Diagnostic Value of Protein C Depletion in Pathologies Associated with the Activation of the Blood Coagulation System
Abstract
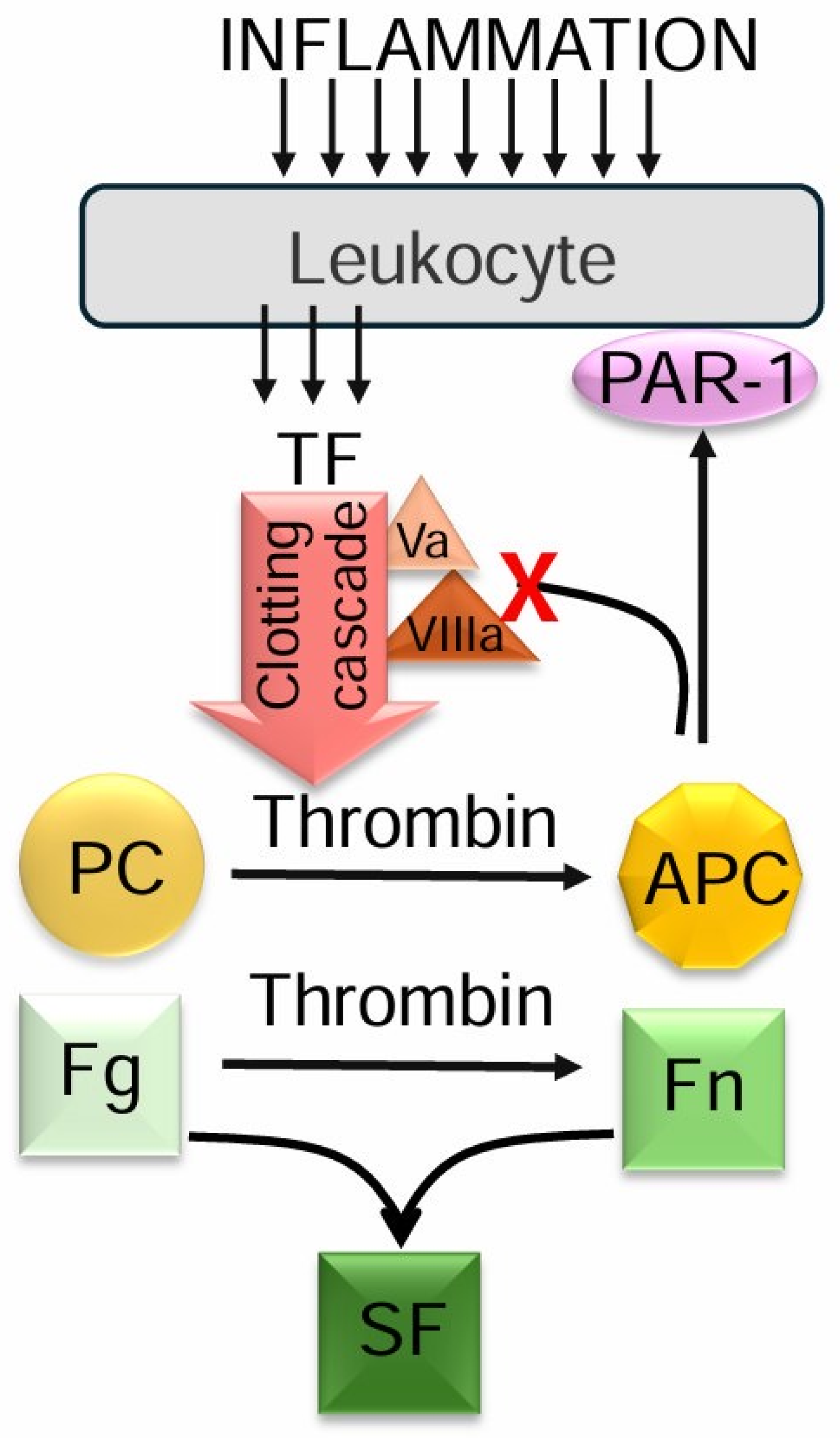
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
2.2. Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)
2.3. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Patient
4.2.1. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
4.2.2. Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)
4.2.3. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
4.3. Methods
4.3.1. Blood Plasma Preparation
4.3.2. Fibrinogen Concentration
4.3.3. Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time
4.3.4. Soluble Fibrin Monomeric Complexes (SFMCs)
4.3.5. Soluble Fibrin (SF)
4.3.6. D-Dimer in Human Blood Plasma
4.3.7. Protein C Level
4.3.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SFMCs | soluble fibrin monomeric complexes |
| SF | soluble fibrin |
| PF1+2 | prothrombin fragment 1+2 |
| SLE | systemic lupus erythematosus |
| APS | antiphospholipid syndrome |
| SLEDAI | SLE Disease Activity Index |
| AMI | acute myocardial infarction |
| AAA | abdominal aortic aneurysm |
| APTT | Activated partial thromboplastin time |
| PC | protein C |
| AT-III | antithrombin III |
| PAR | proteinase-activated receptors |
| IHD | ischemic heart disease |
References
- Brown, A.C.; Levy, J.H. Maintaining Hemostatic Balance in Treating Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation. Anesthesiology 2019, 131, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, T.; Cushing, M.M. Hemostatic Balance in Severe Trauma. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 600501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pablo-Moreno, J.A.; Serrano, L.J.; Revuelta, L.; Sánchez, M.J.; Liras, A. The Vascular Endothelium and Coagulation: Homeostasis, Disease, and Treatment, with a Focus on the Von Willebrand Factor and Factors VIII and V. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbach, S.; Lagrange, J.; Wenzel, P. Thromboinflammation and Vascular Dysfunction. Hamostaseologie 2019, 39, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieczór, R.; Kulwas, A.; Rość, D. Implications of Hemostasis Disorders in Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia-An In-Depth Comparison of Selected Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, K.; Muranishi, K.; Kawano, Y.; Hatomoto, H.; Yamasaki, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Ishikura, H. Soluble fibrin is a useful marker for predicting extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuit exchange because of circuit clots. J. Artif. Organs Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Artif. Organs 2018, 21, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samkari, H.; Song, F.; Van Cott, E.M.; Kuter, D.J.; Rosovsky, R. Evaluation of the prothrombin fragment 1.2 in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.P.; Silveira, J.R.; Maille, N.M.; Haynes, L.M.; Tracy, P.B. Prothrombin activation on the activated platelet surface optimizes expression of procoagulant activity. Blood 2011, 117, 1710–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.Y.; Niikura, T.; Iwakura, T.; Sakai, Y.; Kuroda, R.; Kurosaka, M. Thrombin-antithrombin III complex tests. J. Orthop. Surg. 2017, 25, 170840616684501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, D.K.; Tian, X.; Zheng, X.Y.; Liu, T. Protein C deficiency with venous and arterial thromboembolic events. World J. Clin. Cases 2024, 12, 2000–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmissbah, T.E.; Iderous, M.E.; Al-Qahtani, F.M.; Elaskary, A.; Dahlawi, H. Assessment of Antithrombin III and Protein C in Saudi Myocardial Infarction Patients. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67, 2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esmon, C.T. Inflammation and the activated protein C anticoagulant pathway. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2006, 32 (Suppl. 1), 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, A.R. Regulation of the protein C anticoagulant and antiinflammatory pathways. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majid, Z.; Tahir, F.; Ahmed, J.; Bin Arif, T.; Haq, A. Protein C Deficiency as a Risk Factor for Stroke in Young Adults: A Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiasakul, T.; De Jesus, E.; Tong, J.; Chen, Y.; Crowther, M.; Garcia, D.; Chai-Adisaksopha, C.; Messé, S.R.; Cuker, A. Inherited Thrombophilia and the Risk of Arterial Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart 2019, 8, e012877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afeltra, A.; Vadacca, M.; Conti, L.; Galluzzo, S.; Mitterhofer, A.P.; Ferri, G.M.; Del Porto, F.; Caccavo, D.; Gandolfo, G.M.; Amoroso, A. Thrombosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: Congenital and acquired risk factors. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 53, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xie, S.B.; Wu, C.H.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Fan, Y.G.; Leng, R.X.; Pan, H.F.; Xiong, H.B.; et al. Coagulation cascade and complement system in systemic lupus erythematosus. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 14862–14881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, K.; Massberg, S. Interplay between inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular pathology. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 666–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, M.A.; Paneni, F.; Libby, P.; Frantz, S.; Stähli, B.E.; Templin, C.; Mengozzi, A.; Wang, Y.J.; Kündig, T.M.; Räber, L.; et al. Inflammation in acute myocardial infarction: The good, the bad and the ugly. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oprescu, N.; Micheu, M.M.; Scafa-Udriste, A.; Popa-Fotea, N.M.; Dorobantu, M. Inflammatory markers in acute myocardial infarction and the correlation with the severity of coronary heart disease. Ann. Med. 2021, 53, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Fowkes, F.G.; Lowe, G.D.; Rumley, A. Haemostatic factors, atherosclerosis and risk of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis Int. J. Haemost. Thromb. 1996, 7, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.H.; Liang, P.C.; Huang, S.C.; Chi, N.S.; Lin, F.Y.; Wang, S.S. The significance of endograft geometry on the incidence of intraprosthetic thrombus deposits after abdominal endovascular grafting. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Vasc. Surg. 2009, 38, 741–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golledge, J.; Tsao, P.S.; Dalman, R.L.; Norman, P.E. Circulating markers of abdominal aortic aneurysm presence and progression. Circulation 2008, 118, 2382–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schouten, O.; Kok, N.F.; Hoedt, M.T.; van Laanen, J.H.; Poldermans, D. The influence of aneurysm size on perioperative cardiac outcome in elective open infrarenal aortic aneurysm repair. J. Vasc. Surg. 2006, 44, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmann, D.B.; Grand, D.J.; Freischlag, J.A. Inflammatory abdominal aortic aneurysm. JAMA 2007, 297, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaoutoglou, E.; Kouvelos, G.; Koutsoumpelis, A.; Patelis, N.; Lazaris, A.; Matsagkas, M. An Update on the Inflammatory Response after Endovascular Repair for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 945035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, S.; Lei, R.; Duan, Q.; Li, J.; Meng, J.; Sun, L. Clinical study on the feasibility of new thrombus markers in predicting massive cerebral infarction. Front. Neurol. 2023, 13, 942887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellner, B.; Rohla, M.; Jarai, R.; Smetana, P.; Freynhofer, M.K.; Egger, F.; Zorn, G.; Weiss, T.W.; Huber, K.; Geppert, A. Activated protein C levels and outcome in patients with cardiogenic shock complicating acute myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. Acute Cardiovasc. Care 2017, 6, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, H.; Haracska, B.; Naumann, J.; Westhofen, P.; Hass, M.S.; Kruppenbacher, J.P. Laboratory Limitations of Excluding Hereditary Protein C Deficiency by Chromogenic Assay: Discrepancies of Phenotype and Genotype. Clin. Appl. Thromb./Hemost. Off. J. Int. Acad. Clin. Appl. Thromb./Hemost. 2020, 26, 1076029620912028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankovic, S.; Obradovic, S.; Dzudovic, B.; Djenic, N.; Romanovic, R.; Jovic, Z.; Spasic, M.; Djuric, O.; Malovic, D.; Stavric, M.; et al. Lower plasma protein C activity is associated with early myocardial necrosis and no-reflow phenomenon in patients with ST elevation myocardial infarction. Acta Cardiol. 2019, 74, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovjov, D.A.; Ugarova, T.P. Purification and characterization of α–specific thrombin-like enzymes from the venoms of middle asian pit viper snakes Agkistrodon halys halys and Agkistrodon halys blomhoffii. Biochemistry 1993, 58, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar]
- Pozdnjakova, T.M.; Musjalkovskaja, A.A.; Ugarova, T.P.; Protvin, D.D.; Kotsjuruba, V.N. On the properties of fibrin monomer prepared from fibrin clot with aetic acid. Thromb. Res. 1976, 16, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombardier, C.; Gladman, D.D.; Urowitz, M.B.; Caron, D.; Chang, C.H. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 35, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alarcón-Segovia, D.; Pérez-Vázquez, M.E.; Villa, A.R.; Drenkard, C.; Cabiedes, J. Preliminary classification criteria for the antiphospholipid syndrome within systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 1992, 21, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolovska, A.S.; Chernyshenko, T.M.; Ivanenko, T.I. Comparative characteristic of fibrinogen level determination methods in blood plasma. Exp. Clin. Physiol. Biochem. 2002, 3, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kozynets, G.P.; Tsyhankov, V.P.; Korolova, D.S.; Gornytska, O.V.; Savchuk, O.M.; Chernyshenko, V.O.; Chernyshenko, T.M.; Platonova, T.M. The Rise of Factor X Level in Blood Plasma of Patients at Severe Burn Injuries. J. Burn. Care Res. Off. Publ. Am. Burn. Assoc. 2022, 43, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugovskoi, E.V.; Kolesnikova, I.N.; Lugovskaia, N.E.; Litvinova, L.M.; Gritsenko, P.G.; Gogolinskaia, G.K.; Liashko, E.D.; Kostiuchenko, E.P.; Remizovskiĭ, G.A.; Pedchenko, V.N.; et al. Quantification of D-dimer and soluble fibrin in blood plasma of people with ischemic heart disease and hypertension. Ukr. Biochem. J. 1999, 76, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Korolova, D.; Syrko, M.; Stohnii, Y.; Druzhyna, N.; Chernyshenko, T.; Gogolinska, G. Standardization of the protein calibrators isolation methodology for thrombophilia markers detecting immunodiagnostic test systems. Biotechnol. Acta 2019, 15, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Fibrinogen, mg/mL | APTT, s | SFMCs, μg/mL | AT-III, % | PC, % | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with SLE | SLEDAI ˂ 14 (n = 41) | 2.5 (1.2–7.3) | 45 (28–67) | 7 (0–70) | 93 * (71–123) | 80 * (42–120) |
| SLEDAI 14–23 (n = 108) | 2.9 (8.5–0.6) | 46 (75–29) | 7 (0–150) | 97 (76–128) | 76 * (45–120) | |
| SLEDAI > 23 (n = 43) | 2.9 (1.2–6.1) | 46 (30–110) | 35 *# (0–150) | 94 (60–118) | 72 * (41–110) | |
| Healthy donors (n = 10) | 2.6 (2.2–3.1) | 45 (42–48) | 2 (1–3) | 100 (90–120) | 100 (90–110) | |
| Parameters | Fibrinogen, mg/mL | APTT, s | SFMCs, μg/mL | AT-III, % | PC, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with stable angina pectoris (n = 27) | 2.9 (1.6–5.4) | 50 * (39–99) | 0 (0–45) | 96 (80–100) | 99 (63–100) |
| Patients with unstable angina pectoris (n = 43) | 2.7 (1.5–4.1) | 60 * (33–120) | 25 *# (0–140) | 85 * (50–120) | 60 *# (45–100) |
| Patients with acute myocardial infarction (n = 54) | 3.1 * (2.2–5.5) | 42 * (23–71) | 45 *@ (0–140) | 86 (48–120) | 63 * (40–110) |
| Healthy donors (n = 13) | 2.6 (2.2–3.1) | 45 (42–48) | 2 (1–3) | 100 (90–120) | 100 (90–110) |
| Parameters | Fibrinogen, mg/mL | APTT, s | SF, μg/mL | AT-III, % | PC, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with AAA (n = 20) | 4.0 * (1.8–7.0) | nd | 8.4 * (2.0–128.0) | nd | 87 * (40–119) |
| Healthy donors (n = 10) | 2.5 (2.3–3.0) | 45 (41–49) | 3 (1–9) | 100 (90–120) | 100 (90–110) |
| Parameters | Fibrinogen, mg/mL | APTT, s | SF, μg/mL | AT-III, % | PC, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High blood loss (n = 7) | 3.4 (1.7–6.2) | nd | 57.0 *# (10.3–199.2) | nd | 63 *# (37–85) |
| High blood loss (n = 13) | 3.1 (1.3–9.8) | nd | 19.5 * (3.7–106.6) | nd | 84 * (70–100) |
| Healthy donors (n = 10) | 2.5 (2.3–3.0) | 45 (41–49) | 3 (1–9) | 100 (90–120) | 100 (90–110) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Korolova, D.S.; Platonova, T.M.; Gornytska, O.V.; Chernyshenko, V.; Korchynskyi, O.; Komisarenko, S.V. Diagnostic Value of Protein C Depletion in Pathologies Associated with the Activation of the Blood Coagulation System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136122
Korolova DS, Platonova TM, Gornytska OV, Chernyshenko V, Korchynskyi O, Komisarenko SV. Diagnostic Value of Protein C Depletion in Pathologies Associated with the Activation of the Blood Coagulation System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136122
Chicago/Turabian StyleKorolova, Daria S., Tetyana M. Platonova, Olga V. Gornytska, Volodymyr Chernyshenko, Olexandr Korchynskyi, and Serhiy V. Komisarenko. 2025. "Diagnostic Value of Protein C Depletion in Pathologies Associated with the Activation of the Blood Coagulation System" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136122
APA StyleKorolova, D. S., Platonova, T. M., Gornytska, O. V., Chernyshenko, V., Korchynskyi, O., & Komisarenko, S. V. (2025). Diagnostic Value of Protein C Depletion in Pathologies Associated with the Activation of the Blood Coagulation System. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6122. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136122







