Integrated Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles Reveal Postmortem Biomarkers of Fatal Anaphylaxis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
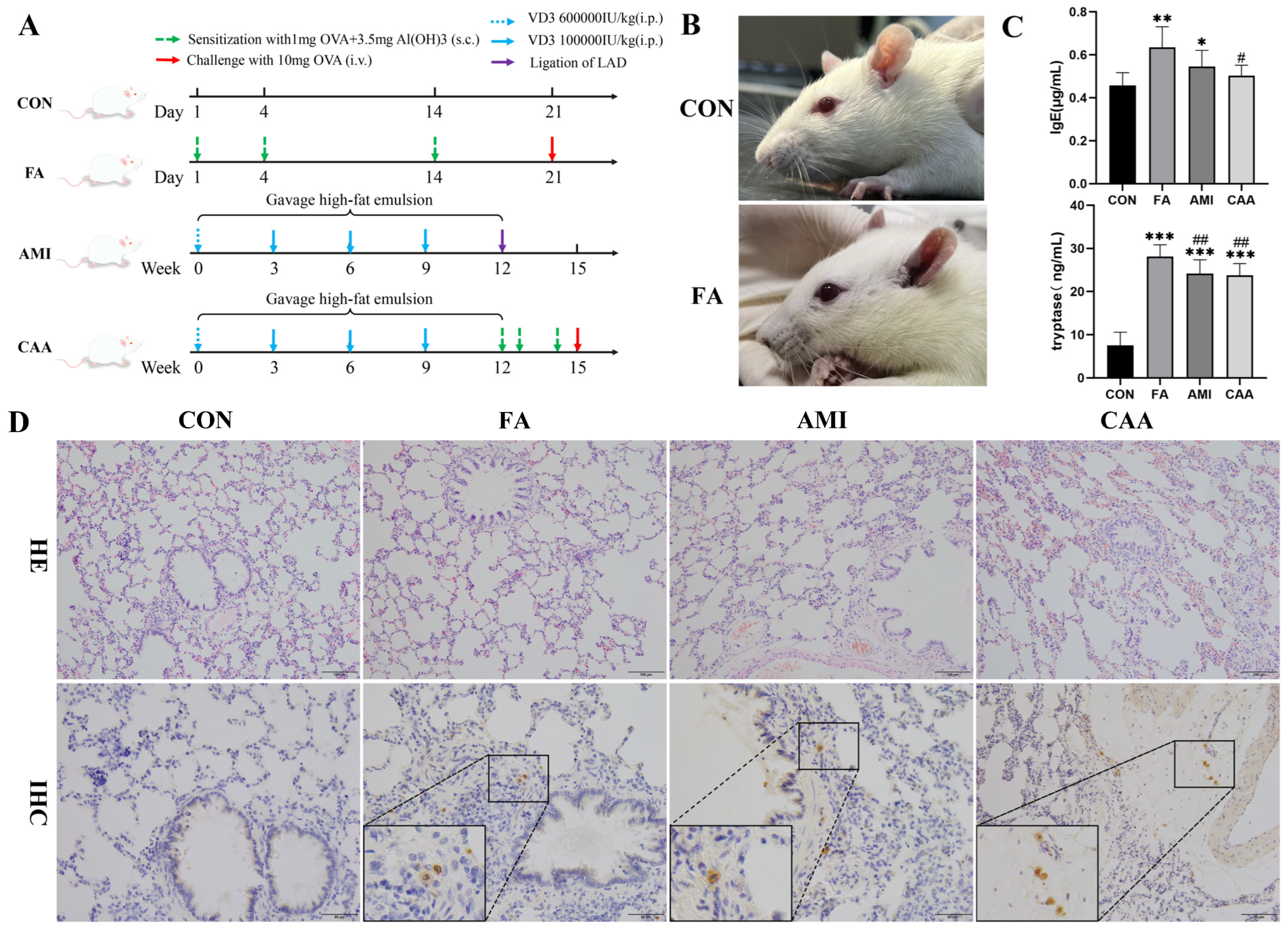
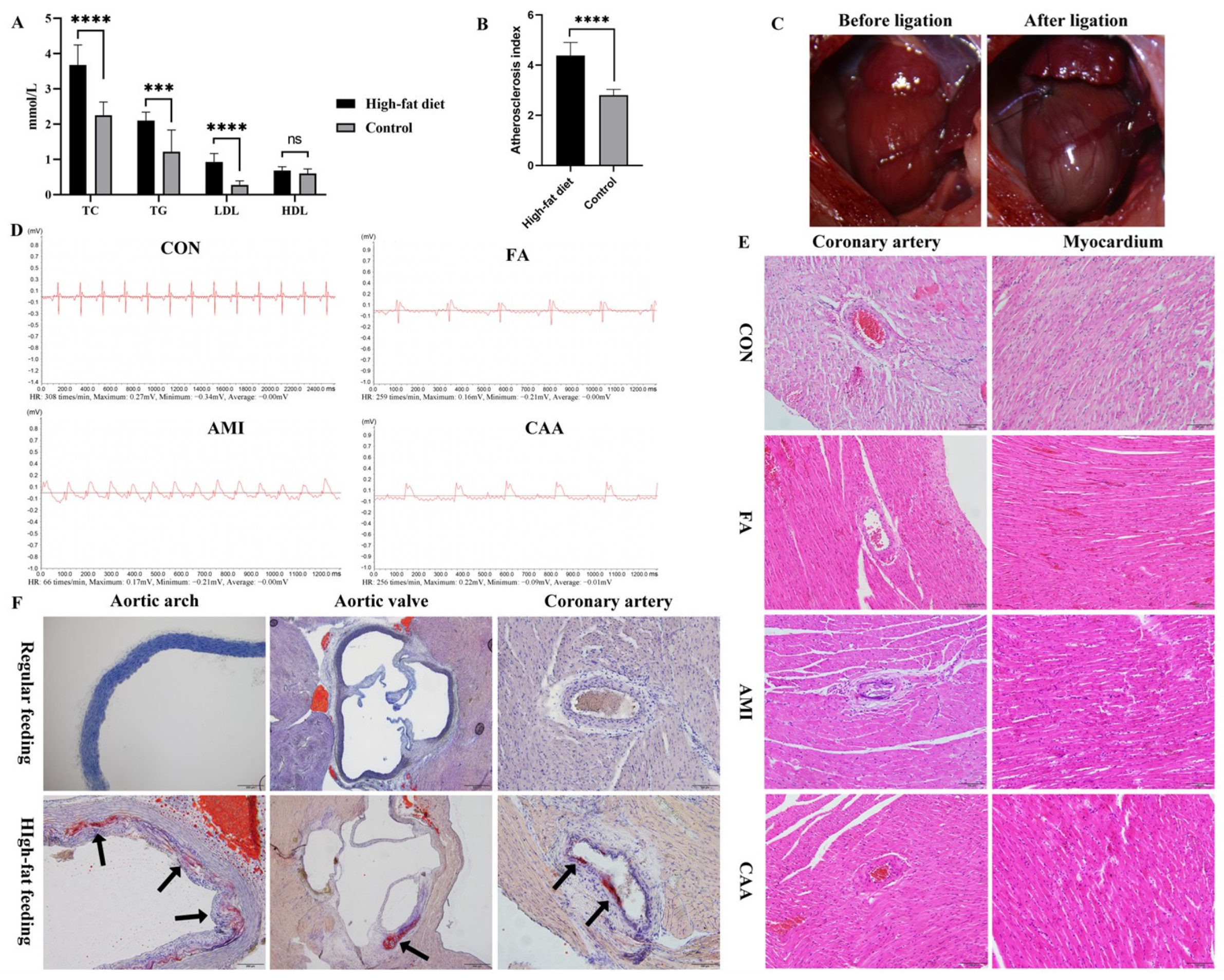
2.1. The Characteristics of Rat Models
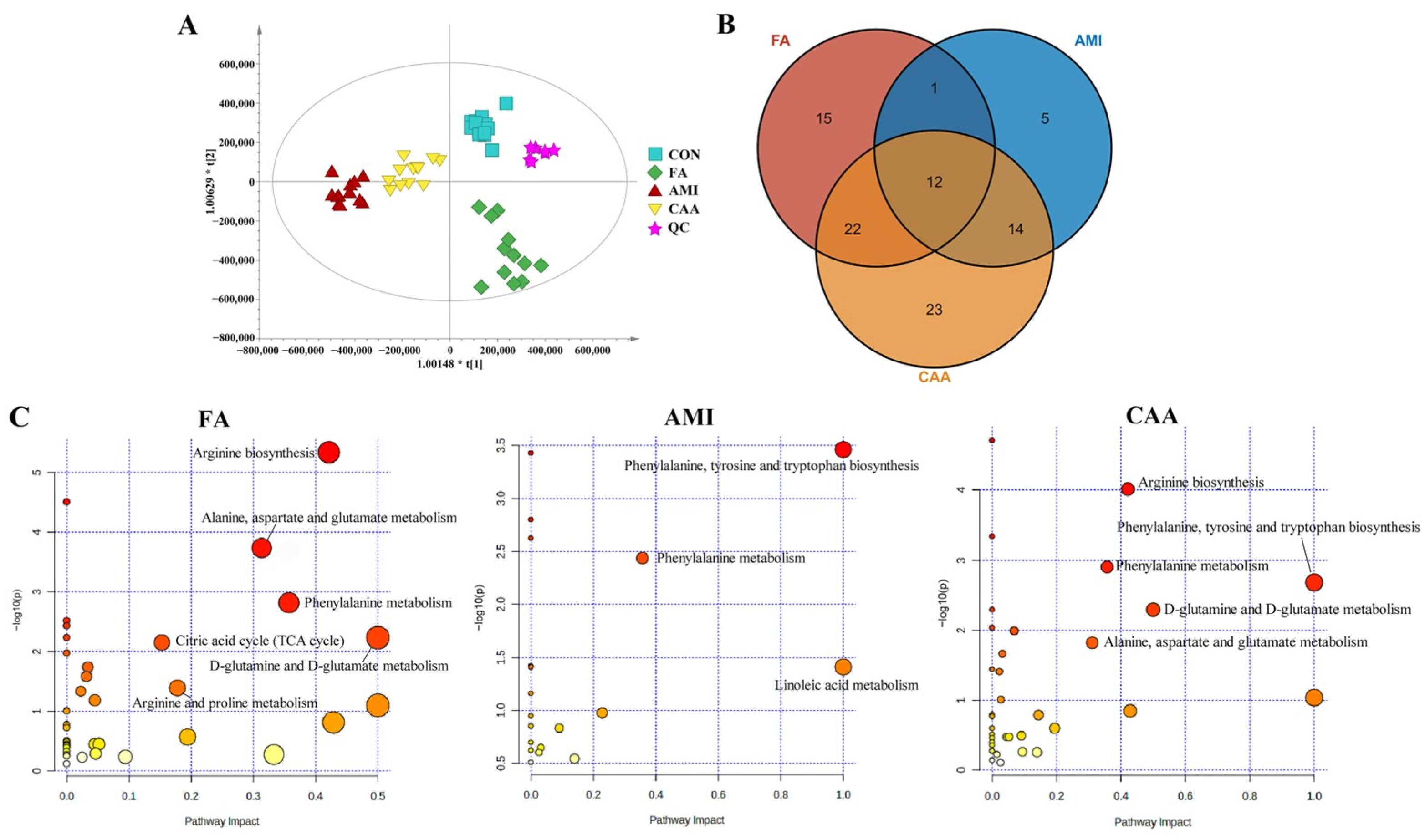
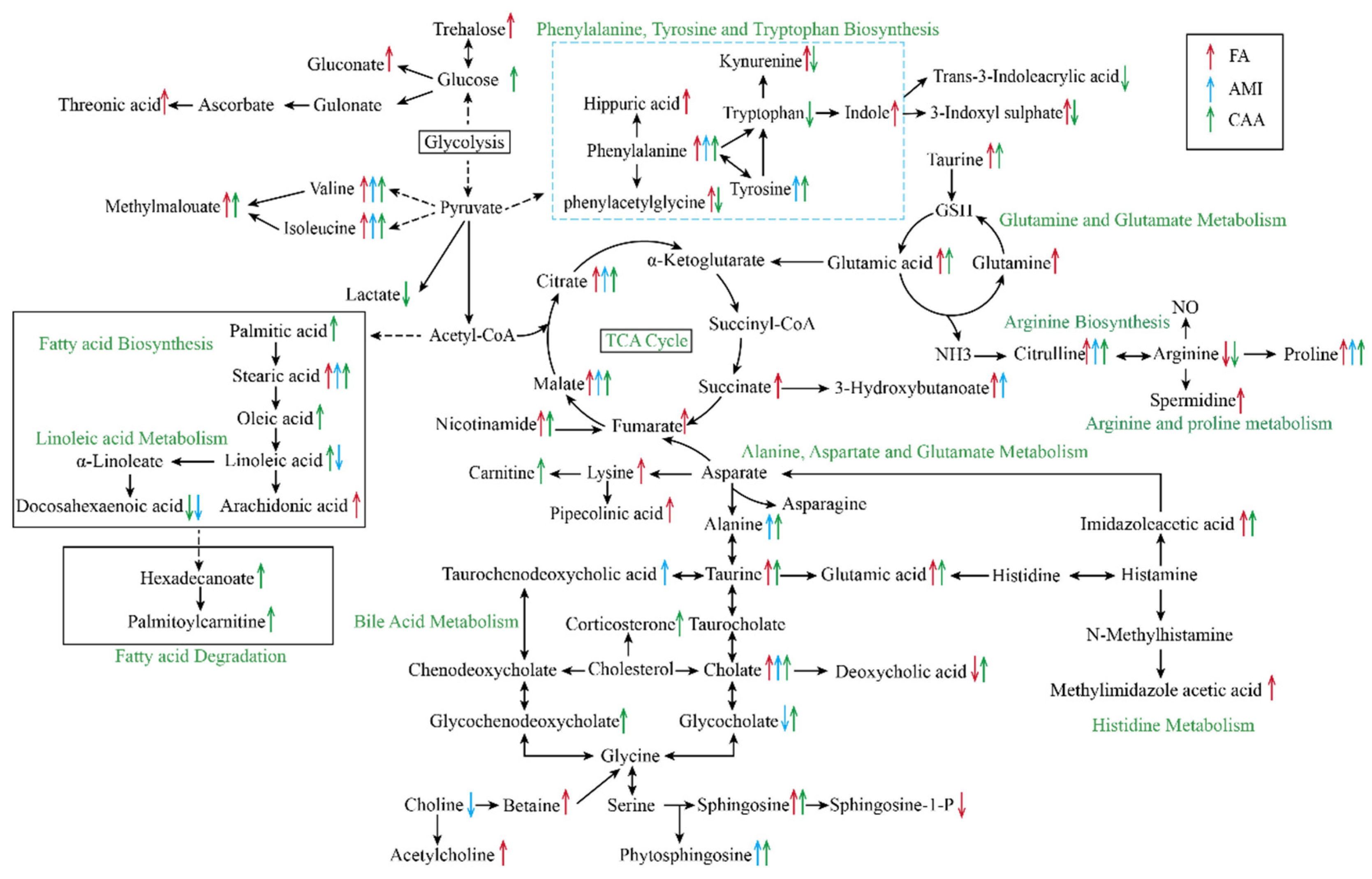
2.2. Different Metabolomic Profiles of Different Models
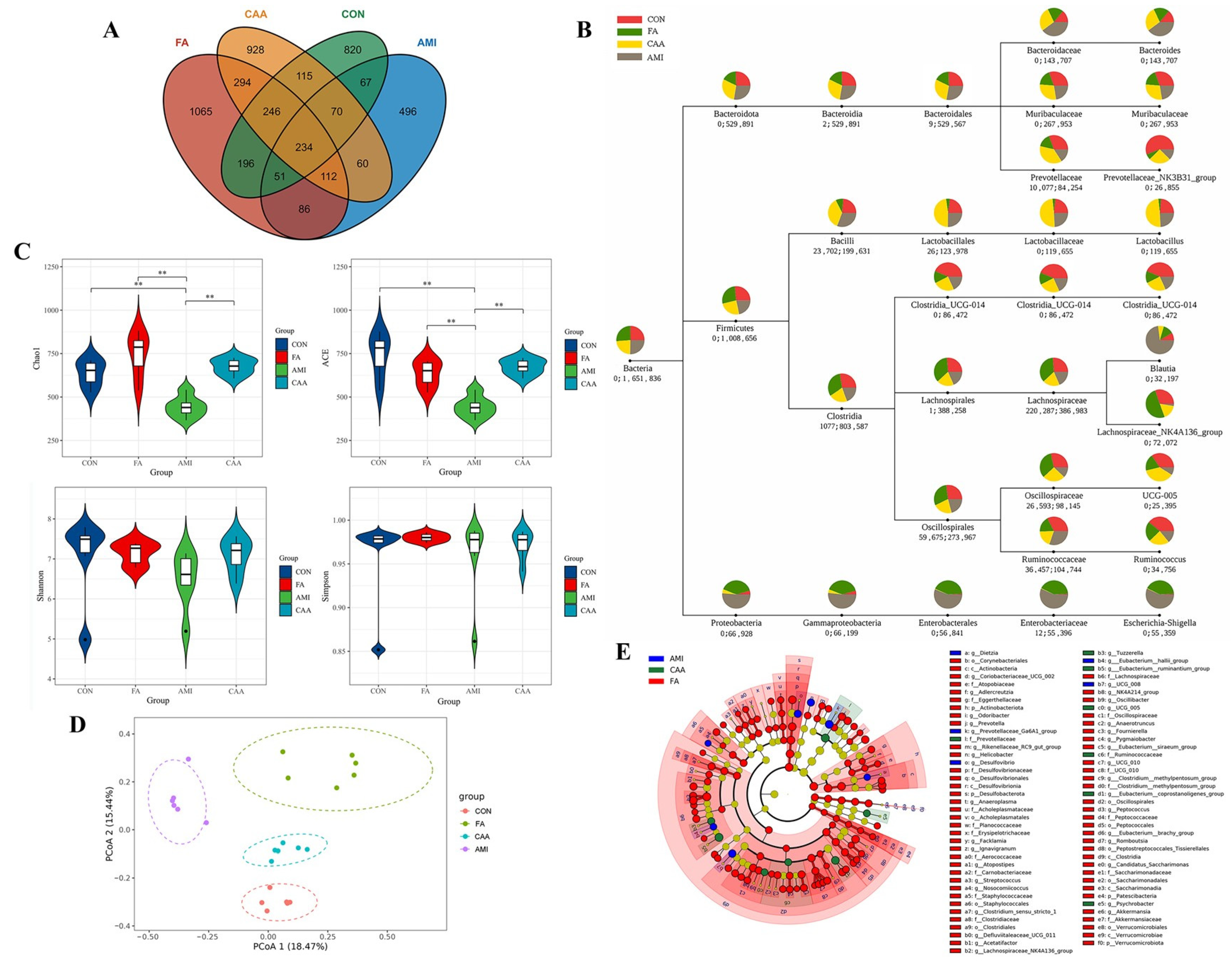
2.3. Altered Gut Microbiota Composition in Different Models
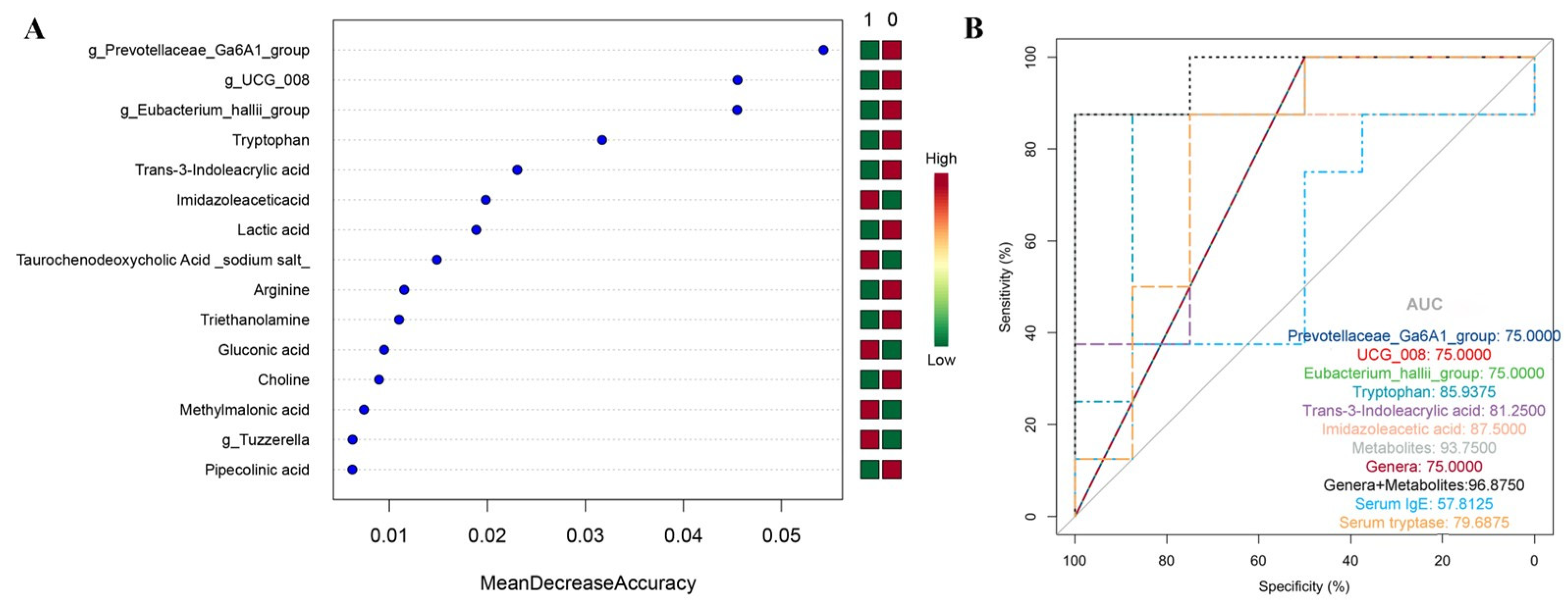
2.4. The Random Forest Classification Model
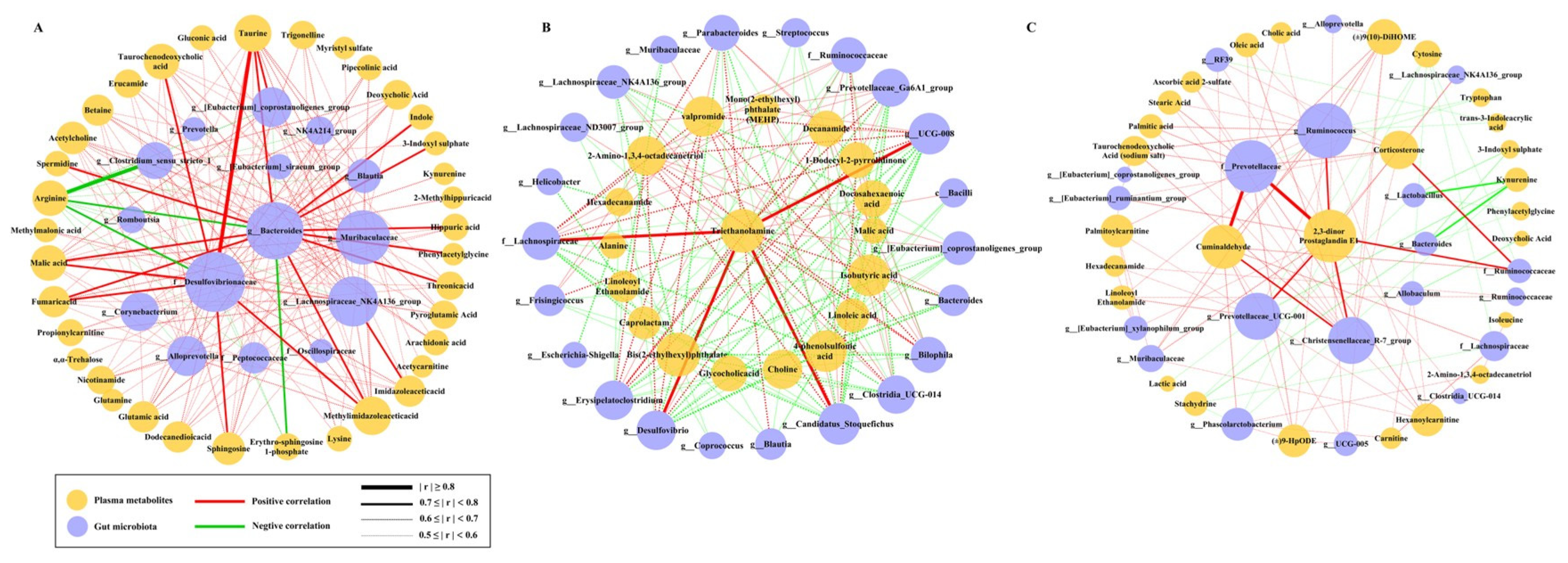
2.5. The Correlation Between Metabolites and Microbiota
2.6. Tryptophan Is a Reliable Biomarker to Distinguish Fatal Anaphylaxis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Establishment of Animal Models
4.3. Sample Collection and Preparation
4.4. Serum IgE and Tryptase Measurement and Tissue Staining
4.5. Plasma Metabolomics Analysis
4.6. 16S rRNA Sequencing
4.7. Random Forest Classification Model
4.8. Correlation Analysis
4.9. Forensic Samples
4.10. Statistics Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FA | Fatal anaphylaxis |
| AMI | Acute myocardial infarction |
| CAA | Coronary atherosclerosis with anaphylaxis |
| CON | Control |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| OVA | Ovalbumin |
| LAD | Left anterior descending coronary artery |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| AI | Atherosclerosis index |
| HE | Hematoxylin and eosin staining |
| IHC | Immunohistochemical staining |
| QC | Quality control |
| ESI | Electrospray ionization |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| PLS-DA | Partial least squares–discriminant analysis |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal partial least squares discrimination analysis |
| VIP | Variable importance in projection |
| MetPA | Metabolic pathways |
| ASV | Amplicon sequence variant |
| DADA2 | Divisive amplicon denoising algorithm |
| OUT | Operational taxonomic unit |
| PCoA | Principal coordinates analysis |
| Anosim | Analysis of similarities |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminative analysis effect size |
| ROC | Receiver operating characteristic curve |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| SCFA | Short-chain fatty acid |
References
- Dribin, T.E.; Muraro, A.; Camargo, C.A., Jr.; Turner, P.J.; Wang, J.; Roberts, G.; Anagnostou, A.; Halken, S.; Liebermann, J.; Worm, M.; et al. Anaphylaxis Definition, Overview, and Clinical Support Tool: 2024 Consensus Report—a GA2LEN project. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pühringer, V.; Jilma, B.; Herkner, H. Population-based incidence of all-cause anaphylaxis and its development over time: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Allergy 2023, 4, 1249280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuToit, G.; Smith, P.; Muraro, A.; Fox, A.T.; Roberts, G.; Ring, J.; Worm, M. Identifying patients at risk of anaphylaxis. World Allergy Organ. J. 2024, 17, 100904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, U.R. Cardiovascular disease and anaphylaxis. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 7, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, V.; Ansotegui, I.J.; Ebisawa, M.; El-Gamal, Y.; Fernandez Rivas, M.; Fineman, S.; Geller, M.; Gonzalez-Estrada, A.; Greenberger, P.A.; Sanchez Borges, M.; et al. World allergy organization anaphylaxis guidance 2020. World Allergy Organ. J. 2020, 13, 100472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, P.J.; Jerschow, E.; Umasunthar, T.; Lin, R.; Campbell, D.E.; Boyle, R.J. Fatal Anaphylaxis: Mortality Rate and Risk Factors. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2017, 5, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, M.S.; Wallace, D.V.; Golden, D.B.K.; Oppenheimer, J.; Bernstein, J.A.; Campbell, R.L.; Dinakar, C.; Ellis, A.; Greenhawt, M.; Khan, D.A.; et al. Anaphylaxis-a 2020 practice parameter update, systematic review, and Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 1082–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, J.; Smith, P.; Tse, R.; Ong, B.; Milne, N. Association Between Cardiovascular Disease and Death by Anaphylaxis: A 20-Year Retrospective Study in Queensland, Australia. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2024, 46, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.X.; Sun, C.H.; Li, Z.D.; Lin, J.Y.; Shao, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, L.L.; Ye, X.; Shen, Y.W. Anaphylactic deaths: A retrospective study of forensic autopsy cases from 2009 to 2019 in Shanghai, China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Fernandez, P.; Vallejo-de-Torres, G.; Sanchez-de-Leon-Robles, M.S.; Navarro-Escayola, E.; Moro-Moro, M.; Alberti-Masgrau, N.; Tejedor-Alonso, M.A. Medical and pathologic characteristics of fatal anaphylaxis: A Spanish nationwide 17-year series. Forensic Sci. Med. Pathol. 2019, 15, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberger, P.A.; Rotskoff, B.D.; Lifschultz, B. Fatal anaphylaxis: Postmortem findings and associated comorbid diseases. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007, 98, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, R.J.; Wainstein, B.K.; Barnes, E.H.; Liew, W.K.; Campbell, D.E. Increases in anaphylaxis fatalities in Australia from 1997 to 2013. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2016, 46, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, B.; James, R.I.; Daniel, J.; Kumar, R.S.; Varughese, B.T.; Manoj, D.; Arakkal, A.L.; Johnson, L.R. Utility of biomarkers in the postmortem diagnosis of fatal Anaphylaxis: A scoping review. Leg. Med. 2025, 74, 102610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhao, C.; Xiong, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Significance of detecting postmortem serum IgE in frozen corpses for the diagnosis of anaphylaxis in forensic. Leg. Med. 2021, 53, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yin, C.; Su, X.; Su, M. Reliable Postmortem Molecular Diagnosis of Anaphylaxis: Co-localization of Mast Cell Degranulation and Immunoglobulin E in Allergic Throat Tissues. Am. J. Forensic Med. Pathol. 2020, 41, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oštrić Pavlović, I.; Radović, S.; Krtinić, D.; Spirić, J.; Kusić, N.; Veličković, A.; Tomić-Spirić, V. Tryptase: The Silent Witness of Past and Ongoing Systemic Events. Medicina 2024, 60, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, K.; Tse, R.; Tettamanti, C.; Scarpelli, M.P.; Rousseau, G.; Bonsignore, A.; Palmiere, C. Postmortem IgE determination in coronary artery disease. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2019, 62, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo, R.; Cohn, R.D.; Crockett, P.W.; Gowdy, K.M.; Zeldin, D.C.; Fessler, M.B. Relation between objective measures of atopy and myocardial infarction in the United States. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 405–411.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Li, D.R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Yu, Y.G.; Wang, H.J. Postmortem Serum Tryptase Levels with Special Regard to Acute Cardiac Deaths. J. Forensic Sci. 2017, 62, 1336–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmiere, C.; Comment, L.; Vilarino, R.; Mangin, P.; Reggiani Bonetti, L. Measurement of β-tryptase in postmortem serum in cardiac deaths. J. Forensic Leg. Med. 2014, 23, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales-Chorda, C.; Obeso, D.; Twomey, L.; Rojas-Benedicto, A.; Puchades-Carrasco, L.; Roca, M.; Pineda-Lucena, A.; Laguna, J.J.; Barbas, C.; Esteban, V.; et al. Characterization of anaphylaxis reveals different metabolic changes depending on severity and triggers. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2021, 51, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Qin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, W.; Xie, Z.; Yu, H.; Huang, Z. Deciphering biochemical basis of Qingkailing injection-induced anaphylaxis in a rat model by time-dependent metabolomic profiling based on metabolite polarity-oriented analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 225, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallizzi, A.A.; Heinken, A.; Guéant-Rodriguez, R.M.; Guéant, J.L.; Safar, R. A systematic review and meta-analysis of proteomic and metabolomic alterations in anaphylaxis reactions. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1328212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Liu, L.W.; Li, J.; Wang, S.L.; Alolga, R.N.; Yin, Y.; Wang, X.M.; et al. Comprehensive Metabolomic Characterization of Coronary Artery Diseases. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 1281–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Yan, H.; Liu, R.; Xiang, P.; Zhang, J.; Deng, K.; Huang, P.; Wang, Z. The Use of Gas Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry-Based Untargeted Metabolomics to Discover Metabolic Changes and Help in the Determination of Complex Causes of Death: A Preliminary Study. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 2100–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H. Immune regulation by microbiome metabolites. Immunology 2018, 154, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, Y.; Grishin, A.; Rose, R.; Zhao, W.; Arditi, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wood, R.A.; Burks, A.W.; Jones, S.M.; Leung, D.Y.M.; et al. Longitudinal dynamics of the gut microbiome and metabolome in peanut allergy development. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, J.; Zhao, P.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, G.; Xu, A. The Multiomics Analyses of Gut Microbiota, Urine Metabolome and Plasma Proteome Revealed Significant Changes in Allergy Featured with Indole Derivatives of Tryptophan. J. Asthma Allergy 2022, 15, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, R.; Hesser, L.A.; He, Z.; Zhou, X.; Nadeau, K.C.; Nagler, C.R. Fecal microbiome and metabolome differ in healthy and food-allergic twins. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e141935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Hu, X.; Niu, H.; Tian, R.; Wang, H.; Pang, H.; Jiang, L.; Qiu, B.; Chen, X.; et al. Alterations in the gut microbiome and metabolism with coronary artery disease severity. Microbiome 2019, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, F.; Sun, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; et al. Gut microbiota combined with metabolites reveals unique features of acute myocardial infarction patients different from stable coronary artery disease. J. Adv. Res. 2023, 46, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Bonilla-Rosso, G.; Kwong Chung, C.K.C.; Bäriswyl, L.; Rodriguez, M.P.; Kim, B.S.; Engel, P.; Noti, M. High dietary fat intake induces a microbiota signature that promotes food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 157–170.e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmati, M.; Kashanipoor, S.; Mazaheri, P.; Alibabaei, F.; Babaeizad, A.; Asli, S.; Mohammadi, S.; Gorgin, A.H.; Ghods, K.; Yousefi, B.; et al. Importance of gut microbiota metabolites in the development of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Life Sci. 2023, 329, 121947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Salam, S.; Aburawi, E.H.; Al-Hammadi, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Shafiuallah, M.; Yasin, J.; Sudhadevi, M.; Awwad, A.; Alper, S.; Kazzam, E.; et al. Cellular and Immunohistochemical Changes in Anaphylactic Shock Induced in the Ovalbumin-Sensitized Wistar Rat Model. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Xie, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Fang, Q.; Wang, J.; Shen, Z. Serum IgE levels are associated with coronary artery disease severity. Atherosclerosis 2016, 251, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallavia, B.; Oguiza, A.; Lopez-Franco, O.; Recio, C.; Ortiz-Muñoz, G.; Lazaro, I.; Lopez-Parra, V.; Egido, J.; Gomez-Guerrero, C. Gene Deficiency in Activating Fcγ Receptors Influences the Macrophage Phenotypic Balance and Reduces Atherosclerosis in Mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centa, M.; Jin, H.; Hofste, L.; Hellberg, S.; Busch, A.; Baumgartner, R.; Verzaal, N.J.; Lind Enoksson, S.; Perisic Matic, L.; Boddul, S.V.; et al. Germinal Center-Derived Antibodies Promote Atherosclerosis Plaque Size and Stability. Circulation 2019, 139, 2466–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Saiz, R.; Ellenbogen, Y.; Koenig, J.F.E.; Gordon, M.E.; Walker, T.D.; Rosace, D.; Spill, P.; Bruton, K.; Kong, J.; Monteiro, K.; et al. IgG1(+) B-cell immunity predates IgE responses in epicutaneous sensitization to foods. Allergy 2019, 74, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jönsson, F.; Chaisemartin, L.d.; Granger, V. An IgG-induced neutrophil activation pathway contributes to human drug-induced anaphylaxis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Gallego, N.; Castillo-González, R.; Méndez-Barbero, N.; López-Sanz, C.; Obeso, D.; Villaseñor, A.; Escribese, M.M.; López-Melgar, B.; Salamanca, J.; Benedicto-Buendía, A.; et al. The impact of type 2 immunity and allergic diseases in atherosclerosis. Allergy 2022, 77, 3249–3266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajiwara, N.; Sasaki, T.; Bradding, P.; Cruse, G.; Sagara, H.; Ohmori, K.; Saito, H.; Ra, C.; Okayama, Y. Activation of human mast cells through the platelet-activating factor receptor. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 1137–1145.e1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mito, N.; Kitada, C.; Hosoda, T.; Sato, K. Effect of diet-induced obesity on ovalbumin-specific immune response in a murine asthma model. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2002, 51, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, T.; Wiese, A.V.; Ender, F.; Quell, K.M.; Vollbrandt, T.; Duhn, J.; Sünderhauf, A.; Künstner, A.; Moreno-Fernandez, M.E.; Derer, S.; et al. Short-term high-fat diet feeding protects from the development of experimental allergic asthma in mice. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1245–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhata, H.; Shimizu, R.; Yokoyama, M.M. Role of nitric oxide in anaphylactic shock. J. Clin. Immunol. 1995, 15, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Gao, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Fu, L. Metabolomics identifies phenotypic biomarkers of amino acid metabolism in milk allergy and sensitized tolerance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, T.; Du, K.; Gao, C.; Guo, X.; Fu, S.; Yun, K. Serum metabolomics analysis reveals potential biomarkers of penicillins-induced fatal anaphylactic shock in rats. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.C.; Yu, Y.C.; Sung, Y.; Han, J.M. Glutamine reliance in cell metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 1496–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hörig, H.; Spagnoli, G.C.; Filgueira, L.; Babst, R.; Gallati, H.; Harder, F.; Juretic, A.; Heberer, M. Exogenous glutamine requirement is confined to late events of T cell activation. J. Cell. Biochem. 1993, 53, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, T.W.; Grusdat, M.; Duncan, G.S.; Dostert, C.; Nonnenmacher, Y.; Cox, M.; Binsfeld, C.; Hao, Z.; Brüstle, A.; Itsumi, M.; et al. Glutathione Primes T Cell Metabolism for Inflammation. Immunity 2017, 46, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Guo, N.; Dou, D.; Ran, X.; Liu, C. Metabolomics analysis of anaphylactoid reaction reveals its mechanism in a rat model. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2017, 35, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, F.; Agostoni, C.; Borghi, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cena, H.; Ghiselli, A.; La Vecchia, C.; Lercker, G.; Manzato, E.; Pirillo, A.; et al. Dietary linoleic acid and human health: Focus on cardiovascular and cardiometabolic effects. Atherosclerosis 2020, 292, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Jia, X.; Liu, R.; Zhang, S.; Liu, S.; An, J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, Y.; Li, X. Metabolic pathway analysis of hyperuricaemia patients with hyperlipidaemia based on high-throughput mass spectrometry: A case–Control study. Lipids Health Dis. 2022, 21, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Gao, X.; Yin, J. Gut microbiome alterations in patients with wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Mao, Y.Y.; Shao, Y.H.; Liu, J.; Tu, Z.C. A comparative study on the allergenic potential of β-lactoglobulin conjugated to glucose, caffeic acid and caffeoyl glucopyranose. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4354–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebar Lozinsky, A.; Loke, P.; Orsini, F.; O’Sullivan, M.; Prescott, S.L.; Gold, M.S.; Quinn, P.; DunnGalvin, A.; Lk Tang, M. Study protocol of a multicentre, randomised, controlled trial evaluating the effectiveness of probiotic and peanut oral immunotherapy (PPOIT) in inducing desensitisation or tolerance in children with peanut allergy compared with oral immunotherapy (OIT) alone and with placebo (the PPOIT-003 study). BMJ Open 2020, 10, e035871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassard, L.; Sperber, K.; Buivan, T.P.; Cotillard, A.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Albert, M.L.; Mottez, E.; Laurent, J.; Guinnepain, M.T.; Daëron, M. Basophils from allergic patients are neither hyperresponsive to activation signals nor hyporesponsive to inhibition signals. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 142, 1548–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shida, K.; Takahashi, R.; Iwadate, E.; Takamizawa, K.; Yasui, H.; Sato, T.; Habu, S.; Hachimura, S.; Kaminogawa, S. Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota suppresses serum immunoglobulin E and immunoglobulin G1 responses and systemic anaphylaxis in a food allergy model. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Bang, J.; Woo, H.J. Effect of orally administered Lactobacillus brevis HY7401 in a food allergy mouse model. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 23, 1636–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Zhao, K.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Nie, L.; Wei, H.; Wan, C. Effect of 3 lactobacilli on immunoregulation and intestinal microbiota in a β-lactoglobulin-induced allergic mouse model. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 1943–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Im, S.H. Probiotics as a Potential Immunomodulating Pharmabiotics in Allergic Diseases: Current Status and Future Prospects. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2018, 10, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berni Canani, R.; Paparo, L.; Nocerino, R.; Di Scala, C.; Della Gatta, G.; Maddalena, Y.; Buono, A.; Bruno, C.; Voto, L.; Ercolini, D. Gut Microbiome as Target for Innovative Strategies Against Food Allergy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, S.H.; Gu, G.J.; Choi, J.H.; Jeong, K.T.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, S.H. Alterations of lung microbial communities in obese allergic asthma and metabolic potential. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Paepe, E.; Plekhova, V.; Vangeenderhuysen, P.; Baeck, N.; Bullens, D.; Claeys, T.; De Graeve, M.; Kamoen, K.; Notebaert, A.; Van de Wiele, T.; et al. Integrated gut metabolome and microbiome fingerprinting reveals that dysbiosis precedes allergic inflammation in IgE-mediated pediatric cow’s milk allergy. Allergy 2024, 79, 949–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, J.; Min, F.; Gao, J.; Liu, W.; Huang, M.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H. Oral administration of egg ovalbumin allergen induces dysregulation of tryptophan metabolism in sensitized BALB/c mice. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 4375–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.K.; Seo, S.H.; Park, S.E.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, J.S.; Pyo, J.Y.; Cho, K.M.; Kwon, S.J.; Park, D.H.; et al. Gut Microbiome and Metabolome Profiles Associated with High-Fat Diet in Mice. Metabolites 2021, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, C.D.; Maukonen, J.; Kaprio, J.; Rissanen, A.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Saarela, M. Habitual dietary intake is associated with stool microbiota composition in monozygotic twins. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, S. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Reduces β-conglycinin-Allergy-Induced Apoptotic Cells by Regulating Bacteroides and Bile Secretion Pathway in Intestinal Contents of BALB/c Mice. Nutrients 2020, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Qu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Sun, S.; Ding, R.; Cang, W.; Wu, R.; Wu, J. Role of the dietary components in food allergy: A comprehensive review. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesza, I.J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Mądry, E. High-Fat, Western-Style Diet, Systemic Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Cells 2021, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.; He, M.; Li, M.; Cheng, G.; Wan, C.; He, F. Dynamic construction of gut microbiota may influence allergic diseases of infants in Southwest China. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Jiang, L.; Guli, A.; Sailike, J.; Sun, X.; Abuduwaili, N.; Tuoliuhan, H.; Maney, K.; et al. Ziziphora clinopodioides flavonoids based on network pharmacology attenuates atherosclerosis in rats induced by high-fat emulsion combined with vitamin D(3) by down-regulating VEGF/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 129, 110399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Pang, L.; Tang, H.; Huang, C. Comparison and improvement of the methods for establishment of rat models of myocardial ischemia. Chin. J. Comp. Med. 2017, 27, 98–101. [Google Scholar]

| Group | Cause of Death/Allergen | N | Male/Female | Age (years) | PMI (h) | IgE (ng/mL) | Tryptase (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | Amniotic fluid embolism | 1 | 10/2 | 31.50 ± 19.62 | 203.50 ± 127.52 | 375.76 ± 351.61 | 30.87 ± 12.25 |
| Death from cold | 1 | ||||||
| Fat embolism | 1 | ||||||
| Sepsis | 1 | ||||||
| Hemorrhagic shock | 4 | ||||||
| Cerebral hemorrhage | 2 | ||||||
| Somedon poisoning | 1 | ||||||
| AMI | Coronary atherosclerotic heart disease | 11 | 11/1 | 51.83 ± 15.20 | 331.50 ± 221.5 | 102.77 ± 191.63 | 33.08 ± 14.53 |
| Muscular bridging of the right coronary artery | 1 | ||||||
| FA | Cefotaxime | 2 | 9/3 | 42.00 ± 17.63 | 203.00 ± 192.49 | 363.71 ± 517.35 | 27.70 ± 5.83 |
| Cefoperazone Sodium and Sulbactam Sodium | 1 | ||||||
| Penicillin | 1 | ||||||
| Ampicillin | 2 | ||||||
| Levofloxacin | 2 | ||||||
| Acetaminophen | 1 | ||||||
| Clindamycin | 1 | ||||||
| Azithromycin | 1 | ||||||
| Ribavirin | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Luo, L.; Wang, J.; Yao, S.; Yun, K.; Gao, C.; Guo, X. Integrated Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles Reveal Postmortem Biomarkers of Fatal Anaphylaxis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136292
Bai Y, Li Z, Chen Z, Luo L, Wang J, Yao S, Yun K, Gao C, Guo X. Integrated Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles Reveal Postmortem Biomarkers of Fatal Anaphylaxis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136292
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yaqin, Zhanpeng Li, Zheng Chen, Li Luo, Jiaqi Wang, Shangman Yao, Keming Yun, Cairong Gao, and Xiangjie Guo. 2025. "Integrated Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles Reveal Postmortem Biomarkers of Fatal Anaphylaxis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136292
APA StyleBai, Y., Li, Z., Chen, Z., Luo, L., Wang, J., Yao, S., Yun, K., Gao, C., & Guo, X. (2025). Integrated Metabolomic and Gut Microbiome Profiles Reveal Postmortem Biomarkers of Fatal Anaphylaxis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6292. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136292






