Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid Associated with Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. Proteomics Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
2.4. Model Development and Validation
3. Results
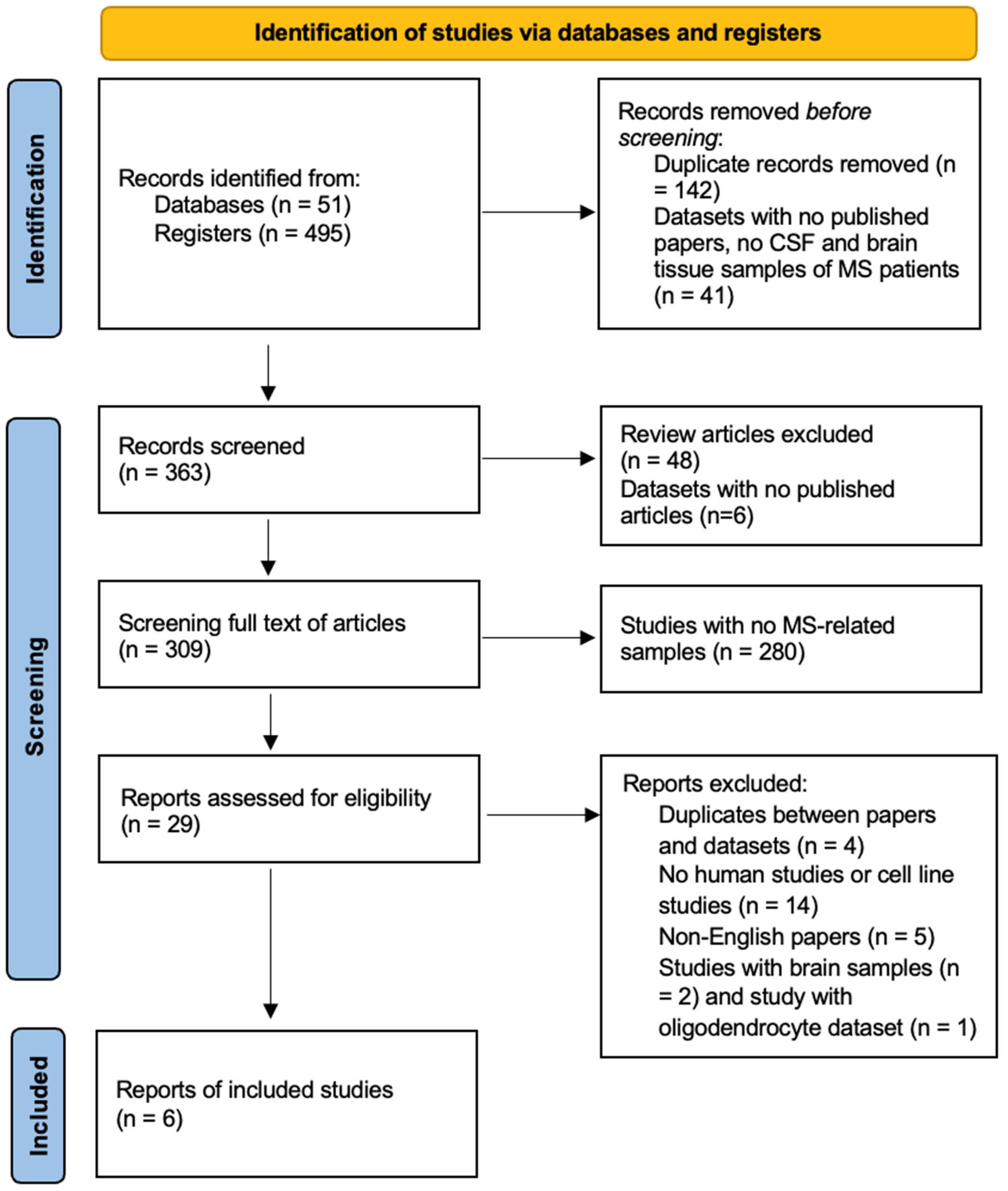
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Data Extraction
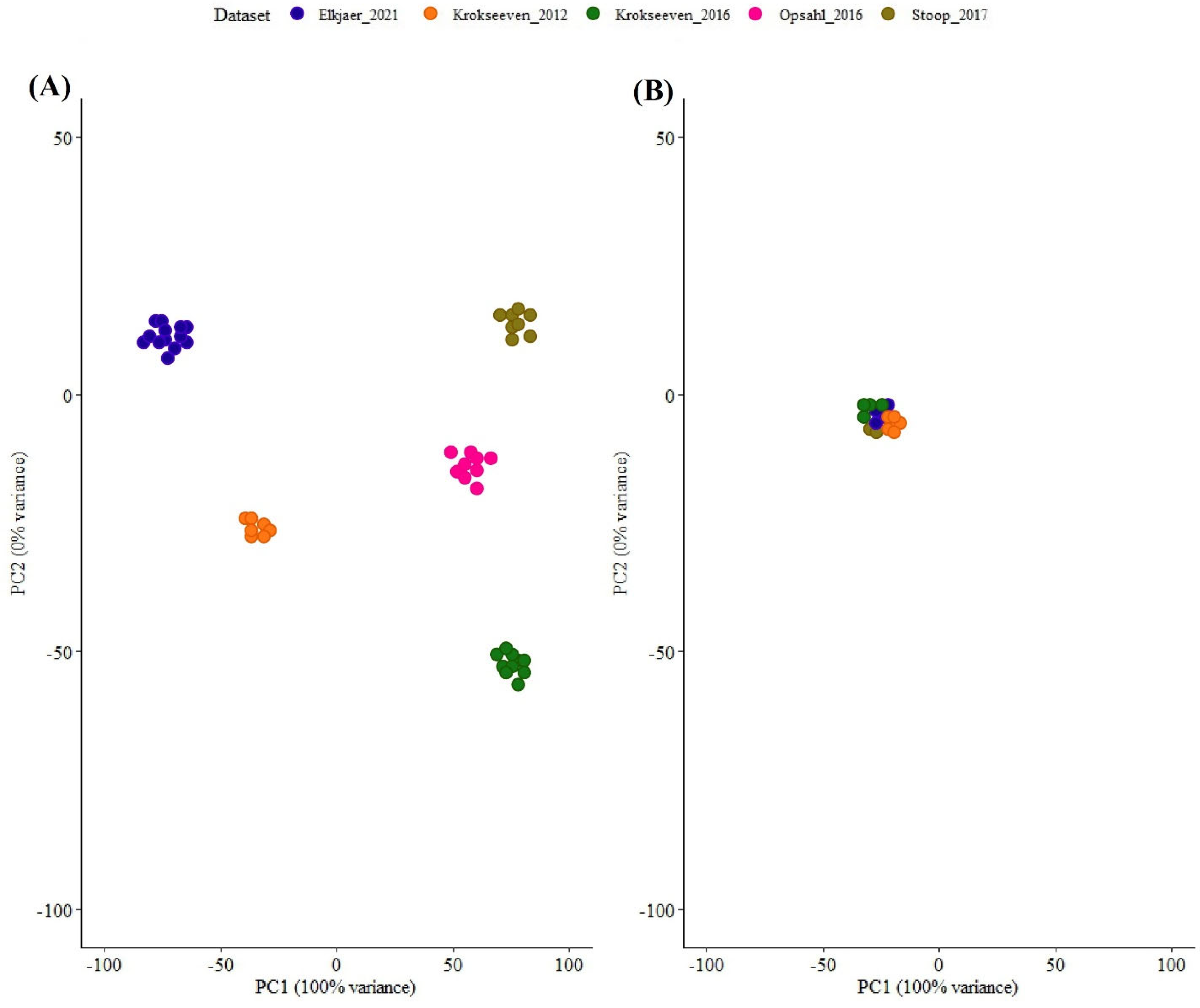
3.3. Data Preprocessing
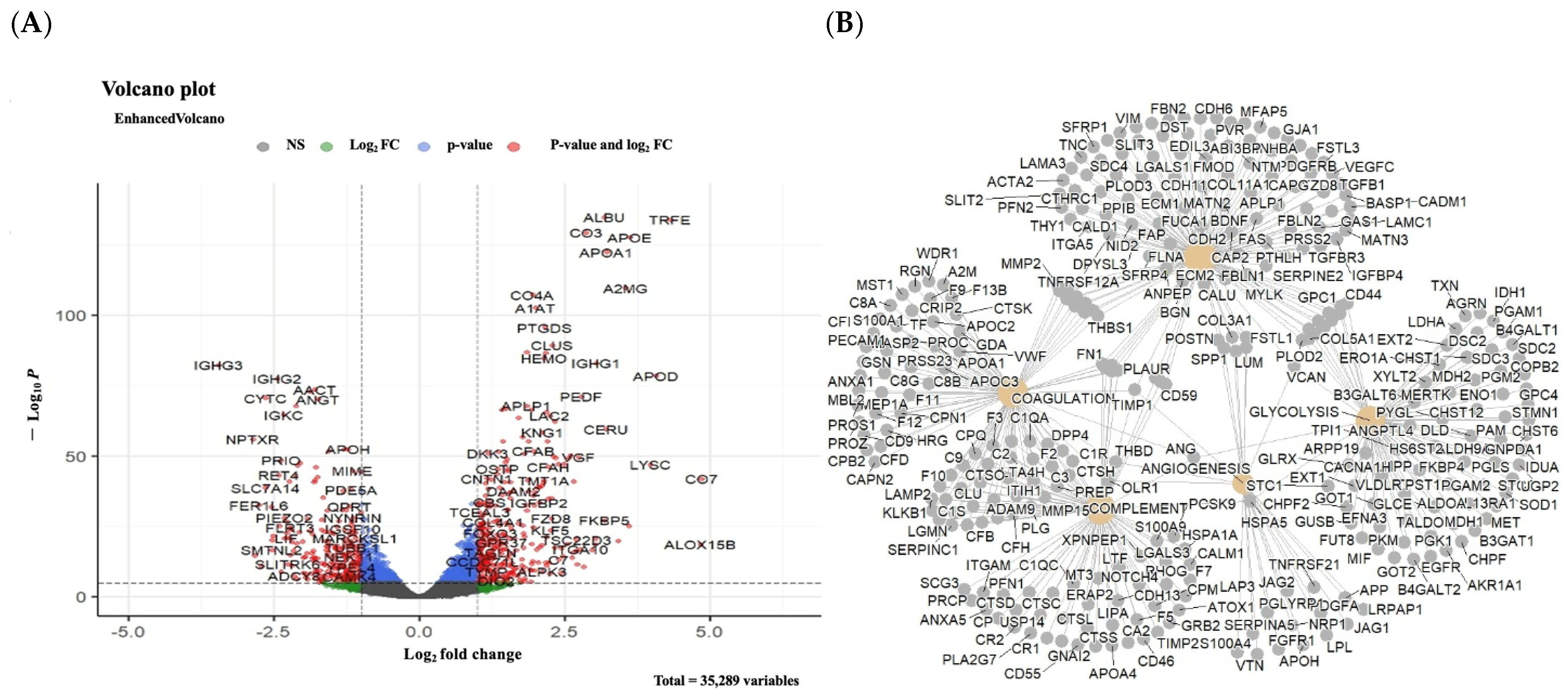
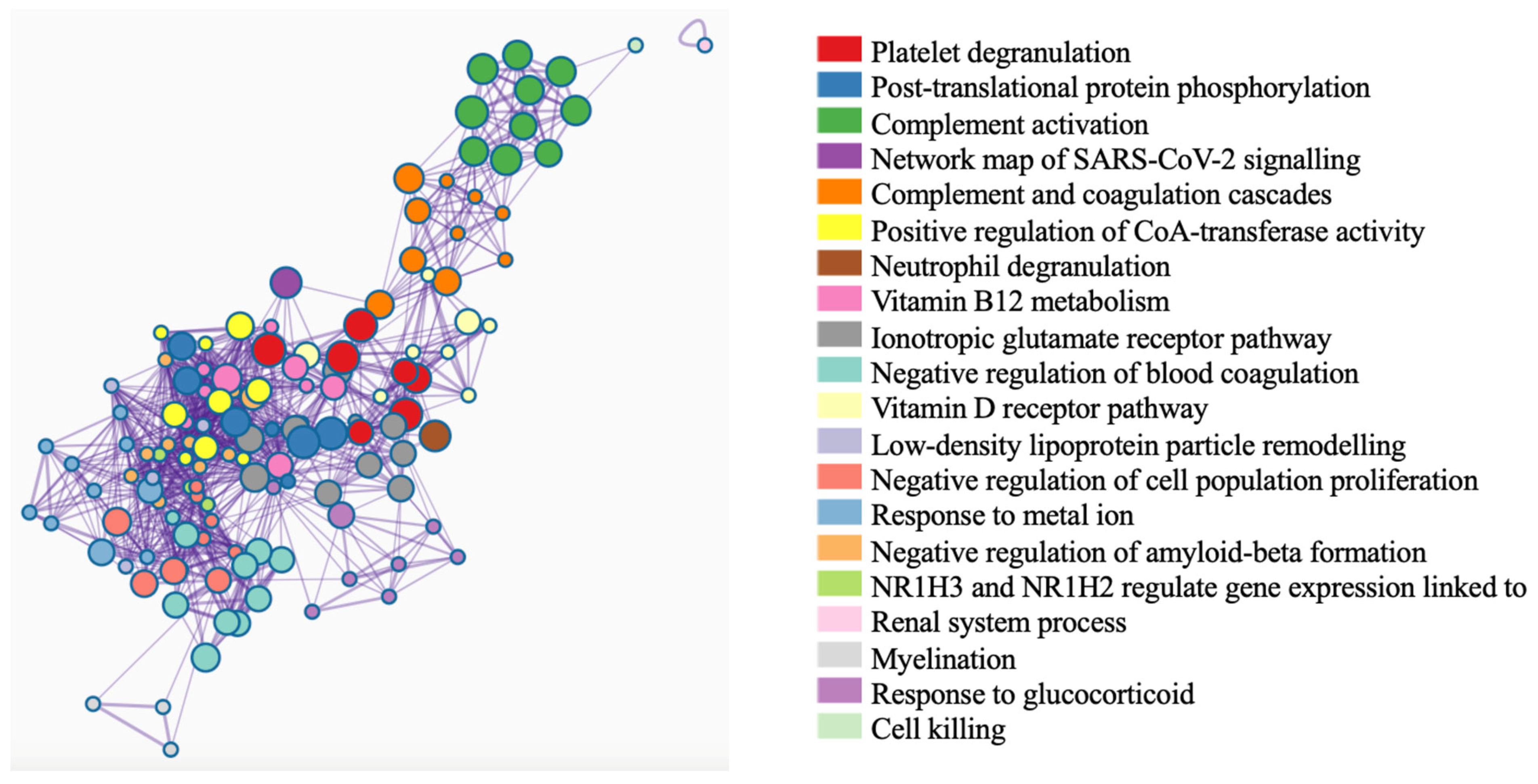
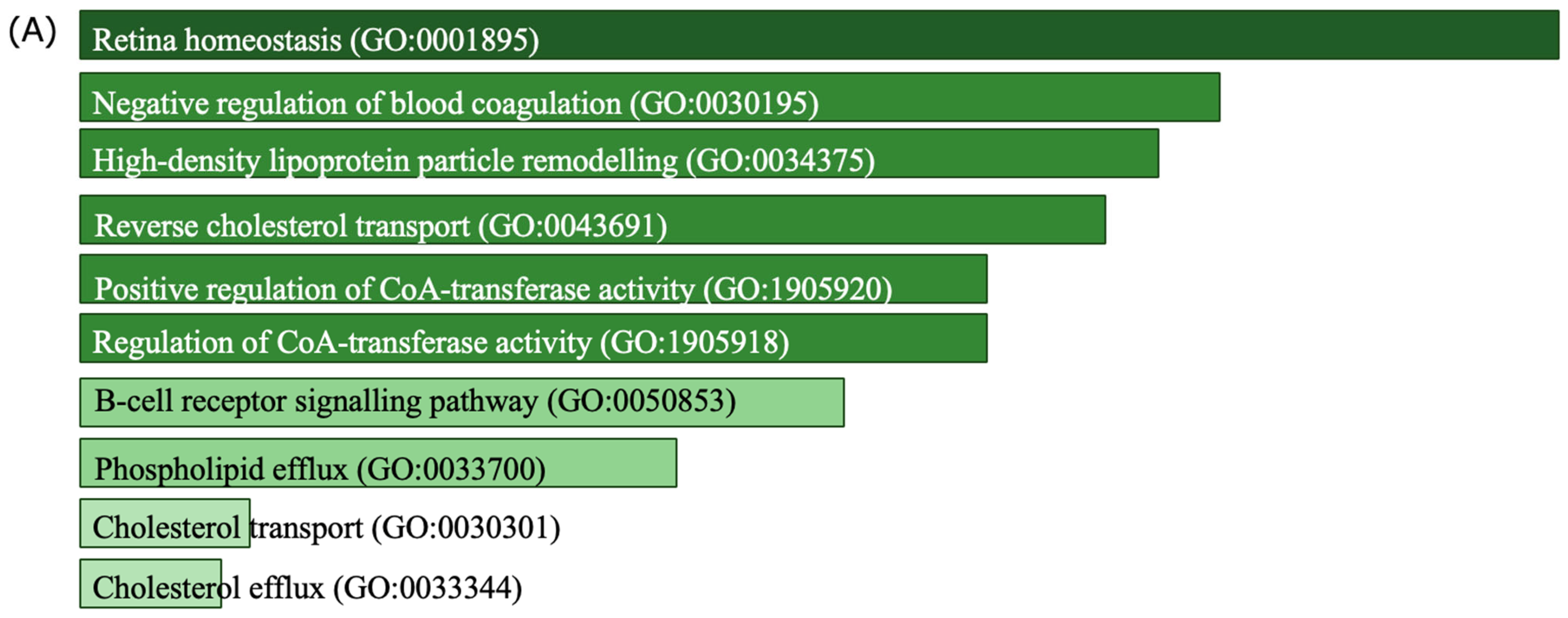
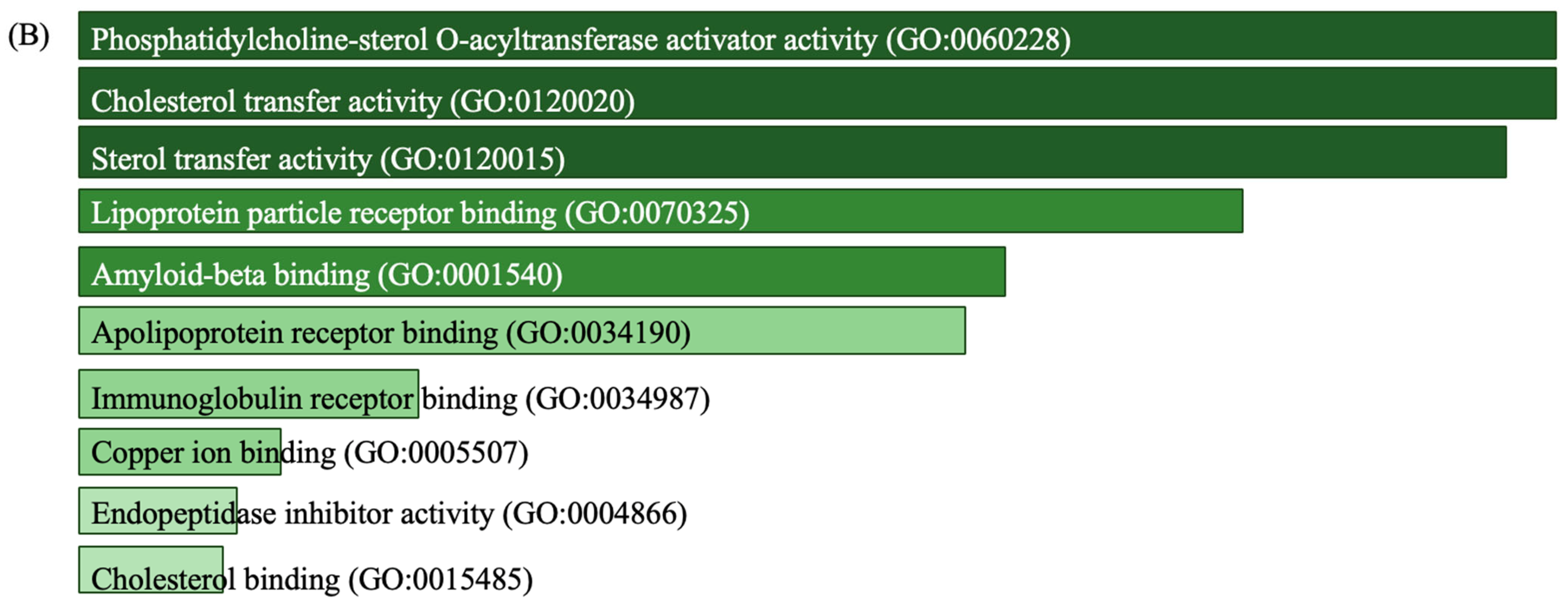
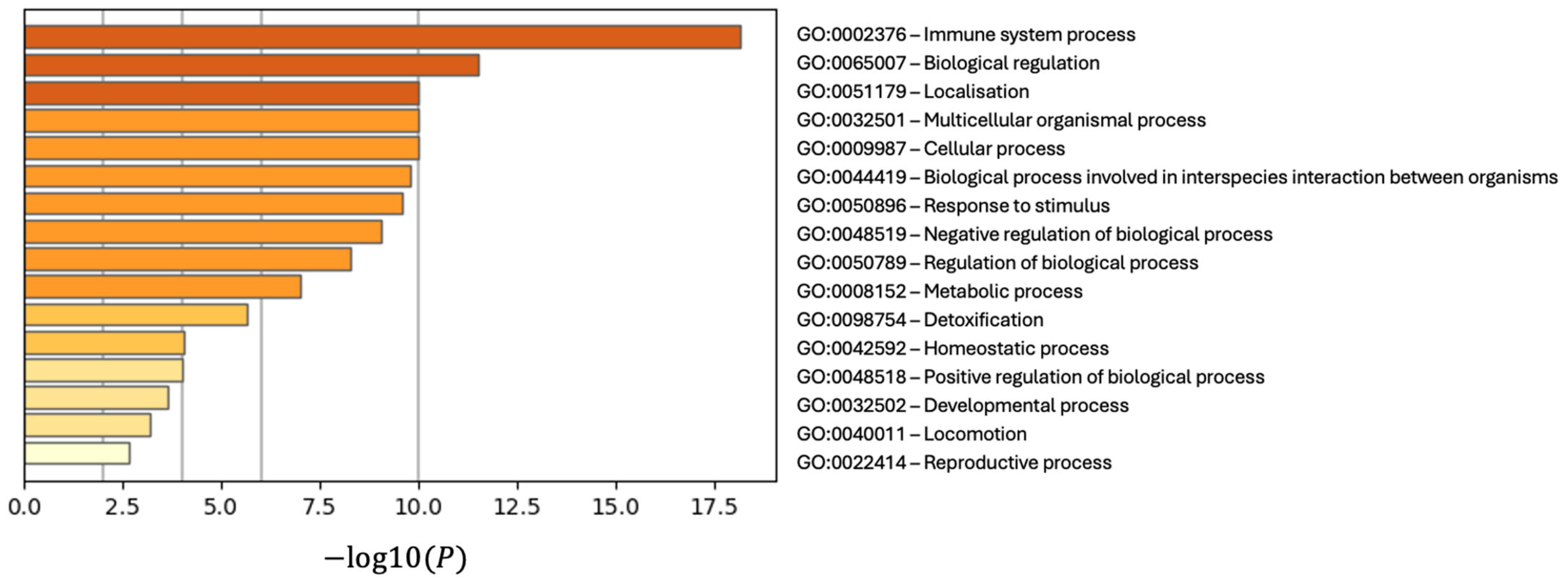
3.4. Discovery of Biomarker Candidates
3.5. Development of a Model Using Biomarker Candidates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trapp, B.D.; Nave, K.-A. Multiple Sclerosis: An Immune or Neurodegenerative Disorder? Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 247–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magyari, M.; Sorensen, P.S. The changing course of multiple sclerosis: Rising incidence, change in geographic distribution, disease course, and prognosis. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2019, 32, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, D.S.; Lucchinetti, C.F.; Calabresi, P.A. Multiple Sclerosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Langelaar, J.; Rijvers, L.; Smolders, J.; van Luijn, M.M. B and T Cells Driving Multiple Sclerosis: Identity, Mechanisms and Potential Triggers. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandi, D.; Kokas, Z.; Biernacki, T.; Bencsik, K.; Klivényi, P.; Vécsei, L. Proteomics in Multiple Sclerosis: The Perspective of the Clinician. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åkesson, J.; Hojjati, S.; Hellberg, S.; Raffetseder, J.; Khademi, M.; Rynkowski, R.; Kockum, I.; Altafini, C.; Lubovac-Pilav, Z.; Mellergård, J.; et al. Proteomics reveal biomarkers for diagnosis, disease activity and long-term disability outcomes in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkjaer, M.L.; Nawrocki, A.; Kacprowski, T.; Lassen, P.; Simonsen, A.H.; Marignier, R.; Sejbaek, T.; Nielsen, H.H.; Wermuth, L.; Rashid, A.Y.; et al. CSF proteome in multiple sclerosis subtypes related to brain lesion transcriptomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Verheul, C.; Willemse, E.A.J. Chapter 1—The use of cerebrospinal fluid in biomarker studies. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Deisenhammer, F., Teunissen, C.E., Tumani, H., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Cross, A.H.; Gelfand, J.M.; Thebault, S.; Bennett, J.L.; von Büdingen, H.C.; Cameron, B.; Carruthers, R.; Edwards, K.; Fallis, R.; Gerstein, R.; et al. Emerging Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers of Disease Activity and Progression in Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol. 2024, 81, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Khademi, M.; Fugger, L.; Lindhe, Ö.; Novakova, L.; Axelsson, M.; Malmeström, C.; Constantinescu, C.; Lycke, J.; Piehl, F.; et al. Inflammation-related plasma and CSF biomarkers for multiple sclerosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 12952–12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, R.M.; Engelhardt, B. The anatomical and cellular basis of immune surveillance in the central nervous system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avsar, T.; Korkmaz, D.; Tütüncü, M.; Demirci, N.O.; Saip, S.; Kamasak, M.; Siva, A.; Turanli, E.T. Protein biomarkers for multiple sclerosis: Semi-quantitative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid candidate protein biomarkers in different forms of multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2012, 18, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosleth, E.F.; Vedeler, C.A.; Liland, K.H.; McLeod, A.; Bringeland, G.H.; Kroondijk, L.; Berven, F.S.; Lysenko, A.; Rawlings, C.J.; Eid, K.E.-H.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid proteome shows disrupted neuronal development in multiple sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Han, B.; Qi, Y.; Wang, H.; Gao, J. Label-free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid and Serum in Patients With Relapse-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 892491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, F.; Makarov, C.; Gasperi, C.; Flaskamp, M.; Grummel, V.; Berthele, A.; Hemmer, B. Proteomics Reveals Age as Major Modifier of Inflammatory CSF Signatures in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2025, 12, e200322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasakin, M.F.; Rogachev, A.D.; Predtechenskaya, E.V.; Zaigraev, V.J.; Koval, V.V.; Pokrovsky, A.G. Targeted metabolomics approach for identification of relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis markers and evaluation of diagnostic models. MedChemComm 2019, 10, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zalm, P.W.; Ahmed, S.; Fatou, B.; Schreiber, R.; Barnaby, O.; Boxer, A.; Zetterberg, H.; Steen, J.A.; Steen, H. Meta-analysis of published cerebrospinal fluid proteomics data identifies and validates metabolic enzyme panel as Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvizhskii, A.I.; Keller, A.; Kolker, E.; Aebersold, R. A statistical model for identifying proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 4646–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Haynes, S.E.; Teo, G.C.; Avtonomov, D.M.; Polasky, D.A.; Nesvizhskii, A.I. Fast Quantitative Analysis of timsTOF PASEF Data with MSFragger and IonQuant. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuleshov, M.V.; Jones, M.R.; Rouillard, A.D.; Fernandez, N.F.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Koplev, S.; Jenkins, S.L.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lachmann, A.; et al. Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W90–W97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Tan, C.M.; Kou, Y.; Duan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Meirelles, G.V.; Clark, N.R.; Ma’ayan, A. Enrichr: Interactive and collaborative HTML5 gene list enrichment analysis tool. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timirci-Kahraman, O.; Karaaslan, Z.; Tuzun, E.; Kurtuncu, M.; Baykal, A.T.; Gunduz, T.; Tuzuner, M.B.; Akgun, E.; Gurel, B.; Eraksoy, M.; et al. Identification of candidate biomarkers in converting and non-converting clinically isolated syndrome by proteomics analysis of cerebrospinal fluid. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2019, 119, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comabella, M.; Sastre-Garriga, J.; Borras, E.; Villar, L.M.; Saiz, A.; Martínez-Yélamos, S.; García-Merino, J.A.; Pinteac, R.; Fissolo, N.; Sánchez López, A.J.; et al. CSF Chitinase 3-Like 2 Is Associated With Long-term Disability Progression in Patients with Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2021, 8, e1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoop, M.P.; Runia, T.F.; Stingl, C.; van der Vuurst de Vries, R.M.; Luider, T.M.; Hintzen, R.Q. Decreased Neuro-Axonal Proteins in CSF at First Attack of Suspected Multiple Sclerosis. Proteom.–Clin. Appl. 2017, 11, 1700005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opsahl, J.A.; Vaudel, M.; Guldbrandsen, A.; Aasebø, E.; Van Pesch, V.; Franciotta, D.; Myhr, K.-M.; Barsnes, H.; Berle, M.; Torkildsen, Ø.; et al. Label-free analysis of human cerebrospinal fluid addressing various normalization strategies and revealing protein groups affected by multiple sclerosis. Proteomics 2016, 16, 1154–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroksveen, A.C.; Guldbrandsen, A.; Vedeler, C.; Myhr, K.M.; Opsahl, J.A.; Berven, F.S. Cerebrospinal fluid proteome comparison between multiple sclerosis patients and controls. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2012, 126, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroksveen, A.C.; Guldbrandsen, A.; Vaudel, M.; Lereim, R.R.; Barsnes, H.; Myhr, K.-M.; Torkildsen, Ø.; Berven, F.S. In-Depth Cerebrospinal Fluid Quantitative Proteome and Deglycoproteome Analysis: Presenting a Comprehensive Picture of Pathways and Processes Affected by Multiple Sclerosis. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, R.E.; Lin, B.; Khera, A.; Davis, M.Y. Lipid Metabolism Influence on Neurodegenerative Disease Progression: Is the Vehicle as Important as the Cargo? Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 788695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, L.; Holmans, P.A.; Hamshere, M.L.; Harold, D.; Moskvina, V.; Ivanov, D.; Pocklington, A.; Abraham, R.; Hollingworth, P.; Sims, R.; et al. Genetic evidence implicates the immune system and cholesterol metabolism in the aetiology of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; LaDu, M.J.; Van Eldik, L.J. A dual role for apolipoprotein E in neuroinflammation. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2004, 23, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-C.; Kanekiyo, T.; Xu, H.; Bu, G. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer disease: Risk, mechanisms and therapy. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J. The Immune-Modulatory Role of Apolipoprotein E with Emphasis on Multiple Sclerosis and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J. Immunol. Res. 2010, 2010, 186813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fransson, J.; Bachelin, C.; Ichou, F.; Guillot-Noël, L.; Ponnaiah, M.; Gloaguen, A.; Maillart, E.; Stankoff, B.; Tenenhaus, A.; Fontaine, B.; et al. Multiple Sclerosis Patient Macrophages Impaired Metabolism Leads to an Altered Response to Activation Stimuli. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflammation 2024, 11, e200312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fransson, J.; Bachelin, C.; Deknuydt, F.; Ichou, F.; Guillot-Noël, L.; Ponnaiah, M.; Gloaguen, A.; Maillart, E.; Stankoff, B.; Tenenhaus, A.; et al. Dysregulated functional and metabolic response in multiple sclerosis patient macrophages correlate with a more inflammatory state, reminiscent of trained immunity. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, S.; Doering, A.; Letiembre, M.; Liu, Y.; Hao, W.; Diem, R.; Bernreuther, C.; Glatzel, M.; Engelhardt, B.; Fassbender, K. The LPS Receptor, CD14 in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis and Multiple Sclerosis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 17, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutterotti, A.; Kuenz, B.; Gredler, V.; Khalil, M.; Ehling, R.; Gneiss, C.; Egg, R.; Deisenhammer, F.; Berger, T.; Reindl, M. Increased serum levels of soluble CD14 indicate stable multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 181, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogers, L.; Engelenburg, H.J.; Janssen, M.; Unger, P.-P.A.; Melief, M.-J.; Wierenga-Wolf, A.F.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Mason, M.R.; Hamann, J.; van Langelaar, J.; et al. Selective emergence of antibody-secreting cells in the multiple sclerosis brain. EBioMedicine 2023, 89, 104465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkildsen, Ø.; Stansberg, C.; Angelskår, S.M.; Kooi, E.; Geurts, J.J.; Van Der Valk, P.; Myhr, K.; Steen, V.M.; Bø, L. Upregulation of Immunoglobulin-related Genes in Cortical Sections from Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Brain Pathol. 2010, 20, 720–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtz, L.I.; Knyazhanskaya, E.; Sohaei, D.; Prassas, I.; Pittock, S.; Willrich, M.A.V.; Saadeh, R.; Gupta, R.; Atkinson, H.J.; Grill, D.; et al. Identification of brain-enriched proteins in CSF as biomarkers of relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. Clin. Proteom. 2024, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borràs, E.; Cantó, E.; Choi, M.; Villar, L.M.; Álvarez-Cermeño, J.C.; Chiva, C.; Montalban, X.; Vitek, O.; Comabella, M.; Sabidó, E. Protein-Based Classifier to Predict Conversion from Clinically Isolated Syndrome to Multiple Sclerosis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2016, 15, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtada, J.; Thibaudeau, C.; Wasylyk, B.; Jung, A.C. The Multifaceted Role of Human Dickkopf-3 (DKK-3) in Development, Immune Modulation and Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federico, G.; Meister, M.; Mathow, D.; Heine, G.H.; Moldenhauer, G.; Popovic, Z.V.; Nordström, V.; Kopp-Schneider, A.; Hielscher, T.; Nelson, P.J.; et al. Tubular Dickkopf-3 promotes the development of renal atrophy and fibrosis. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e84916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, M.; Papatriantafyllou, M.; Nordstrã, M.V.; Kumar, V.; Ludwig, J.; Lui, K.O.; Boyd, A.S.; Popovic, Z.V.; Fleming, T.H.; Moldenhauer, G.; et al. Dickkopf-3, a tissue-derived modulator of local T-cell responses. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez de San José, N.; Massa, F.; Halbgebauer, S.; Oeckl, P.; Steinacker, P.; Otto, M. Neuronal pentraxins as biomarkers of synaptic activity: From physiological functions to pathological changes in neurodegeneration. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 207–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohri, I.; Taniike, M.; Taniguchi, H.; Kanekiyo, T.; Aritake, K.; Inui, T.; Fukumoto, N.; Eguchi, N.; Kushi, A.; Sasai, H.; et al. Prostaglandin D2-mediated microglia/astrocyte interaction enhances astrogliosis and demyelination in twitcher. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 4383–4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, S.S.; Zaman, A.; Simas, T.; Fournier, A.E. Comparing RNA-sequencing datasets from astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglia in multiple sclerosis identifies novel dysregulated genes relevant to inflammation and myelination. WIREs Mech. Dis. 2023, 15, e1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, M.G.; Fonteh, A.N.; Biringer, R.G.; Xfc, H.; Hühmer, A.F.R.; Cowan, R.P. Prostaglandin D synthase isoforms from cerebrospinal fluid vary with brain pathology. Dis. Markers 2006, 22, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kihara, Y. Systematic Understanding of Bioactive Lipids in Neuro-Immune Interactions: Lessons from an Animal Model of Multiple Sclerosis. In The Role of Bioactive Lipids in Cancer Inflammation Related Diseases; Honn, K.V., Zeldin, D.C., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 133–148. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, M.S.; Bal, L.C.; Winschel, I.; Manca, E.; Walkenhorst, M.; Sevgili, B.; Sonner, J.K.; Di Liberto, G.; Mayer, C.; Binkle-Ladisch, L.; et al. The NR4A2/VGF pathway fuels inflammation-induced neurodegeneration via promoting neuronal glycolysis. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e177692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLuca, J.; Chiaravalloti, N.D.; Sandroff, B.M. Treatment and management of cognitive dysfunction in patients with multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avsar, T.; Durası, İ.M.; Uygunoğlu, U.; Tütüncü, M.; Demirci, N.O.; Saip, S.; Sezerman, O.U.; Siva, A.; Turanlı, E.T. CSF Proteomics Identifies Specific and Shared Pathways for Multiple Sclerosis Clinical Subtypes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample ID | Author, Year | Number of Control Samples | Number of MS Samples | Sample Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Timirci, 2019 [24] | 19 | 23 | CSF |
| 6 | Stoop, 2017 [26] | 45 | 47 | CSF |
| 7 | Opsahl, 2016 [27] | 14 | 50 | CSF |
| 8 | Krokseeven, 2012 [28] | 17 | 17 | CSF |
| PXD004572 | Kroksveen, 2017 [29] | 21 | 21 | CSF |
| PXD017643 | Elkjaer, 2021 [7] | 33 | 103 | CSF |
| PXD022958 | Comabella, 2021 [25] | 44 | 28 | CSF |
| PXD004540 | Kroksveen, 2016 [29] | 21 | 216 | CSF |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sakiz, E.; Amanzadeh Jajin, E.; Cubeddu, L.; Gamsjaeger, R.; Avsar, T. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid Associated with Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136171
Sakiz E, Amanzadeh Jajin E, Cubeddu L, Gamsjaeger R, Avsar T. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid Associated with Multiple Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136171
Chicago/Turabian StyleSakiz, Elif, Elnaz Amanzadeh Jajin, Liza Cubeddu, Roland Gamsjaeger, and Timucin Avsar. 2025. "Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid Associated with Multiple Sclerosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136171
APA StyleSakiz, E., Amanzadeh Jajin, E., Cubeddu, L., Gamsjaeger, R., & Avsar, T. (2025). Comprehensive Meta-Analysis of Differentially Expressed Proteins in Cerebrospinal Fluid Associated with Multiple Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6171. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136171






