Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals the Molecular Characteristics, Tumor Microenvironment, and Clinical Significance of Ubiquitination Mechanisms in Lung Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Recognition of Hub UBRs
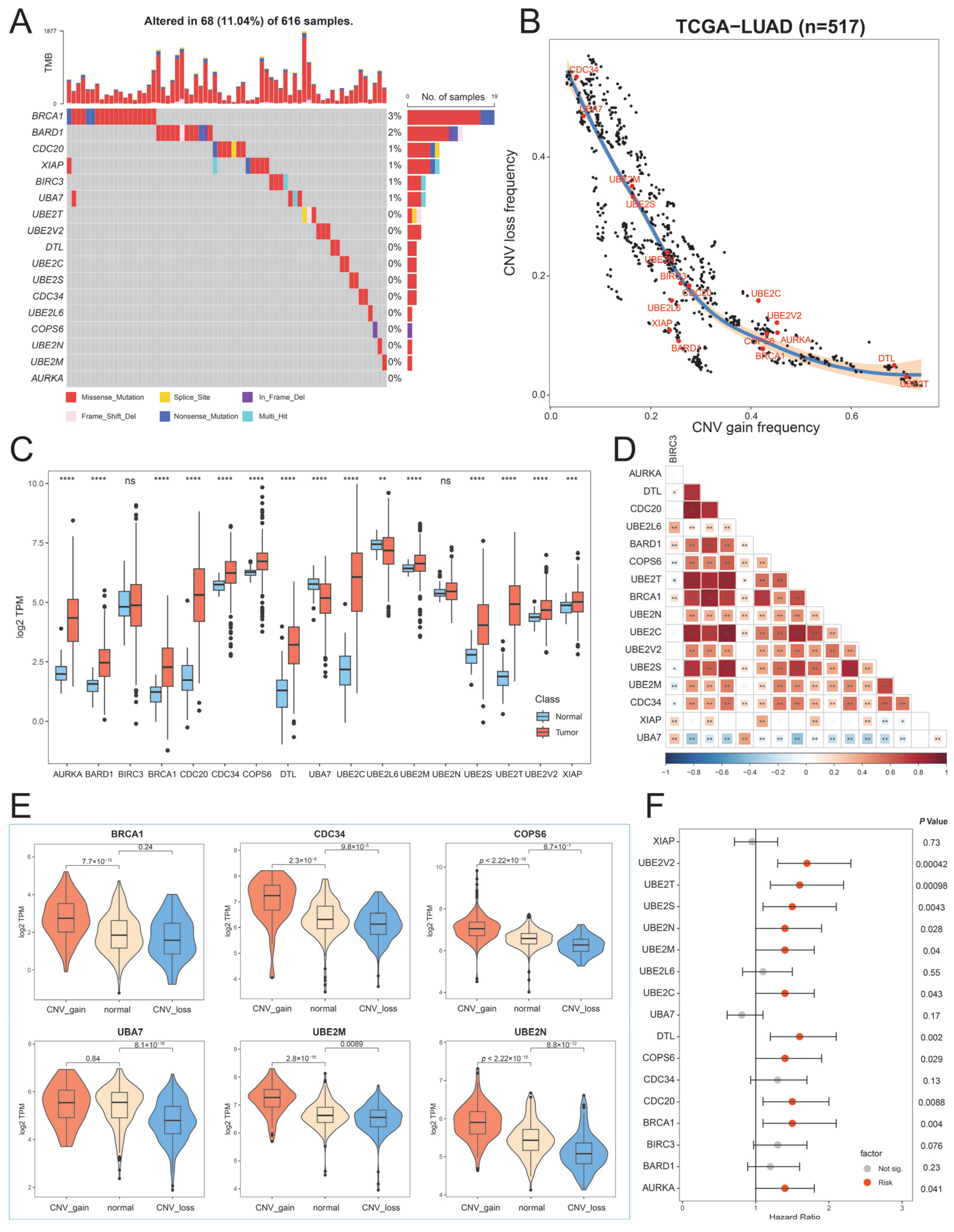
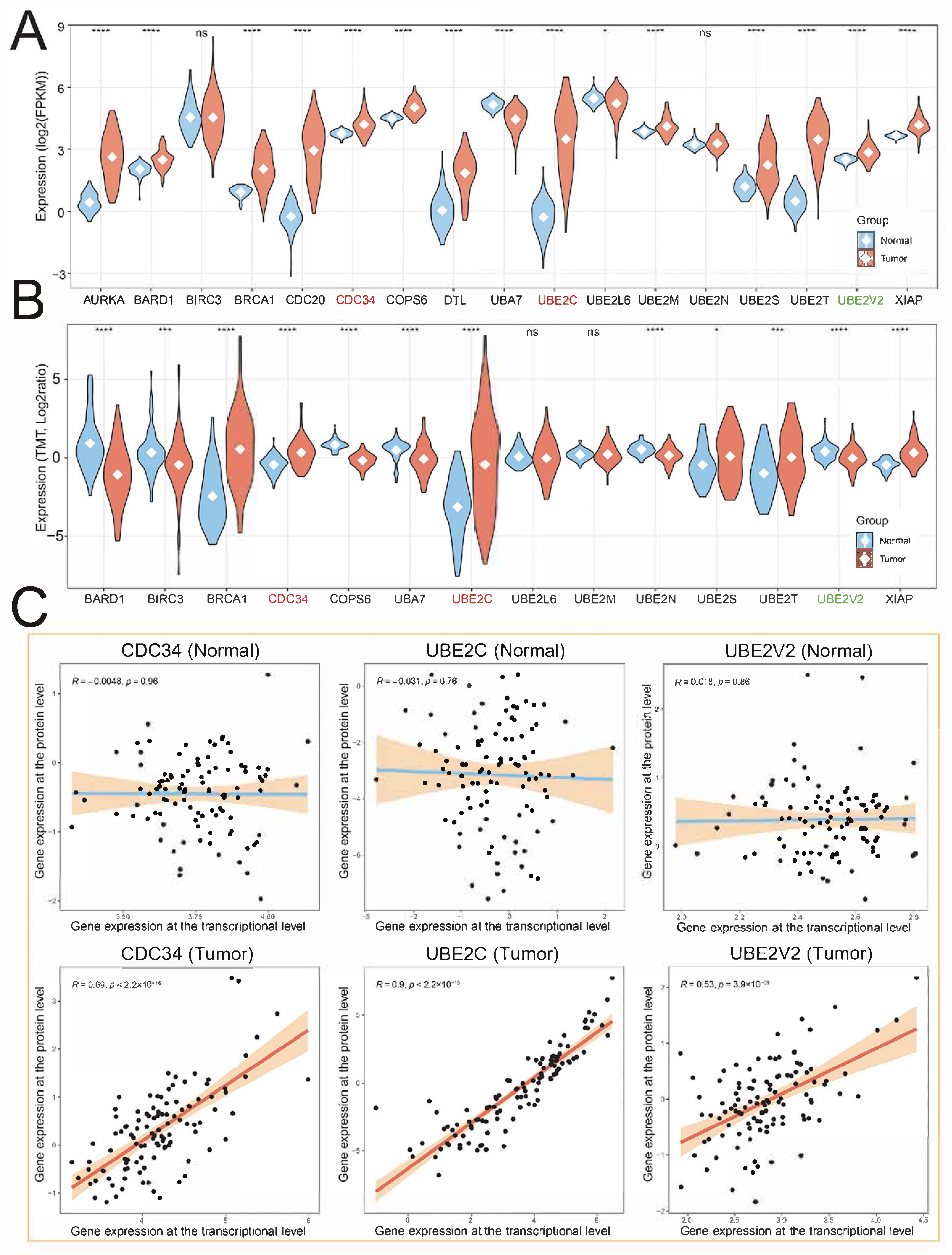
2.2. Genetic and Transcriptional Alterations of Hub UBRs
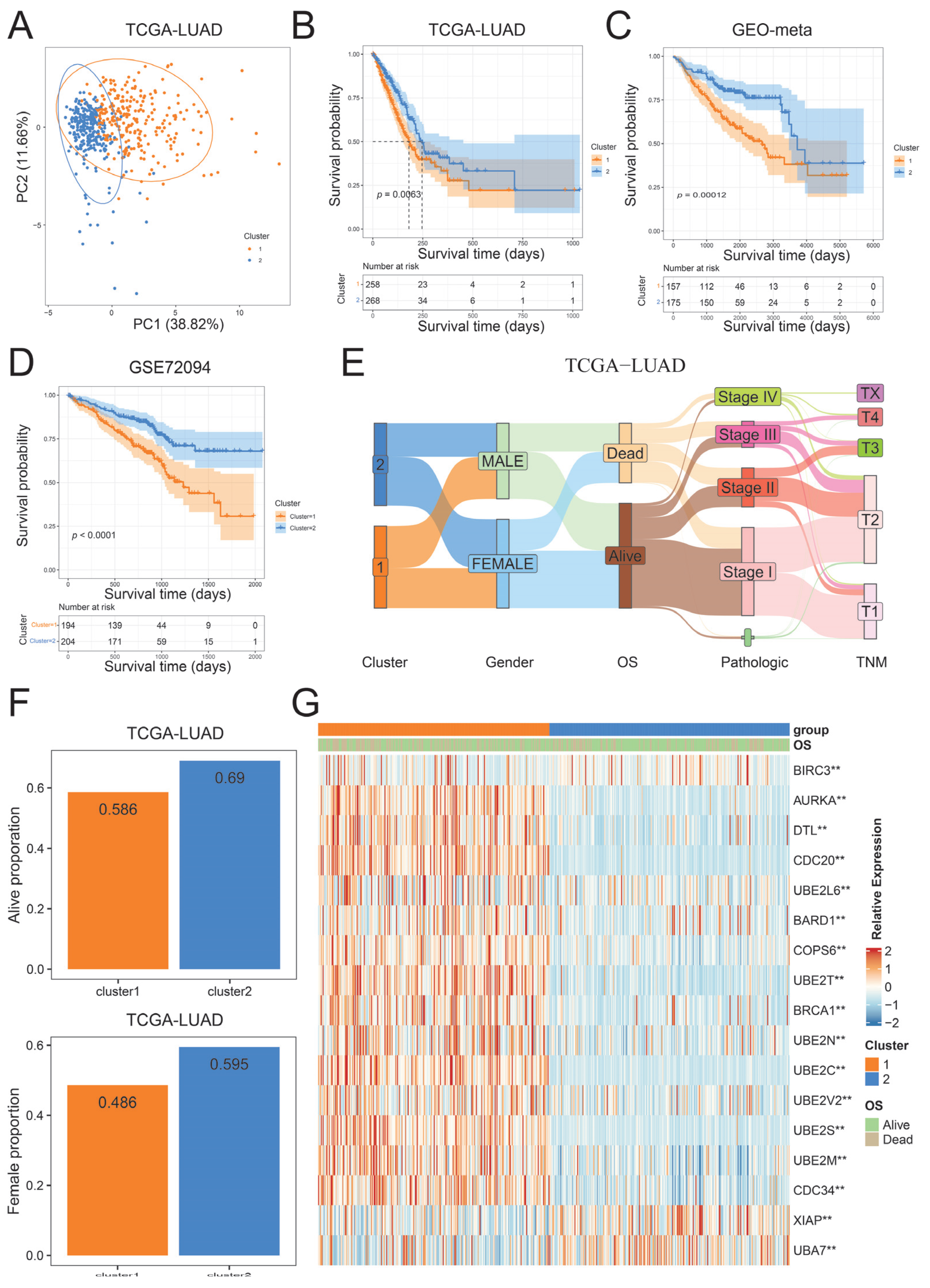
2.3. Identification of Ubiquitination Subtypes in LUAD
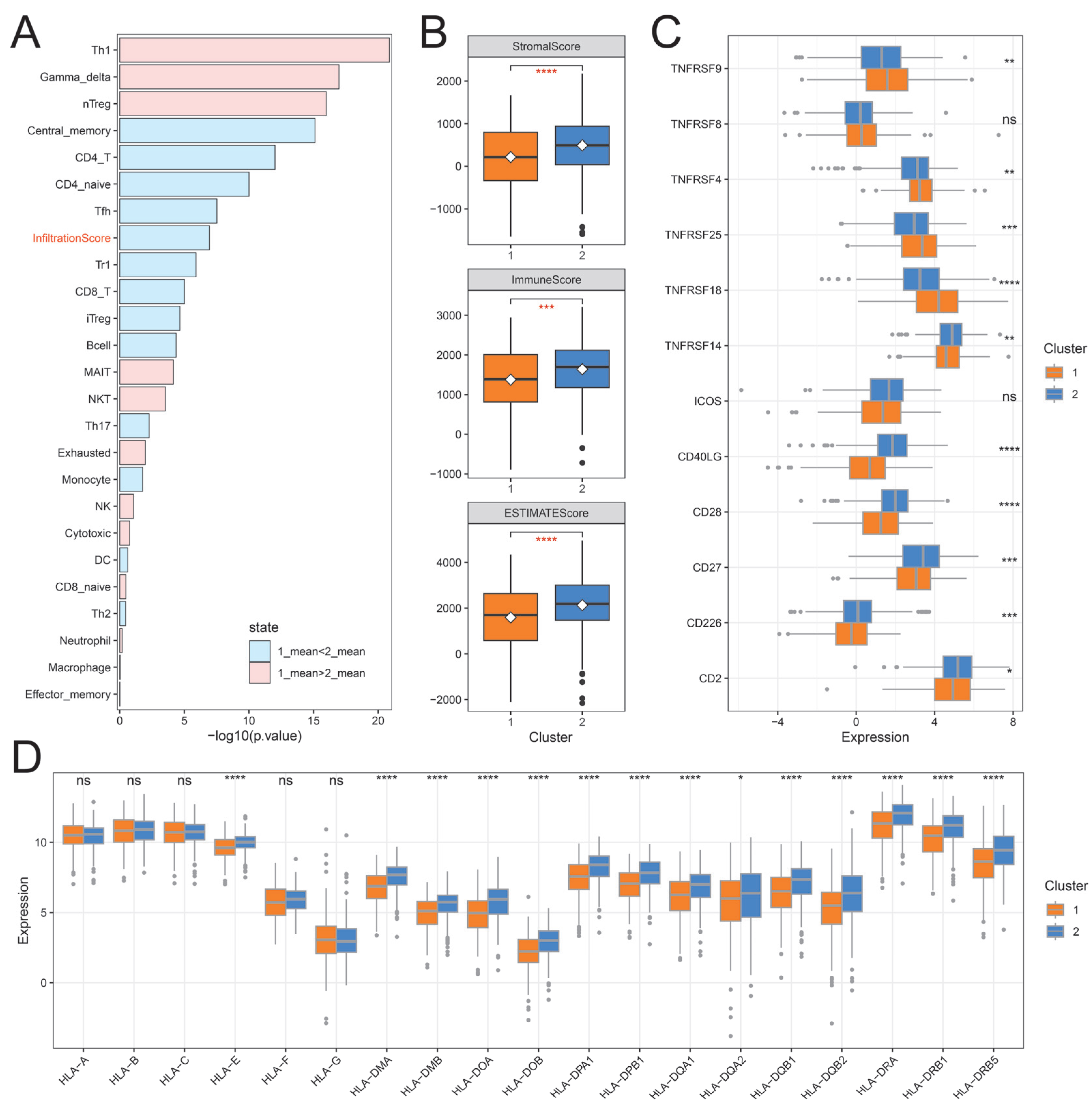
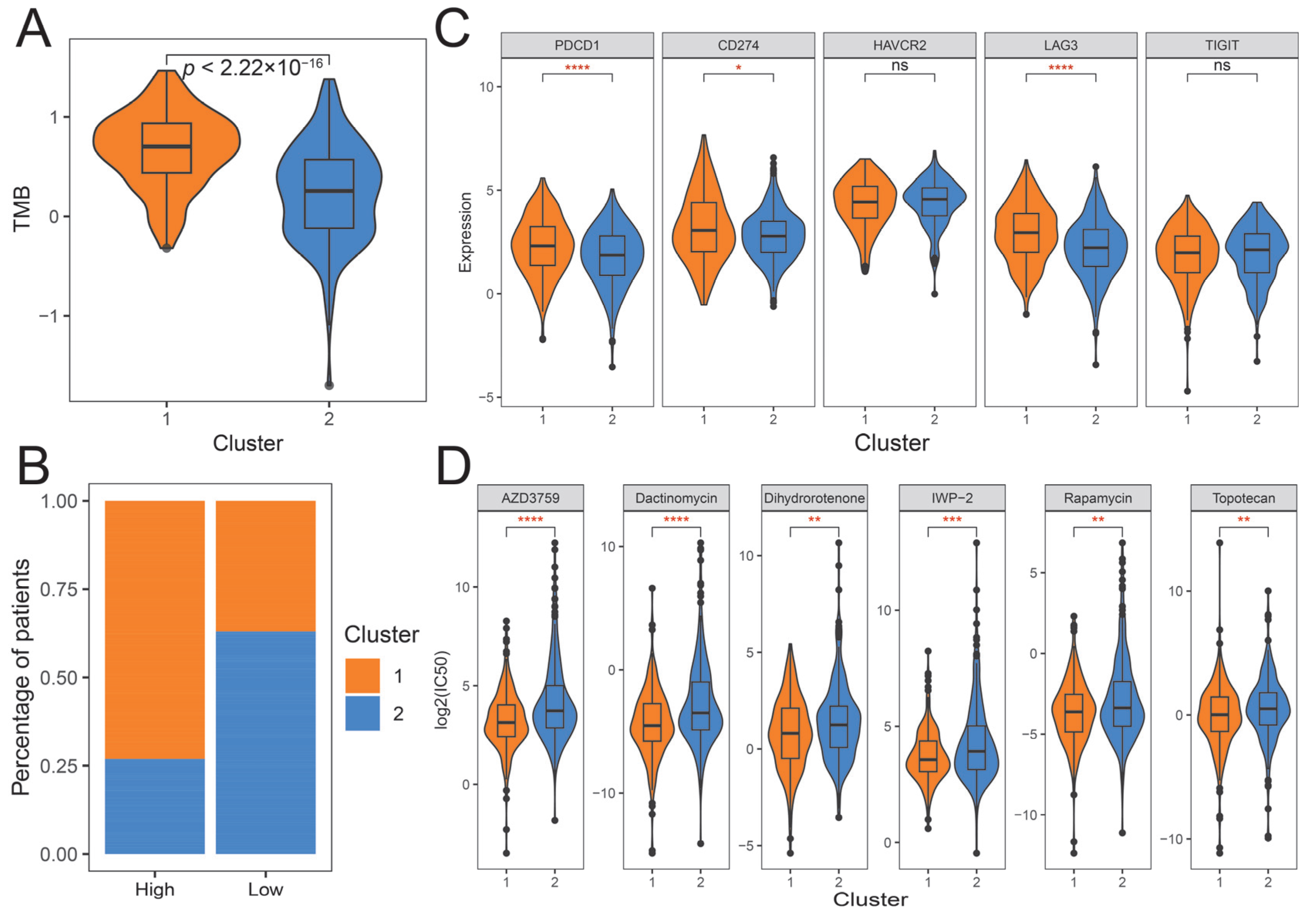
2.4. The Immune Landscape of Distinct Ubiquitination Subtypes
2.5. Construction of the Ubiquitination Score and Its Clinical Characteristics
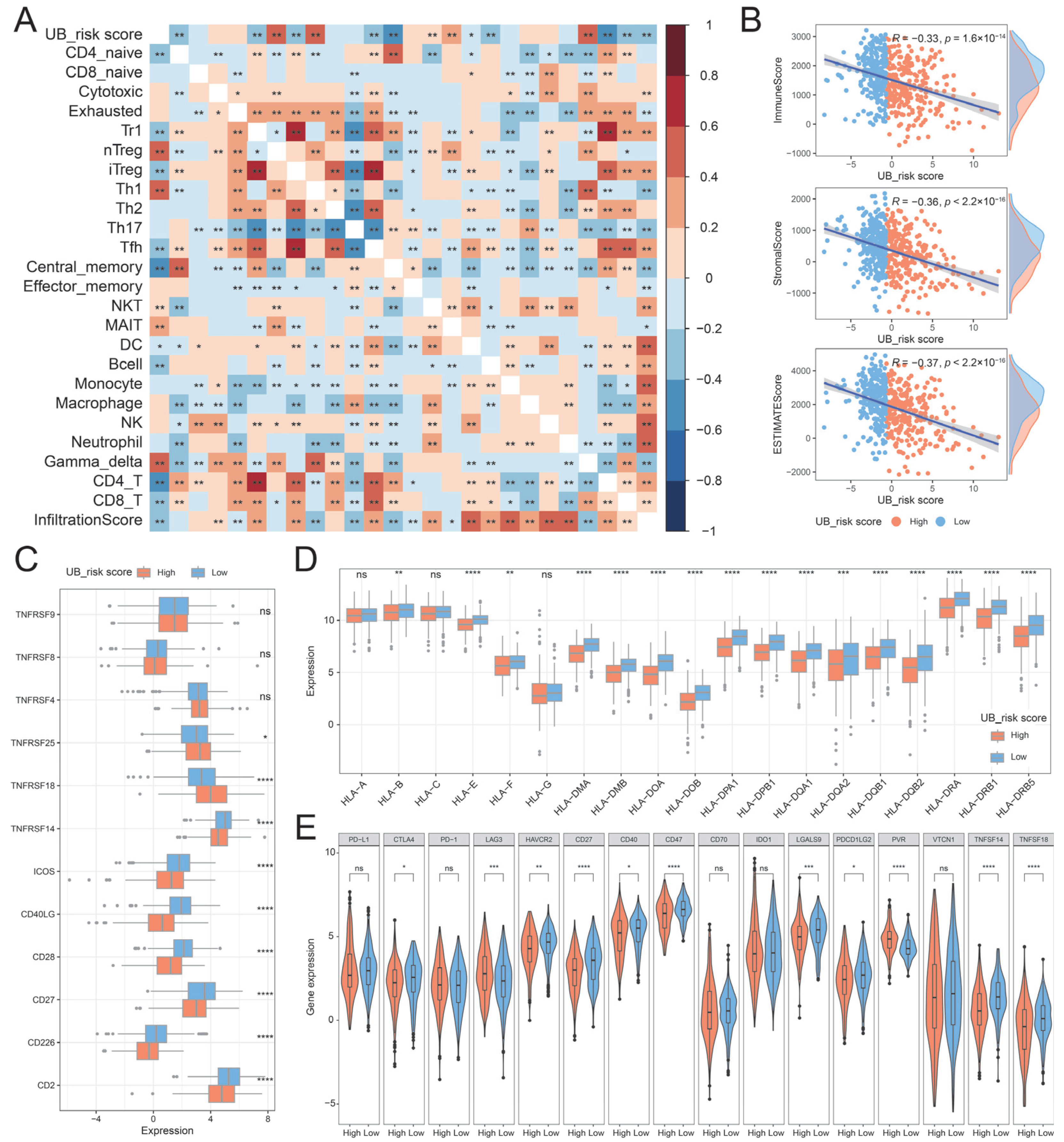
2.6. Immune Characteristics of UB_Risk Score
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Source of UBRs
4.2. Collection and Processing of Publicly Available LUAD Cohort Datasets
4.3. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSVA) and Identification of Hub Genes
4.4. Analysis of Genetic Alterations
4.5. Consensus Clustering Analysis of Hub UBRs
4.6. Analysis of Immune Characteristics of Ubiquitination Subtypes
4.7. Construction of Ubiquitination-Related Risk Scores
4.8. Survival and Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Tao, W.; Zhou, X.; Xu, L.-D.; Luo, Y.; Yang, X.; Min, Q.; Huang, M.; Zhu, Y.; Cui, X.; et al. Multi-omics analysis identifies different molecular subtypes with unique outcomes in early-stage poorly differentiated lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, A.; Salvucci, C.; Castelli, S.; Carraturo, A.; de Vitis, C.; D’Ascanio, M. Adenocarcinomas of the Lung and Neurotrophin System: A Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrend, S.J.; Giotopoulou, G.A.; Spella, M.; Stathopoulos, G.T. A role for club cells in smoking-associated lung adenocarcinoma. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2021, 30, 210122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Ding, Y.; Wang, P.; Wei, L.; Ma, K. Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Immune Infiltration and Clinical Significance of Phosphorylation Modification Enzymes in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Wan, F.; Xiao, B.; Du, J.; Peng, C.; Peng, F. Cell components of tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma: Promising targets for small-molecule compounds. Chin. Med. J. 2024, 138, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Chen, J.; Li, K.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Lu, B.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; et al. Ubiquitination and deubiquitination in cancer: From mechanisms to novel therapeutic approaches. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, D.; Vucic, D.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitination in disease pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 1242–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xu, Y.; Lin, S.; Guo, Y.; Deng, W.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, A.; Xue, Y. iUUCD 2.0: An update with rich annotations for ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like conjugations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D447–D453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; He, M.; Kong, X.; Jiang, P.; Liu, X.; Diao, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Ling, X.; et al. UbiBrowser 2.0: A comprehensive resource for proteome-wide known and predicted ubiquitin ligase/deubiquitinase-substrate interactions in eukaryotic species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D719–D728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Yang, Q.; Guo, A.; Ren, J.; Xue, Y. UUCD: A family-based database of ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like conjugation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D445–D451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Zhang, R.; Du, C.; Tong, J.; Ni, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Liao, M. Integrated analysis of the ubiquitination mechanism reveals the specific signatures of tissue and cancer. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikic, I.; Schulman, B.A. An expanded lexicon for the ubiquitin code. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 24, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Meng, T.; Chen, L.; Wei, W.; Wang, P. The role of ubiquitination in tumorigenesis and targeted drug discovery. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.-K.; Chou, C.-K.; Lin, I.L.; Chang, W.-T.; Kuo, I.Y.; Chiu, C.-C. Deubiquitinating enzymes: Potential regulators of the tumor microenvironment and implications for immune evasion. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, L.; Ji, C.; Xing, F. Cellular functions, molecular signalings and therapeutic applications: Translational potential of deubiquitylating enzyme USP9X as a drug target in cancer treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, H.; Li, B.; Jiang, J.; Qin, S.; Nice, E.C.; He, W.; Lang, T.; Huang, C. Protein degradation: Expanding the toolbox to restrain cancer drug resistance. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 16, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.-M.; Zhao, Z.-Y.; Yu, X.; Xia, Q.-D.; Zhou, P.; Wang, S.-G.; Wu, H.-L.; Hu, J. Exploiting E3 ubiquitin ligases to reeducate the tumor microenvironment for cancer therapy. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Meng, T.; Cui, S.; Liu, D.; Pang, Q.; Wang, P. Roles of ubiquitination in the crosstalk between tumors and the tumor microenvironment (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2022, 61, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Acevedo, J.A.; Dholaria, B.; Soyano, A.E.; Knutson, K.L.; Chumsri, S.; Lou, Y. Next generation of immune checkpoint therapy in cancer: New developments and challenges. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillette, M.A.; Satpathy, S.; Cao, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Vasaikar, S.V.; Krug, K.; Petralia, F.; Li, Y.; Liang, W.-W.; Reva, B.; et al. Proteogenomic Characterization Reveals Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cell 2020, 182, 200–225.e235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H.-K.; Xu, C. Insights into the post-translational modification and its emerging role in shaping the tumor microenvironment. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.-C. Deubiquitylation and regulation of the immune response. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vucic, D.; Dixit, V.M.; Wertz, I.E. Ubiquitylation in apoptosis: A post-translational modification at the edge of life and death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S.; Rajalingam, K.; Dikic, I. Ubiquitylation in immune disorders and cancer: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic implications. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Okoye, I.; Chaleshtari, M.G.; Hazhirkarzar, B.; Mohamadnejad, J.; Azizi, G.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Mohammadi, H.; Shotorbani, S.S.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes in cancer: Implications for immunotherapeutic interventions. Clin. Chim. Acta 2019, 498, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; You, X.; Zheng, Y.; Shen, Y.; Xiong, X.; Sun, Y. The UBE2C/CDH1/DEPTOR axis is an oncogene and tumor suppressor cascade in lung cancer cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e162434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Ze’ev, R.A. Dysregulation of ubiquitin ligases in cancer. Drug Resist. Updates 2015, 23, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senft, D.; Qi, J.; Ronai, Z.A. Ubiquitin ligases in oncogenic transformation and cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 18, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, C.; Wang, Q.; Otkur, W.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X.; Piao, H. The roles of E3 ubiquitin ligases in cancer progression and targeted therapy. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapanidou, M.; Curtis, N.L.; Bolanos-Garcia, V.M. Cdc20: At the Crossroads between Chromosome Segregation and Mitotic Exit. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wan, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Wei, W. Targeting Cdc20 as a novel cancer therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 151, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Liu, Y.-J.; Yu, J.; Wang, R.; Shi, J.-J.; Chen, R.-Y.; Yang, G.-J.; Chen, J. Unraveling the Role of Ubiquitin-Conjugating Enzyme UBE2T in Tumorigenesis: A Comprehensive Review. Cells 2024, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Sun, Y. Targeting CDC34 E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzyme for lung cancer therapy. EBioMedicine 2020, 54, 102718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.-Z.; Jin, W.-L. The updated landscape of tumor microenvironment and drug repurposing. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagaev, A.; Kotlov, N.; Nomie, K.; Svekolkin, V.; Gafurov, A.; Isaeva, O.; Osokin, N.; Kozlov, I.; Frenkel, F.; Gancharova, O.; et al. Conserved pan-cancer microenvironment subtypes predict response to immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 845–865.e847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Duan, X.; Li, N.; Qiao, O.; Hou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, S.; Gong, Y.; Liu, Z. Construction of ubiquitination-related risk model for predicting prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, P.; Yu, J.; Liu, T. Multi-Omics Analysis Elucidates The Immune And Intratumor Microbes Characteristics Of Ubiquitination Subtypes In Lung Adenocarcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 36, 101754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Gong, J.; Pan, J. Prognostic Signature, Immune Features, and Therapeutic Responses of a Novel Ubiquitination-Related Gene Signature in Lung Adenocarcinoma. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 2524649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Lu, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.Y. A novel protein ubiquitination-related five-gene signature predicts overall survival in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Aging 2021, 13, 8510–8523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaprico, A.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Garofano, L.; Cava, C.; Garolini, D.; Sabedot, T.S.; Malta, T.M.; Pagnotta, S.M.; Castiglioni, I.; et al. TCGAbiolinks: An R/Bioconductor package for integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leek, J.T.; Johnson, W.E.; Parker, H.S.; Jaffe, A.E.; Storey, J.D. The sva package for removing batch effects and other unwanted variation in high-throughput experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wu, H.H.; Ho, C.W.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, C.Y. cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. S4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayakonda, A.; Lin, D.C.; Assenov, Y.; Plass, C.; Koeffler, H.P. Maftools: Efficient and comprehensive analysis of somatic variants in cancer. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkerson, M.D.; Hayes, D.N. ConsensusClusterPlus: A class discovery tool with confidence assessments and item tracking. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1572–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.R.; Zhang, Q.; Lei, Q.; Luo, M.; Xie, G.Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, A.Y. ImmuCellAI: A Unique Method for Comprehensive T-Cell Subsets Abundance Prediction and its Application in Cancer Immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becht, E.; Giraldo, N.A.; Lacroix, L.; Buttard, B.; Elarouci, N.; Petitprez, F.; Selves, J.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Sautes-Fridman, C.; Fridman, W.H.; et al. Estimating the population abundance of tissue-infiltrating immune and stromal cell populations using gene expression. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 218. [Google Scholar]
- Geeleher, P.; Cox, N.; Huang, R.S. pRRophetic: An R package for prediction of clinical chemotherapeutic response from tumor gene expression levels. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeser, D.; Gruener, R.F.; Huang, R.S. oncoPredict: An R package for predicting in vivo or cancer patient drug response and biomarkers from cell line screening data. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, bbab260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wu, Q.; Li, B.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.L. m(6)A regulator-mediated methylation modification patterns and tumor microenvironment infiltration characterization in gastric cancer. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Li, M.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Shi, M.; Bin, J.; Liao, Y.; Rao, J.; Liao, W. Tumor Microenvironment Characterization in Gastric Cancer Identifies Prognostic and Immunotherapeutically Relevant Gene Signatures. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 737–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, C.; Wirapati, P.; Loi, S.; Harris, A.; Fox, S.; Smeds, J.; Nordgren, H.; Farmer, P.; Praz, V.; Haibe-Kains, B.; et al. Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: Understanding the molecular basis of histologic grade to improve prognosis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Long, D.; Xue, Y.; Yu, X.; Qin, X.; Chen, J.; Luo, J.; Ma, K.; Wei, L.; Li, X. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals the Molecular Characteristics, Tumor Microenvironment, and Clinical Significance of Ubiquitination Mechanisms in Lung Adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136501
Long D, Xue Y, Yu X, Qin X, Chen J, Luo J, Ma K, Wei L, Li X. Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals the Molecular Characteristics, Tumor Microenvironment, and Clinical Significance of Ubiquitination Mechanisms in Lung Adenocarcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136501
Chicago/Turabian StyleLong, Deyu, Yajing Xue, Xiushi Yu, Xue Qin, Jiaxin Chen, Jia Luo, Ketao Ma, Lili Wei, and Xinzhi Li. 2025. "Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals the Molecular Characteristics, Tumor Microenvironment, and Clinical Significance of Ubiquitination Mechanisms in Lung Adenocarcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136501
APA StyleLong, D., Xue, Y., Yu, X., Qin, X., Chen, J., Luo, J., Ma, K., Wei, L., & Li, X. (2025). Integrative Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals the Molecular Characteristics, Tumor Microenvironment, and Clinical Significance of Ubiquitination Mechanisms in Lung Adenocarcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136501




