Isorhamnetin Modulates Drug-Resistance-Related Biomarkers in Colon Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anticancer Potential of Isorhamnetin: Cytotoxicity and Proapoptotic Activity
2.1.1. Cytotoxic Effect of Isorhamnetin
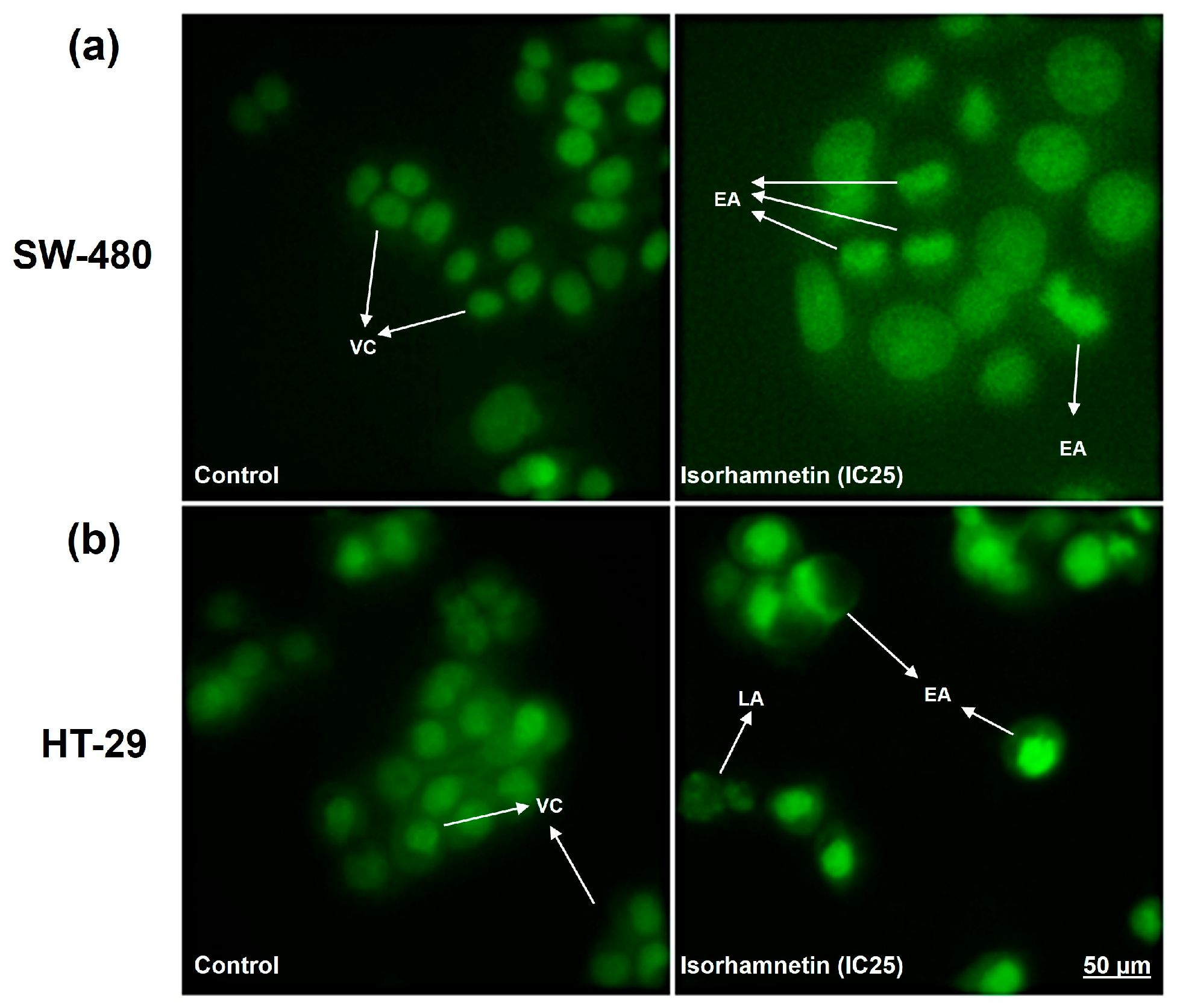
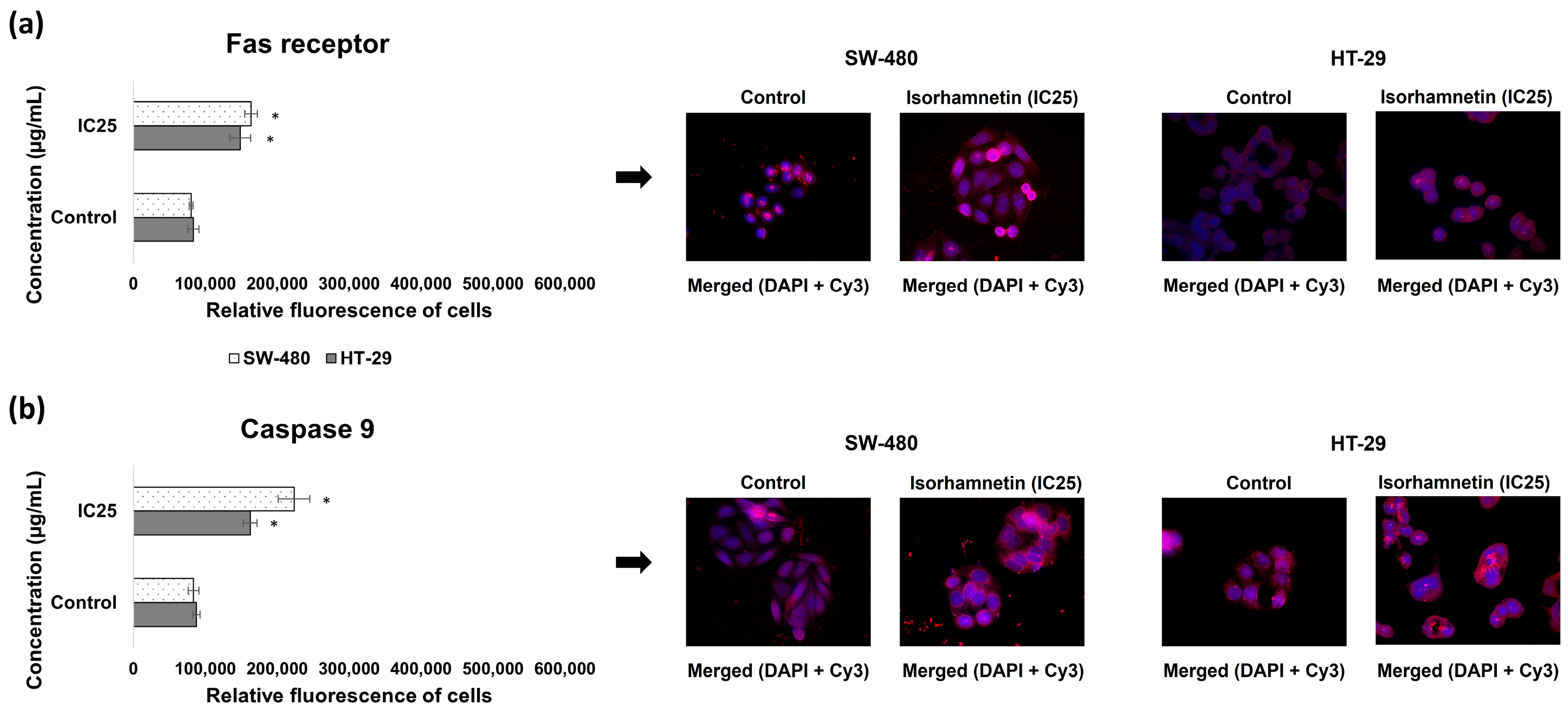
2.1.2. Isorhamnetin Exerts Cytotoxicity in SW-480 and HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells Through Apoptosis Activation
2.2. Isorhamnetin Affects the Expression of Drug-Resistance-Related Biomarkers in SW-480 and HT-29 Colon Cancer Cells
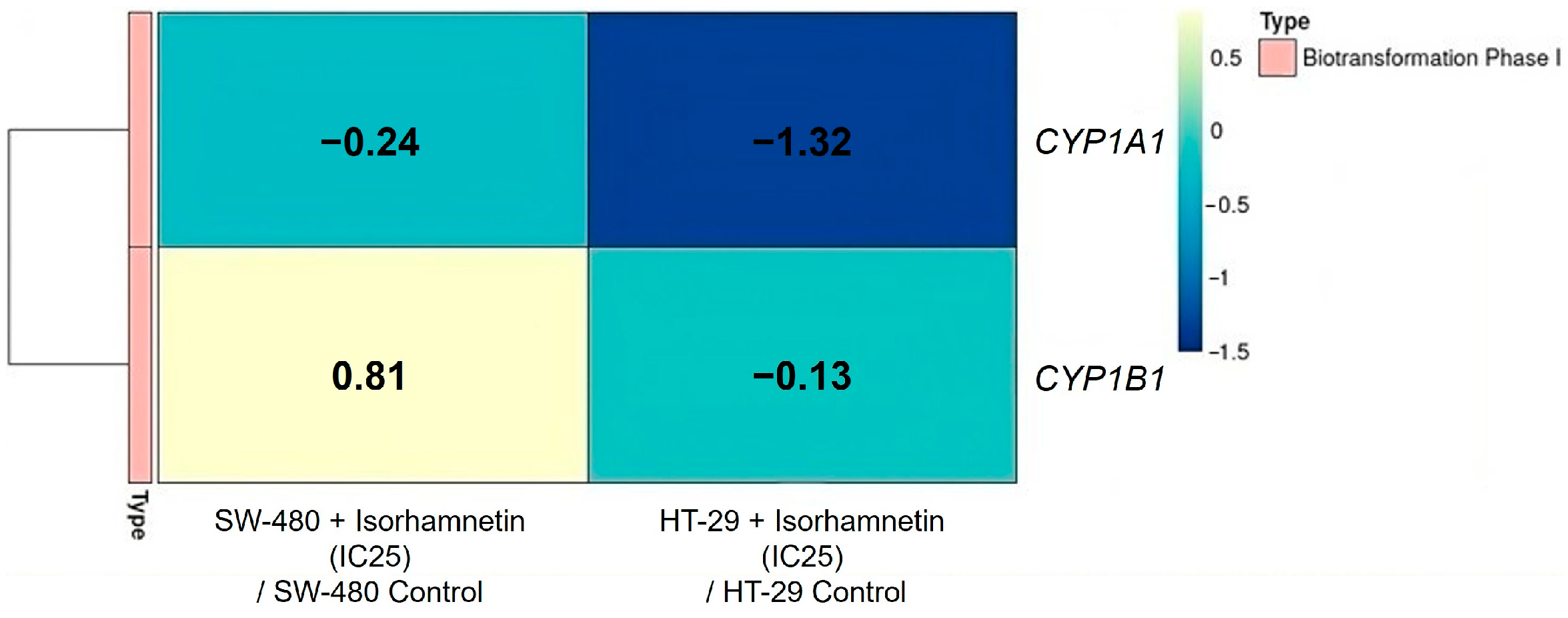
2.2.1. Isorhamnetin Reduces the mRNA Expression of CYP Enzymes
2.2.2. Isorhamnetin Increases GSTP1 mRNA Expression and Glutathione Synthesis
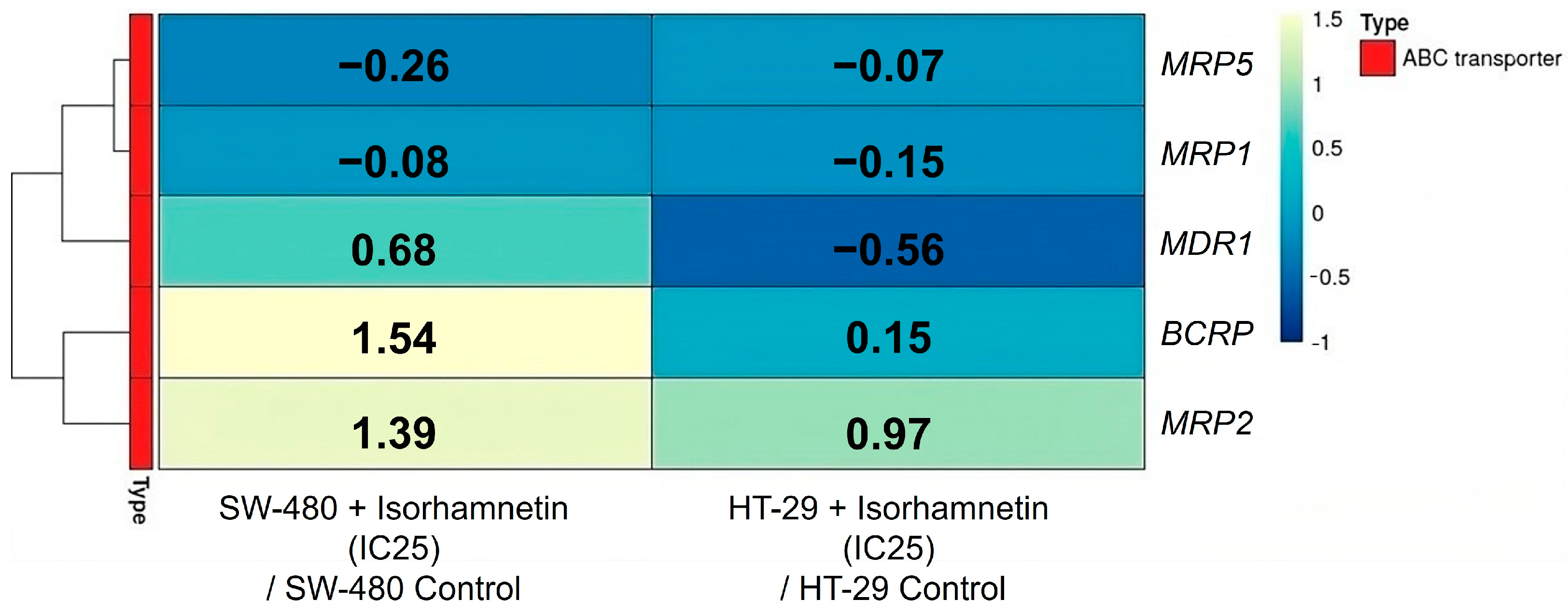
2.2.3. Isorhamnetin Alters Expression of ABC Transporters on the Transcriptional and Protein Levels
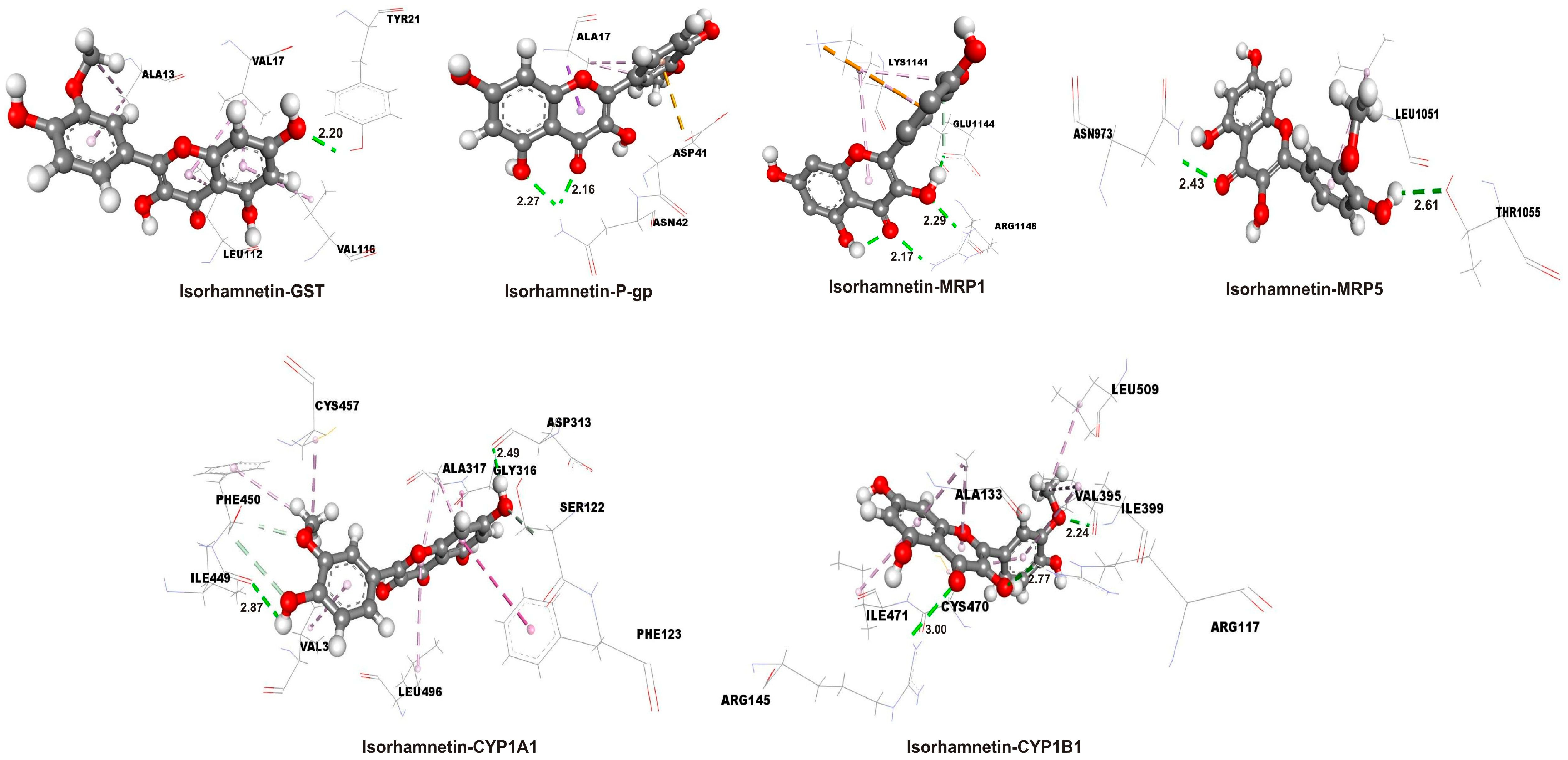
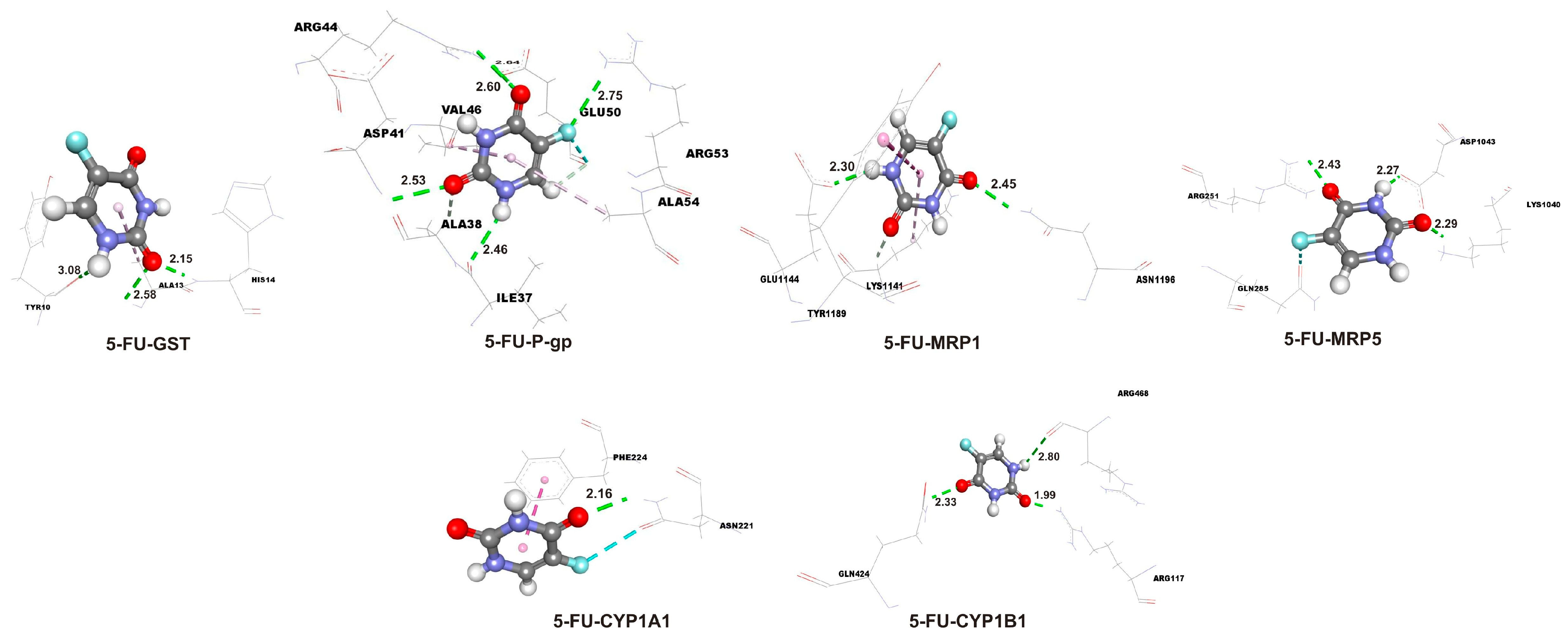
2.3. Enhanced Binding Affinity of Isorhamnetin over 5-FU in Molecular Docking with Target Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Cell Lines
4.3. Isorhamnetin
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Cell Death Analysis by Fluorescent Staining
4.6. Concentration of Reduced Glutathione
4.7. RNA Isolation, Reverse Transcription, and Relative mRNA Quantification
4.8. Immunofluorescence
4.9. Statistical Analysis
4.10. Molecular Docking
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 5-FU | 5-fluorouracil |
| ABC transporters | ATP Binding Cassette (ABC) transporters |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AO | Acridine Orange |
| BCRP | Breast cancer resistance protein |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| CYP | Cytochrome P450 |
| DAPI | Diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EA | Early apoptotic cells |
| EB | Ethidium bromide |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FC | Fold change |
| GCO | Global Cancer Observatory |
| GSH | Reduced glutathione |
| GSS | Glutathione synthetase |
| GSTs | Glutathione S-transferases |
| IC50 | The concentration that inhibits 50% of cell growth |
| LA | Late apoptotic cells |
| LE | Ligand efficiency |
| MRP1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 |
| MRP5 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 5 |
| MTT | 3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NBDs | Nucleotide-binding domains |
| NC | Necrotic cells |
| NCI | National Cancer Institute |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| P-gp | P-glycoprotein |
| SE | Standard error |
| SI | Selectivity index |
| TMDs | Transmembrane domains |
| VC | Viable cells |
References
- Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today (Version 1.0). International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2024. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Tomorrow (Version 1.0). International Agency for Research on Cancer. 2024. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/tomorrow/ (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- Diasio, R.B.; Innocenti, F.; Offer, S.M. Pharmacogenomic-Guided Therapy in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 110, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vodenkova, S.; Buchler, T.; Cervena, K.; Veskrnova, V.; Vodicka, P.; Vymetalkova, V. 5-fluorouracil and other fluoropyrimidines in colorectal cancer: Past, present and future. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 206, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omiecinski, C.J.; Vanden Heuvel, J.P.; Perdew, G.H.; Peters, J.M. Xenobiotic metabolism, disposition, and regulation by receptors: From biochemical phenomenon to predictors of major toxicities. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120, S49–S75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housman, G.; Byler, S.; Heerboth, S.; Lapinska, K.; Longacre, M.; Snyder, N.; Sarkar, S. Drug resistance in cancer: An overview. Cancers 2014, 6, 1769–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, F.U.; Sufiyan Chhipa, A.; Mishra, V.; Gupta, V.K.; Rawat, S.G.; Kumar, A.; Pathak, C. Molecular and cellular paradigms of multidrug resistance in cancer. Cancer Rep. 2022, 5, e1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.N.; Tian, Q.; Teng, Q.X.; Wurpel, J.N.D.; Zeng, L.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Z.S. Understanding and targeting resistance mechanisms in cancer. MedComm 2023, 4, e265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharom, F.J. ABC multidrug transporters: Structure, function and role in chemoresistance. Pharmacogenomics 2008, 9, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sodani, K.; Patel, A.; Kathawala, R.J.; Chen, Z.S. Multidrug resistance associated proteins in multidrug resistance. Chin. J. Cancer 2012, 31, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, S.; Shepard, R.L.; Kandasamy, R.A.; Johnston, P.A.; Perry, W.; Dantzig, A.H. The multidrug resistance protein 5 (ABCC5) confers resistance to 5-fluorouracil and transports its monophosphorylated metabolites. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2005, 4, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Locher, K.P. Structure and Mechanism of Human ABC Transporters. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2023, 52, 275–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milroy, R. A randomised clinical study of verapamil in addition to combination chemotherapy in small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1993, 68, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robey, R.W.; Pluchino, K.M.; Hall, M.D.; Fojo, A.T.; Bates, S.E.; Gottesman, M.M. Revisiting the role of ABC transporters in multidrug-resistant cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jaitak, V. Natural products as multidrug resistance modulators in cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 176, 268–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milutinović, M.G.; Maksimović, V.M.; Cvetković, D.M.; Nikodijević, D.D.; Stanković, M.S.; Pešić, M.; Marković, S.D. Potential of Teucrium chamaedrys L. to modulate apoptosis and biotransformation in colorectal carcinoma cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 240, 111951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewanjee, S.; Dua, T.K.; Bhattacharjee, N.; Das, A.; Gangopadhyay, M.; Khanra, R.; Joardar, S.; Riaz, M.; Feo, V.; Zia-Ul-Haq, M. Natural Products as Alternative Choices for P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) Inhibition. Molecules 2017, 22, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, M.; Kanimozhi, G.; Pradhapsingh, B.; Khan, H.A.; Alhomida, A.S.; Ekhzaimy, A.; Brindha, G.R.; Prasad, N.R. Phytochemicals reverse P-glycoprotein mediated multidrug resistance via signal transduction pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 139, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoush, B.; Shirdel, I.; Wink, M. Phytochemicals: Potential Lead Molecules for MDR Reversal. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, B.; Du, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Guo, F. Structures, Sources, Identification/Quantification Methods, Health Benefits, Bioaccessibility, and Products of Isorhamnetin Glycosides as Phytonutrients. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.; Guan, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.L.; Rahman, K.; Wang, S.J.; Zhou, S.; Luan, X.; Zhang, H. Isorhamnetin: A review of pharmacological effects. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, S.; Lopez, S.; Varela, L.M.; Rodriguez-Arcos, R.; Jimenez, A.; Abia, R.; Guillen, R.; Muriana, F.J. The flavonol isorhamnetin exhibits cytotoxic effects on human colon cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10869–10875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes-Ricardo, M.; Moreno-García, B.E.; Gutiérrez-Uribe, J.A.; Aráiz-Hernández, D.; Alvarez, M.M.; Serna-Saldivar, S.O. Induction of apoptosis in colon cancer cells treated with isorhamnetin glycosides from Opuntia ficus-indica pads. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2014, 69, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Huang, L.; Meng, L.; Sun, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y. Isorhamnetin inhibits cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in breast cancer via Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase signaling pathways. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 6745–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Cha, H.J.; Choi, E.O.; Lee, H.; Hwang-Bo, H.; Ji, S.Y.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Hong, S.H.; Cheong, J.; et al. Isorhamnetin Induces Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Via Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Pathway Activation in Human Bladder Cancer Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, B.S.; Lu, Y.H.; Wang, Z.T.; Tao, X.Y.; Wei, D.Z. In vitro anti-tumor activity of isorhamnetin isolated from Hippophae rhamnoides L. against BEL-7402 cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2006, 54, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Liang, X.; Chai, B.; Zhou, Y.; Du, H.; Suo, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Q.; Huang, X. Isorhamnetin Induces Melanoma Cell Apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB Pathways. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1057943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milutinović, M.; Ristanović, F.; Radenković, N.; Cvetković, D.; Radenković, S.; Stanković, M.; Nikodijević, D. Modulation of the Main Resistance-Associated ABC Transporter’s Expression by Plant Flavonol Isorhamnetin. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cao, J.; Zeng, S. Involvement of P-glycoprotein in regulating cellular levels of Ginkgo flavonols: Quercetin, kaempferol, and isorhamnetin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, K.; He, J.L.; Tian, Y.; Tan, F.; Jiang, X.H.; Wang, L.; Ye, L.M. Intra-herb pharmacokinetics interaction between quercetin and isorhamentin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 11, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Karuniawati, H.; Jairoun, A.A.; Urbi, Z.; Ooi, J.; John, A.; Lim, Y.C.; Kibria, K.M.K.; Mohiuddin, A.K.M.; Ming, L.C.; et al. Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Carcinogenesis, Global Epidemiology, Current Challenges, Risk Factors, Preventive and Treatment Strategies. Cancers 2022, 14, 1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, Y.; Su, H.; Zhou, B.; Liu, S. The function of natural compounds in important anticancer mechanisms. Front. Oncol. 2023, 12, 1049888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Hu, P.; Yang, M.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, Q. Natural Products as Anticancer Agents: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2022, 27, 8367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raja, S.B.; Rajendiran, V.; Kasinathan, N.K.; Amrithalakshmi, P.; Venkatabalasubramanian, S.; Murali, M.R.; Devaraj, H.; Devaraj, S.N. Differential cytotoxic activity of Quercetin on colonic cancer cells depends on ROS generation through COX-2 expression. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 106, 92–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.A.; Zhang, S.; Yin, Q.; Zhang, J. Quercetin induces human colon cancer cells apoptosis by inhibiting the nuclear factor-kappa B Pathway. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatiya, M.; Pathak, S.; Jothimani, G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Banerjee, A. A Comprehensive Study on the Anti-cancer Effects of Quercetin and Its Epigenetic Modifications in Arresting Progression of Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2023, 71, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiandani, T.; Tandian, T.; Zufar, B.D.; Suryadi, A.; Purwanto, B.T.; Hardjono, S.; Siswandono, S. In vitro study of pinostrobin propionate and pinostrobin butyrate: Cytotoxic activity against breast cancer cell T47D and its selectivity index. J. Public Health Afr. 2023, 14, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radenković, N.; Nikodijević, D.; Jovankić, J.; Blagojević, S.; Milutinović, M. Resistance to 5-fluorouracil: The molecular mechanisms of development in colon cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 983, 176979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.H.; Choo, J.J.; Choi, S.N. Tissue concentrations of quercetin and its metabolite isorhamnetin following oral administration of quercetin in mice. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 37, 90–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bredel, M. Anticancer drug resistance in primary human brain tumors. Brain Res. Rev. 2001, 35, 161–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, T.; Fujii-Kuriyama, Y. Metabolic activation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons to carcinogens by cytochromes P450 1A1 and 1B1. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsopoulos, V.P.; Spyrou, I.; Ploumidis, A.; Papalampros, A.E.; Kyriakakis, M.; Delakas, D.; Spandidos, D.A.; Tsatsakis, A.M. Expression Profile of CYP1A1 and CYP1B1 Enzymes in Colon and Bladder Tumors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niestroy, J.; Barbara, A.; Herbst, K.; Rode, S.; van Liempt, M.; Roos, P.H. Single and concerted effects of benzo[a]pyrene and flavonoids on the AhR and Nrf2-pathway in the human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2. Toxicol. In Vitr. 2011, 25, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pljesa-Ercegovac, M.; Savic-Radojevic, A.; Matic, M.; Coric, V.; Djukic, T.; Radic, T.; Simic, T. Glutathione Transferases: Potential Targets to Overcome Chemoresistance in Solid Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szakács, G.; Paterson, J.K.; Ludwig, J.A.; Booth-Genthe, C.; Gottesman, M.M. Targeting multidrug resistance in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 219–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leslie, E.M.; Deeley, R.G.; Cole, S.P. Multidrug resistance proteins: Role of P-glycoprotein, MRP1, MRP2, and BCRP (ABCG2) in tissue defense. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 204, 216–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Beyer, A.; Aebersold, R. On the Dependency of Cellular Protein Levels on mRNA Abundance. Cell 2016, 165, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganbold, M.; Shimamoto, Y.; Ferdousi, F.; Tominaga, K.; Isoda, H. Antifibrotic effect of methylated quercetin derivatives on TGFβ-induced hepatic stellate cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2019, 20, 100678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikodijević, D.D.; Jovankić, J.V.; Cvetković, D.M.; Anđelković, M.Z.; Nikezić, A.G.; Milutinović, M.G. L-amino acid oxidase from snake venom: Biotransformation and induction of apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 910, 174466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskić, D.; Popović, S.; Ristić, P.; Arsenijević, N.N. Analysis of cycloheximide-induced apoptosis in human leukocytes: Fluorescence microscopy using annexin V/propidium iodide versus acridin orange/ethidium bromide. Cell Biol. Int. 2006, 30, 924–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, M.A.; Cerniglia, G.J.; Zaman, A. Microtiter plate assay for the measurement of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in large numbers of biological samples. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 190, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomczynski, P.; Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 1987, 162, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, H.; Bronk, S.F.; Takikawa, Y.; Werneburg, N.; Takimoto, R.; El-Deiry, W.; Gores, G.J. The bile acid glycochenodeoxycholate induces trail-receptor 2/DR5 expression and apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 38610–38618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Tresanco, M.S.; Valdés-Tresanco, M.E.; Valiente, P.A.; Moreno, E. AMDock: A versatile graphical tool for assisting molecular docking with Autodock Vina and Autodock4. Biol. Direct. 2020, 15, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Isorhamnetin | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 Value (µg/mL) | SI | |||
| Cell line | 24 h | 72 h | 24 h | 72 h |
| HaCaT | 24.70 ± 1.89 | 23.33 ± 0.42 | ||
| SW-480 | 1.59 ± 0.09 | 2.09 ± 0.09 | 15.54 | 11.16 |
| HT-29 | 26.07 ± 0.34 | 8.65 ± 0.20 | 0.95 | 2.69 |
| Isorhamnetin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Line | µg/mL | Viable Cells | Early Apoptosis | Late Apoptosis | Necrosis |
| SW-480 | 0 | 92.92 ± 0.07 | 5.88 ± 0.31 | 1.08 ± 0.38 | 0.12 ± 0.12 |
| IC25 | 80.36 ± 1.44 * | 15.69 ± 1.12 * | 3.86 ± 0.52 * | 0.09 ± 0.09 | |
| HT-29 | 0 | 96.42 ± 0.44 | 3.23 ± 0.61 | 0.35 ± 0.17 | 0 |
| IC25 | 66.13 ± 0.95 * | 24.32 ± 2.86 * | 9.10 ± 2.94 * | 0.45 ± 0.45 | |
| Complex | ΔGbind (kcal mol−1) | Ki (µM) | LE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Isorhamnetin-CYP1 A1 | −9.0 | 2.50 × 10−1 | −0.39 |
| Isorhamnetin-CYP1B1 | −8.5 | 5.90 × 10−1 | −0.37 |
| Isorhamnetin-GST | −5.4 | 1.10 × 102 | −0.23 |
| Isorhamnetin-P-gp | −6.5 | 1.72 × 101 | −0.28 |
| Isorhamnetin-MRP1 | −5.8 | 5.61 × 101 | −0.25 |
| Isorhamnetin-MRP5 | −6.7 | 1.23 × 101 | −0.29 |
| 5-FU-CYP1A1 | −5.3 | 1.30 × 102 | −0.59 |
| 5-FU-CYP1B1 | −4.7 | 3.60 × 102 | −0.52 |
| 5-FU-GST | −4.5 | 5.00 × 102 | −0.50 |
| 5-FU-P-gp | −4.3 | 7.00 × 102 | −0.48 |
| 5-FU-MRP1 | −3.7 | 1.94 × 103 | −0.41 |
| 5-FU-MRP5 | −4.1 | 9.90 × 102 | −0.46 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radenković, N.; Milenković, D.; Nikodijević, D.; Jovanović Stojanov, S.; Podolski Renić, A.; Milutinović, M. Isorhamnetin Modulates Drug-Resistance-Related Biomarkers in Colon Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136208
Radenković N, Milenković D, Nikodijević D, Jovanović Stojanov S, Podolski Renić A, Milutinović M. Isorhamnetin Modulates Drug-Resistance-Related Biomarkers in Colon Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136208
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadenković, Nikola, Dejan Milenković, Danijela Nikodijević, Sofija Jovanović Stojanov, Ana Podolski Renić, and Milena Milutinović. 2025. "Isorhamnetin Modulates Drug-Resistance-Related Biomarkers in Colon Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136208
APA StyleRadenković, N., Milenković, D., Nikodijević, D., Jovanović Stojanov, S., Podolski Renić, A., & Milutinović, M. (2025). Isorhamnetin Modulates Drug-Resistance-Related Biomarkers in Colon Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6208. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136208








