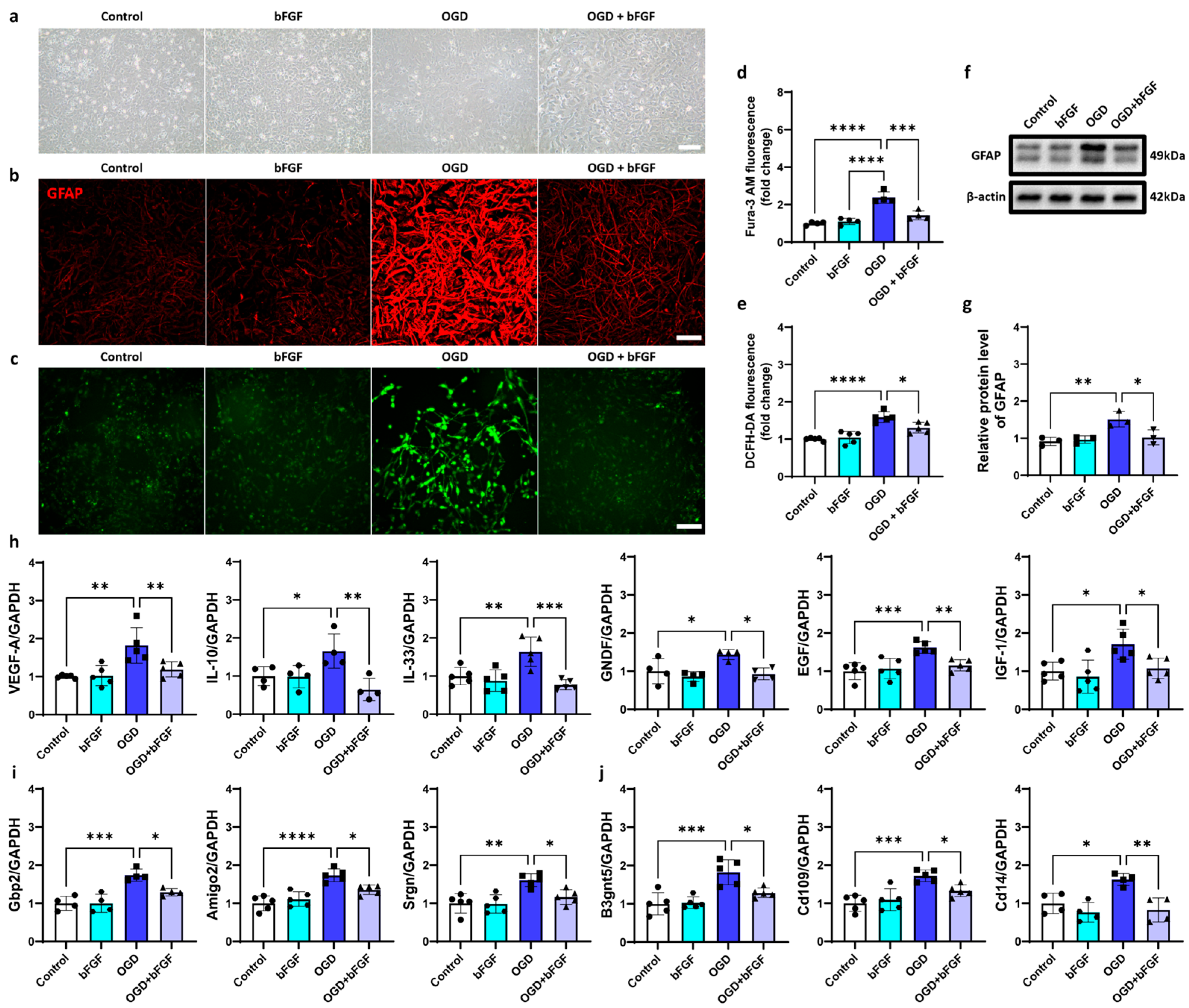
2.5. bFGF Inhibits Astrocyte Activation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Experimental Design
4.2. Reagents
4.3. Photothrombotic (PT) Ischemic Model
4.4. Laser Stimulation
4.5. Neurobehavioral Function Examination
4.6. Cell Culture
4.7. Oxygen–Glucose Deprivation and Reoxygenation Treatment in Cell Model
4.8. Brain Infarct and Edema Volume Measurements
4.9. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assessment
4.10. Western Blot Analysis Determination
4.11. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.12. Reactive Oxygen Species Production Assay
4.13. Intracellular Calcium Measurement
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Amigo2 | adhesion molecule with Ig-like domain 2 |
| B3gnt5 | β-1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase 5 |
| BBB | blood–brain barrier |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| bFGF | basic fibroblast growth factor |
| C1q | complement component 1q |
| C3 | complement component 3 |
| CCK-8 | cell counting kit-8 |
| Cd14 | cluster of differentiation 14 |
| Cd31 | cluster of differentiation 31 |
| Cd109 | cluster of differentiation 109 |
| ChR2 | channelrhodopsin 2 |
| Clcf1 | cardiotrophin-like cytokine factor 1 |
| CXCL | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand |
| EGF | epidermal growth factor |
| Emp1 | epithelial membrane protein 1 |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| EYFP | enhanced yellow fluorescent protein |
| Gbp2 | guanine-binding protein 2 |
| GDNF | glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor |
| GFAP | glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| Ggta1 | α-1,3-galactosyltransferase |
| IFNγ | interferon γ |
| IGF-1 | insulin-like growth factor-1 |
| IL-1α | interleukin-1α |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| IL-10 | interleukin-10 |
| IL-33 | interleukin-33 |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| MCP | monocyte chemotactic protein |
| MMP2 | matrix metalloproteinase 2 |
| MMP9 | matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| mNSS | modified neurologic severity score |
| NGF | nerve growth factor |
| NT-3 | neurotrophin-3 |
| OGD | oxygen–glucose deprivation |
| PT | photothrombotic |
| PT + S | photothrombotic stroke group with laser stimulation |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| Srgn | serglycin |
| TGFβ | transforming growth factor-β |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
Appendix A
| Figure | Group and Number |
|---|---|
| Figure 1b | PT (N = 10); PT + S (N = 16) |
| Figure 1c | PT (N = 7); PT + S (N = 13) |
| Figure 1f,h | N = 5 for each group |
| Figure 1g,i | N = 5 for each group |
| Figure 2a | Sham (N = 3~6); PT (N = 6~9); PT + S (N = 6~7) |
| Figure 2c | N = 3 for each group |
| Figure 2d | Sham (N = 5); PT (N = 8); PT + S (N = 6~7) |
| Figure 2e | Sham (N = 5); PT (N = 7~8); PT + S (N = 7) |
| Figure 2f | Sham (N = 4~5); PT (N = 6~8); PT + S (N = 6~7) |
| Figure 3c | N = 3 for each group |
| Figure 3d | N = 3 for each group |
| Figure 3e | N = 3 for each group |
| Figure 3f | N = 3 for each group |
| Figure 4b | N = 3 for each group |
| Figure 4d | N = 4~5 for each group |
| Figure 5d | N = 4 for each group |
| Figure 5e | N = 5 for each group |
| Figure 5g | N = 3 for each group |
| Figure 5h | N = 4~5 for each group |
| Figure 5i | N = 4~5 for each group |
| Figure 5j | N = 4~5 for each group |
| Figure A2a–h | N = 5~6 for each group |
| Figure A3d | N = 4 for each group |
| Figure A33e | N = 4 for each group |
| Figure A3f | N = 5 for each group |


References
- Liu, C.; Guo, Y.; Deng, S.; Zhou, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, T.; Shi, X.; Mamtilahun, M.; Xu, T.; Liu, Z.; et al. Hemorrhagic stroke-induced subtype of inflammatory reactive astrocytes disrupts blood-brain barrier. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2024, 44, 1102–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanmarco, L.M.; Polonio, C.M.; Wheeler, M.A.; Quintana, F.J. Functional immune cell-astrocyte interactions. J. Exp. Med. 2021, 218, e20202715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Shi, X.J.; Qi, L.; Wang, C.; Mamtilahun, M.; Zhang, Z.J.; Chung, W.S.; Yang, G.Y.; Tang, Y.H. Microglia and astrocytes mediate synapse engulfment in a MER tyrosine kinase-dependent manner after traumatic brain injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 1770–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Liu, C.; Deng, S.; Gan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.Y.; Tian, H.; Tang, Y. The roles of microglia and astrocytes in myelin phagocytosis in the central nervous system. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 325–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, E.; Farina, C. Astrocytes: Key Regulators of Neuroinflammation. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Yuanshao, L.; Wensi, H.; Yulei, Z.; Xiaoli, C.; Brian, W.; Wanli, Z.; Zhengyi, C.; Jie, X.; Wenhui, Z.; et al. Serum IL-33 Is a Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis. 2016, 7, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocyte barriers to neurotoxic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Xu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, F.; Xu, X.; Wen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Li, J.; Li, R.; et al. Lipocalin-2 may produce damaging effect after cerebral ischemia by inducing astrocytes classical activation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Estrada, E.Y.; Thompson, J.F.; Liu, W.; Rosenberg, G.A. Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2007, 27, 697–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liddelow, S.A.; Guttenplan, K.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Bennett, F.C.; Bohlen, C.J.; Schirmer, L.; Bennett, M.L.; Münch, A.E.; Chung, W.S.; Peterson, T.C.; et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature 2017, 541, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyden, E.S.; Zhang, F.; Bamberg, E.; Nagel, G.; Deisseroth, K. Millisecond-timescale, genetically targeted optical control of neural activity. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Lu, Y.; Lin, X.; Jiang, L.; Tang, Y.; Tang, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.Y. Optical inhibition of striatal neurons promotes focal neurogenesis and neurobehavioral recovery in mice after middle cerebral artery occlusion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Li, W.; Mamtilahun, M.; Song, Y.; Ma, Y.; Qu, M.; Lu, Y.; He, X.; Zheng, J.; Fu, Z.; et al. Optogenetic Inhibition of Striatal GABAergic Neuronal Activity Improves Outcomes After Ischemic Brain Injury. Stroke 2017, 48, 3375–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, K.; Suzuki, H.; Higa, M.; Tabata, K.; Sawada, M. Glutamate release from astrocyte cell-line GL261 via alterations in the intracellular ion environment. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rost, B.R.; Schneider-Warme, F.; Schmitz, D.; Hegemann, P. Optogenetic Tools for Subcellular Applications in Neuroscience. Neuron 2017, 96, 572–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamsky, A.; Kol, A.; Kreisel, T.; Doron, A.; Ozeri-Engelhard, N.; Melcer, T.; Refaeli, R.; Horn, H.; Regev, L.; Groysman, M.; et al. Astrocytic Activation Generates De Novo Neuronal Potentiation and Memory Enhancement. Cell 2018, 174, 59–71.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poskanzer, K.E.; Yuste, R. Astrocytes regulate cortical state switching in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2675–E2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Liu, Y.; Tu, J.; Wan, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, B.; Chen, S.; Zhou, J.; Mu, Y.; Wang, L. Activated astrocytes enhance the dopaminergic differentiation of stem cells and promote brain repair through bFGF. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almad, A.; Maragakis, N.J. A stocked toolbox for understanding the role of astrocytes in disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiisen, T.M.; Lehre, K.P.; Danbolt, N.C.; Ottersen, O.P. The perivascular astroglial sheath provides a complete covering of the brain microvessels: An electron microscopic 3D reconstruction. Glia 2010, 58, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Ye, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Wu, S.; Shen, H.; Suo, Q.; Li, W.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Tropism-shifted AAV-PHP.eB-mediated bFGF gene therapy promotes varied neurorestoration after ischemic stroke in mice. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 21, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassi, R.; Anelli, V.; Giussani, P.; Tettamanti, G.; Viani, P.; Riboni, L. Sphingosine-1-phosphate is released by cerebellar astrocytes in response to bFGF and induces astrocyte proliferation through Gi-protein-coupled receptors. Glia 2006, 53, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornitz, D.M.; Itoh, N. The Fibroblast Growth Factor signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2015, 4, 215–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechan, P.A.; Chowdhury, K.; Seifert, W. Free radicals induce gene expression of NGF and bFGF in rat astrocyte culture. Neuroreport 1992, 3, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cai, P.; Li, R.; Chen, D.; Wei, X.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Xiao, J.; et al. The Role of bFGF in the Excessive Activation of Astrocytes Is Related to the Inhibition of TLR4/NFκB Signals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 17, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamata, T.; Dietrich, W.D.; Schallert, T.; Gotts, J.E.; Cocke, R.R.; Benowitz, L.I.; Finklestein, S.P. Intracisternal basic fibroblast growth factor enhances functional recovery and up-regulates the expression of a molecular marker of neuronal sprouting following focal cerebral infarction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 8179–8184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Leak, R.K.; Yang, G.Y. Perspective for stroke and brain injury research: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2015, 21, 301–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautzky-Willer, A. [Gender medicine. Sex- and gender-specific aspects of clinical medicine]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz 2014, 57, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Li, S.; Zhu, S.; Yi, Q.; Liu, W.; Wu, Y.; Wu, F.; Ji, Y.; Song, P.; Rahimi, K. Lifetime Cumulative Effect of Reproductive Factors on Stroke and Its Subtypes in Postmenopausal Chinese Women: A Prospective Cohort Study. Neurology 2023, 100, e1574–e1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Azbukina, N.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. Sex-Mediated Differences in LPS Induced Alterations of TNFα, IL-10 Expression, and Prostaglandin Synthesis in Primary Astrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Q.; Deng, L.; Chen, T.; Wu, S.; Qi, L.; Liu, Z.; He, T.; Tian, H.L.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; et al. Optogenetic Activation of Astrocytes Reduces Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption via IL-10 in Stroke. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 1870–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Li, Z.; Huang, M.; Huang, L.; Huang, Y.; Lv, S.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Z.; Ke, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Gli1-mediated tumor cell-derived bFGF promotes tumor angiogenesis and pericyte coverage in non-small cell lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.Y.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, J.F.; Chen, P.; Li, W. Changes of expressions of VEGF, bFGF, and angiogenesis, and effect of benazepril, bFGF on angiogenesis in acute myocardial infarction model of the rabbits. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Przybylski, M. A review of the current research on the role of bFGF and VEGF in angiogenesis. J. Wound Care 2009, 18, 516–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Sareddy, G.R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, F.L.; Pratap, U.P.; Tekmal, R.R.; Vadlamudi, R.K.; Brann, D.W. Neuron-Derived Estrogen Is Critical for Astrocyte Activation and Neuroprotection of the Ischemic Brain. J. Neurosci. 2020, 40, 7355–7374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Halim, N.Y.; Mohamed, G.H.; Elhusseiny, A.; Abdelgwad, M.; Imam, R.A. IGF 1, BDNF, and NGF mediate the neuro-modulatory role of stem cells in acrylamide-induced hippocampal toxic changes in rats. Folia Morphol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Sun, Y.; Yin, Z.; Wang, D.; Shi, K.; Fu, Y.; Cao, X.; Ge, Y. Analysis of FK506-mediated functional recovery and neuroprotection in a rat model of spinal cord injury indicates that EGF is modulated in astrocytes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Yuan, B.; Liu, T.; Dong, Q.; Mei, H.; Yin, H. Neuroprotective effect of astrocyte-derived IL-33 in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, S.S.; Huang, S.J.; Nite, W.; Ren, F.; Yan, J.Q.; Luo, J.G. Interleukin-33 modulates lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammatory response in rat primary astrocytes. Neuroreport 2021, 32, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Suzuki, A.; Guo, Z.; Mizuno, Y.; Urabe, T. Intrinsic and extrinsic erythropoietin enhances neuroprotection against ischemia and reperfusion injury in vitro. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, S.M.; Cristovão, A.C.; Campos, F.L.; Fonseca, C.P.; Baltazar, G. Astrocyte-derived GDNF is a potent inhibitor of microglial activation. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 47, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, J.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, K. The effect of salidroside in promoting endogenous neural regeneration after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion involves notch signaling pathway and neurotrophic factors. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2024, 24, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mederos, S.; Hernández-Vivanco, A.; Ramírez-Franco, J.; Martín-Fernández, M.; Navarrete, M.; Yang, A.; Boyden, E.S.; Perea, G. Melanopsin for precise optogenetic activation of astrocyte-neuron networks. Glia 2019, 67, 915–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charriaut-Marlangue, C.; Besson, V.C.; Baud, O. Sexually Dimorphic Outcomes after Neonatal Stroke and Hypoxia-Ischemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, P.; Machado, S.; Meyer, I.; Amiguet, M.; Eskandari, A.; Michel, P. Ischemic stroke on hormonal contraceptives: Characteristics, mechanisms and outcome. Eur. Stroke J. 2021, 6, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekker, M.S.; Verhoeven, J.I.; Vaartjes, I.; van Nieuwenhuizen, K.M.; Klijn, C.J.M.; de Leeuw, F.E. Stroke incidence in young adults according to age, subtype, sex, and time trends. Neurology 2019, 92, e2444–e2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexrode, K.M.; Madsen, T.E.; Yu, A.Y.X.; Carcel, C.; Lichtman, J.H.; Miller, E.C. The Impact of Sex and Gender on Stroke. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 512–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy-O’Reilly, M.; McCullough, L.D. Sex differences in stroke: The contribution of coagulation. Exp. Neurol. 2014, 259, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Fang, M.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, C.; Han, Y.; Lu, Q.; Du, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. Iron-Deficiency and Estrogen Are Associated with Ischemic Stroke by Up-Regulating Transferrin to Induce Hypercoagulability. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, B.; Sun, H.; Ru, X.; Sun, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Prevalence, Incidence, and Mortality of Stroke in China: Results from a Nationwide Population-Based Survey of 480 687 Adults. Circulation 2017, 135, 759–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Lou, Y.; Hao, Y.; Li, H.; Feng, J.; Liu, S. The Relationship of Astrocytes and Microglia with Different Stages of Ischemic Stroke. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2023, 21, 2465–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, X.C.; Wang, H.F.; Cai, Y.Y.; Yang, D.; Alolga, R.N.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Huang, F.Q. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits astrocyte activation and promotes transfer of astrocytic mitochondria to neurons against ischemic stroke. Redox Biol. 2022, 54, 102363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patabendige, A.; Singh, A.; Jenkins, S.; Sen, J.; Chen, R. Astrocyte Activation in Neurovascular Damage and Repair Following Ischaemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, M.R.; Fuertes, C.J.A.; Dunn, A.K.; Drew, M.R.; Jones, T.A. Reactive astrocytes facilitate vascular repair and remodeling after stroke. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, K. Astrocyte-induced synapse formation and ischemic stroke. J. Neurosci. Res. 2021, 99, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Tan, S.; Lin, Y.; Liao, S.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, Z.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, L.; et al. The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist reduces inflammation and blood-brain barrier breakdown in an astrocyte-dependent manner in experimental stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Lu, J.; Mei, S.; Wu, H.; Sun, Z.; Fang, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, X.; Shi, L.; Xu, W.; et al. Ceria nanoparticles ameliorate white matter injury after intracerebral hemorrhage: Microglia-astrocyte involvement in remyelination. J. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 18, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Zuo, X.; Ju, C.; Song, Z.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, Z. Photobiomodulation Promotes Repair Following Spinal Cord Injury by Regulating the Transformation of A1/A2 Reactive Astrocytes. Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 768262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Li, H.N.; Zhang, S.T.; Yu, Y.L.; Wei, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.Y.; Zeng, X.Y. Red nucleus IL-6 mediates the maintenance of neuropathic pain by inducing the productions of TNF-α and IL-1β through the JAK2/STAT3 and ERK signaling pathways. Neuropathology 2020, 40, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, B.; Wen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Ye, L. IL-33/ST2-mediated inflammation in macrophages is directly abrogated by IL-10 during rheumatoid arthritis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32407–32418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, B.; Wu, W. Biomaterial-Based bFGF Delivery for Nerve Repair. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2023, 2023, 8003821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koketsu, N.; Berlove, D.J.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Kowall, N.W.; Caday, C.G.; Finklestein, S.P. Pretreatment with intraventricular basic fibroblast growth factor decreases infarct size following focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Ann. Neurol. 1994, 35, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lu, J.B.; Ye, Z.R. Permeability of injured blood brain barrier for exogenous bFGF and protection mechanism of bFGF in rat brain ischemia. Neuropathology 2006, 26, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, S.; Qian, X. bFGF, neurotrophins, and the control or cortical neurogenesis. Neuron 1995, 15, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahra, F.T.; Sajib, M.S.; Mikelis, C.M. Role of bFGF in Acquired Resistance upon Anti-VEGF Therapy in Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, M.A.; Arboix, A.; Krupinski, J. Angiogenesis, neurogenesis and neuroplasticity in ischemic stroke. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2010, 6, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupinski, J.; Kaluza, J.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, S.; Wang, J.M. Role of angiogenesis in patients with cerebral ischemic stroke. Stroke 1994, 25, 1794–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, K.; Hassan, S.H.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Pu, H.; Stetler, R.A.; Chen, J.; Yin, K.J. Endothelium-Targeted Deletion of microRNA-15a/16-1 Promotes Poststroke Angiogenesis and Improves Long-Term Neurological Recovery. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1040–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Torbey, M.T. Angiogenesis and Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability in Vascular Remodeling after Stroke. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2020, 18, 1250–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.; Plate, K.H. Angiogenesis after cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 117, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupinski, J.; Stroemer, P.; Slevin, M.; Marti, E.; Kumar, P.; Rubio, F. Three-dimensional structure and survival of newly formed blood vessels after focal cerebral ischemia. Neuroreport 2003, 14, 1171–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, X.; Qin, L.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, Z.; et al. Activation of astrocytes in hippocampus decreases fear memory through adenosine A(1) receptors. Elife 2020, 9, e57155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.Y.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z. Endothelial progenitor cell transplantation attenuates synaptic loss associated with enhancing complement receptor 3-dependent microglial/macrophage phagocytosis in ischemic mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2023, 43, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Haroon, K.; Liu, M.; Hu, X.; Xu, Q.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, G.Y.; Zhang, Z. Monomeric CXCL12-Engineered Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Transplantation for the Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haroon, K.; Ruan, H.; Zheng, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Shi, X.; Tang, Y.; Yang, G.Y.; Zhang, Z. Bio-clickable, small extracellular vesicles-COCKTAIL therapy for ischemic stroke. J. Control. Release 2023, 363, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Bi, X.; Deng, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Suo, Q.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Qian, K.; et al. Hypoxanthine is a metabolic biomarker for inducing GSDME-dependent pyroptosis of endothelial cells during ischemic stroke. Theranostics 2024, 14, 6071–6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name | Forward Primer (5′–3′) | Reverse Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| bFGF | CAACACTTACCGGTCACGGA | CCCCGTTTTGGATCCGAGTT |
| IL-10 | GCTCTTACTGGCTGGAGTGAG | CTCAGCTCTCGGAGCATGTG |
| IL-6 | TCCTACCCCAACTTCCAATGCTC | TTGGATGGTCTTGGTCCTTAGCC |
| IL-1β | CACCTCTCAAGCAGAGCACAG | GGGTTCCATGGTGAAGTCAAC |
| TNFα | AAATGGGCTCCCTCTCATCAGTTC | TCTGCTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGAC |
| TGFβ | CCACCTCCTGAGGGTGCTT | ATGTCGGAGAAAGGCGCG |
| IFNγ | GTCATCGAATCGCACCTGA | GTGCTGGATCTGTGGGTTG |
| iNOS | TTYGATGTGCTGCCTCTGGT | CATTCTGCTTCTGGAAACTATGG |
| MMP2 | CTGATAACCTGGATGCAGTCGT | CCAGCCAGTCCGATTTGA |
| MMP9 | ATGTCACTTTCCCTTCACCT | TTAGAGCCACGACCATACAG |
| VEGF-A | GAGTCTGTGCTCTGGGATTTG | TCCTGCTACCTCTTTCCTCTG |
| IL-33 | CCCTGAGCACATACAACGACC | CACCATCAGCTTCTTCCCATC |
| GDNF | ATTCCTGGCGTTACCTTG | CTGTATTCCGTCTCCTTGG |
| BDNF | CTACGAGACCAAGTGTAATC | TTATGAATCGCCAGCCAAT |
| NGF | GAGCGCATCGCTCTCCTT | GAGCGCATCGCTCTCCTT |
| NT-3 | GGTGAACAAGGTGATGTCCATC | GGCAGGGTGCTCTGGTAATTTTCCT |
| EPO | TCCTTGCTACTGATTCCTCTCTGG | AAGTATCCGCTGTGAGTGTTCG |
| EGF | CTTAGGGATGTGGGGGACTT | TTGGGCTGTTGGTGTTCCTC |
| IGF-1 | CAGTTCGTGTGTGGACCAAG | TCAGCGGAGCACAGTACATC |
| CXCL | TGAGCTGCGCTGTCAGTGCCT | AGAAGCCAGCGTTCACCAGA |
| MCP | GCGCCGGAAAGCTGTAGATG | TTTGCTTGTCCAGGTGGTC |
| IL-1α | TCAAAGATGTCCACCTTCACC | CTGATCTGGGTTGGATGGTC |
| C1q | TTCTGTGACTATGCCTACAACAC | GCCCAGTAGTGAGTTCTTGTC |
| C3 | GCCAGCAGCTCTACAATGTG | GACTGCCACTTTCCCATAGC |
| Amigo2 | GTTCGCCACAACAACATCAC | GTTTCTGCAAGTGGGAGAGC |
| Gbp2 | TAAAGGTCCGAGGCCCAAAC | AACATATGTGGCTGGGCGAA |
| Ggta1 | TCTCAGGATCTGGGAGTTGGA | GAGTTCTATGGAGCTCCCGC |
| Srgn | GTTCAAGGTTATCCTGCTCGGA | AAACAGGATCGGTCATCGGG |
| B3gnt5 | TGCTCCTGGATGAAAGGTCC | ACATGCTTGATCCGTGTGGT |
| Cd14 | TCAGAATCTACCGACCATGAAGC | GGACACTTTCCTCGTCCTGG |
| Cd109 | GTCGCTCACAGGTACCTCAA | CTGTGAAGTTGAGCGTTGGC |
| Clcf1 | GACTCGTGGGGGATGTTAGC | CCCCAGGTAGTTCAGGTAGGT |
| Emp1 | ACCATTGCCAACGTCTGGAT | TGGAACACGAAGACCACGAG |
| GAPDH | GATGGTGAAGGTCGGTGTGA | TGAACTTGCCGTGGGTAGAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, X.; Yao, Y.; Shi, V.; Suo, Q.; Wu, S.; Wang, H.; Mamtilahun, M.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Yang, G.-Y.; et al. bFGF-Mediated Inhibition of Astrocytes’ Optogenetic Activation Impairs Neuronal Repair in Female Rats After Stroke. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136521
Shao X, Yao Y, Shi V, Suo Q, Wu S, Wang H, Mamtilahun M, Li W, Tang Y, Yang G-Y, et al. bFGF-Mediated Inhibition of Astrocytes’ Optogenetic Activation Impairs Neuronal Repair in Female Rats After Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136521
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Xinfa, Yangqianbo Yao, Victoria Shi, Qian Suo, Shengju Wu, Han Wang, Muyassar Mamtilahun, Wanlu Li, Yaohui Tang, Guo-Yuan Yang, and et al. 2025. "bFGF-Mediated Inhibition of Astrocytes’ Optogenetic Activation Impairs Neuronal Repair in Female Rats After Stroke" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136521
APA StyleShao, X., Yao, Y., Shi, V., Suo, Q., Wu, S., Wang, H., Mamtilahun, M., Li, W., Tang, Y., Yang, G.-Y., Xu, Q., & Zhang, Z. (2025). bFGF-Mediated Inhibition of Astrocytes’ Optogenetic Activation Impairs Neuronal Repair in Female Rats After Stroke. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136521





