Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation Using Bumpy Gold Nanoshell Films with Controlled Shell Thickness
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Bumpy Gold Nanoshells with Optimized Morphology for Photothermal Activity
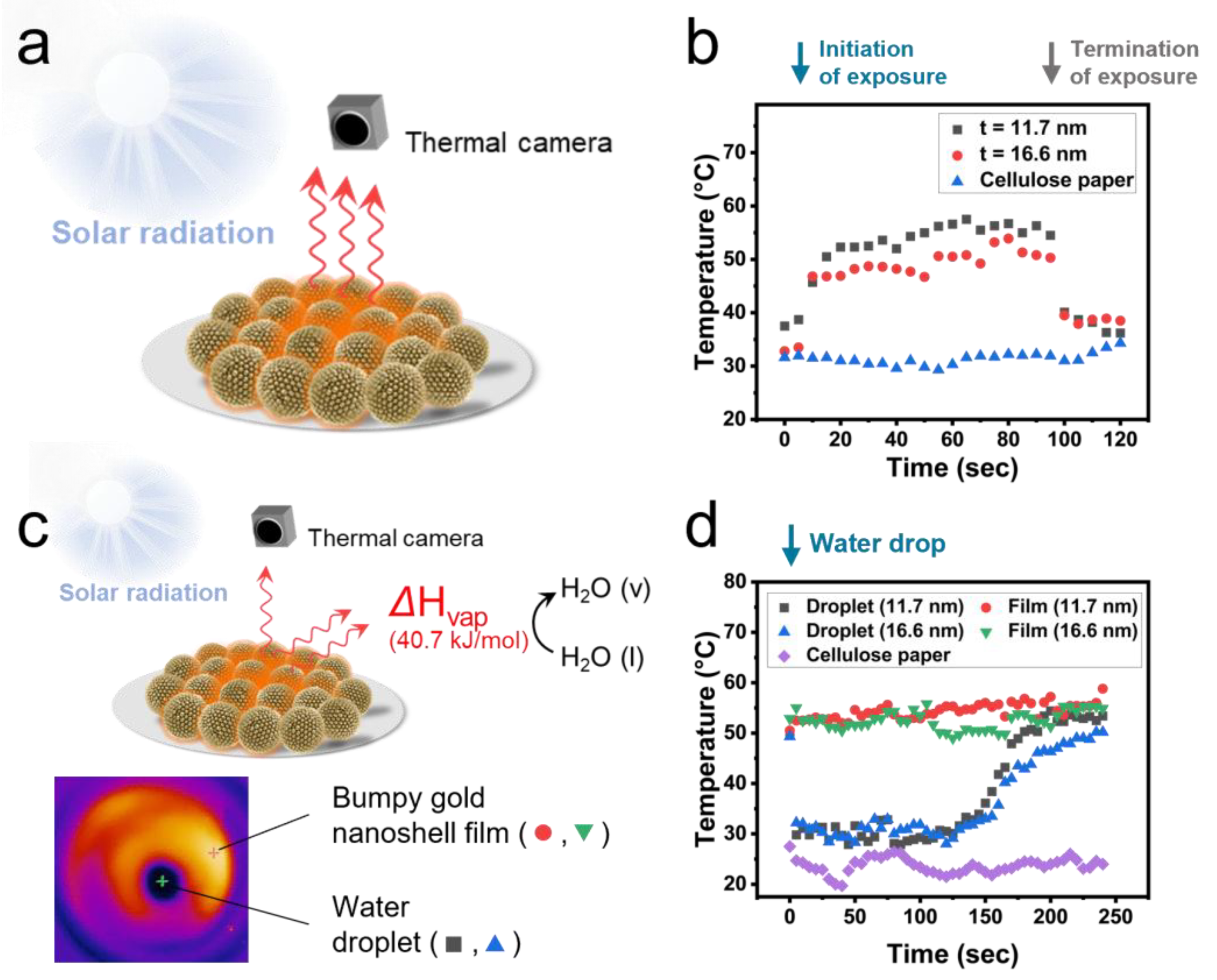
2.2. Solar-Driven Evaporation Using Bumpy Gold Nanoshell Film
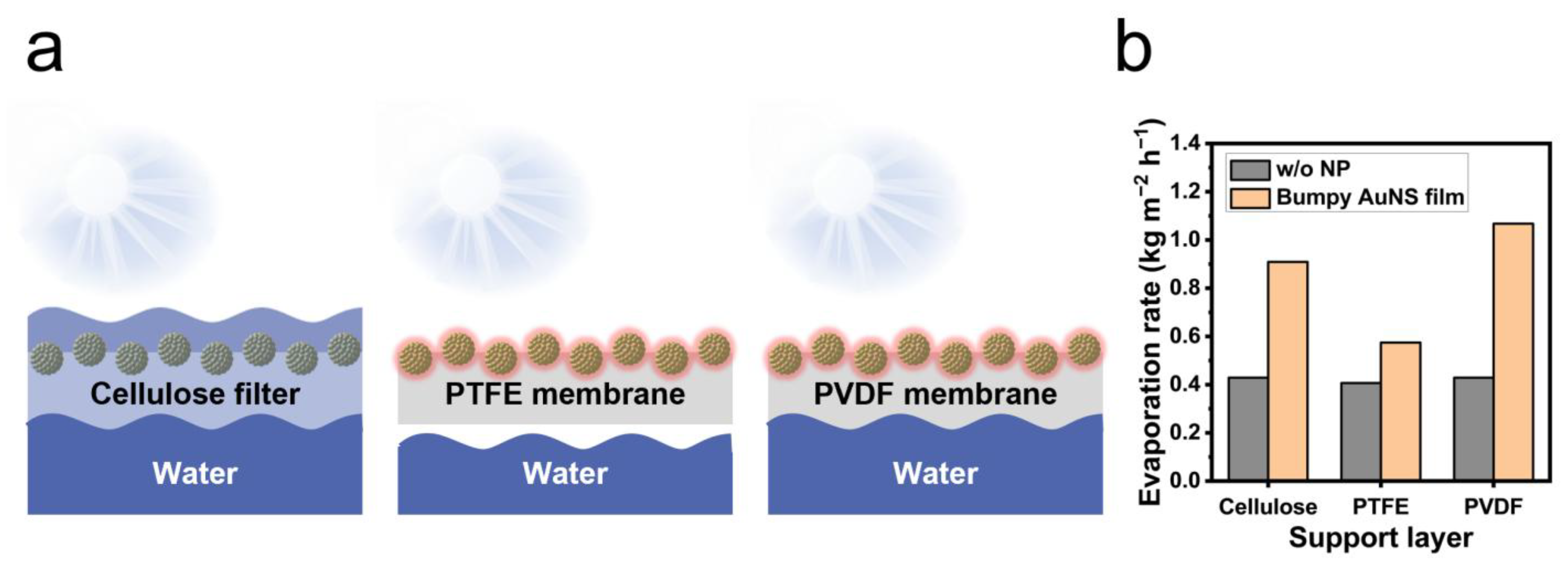
2.3. Evaporation Rate on Different Support Membranes
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Characterization
3.3. Synthesis of AuNP Seeds
3.4. Synthesis of Bumpy Gold Nanoshell
3.5. FDTD Simulation
- (A)
- The surface of the silica sphere (diameter: 145.5 nm) is composed of 619 gold spheres with diameter: 11.7 nm;
- (B)
- The surface of the silica sphere (diameter: 145.5 nm) is composed of 308 gold spheres with diameter: 16.6 nm.
3.6. Fabrication of Photothermal Films with Bumpy Gold Nanoshell Layer
3.7. Characterization of Photothermal Effect
3.8. Evaporation of a Droplet of Water Under Laser and Sunlight Exposure
3.9. Investigation of Evaporation Rate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Karaghouli, A.; Kazmerski, L.L. Energy Consumption and Water Production Cost of Conventional and Renewable-Energy-Powered Desalination Processes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Ni, G.; Song, C.; Shang, W.; Wu, J.; Zhu, J.; Chen, G.; Deng, T. Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation. Nat. Energy 2018, 3, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Kuang, Y.; Hu, L. Challenges and Opportunities for Solar Evaporation. Joule 2019, 3, 683–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, W.; Tang, M.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, S.; Zhu, J. Graphene Oxide-Based Efficient and Scalable Solar Desalination under One Sun with a Confined 2D Water Path. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 13953–13958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Pang, Y.; Huang, W.; Shaw, S.K.; Schiffbauer, J.; Pillers, M.A.; Mu, X.; Luo, S.; Zhang, T.; Huang, Y.; et al. Functionalized Graphene Enables Highly Efficient Solar Thermal Steam Generation. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 5510–5518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Song, J.; Yang, Z.; Kuang, Y.; Hitz, E.; Jia, C.; Gong, A.; Jiang, F.; Zhu, J.Y.; et al. Highly Flexible and Efficient Solar Steam Generation Device. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Huang, F. Constructing Black Titania with Unique Nanocage Structure for Solar Desalination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 31716–31721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Huang, W.; Song, C.; Yan, M.; Guo, C.; Liu, S. Non-Stoichiometric MoO3-x Quantum Dots as a Light-Harvesting Material for Interfacial Water Evaporation. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 6744–6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; He, Y.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, B. Bifunctional Au@TiO2 Core–Shell Nanoparticle Films for Clean Water Generation by Photocatalysis and Solar Evaporation. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 132, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, O.; Urban, A.S.; Day, J.; Lal, S.; Nordlander, P.; Halas, N.J. Solar Vapor Generation Enabled by Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Li, H.; Xie, M.; Shen, S.; Wang, W.; Zhao, M.; Mo, X.; Xia, Y. Incorporation of Gold Nanocages into Electrospun Nanofibers for Efficient Water Evaporation through Photothermal Heating. Mater. Today Energy 2019, 12, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, S.J.; Averitt, R.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Halas, N.J. Nanoengineering of Optical Resonances; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; Volume 288. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Xia, Y. Gold and Silver Nanoparticles: A Class of Chromophores with Colors Tunable in the Range from 400 to 750 Nm. Analyst 2003, 128, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prodan, E.; Radloff, C.; Halas, N.J.; Nordlander, P. A Hybridization Model for the Plasmon Response of Complex Nanostructures. Science 2003, 302, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiles, P.L.; Dieringer, J.A.; Shah, N.C.; Van Duyne, R.P. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2008, 1, 601–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heck, K.N.; Janesko, B.G.; Scuseria, G.E.; Halas, N.J.; Wong, M.S. Using Catalytic and Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy-Active Gold Nanoshells to Understand the Role of Basicity in Glycerol Oxidation. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Kim, Y.H.; Jo, G.; Yoo, J.; Park, S.M.; Jun, B.H.; Yeo, W.S. Efficient Analysis of Small Molecules via Laser Desorption/Ionization Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (LDI–TOF MS) Using Gold Nanoshells with Nanogaps. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, S.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, M.; Yun, Y.; Pham, X.H.; Kim, J.; Seong, B.; Kim, W.; Jo, A.; Ham, K.M.; et al. Highly Sensitive Near-Infrared SERS Nanoprobes for in Vivo Imaging Using Gold-Assembled Silica Nanoparticles with Controllable Nanogaps. J. Nanobiotechnol 2022, 20, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Cho, H.S.; Yoo, K.; Ham, K.M.; Kang, H.; Pham, X.H.; Jun, B.H. High-Throughput Synthesis of Nanogap-Rich Gold Nanoshells Using Dual-Channel Infusion System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Hallinan, D.T. Gold Nanoparticle Monolayers from Sequential Interfacial Ligand Exchange and Migration in a Three-Phase System. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yu, H.; Yu, J. Emerging S-Scheme Photocatalyst. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soc, J.C.; Commun, C. A New Hydrosol of Gold Clusters. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1993, 1, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stober, W.; Fink, A.; Ernst Bohn, D. Controlled Growth of Monodisperse Silica Spheres in the Micron Size Range 1; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1968; Volume 26. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-H.; Cho, H.-S.; Yoo, K.; Yang, C.-H.; Lee, S.-K.; Kang, H.; Jun, B.-H. Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation Using Bumpy Gold Nanoshell Films with Controlled Shell Thickness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136160
Kim Y-H, Cho H-S, Yoo K, Yang C-H, Lee S-K, Kang H, Jun B-H. Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation Using Bumpy Gold Nanoshell Films with Controlled Shell Thickness. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136160
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yoon-Hee, Hye-Seong Cho, Kwanghee Yoo, Cho-Hee Yang, Sung-Kyu Lee, Homan Kang, and Bong-Hyun Jun. 2025. "Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation Using Bumpy Gold Nanoshell Films with Controlled Shell Thickness" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136160
APA StyleKim, Y.-H., Cho, H.-S., Yoo, K., Yang, C.-H., Lee, S.-K., Kang, H., & Jun, B.-H. (2025). Solar-Driven Interfacial Evaporation Using Bumpy Gold Nanoshell Films with Controlled Shell Thickness. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6160. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136160







