Transporter-Mediated Interactions Between Uremic Toxins and Drugs: A Hidden Driver of Toxicity in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
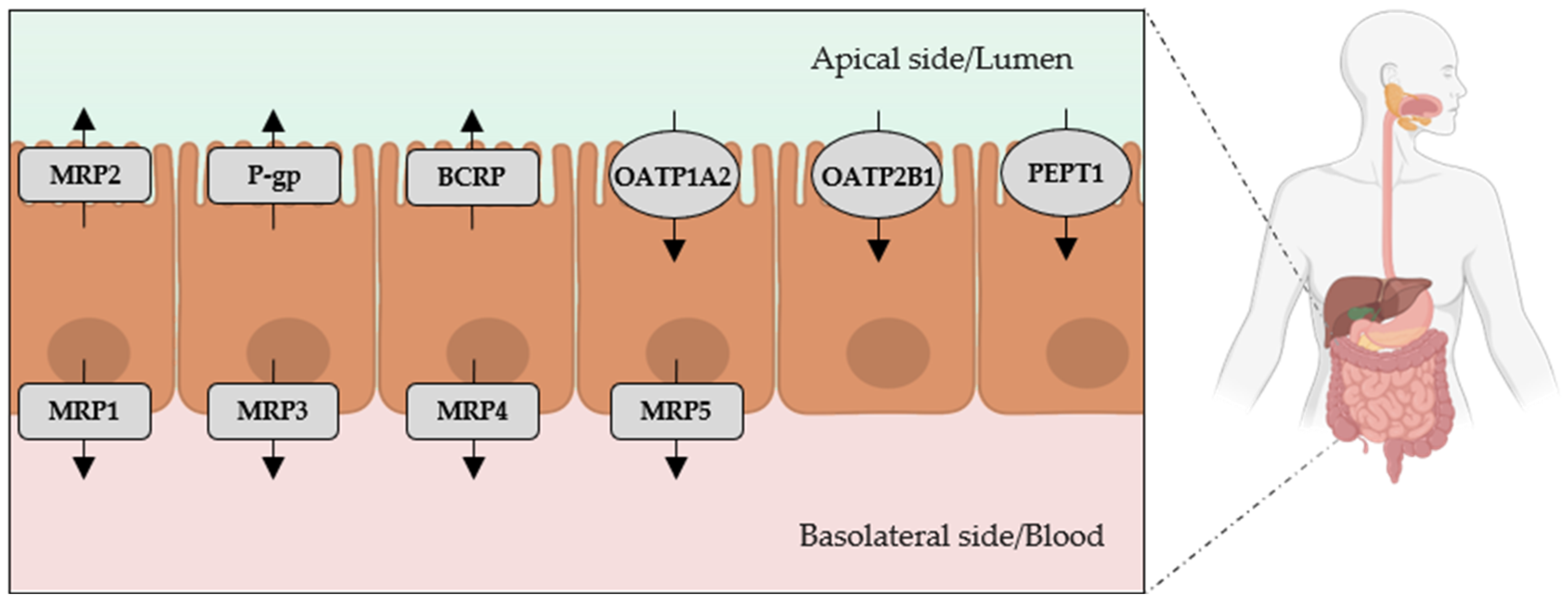
2. Intestinal Passage of Indole and p-Cresol
3. Transport of IS and PCS Across the BBB
3.1. Transport of Indoxyl Sulfate (IS) Across the BBB
3.2. Transport of Para-Cresyl Sulfate (PCS) Across the BBB
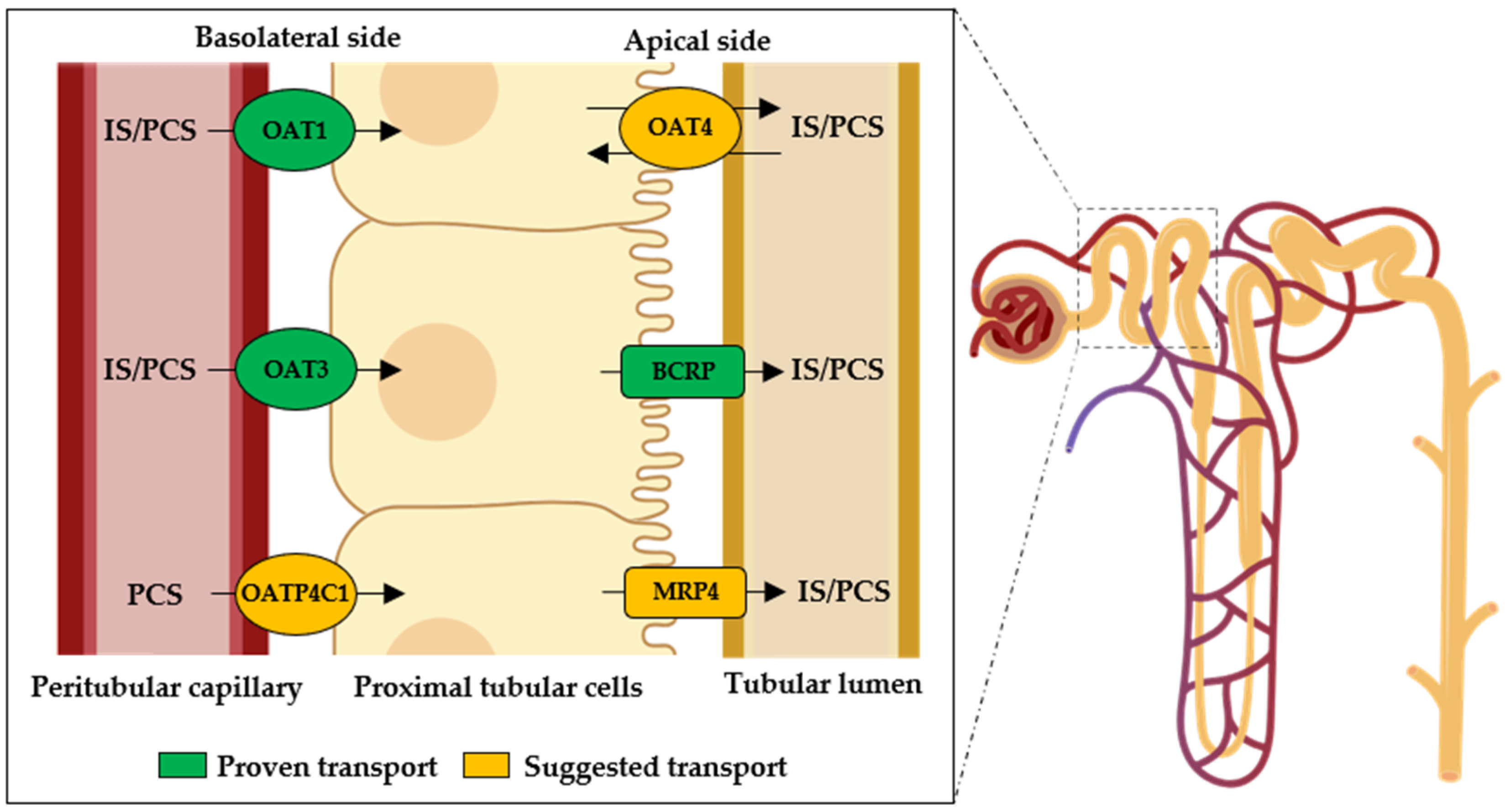
4. Renal Excretion of IS and PCS
4.1. Renal Excretion of Indoxyl Sulfate (IS)
4.2. Renal Excretion of Para-Cresyl Sulfate (PCS)
5. Drug–Transporter Interactions Affecting the Disposition of IS and PCS in CKD
5.1. Polypharmacy in CKD
5.2. Impact of Prescribed Medications on IS and PCS Distribution and Elimination
6. Final Considerations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 6-CF | 6-Carboxyfluorescein |
| ABC | ATP-binding cassette |
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ARBs | Angiotensin II receptor blockers |
| BBB | Blood–brain barrier |
| BCRP | Breast cancer resistant protein |
| BMECs | Human brain microvascular endothelial cells |
| CHO | Chinese hamster ovary cells |
| ciPTEC | Conditionally immortalized proximal tubule epithelial cells |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CKD-MBD | Chronic kidney disease—mineral and bone disorder |
| CKD-REIN | Chronic Kidney Disease—Renal Epidemiology and Information Network |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CYP2E1 | Cytochrome P450 2E1 |
| DOACs | Direct oral anticoagulants |
| EPO | Erythropoietin |
| ES | Estrone sulfate |
| GERD | Gastroesophageal reflux disease |
| HEK293 | Human embryonic kidney cells |
| HK-2 | Human kidney-2 cells |
| HMG-CoA | 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A |
| hOAT | Human organic anion transporter |
| HSA | Human serum albumin |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| IS | Indoxyl sulfate |
| LLC-PK1 | Porcine kidney 1 epithelial cells |
| MDCK | Madin–Darby canine kidney cells |
| MRP | Multidrug resistance protein |
| MTX | Methotrexate |
| NSAIDs | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| OAT | Organic anion transporter |
| OATP | Organic anion transporting polypeptide |
| PAH | p-Amminohippuric acid |
| PBUTs | Protein-bound uremic toxins |
| PCS | p-Cresyl sulfate |
| PEPT1 | Peptide transporter 1 |
| P-gp | P-Glycoprotein |
| PPIs | Proton pump inhibitors |
| rOAT | Rat organic anion transporter |
| S2-cells | Immortalized cell line derived from the second segment of mice proximal tubule |
| SLC | Solute carrier transporter |
| SULT1A1 | Sulfotransferase 1A1 |
| TAT | Tyrosine aminotransferase |
| UT | Uremic toxin |
| VKA | Vitamin K antagonist |
References
- Hénaut, L.; Chillon, J.-M.; Kamel, S.; Massy, Z.A. Updates on the Mechanisms and the Care of Cardiovascular Calcification in Chronic Kidney Disease. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 233–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.K.; Knicely, D.H.; Grams, M.E. Chronic Kidney Disease Diagnosis and Management: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liabeuf, S.; Pepin, M.; Franssen, C.F.M.; Viggiano, D.; Carriazo, S.; Gansevoort, R.T.; Gesualdo, L.; Hafez, G.; Malyszko, J.; Mayer, C.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease and Neurological Disorders: Are Uraemic Toxins the Missing Piece of the Puzzle? Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2021, 37, ii33–ii44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, C.J.; Harrison, L.E.; Hoad, C.L.; Marciani, L.; Gowland, P.A.; McIntyre, C.W. Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Have Abnormal Upper Gastro-intestinal Tract Digestive Function: A Study of Uremic Enteropathy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczak, M.; Surma, S. Metabolic Acidosis in Patients with CKD: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Treatment. Kidney Dis. 2021, 7, 452–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, A.S.; McCulloch, C.E. Chronic Kidney Disease and the Risks of Death, Cardiovascular Events, and Hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.J.; Sidor, N.A.; Tonial, N.C.; Che, A.; Urquhart, B.L. Uremic Toxins in the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Toxins 2021, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graboski, A.L.; Redinbo, M.R. Gut-Derived Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins 2020, 12, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryp, T.; Vanholder, R.; Vaneechoutte, M.; Glorieux, G. P-Cresyl Sulfate. Toxins 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; Pletinck, A.; Schepers, E.; Glorieux, G. Biochemical and Clinical Impact of Organic Uremic Retention Solutes: A Comprehensive Update. Toxins 2018, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, S.; Kuo, K.; Wu, C.; Tarng, D. Indoxyl Sulfate: A Novel Cardiovascular Risk Factor in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobot, M. Atteinte neurocognitive et barrière hémato-encéphalique au cours de la maladie rénale chronique: Rôle des toxines urémiques. Néphrol. Thér. 2023, 19, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreto, F.C.; Barreto, D.V.; Liabeuf, S.; Drüeke, T.B.; Massy, Z.A. Progress in Uremic Toxin Research: Effects of Uremic Toxins on Vascular and Bone Remodeling. Semin. Dial. 2009, 22, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikoff, W.R.; Anfora, A.T.; Liu, J.; Schultz, P.G.; Lesley, S.A.; Peters, E.C.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics Analysis Reveals Large Effects of Gut Microflora on Mammalian Blood Metabolites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3698–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Li, H.; Anjum, K.; Zhong, X.; Miao, S.; Zheng, G.; Liu, W.; Li, L. Dual Role of Indoles Derived From Intestinal Microbiota on Human Health. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 903526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunevičius, A.; Sadauskas, M.; Raudytė, J.; Meškys, R.; Burokas, A. Unraveling the Dynamics of Host–Microbiota Indole Metabolism: An Investigation of Indole, Indolin-2-One, Isatin, and 3-Hydroxyindolin-2-One. Molecules 2024, 29, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloot, S.; Schneditz, D.; Cornelis, T.; Van Biesen, W.; Glorieux, G.; Dhondt, A.; Kooman, J.; Vanholder, R. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxin Profiling as a Tool to Optimize Hemodialysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0147159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabresse, N.; Uteem, I.; Lamy, E.; Massy, Z.; Larabi, I.A.; Alvarez, J.-C. Quantification of Free and Protein Bound Uremic Toxins in Human Serum by LC-MS/MS: Comparison of Rapid Equilibrium Dialysis and Ultrafiltration. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 507, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, C.; Bodeau, S.; Kamel, S.; Bennis, Y.; Caillard, P. The AKI-to-CKD Transition: The Role of Uremic Toxins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glatt, H.; Meinl, W. Sulphotransferase-Mediated Toxification of Chemicals in Mouse Models: Effect of Knockout or Humanisation of SULT Genes. Essays Biochem. 2024, 68, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranade, V.V. Impact of Drug Transport Proteins. In Biotechnology: Pharmaceutical Aspects; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 559–576. ISBN 978-0-387-74900-6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, K. The Transporters of Intestinal Tract and Techniques Applied to Evaluate Interactions between Drugs and Transporters. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 8, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estudante, M.; Morais, J.G.; Soveral, G.; Benet, L.Z. Intestinal Drug Transporters: An Overview. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1340–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauriola, M.; Zadora, W.; Farré, R.; Meijers, B. Intestinal Transport of Organic Food Compounds and Drugs: A Scoping Review on the Alterations Observed in Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2024, 64, 461–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatosian, D.A.; Yee, K.L.; Zhang, Z.; Mostoller, K.; Paul, E.; Sutradhar, S.; Larson, P.; Chhibber, A.; Wen, J.; Wang, Y.; et al. A Microdose Cocktail to Evaluate Drug Interactions in Patients with Renal Impairment. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 109, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naud, J.; Michaud, J.; Boisvert, C.; Desbiens, K.; Leblond, F.A.; Mitchell, A.; Jones, C.; Bonnardeaux, A.; Pichette, V. Down-Regulation of Intestinal Drug Transporters in Chronic Renal Failure in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 320, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veau, C.; Leroy, C.; Banide, H.; Auchère, D.; Tardivel, S.; Farinotti, R.; Lacour, B. Effect of Chronic Renal Failure on the Expression and Function of Rat Intestinal P-glycoprotein in Drug Excretion. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2001, 16, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolin, T.D.; Frye, R.F.; Le, P.; Sadr, H.; Naud, J.; Leblond, F.A.; Pichette, V.; Himmelfarb, J. ESRD Impairs Nonrenal Clearance of Fexofenadine but Not Midazolam. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimoto, M.; Hatozaki, D.; Shima, D.; Yokota, H.; Furukubo, T.; Izumi, S.; Yamakawa, T.; Minegaki, T.; Nishiguchi, K. Influence of Serum in Hemodialysis Patients on the Expression of Intestinal and Hepatic Transporters for the Excretion of Pravastatin. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2012, 16, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, S.; Tsujimoto, M.; Uchiyama, H.; Ito, N.; Morishita, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Irie, R.; Sakashita, T.; Tachiki, H.; Furukubo, T.; et al. Uremic Serum Residue Decreases SN-38 Sensitivity through Suppression of Organic Anion Transporter Polypeptide 2B1 in LS-180 Colon Cancer Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, H.; Tamura, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Tanemoto, M.; Uchida, S. Uric Acid Transporter ABCG2 Is Increased in the Intestine of the 5/6 Nephrectomy Rat Model of Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2014, 18, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Nakanishi, T.; Hosomi, A.; Komori, H.; Tamai, I. In-Vitro Evidence of Enhanced Breast Cancer Resistance Protein-Mediated Intestinal Urate Secretion by Uremic Toxins in Caco-2 Cells. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2015, 67, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; Masuda, S.; Nishihara, K.; Ji, L.; Okuda, M.; Inui, K. Increased Protein Level of PEPT1 Intestinal H+-Peptide Cotransporter Upregulates Absorption of Glycylsarcosine and Ceftibuten in 5/6 Nephrectomized Rats. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 288, G664–G670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bean, R.C.; Shepherd, W.C.; Chan, H. Permeability of Lipid Bilayer Membranes to Organic Solutes. J. Gen. Physiol. 1968, 52, 495–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinero-Fernandez, S.; Chimerel, C.; Keyser, U.F.; Summers, D.K. Indole Transport across Escherichia Coli Membranes. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banoglu, E.; Jha, G.G.; King, R.S. Hepatic Microsomal Metabolism of Indole to Indoxyl, a Precursor of Indoxyl Sulfate. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2001, 26, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijers, B.K.I.; Evenepoel, P. The Gut-Kidney Axis: Indoxyl Sulfate, p-Cresyl Sulfate and CKD Progression. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 759–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-J.; Liou, T.-C.; Pan, C.-F.; Wu, P.-C.; Sun, F.-J.; Liu, H.-L.; Chen, H.-H.; Wu, C.-J. The Role of Liver in Determining Serum Colon-Derived Uremic Solutes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teubner, W.; Meinl, W.; Florian, S.; Kretzschmar, M.; Glatt, H. Identification and Localization of Soluble Sulfotransferases in the Human Gastrointestinal Tract. Biochem. J. 2007, 404, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soulage, C.O.; Koppe, L. The Very Last Dance of Unconjugated p -Cresol… Historical Artefact of Uraemic Research. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 807–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.W.; Recht, N.S.; Hostetter, T.H.; Meyer, T.W. Removal of P-Cresol Sulfate by Hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3430–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meert, N.; Schepers, E.; Glorieux, G.; Van Landschoot, M.; Goeman, J.L.; Waterloos, M.-A.; Dhondt, A.; Van Der Eycken, J.; Vanholder, R. Novel Method for Simultaneous Determination of P-Cresylsulphate and p-Cresylglucuronide: Clinical Data and Pathophysiological Implications. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2388–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Loor, H.; Bammens, B.; Evenepoel, P.; De Preter, V.; Verbeke, K. Gas Chromatographic–Mass Spectrometric Analysis for Measurement of p-Cresol and Its Conjugated Metabolites in Uremic and Normal Serum. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Dajani, A.R.; Hou, Q.K.; Kiang, T.K.L. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Analytical Methods for the Quantitation of p-Cresol Sulfate and Indoxyl Sulfate in Human Matrices: Biological Applications and Diagnostic Potentials. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, T. Indoxyl Sulfate Is a Nephro-Vascular Toxin. J. Ren. Nutr. 2010, 20, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, S.A. Neurologic Conditions and Disorders of Uremic Syndrome of Chronic Kidney Disease: Presentations, Causes, and Treatment Strategies. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 61–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, E.; Saigusa, D.; Mishima, E.; Uchida, T.; Miura, D.; Morikawa-Ichinose, T.; Kisu, K.; Sekimoto, A.; Saito, R.; Oe, Y.; et al. Impact of the Oral Adsorbent AST-120 on Organ-Specific Accumulation of Uremic Toxins: LC-MS/MS and MS Imaging Techniques. Toxins 2017, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-Y.; Li, J.-R.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y.; Ou, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-J.; Wang, J.-D.; Liao, S.-L.; Chen, C.-J. P-Cresol Sulfate Caused Behavior Disorders and Neurodegeneration in Mice with Unilateral Nephrectomy Involving Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowska, M.; Hermanowicz, J.M.; Tankiewicz-Kwedlo, A.; Kalaska, B.; Kaminski, T.W.; Nosek, K.; Wisniewska, R.J.; Pawlak, D. Neurobehavioral Effects of Uremic Toxin–Indoxyl Sulfate in the Rat Model. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-C.; Chen, W.-Y.; Chen, J.-B.; Lee, W.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Tzeng, H.-T.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-J.; Yang, J.-L. The AST-120 Recovers Uremic Toxin-Induced Cognitive Deficit via NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway in Astrocytes and Microglia. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscher, W.; Potschka, H. Blood-Brain Barrier Active Efflux Transporters: ATP-Binding Cassette Gene Family. NeuroRx 2005, 2, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahringer, A.; Fricker, G. ABC Transporters at the Blood–Brain Barrier. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2016, 12, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, M.D.; Zhao, Z.; Montagne, A.; Nelson, A.R.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood-Brain Barrier: From Physiology to Disease and Back. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 21–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandit, R.; Chen, L.; Götz, J. The Blood-Brain Barrier: Physiology and Strategies for Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 165–166, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faucher, Q.; Van Der Made, T.K.; De Lange, E.; Masereeuw, R. Blood-Brain Barrier Perturbations by Uremic Toxins: Key Contributors in Chronic Kidney Disease-Induced Neurological Disorders? Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 187, 106462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huttunen, K.M.; Terasaki, T.; Urtti, A.; Montaser, A.B.; Uchida, Y. Pharmacoproteomics of Brain Barrier Transporters and Substrate Design for the Brain Targeted Drug Delivery. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 1363–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, J.R.; Spitzer, S.O.; Diaz Heijtz, R. Developmental Signatures of Microbiota-Derived Metabolites in the Mouse Brain. Metabolites 2020, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, T.; Kusuhara, H.; Takadate, A.; Endou, H.; Otagiri, M.; Sugiyama, Y. Characterization of Uremic Toxin Transport by Organic Anion Transporters in the Kidney. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Bush, K.T.; Nigam, S.K. Key Role for the Organic Anion Transporters, OAT1 and OAT3, in the in Vivo Handling of Uremic Toxins and Solutes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Matsuo, H.; Tan, J.K.; Ooyama, K.; Sakiyama, M.; Miyata, H.; Yamanashi, Y.; Toyoda, Y.; Higashino, T.; et al. Identification of ABCG2 as an Exporter of Uremic Toxin Indoxyl Sulfate in Mice and as a Crucial Factor Influencing CKD Progression. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla, C.; Pavlidi, P.; Sakelliadou, D.-G.; Grammatikopoulou, T.; Kokras, N. Sex Differences in Blood–Brain Barrier Transport of Psychotropic Drugs. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 844916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, T.; Isozaki, K.; Yousuke, K.; Terasaki, T.; Otagiri, M. Involvement of Organic Anion Transporters in the Efflux of Uremic Toxins across the Blood–Brain Barrier. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuki, S.; Asaba, H.; Takanaga, H.; Deguchi, T.; Hosoya, K.; Otagiri, M.; Terasaki, T. Role of Blood–Brain Barrier Organic Anion Transporter 3 (OAT3) in the Efflux of Indoxyl Sulfate, a Uremic Toxin: Its Involvement in Neurotransmitter Metabolite Clearance from the Brain. J. Neurochem. 2002, 83, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoya, K.; Tachikawa, M. Roles of Organic Anion/Cation Transporters at the Blood–Brain and Blood–Cerebrospinal Fluid Barriers Involving Uremic Toxins. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2011, 15, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.M.; Dnyanmote, A.V.; Granados, J.C.; Nigam, S.K. Renal and Non-Renal Response of ABC and SLC Transporters in Chronic Kidney Disease. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 515–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burek, M.; Burmester, S.; Salvador, E.; Möller-Ehrlich, K.; Schneider, R.; Roewer, N.; Nagai, M.; Förster, C.Y. Kidney Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Induces Changes in the Drug Transporter Expression at the Blood–Brain Barrier In Vivo and In Vitro. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 569881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naud, J.; Laurin, L.-P.; Michaud, J.; Beauchemin, S.; Leblond, F.A.; Pichette, V. Effects of Chronic Renal Failure on Brain Drug Transporters in Rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urich, E.; Lazic, S.E.; Molnos, J.; Wells, I.; Freskgård, P.-O. Transcriptional Profiling of Human Brain Endothelial Cells Reveals Key Properties Crucial for Predictive In Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Models. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speir, M.L.; Bhaduri, A.; Markov, N.S.; Moreno, P.; Nowakowski, T.J.; Papatheodorou, I.; Pollen, A.A.; Raney, B.J.; Seninge, L.; Kent, W.J.; et al. UCSC Cell Browser: Visualize Your Single-Cell Data. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 4578–4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wälchli, T.; Ghobrial, M.; Schwab, M.; Takada, S.; Zhong, H.; Suntharalingham, S.; Vetiska, S.; Gonzalez, D.R.; Wu, R.; Rehrauer, H.; et al. Single-Cell Atlas of the Human Brain Vasculature across Development, Adulthood and Disease. Nature 2024, 632, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.N.; Knausenberger, T.B.-A.; Pontifex, M.G.; Connell, E.; Le Gall, G.; Hardy, T.A.J.; Randall, D.W.; McCafferty, K.; Yaqoob, M.M.; Solito, E.; et al. Cerebrovascular Damage Caused by the Gut Microbe/Host Co-Metabolite p-Cresol Sulfate Is Prevented by Blockade of the EGF Receptor. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2431651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poesen, R.; Viaene, L.; Verbeke, K.; Claes, K.; Bammens, B.; Sprangers, B.; Naesens, M.; Vanrenterghem, Y.; Kuypers, D.; Evenepoel, P.; et al. Renal Clearance and Intestinal Generation of P-Cresyl Sulfate and Indoxyl Sulfate in CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, A.; Takeda, M.; Tojo, A.; Sekine, T.; Cha, S.H.; Khamdang, S.; Takayama, F.; Aoyama, I.; Nakamura, S.; Endou, H.; et al. Role of Organic Anion Transporters in the Tubular Transport of Indoxyl Sulfate and the Induction of Its Nephrotoxicity. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, T.; Omura, K.; Motoki, K.; Sakai, M.; Chikamatsu, N.; Ashizawa, N.; Takada, T.; Iwanaga, T. Hypouricemic Agents Reduce Indoxyl Sulfate Excretion by Inhibiting the Renal Transporters OAT1/3 and ABCG2. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motojima, M.; Hosokawa, A.; Yamato, H.; Muraki, T.; Yoshioka, T. Uraemic Toxins Induce Proximal Tubular Injury via Organic Anion Transporter 1-mediated Uptake. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 135, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, A.; Takeda, M.; Taki, K.; Takayama, F.; Noshiro, R.; Niwa, T.; Endou, H. Interactions of Human Organic Anion as Well as Cation Transporters with Indoxyl Sulfate. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 466, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favretto, G.; Souza, L.M.; Gregório, P.C.; Cunha, R.S.; Maciel, R.A.P.; Sassaki, G.L.; Toledo, M.G.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Souza, W.M.; Stinghen, A.E.M. Role of Organic Anion Transporters in the Uptake of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins by Human Endothelial Cells and Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 Expression. J. Vasc. Res. 2017, 54, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taki, K.; Nakamura, S.; Miglinas, M.; Enomoto, A.; Niwa, T. Accumulation of Indoxyl Sulfate in OAT1/3-Positive Tubular Cells in Kidneys of Patients With Chronic Renal Failure. J. Ren. Nutr. 2006, 16, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, J.C.; Ermakov, V.; Maity, K.; Vera, D.R.; Chang, G.; Nigam, S.K. The Kidney Drug Transporter OAT1 Regulates Gut Microbiome–Dependent Host Metabolism. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e160437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, C.-H.; Yoshida, K.; Zhao, P.; Meyer, T.W.; Zhang, L.; Huang, S.-M.; Giacomini, K.M. Identification and Quantitative Assessment of Uremic Solutes as Inhibitors of Renal Organic Anion Transporters, OAT1 and OAT3. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 3130–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikoff, W.R.; Nagle, M.A.; Kouznetsova, V.L.; Tsigelny, I.F.; Nigam, S.K. Untargeted Metabolomics Identifies Enterobiome Metabolites and Putative Uremic Toxins as Substrates of Organic Anion Transporter 1 (Oat1). J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 2842–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tust, M.; Müller, J.P.; Fischer, D.; Gründemann, D. SLC22A11 Inserts the Uremic Toxins Indoxyl Sulfate and P-Cresol Sulfate into the Plasma Membrane. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutsaers, H.A.M.; Van Den Heuvel, L.P.; Ringens, L.H.J.; Dankers, A.C.A.; Russel, F.G.M.; Wetzels, J.F.M.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Masereeuw, R. Uremic Toxins Inhibit Transport by Breast Cancer Resistance Protein and Multidrug Resistance Protein 4 at Clinically Relevant Concentrations. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e18438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.; Fedecostante, M.; Wilmer, M.J.; Peters, J.G.; Kreuser, U.M.; Van Den Broek, P.H.; Mensink, R.A.; Boltje, T.J.; Stamatialis, D.; Wetzels, J.F.; et al. Bioengineered Kidney Tubules Efficiently Excrete Uremic Toxins. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Watanabe, H.; Noguchi, T.; Kotani, S.; Nakajima, M.; Kadowaki, D.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Organic Anion Transporters Play an Important Role in the Uptake of P-Cresyl Sulfate, a Uremic Toxin, in the Kidney. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 2498–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsaers, H.A.M.; Wilmer, M.J.G.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Masereeuw, R. Basolateral Transport of the Uraemic Toxin P-Cresyl Sulfate: Role for Organic Anion Transporters? Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Sugimoto, R.; Kaneko, K.; Iwata, H.; Kotani, S.; Nakajima, M.; Ishima, Y.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Human Organic Anion Transporters Function as a High-Capacity Transporter for p-Cresyl Sulfate, a Uremic Toxin. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2014, 18, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, C.; Mernissi, T.; Choukroun, G.; Bennis, Y.; Kamel, S.; Liabeuf, S.; Bodeau, S. The Prescription of Drugs That Inhibit Organic Anion Transporters 1 or 3 Is Associated with the Plasma Accumulation of Uremic Toxins in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Toxins 2021, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutsaers, H.A.M.; Caetano-Pinto, P.; Seegers, A.E.M.; Dankers, A.C.A.; Van Den Broek, P.H.H.; Wetzels, J.F.M.; Van Den Brand, J.A.J.G.; Van Den Heuvel, L.P.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Wilmer, M.J.G.; et al. Proximal Tubular Efflux Transporters Involved in Renal Excretion of P-Cresyl Sulfate and p-Cresyl Glucuronide: Implications for Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology. Toxicol. In Vitro 2015, 29, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Extensive Impact of Non-Antibiotic Drugs on Human Gut Bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.; Goemans, C.V.; Wirbel, J.; Kuhn, M.; Eberl, C.; Pruteanu, M.; Müller, P.; Garcia-Santamarina, S.; Cacace, E.; Zhang, B.; et al. Unravelling the Collateral Damage of Antibiotics on Gut Bacteria. Nature 2021, 599, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beker, B.M.; Colombo, I.; Gonzalez-Torres, H.; Musso, C.G. Decreasing Microbiota-Derived Uremic Toxins to Improve CKD Outcomes. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 2214–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, N.; Jeong, H.; Kwon, D.; Kim, J.; Moon, Y. Antibiotic Exposure Aggravates Bacteroides-Linked Uremic Toxicity in the Gut-Kidney Axis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 737536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, T.; Takadate, A.; Otagiri, M. Characterization of Binding Site of Uremic Toxins on Human Serum Albumin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P.; Ho, C.-H.; Henrie, M.; Stroup, E.; Handelman, G. Improved Dialytic Removal of Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins with Use of Albumin Binding Competitors: An in Vitro Human Whole Blood Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, F. Effect of Ionic Strength, pH and Chemical Displacers on the Percentage Protein Binding of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Blood Purif. 2019, 47, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihaila, S.M.; Faria, J.; Stefens, M.F.J.; Stamatialis, D.; Verhaar, M.C.; Gerritsen, K.G.F.; Masereeuw, R. Drugs Commonly Applied to Kidney Patients May Compromise Renal Tubular Uremic Toxins Excretion. Toxins 2020, 12, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2012, 379, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laville, S.M.; Metzger, M.; Stengel, B.; Jacquelinet, C.; Combe, C.; Fouque, D.; Laville, M.; Frimat, L.; Ayav, C.; Speyer, E.; et al. Evaluation of the Adequacy of Drug Prescriptions in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: Results from the CKD-REIN Cohort. Brit. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 84, 2811–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-J.; Chien, M.-H.; Yang, M.-J.; Lin, M.-H.; Hsu, C.-C.; Chu, P.-L. Trends of Medication Used in Patients with Pre-ESKD from 2010 to 2018 in Taiwan. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2022, 121, S30–S38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Sun, A.; Wu, F.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, Z. Trends in Using of Antihypertensive Medication among US CKD Adults, NHANES 2001–2018. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 990997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, J.T.; Chang, T.I.; Yoo, T.-H.; Park, S.K.; Lee, K.B.; Jung, J.Y.; Jeong, J.C.; Oh, K.-H.; et al. Association between Progression of Coronary Artery Calcification and Development of Kidney Failure with Replacement Therapy: Findings from KNOW-CKD Study. Atherosclerosis 2024, 395, 117563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, I.M.; Hübner, S.; Nadal, J.; Titze, S.; Schmid, M.; Bärthlein, B.; Schlieper, G.; Dienemann, T.; Schultheiss, U.T.; Meiselbach, H.; et al. Patterns of Medication Use and the Burden of Polypharmacy in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: The German Chronic Kidney Disease Study. Clin. Kidney J. 2019, 12, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Zhao, J.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, H. Proton Pump Inhibitor-Induced Risk of Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Increase of Indoxyl Sulfate Synthesis via Inhibition of CYP2E1 Protein Degradation. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2022, 368, 110219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.-P.; Sweet, D.H.; Peng, Y.-H.; Hsieh, Y.-W.; Chao, P.-D.L.; Hou, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-P. Effects of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs on the Renal Excretion of Indoxyl Sulfate, a Nephro-Cardiovascular Toxin, in Rats. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 101, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.-S.; Yu, C.-P.; Hsieh, Y.-W.; Chao, P.-D.L.; Sweet, D.H.; Hou, Y.-C.; Lin, S.-P. Effects of Antibiotics on the Pharmacokinetics of Indoxyl Sulfate, a Nephro-Cardiovascular Toxin. Xenobiotica 2020, 50, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Ishihara, K.; Yasuda, S.; Nakamura, T.; Maeda, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Sahashi, K.; Ikeda, Y.; Kumagai, Y.; Majima, M. In Vivo Kinetics of Indoxyl Sulfate in Humans and Its Renal Interaction with Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitor Quinapril in Rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 626–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, J.C.; Richelle, A.; Gutierrez, J.M.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.; Bhatnagar, V.; Lewis, N.E.; Nigam, S.K. Coordinate Regulation of Systemic and Kidney Tryptophan Metabolism by the Drug Transporters OAT1 and OAT3. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narumi, K.; Sato, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Furugen, A.; Kasashi, K.; Yamada, T.; Teshima, T.; Iseki, K. Effects of Proton Pump Inhibitors and Famotidine on Elimination of Plasma Methotrexate: Evaluation of Drug–Drug Interactions Mediated by Organic Anion Transporter 3. Biopharm. Drug Disp. 2017, 38, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioukh, R.; Noel-Hudson, M.-S.; Ribes, S.; Fournier, N.; Becquemont, L.; Verstuyft, C. Proton Pump Inhibitors Inhibit Methotrexate Transport by Renal Basolateral Organic Anion Transporter hOAT3. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaler, G.; Truong, D.M.; Khandelwal, A.; Nagle, M.; Eraly, S.A.; Swaan, P.W.; Nigam, S.K. Structural Variation Governs Substrate Specificity for Organic Anion Transporter (OAT) Homologs. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23841–23853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, E.; Takeda, M.; Narikawa, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Cha, S.H.; Sekine, T.; Sakthisekaran, D.; Endou, H. Human Organic Anion Transporters Mediate the Transport of Tetracycline. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 88, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, Y.; Kamiie, J.; Ohtsuki, S.; Terasaki, T. Multichannel Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry Cocktail Method for Comprehensive Substrate Characterization of Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 4 Transporter. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 2281–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, M.; Babu, E.; Narikawa, S.; Endou, H. Interaction of Human Organic Anion Transporters with Various Cephalosporin Antibiotics. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 438, 137–142, Erratum in Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 450, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- VanWert, A.L.; Sweet, D.H. Impaired Clearance of Methotrexate in Organic Anion Transporter 3 (Slc22a8) Knockout Mice: A Gender Specific Impact of Reduced Folates. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, G.; Cihlar, T.; Oo, C.; Ho, E.S.; Prior, K.; Wiltshire, H.; Barrett, J.; Liu, B.; Ward, P. The Anti-Influenza Drug Oseltamivir Exhibits Low Potential to Induce Pharmacokinetic Drug Interactions via Renal Secretion—Correlation of in Vivo and in Vitro Studies. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2002, 30, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueo, H.; Motohashi, H.; Katsura, T.; Inui, K. Human Organic Anion Transporter hOAT3 Is a Potent Transporter of Cephalosporin Antibiotics, in Comparison with hOAT1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1104–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.Y.; Takeda, M.; Kim, D.K.; Tojo, A.; Narikawa, S.; Yoo, B.S.; Hosoyamada, M.; Cha, S.H.; Sekine, T.; Endou, H. Characterization of Ochratoxin A Transport by Human Organic Anion Transporters. Life Sci. 2001, 69, 2123–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Terada, T.; Ogasawara, K.; Katsura, T.; Inui, K. Adaptive Responses of Renal Organic Anion Transporter 3 (OAT3) during Cholestasis. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2008, 295, F247–F252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, T.; Sugiyama, D.; Kamiyama, E.; Tokui, T.; Hirota, T.; Ikeda, T. Characterization of CS-023 (RO4908463), a Novel Parenteral Carbapenem Antibiotic, and Meropenem as Substrates of Human Renal Transporters. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2007, 22, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kusuhara, H.; Endou, H.; Sugiyama, Y. Contribution of Organic Anion Transporters to the Renal Uptake of Anionic Compounds and Nucleoside Derivatives in Rat. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 305, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Feng, B.; Yu, Y.; Chupka, J.; Zheng, J.Y.; Heath, T.G.; Bond, B.R. Renal Organic Anion Transporter-Mediated Drug-Drug Interaction between Gemcabene and Quinapril. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, M.; Mochizuki, T.; Takekuma, Y.; Miyazaki, K. Structure–Affinity Relationship in the Interactions of Human Organic Anion Transporter 1 with Caffeine, Theophylline, Theobromine and Their Metabolites. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2005, 1714, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueo, H.; Motohashi, H.; Katsura, T.; Inui, K. Cl−-Dependent Upregulation of Human Organic Anion Transporters: Different Effects on Transport Kinetics between hOAT1 and hOAT3. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2007, 293, F391–F397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ohshiro, N.; Tsuchiya, A.; Kohyama, N.; Ohbayashi, M.; Yamamoto, T. Renal transport of organic compounds mediated by mouse organic anion transporter 3 (mOat3): Further substrate specificity of mOat3. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.-Y.; Bleasby, K.; Yabut, J.; Cai, X.; Chan, G.H.; Hafey, M.J.; Xu, S.; Bergman, A.J.; Braun, M.P.; Dean, D.C.; et al. Transport of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Sitagliptin by Human Organic Anion Transporter 3, Organic Anion Transporting Polypeptide 4C1, and Multidrug Resistance P-Glycoprotein. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 321, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, M.; Iwanaga, T.; Mamada, H.; Ogihara, T.; Yabuuchi, H.; Maeda, T.; Tamai, I. Involvement of Uric Acid Transporters in Alteration of Serum Uric Acid Level by Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, A.; Maeda, K.; Kamiyama, E.; Sugiyama, D.; Kondo, T.; Shiroyanagi, Y.; Nakazawa, H.; Okano, T.; Adachi, M.; Schuetz, J.D.; et al. Multiple Human Isoforms of Drug Transporters Contribute to the Hepatic and Renal Transport of Olmesartan, a Selective Antagonist of the Angiotensin II AT1-Receptor. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2007, 35, 2166–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuze, K.; Graves, P.; Leahy, A.; Wilson, P.; Stuhlmann, H.; You, G. Heterologous Expression and Functional Characterization of a Mouse Renal Organic Anion Transporter in Mammalian Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1519–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sato, M.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Mamada, H.; Fukushi, A.; Mikami, K.; Shirasaka, Y.; Tamai, I. Effects of Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers on Renal Handling of Uric Acid in Rats. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2008, 23, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Lai, L.; Yeo, H.C.; Goh, B.C.; Tan, T.M.C. Multidrug Resistance Protein 4 (MRP4/ABCC4) Mediates Efflux of Bimane-Glutathione. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Race, J.E.; Grassl, S.M.; Williams, W.J.; Holtzman, E.J. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of Two Novel Human Renal Organic Anion Transporters (hOAT1 and hOAT3). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 255, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasannejad, H.; Takeda, M.; Taki, K.; Shin, H.J.; Babu, E.; Jutabha, P.; Khamdang, S.; Aleboyeh, M.; Onozato, M.L.; Tojo, A.; et al. Interactions of Human Organic Anion Transporters with Diuretics. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuhara, H.; Sekine, T.; Utsunomiya-Tate, N.; Tsuda, M.; Kojima, R.; Cha, S.H.; Sugiyama, Y.; Kanai, Y.; Endou, H. Molecular Cloning and Characterization of a New Multispecific Organic Anion Transporter from Rat Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 13675–13680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Ohbayashi, M.; Kohyama, N.; Yamamoto, T. Mouse Organic Anion Transporter 2 and 3 (mOAT2/3[Slc22a7/8]) Mediates the Renal Transport of Bumetanide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 524, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagos, Y.; Bahn, A.; Vormfelde, S.V.; Brockmöller, J.; Burckhardt, G. Torasemide Transport by Organic Anion Transporters Contributes to Hyperuricemia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 3101–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahn, A.; Ebbinghaus, C.; Ebbinghaus, D.; Ponimaskin, E.G.; Fuzesï, L.; Burckhardt, G.; Hagos, Y. Expression studies and functional characterization of renal human organic anion transporter 1 isoforms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kusuhara, H.; Adachi, M.; Schuetz, J.D.; Takeuchi, K.; Sugiyama, Y. Multidrug Resistance–Associated Protein 4 Is Involved in the Urinary Excretion of Hydrochlorothiazide and Furosemide. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoyamada, M.; Sekine, T.; Kanai, Y.; Endou, H. Molecular Cloning and Functional Expression of a Multispecific Organic Anion Transporter from Human Kidney. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 1999, 276, F122–F128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakos, E.V.; Evers, R.; Sinko, E.; Radi, A.S.V.; Borst, P.; Sarkadi, B.Z. Interactions of the Human Multidrug Resistance Proteins MRP1 and MRP2 with Organic Anions. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, M.; Noshiro, R.; Onozato, M.L.; Tojo, A.; Hasannejad, H.; Huang, X.-L.; Narikawa, S.; Endou, H. Evidence for a Role of Human Organic Anion Transporters in the Muscular Side Effects of HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 483, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windass, A.S.; Lowes, S.; Wang, Y.; Brown, C.D.A. The Contribution of Organic Anion Transporters OAT1 and OAT3 to the Renal Uptake of Rosuvastatin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 1221–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamdang, S.; Takeda, M.; Shimoda, M.; Noshiro, R.; Narikawa, S.; Huang, X.-L.; Enomoto, A.; Piyachaturawat, P.; Endou, H. Interactions of Human- and Rat-Organic Anion Transporters With Pravastatin and Cimetidine. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 94, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kusuhara, H.; Sugiyama, D.; Ito, K.; Ueda, S.; Endou, H.; Sugiyama, Y. Functional Involvement of Rat Organic Anion Transporter 3 (rOat3;Slc22a8) in the Renal Uptake of Organic Anions. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2002, 300, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagomi-Hagihara, R.; Nakai, D.; Tokui, T. Inhibition of Human Organic Anion Transporter 3 Mediated Pravastatin Transport by Gemfibrozil and the Metabolites in Humans. Xenobiotica 2007, 37, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivistö, K.T.; Grisk, O.; Hofmann, U.; Meissner, K.; Möritz, K.-U.; Ritter, C.; Arnold, K.A.; Lutjöohann, D.; Von Bergmann, K.; Klöting, I.; et al. Disposition of oral and intravenous pravastatin in MRP2-deficient TR–rats. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2005, 33, 1593–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, S.; Kikkawa, T.; Mori, S.; Hori, S.; Takanaga, H.; Otagiri, M.; Terasaki, T. Mouse Reduced in Osteosclerosis Transporter Functions as an Organic Anion Transporter 3 and Is Localized at Abluminal Membrane of Blood-Brain Barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 309, 1273–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uwai, Y.; Saito, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Inui, K. Inhibitory Effect of Anti-Diabetic Agents on Rat Organic Anion Transporter rOAT1. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 398, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedeon, C.; Behravan, J.; Koren, G.; Piquette-Miller, M. Transport of Glyburide by Placental ABC Transporters: Implications in Fetal Drug Exposure. Placenta 2006, 27, 1096–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Therapeutics Class | Examples | References |
|---|---|---|
| Antianemics | Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (EPO) | [100] |
| Anti-GERD agents | Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) | [99] |
| Anticoagulants | Clopidogrel | [100,102] |
| Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) | [100] | |
| Vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) | [99,100] | |
| Antidiabetics | Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors | [100] |
| Glinides | [100] | |
| Insulin | [99,100] | |
| Metformin | [100] | |
| Sulfonylureas | [100] | |
| Antigout agents | Allopurinol | [99,103] |
| Antihypertensives | Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors | [99,100,101,102,103] |
| Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) | [99,100,101,102] | |
| Beta blockers | [99,100,101,103] | |
| Calcium channel blockers | [99,100,101,102] | |
| Diuretics | [99,100,101,102,103] | |
| CKD-MBD medications | Vitamin D | [99,103] |
| Lipid-lowering agents | Statins | [99,100,102,103] |
| Therapeutic Classes | Molecule | Observed Interactions with IS and PCS | Experimental System (Cell Line/Animal Model) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-GERD | Cimetidine | OAT3 inhibition, increasing central concentrations of IS | In vivo (rat) | [63] |
| Lansoprazole, omeprazole | OAT1 and OAT3-mediated IS transport inhibition | In vitro (MDCK-hOAT1/HEK293-hOAT3) | [104] | |
| [104] | ||||
| Anti-inflammatory agents | Diclofenac | OAT1 and OAT3 inhibition, increasing mean residence time of IS while decreasing its renal clearance | In vitro (CHO-hOAT1/HEK293-hOAT3) In vivo (rat) | [105] |
| Ketoprofen | In vitro (CHO-hOAT1/HEK293-hOAT3/ OAT3-oocytes) In vivo (rat) | [63,105] | ||
| Antibiotics | Benzylpenicillin | OAT3 inhibition, increasing central and systemic concentrations of IS or PCS | In vivo (rat) | [63,85] |
| Cefazolin | OAT3-mediated transport inhibition of IS | In vitro (OAT3-oocytes) | [63] | |
| Ciprofloxacin | OAT3 inhibition, increasing area under curve and t1/2 of IS while decreasing its renal clearance | In vitro (HEK293-OAT3) In vivo (rat) | [106] | |
| Antigout agents | Febuxostat | BCRP inhibition, inducing IS accumulation in the renal tubule | In vivo (rat) | [74] |
| Probenecid | OAT1, OAT3 and OAT4 inhibition, increasing plasmatic concentrations of IS and PCS | In vivo (mouse/rat/human) In vitro (HUVEC, HK-2, S2-cells, HEK293-OAT1/ HEK293-OAT3) Ex vivo (Bioengineered kidney tubules) | [59,63,73,74,76,77,84,85,87,107,108] | |
| Antihypertensives | Quinalapril | OAT3-mediated transport inhibition, increasing IS serum concentrations | In vivo (rat) | [107] |
| Antiviral | Acyclovir | OAT3-mediated transport inhibition of IS | In vitro (OAT3-oocytes) | [63] |
| Lipid-lowering agents | Pravastatin | OAT1, OAT3 and OAT4-mediated transport inhibition of IS | In vitro (S2-cells) | [76] |
| Family/Therapeutic Class | Molecule | Inhibitor/Substrate | Transporter | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-GERD (PPIs) | Esomeprazole, rabeprazole | Inhibitor | OAT3 | [109] |
| Lansoprazole, omeprazole, pantoprazole | OAT1, OAT3 | [109,110] | ||
| Antibiotics (β-lactams, fluoroquinolones, tetracyclines) | Cloxacillin, doxycycline, minocycline, nafcillin, oxytetracycline, piperacillin, tetracycline | Inhibitor | OAT1 | [111,112,113] |
| Cefalotin, ciprofloxacin | OAT3 | [114,115] | ||
| Cefamandole | OAT1, OAT3 | [114] | ||
| Amoxicillin, ceftibuten | Substrate | OAT1 | [116,117] | |
| Cefaclor, cefdinir, cefoselis | OAT3 | [117] | ||
| Cefazoline, cefotiam, ceftizoxime, meropenem | OAT1, OAT3 | [114,117,118,119,120] | ||
| Tetracycline | OAT1, OAT3, OAT4 | [112,113] | ||
| Ampicilline, ceftazidime, piperacillin, tetracycline | MRP4 | [111,112,113] | ||
| Antihypertensive (ACE inhibitors, ARBs, calcium channel blockers) | Captopril | Inhibitor | OAT1 | [121,122,123,124,125,126] |
| Olmesartan | OAT3 | [127,128] | ||
| Candesartan, enalapril, losartan, pratosartan, telmisartan, valsartan | OAT1, OAT3 | [97,122,123,125,126,127,129,130] | ||
| Verapamil | MRP4 | [131] | ||
| Captopril, olmesartan, quinalapril | Substrate | OAT1, OAT3 | [113,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128] | |
| Alacepril, enalapril | MRP4 | [113,122,123,125,126,129] | ||
| Diuretics (loop diuretics, thiazide-like diuretics) | Bumetanide, chlorothiazide, cyclothiazide, trichloromethiazide | Inhibitor | OAT1, OAT3 | [113,132,133,134,135,136,137] |
| Hydrochlorothiazide | OAT1, OAT3, OAT4 | [113,126,133,136,138] | ||
| Furosemide | OAT1, OAT3, OAT4, MRP2 | [97,113,126,133,134,136,137,138,139,140] | ||
| Hydrochlorothiazide | Substrate | OAT1, MRP4 | [113,126,133,136,138] | |
| Furosemide | OAT1, OAT3, MRP4 | [97,113,126,133,134,136,137,138,139,140] | ||
| Bumetanide | OAT1, OAT3, OAT4, MRP4 | [113,132,133,134,135,136,137] | ||
| Lipid lowering agents (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, fibrates) | Atorvastatin, gemfibrozil, rosuvastatine | Inhibitor | OAT3 | [141,142,143,144,145] |
| Fluvastatin, simvastatin | OAT1, OAT3 | [141,142,143] | ||
| Pravastatin | OAT1, OAT3, OAT4 | [76,113,141,142,143,144,146,147] | ||
| Rosuvastatine | Substrate | OAT3 | [141,142,143,144] | |
| Lipid lowering agents (HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, fibrates) | Pravastatin | Substrate | OAT3, MRP2, MRP4 | [76,113,141,142,143,144,146,147] |
| Bezafibrate | MRP4 | [113] | ||
| Oral antidiabetics (sulfonylureas, glinides) | Chlorpropamide, nateglinide, tolbutamide | Inhibitor | OAT1 | [148] |
| Glibenclamide | OAT1, MRP2 | [148,149] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spicher, P.; Brazier, F.; Laville, S.M.; Liabeuf, S.; Kamel, S.; Culot, M.; Bodeau, S. Transporter-Mediated Interactions Between Uremic Toxins and Drugs: A Hidden Driver of Toxicity in Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136328
Spicher P, Brazier F, Laville SM, Liabeuf S, Kamel S, Culot M, Bodeau S. Transporter-Mediated Interactions Between Uremic Toxins and Drugs: A Hidden Driver of Toxicity in Chronic Kidney Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136328
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpicher, Pierre, François Brazier, Solène M. Laville, Sophie Liabeuf, Saïd Kamel, Maxime Culot, and Sandra Bodeau. 2025. "Transporter-Mediated Interactions Between Uremic Toxins and Drugs: A Hidden Driver of Toxicity in Chronic Kidney Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136328
APA StyleSpicher, P., Brazier, F., Laville, S. M., Liabeuf, S., Kamel, S., Culot, M., & Bodeau, S. (2025). Transporter-Mediated Interactions Between Uremic Toxins and Drugs: A Hidden Driver of Toxicity in Chronic Kidney Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136328







