Therapeutic Benefits of Nano-Echinacea Extract on Reproductive Injury Induced by Polystyrene Plastic Materials in Rat Model via Regulating Gut–Brain Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
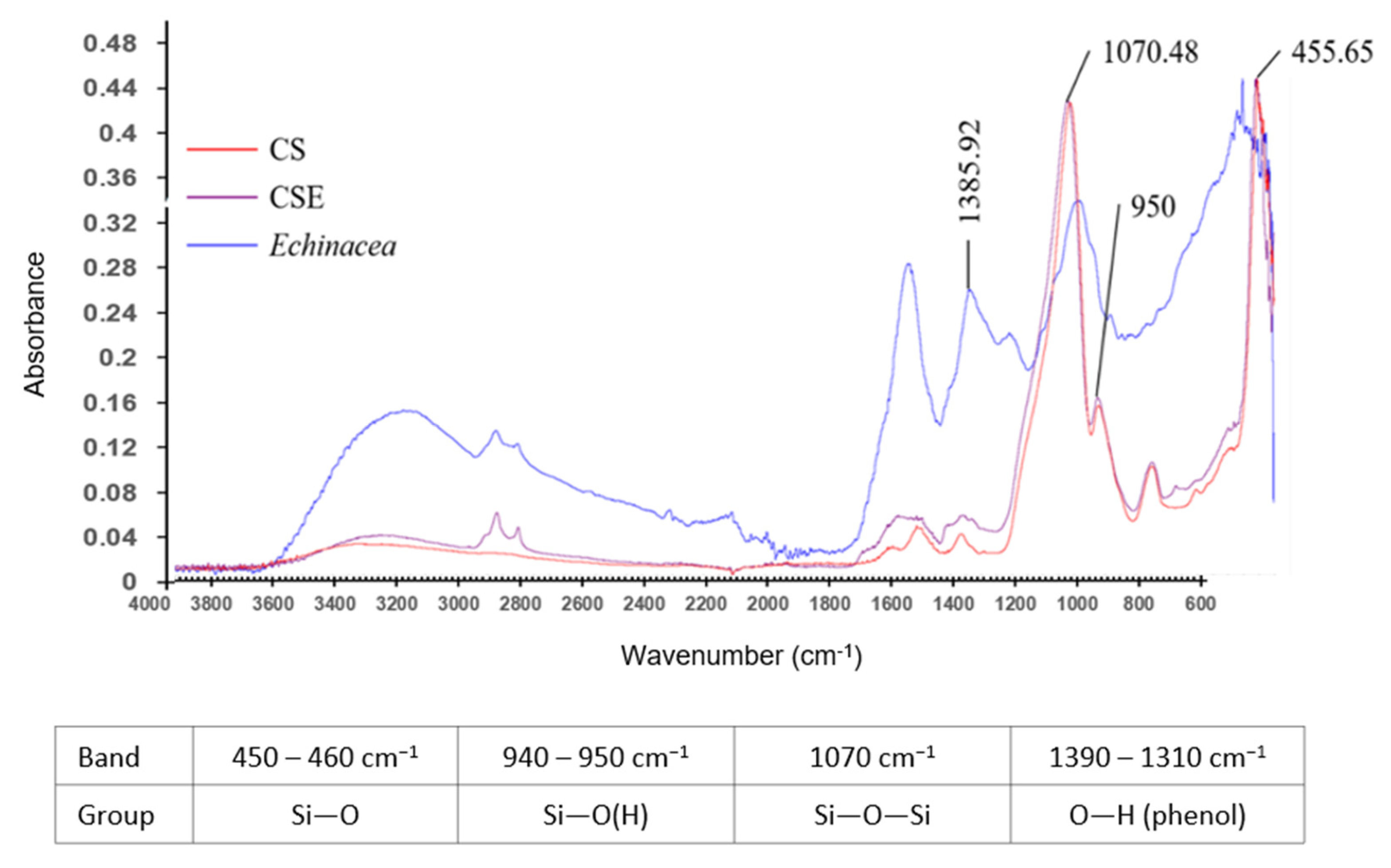
2.1. FTIR Analysis
2.2. DLS Analysis of Nanoparticles
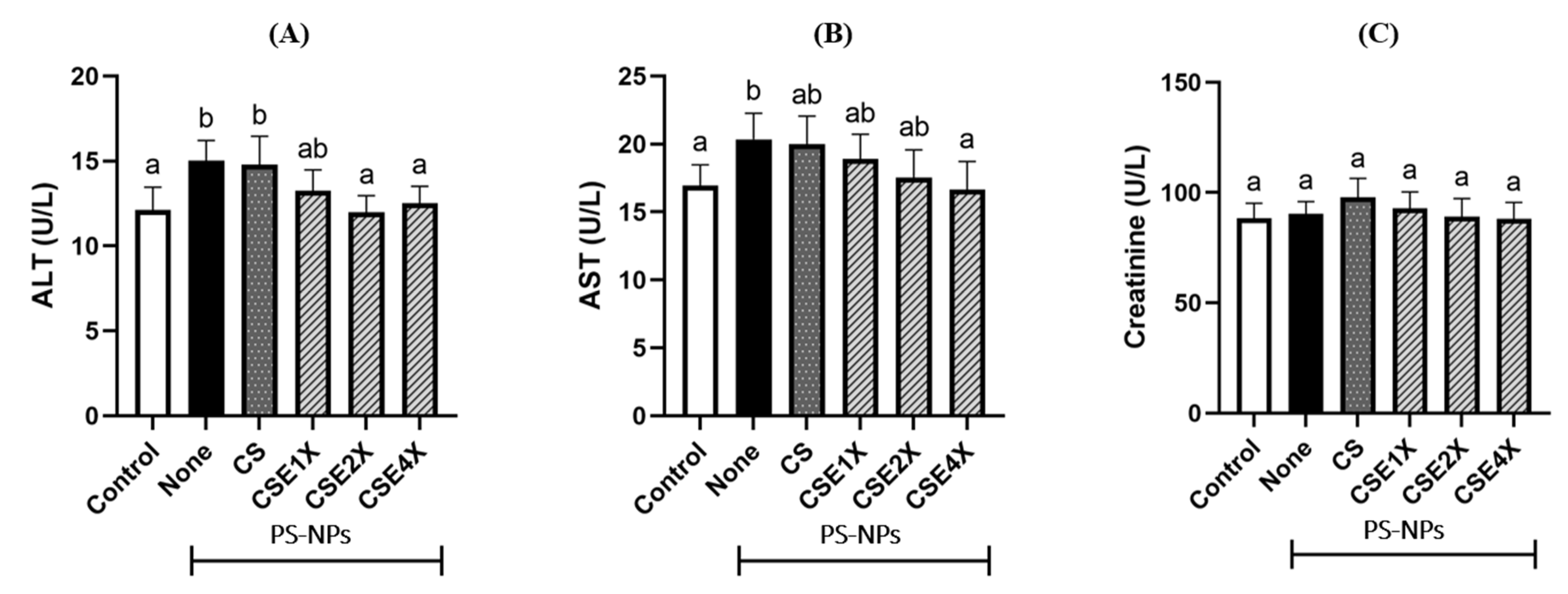
2.3. Level of Biomarkers for Liver Damage
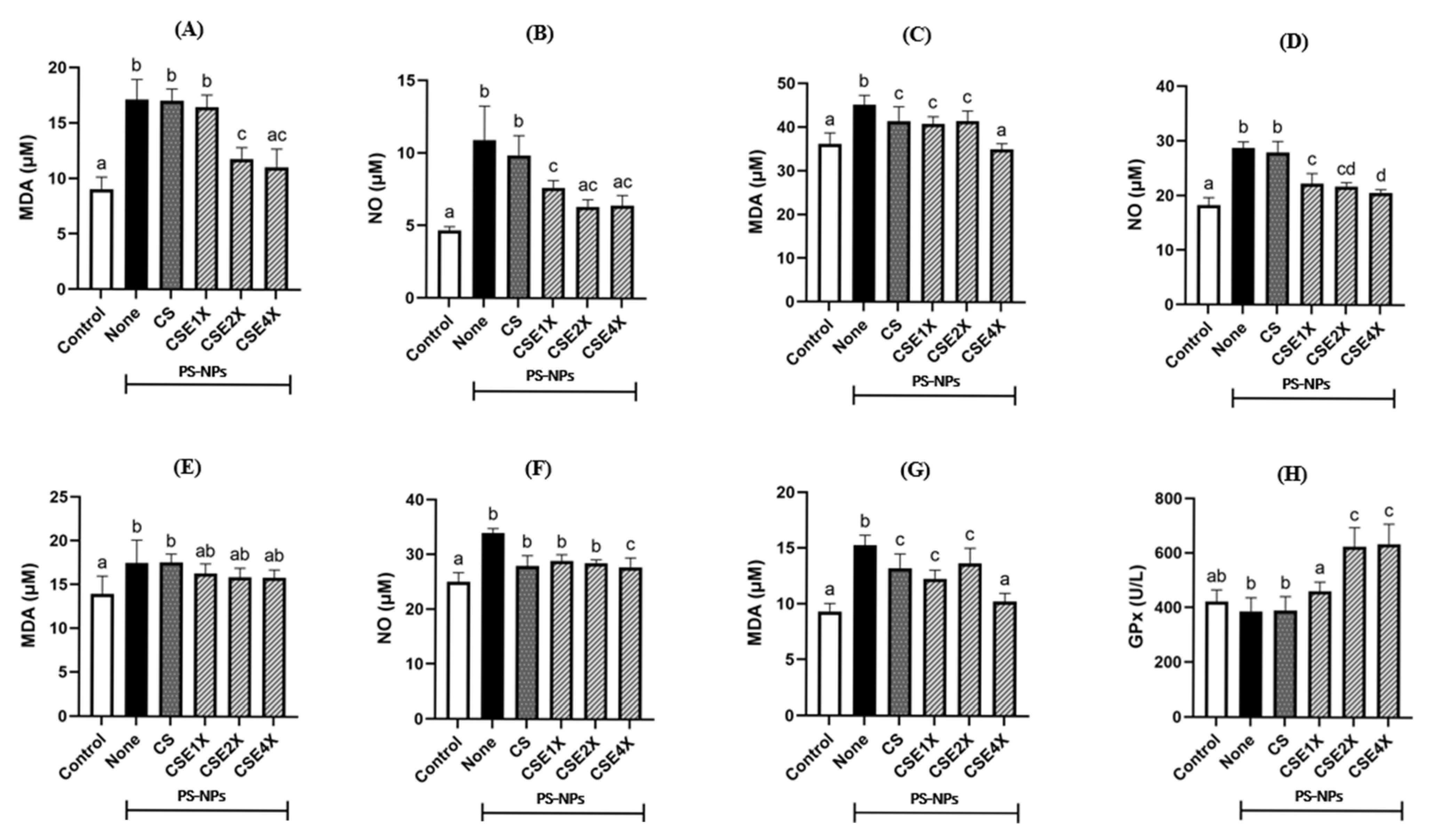
2.4. Antioxidant Properties of CSE
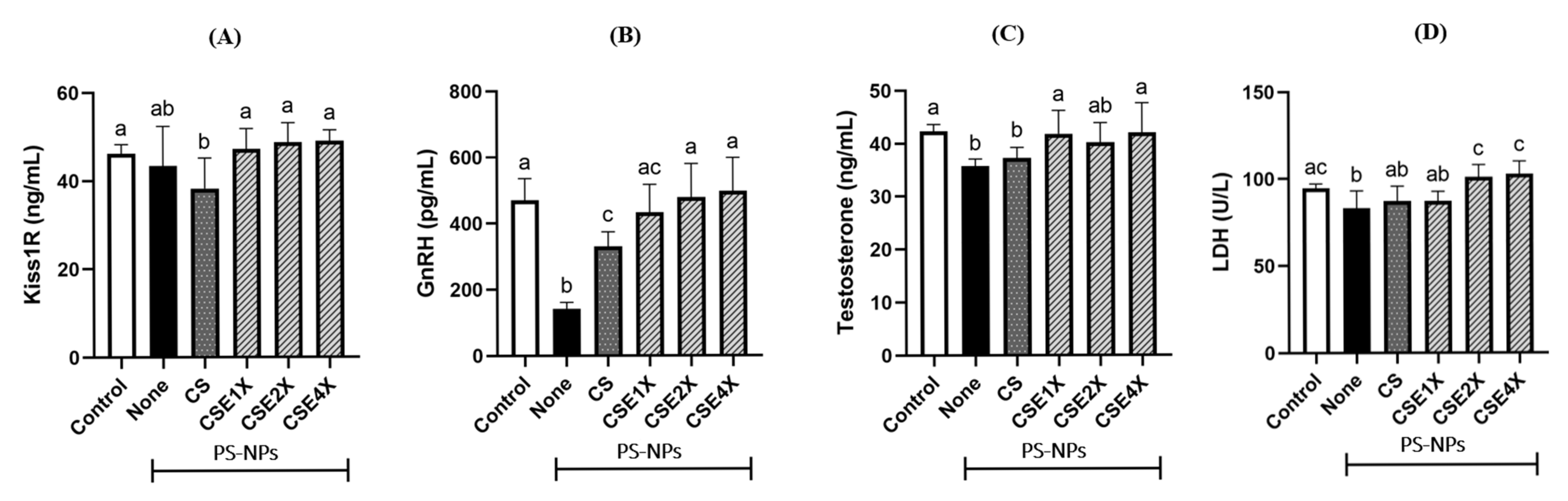
2.5. Effect of CSE on Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Gonadal (HPG) Axis and Sperm Metabolism
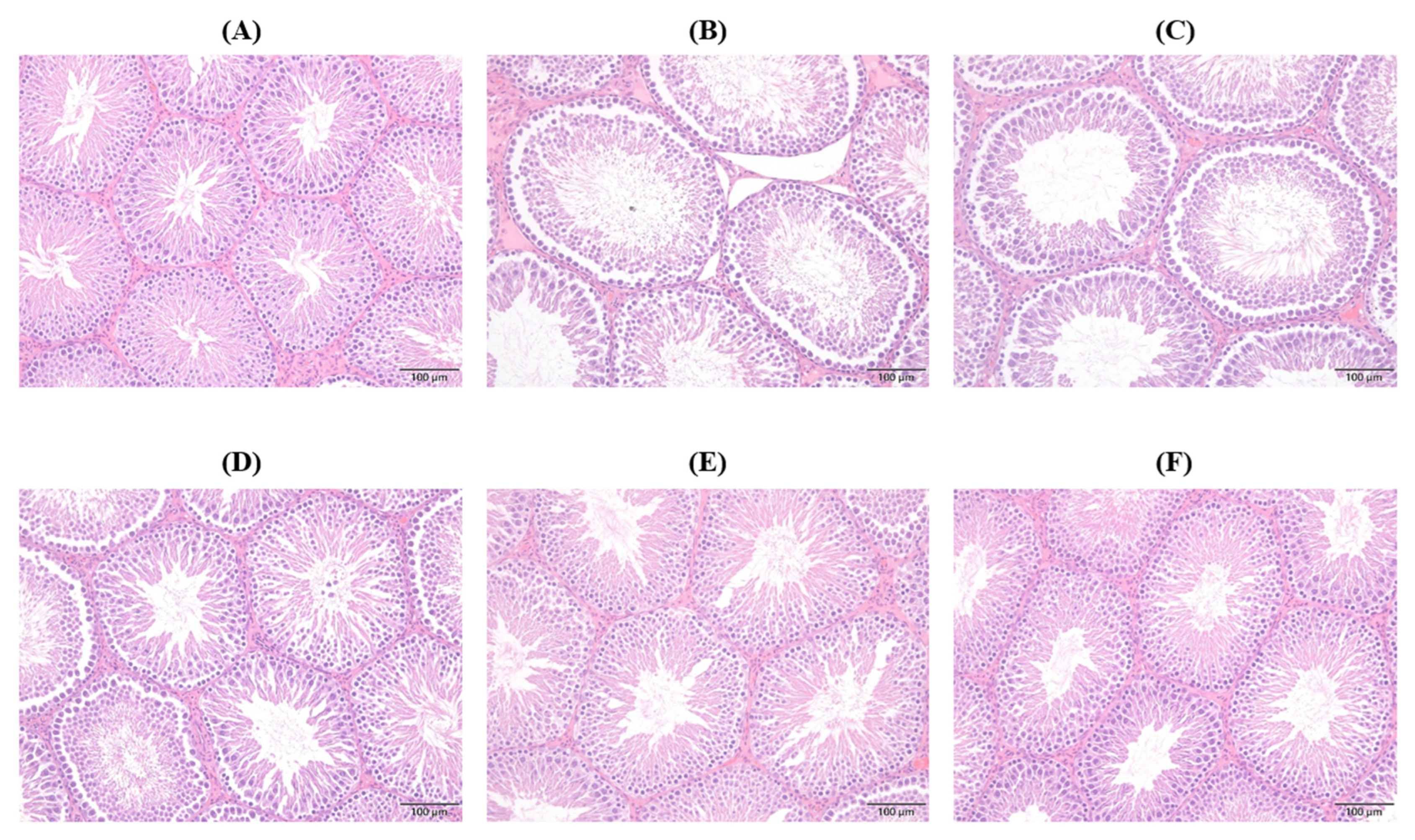
2.6. Histopathological Changes in Seminiferous Tubule (ST)
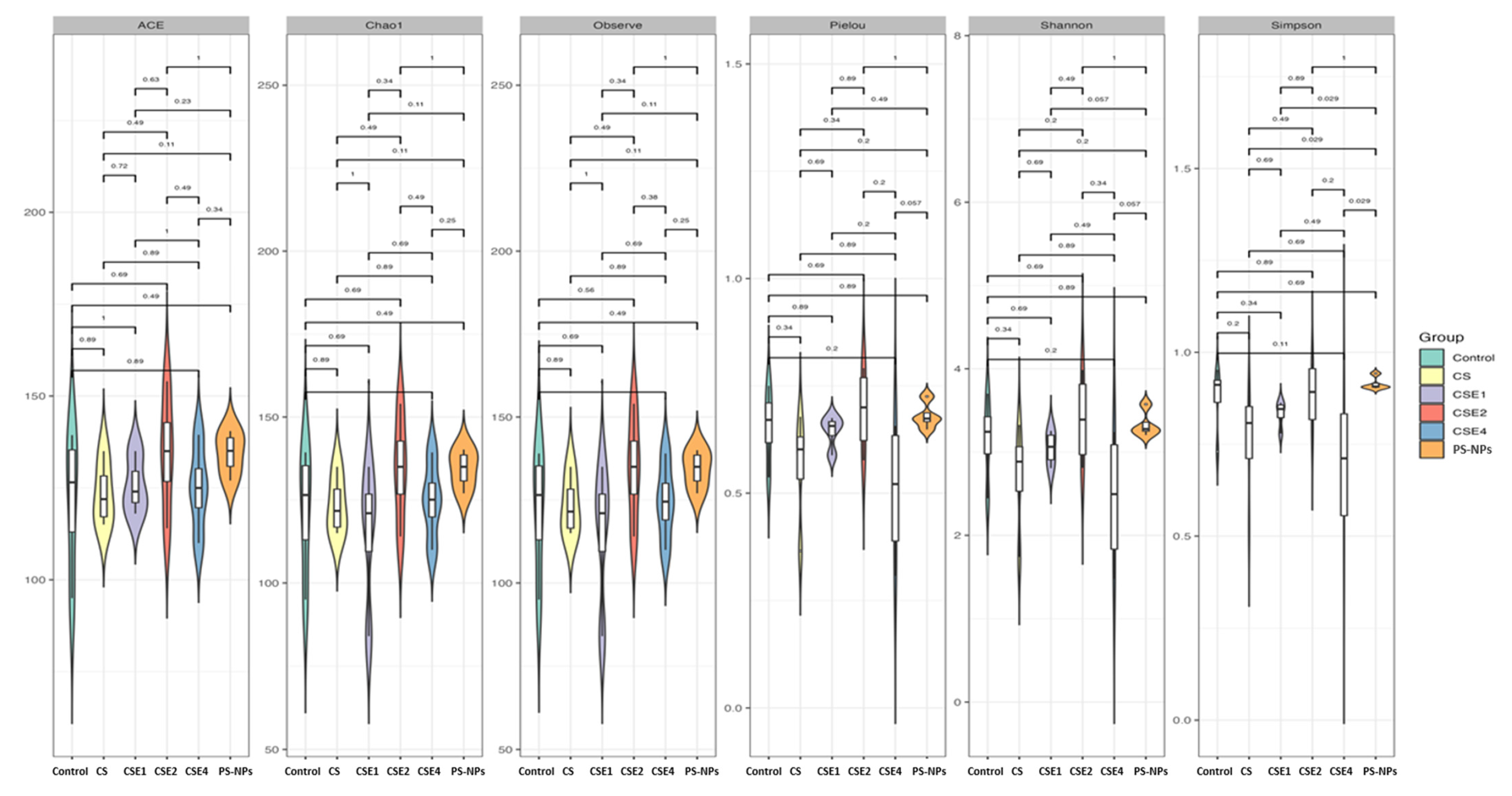
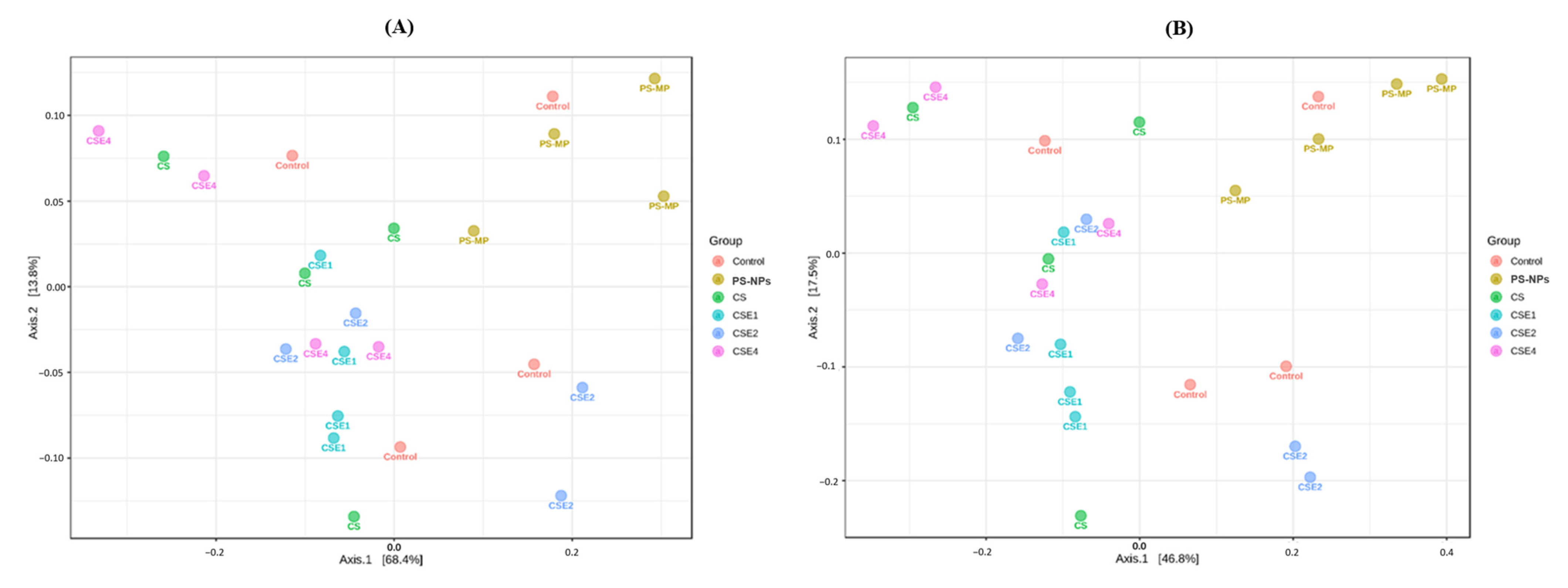
2.7. Microbial Diversity in the Gut
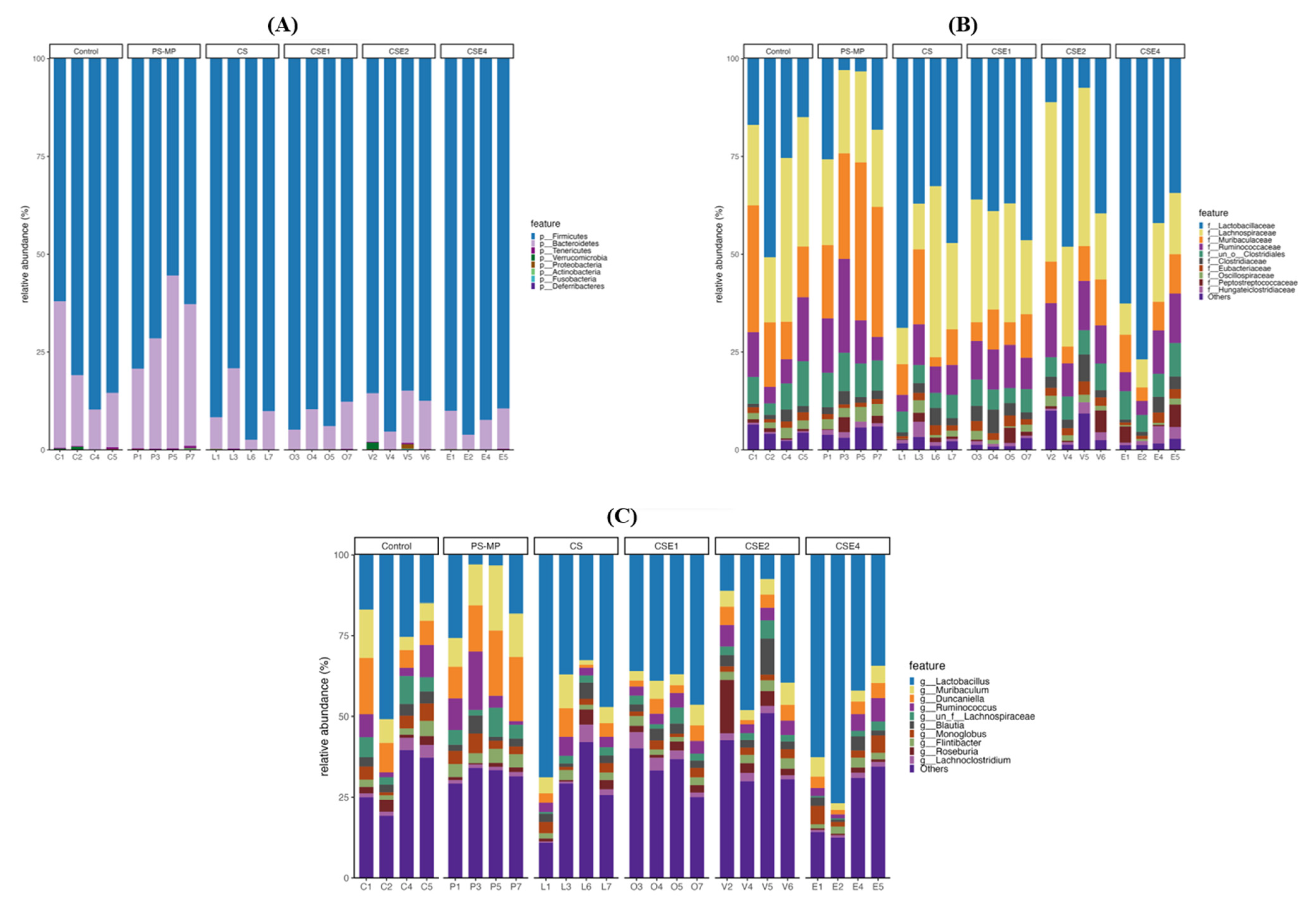
2.8. Microbial Composition in Gut
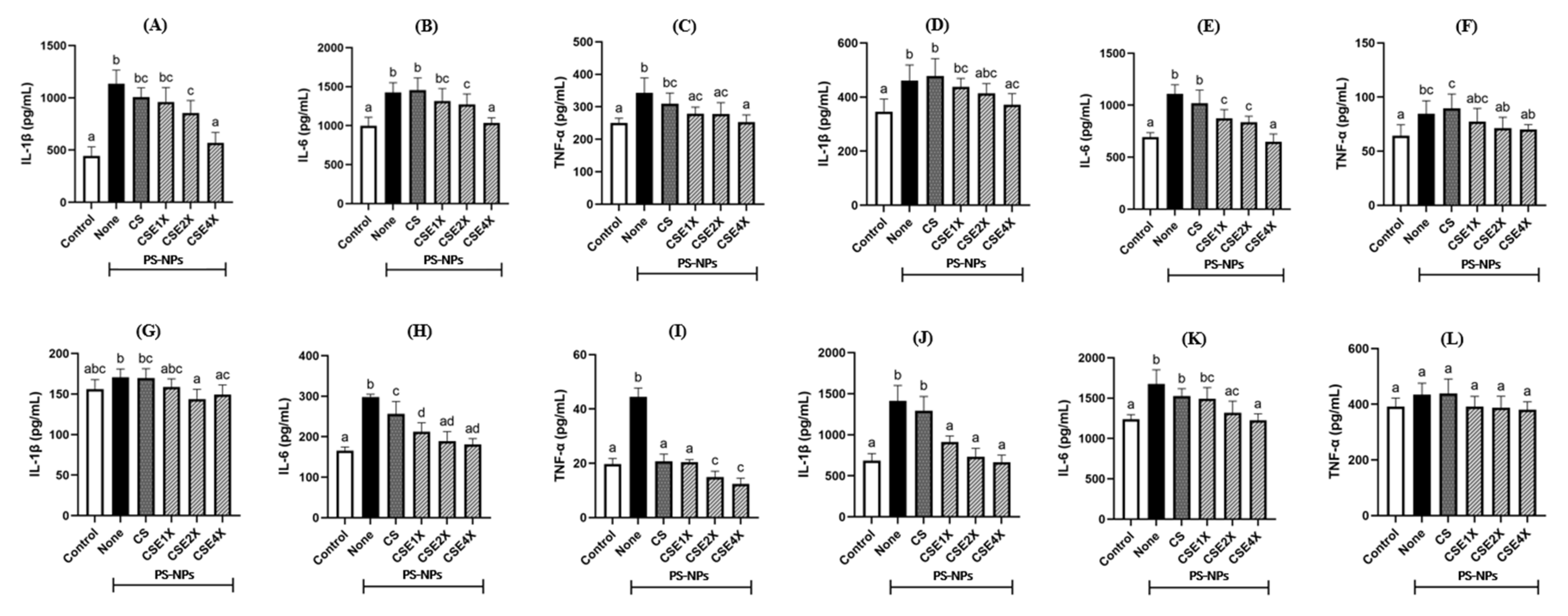
2.9. Effect of CSE on Inflammatory Cytokines
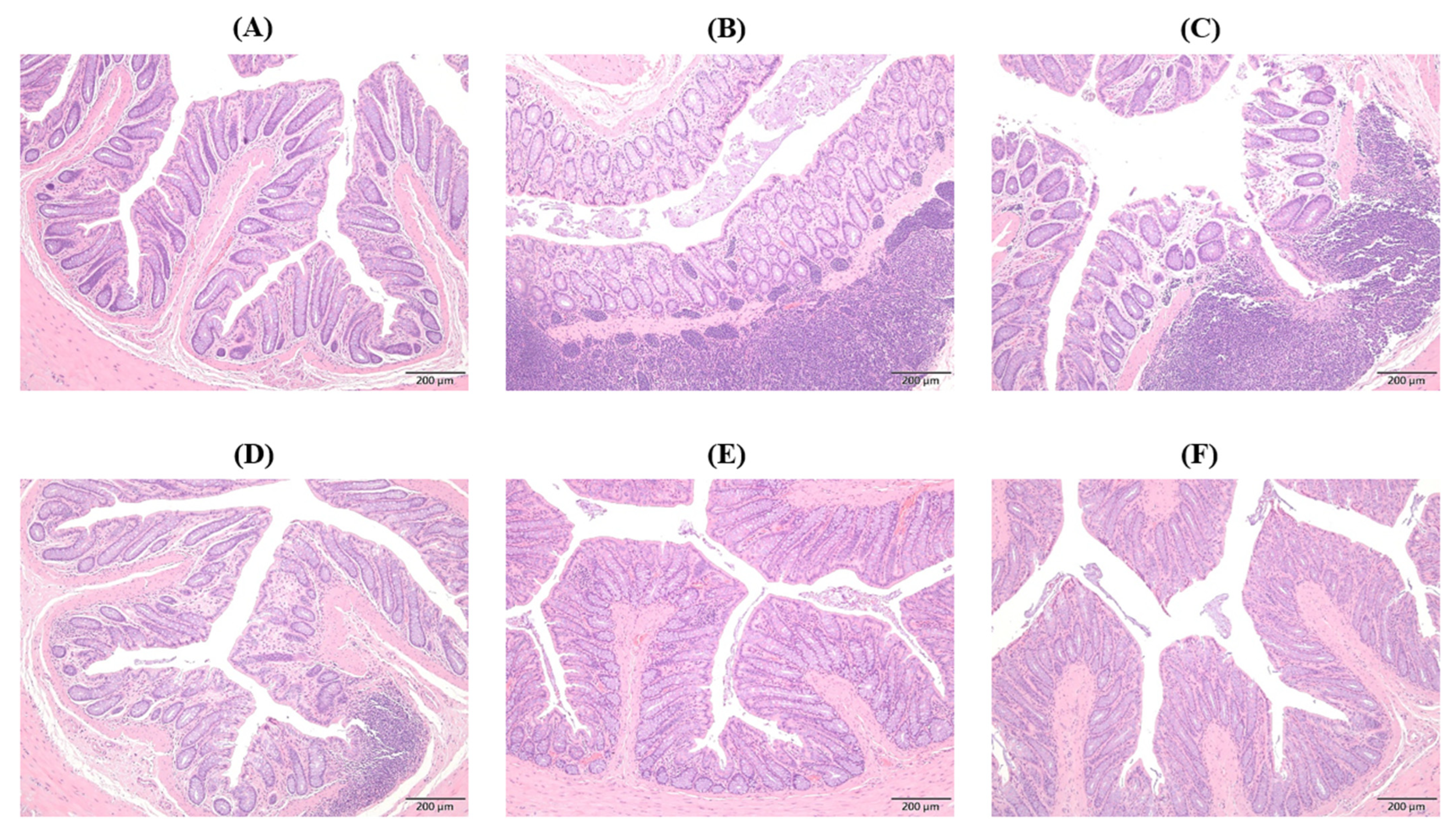
2.10. Histopathological Changes in Colon
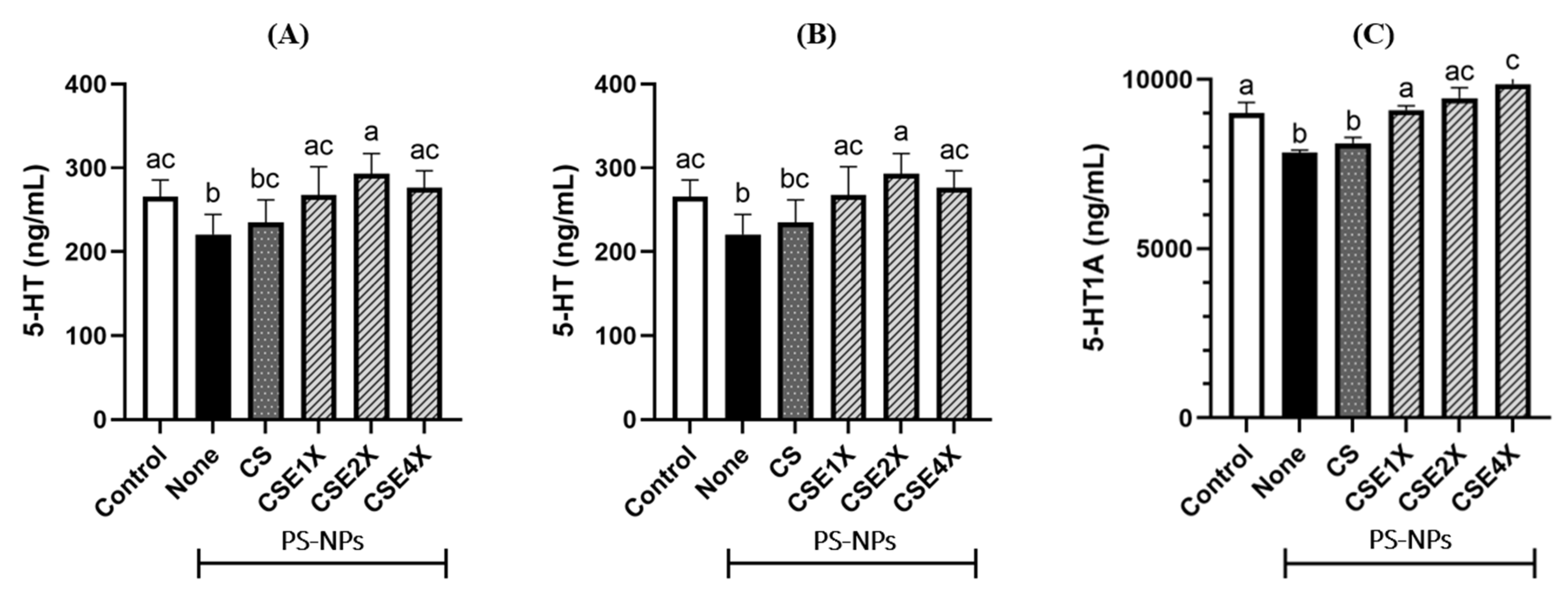
2.11. Effect of CSE on Neurotransmitter Level
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Polystyrene Nanoplastics (PS-NPs) Suspension
4.3. Preparation of Chitosan-Silica Nanoparticle (CS)
4.4. Preparation of Echinacea Purpurea Extract Loaded Chitosan-Silica Nanoparticle (CSE)
4.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
4.6. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) Analysis
4.7. Animal Study
4.7.1. Blood Sample Collection
4.7.2. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing Analysis
4.7.3. Histopathological Analysis
4.7.4. Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Level
4.7.5. Determination of Nitric Oxide (NO) Level
4.7.6. Determination of Biomarkers Related to Liver Damage, Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, Enzymatic Antioxidant, and Reproductive Function
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, J.; Ren, Y.; Dong, Y.; Fan, D. Understanding the impact of nanoplastics on reproductive health: Exposure pathways, mechanisms, and implications. Toxicology 2024, 504, 153792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dada, R.; Bisht, S. Oxidative stress and male infertility. In Male Infertility: Understanding, Causes and Treatment; Singh, R., Singh, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 151–165. [Google Scholar]
- Inhorn, M.C.; Patrizio, P. Infertility around the globe: New thinking on gender, reproductive technologies and global movements in the 21st century. Hum. Reprod. Update 2015, 21, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Li, B.; Xu, K.; Liu, D.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Nie, H.; Fan, L.; Zhu, W. Decline in semen quality among 30,636 young chinese men from 2001 to 2015. Fertil. Steril. 2017, 107, 83–88.e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, J.-P.W.; Galbraith, M.; Ross, P.S. Ingestion of microplastics by zooplankton in the northeast pacific ocean. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 69, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setälä, O.; Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Lehtiniemi, M. Ingestion and transfer of microplastics in the planktonic food web. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prüst, M.; Meijer, J.; Westerink, R.H.S. The plastic brain: Neurotoxicity of micro- and nanoplastics. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, L.; Cheng, J. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics impairs gonads of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, L.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, X.; Tian, H.; Wang, W.; Ru, S. Polystyrene microplastics cause tissue damages, sex-specific reproductive disruption and transgenerational effects in marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma). Environ. Pollut. 2019, 254, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Kurobe, T.; Flores, I.; Teh, S.J. Early warning signs of endocrine disruption in adult fish from the ingestion of polyethylene with and without sorbed chemical pollutants from the marine environment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovanović, B. Ingestion of microplastics by fish and its potential consequences from a physical perspective. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Deng, T.; Duan, J.; Xie, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, M. Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p38 mapk signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 190, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komiya, A.; Watanabe, A.; Kawauchi, Y.; Fuse, H. Sperm with large nuclear vacuoles and semen quality in the evaluation of male infertility. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2012, 59, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fackelmann, G.; Sommer, S. Microplastics and the gut microbiome: How chronically exposed species may suffer from gut dysbiosis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 143, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Ding, Y.; Cheng, X.; Sheng, D.; Xu, Z.; Rong, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ji, X.; Zhang, Y. Polyethylene microplastics affect the distribution of gut microbiota and inflammation development in mice. Chemosphere 2020, 244, 125492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, R.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wolosker, M.B.; Zhu, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, Y. Accumulation of different shapes of microplastics initiates intestinal injury and gut microbiota dysbiosis in the gut of zebrafish. Chemosphere 2019, 236, 124334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, Z.T.R.; Abtahi, B.; Grossart, H.-P.; Khodabandeh, S. Microplastic content of kutum fish, rutilus frisii kutum in the southern caspian sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.M.; Rodríguez, Y.; Blasco-Monleon, S.; Porter, A.; Lewis, C.; Pham, C.K. Microplastic in the stomachs of open-ocean and deep-sea fishes of the north-east atlantic. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 265, 115060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, L.; Tu, W.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z. Impacts of polystyrene microplastic on the gut barrier, microbiota and metabolism of mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wan, Z.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z.; Jin, Y. Polystyrene microplastics induce gut microbiota dysbiosis and hepatic lipid metabolism disorder in mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.-B.; Won, E.-J.; Kang, H.-M.; Lee, M.-C.; Hwang, D.-S.; Hwang, U.-K.; Zhou, B.; Souissi, S.; Lee, S.-J.; Lee, J.-S. Microplastic size-dependent toxicity, oxidative stress induction, and p-jnk and p-p38 activation in the monogonont rotifer (Brachionus koreanus). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 8849–8857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rist, S.; Baun, A.; Hartmann, N.B. Ingestion of micro- and nanoplastics in daphnia magna—Quantification of body burdens and assessment of feeding rates and reproduction. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manayi, A.; Vazirian, M.; Saeidnia, S. Echinacea purpurea: Pharmacology, phytochemistry and analysis methods. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2015, 9, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, C.-F.; Zhang, X.-R.; Johnson, A.; He, J.-L.; Kong, Z.-L. Modulation of diabetes mellitus-induced male rat reproductive dysfunction with micro-nanoencapsulated Echinacea purpurea ethanol extract. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4237354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Simon, J.E.; Aviles, I.F.; He, K.; Zheng, Q.-Y.; Tadmor, Y. Analysis of antioxidative phenolic compounds in artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, F. Phytochemistry, mechanisms, and preclinical studies of echinacea extracts in modulating immune responses to bacterial and viral infections: A comprehensive review. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, J.B. Applications of the phytomedicine Echinacea purpurea (Purple Coneflower) in infectious diseases. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 769896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, B. Medicinal properties of echinacea: A critical review. Phytomedicine 2003, 10, 66–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfanjani, A.F.; Assadpour, E.; Jafari, S.M. Improving the bioavailability of phenolic compounds by loading them within lipid-based nanocarriers. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 76, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfanjani, A.F.; Jafari, S.M. Biopolymer nano-particles and natural nano-carriers for nano-encapsulation of phenolic compounds. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Xia, M.; Yao, Z.; Han, C. Chitosan/silica nanocomposite preparation from shrimp shell and its adsorption performance for methylene blue. Sustainability 2022, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Farooq, M.A.; Li, T.; Geng, T.; Kutoka, P.T.; Wang, B. Cationic chitosan-modified silica nanoparticles for oral delivery of protein vaccine. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 109, 2111–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakkani, M.F.; Gouda, G.A.; Hassan, S.H.; Nagiub, A.M. Echinacea purpurea mediated hematite nanoparticles (α-hnps) biofabrication, characterization, physicochemical properties, and its in-vitro biocompatibility evaluation. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 24, 101113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Zhang, H.; Cao, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Huang, Q. Quaternized chitosan-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers for controlled pesticide release. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, B.; Rafique, U. Synthesis and application of metal doped silica particles for adsorptive desulphurization of fuels. Environ. Eng. Res. 2014, 19, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, M.A.; Jain, P.K. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications. In Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications; Chung, E.J., Leon, L., Rinaldi, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 267–281. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, J.-S.; Kong, Z.-L.; Hwang, D.-F.; Chang, K.L.B. Chitosan-catalyzed aggregation during the biomimetic synthesis of silica nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2006, 18, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thukral, A.K. A review on measurement of alpha diversity in biology. Agric. Res. J 2017, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, H.; Fang, M.; Wang, Q.; Chen, W.; Hale, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. Long-term exposure to environmentally relevant doses of large polystyrene microplastics disturbs lipid homeostasis via bowel function interference. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 15805–15817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, C.; Chen, B.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Sun, Z.; Juventus, A.J.; Ma, H.; Li, Y. Effects of dietary lipid sources on the intestinal microbiome and health of golden pompano (Trachinotus ovatus). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 89, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The controversial role of human gut lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddik, H.A.; Bendali, F.; Gancel, F.; Fliss, I.; Spano, G.; Drider, D. Lactobacillus plantarum and its probiotic and food potentialities. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beek, J.H.; de Moor, M.H.; de Geus, E.J.; Lubke, G.H.; Vink, J.M.; Willemsen, G.; Boomsma, D.I. The genetic architecture of liver enzyme levels: GGT, ALT and AST. Behav. Genet. 2013, 43, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Hofmann, W.; Lueth, S.; Malinski, P.; Thimme, R.; Tacke, F.; Wiegand, J. ALT als screeningparameter für lebererkrankungen: Eine kritische evaluation der evidenz. Z. Gastroenterol. 2010, 48, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peppas, N.A.; Huang, Y. Nanoscale technology of mucoadhesive interactions. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senchina, D.S.; McCann, D.A.; Asp, J.M.; Johnson, J.A.; Cunnick, J.E.; Kaiser, M.S.; Kohut, M.L. Changes in immunomodulatory properties of Echinacea spp. Root infusions and tinctures stored at 4 c for four days. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 355, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, A.A.; Quinton, R. Anatomy and physiology of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis. In Advanced Practice in Endocrinology Nursing; Llahana, S., Follin, C., Yedinak, C., Grossman, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 839–852. [Google Scholar]
- Siu, E.R.; Wong, E.W.P.; Mruk, D.D.; Porto, C.S.; Cheng, C.Y. Focal adhesion kinase is a blood–testis barrier regulator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9298–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, M.U.; Shahzadi, S.; Samad, A.; Ehsan, N.; Ahmed, H.; Tahir, A.; Rehman, H.; Anwar, H. Dose-dependent effect of polystyrene microplastics on the testicular tissues of the male sprague dawley rats. Dose-Response 2021, 19, 15593258211019882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewski, P.; Romano, R.M.; Kizys, M.M.; Oliveira, K.C.; Kasamatsu, T.; Giannocco, G.; Chiamolera, M.I.; Dias-da-Silva, M.R.; Romano, M.A. Adult exposure to bisphenol a (bpa) in wistar rats reduces sperm quality with disruption of the hypothalamic–pituitary–testicular axis. Toxicology 2015, 329, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.-L.; Johnson, A.; Ting, T.-L.; Cheng, P.-J.; Mao, C.-F. Protective effects of echinacea purpurea ethanol extract on male reproductive dysfunction in obese rats. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Sun, H.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J.; Song, M.; Li, M.; Li, Y.F.; Miao, L.G. Effects of sub-chronic aluminum chloride on spermatogenesis and testicular enzymatic activity in male rats. Life Sci. 2014, 102, 36–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, R.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Hoque, S.M.; Lv, Y.; Zeng, W. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates sperm motility and acrosome reaction via affecting energy metabolism in goats. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Yue, D.; Luo, H.; Jin, X.; Xu, X. Effect of vitamin e supplementation on the enzymatic activity of selected markers in aohan fine-wool sheep testis. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 122, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutsch, A.; Kantsjö, J.B.; Ronchi, F. The gut-brain axis: How microbiota and host inflammasome influence brain physiology and pathology. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 604179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-X.; Wang, Y.-P. Gut microbiota-brain axis. Chin. Med. J. 2016, 129, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoi, T.; Okuma, Y.; Nomura, Y. Electrical stimulation of afferent vagus nerve induces il-1β expression in the brain and activates hpa axis. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 279, R141–R147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Zhong, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, J.; Lin, L.; Hu, M.; Jiang, J.; Dai, M.; Wang, B.; et al. Underestimated health risks: Polystyrene micro- and nanoplastics jointly induce intestinal barrier dysfunction by ros-mediated epithelial cell apoptosis. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Tato, C.M.; Joyce-Shaikh, B.; Gulen, M.F.; Cayatte, C.; Chen, Y.; Blumenschein, W.M.; Judo, M.; Ayanoglu, G.; McClanahan, T.K. Interleukin-23-independent il-17 production regulates intestinal epithelial permeability. Immunity 2015, 43, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kivit, S.; Tobin, M.C.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A.; Landay, A.L. Regulation of intestinal immune responses through tlr activation: Implications for pro-and prebiotics. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval-Ramírez, B.A.; Catalán, Ú.; Pedret, A.; Valls, R.M.; Motilva, M.J.; Rubió, L.; Solà, R. Exploring the effects of phenolic compounds to reduce intestinal damage and improve the intestinal barrier integrity: A systematic review of in vivo animal studies. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1719–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morais, L.H.; Schreiber, H.L., IV; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota–brain axis in behaviour and brain disorders. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranuh, R.; Athiyyah, A.F.; Darma, A.; Risky, V.P.; Riawan, W.; Surono, I.S.; Sudarmo, S.M. Effect of the probiotic lactobacillus plantarum is-10506 on bdnf and 5ht stimulation: Role of intestinal microbiota on the gut-brain axis. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2019, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’mahony, S.; Chua, A.; Quigley, E.; Clarke, G.; Shanahan, F.; Keeling, P.; Dinan, T. Evidence of an enhanced central 5ht response in irritable bowel syndrome and in the rat maternal separation model. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popova, N.K.; Naumenko, V.S. 5-HT1A receptor as a key player in the brain 5-ht system. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 24, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Lin, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Hgf aggravated periodontitis-associated gut barrier and microbial dysfunction: Implications for oral–gut axis regulation. Biology 2025, 14, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Chan, Y.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Lin, F.; Mehmood, K.; Idrees, A.; Lin, R.; Su, Y.; et al. Effect of Echinacea purpurea (L.) moench and its extracts on the immunization outcome of avian influenza vaccine in broilers. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 319, 117306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, J.; Masood, S.; Qaisar, S.; Rabbani, I.; Khan, F.; Din, A.-u.; Hadi, S.A.; Gandahi, J.A.; Lochi, G.M.; Saleem, M.U.; et al. Different dietary levels of lysine have beneficial effects on intestinal morphology in japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix Japonica). Pak. Vet. J. 2022, 42, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomaszewska, E.; Rudyk, H.; Dobrowolski, P.; Donaldson, J.; Świetlicka, I.; Puzio, I.; Kamiński, D.; Wiącek, D.; Kushnir, V.; Brezvyn, O.; et al. Changes in the intestinal histomorphometry, the expression of intestinal tight junction proteins, and the bone structure and liver of pre-laying hens following oral administration of fumonisins for 21 days. Toxins 2021, 13, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Guan, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, W.; Guo, S.; Zhang, A. The communication mechanism of the gut-brain axis and its effect on central nervous system diseases: A systematic review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lu, Y. The microbiota-gut-brain axis and central nervous system diseases: From mechanisms of pathogenesis to therapeutic strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1583562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florio, M.; Crudele, L.; Sallustio, F.; Moschetta, A.; Cariello, M.; Gadaleta, R.M. Disentangling the nutrition-microbiota liaison in inflammatory bowel disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2025, 102, 101349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acevedo-Román, A.; Pagán-Zayas, N.; Velázquez-Rivera, L.I.; Torres-Ventura, A.C.; Godoy-Vitorino, F. Insights into gut dysbiosis: Inflammatory diseases, obesity, and restoration approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanov, S.; Berlec, A.; Štrukelj, B. The influence of probiotics on the firmicutes/bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amereh, F.; Babaei, M.; Eslami, A.; Fazelipour, S.; Rafiee, M. The emerging risk of exposure to nano(micro)plastics on endocrine disturbance and reproductive toxicity: From a hypothetical scenario to a global public health challenge. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 261, 114158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena-Aguilar, G.; Sánchez-López, A.M.; Barberán-Aceituno, C.; Carrillo-Ávila, J.A.; López-Guerrero, J.A.; Aguilar-Quesada, R. DNA source selection for downstream applications based on DNA quality indicators analysis. Biopreservation Biobanking 2016, 14, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liao, Y.; Luo, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, F. Non-surgical periodontal treatment restored the gut microbiota and intestinal barrier in apolipoprotein e−/− mice with periodontitis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudirman, S.; Hsu, Y.-H.; He, J.-L.; Kong, Z.-L. Dietary polysaccharide-rich extract from eucheuma cottonii modulates the inflammatory response and suppresses colonic injury on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, D.M.; DeLong, J.M.; Forney, C.F.; Prange, R.K. Improving the thiobarbituric acid-reactive-substances assay for estimating lipid peroxidation in plant tissues containing anthocyanin and other interfering compounds. Planta 1999, 207, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Broderick, M.; Fein, H. Measurement of nitric oxide production in biological systems by using griess reaction assay. Sensors 2003, 3, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, Y.-Y.; Sudirman, S.; Tsai, P.-X.; Mao, C.-F.; Johnson, A.; Chen, T.-Y.; Hwang, D.-F.; Kong, Z.-L. Therapeutic Benefits of Nano-Echinacea Extract on Reproductive Injury Induced by Polystyrene Plastic Materials in Rat Model via Regulating Gut–Brain Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136097
Hwang Y-Y, Sudirman S, Tsai P-X, Mao C-F, Johnson A, Chen T-Y, Hwang D-F, Kong Z-L. Therapeutic Benefits of Nano-Echinacea Extract on Reproductive Injury Induced by Polystyrene Plastic Materials in Rat Model via Regulating Gut–Brain Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(13):6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136097
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Yi-Yuh, Sabri Sudirman, Pei-Xuan Tsai, Chine-Feng Mao, Athira Johnson, Tai-Yuan Chen, Deng-Fwu Hwang, and Zwe-Ling Kong. 2025. "Therapeutic Benefits of Nano-Echinacea Extract on Reproductive Injury Induced by Polystyrene Plastic Materials in Rat Model via Regulating Gut–Brain Axis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 13: 6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136097
APA StyleHwang, Y.-Y., Sudirman, S., Tsai, P.-X., Mao, C.-F., Johnson, A., Chen, T.-Y., Hwang, D.-F., & Kong, Z.-L. (2025). Therapeutic Benefits of Nano-Echinacea Extract on Reproductive Injury Induced by Polystyrene Plastic Materials in Rat Model via Regulating Gut–Brain Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(13), 6097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26136097








