miRNA-21 and miRNA-27b Expression in Saliva of Patients with Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Oral Lichen Planus
1.2. MicroRNAs
1.3. Aim
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Registration
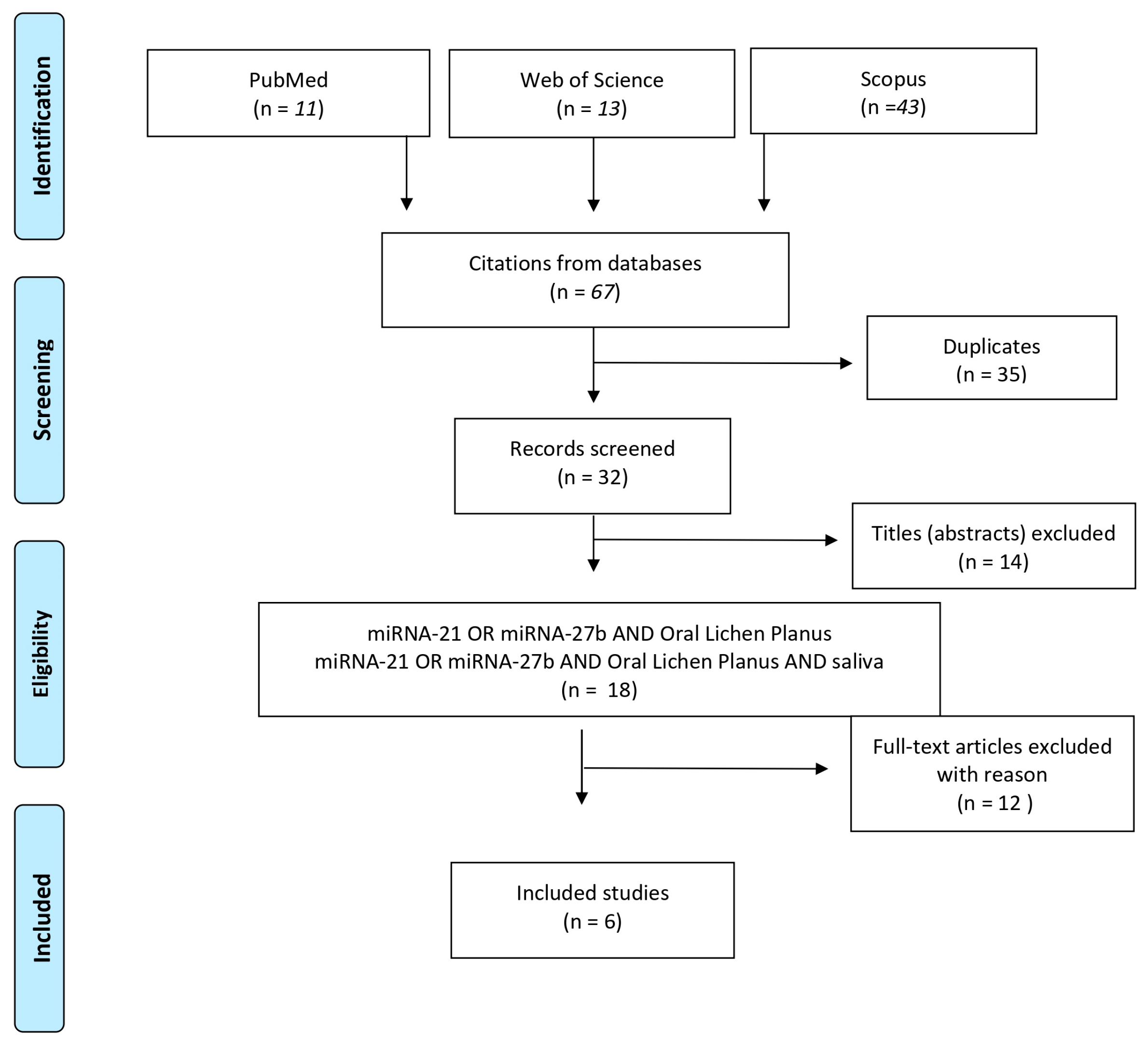
2.2. Search Strategy
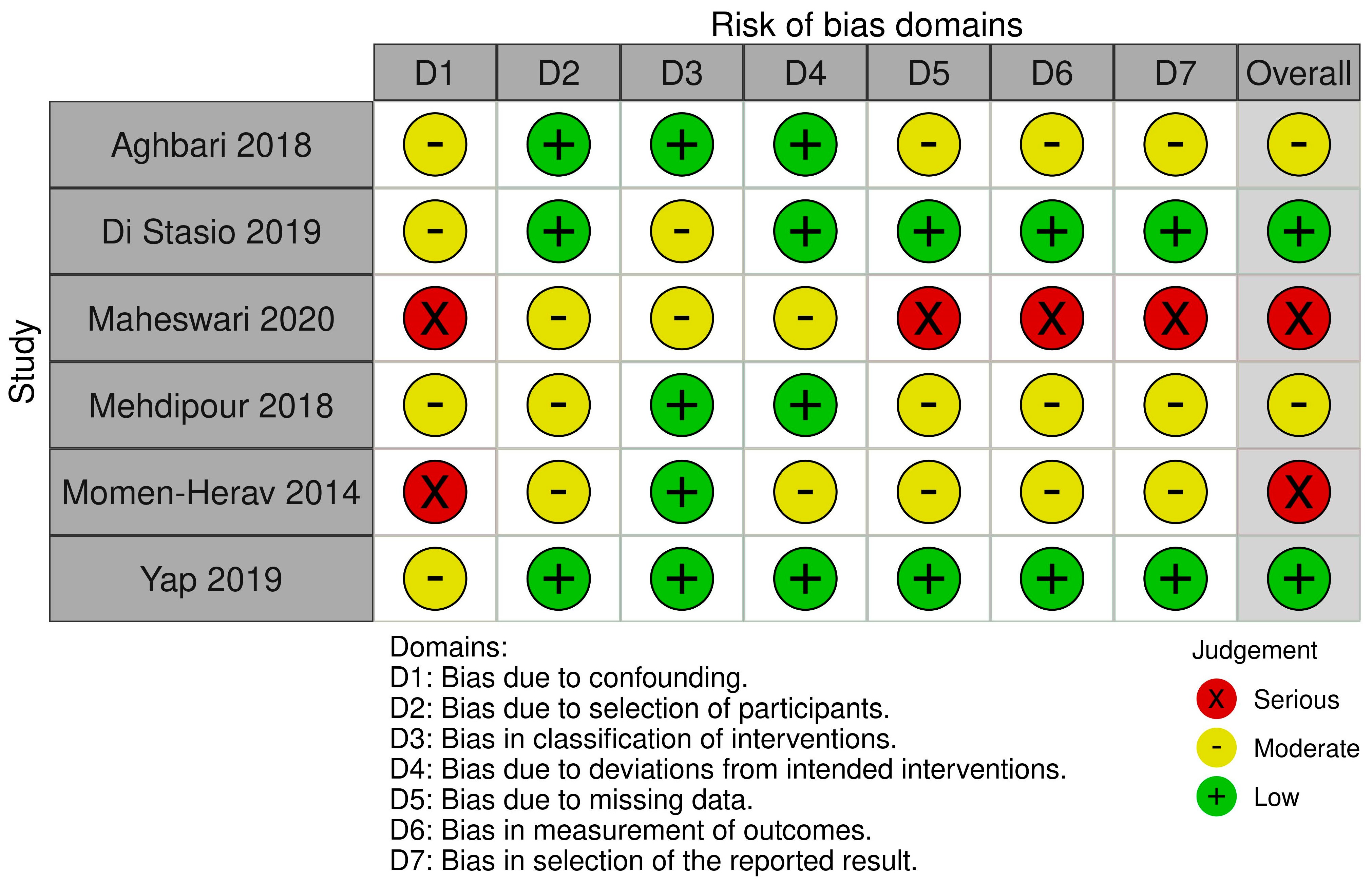
3. Results
3.1. miRNA-21
3.2. miRNA-27b
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Oral Lichen Planus | OLP |
| Area Under the Curve | AUC |
| Quantitative Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction | qRT-PCR |
| Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders | OPMDs |
| Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma | OSCC |
References
- Lucchese, A.; Gentile, E.; Capone, G.; De Vico, G.; Serpico, R.; Landini, G. Fractal Analysis of Mucosal Microvascular Patterns in Oral Lichen Planus: A Preliminary Study. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 120, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, G.; Mei, L.; Polonowita, A.; Hussaini, H.; Seo, B.; Rich, A.M. Malignant Transformation in Oral Lichen Planus and Lichenoid Lesions: A 14-Year Longitudinal Retrospective Cohort Study of 829 Patients in New Zealand. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2020, 130, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idrees, M.; Kujan, O.; Shearston, K.; Farah, C.S. Oral Lichen Planus Has a Very Low Malignant Transformation Rate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Using Strict Diagnostic and Inclusion Criteria. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbari, S.M.H.; Abushouk, A.I.; Attia, A.; Elmaraezy, A.; Menshawy, A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Elsaadany, B.A.; Ahmed, E.M. Malignant Transformation of Oral Lichen Planus and Oral Lichenoid Lesions: A Meta-Analysis of 20095 Patient Data. Oral Oncol. 2017, 68, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, D. Malignant Transformation Rates in Oral Lichen Planus. Evid. Based. Dent. 2018, 19, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payeras, M.R.; Cherubini, K.; Figueiredo, M.A.; Salum, F.G. Oral Lichen Planus: Focus on Etiopathogenesis. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassling, V.; Hampe, J.; Açil, Y.; Braesen, J.H.; Wiltfang, J.; Häsler, R. Disease-Associated MiRNA-MRNA Networks in Oral Lichen Planus. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.; Hong, S.; Choi, J.; Jung, J.; Lee, H. Diagnostic Profiling of Salivary Exosomal MicroRNAs in Oral Lichen Planus Patients. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Dan, H.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Q. MicroRNAs in Oral Lichen Planus and Potential MiRNA–MRNA Pathogenesis with Essential Cytokines: A Review. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2016, 122, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitão, A.L.; Enguita, F.J. A Structural View of MiRNA Biogenesis and Function. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onofrio, N.; Prattichizzo, F.; Martino, E.; Anastasio, C.; Mele, L.; La Grotta, R.; Sardu, C.; Ceriello, A.; Marfella, R.; Paolisso, G.; et al. MiR-27b Attenuates Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Endothelial Cells. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Monterde, M.; Serrano-Valcarce, A.; Almiñana-Pastor, P.J.; Micó-Martínez, P.; López-Roldán, A. MiRNAs as Epigenetic Biomarkers in the Study of the Bidirectional Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontitis: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 10723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-X.; Wang, N.; Wu, W.-C.; Li, C.-Q.; Chen, R.-H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. The Role of MiR-23b in Cancer and Autoimmune Disease. J. Oncol. 2021, 2021, 6473038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stasio, D.; Romano, A.; Boschetti, C.E.; Montella, M.; Mosca, L.; Lucchese, A. Salivary MiRNAs Expression in Potentially Malignant Disorders of the Oral Mucosa and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Pilot Study on MiR-21, MiR-27b, and MiR-181b. Cancers 2022, 15, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stasio, D.D.; Mosca, L.; Lucchese, A.; Cave, D.D.; Kawasaki, H.; Lombardi, A.; Porcelli, M.; Caraglia, M. Salivary Mir-27b Expression in Oral Lichen Planus Patients: A Series of Cases and a Narrative Review of Literature. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 2816–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koopaie, M.; Akhbari, P.; Fatahzadeh, M.; Kolahdooz, S. Identification of Common Salivary MiRNA in Oral Lichen Planus and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Sánchez, D.; Arriaga-Canon, C.; Pedroza-Torres, A.; De La Rosa-Velázquez, I.A.; González-Barrios, R.; Contreras-Espinosa, L.; Montiel-Manríquez, R.; Castro-Hernández, C.; Fragoso-Ontiveros, V.; Álvarez-Gómez, R.M.; et al. The Promising Role of MiR-21 as a Cancer Biomarker and Its Importance in RNA-Based Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtarkhavari, T.; Bahrami, A.R.; Matin, M.M. Downregulation of MiR-21 as a Promising Strategy to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 932, 175233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdipour, M.; Shahidi, M.; Manifar, S.; Jafari, S.; Mashhadi Abbas, F.; Barati, M.; Mortazavi, H.; Shirkhoda, M.; Farzanegan, A.; Elmi Rankohi, Z. Diagnostic and Prognostic Relevance of Salivary MicroRNA-21, -125a, -31 and -200a Levels in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus—A Short Report. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xu, M.; Ding, L.; Tang, J. MiR-27a: A Novel Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target in Tumors. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2836–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbich, C.; Kuehbacher, A.; Dimmeler, S. Role of MicroRNAs in Vascular Diseases, Inflammation, and Angiogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschberger, S.; Hinske, L.C.; Kreth, S. MiRNAs: Dynamic Regulators of Immune Cell Functions in Inflammation and Cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 431, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, G. Altered MicroRNA Expression Profile with MiR-27b Down-regulation Correlated with Disease Activity of Oral Lichen Planus. Oral Dis. 2012, 18, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momen-Heravi, F.; Trachtenberg, A.J.; Kuo, W.P.; Cheng, Y.S. Genomewide Study of Salivary MicroRNAs for Detection of Oral Cancer. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93 (Suppl. S7), 86S–93S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaiq, M.; Ashraf, B. Modifying “Pico” Question into “Picos” Model for More Robust and Reproducible Presentation of the Methodology Employed in A Scientific Study. World J. Plast. Surg. 2017, 6, 390–392. [Google Scholar]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghbari, S.M.H.; Gaafar, S.M.; Shaker, O.G.; Ashiry, S.E.; Zayed, S.O. Evaluating the Accuracy of MicroRNA27b and MicroRNA137 as Biomarkers of Activity and Potential Malignant Transformation in Oral Lichen Planus Patients. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2018, 310, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uma Maheswari, T.N.; Nivedhitha, M.S.; Ramani, P. Expression Profile of Salivary Micro RNA-21 and 31 in Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders. Braz. Oral Res. 2020, 34, e002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.; Seers, C.; Koo, K.; Cheng, L.; Vella, L.J.; Hill, A.F.; Reynolds, E.; Nastri, A.; Cirillo, N.; McCullough, M. Non-Invasive Screening of a MicroRNA-Based Dysregulation Signature in Oral Cancer and Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders. Oral Oncol. 2019, 96, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, T.; Koo, K.; Cheng, L.; Vella, L.J.; Hill, A.F.; Reynolds, E.; Nastri, A.; Cirillo, N.; Seers, C.; McCullough, M. Predicting the Presence of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using Commonly Dysregulated MicroRNA in Oral Swirls. Cancer Prev. Res. 2018, 11, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, K.; Wahlin, Y.B.; Gu, X.; Boldrup, L.; Nylander, K. Altered Expression of MiR-21, MiR-125b, and MiR-203 Indicates a Role for These MicroRNAs in Oral Lichen Planus. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2012, 41, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, G.; El-Nahass, H.; Abd, W.; Mohamad, M. Expression Levels of MicroRNA-21 and MicroRNA-146a in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus. Life Sci. J. 2012, 9, 4666–4670. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Du, G.; Zhang, W.; Cao, T.; Shi, L.; Wang, Y.; Mi, J.; Tang, G. Down-regulation of MiRNA-27b-3p Suppresses Keratinocytes Apoptosis in Oral Lichen Planus. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4326–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polizzi, A.; Santonocito, S.; Distefano, A.; De Pasquale, R.; Alibrandi, A.; Alanazi, A.M.; Li Volti, G.; Isola, G. Analysis of Oral Lichen Planus Severity on Micro-RNA Linked with Malignant Transformation Risks. Oral Dis. 2024, 30, 2918–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, G.; Seers, C.; Reynolds, E.; McCullough, M.J. A Panel of MicroRNAs Can Be Used to Determine Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Aim | Sequencing Method | Patients | OLP Pattern | miRNA Investigated | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aghbari, 2018 [27] | To compare the expression of miRNA-27b and miRNA-137 in tissues and saliva between OLP patients and controls. | qRT-PCR | 20 OLP + 20 controls | 5 white, 7 erosive, 8 atrophic | 27b, 137 | miRNA-27b and miRNA-137 were downregulated in patients affected by OLP. A statistical difference was found between OLP and control groups in both saliva and tissue samples, with no statistical difference between each OLP subgroup for miRNA27b. A statistical difference was also found between the saliva samples of each OLP subgroup. |
| Di Stasio, 2019 [15] | To analyze the expression of salivary miR-27b in oral lichen planus (OLP) patients using microarray technology and qRT-PCR validation and explore its potential as a non-invasive biomarker for OLP diagnosis and disease activity monitoring. | qRT-PCR, microarray analysis | 5 OLP + 5 controls | 3 atrophic/erosive, 2 mixed | 15b, 21, 27b, 125b, 203 | miR-27b was downregulated in the saliva of all OLP patients (~3-fold decrease compared to controls, p < 0.001), while miR-15b, miR-21, miR-125b, and miR-203 were upregulated (miR-15b by ~85-fold). Validation confirmed the downregulation of miR-27b, suggesting its role in keratinocyte activity and OLP pathogenesis. Salivary collection was a well-tolerated, non-invasive procedure, highlighting its potential for clinical applications. |
| Maheswari, 2020 [28] | To evaluate the expression levels of salivary miRNA-21 and miRNA-31 in oral potentially malignant disorders (OPMD) and assess their diagnostic potential as biomarkers for early malignant changes. | qRT-PCR | 12 OSF, 8 OL, 9 OLP, 7 OSF + OL + 36 controls | n.s. | 21, 31 | miR 21 was significantly upregulated in OPMD patients compared to controls (2.44-fold in leukoplakia and 2.03-fold in oral lichen planus, p < 0.05). It was associated with severe dysplasia (3.6-fold increase, p < 0.01). Area under the curve (AUC) was 0.82, with 69% sensitivity and 66% specificity. miR-31 was elevated in OPMD (1.6-fold in leukoplakia and 1.2-fold in oral lichen planus, p > 0.05) and significantly associated with severe dysplasia (2.5-fold increase, p < 0.01). AUC was 0.51, with lower diagnostic efficiency compared to miRNA-21. Salivary miRNA-21 demonstrated potential as a non-invasive biomarker for detecting early malignant changes in OPMD. |
| Mehdipour, 2018 [19] | To evaluate the diagnostic and prognostic potential of salivary miRNAs in OLP patients with and without dysplasia and their relationship to malignant transformation. | qRT-PCR | 30 OLP (20 dysplasia), 15 OSCC + 15 controls | n.s. | 21, 125a, 31, 200a | miR-21 was significantly increased in OLP (p = 0.012), dysplastic OLP (p = 0.0017), and OSCC patients (p < 0.0001) compared to controls. miR-125 was significantly decreased in OLP (p < 0.001), dysplastic OLP (p < 0.0001), and OSCC (p < 0.0001), with lower levels in dysplastic OLP compared to non-dysplastic OLP (p = 0.002). miR-31 was elevated in dysplastic OLP (p = 0.01) and OSCC (p = 0.004) but not significantly altered in non-dysplastic OLP. miR-200a showed no significant changes in OLP patients with or without dysplasia but was significantly reduced in OSCC patients (p < 0.0001). Increased miR-21 and decreased miR-125a levels may indicate poor prognosis in OLP, while lack of significant changes in miR-31 and miR-200a may suggest absence of malignant transformation. |
| Momen-Herav, 2014 [24] | To evaluate the differential expression of miRNAs in the saliva of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC), patients in remission from OSCC (OSCC-R), patients with oral lichen planus (OLP), and healthy controls to identify potential salivary biomarkers for OSCC diagnosis. | NanoString nCounter miRNA expression assay, with validation by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) | 34 patients: 9 with OSCC, 8 with OSCC in remission (OSCC-R), 8 with OLP, and 9 healthy controls (HCs) | n.s. | Over 700 miRNAs were analyzed, and 13 miRNAs were found to be significantly deregulated in OSCC patients compared to healthy controls, as follows: Downregulated: miRNA-136, miRNA-147, miRNA-1250, miRNA-148a, miRNA-632, miRNA-646, miRNA-668, miRNA-877, miRNA-503, miRNA-220a, and miRNA-323-5p. Upregulated: miRNA-24, miRNA-27b | miRNA-27b was found to be significantly upregulated in OSCC patients compared to those with OSCC-R, OLP, and healthy controls, suggesting its potential as a diagnostic biomarker for OSCC. miRNA-136 was found to be downregulated in OSCC patients compared to healthy controls and OSCC-R patients, making it useful for distinguishing OSCC from OSCC-R. ROC curve analysis showed that miRNA-27b and miRNA-136 had high sensitivity and specificity in distinguishing OSCC patients from other groups. |
| Yap 2019 [29] | To evaluate a panel of OSCC-associated microRNAs in oral swirls as a non-invasive diagnostic tool for OSCC and OPMDs, including OLP, using dSCORE and an algorithm for risk classification. | qRT-PCR | 53 OSCC, 31 OLP, 15 OLL, 26 OL, 2 TUGSE + 63 controls | n.s. | 24-3p, 21-5p, 99a-5p, 100-5p | dSCORE and the algorithm demonstrated 86.8% sensitivity, 81.5% specificity, and 84.2% accuracy for OSCC diagnosis. miR-24-3p was deregulated in OSCC and was linked to cell proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis. miR-21-5p was upregulated in OSCC and was strongly associated with oncogenic processes. miR-99a-5p and miR-100-5p both targeted tumor-related pathways (e.g., mTOR and PI3K) and contributed to differentiating OSCC from OPMDs. The identified miRNA panel effectively distinguished OSCC from OPMDs and highlighted the potential of miRNA-based tools for non-invasive monitoring and early detection of malignant transformations in disorders like OLP. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Stasio, D.; Fiori, F.; Romano, A.; Palmieri, A.; Mosca, L.; Ruiz Roca, J.A.; Lopez-Jornet, P.; Lucchese, A. miRNA-21 and miRNA-27b Expression in Saliva of Patients with Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125824
Di Stasio D, Fiori F, Romano A, Palmieri A, Mosca L, Ruiz Roca JA, Lopez-Jornet P, Lucchese A. miRNA-21 and miRNA-27b Expression in Saliva of Patients with Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125824
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Stasio, Dario, Fausto Fiori, Antonio Romano, Annalisa Palmieri, Laura Mosca, Juan Antonio Ruiz Roca, Pia Lopez-Jornet, and Alberta Lucchese. 2025. "miRNA-21 and miRNA-27b Expression in Saliva of Patients with Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125824
APA StyleDi Stasio, D., Fiori, F., Romano, A., Palmieri, A., Mosca, L., Ruiz Roca, J. A., Lopez-Jornet, P., & Lucchese, A. (2025). miRNA-21 and miRNA-27b Expression in Saliva of Patients with Oral Lichen Planus: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5824. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125824