The Prognostic Value of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. General and Subset-Specific Correlation of HH Members’ Overexpression to the Survival Rates
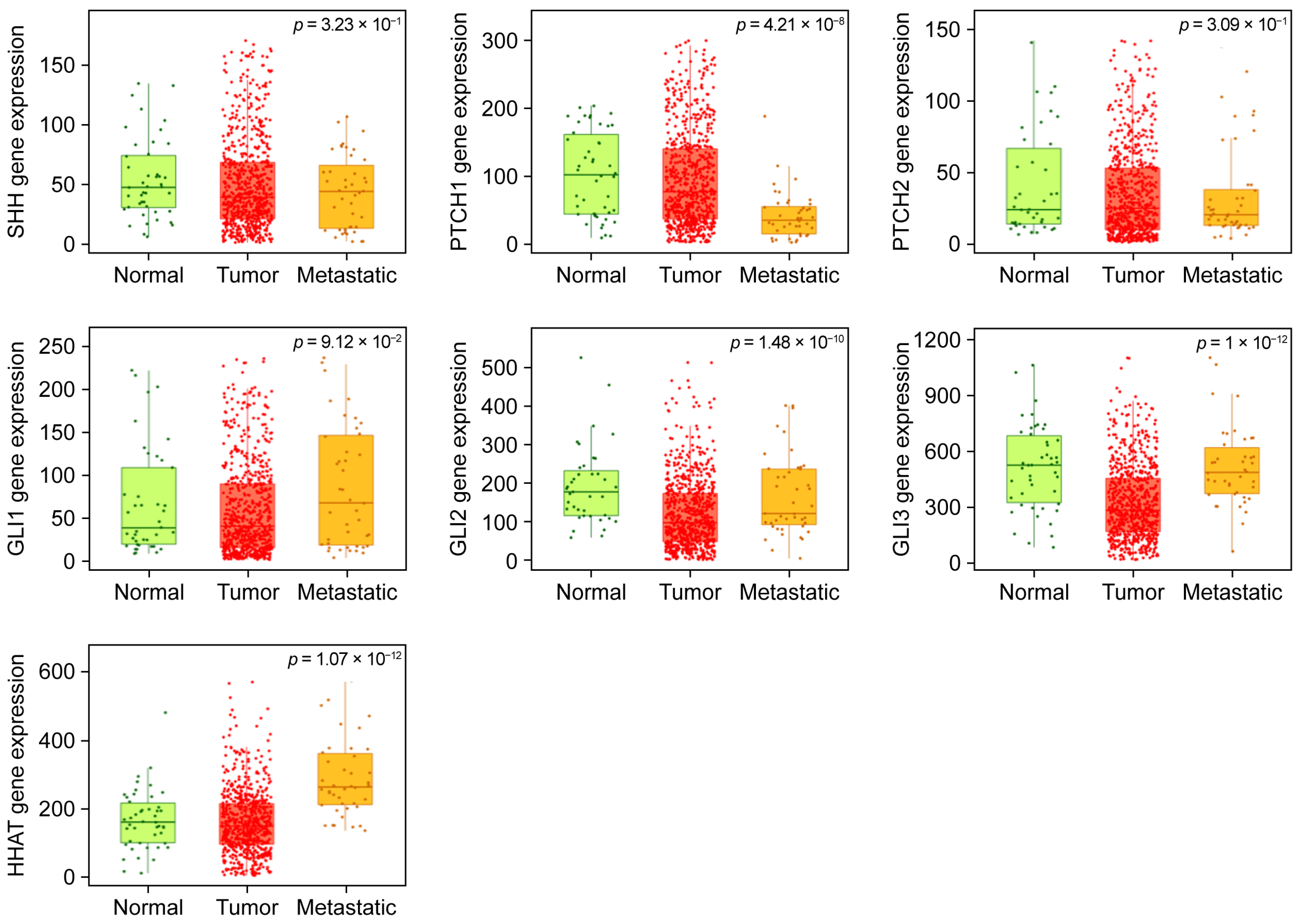
2.2. TNMplot-Based Comparative Analysis Reveals Gene Expression Differences Across Ovarian Tissue States
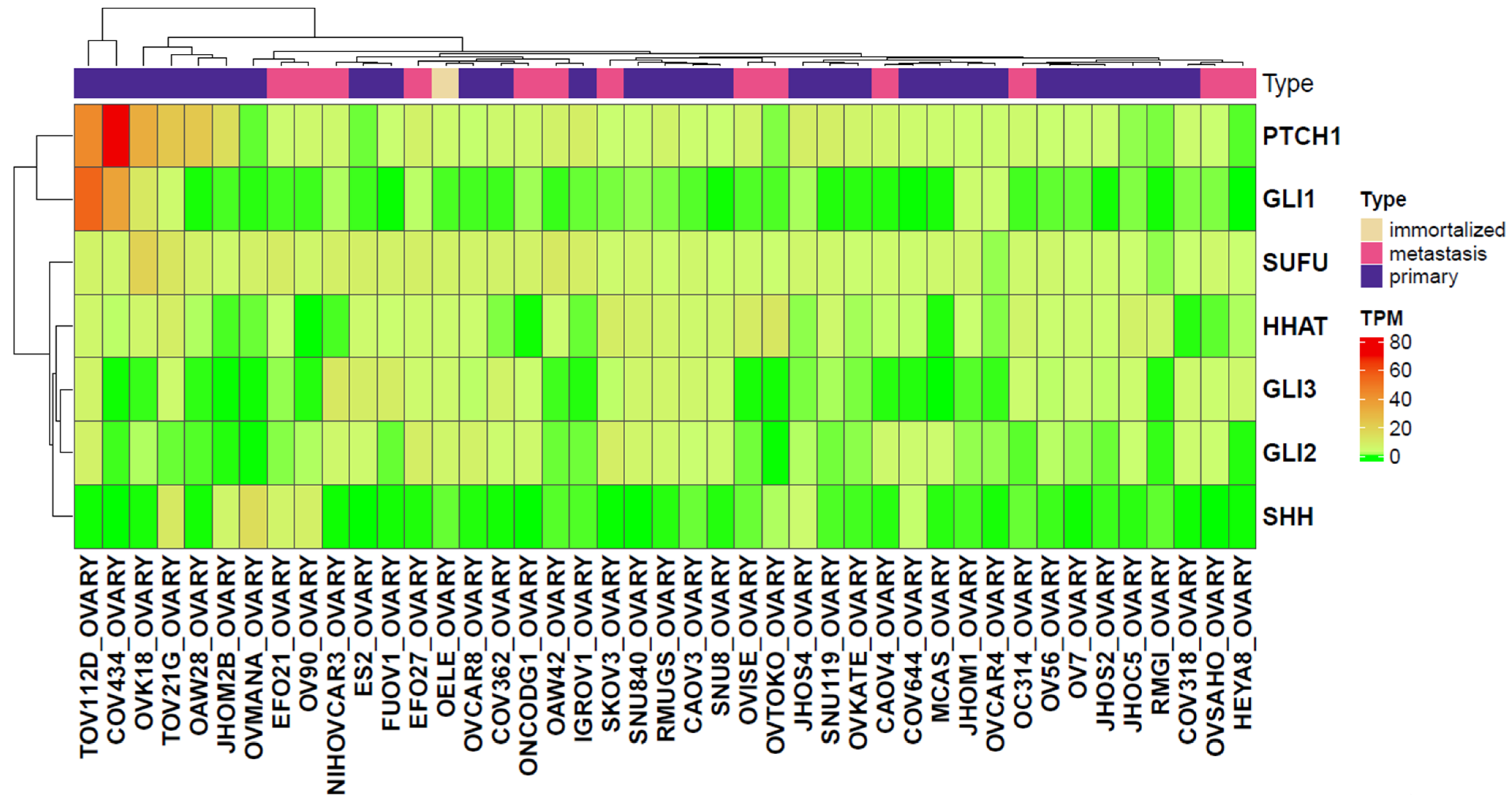
2.3. Analysis of Gene Expression Levels in Primary and Metastatic Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines Derived from the CCLE Dataset
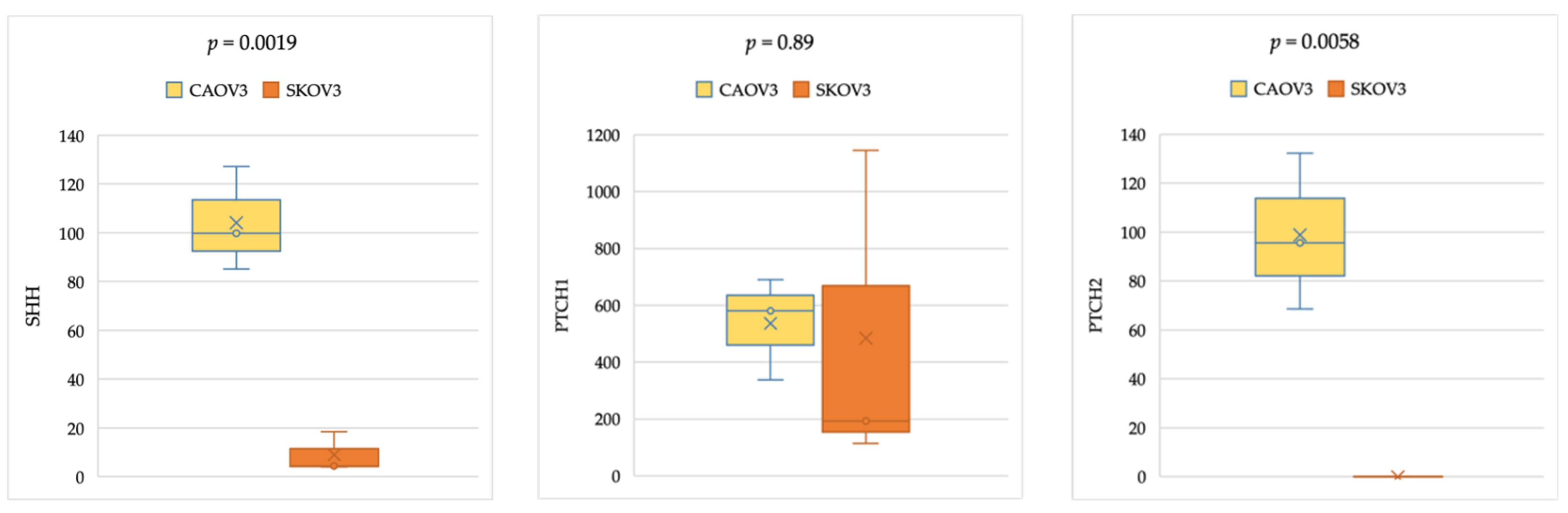
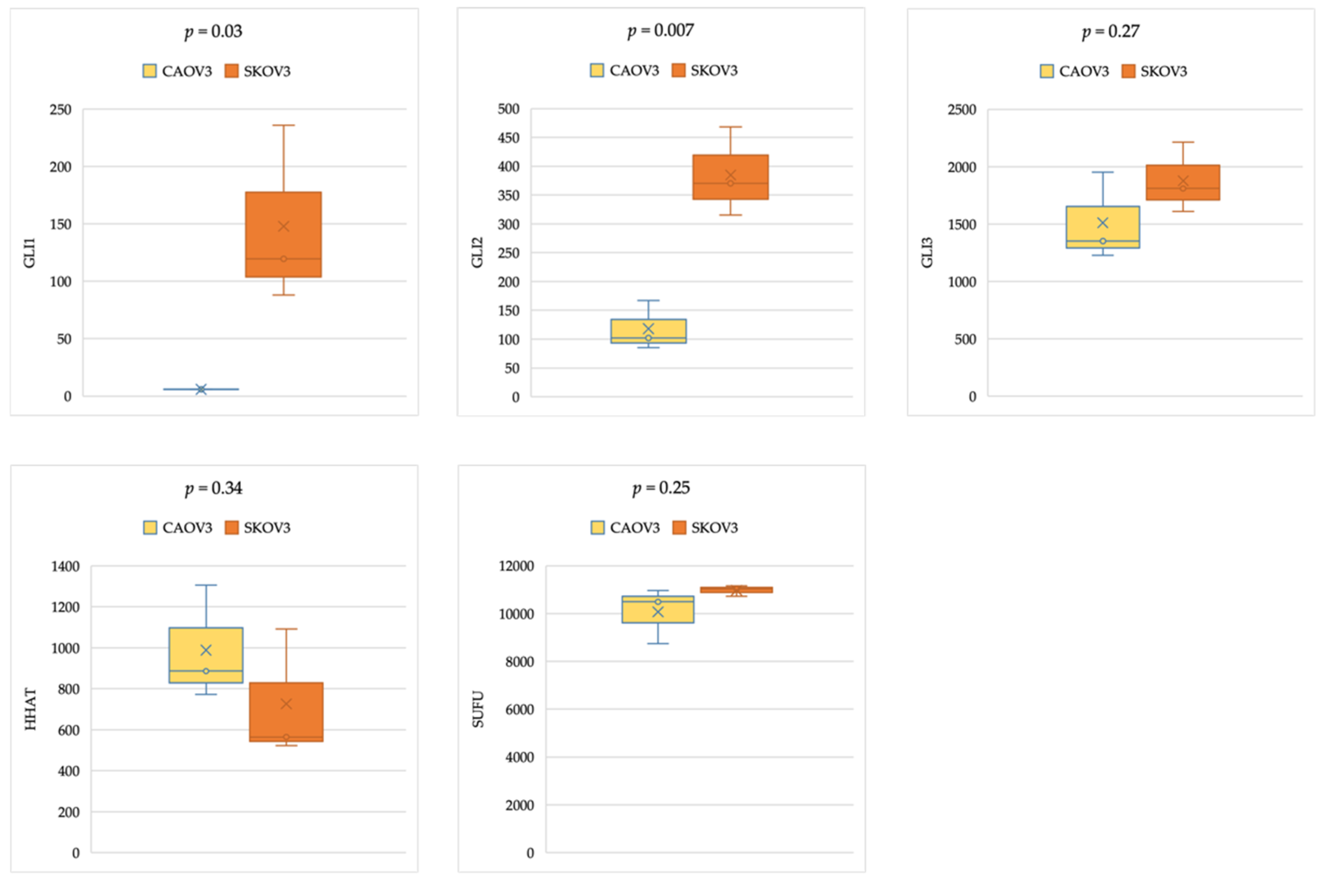
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis in Cancer Cell Lines
3. Discussion
3.1. Gene Expression Analysis Indicates HH-Related Genes as Potential Prognostic Markers in Ovarian Cancer
3.2. Differential Involvement of HH-Related Genes in Tumorigenesis
3.3. Comparable Expression Levels of Hedgehog Pathway Genes in Ovarian Cell Lines Analyzed from CCLE Gene Expression Data
3.4. Comparable HH Gene Expression in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines of Primary and Metastatic Origin, With and Without TP53 Mutation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Kaplan–Meier (KM) Plotter Tool for Survival Assessment
4.2. Comparative Online Gene Expression Analysis Using TNM Plots
4.3. Analysis of Ovarian Cell Line Gene Expression Data from the CCLE Datasets
4.4. Cell Culture and Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurman, R.J.; Shih, I. The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer: A proposed unifying theory. American Journal of Surgical Pathology 2010, 34, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.K.; Ding, D.C. Early Diagnosis of Ovarian Cancer: A Comprehensive Review of the Advances, Challenges, and Future Directions. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinca, A.L.; Daniela Birla, R.; Dinca, V.G.; Marica, C.; Panaitescu, E.; Constantinoiu, S.; Birla, R. Prognostic Factors in Advanced Ovarian Cancer—A Clinical Trial. Chirurgia 2020, 115, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, V.; Marques, I.S.; de Melo, I.G.; Assis, J.; Pereira, D.; Medeiros, R. Paradigm Shift: A Comprehensive Review of Ovarian Cancer Management in an Era of Advancements. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, K.-S.; Chang, C.-F.; Lin, S.-S. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling in Organogenesis, Tumors, and Tumor Microenvironments. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2020, 21, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Gao, G.; Luo, S. Hedgehog Signaling Pathway and Ovarian Cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 25, 346–353. [Google Scholar]
- Szotek, P.P.; Pieretti-Vanmarcke, R.; Masiakos, P.T.; Dinulescu, D.M.; Connolly, D.; Foster, R.; Dombkowski, D.; Preffer, F.; Maclaughlin, D.T.; Donahoe, P.K. Ovarian Cancer Side Population Defines Cells with Stem Cell-like Characteristics and Mullerian Inhibiting Substance Responsiveness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11154–11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, R.; Kwon, J.; Ali, B.; Wang, E.; Patra, S.; Shridhar, V.; Mukherjee, P. Role of Hedgehog Signaling in Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 7659–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Horiuchi, A.; Kikuchi, N.; Osada, R.; Yoshida, J.; Shiozawa, T.; Konishi, I. Hedgehog Signal Pathway Is Activated in Ovarian Carcinomas, Correlating with Cell Proliferation: It’s Inhibition Leads to Growth Suppression and Apoptosis. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Chang, C.J.; Lin, C.P.; Chang, S.Y.; Chu, P.Y.; Tai, S.K.; Li, W.Y.; Chao, K.S.C.; Chen, Y.J. Expression of Hedgehog Signaling Molecules as a Prognostic Indicator of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Head Neck 2012, 34, 1556–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Lim, S.M.; Kim, M.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, J.H. Sonic Hedgehog Pathway as the Prognostic Marker in Patients with Extensive Stage Small Cell Lung Cancer. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhan, H.; Yuan, Z.; Lu, P.; Zhan, L.; Xu, W. The Hedgehog Signalling Pathway and Its Prognostic Impact in Human Gliomas. ANZ J. Surg. 2011, 81, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Zhu, S.; Li, W.; Yao, M.; Song, H.; Wang, R.B. Current Approaches and Strategies to Identify Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 244, 114867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habashy, S.; Jafri, A.; Osman, H.O.; Thomas, N.E.; Udekwe, S.; Heindl, S.E. Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors: Clinical Implications and Resistance in the Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinoma. Cureus 2021, 13, e13859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Q. Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Regulates Ovarian Cancer Invasion and Migration via Adhesion Molecule CD24. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, S.; Bieber, M.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, M.; He, B.; Jablons, D.; Teng, N.N.H. Wnt and Hedgehog Gene Pathway Expression in Serous Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2011, 21, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lengyel, E.; Burdette, J.E.; Kenny, H.A.; Matei, D.; Pilrose, J.; Haluska, P.; Nephew, K.P.; Hales, D.B.; Stack, M.S. Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Experimental Models. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3619–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, A. Hedgehog Signaling Pathway: A Novel Target for Cancer Therapy: Vismodegib, a Promising Therapeutic Option in Treatment of Basal Cell Carcinomas. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2014, 46, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanat, S.; Sabol, M.; Musani, V.; Ozretić, P.; Trnski, D. Hedgehog Signaling Pathway as Genetic and Epigenetic Target in Ovarian Tumors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijgerde, M.; Ooms, M.; Hoogerbrugge, J.W.; Grootegoed, J.A. Hedgehog Signaling in Mouse Ovary: Indian Hedgehog and Desert Hedgehog from Granulosa Cells Induce Target Gene Expression in Developing Theca Cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 3558–3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Lv, M.; Li, F.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, R.; Wei, X.; Lou, J.; et al. Human CAFs Promote Lymphangiogenesis in Ovarian Cancer via the Hh-VEGF-C Signaling Axis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 67315–67328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Qi, W.; Cui, Y.; Xuan, Y. GLI1 Promotes Cancer Stemness through Intracellular Signaling Pathway PI3K/Akt/NFκB in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 373, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, L.; Yang, Z.; Ma, T.; Xuan, Y. Gli1, a Potential Cancer Stem Cell Marker, Is Strongly Associated with Prognosis in Prostate Cancer Lili. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 4957–4966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, W.; Cheng, M.; Chen, Q. Aberrant Activation of Hedgehog Signalling Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion via Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Ovarian Cancer Cells. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 990–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rather, T.B.; Parveiz, I.; Rashid, G.; Akhtar, K.; Mudassar, S.; Wani, R.A.; Besina, S.; Haq, R.I.U. GLI1 Subcellular Localization and Overexpression as Prognostic Factors for Disease-Free Survival in Colorectal Carcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2024, 55, 1359–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haaf, A.T.; Bektas, N.; von Serenyi, S.; Losen, I.; Arweiler, E.C.; Hartmann, A.; Knüchel, R.; Dahl, E. Expression of the Glioma-Associated Oncogene Homolog (GLI) 1 in Human Breast Cancer Is Associated with Unfavourable Overall Survival. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Wu, M.; Zhao, F.; Fu, W.; Li, W.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Lu, L.; Wu, M.; Zhao, F.; et al. Prognostic and Clinicopathological Value of Gli-1 Expression in Gastric Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 69087–69096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steg, A.D.; Bevis, K.S.; Katre, A.A.; Ziebarth, A.; Dobbin, Z.C.; Alvarez, R.D.; Zhang, K.; Conner, M.; Landen, C.N. Cancer Therapy: Clinical Stem Cell Pathways Contribute to Clinical Chemoresistance in Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 18, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Siu, M.K.Y.; Au, C.W.H.; Wong, E.S.Y.; Chan, H.Y.; Ip, P.P.C.; Ngan, H.Y.S.; Cheung, A.N.Y. Aberrant Activation of Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Cancers: Effect on Prognosis, Cell Invasion and Differentiation. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.; Berchuck, A.; Birrer, M.; Chien, J.; Cramer, D.W.; Dao, F.; Dhir, R.; Disaia, P.; Gabra, H.; Glenn, P.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analyses of Ovarian Carcinoma. Nature 2011, 474, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoda, A.M.; Simovic, D.; Karin, V.; Kardum, V.; Vranic, S.; Serman, L. The Role of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Cancer: A Comprehensive Review. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 18, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciucci, A.; De Stefano, I.; Vellone, V.G.; Lisi, L.; Bottoni, C.; Scambia, G.; Zannoni, G.F.; Gallo, D. Expression of the Glioma-Associated Oncogene Homolog 1 (Gli1) in Advanced Serous Ovarian Cancer Is Associated with Unfavorable Overall Survival. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svärd, J.; Henricson, K.H.; Persson-Lek, M.; Rozell, B.; Lauth, M.; Bergström, Å.; Ericson, J.; Toftgård, R.; Teglund, S. Genetic Elimination of Suppressor of Fused Reveals an Essential Repressor Function in the Mammalian Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raducu, M.; Fung, E.; Serres, S.; Infante, P.; Barberis, A.; Fischer, R.; Bristow, C.; Thézénas, M.-L.; Finta, C.; Christianson, J.C.; et al. SCF (Fbxl17) Ubiquitylation of Sufu Regulates Hedgehog Signaling and Medulloblastoma Development. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1400–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrini-Rousseau, L.; Dufour, C.; Varlet, P.; Masliah-Planchon, J.; Bourdeaut, F.; Guillaud-Bataille, M.; Abbas, R.; Bertozzi, A.I.; Fouyssac, F.; Huybrechts, S.; et al. Germline SUFU Mutation Carriers and Medulloblastoma: Clinical Characteristics, Cancer Risk, and Prognosis. Neuro Oncol. 2018, 20, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, C.K.; Growdon, W.B.; Kulkarni-Datar, K.; Curley, M.D.; Friel, A.M.; Proctor, J.L.; Sheikh, H.; Deyneko, I.; Ferguson, J.A.; Vathipadiekal, V.; et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog Signaling Antagonizes Serous Ovarian Cancer Growth in a Primary Xenograft Model. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. Sonic Hedgehog–Gli1 Signals Promote Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Ovarian Cancer by Mediating PI3K/AKT Pathway. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; He, J.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X.; Bian, Y.; He, N.; Zhang, H.; Xie, J. Activation of Hedgehog Signaling Is Not a Frequent Event in Ovarian Cancers. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotnik, E.N.; Mullen, M.M.; Spies, N.C.; Li, T.; Inkman, M.; Zhang, J.; Martins-Rodrigues, F.; Hagemann, I.S.; Mccourt, C.K.; Thaker, P.H.; et al. Genetic Characterization of Primary and Metastatic High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer Tumors Reveals Distinct Features Associated with Survival. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, M.; Tateishi, K.; Kanai, F.; Watabe, H.; Kondo, S.; Guleng, B.; Tanaka, Y.; Asaoka, Y.; Jazag, A.; Imamura, J.; et al. P53-Independent Negative Regulation of P21/Cyclin-Dependent Kinase-Interacting Protein 1 by the Sonic Hedgehog-Glioma-Associated Oncogene 1 Pathway in Gastric Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10822–10829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.N.; Fu, J.; Nall, D.; Rodova, M.; Shankar, S.; Srivastava, R.K. Inhibition of Sonic Hedgehog Pathway and Pluripotency Maintaining Factors Regulate Human Pancreatic Cancer Stem Cell Characteristics. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozretić, P.; Trnski, D.; Musani, V.; Maurac, I.; Kalafatić, D.; Orešković, S.; Levanat, S.; Sabol, M. Non-Canonical Hedgehog Signaling Activation in Ovarian Borderline Tumors and Ovarian Carcinomas. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, S.B.; Fehrenbacher, L.; Holloway, R.; Amit, A.; Karlan, B.; Slomovitz, B.; Sabbatini, P.; Fu, L.; Yauch, R.L.; Chang, I.; et al. A Phase II, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of Vismodegib as Maintenance Therapy in Patients with Ovarian Cancer in Second or Third Complete Remission. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 6509–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, C.; Tripathi, K.; Chaudhary, S.; Somasagara, R.R.; Rocconi, R.P.; Crasto, C.; Reedy, M.; Athar, M.; Palle, K. Hedgehog/GLI1 Transcriptionally Regulates FANCD2 in Ovarian Tumor Cells: Its Inhibition Induces HR-Deficiency and Synergistic Lethality with PARP Inhibition. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 1002–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the Regulation of Protein Abundance from Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutros, P.C. The Path to Routine Use of Genomic Biomarkers in the Cancer Clinic. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Győrffy, B. Discovery and Ranking of the Most Robust Prognostic Biomarkers in Serous Ovarian Cancer Balázs Győrffy. GeroScience 2023, 45, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Birkbak, N.J.; Gyorffy, B.; Szallasi, Z.; Eklund, A.C. Jetset: Selecting the Optimal Microarray Probe Set to Represent a Gene. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 15, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartha, Á.; Győrffy, B. TNMplot.com: A Web Tool for the Comparison of Gene Expression in Normal, Tumor and Metastatic Tissues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsherniak, A.; Vazquez, F.; Montgomery, P.G.; Weir, B.A.; Kryukov, G.; Cowley, G.S.; Gill, S.; Harrington, W.F.; Pantel, S.; Krill-Burger, J.M.; et al. Defining a Cancer Dependency Map. Cell 2017, 70, 564–576.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex Heatmaps Reveal Patterns and Correlations in Multidimensional Genomic Data. Bioinfarmatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
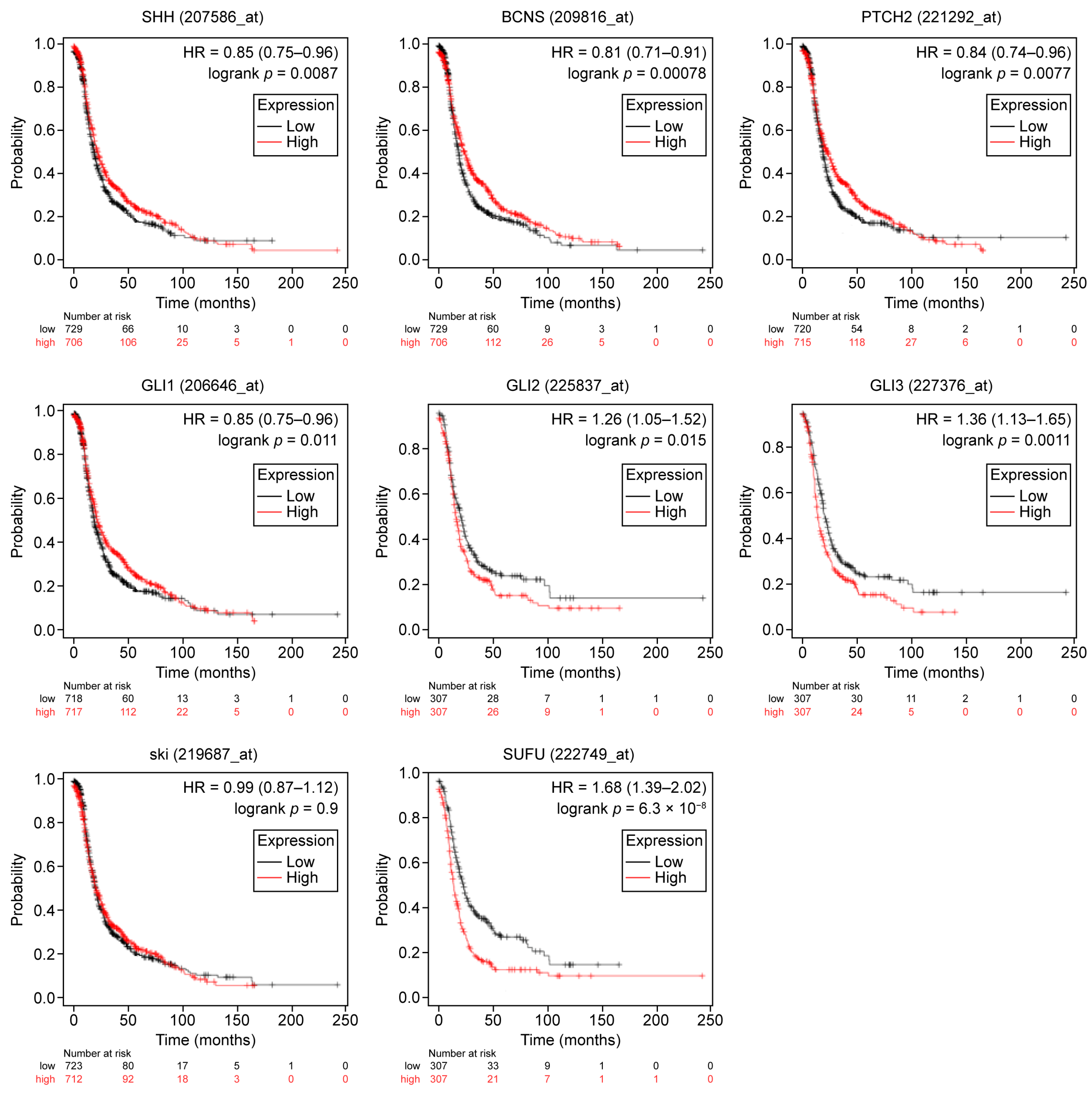
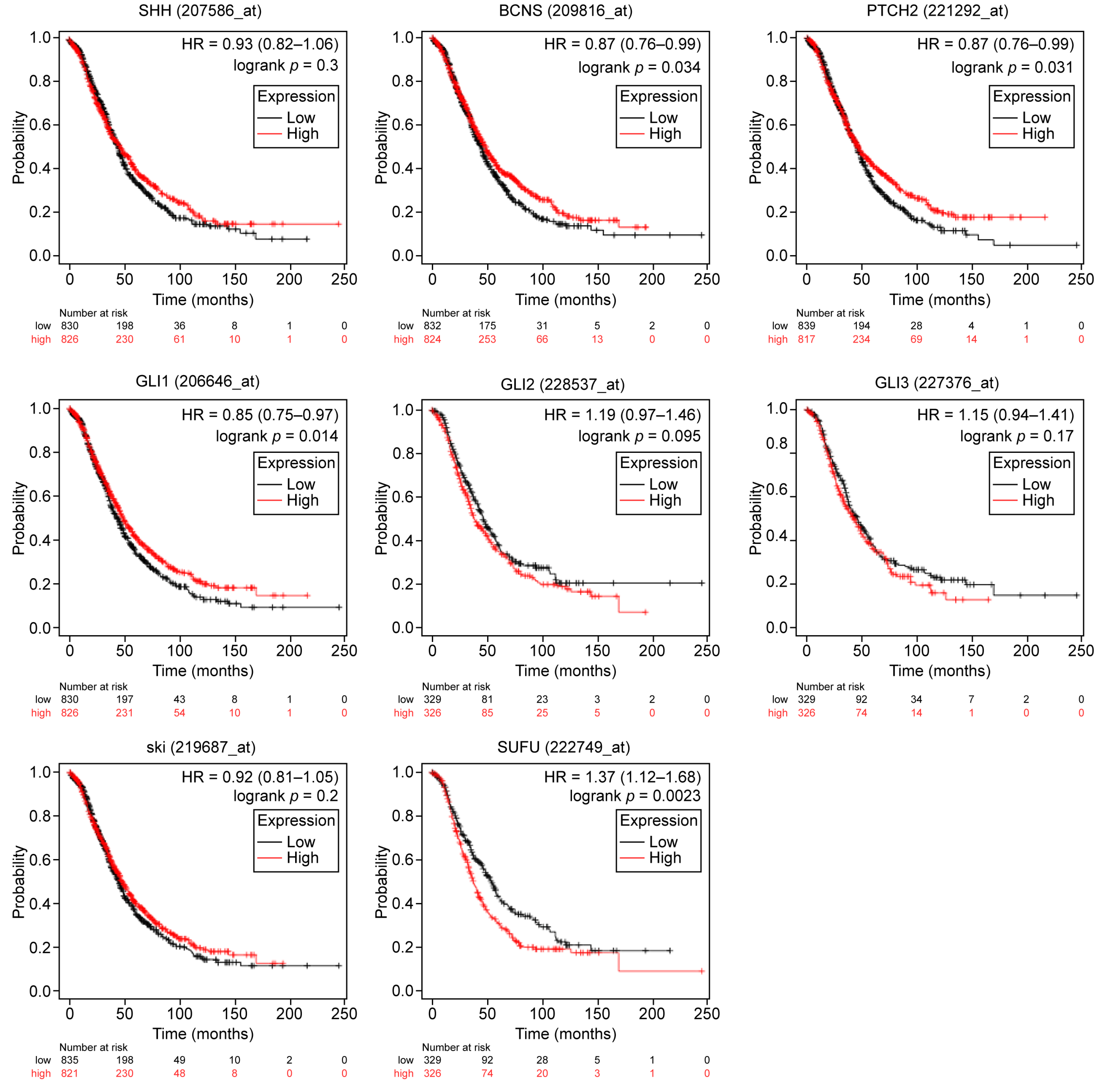
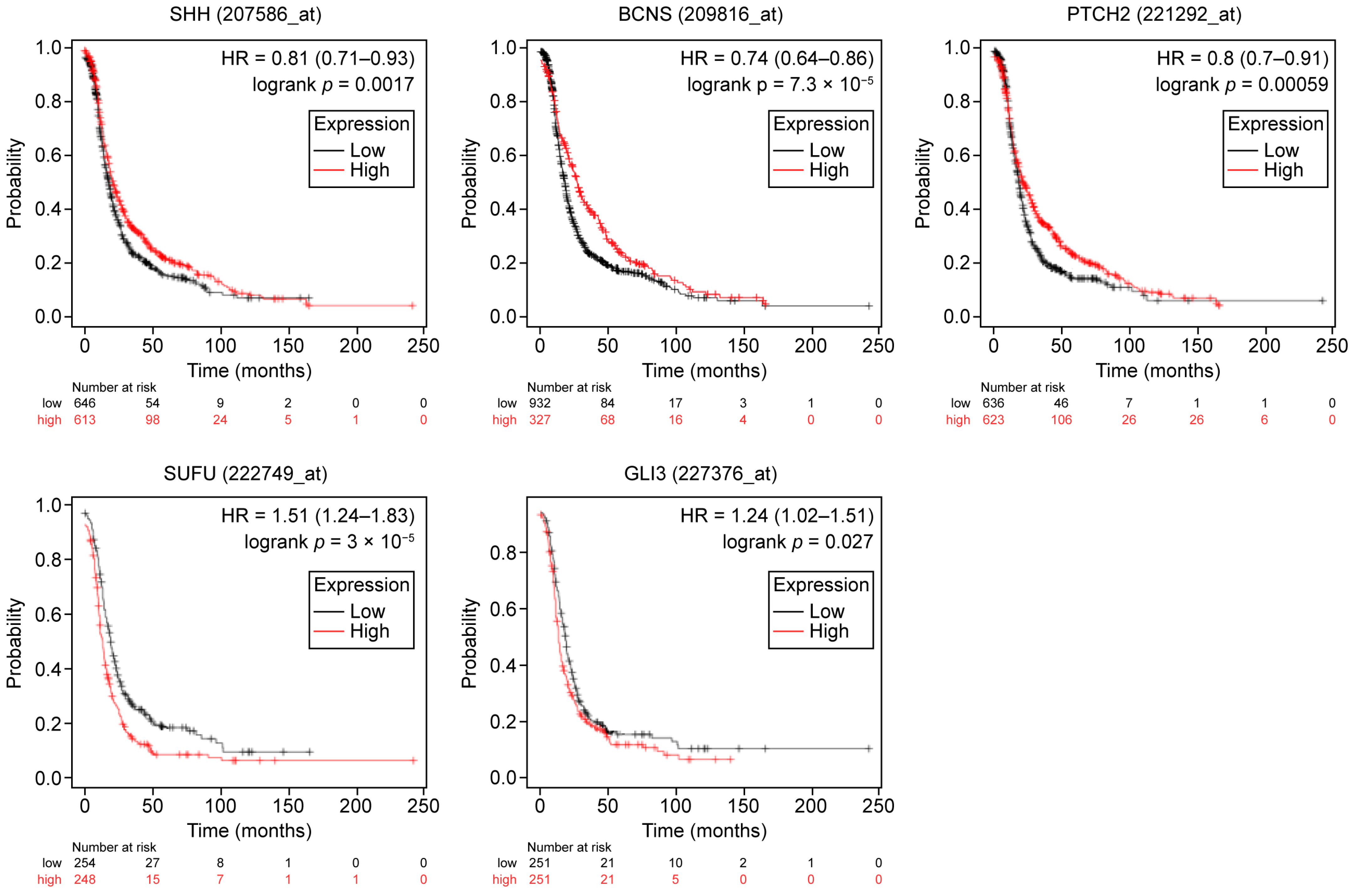
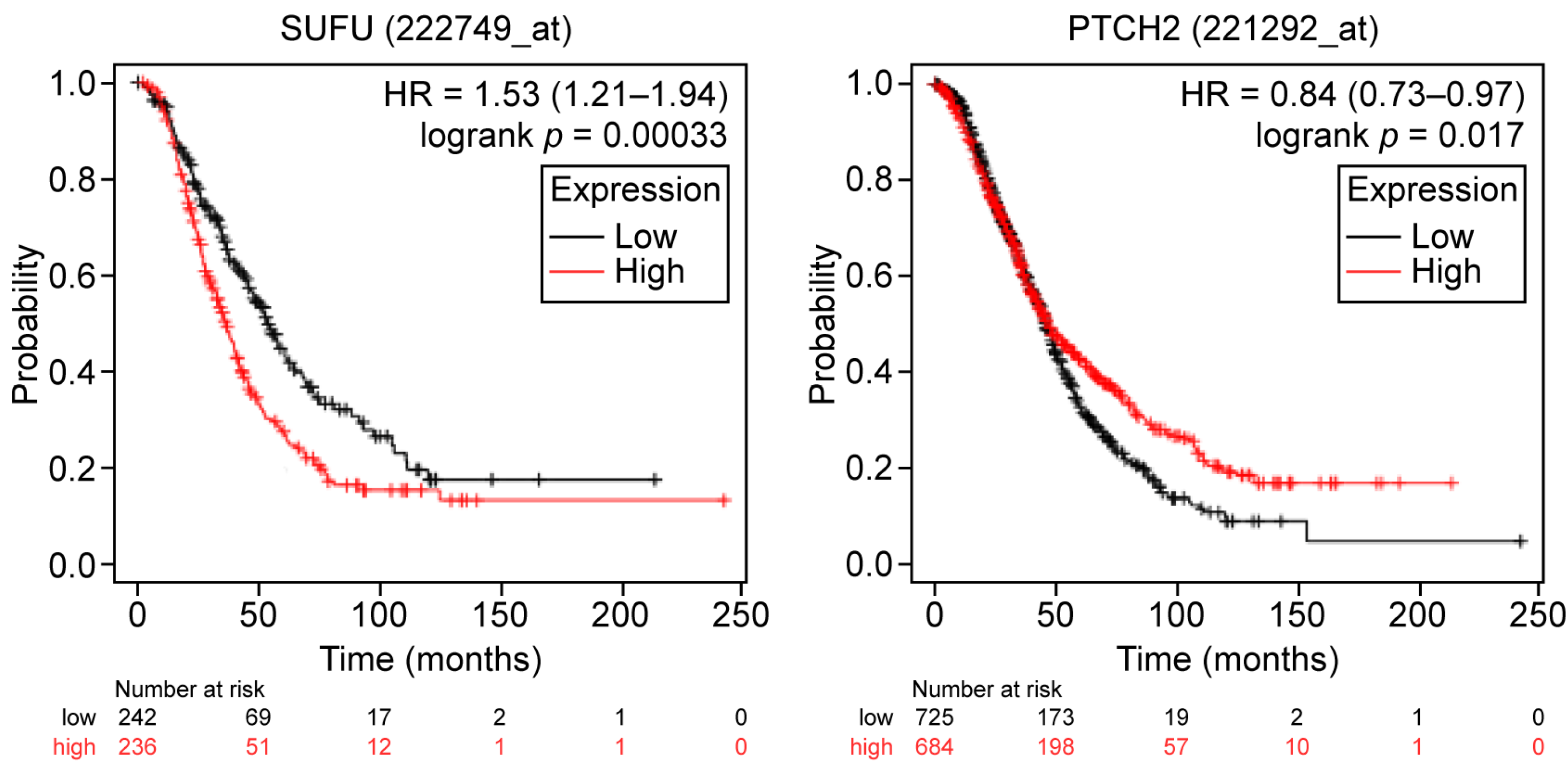
| Gene | Affymetrix ID | No. | Progression-Free Survival | No. | Overall Survival | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | p-Value | HR | p-Value | ||||
| SHH | 207586_at | 1435 | 0.85 | 0.0087 | 1656 | 0.93 | 0.3 |
| PTCH1 | 209816_at | 1435 | 0.81 | 0.00078 | 1656 | 0.87 | 0.034 |
| PTCH2 | 221292_at | 1435 | 0.84 | 0.00077 | 1656 | 0.87 | 0.031 |
| GLI1 | 206646_at | 1435 | 0.85 | 0.011 | 1656 | 0.85 | 0.014 |
| GLI2 | 228537_at | 614 | 1.26 | 0.015 | 655 | 1.19 | 0.095 |
| GLI3 | 227376_at | 614 | 1.36 | 0.0011 | 655 | 1.15 | 0.17 |
| SUFU | 222749_at | 614 | 1.68 | 6.3 × 10−8 | 655 | 1.37 | 0.0023 |
| HHAT | 219687_at | 1435 | 0.99 | 0.9 | 1656 | 0.92 | 0.2 |
| I | Histology (Serous) | Grade 3 | Mutated TP53 | Stage III + IV |
| SHH | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | OS 0.03/0.85 |
| HHAT | n.s. | n.s. | PFS 0.01/1.33 | OS 3.6 × 10−7/1.7 |
| PTCH1 | n.s. | n.s. | OS 0.04/1.26 | OS 0.01/0.8 |
| PTCH2 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | OS 0.003/0.72 |
| GLI1 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | OS 0.035/0.85 |
| GLI2 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| GLI3 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | PFS 0.005/1.4 |
| SUFU | PFS 5.0 × 10−7/1.7 OS 5.0 × 10−4/1.5 | PFS 6.3 × 10−5/1.38 OS 0.007/1.4 | PFS 0.02/1.56 | PFS 6.3 × 10−6/1.59 OS 1.37/0.006 |
| II | Optimal Debulking | Suboptimal Debulking | Platinum Chemotherapy | |
| SHH | PFS 0.001/0.7 | n.s. | PFS 0.001/0.8 | |
| HHAT | OS 0.01/0.78 | n.s. | n.s. | |
| PTCH1 | PFS 2.1 × 10−5/0.6 OS 0.015/0.8 | n.s. | PFS 0.0004/0.08 | |
| PTCH2 | OS 0.0005/0.7 | OS 0.0004/0.7 | PFS 0.0006/0.8 OS 0.017/0.8 | |
| GLI1 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| GLI2 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | |
| GLI3 | n.s. | n.s. | PFS 0.005/1.4 | |
| SUFU | PFS 0.002/1.66 OS 0.05/1.5 | PFS 0.013/1.4 OS 0.03/1.4 | PFS 3 × 10−5/1.5 OS 0.0003/1.5 |
| Gene | p-Value | Tumor/Normal Fold Change p-Value | Metastatic/Tumor Fold Change p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SHH | 3.2 × 10−1 | 1.03 | 2.01 × 10−1 | 0.71 | 6.86 × 10−2 |
| PTCH1 | 4.2 × 10−8 | 1.07 | 2.67 × 10−1 | 0.37 | 1.45 × 10−6 |
| PTCH2 | 3.1 × 10−1 | 0.73 | 1.36 × 10−1 | 0.67 | 6.31 × 10−2 |
| GLI1 | 9.1 × 10−2 | 0.76 | 7.59 × 10−2 | 1.2 | 4.04 × 10−1 |
| GLI2 | 1.5 × 10−10 | 0.42 | 6.95 × 10−10 | 1.41 | 2.51 × 10−2 |
| GLI3 | 1 × 10−12 | 0.67 | 1.84 × 10−7 | 1.65 | 2.97 × 10−1 |
| HHAT | 1.0 × 10−12 | 0.97 | 2.30 × 10−1 | 1.95 | 4.21 × 10−7 |
| GeneID | p-Value | Mean in Primary | Mean in Metastatic | Median in Primary | Median in Metastatic | Fold Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HHAT | 0.93 | 3.21 | 3.82 | 2.76 | 2.14 | 1.19 |
| GLI2 | 0.75 | 2.26 | 2.91 | 1.71 | 1.71 | 1.29 |
| GLI3 | 0.93 | 2.63 | 2.48 | 1.93 | 1.97 | 0.94 |
| SUFU | 0.63 | 5.47 | 5.71 | 5.02 | 4.50 | 1.04 |
| GLI1 | 0.97 | 4.15 | 0.65 | 0.40 | 0.34 | 0.16 |
| SHH | 0.97 | 1.37 | 1.37 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 1.00 |
| PTCH1 | 0.87 | 9.89 | 4.02 | 3.23 | 4.30 | 0.41 |
| GEO ID | GEO Platform | No. of Samples in Dataset | Death Event | Median Overall Survival | Serous/Endometrioid and Others | Grade (1/2/3) | Stage (1/2/3/4) | Optimal Debulking | Platinum-Based Chemotherapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSE14764—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE14764 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL96 | 80 | 21 | 33.7 | 68/7 | NA | 8/1/69/2 | 27 | 78 |
| GSE15622—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE15622 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL571 | 35 | 28 | 37.8 | 31/0 | 0/7/28 | 0/0/26/9 | NA | 20 |
| GSE19829—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE19829 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL570 | 28 | 17 | 43.0 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| GSE3149—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE3149 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL96 | 116 | 68 | 48.5 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| GSE9891—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE9891 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL570 | 285 | 110 | 31.0 | 264/20 | 19/97/164 | 24/18/217/22 | 160 | 242 |
| GSE18520—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE18520 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL570 | 53 | 41 | 40.4 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| GSE26712—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE26712 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL96 | 185 | 129 | 47.6 | NA | NA | NA | 90 | 184 |
| GSE23554—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE23554 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL96 | 28 | 14 | 49.3 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 28 |
| GSE26193—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE26193 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL570 | 107 | 76 | 49.9 | 79/8 | 7/33/67 | 20/11/59/17 | 38 | 93 |
| GSE27651—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE27651 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL570 | 39 | 25 | 57.5 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| GSE30161—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE30161 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL570 | 58 | 36 | 45.8 | 44/1 | 2/19/29 | 0/0/49/5 | 23 | 58 |
| GSE32062—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE32062 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL570/GPL6480 | 10 | 7 | 70.3 | 10/0 | 0/0/10 | All advanced | NA | NA |
| GSE63885—available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE63885 (accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL570 | 75 | 66 | 42.7 | 70/1 | 0/9/48 | 0/2/63/10 | 15 | 75 |
| TCGA—available online: http://cancergenome.nih.gov/(accessed on 7 April 2025). | GPL3921 | 557 | 292 | 33.3 | 522/0 | 4/65/440 | 14/25/400/81 | 340 | 505 |
| Total | 1656 | 39.1 | 1122/51 | 56/325/1024 ∗ | 107/72/1079/189 | 801 | 1409/1438 * |
| Parameter | Cohort | Proportion of Patients |
|---|---|---|
| Platform | GPL96 (Affymetrix HG-U133A), | 25% |
| GPL570 (Affymetrix HG-U133 Plus 2.0) | 46.7% | |
| GPL571/GPL3921 (Affymetrix HG-U133A 2.0) | 2% | |
| GPL3921 | 34% | |
| GPL6480 | NA | |
| Histology | Serous | 67.7% |
| Endometrioid/others | 3% | |
| Grading | 1 | 3.3% |
| 2 | 19.6% | |
| 3 | 61.7% | |
| Stage | 1 | 6% |
| 2 | 4% | |
| 3 | 65% | |
| 4 | 11% | |
| Surgical debulking | Optimal (residual tumor <1 cm) | 48% |
| Suboptimal | NA | |
| Chemotherapy | Platinum-based | 77% |
| OS | Follow-up time (months) | 39.1 |
| Proportion of events (death) | 56% |
| SHH PFS/OS | HHAT PFS/OS | PTCH1 PFS/OS | PTCH2 PFS/OS | GLI1 PFS/OS | GLI2 PFS/OS | GLI3 PFS/OS | SUFU PFS/OS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serous | 1104/1207 | 483/523 | 1104/1207 | 1104/1207 | 1104/1207 | 483/523 | 483/523 | 483/523 |
| Endometrioid | 51/37 | 44/30 | 51/37 | 51/37 | 51/37 | 44/30 | 44/30 | 44/30 |
| G 1 + 2 | 293/380 | 189/203 | 293/380 | 293/380 | 293/380 | 189/203 | 189/203 | 189/203 |
| G 3 | 837/1015 | 315/392 | 837/1015 | 837/1015 | 837/1015 | 315/392 | 315/392 | 315/392 |
| Stage I + II | 163/135 | 115/83 | 163/135 | 163/135 | 163/135 | 115/83 | 115/83 | 115/83 |
| Stages III + IV | 1081/1220 | 494/487 | 1081/1220 | 1081/1220 | 1081/1220 | 494/487 | 494/487 | 494/487 |
| mTP53 | 483/506 | 124/124 | 483/506 | 483/506 | 483/506 | 124/124 | 124/124 | 124/124 |
| Opt. Debulking | 696/801 | 240/243 | 696/801 | 696/801 | 696/801 | 240/243 | 240/243 | 240/243 |
| Subop. Debulking | 459/536 | 234/235 | 459/536 | 459/536 | 459/536 | 234/235 | 234/235 | 234/235 |
| Platinum | 1259/1409 | 502/478 | 1259/1409 | 1259/1409 | 1259/1409 | 502/478 | 502/478 | 502/478 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salman, N.D.; Hanker, L.C.; Győrffy, B.; Bartha, Á.; Proppe, L.; Götte, M. The Prognostic Value of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125888
Salman ND, Hanker LC, Győrffy B, Bartha Á, Proppe L, Götte M. The Prognostic Value of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125888
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalman, Noor D., Lars C. Hanker, Balázs Győrffy, Áron Bartha, Louisa Proppe, and Martin Götte. 2025. "The Prognostic Value of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125888
APA StyleSalman, N. D., Hanker, L. C., Győrffy, B., Bartha, Á., Proppe, L., & Götte, M. (2025). The Prognostic Value of the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway in Ovarian Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125888






