PROM1 and EFTUD2 Expression in High-Grade Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma as a Molecular Marker for Survival Rate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Protein Expression Values in CPTAC ccRCC
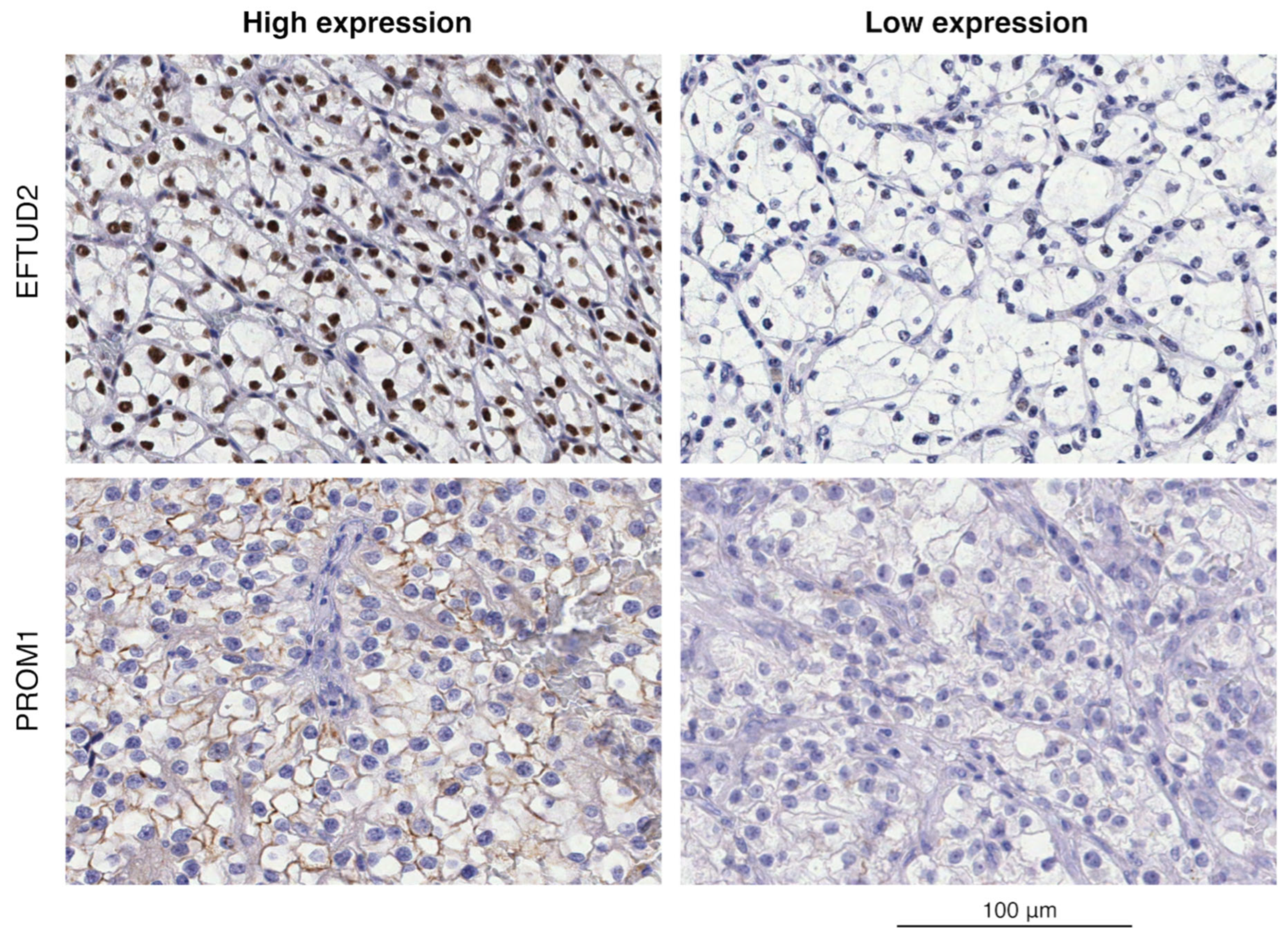
2.2. Immunohistochemical Analysis of EFTUD2 and PROM1
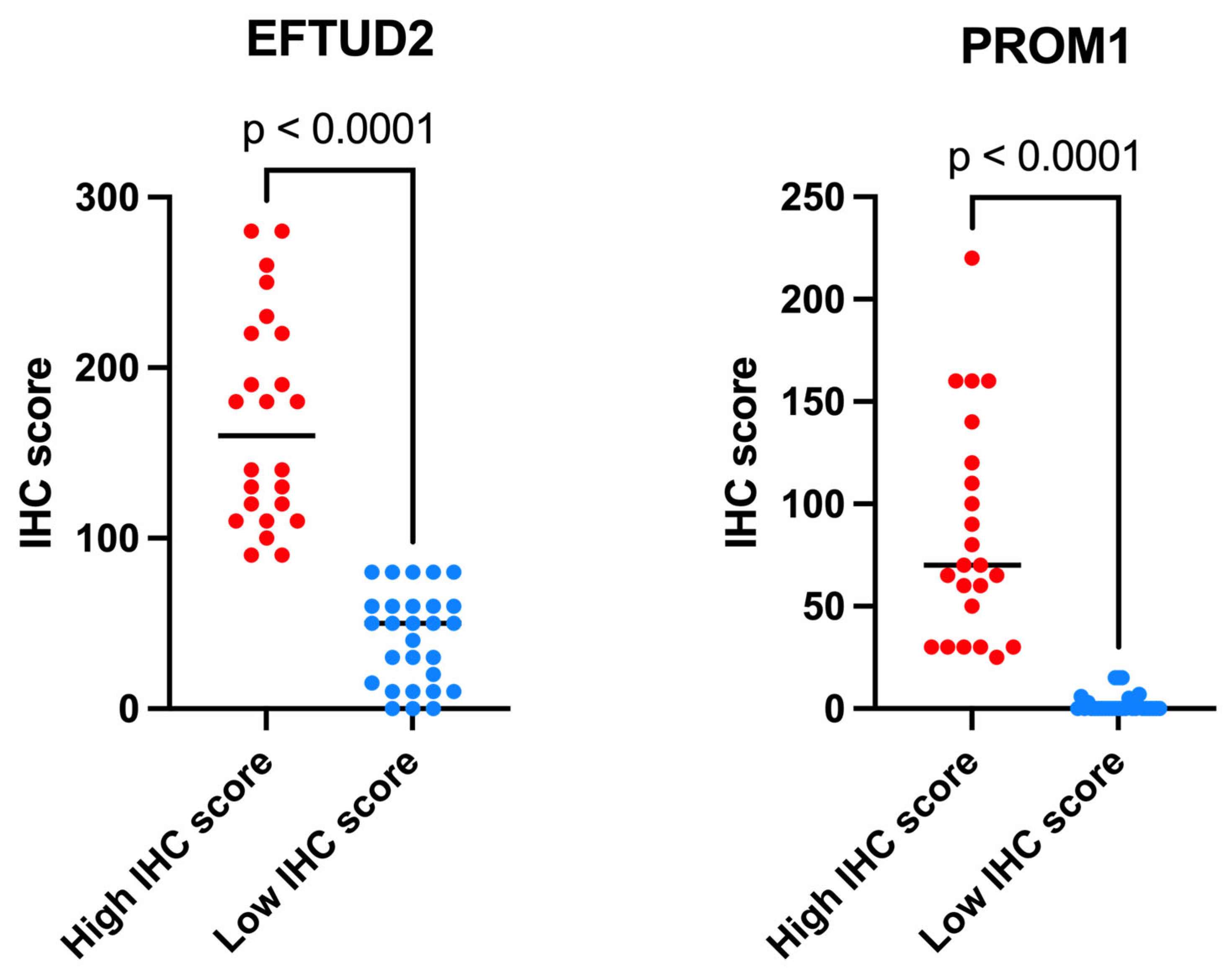
2.3. EFTUD2 and PROM1 Protein Expression as Measured by IHC
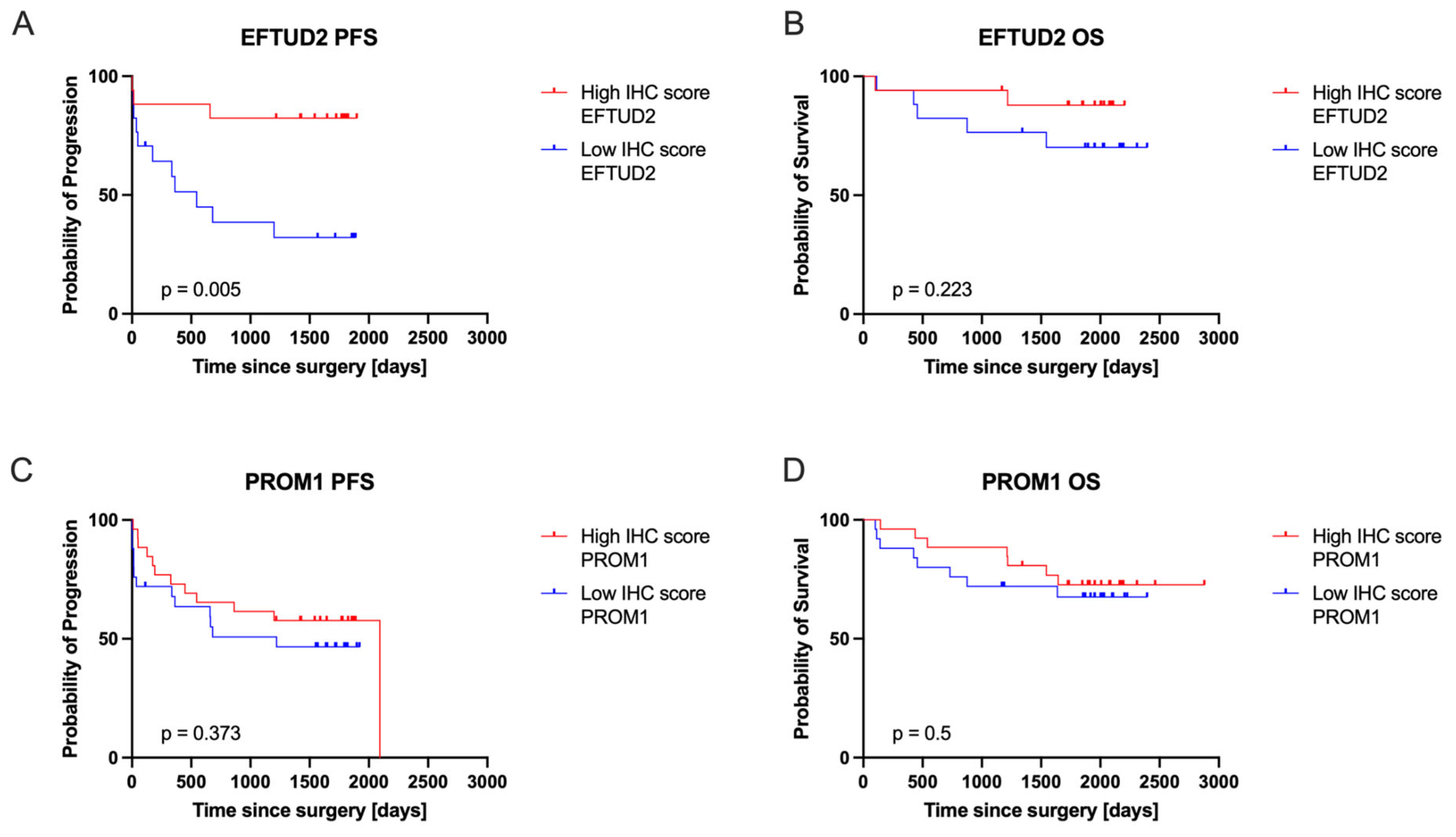
2.4. EFTUD2 and PROM1 Protein Expression Correlated with Patients’ Clinical Outcomes
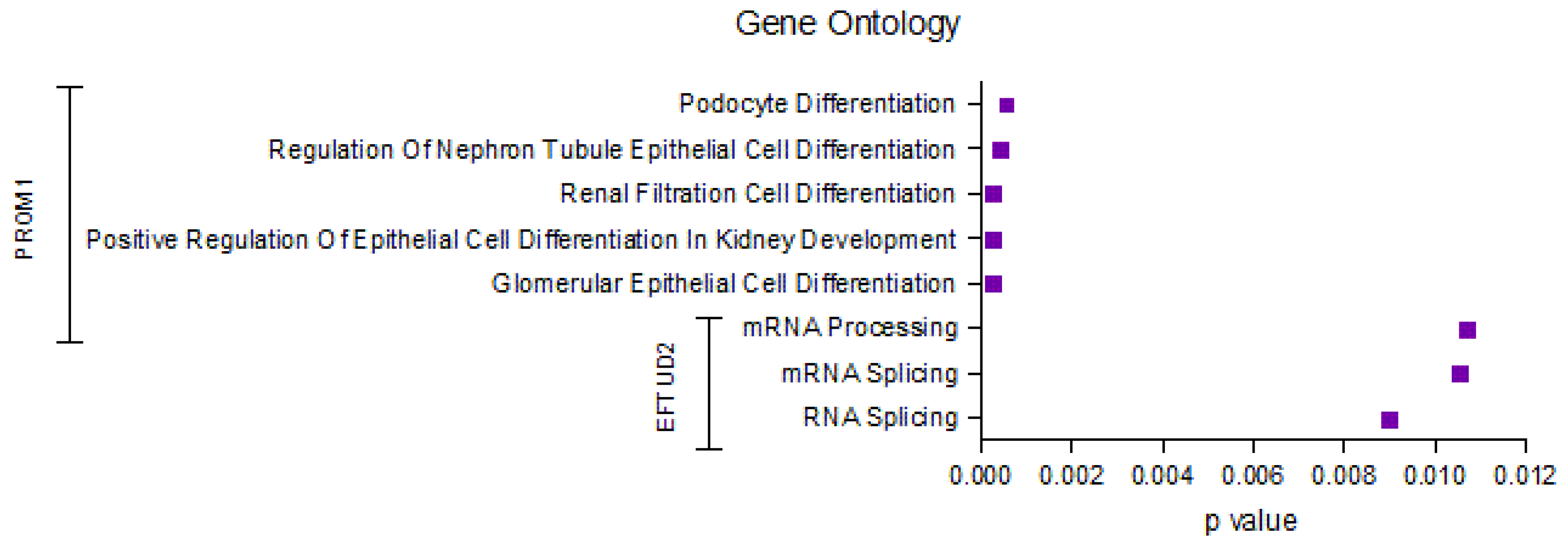
2.5. Identification of the Top Significantly Enriched Gene Ontologies Associated with EFTUD2 and PROM1
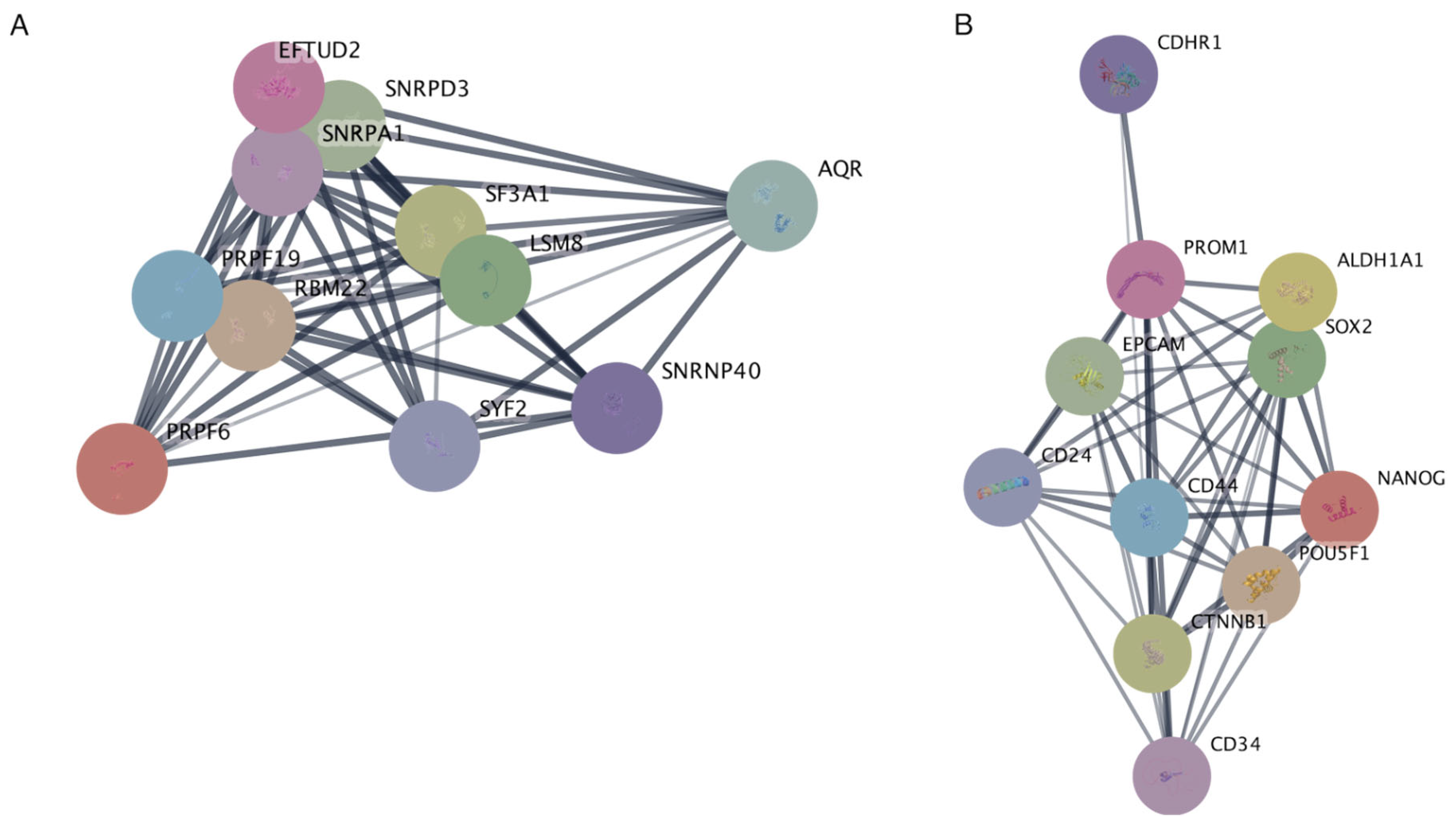
2.6. Protein–Protein Interaction Networks Reveal Key Associations of EFTUD2 and PROM1 at the Protein Level
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Cohorts
4.2. Immunohistochemistry and Pathology Evaluation
- Intensity 1 indicates weak staining;
- Intensity 2 indicates moderate staining;
- Intensity 3 indicates strong staining.
4.3. Digital Image Acquisition and Archiving
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. Gene Ontology Enrichment Analysis
4.6. Protein–Protein Interaction as Determined by String Database
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dyba, T.; Randi, G.; Bettio, M.; Gavin, A.; Visser, O.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 103, 356–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capitanio, U.; Bensalah, K.; Bex, A.; Boorjian, S.A.; Bray, F.; Coleman, J.; Gore, J.L.; Sun, M.; Wood, C.; Russo, P.; et al. Epidemiology of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2019, 75, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCastro, G.J.; McKiernan, J.M. Epidemiology, Clinical Staging, and Presentation of Renal Cell Carcinoma. Urol. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 35, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevrier, S.; Levine, J.H.; Zanotelli, V.R.T.; Silina, K.; Schulz, D.; Bacac, M.; Ries, C.H.; Ailles, L.; Jewett, M.A.S.; Moch, H.; et al. An Immune Atlas of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell 2017, 169, 736–749.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creighton, C.J.; Hernandez-Herrera, A.; Jacobsen, A.; Levine, D.A.; Mankoo, P.; Schultz, N.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Larsson, E.; Sheridan, R.; et al. Integrated analyses of microRNAs demonstrate their widespread influence on gene expression in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, W.H.; Dong, L.M.; Devesa, S.S. Epidemiology and risk factors for kidney cancer. Urology 2010, 7, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Brest, A.; Yu, M.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; Mariotto, A.; Lewis, D.R.; et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2016; National Cancer Institute: Rockville, MD, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Capitanio, U.; Montorsi, F. Renal cancer. Lancet 2016, 387, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achsel, T.; Ahrens, K.; Brahms, H.; Teigelkamp, S.; Lührmann, R. The Human U5-220kD Protein (hPrp8) Forms a Stable RNA-Free Complex with Several U5-Specific Proteins, Including an RNA Unwindase, a Homologue of Ribosomal Elongation Factor EF-2, and a Novel WD-40 Protein. Mol. Cell Biol. 1998, 18, 6756–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wood, K.A.; Eadsforth, M.A.; Newman, W.G.; O’Keefe, R.T. The Role of the U5 snRNP in Genetic Disorders and Cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 636620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, C.; Li, X.J.; Hao, L.X.; Zhang, S.; Song, Z.; Ji, X.D.; Gong, B. Over-activation of EFTUD2 correlates with tumor propagation and poor survival outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.; He, L.; You, Y.; Li, J.; Yao, N.; Qu, C.; Huang, W.; Xu, L.; Luo, R.; Hong, J. EFTUD2 maintains the survival of tumor cells and promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the activation of STAT3. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, G.; Wang, R.; Xiao, H.; Li, X.; Hou, C.; Feng, J.; et al. Spliceosome protein Eftud2 promotes colitis-associated tumorigenesis by modulating inflammatory response of macrophage. Mucosal Immunol 2019, 12, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigmann, A.; Corbeil, D.; Hellwig, A.; Huttner, W.B. Prominin, a novel microvilli-specific polytopic membrane protein of the apical surface of epithelial cells, is targeted to plasmalemmal protrusions of non-epithelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 12425–12430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röper, K.; Corbeil, D.; Huttner, W.B. Retention of prominin in microvilli reveals distinct cholesterol-based lipid micro-domains in the apical plasma membrane. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, Z.; Tunici, P.; Ng, H.; Abdulkadir, I.R.; Lu, L.; Irvin, D.; Black, K.L.; Yu, J.S. Analysis of gene expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer 2006, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florek, M.; Haase, M.; Marzesco, A.M.; Freund, D.; Ehninger, G.; Huttner, W.B.; Corbeil, D. Prominin-1/CD133, a neural and hematopoietic stem cell marker, is expressed in adult human differentiated cells and certain types of kidney cancer. Cell Tissue Res. 2005, 319, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Lombardi, D.G.; Pilozzi, E.; Biffoni, M.; Todaro, M.; Peschle, C.; De Maria, R. Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 2007, 445, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Li, J.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Yao, M.; Yan, M.; Jiang, G.; Ge, C.; Xie, H.; Wan, D.; et al. CD133 positive hepatocellular carcinoma cells possess high capacity for tumorigenicity. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 1444–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yuan, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, K.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X. Bioinformatics and functional analyses of key genes and pathways in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 9133–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alterio, C.; Cindolo, L.; Portella, L.; Polimeno, M.; Consales, C.; Riccio, A.; Cioffi, M.; Franco, R.; Chiodini, P.; Cartenì, G.; et al. Differential role of CD133 and CXCR4 in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 4492–4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sagrinati, C.; Netti, G.S.; Mazzinghi, B.; Lazzeri, E.; Liotta, F.; Frosali, F.; Ronconi, E.; Meini, C.; Gacci, M.; Squecco, R.; et al. Isolation and characterization of multipotent progenitor cells from the Bowman’s capsule of adult human kidneys. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2443–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronconi, E.; Sagrinati, C.; Angelotti, M.L.; Lazzeri, E.; Mazzinghi, B.; Ballerini, L.; Parente, E.; Becherucci, F.; Gacci, M.; Carini, M.; et al. Regeneration of glomerular podocytes by human renal progenitors. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussolati, B.; Bruno, S.; Grange, C.; Buttiglieri, S.; Deregibus, M.C.; Cantino, D.; Camussi, G. Isolation of Renal Progenitor Cells from Adult Human Kidney. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussolati, B.; Grange, C.; Collino, F.; Graziano, M.E.; Ferrando, U.; Camussi, G. CD133+ Renal Progenitor Cells Contribute to Tumor Angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 2223–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Ihm, H.; Ro, J.Y.; Cho, Y.M. High-level expression of stem cell marker CD133 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma with favorable prognosis. Oncol. Lett. 2011, 2, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, K.H.; Wong, T.L.; Zhang, Z.; Chan, C.H.; Loong, J.H.; Che, N.; Yu, H.J.; Tan, K.V.; Tong, M.; et al. Lineage tracing and single-cell analysis reveal proliferative Prom1+ tumour-propagating cells and their dynamic cellular transition during liver cancer progression. Gut 2022, 71, 1656–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dansonka-Mieszkowska, A.; Szafron, L.A.; Kulesza, M.; Stachurska, A.; Leszczynski, P.; Tomczyk-Szatkowska, A.; Sobiczewski, P.; Parada, J.; Kulinczak, M.; Moes-Sosnowska, J.; et al. PROM1, CXCL8, RUNX1, NAV1 and TP73 genes as independent markers predictive of prognosis or response to treatment in two cohorts of high-grade serous ovarian cancer patients. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.J.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Petralia, F.; Pan, J.; Song, X.; Hu, Y.; da Veiga Leprevost, F.; Reva, B.; Lih, T.-S.M.; Chang, H.-Y.; et al. Integrated Proteogenomic Characterization of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell 2019, 179, 964–983.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Varella-Garcia, M.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Di Maria, M.V.; Veve, R.; Bremmes, R.M.; Barón, A.E.; Zeng, C.; Franklin, W.A. Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas: Correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and impact on prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3798–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Bailey, A.; Kuleshov, M.V.; Clarke, D.J.B.; Evangelista, J.E.; Jenkins, S.L.; Lachmann, A.; Wojciechowicz, M.L.; Kropiwnicki, E.; Jagodnik, K.M.; et al. Gene Set Knowledge Discovery with Enrichr. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhou, H.; Bu, F.; Chen, J.; Mao, X.; He, Y.; et al. The feedback loop of EFTUD2/c-MYC impedes chemotherapeutic efficacy by enhancing EFTUD2 transcription and stabilizing c-MYC protein in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Suo, L.; Zhao, J.; Ma, R.; Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Qiao, J.; Wu, J.; An, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Prognostic biomarkers based on GUF1, EFTUD2 and GSPT1 targets affecting migration of gastric cancer cells. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 4827–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y. The construction and validation of an RNA binding protein-related prognostic model for bladder cancer. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chen, Y.; Luo, R.; Li, Z.; Jiang, G.; Ou, X. Identification of Biomarkers Related to Immune Cell Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Gene Co-Expression Network. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2021, 27, 601693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.G.; Shi, Z.D.; Dong, J.J.; Chen, Y.A.; Cao, M.Y.; Li, Y.T.; Ma, W.M.; Hao, L.; Pang, K.; Zhou, J.H.; et al. Novel potential urinary biomarkers for effective diagnosis and prognostic evaluation of high-grade bladder cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 2023, 12, 1992–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, S.; Müller, L.; Mitter, S.; Keilmann, L.; Meister, S.; Buschmann, C.; Kraus, F.; Topalov, N.E.; Czogalla, B.; Trillsch, F.; et al. High RIG-I and EFTUD2 expression predicts poor survival in endometrial cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 149, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Ni, W.; Qin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Huo, J.; Bian, L.; Zhou, A.; Li, J. A functional loop between YTH domain family protein YTHDF3 mediated m6A modification and phosphofructokinase PFKL in glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, N.; Maeda, M.; Sugiyama, M.; Ito, S.; Hyodo, T.; Masuda, A.; Tsunoda, N.; Kokuryo, T.; Hamaguchi, M.; Nagino, M.; et al. Inhibition of SNW1 association with spliceosomal proteins promotes apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, M.S.; Ko, Y.G. PROM1-mediated cell signal transduction in cancer stem cells and hepatocytes. BMB Rep. 2023, 56, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Costa, W.H.; Rocha, R.M.; da Cunha, I.W.; da Fonseca, F.P.; Guimaraes, G.C.; de Cassio Zequi, S. CD133 immunohistochemical expression predicts progression and cancer-related death in renal cell carcinoma. World J. Urol. 2012, 30, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, A.H.; Miraglia, S.; Zanjani, E.D.; Almeida-Porada, G.; Ogawa, M.; Leary, A.G.; Olweus, J.; Kearney, J.; Buck, D.W. AC133, a Novel Marker for Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Blood 1997, 90, 5002–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussolati, B.; Collino, F.; Camussi, G. CD133+ cells as a therapeutic target for kidney diseases. Expert. Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, H. A pan-cancer perspective analysis reveals the opposite prognostic significance of CD133 in lower grade glioma and papillary renal cell carcinoma. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.C.; Rajan, A.; Landers, S.; Kelley, S.; Bellizzi, A.M.; Lal, G.; Sugg, S.L.; Howe, J.R.; Chan, C.H.; Weigel, R.J. Expression of cancer stem cell markers in tall cell variant papillary thyroid cancer identifies a molecular profile predictive of recurrence in classic papillary thyroid cancer. Surgery 2022, 171, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeednejad Zanjani, L.; Madjd, Z.; Abolhasani, M.; Andersson, Y.; Rasti, A.; Shariftabrizi, A.; Asgari, M. Cytoplasmic expression of CD133 stemness marker is associated with tumor aggressiveness in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2017, 103, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasmim, M.; Bruno, S.; Azzi, S.; Gallerne, C.; Michel, J.G.; Chiabotto, G.; Lecoz, V.; Romei, C.; Spaggiari, G.M.; Pezzolo, A.; et al. Isolation and characterization of renal cancer stem cells from patient-derived xenografts. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 15507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Jiang, F.; Pan, C.; Pu, C.; Huang, H.; Li, G. Quantification of peripheral blood CD133 mRNA in identifying metastasis and in predicting recurrence of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2014, 32, 44.e9–44.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.R.; Wang, J.; Pacey, S.; Warren, A.Y.; Pober, J.S.; Al-Lamki, R.S. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-2 signaling pathways promote survival of cancer stem-like CD133+ cells in clear cell renal carcinoma. FASEB Bioadv. 2020, 2, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, I.; De Grossi, F.; Lai, G.; Oliveto, S.; Deroma, G.; Biffo, S.; Manfrini, N. CancerHubs: A systematic data mining and elaboration approach for identifying novel cancer-related protein interaction hubs. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 26, bbae635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.; Heng, D.Y.C.; Brugarolas, J.; Vaishampayan, U. Personalized Management of Advanced Kidney Cancer. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book 2018, 38, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saliby, R.M.; Saad, E.; Kashima, S.; Schoenfeld, D.A.; Braun, D.A. Update on Biomarkers in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2024, 44, e430734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laru, L.; Ronkainen, H.; Ohtonen, P.; Vaarala, M.H. The impact of metastasectomy on survival of patients with synchronous metastatic renal cell cancer in Finland: A nationwide study. Scand. J. Surg. 2024, 113, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriero, M.; Cacciatore, L.; Ochoa, M.; Mastroianni, R.; Tuderti, G.; Costantini, M.; Anceschi, U.; Misuraca, L.; Brassetti, A.; Guaglianone, S.; et al. The Impact of Metastasectomy on Survival Outcomes of Renal Cell Carcinoma: A 10-Year Single Center Experience. Cancers 2023, 15, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, R.; Takemura, K.; Urasaki, T.; Fujiwara, R.; Numao, N.; Yonese, J.; Miura, Y.; Yuasa, T. Prevailing challenges in personalized treatment for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A narrative review. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2025, 25, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibody | Source | Identifier | Clone | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-EFTUD2 | Atlas Antibodies | Cat# HPA022021, RRID:AB_1848032 | Polyclonal | 1:400 |
| Rabbit polyclonal anti-PROM1 | Atlas Antibodies | Cat# HPA004922, RRID:AB_1846238 | Polyclonal | 1:250 |
| Protein | H-Score Range—High IHC Score Group | H-Score Range—Low IHC Score Group | Reaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| EFTUD2 | 90–280, n = 24 | 10–80, n = 28 | Nuclear |
| PROM1 | 25–220, n = 24 | 0–15, n = 28 | Cytoplasmic, membranous |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kasperczak, M.; Kołodziejczak-Guglas, I.; Kasperczak, F.; Wiznerowicz, M.; Antczak, A. PROM1 and EFTUD2 Expression in High-Grade Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma as a Molecular Marker for Survival Rate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136296
Kasperczak M, Kołodziejczak-Guglas I, Kasperczak F, Wiznerowicz M, Antczak A. PROM1 and EFTUD2 Expression in High-Grade Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma as a Molecular Marker for Survival Rate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136296
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasperczak, Michał, Iga Kołodziejczak-Guglas, Filip Kasperczak, Maciej Wiznerowicz, and Andrzej Antczak. 2025. "PROM1 and EFTUD2 Expression in High-Grade Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma as a Molecular Marker for Survival Rate" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136296
APA StyleKasperczak, M., Kołodziejczak-Guglas, I., Kasperczak, F., Wiznerowicz, M., & Antczak, A. (2025). PROM1 and EFTUD2 Expression in High-Grade Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma as a Molecular Marker for Survival Rate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6296. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136296








