Cardiovascular Toxicity of Metal-Based Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
| MNPs | Usage | Toxicity |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum oxide nanoparticles (AlO-NPs) | Cosmetics [26], Solid rocket propellants, Lubrication, and Drug delivery [27] | Neurotoxicity [28,29] |
| Cadmium oxide nanoparticles (CdO-NPs) | Paint pigments [30], Solar cells, and Phototransistors [31] | Genotoxicity [30], Developmental toxicity [32] |
| Copper nanoparticles (Cu-NPs) | Wastewater treatment [33] | Reproductive toxicity [34] |
| Copper oxide nanoparticles (CuO-NPs) | Nanofertilizers [35], Antifungal and antibacterial agent [36], Food packaging [37] | Respiratory toxicity [38], Neurotoxicity [39] |
| Gold nanoparticles (Au-NPs) | Photothermal therapy [40], Gene delivery and Targeted drug delivery [41], Biolabels [42] | Hepatotoxicity [43,44] |
| Iron oxide nanoparticles 1 (IO-NPs) | Cancer immunotherapy [45], Drug delivery [46] | Neurotoxicity [47,48] |
| Nickel oxide nanoparticles (NiO-NPs) | Lithium-ion batteries [49], Fuel cells, Drug delivery, and Antibiotics [50] | Hepatotoxicity [51], Respiratory toxicity [52] |
| Palladium nanoparticles (Pd-NPs) | Organic catalysis, Fuel cells, Biosensors and Electrocatalysis [53] | Immunotoxicity [54] |
| Rhenium nanoparticles (Re-NPs) | Tumor treatment therapy and Coatings [55] | - |
| Silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) | Anticancer therapy [56], Antiinflammatory drugs and Antibiotics [57] | Developmental toxicity [58], Genotoxicity [59], Hepatotoxicity [60] |
| Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2-NPs) | Photodynamic therapy [61], Toothpaste [62], Food additives [63], Sunscreen [64] | Respiratory toxicity [65], Neurotoxicity [66], Developmental toxicity [67] |
| Zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) | Cosmetics, Sunscreen and Textile finishes [68], Drug carriers [69], Food packaging [26] | Developmental toxicity [70], Respiratory toxicity [71], Immunotoxicity [72] |
2. Exposure and Biodistribution of MNPs
2.1. TiO2-NPs
2.2. Ag-NPs
2.3. Au-NPs
2.4. ZnO-NPs
2.5. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles (IO-NPs)
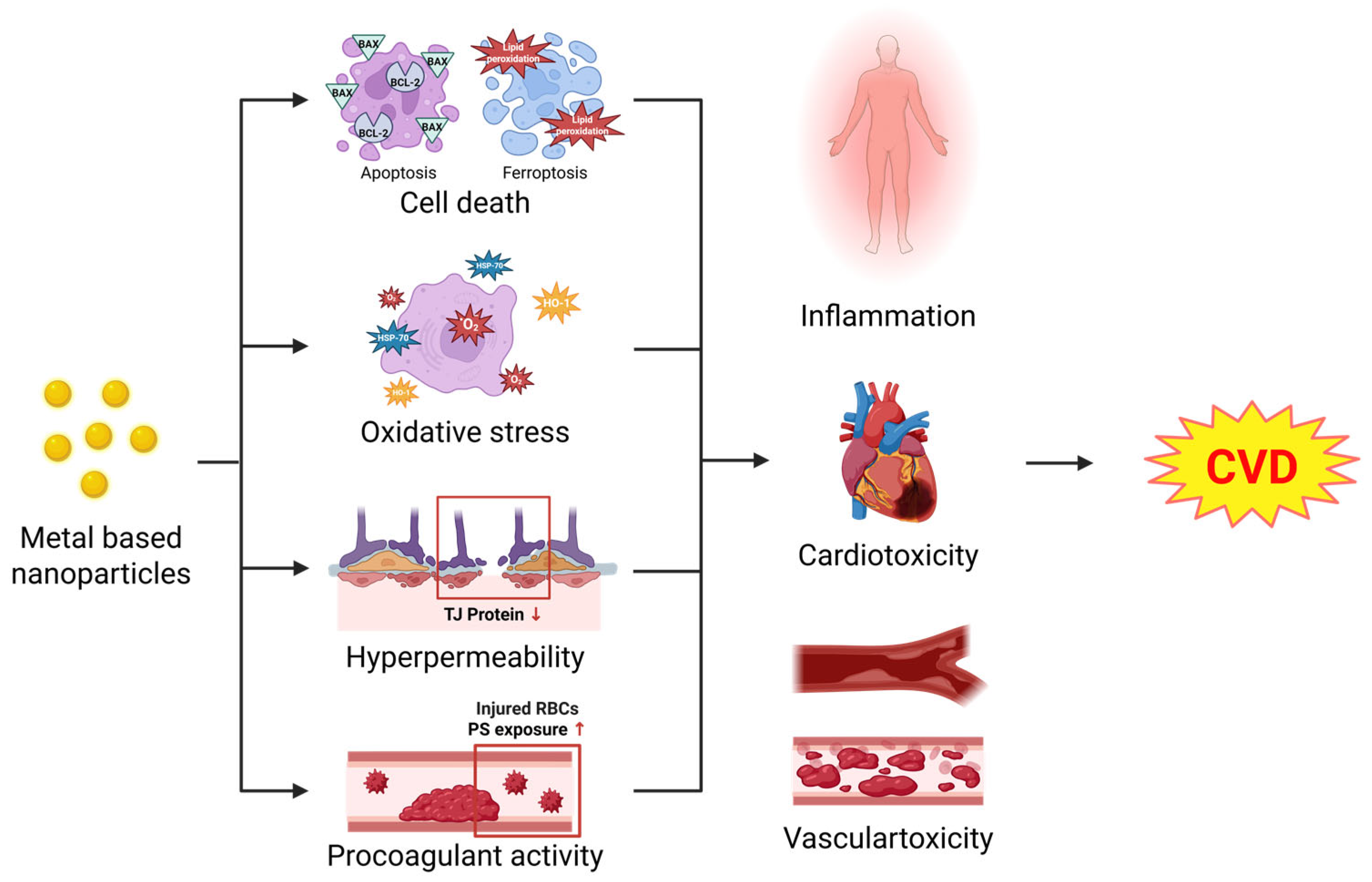
3. Cellular Effects of MNPs in the Cardiovascular System
3.1. Cell Death
3.1.1. Apoptosis
3.1.2. Ferroptosis
3.2. Oxidative Stress
3.3. Hyperpermeability
3.4. Procoagulant Activity
4. Pathological Conditions Induced by MNPs in the Cardiovascular System
4.1. Inflammation
4.2. Cardiotoxicity
4.3. Vascular Toxicity
5. Comparative Toxicity Between Metal Ions and MNPs
6. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgOAc | Silver Acetate |
| Ag-NP | Silver Nanoparticle |
| Au-NP | Gold Nanoparticle |
| BBB | Blood–brain Barrier |
| HAEC | Human Aortic Endothelial Cell |
| HBMEC | Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell |
| HCMEC | Human Cardiac Microvascular Endothelial Cell |
| HUVEC | Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell |
| HSP | Heat Shock Protein |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IO-NP | Iron Oxide Nanoparticle |
| IT | Intratracheal |
| IV | Intravenous |
| MNP | Metal-based Nanoparticle |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| RBC | Red Blood Cell |
| TiO2-NP | Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| ZnO-NP | Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle |
References
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Emerging Applications of Nanotechnology in Healthcare and Medicine. Molecules 2023, 28, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, S.; Muhammad, K.; Waheed, Y. Nanotechnology: A Revolution in Modern Industry. Molecules 2023, 28, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, S.; Ud Din, S.R.; Khan, S.U.; Gul, R.; Kiani, F.A.; Wahab, A.; Zhong, M. Nanoparticle: A Promising Player in Nanomedicine and its Theranostic Applications for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2023, 48, 101599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.; Mohapatra, S.; Mishra, H.; Farooq, U.; Kumar, K.; Ansari, M.J.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Alalaiwe, A.S.; Mirza, M.A.; Iqbal, Z. Nanotechnology in Cosmetics and Cosmeceuticals-A Review of Latest Advancements. Gels 2022, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameen, F.; Alsamhary, K.; Alabdullatif, J.A.; Alnadhari, S. A review on metal-based nanoparticles and their toxicity to beneficial soil bacteria and fungi. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.; Ju, Z.; Skonieczna, M.; Zhou, P.K.; Huang, R. Nanoparticles-induced potential toxicity on human health: Applications, toxicity mechanisms, and evaluation models. MedComm 2023, 4, e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.S.-L.; Hii, L.-W.; Looi, C.K.; Lim, W.-M.; Wong, S.-F.; Kok, Y.-Y.; Tan, B.-K.; Wong, C.-Y.; Leong, C.-O. Impact of Microplastics and Nanoplastics on Human Health. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdorster, G.; Oberdorster, E.; Oberdorster, J. Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Perspect 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A.; Ahmed, I.A.; Karloukovski, V.; MacLaren, D.A.; Foulds, P.G.; Allsop, D.; Mann, D.M.; Torres-Jardon, R.; Calderon-Garciduenas, L. Magnetite pollution nanoparticles in the human brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10797–10801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.U.; Suleman, M.; Khan, M.U.; Khan, M.S.; Arbi, F.M.; Hussain, T.; Alsuhaibani, A.M.; Refat, M.S. Natural Allies for Heart Health: Nrf2 Activation and Cardiovascular Disease Management. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49 Pt B, 102084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, M.; Bibi, A.; Wahab, A.; Hamayun, S.; Rehman, M.U.; Khan, S.U.; Awan, U.A.; Riaz, N.-U.; Naeem, M.; Saeed, S.; et al. Shaping the Future of Cardiovascular Disease by 3D Printing Applications in Stent Technology and its Clinical Outcomes. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49 Pt A, 102039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Shen, D.; Wu, F.; Pleixats, R.; Pan, J. Functionalized silica nanoparticles: Classification, synthetic approaches and recent advances in adsorption applications. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 15998–16016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burlec, A.F.; Corciova, A.; Boev, M.; Batir-Marin, D.; Mircea, C.; Cioanca, O.; Danila, G.; Danila, M.; Bucur, A.F.; Hancianu, M. Current Overview of Metal Nanoparticles’ Synthesis, Characterization, and Biomedical Applications, with a Focus on Silver and Gold Nanoparticles. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabeo, A.; Basei, G.; Tsiliki, G.; Peijnenburg, W.; Hristozov, D. Ordered weighted average based grouping of nanomaterials with Arsinh and dose response similarity models. NanoImpact 2022, 25, 100370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, A.; Benford, D.; Halldorsson, T.; Jeger, M.J.; Knutsen, H.K.; More, S.; Naegeli, H.; Noteborn, H.; Ockleford, C.; Ricci, A.; et al. Guidance on risk assessment of the application of nanoscience and nanotechnologies in the food and feed chain: Part 1, human and animal health. EFSA J 2018, 16, e05327. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, E.J.; Ceger, P.; Allen, D.G.; Coyle, J.; Derk, R.; Garcia-Reyero, N.; Gordon, J.; Kleinstreuer, N.C.; Matheson, J.; McShan, D.; et al. U.S. Federal Agency interests and key considerations for new approach methodologies for nanomaterials. ALTEX 2022, 39, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdely, A.; Dahm, M.M.; Schubauer-Berigan, M.K.; Chen, B.T.; Antonini, J.M.; Hoover, M.D. Bridging the gap between exposure assessment and inhalation toxicology: Some insights from the carbon nanotube experience. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2016, 99, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadavalli, T.; Shukla, D. Role of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles as diagnostic and therapeutic tools for highly prevalent viral infections. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornberg, T.G.; Stueckle, T.A.; Antonini, J.A.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Castranova, V.; Yang, Y.; Wang, L. Potential Toxicity and Underlying Mechanisms Associated with Pulmonary Exposure to Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Conflicting Literature and Unclear Risk. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Izumi, H.; Tomonaga, T.; Nishida, C.; Higashi, H. Adverse effects of nanoparticles on humans. J. Occup Health 2025, 67, uiaf002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Jin, W.; Ma, J. Lung inflammation perturbation by engineered nanoparticles. Front. Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1199230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Lee, Y.-H.; Chou, C.-L.; Chang, Y.-S.; Liu, W.-C.; Chiu, H.-W. Oxidative stress and potential effects of metal nanoparticles: A review of biocompatibility and toxicity concerns. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 346, 123617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xiong, G.; Liu, Z. Toxicity of metal-based nanoparticles: Challenges in the nano era. Front. Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1001572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortezaee, K.; Najafi, M.; Samadian, H.; Barabadi, H.; Azarnezhad, A.; Ahmadi, A. Redox interactions and genotoxicity of metal-based nanoparticles: A comprehensive review. Chem. Biol. Interact 2019, 312, 108814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, P.; Huang, X.; Ye, N.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Peng, S.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y. Cytotoxicity of Metal-Based Nanoparticles: From Mechanisms and Methods of Evaluation to Pathological Manifestations. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2106049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousef, M.; Roychoudhury, S.; Jafaar, K.; Slama, P.; Kesari, K.; Kamel, M. Aluminum oxide and zinc oxide induced nanotoxicity in rat brain, heart, and lung. Physiol. Res. 2022, 71, 677–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Lim, J.-O.; Kim, W.-I.; Park, S.-W.; Lee, S.-J.; Shin, I.-S.; Moon, C.; Kim, J.-H.; Heo, J.-D.; Kim, J.-C. Subchronic Toxicity Evaluation of Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticles in Rats Following 28-Day Repeated Oral Administration. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2022, 200, 3215–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Chang, L.; Shang, N.; Chen, J.; Fan, R.; Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Niu, Q.; et al. Involvement of Mitophagy in Aluminum Oxide Nanoparticle-Induced Impairment of Learning and Memory in Mice. Neurotox Res. 2021, 39, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jia, L.; Wang, Z.; Guo, W.; Qin, X.; Ge, C.; Niu, Q.; Zhang, Q. Alumina nanoparticles induce learning and memory impairment in a particle size-dependent and time-dependent manner. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 295, 118177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Qin, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Ingle, T.; Yan, J.; Orza, A.I.; Biris, A.S.; Ghorai, S.; et al. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of cadmium oxide nanoparticles evaluated using in vitro assays. Mutat. Res. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2020, 850–851, 503149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabour, K.; Al Naggar, Y.; Masry, S.; Naiem, E.; Giesy, J.P. Cellular alterations in midgut cells of honey bee workers (Apis millefera L.) exposed to sublethal concentrations of CdO or PbO nanoparticles or their binary mixture. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 651 Pt 1, 1356–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, J.L.; Xiong, J.Q.; Hoffman, C.; Zelikoff, J.T. Cadmium associated with inhaled cadmium oxide nanoparticles impacts fetal and neonatal development and growth. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 126, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameh, T.; Sayes, C.M. The potential exposure and hazards of copper nanoparticles: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 71, 103220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anima, B.; Mondal, P.; Gurusubramanian, G.; Roy, V.K. Mechanistic study of copper nanoparticle (CuNP) toxicity on the mouse uterus via apelin signaling. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. Int. 2023, 30, 88824–88841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaraji, M.; Thanikachalam, P.V.; Elumalai, K. The potential of copper oxide nanoparticles in nanomedicine: A comprehensive review. Biotechnol. Notes 2024, 5, 80–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letchumanan, D.; Sok, S.P.M.; Ibrahim, S.; Nagoor, N.H.; Arshad, N.M. Plant-Based Biosynthesis of Copper/Copper Oxide Nanoparticles: An Update on Their Applications in Biomedicine, Mechanisms, and Toxicity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, K.K.; Deka, P.; Bangar, S.P.; Chaudhary, V.; Trif, M.; Rusu, A. Applications of Inorganic Nanoparticles in Food Packaging: A Comprehensive Review. Polymers 2022, 14, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Mo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, Q. MMP-3 mediates copper oxide nanoparticle-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goma, A.A.; El Okle, O.S.; Tohamy, H.G. Protective effect of methylene blue against copper oxide nanoparticle-induced neurobehavioral toxicity. Behav. Brain. Res. 2021, 398, 112942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Pandit, S.; Mokkapati, V.; Garg, A.; Ravikumar, V.; Mijakovic, I. Gold Nanoparticles in Diagnostics and Therapeutics for Human Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golchin, K.; Golchin, J.; Ghaderi, S.; Alidadiani, N.; Eslamkhah, S.; Eslamkhah, M.; Davaran, S.; Akbarzadeh, A. Gold nanoparticles applications: From artificial enzyme till drug delivery. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 250–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daraee, H.; Eatemadi, A.; Abbasi, E.; Fekri Aval, S.; Kouhi, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. Application of gold nanoparticles in biomedical and drug delivery. Artif Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enea, M.; Pereira, E.; Costa, J.; Soares, M.E.; Dias da Silva, D.; Bastos, M.L.; Carmo, H.F. Cellular uptake and toxicity of gold nanoparticles on two distinct hepatic cell models. Toxicol In Vitro 2021, 70, 105046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, S.; Chen, Q.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Xia, L.; Huang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Liu, X. Correction: Acute exposure to gold nanoparticles aggravates lipopolysaccharide-induced liver injury by amplifying apoptosis via ROS-mediated macrophage-hepatocyte crosstalk. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.Q.; Shi, Y.N.; Zhu, Y.P.; Liu, Y.Q.; Gu, L.W.; Liu, D.D.; Ma, A.; Xia, F.; Guo, Q.Y.; Xu, C.C.; et al. Recent trends in preparation and biomedical applications of iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, S.; Gutierrez, L.; Vaquero, M.P.; Verdoy, D.; Salas, G.; Luengo, Y.; Brenes, A.; Jose Teran, F. Safety assessment of chronic oral exposure to iron oxide nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 205101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dora, M.F.; Taha, N.M.; Lebda, M.A.; Hashem, A.E.; Elfeky, M.S.; El-Sayed, Y.S.; Jaouni, S.A.; El-Far, A.H. Quercetin Attenuates Brain Oxidative Alterations Induced by Iron Oxide Nanoparticles in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Jana, S.; Chetty, R.; Thakore, S.; Singh, M.; Devkar, R. Toxicity evaluation of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles reveals neuronal loss in chicken embryo. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 42, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, S.L.; Kovochich, M.; Lyons-Darden, T.; Taylor, M.; Schulte, A.M.; Madl, A.K. Review and Evaluation of the Potential Health Effects of Oxidic Nickel Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhe, M.G.; Gebreslassie, Y.T. Biomedical Applications of Biosynthesized Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 4229–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adiguzel, C.; Karaboduk, H.; Apaydin, F.G.; Kalender, S.; Kalender, Y. Comparison of nickel oxide nano and microparticles toxicity in rat liver: Molecular, biochemical, and histopathological study. Toxicol. Res. 2023, 12, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, Y.; Hirohashi, M.; Ogami, A.; Oyabu, T.; Myojo, T.; Hashiba, M.; Mizuguchi, Y.; Kambara, T.; Lee, B.W.; Kuroda, E.; et al. Pulmonary toxicity following an intratracheal instillation of nickel oxide nanoparticle agglomerates. J. Occup. Health 2011, 53, 293–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leso, V.; Iavicoli, I. Palladium Nanoparticles: Toxicological Effects and Potential Implications for Occupational Risk Assessment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Kim, J.H. Palladium Nanoparticle-Induced Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Apoptosis, and Immunomodulation Enhance the Biogenesis and Release of Exosome in Human Leukemia Monocytic Cells (THP-1). Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2849–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepceoglu, A.; Gundogdu, Y.; Sarilmaz, A.; Ersoz, M.; Ozel, F.; Kilic, H.S. Rhenium/rhenium oxide nanoparticles production using femtosecond pulsed laser ablation in liquid. Turk. J. Chem. 2021, 45, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, C.Y.; Wang, Z.X.; Xie, H. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, medical applications and biosafety. Theranostics 2020, 10, 8996–9031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatroudi, A. Unlocking the Potential of Silver Nanoparticles: From Synthesis to Versatile Bio-Applications. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo, A.C.; Lynch, I.; Valsami-Jones, E. Silver nanoparticle induced toxicity and cell death mechanisms in embryonic zebrafish cells. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 6142–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AshaRani, P.V.; Low Kah Mun, G.; Hande, M.P.; Valiyaveettil, S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assar, D.H.; Mokhbatly, A.-A.A.; Ghazy, E.W.; Elbialy, Z.I.; Gaber, A.A.; Hassan, A.A.; Nabil, A.; Asa, S.A. Silver nanoparticles induced hepatoxicity via the apoptotic/antiapoptotic pathway with activation of TGFbeta-1 and alpha-SMA triggered liver fibrosis in Sprague Dawley rats. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. Int. 2022, 29, 80448–80465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesmeli, S.; Biray Avci, C. Application of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in cancer therapies. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakeel, M.; Jabeen, F.; Shabbir, S.; Asghar, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Chaudhry, A.S. Toxicity of Nano-Titanium Dioxide (TiO2-NP) Through Various Routes of Exposure: A Review. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2016, 172, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranowska-Wojcik, E.; Szwajgier, D.; Oleszczuk, P.; Winiarska-Mieczan, A. Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Exposure on Human Health-a Review. Biol. Trace Element Res. 2020, 193, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.L.; Lim, H.W. A review of inorganic UV filters zinc oxide and titanium dioxide. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2019, 35, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.S.; Jegal, H.; Ko, J.W.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, E.H.; Boo, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, G.W.; Park, S.M.; et al. Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle Exposure Provokes Greater Lung Inflammation in Females Than Males in the Context of Obesity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2025, 20, 5321–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, A.; Ghaleb, S.S.; Zaki, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Farghali, A.A.; Ali, L.E.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Al-Serwi, R.H.; Hassan, R.M.; et al. Hesperidin Attenuates Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats by Regulating Nrf-2/TNF-alpha Signaling Pathway, the Suppression of Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 37584–37591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadzadeh, N.; Zirak Javanmard, M.; Karimipour, M.; Farjah, G. Developmental Toxicity of the Neural Tube Induced by Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles in Mouse Embryos. Avicenna J. Med. Biotechnol. 2021, 13, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Pi, J.; Cai, J. The Advancing of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2018, 2018, 1062562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.K.; Mishra, H.; Ekielski, A.; Talegaonkar, S.; Vaidya, B. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: A promising nanomaterial for biomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kteeba, S.M.; El-Adawi, H.I.; El-Rayis, O.A.; El-Ghobashy, A.E.; Schuld, J.L.; Svoboda, K.R.; Guo, L. Zinc oxide nanoparticle toxicity in embryonic zebrafish: Mitigation with different natural organic matter. Environ. Pollut 2017, 230, 1125–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, Y.; Izumi, H.; Yoshiura, Y.; Tomonaga, T.; Oyabu, T.; Myojo, T.; Kawai, K.; Yatera, K.; Shimada, M.; Kubo, M.; et al. Evaluation of Pulmonary Toxicity of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Following Inhalation and Intratracheal Instillation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senapati, V.A.; Gupta, G.S.; Pandey, A.K.; Shanker, R.; Dhawan, A.; Kumar, A. Zinc oxide nanoparticle induced age dependent immunotoxicity in BALB/c mice. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 342–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andujar, P.; Lanone, S.; Brochard, P.; Boczkowski, J. Respiratory effects of manufactured nanoparticles. Rev. Mal. Respir. 2011, 28, e66–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szucs-Somlyo, E.; Lehel, J.; Majlinger, K.; Lorincz, M.; Kovago, C. Metal-oxide inhalation induced fever-Immuntoxicological aspects of welding fumes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 175, 113722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monse, C.; Raulf, M.; Jettkant, B.; van Kampen, V.; Kendzia, B.; Schurmeyer, L.; Seifert, C.E.; Marek, E.M.; Westphal, G.; Rosenkranz, N.; et al. Health effects after inhalation of micro- and nano-sized zinc oxide particles in human volunteers. Arch. Toxicol. 2021, 95, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemi, J.O.; Fawole, O.A. Metal-Based Nanoparticles in Food Packaging and Coating Technologies: A Review. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, L.; Jia, M.; Xiong, Y. Nanofillers in Novel Food Packaging Systems and Their Toxicity Issues. Foods 2024, 13, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemifard Dehkordi, P.; Moshtaghi, H.; Abbasvali, M. Effects of magnesium oxide and copper oxide nanoparticles on biofilm formation ofEscherichia coliandListeria monocytogenes. Nanotechnology 2023, 34, 155102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshani, M.; Rezaian-Isfahni, A.; Lotfalizadeh, M.H.; Khassafi, N.; Abadi, M.; Nejati, M. Metal nanoparticles as a potential technique for the diagnosis and treatment of gastrointestinal cancer: A comprehensive review. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scafa Udriste, A.; Burdusel, A.C.; Niculescu, A.G.; Radulescu, M.; Grumezescu, A.M. Metal-Based Nanoparticles for Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibuyi, N.R.S.; Moabelo, K.L.; Fadaka, A.O.; Meyer, S.; Onani, M.O.; Madiehe, A.M.; Meyer, M. Multifunctional Gold Nanoparticles for Improved Diagnostic and Therapeutic Applications: A Review. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahajuddin; Arora, S. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Magnetic nanoplatforms as drug carriers. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3445–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomer, M.C.; Hutchinson, C.; Volkert, S.; Greenfield, S.M.; Catterall, A.; Thompson, R.P.; Powell, J.J. Dietary sources of inorganic microparticles and their intake in healthy subjects and patients with Crohn’s disease. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedle, S.; Wills, J.W.; Miniter, M.; Otter, D.E.; Singh, H.; Brown, A.P.; Micklethwaite, S.; Rees, P.; Jugdaohsingh, R.; Roy, N.C.; et al. A Murine Oral-Exposure Model for Nano- and Micro-Particulates: Demonstrating Human Relevance with Food-Grade Titanium Dioxide. Small 2020, 16, e2000486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disdier, C.; Devoy, J.; Cosnefroy, A.; Chalansonnet, M.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Brun, E.; Lund, A.; Mabondzo, A. Tissue biodistribution of intravenously administrated titanium dioxide nanoparticles revealed blood-brain barrier clearance and brain inflammation in rat. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 12, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H. Synthesis, applications, toxicity and toxicity mechanisms of silver nanoparticles: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 253, 114636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, Z.; Nemmar, A. Health Impact of Silver Nanoparticles: A Review of the Biodistribution and Toxicity Following Various Routes of Exposure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Wang, W.X. Maternal transfer and biodistribution of citrate and luminogens coated silver nanoparticles in medaka fish. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 128862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, Z.; Al-Salam, S.; Yuvaraju, P.; Ali, B.H.; Nemmar, A. Remote effects and biodistribution of pulmonary instilled silver nanoparticles in mice. NanoImpact 2021, 22, 100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-Y.; Choi, Y.-J.; Jung, E.-J.; Yin, H.-Q.; Kwon, J.-T.; Kim, J.-E.; Im, H.-T.; Cho, M.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, H.-Y.; et al. Genomics-based screening of differentially expressed genes in the brains of mice exposed to silver nanoparticles via inhalation. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.R.; Raftis, J.B.; Langrish, J.P.; McLean, S.G.; Samutrtai, P.; Connell, S.P.; Wilson, S.; Vesey, A.T.; Fokkens, P.H.; Boere, A.J.F. Inhaled Nanoparticles Accumulate at Sites of Vascular Disease. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4542–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, G.; Kreyling, W.G.; Simon, U. Toxic effects and biodistribution of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 3011–3037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvin-Choy, N.S.; Nelson, K.M.; Dang, M.N.; Gleghorn, J.P.; Day, E.S. Gold nanoparticle biodistribution in pregnant mice following intravenous administration varies with gestational age. Nanomedicine 2021, 36, 102412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.L.; Chang, H.L.; Tsai, F.M.; Lee, Y.H.; Wang, C.H.; Cheng, T.J. The effect of the inhalation of and topical exposure to zinc oxide nanoparticles on airway inflammation in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 384, 114787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossner, P.; Vrbova, K.; Strapacova, S.; Rossnerova, A.; Ambroz, A.; Brzicova, T.; Libalova, H.; Javorkova, E.; Kulich, P.; Vecera, Z.; et al. Inhalation of ZnO Nanoparticles: Splice Junction Expression and Alternative Splicing in Mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 168, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamcakova-Dodd, A.; Stebounova, L.V.; Kim, J.S.; Vorrink, S.U.; Ault, A.P.; O’sHaughnessy, P.T.; Grassian, V.H.; Thorne, P.S. Toxicity assessment of zinc oxide nanoparticles using sub-acute and sub-chronic murine inhalation models. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Fang, J.; Hu, J.; Geng, X.; Liu, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Cui, W.; Yu, Z.; Jia, X. Toxicokinetics of zinc oxide nanoparticles and food grade bulk-sized zinc oxide in rats after oral dosages. NanoImpact 2022, 25, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadfar, S.M.; Roemhild, K.; Drude, N.I.; von Stillfried, S.; Knuchel, R.; Kiessling, F.; Lammers, T. Iron oxide nanoparticles: Diagnostic, therapeutic and theranostic applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2019, 138, 302–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kulkarni, P.; Liu, S.; Chemuturi, N.; Shah, D.K. Nanoparticle biodistribution coefficients: A quantitative approach for understanding the tissue distribution of nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 194, 114708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, L.; Yousefi Babadi, V.; Espanani, H.R. Toxic effects of the Fe2O3 nanoparticles on the liver and lung tissue. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2015, 116, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alphandery, E. Biodistribution and targeting properties of iron oxide nanoparticles for treatments of cancer and iron anemia disease. Nanotoxicology 2019, 13, 573–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Shao, Y.; Li, C. Different types of cell death and their shift in shaping disease. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Gustafsson, A.B. Role of apoptosis in cardiovascular disease. Apoptosis 2009, 14, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromell, K.; Johansson, U.; Abadgar, S.; Bourzeix, P.; Lundholm, L.; Elihn, K. The effect of airborne Palladium nanoparticles on human lung cells, endothelium and blood-A combinatory approach using three in vitro models. Toxicol. Vitr. 2023, 89, 105586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, F.; Liao, F.; Liu, Y.; Feng, S. The size-dependent apoptotic effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on endothelial cells by the intracellular pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, R.; Chaudhry, G.E. Understanding Apoptosis and Apoptotic Pathways Targeted Cancer Therapeutics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, S.W.; Green, D.R. Mitochondrial regulation of cell death. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a008706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yokel, R.A.; Hennig, B.; Toborek, M. Manufactured aluminum oxide nanoparticles decrease expression of tight junction proteins in brain vasculature. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2008, 3, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.A.; Cao, Y.; Yan, Q.; Wang, W.; Feng, S. Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of Commercial Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Induce Ferroptosis in HUVECs. Environ. Toxicol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascon, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, X. Ferroptosis as a novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular disease. Theranostics 2021, 11, 3052–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kong, F.; Wang, T.; Huang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, M.; Wen, T.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, J.; et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles cause surface coating- and core chemistry-dependent endothelial cell ferroptosis. Nanotoxicology 2022, 16, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Xu, G.; Yang, X.; Zou, Z.; Yu, C. Ferritinophagy is involved in the zinc oxide nanoparticles-induced ferroptosis of vascular endothelial cells. Autophagy 2021, 17, 4266–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzino, G.; Irrera, N.; Cucinotta, M.; Pallio, G.; Mannino, F.; Arcoraci, V.; Squadrito, F.; Altavilla, D.; Bitto, A. Oxidative Stress: Harms and Benefits for Human Health. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 8416763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, S.; Seven, E. Assessment of serum catalase, reduced glutathione, and superoxide dismutase activities and malondialdehyde levels in keratoconus patients. Eye 2022, 36, 2062–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, A.B.; Samal, R.R.; Bhol, N.K.; Duttaroy, A.K. Cellular Red-Ox system in health and disease: The latest update. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, P.; Verma, H.K.; Lakkakula, S.; Merchant, N.; Kadir, F.; Rahman, S.; Jeffree, M.S.; Lakkakula, B.; Rao, P.V. Biomarkers of Oxidative Stress Tethered to Cardiovascular Diseases. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 9154295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Li, H.; Chai, S.; Zhang, L.; Fan, T.; Hu, Z.; Feng, Y. The relationship between cardiac oxidative stress, inflammatory cytokine response, cardiac pump function, and prognosis post-myocardial infarction. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 8985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Castiglione, V.; Borrelli, C.; Saccaro, L.F.; Franzini, M.; Masi, S.; Emdin, M.; Giannoni, A. Oxidative stress and inflammation in the evolution of heart failure: From pathophysiology to therapeutic strategies. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2020, 27, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, D.K.; Kortekaas, K.A.; Tsikas, D.; Wijermars, L.G.; van Noorden, C.J.; Suchy, M.T.; Cobbaert, C.M.; Klautz, R.J.; Schaapherder, A.F.; Lindeman, J.H. Oxidative damage in clinical ischemia/reperfusion injury: A reappraisal. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2013, 19, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.C.; Hsiao, I.L.; Lin, H.C.; Wu, C.H.; Chuang, C.Y.; Huang, Y.J. Influence of silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles on in vitro blood-brain barrier permeability. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 47, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.; Park, S.; Choi, I.H. Increased Interleukin-11 and Stress-Related Gene Expression in Human Endothelial and Bronchial Epithelial Cells Exposed to Silver Nanoparticles. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, M.A.; Wahab, R.; Saquib, Q.; Ahmad, J.; Farshori, N.N.; Al-Sheddi, E.S.; Al-Oqail, M.M.; Al-Massarani, S.M.; Al-Khedhairy, A.A. Iron oxide nanoparticles induced cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, cell cycle arrest, and DNA damage in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2023, 80, 127302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Sun, X.; Lin, Y.; Zou, X.; Li, Z.; Liao, Y.; Du, M.; Zhang, H. Endothelial cell injury and dysfunction induced by silver nanoparticles through oxidative stress via IKK/NF-kappaB pathways. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 6657–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholinejad, Z.; Khadem Ansari, M.H.; Rasmi, Y. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce endothelial cell apoptosis via cell membrane oxidative damage and p38, PI3K/Akt, NF-kappaB signaling pathways modulation. J. Trace. Elem. Med. Biol. 2019, 54, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, T.; Garcia, J.G.; Shasby, D.M.; Bhattacharya, J.; Malik, A.B. Mechanisms regulating endothelial cell barrier function. Am. J. Physiol. Lung. Cell Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L419–L422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson-Welsh, L.; Dejana, E.; McDonald, D.M. Permeability of the Endothelial Barrier: Identifying and Reconciling Controversies. Trends Mol. Med. 2021, 27, 314–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Leyte, D.J.; Zepeda-Garcia, O.; Dominguez-Perez, M.; Gonzalez-Garrido, A.; Villarreal-Molina, T.; Jacobo-Albavera, L. Endothelial Dysfunction, Inflammation and Coronary Artery Disease: Potential Biomarkers and Promising Therapeutical Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood-brain barrier: Structure, regulation, and drug delivery. Signal. Transduct. Target Ther. 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Dai, Y.; Hu, C.; Lin, Z.; Wang, S.; Yang, J.; Zeng, L.; Li, S.; Li, W. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the blood-brain barrier dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Fluids Barriers CNS 2024, 21, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Dan, M.; Shao, A.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Yokel, R.A.; Takemura, T.; Hanagata, N.; Niwa, M.; Watanabe, D. Silver nanoparticles induce tight junction disruption and astrocyte neurotoxicity in a rat blood-brain barrier primary triple coculture model. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 6105–6118. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, Y.J.; Liao, P.L.; Tsai, C.H.; Cheng, Y.W.; Lin, F.L.; Ho, J.D.; Chen, C.Y.; Li, C.H. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles impair the inner blood-retinal barrier and retinal electrophysiology through rapid ADAM17 activation and claudin-5 degradation. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, Y.; Xin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, K.; Luo, Y.; Wang, B. Red blood cells in biology and translational medicine: Natural vehicle inspires new biomedical applications. Theranostics 2024, 14, 220–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. Purinergic interplay between erythrocytes and platelets in diabetes-associated vascular dysfunction. Purinergic. Signal. 2021, 17, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, J.R.; Wolberg, A.S. Red blood cells in thrombosis. Blood 2017, 130, 1795–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernow, J.; Mahdi, A.; Yang, J.; Zhou, Z. Red blood cell dysfunction: A new player in cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Vyas, P.; Mann, S.; Paganini-Hill, A.; Nunes, A.C.F.; Lau, W.L.; Cribbs, D.H.; Fisher, M.J.; Sumbria, R.K. Insights Into the Mechanisms of Brain Endothelial Erythrophagocytosis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 672009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlamal, J.; Singh, A.; Weich, K.; Jaffal, H.; Uzun, G.; Pelzl, L.; Althaus, K.; Bakchoul, T. Platelet phosphatidylserine is the critical mediator of thrombosis in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Haematologica 2023, 108, 2690–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Bi, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, T.; Tong, D.; Yang, X.; Zhang, C.; Guo, L.; Wang, C.; Kou, Y.; et al. Phosphatidylserine-exposing blood cells and microparticles induce procoagulant activity in non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 258, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.H.; Baek, S.M.; Choi, S.; Cho, J.; Tahmasebi, S.; Bae, O.N. Promoted coagulant activity and disrupted blood-brain barrier depending on phosphatidylserine externalization of red blood cells exposed to ZnO nanoparticles. Environ. Pollut 2024, 362, 124921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.; Kim, K.; Ngo, T.; Kim, I.; Bae, O.N.; Lim, K.M.; Chung, J.H. Silver nanoparticles promote procoagulant activity of red blood cells: A potential risk of thrombosis in susceptible population. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2019, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, Y.; Chung, H.Y.; Bae, O.N.; Lim, K.M.; Chung, J.H.; Pi, J. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles enhance thrombosis through triggering the phosphatidylserine exposure and procoagulant activation of red blood cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2021, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henein, M.Y.; Vancheri, S.; Longo, G.; Vancheri, F. The Role of Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerogianni, A.; Bal, M.; Mohlin, C.; Woodruff, T.M.; Lambris, J.D.; Mollnes, T.E.; Sjostrom, D.J.; Nilsson, P.H. In vitro evaluation of iron oxide nanoparticle-induced thromboinflammatory response using a combined human whole blood and endothelial cell model. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1101387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.J.; Kim, S.N.; Yoon, C.; Cho, J.W.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, D.W.; Park, J.; Choi, I.; Lee, S.H.; Song, J.; et al. Repeated intratracheal instillation of zinc oxide nanoparticles induced pulmonary damage and a systemic inflammatory response in cynomolgus monkeys. Nanotoxicology 2021, 15, 621–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monse, C.; Hagemeyer, O.; Raulf, M.; Jettkant, B.; van Kampen, V.; Kendzia, B.; Gering, V.; Kappert, G.; Weiss, T.; Ulrich, N.; et al. Concentration-dependent systemic response after inhalation of nano-sized zinc oxide particles in human volunteers. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2018, 15, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajoolabady, A.; Pratico, D.; Lin, L.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Bahijri, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ren, J. Inflammation in atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology and mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.T.; Wang, B.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wang, H.J.; Wang, M.; Ouyang, H.; Chai, Z.F.; Feng, W.Y.; Zhao, Y.L. Endothelial dysfunction and inflammation induced by iron oxide nanoparticle exposure: Risk factors for early atherosclerosis. Toxicol. Lett. 2011, 203, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojova, A.; Guo, B.; Kota, R.S.; Rutledge, J.C.; Kennedy, I.M.; Barakat, A.I. Induction of inflammation in vascular endothelial cells by metal oxide nanoparticles: Effect of particle composition. Environ. Health Perspect 2007, 115, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojova, A.; Lee, J.T.; Jung, H.S.; Guo, B.; Barakat, A.I.; Kennedy, I.M. Effect of cerium oxide nanoparticles on inflammation in vascular endothelial cells. Inhal. Toxicol. 2009, 21 (Suppl. S1), 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, M.I.; Abuzreda, A.A.; Kamel, M.A. Cardiotoxicity and lung toxicity in male rats induced by long-term exposure to iron oxide and silver nanoparticles. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 4329–4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Wen, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Cao, J.; Qi, X.; Shen, S. Ultrasmall iron oxide nanoparticles cause significant toxicity by specifically inducing acute oxidative stress to multiple organs. Part. Fibre. Toxicol. 2022, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avsievich, T.; Popov, A.; Bykov, A.; Meglinski, I. Mutual interaction of red blood cells influenced by nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magaye, R.R.; Yue, X.; Zou, B.; Shi, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, K.; Lin, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, C.; Wu, A.; et al. Acute toxicity of nickel nanoparticles in rats after intravenous injection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhuo, L.; Chen, S.; Zhao, L.; Luan, X.; Wang, H.; Jia, G. Effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the cardiovascular system after oral administration. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 239, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odzak, N.; Kistler, D.; Behra, R.; Sigg, L. Dissolution of metal and metal oxide nanoparticles in aqueous media. Environ. Pollut 2014, 191, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, Z.; Xia, T.; Meng, H.; Low-Kam, C.; Liu, R.; Pokhrel, S.; Lin, S.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.P.; et al. Use of metal oxide nanoparticle band gap to develop a predictive paradigm for oxidative stress and acute pulmonary inflammation. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4349–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehmas, L.C.; Anders, C.; Chess, J.; Punnoose, A.; Pereira, C.B.; Greenwood, J.A.; Tanguay, R.L. Comparative Metal Oxide Nanoparticle Toxicity Using Embryonic Zebrafish. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Vijver, M.G.; Chen, G.; Peijnenburg, W.J. Toxicity and accumulation of Cu and ZnO nanoparticles in Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4657–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanshenas, M.R.; Rezaei, M.R.; Kharkan, J. Comparative toxicity of zinc oxide nanoparticles and zinc salts in male mice: Hematological, biochemical, and histopathological impacts. Toxicol. Rep. 2025, 14, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.C.; Ko, J.W.; Park, S.H.; Lim, J.O.; Shin, I.S.; Moon, C.; Kim, S.H.; Heo, J.D.; Kim, J.C. Comparative toxicity and biodistribution of copper nanoparticles and cupric ions in rats. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2883–2900. [Google Scholar]
- Boudreau, M.D.; Imam, M.S.; Paredes, A.M.; Bryant, M.S.; Cunningham, C.K.; Felton, R.P.; Jones, M.Y.; Davis, K.J.; Olson, G.R. Differential Effects of Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions on Tissue Accumulation, Distribution, and Toxicity in the Sprague Dawley Rat Following Daily Oral Gavage Administration for 13 Weeks. Toxicol. Sci. 2016, 150, 131–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Naqvi, A.H.; Ahmad, M. Comparative study of the cytotoxic and genotoxic potentials of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Toxicol. Rep. 2015, 2, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Alba-Gonzalez, A.; Fernandez-Bertolez, N.; Touzani, A.; Ramos-Pan, L.; Reis, A.T.; Moreda-Pineiro, J.; Yanez, J.; Laffon, B.; Folgueira, M. Effects of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticle Exposure on Human Glial Cells and Zebrafish Embryos. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Song, E.; Song, Y. “Iron free” zinc oxide nanoparticles with ion-leaking properties disrupt intracellular ROS and iron homeostasis to induce ferroptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
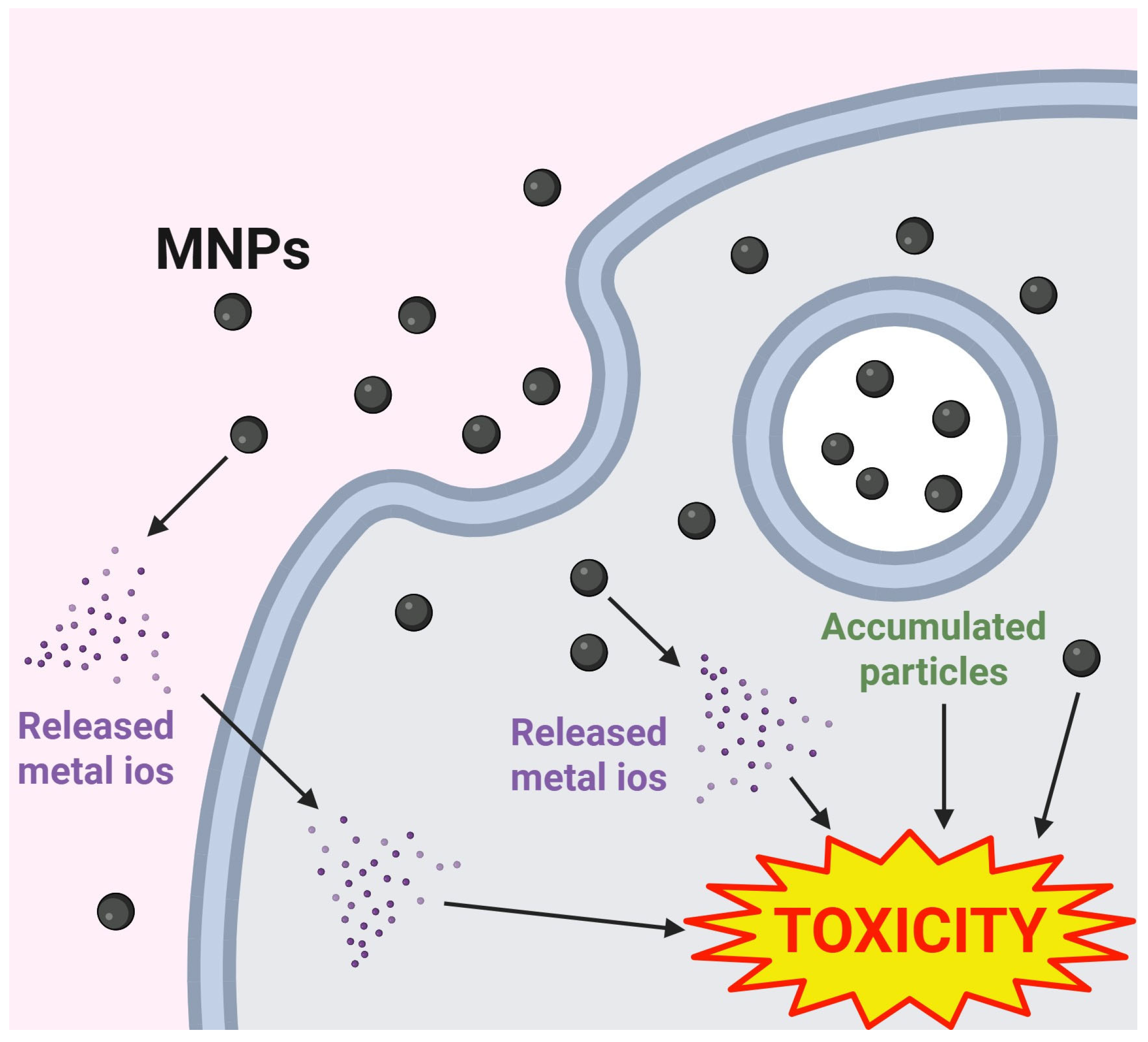
| Category | Metal-Ions | Particles |
|---|---|---|
| Distribution | Rapid distribution into various tissues via circulation | Accumulate in tissues and cells over extended periods |
| Toxicity onset | Rapid onset (e.g., CuCl2 toxicity within 24 h) | Delayed toxicity (e.g., Cu-NPs effects after 48 h) |
| Toxic mechanisms | Mainly due to free metal ions | Primarily caused by the particles per se (e.g., glial cells) |
| Pathological effects | Strong acute toxicity (e.g., AgOAc) | Some show no pathological symptoms (e.g., Ag-NPs) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.-H.; Park, S.; Bae, O.-N. Cardiovascular Toxicity of Metal-Based Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125816
Kim E-H, Park S, Bae O-N. Cardiovascular Toxicity of Metal-Based Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125816
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eun-Hye, Sehyeon Park, and Ok-Nam Bae. 2025. "Cardiovascular Toxicity of Metal-Based Nanoparticles" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125816
APA StyleKim, E.-H., Park, S., & Bae, O.-N. (2025). Cardiovascular Toxicity of Metal-Based Nanoparticles. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5816. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125816






