Rebamipide Attenuates Lupus Nephritis by Enhancing Antioxidative Defense in Podocytes: Evidence from a Lupus-Prone Mouse Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
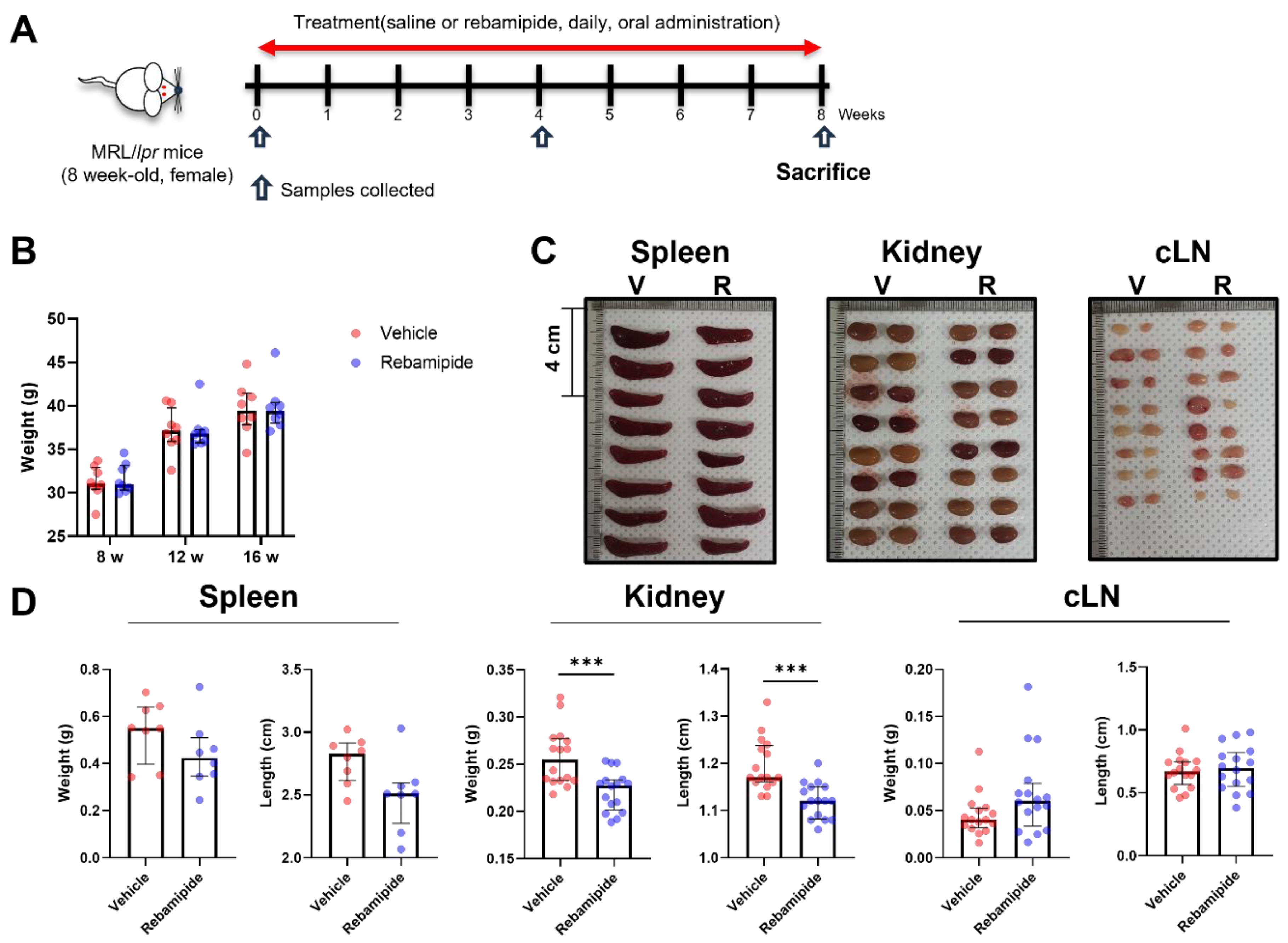
2.1. Effects of In Vivo Rebamipide Treatment on Lupus-like Phenotypes in a Mouse Model
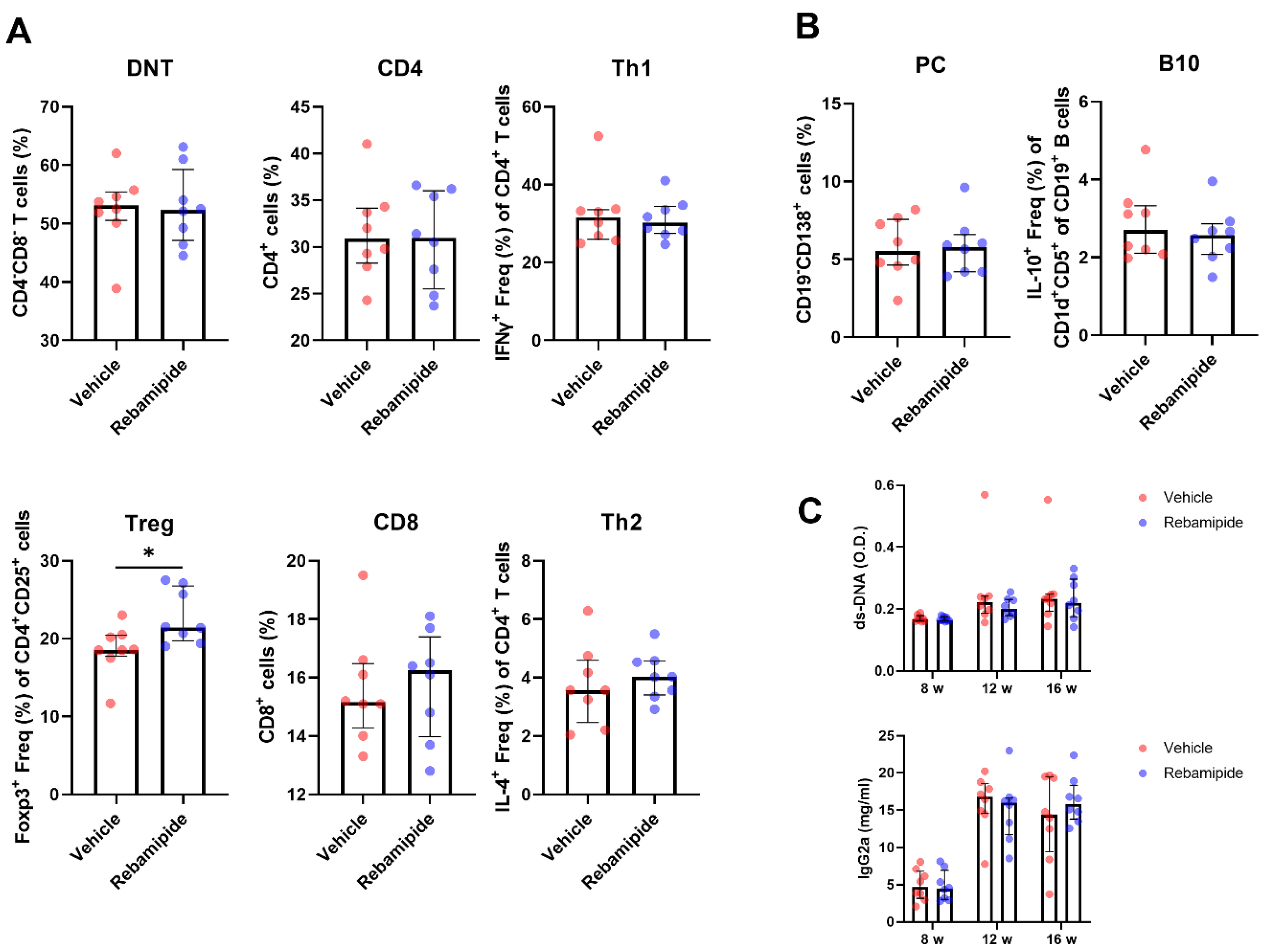
2.2. Effects of In Vivo Rebamipide Treatment on Immune Cell Subsets and Serologic Phenotypes
2.3. Effects of In Vivo Rebamipide Treatment on Renal Manifestations
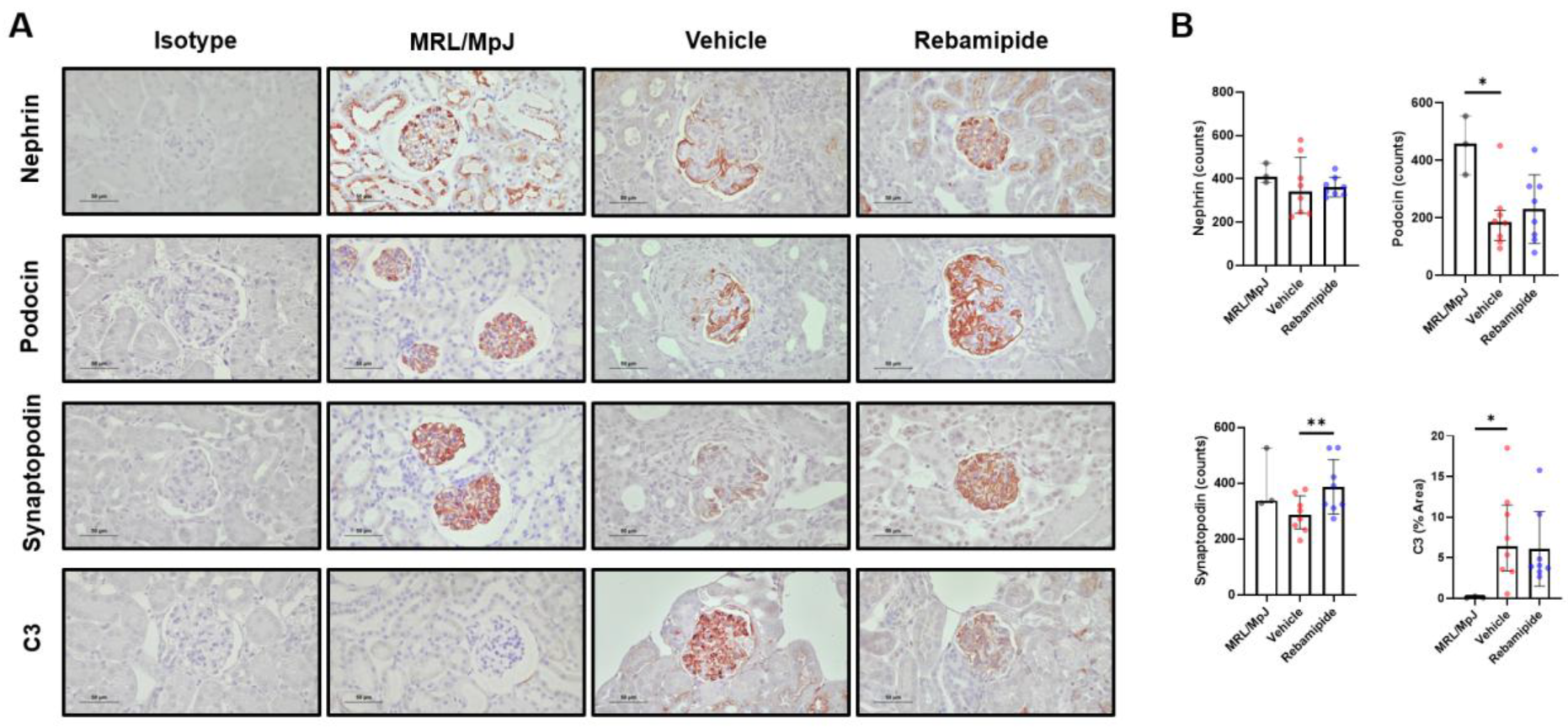
2.4. Expression Levels of Functional Proteins in Podocytes of Lupus-Prone Mice
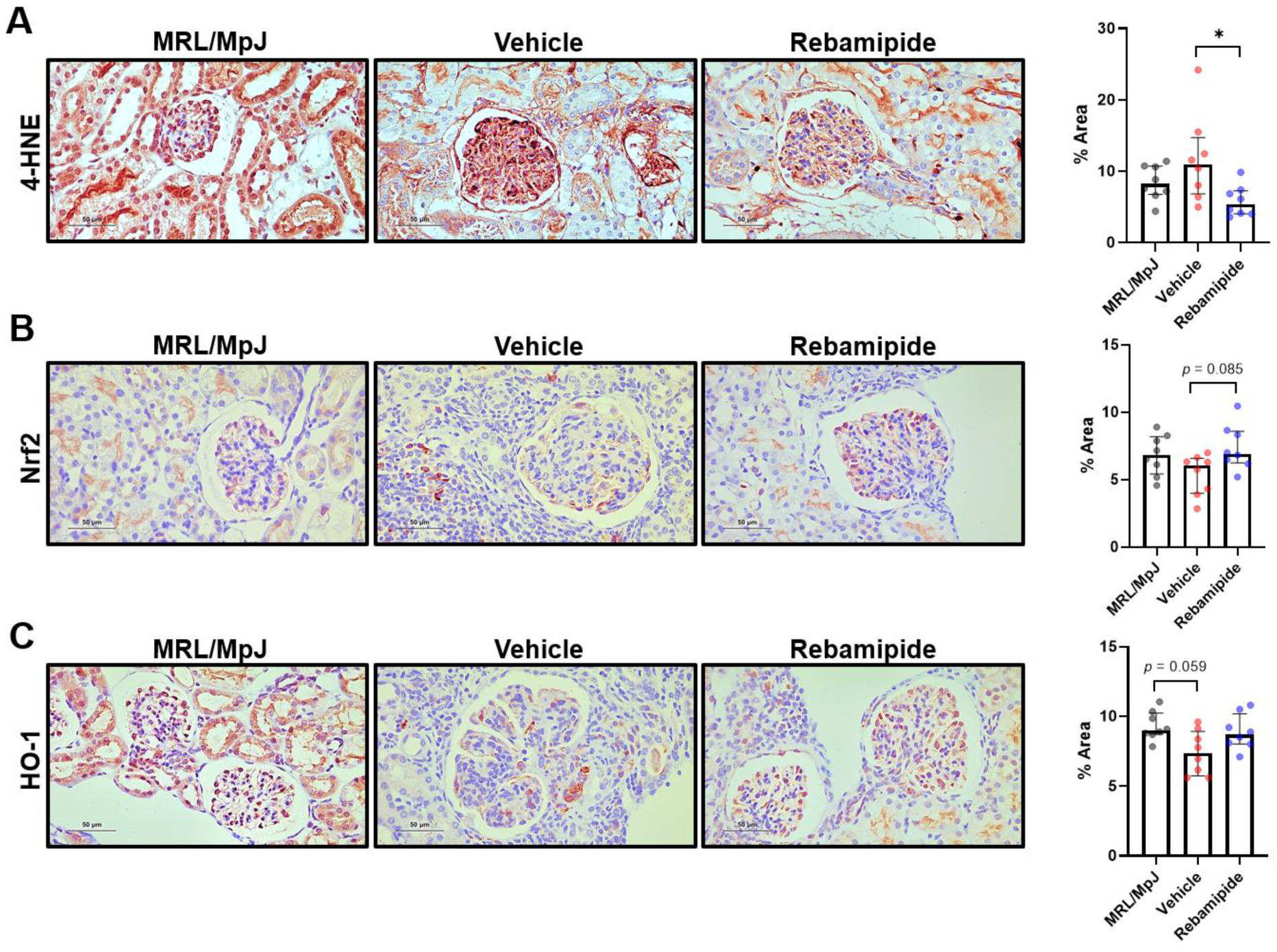
2.5. Expression Levels of Oxidative Stress-Related Factors in Mouse Kidneys
2.6. Effects of In Vitro Rebamipide Treatment on Murine Podocytes and Immune Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Primary Mouse Podocyte Isolation
4.3. Human Podocyte Cell Line Culture and Treatments
4.4. Histologic Assessment of Kidneys
4.5. Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
4.6. Flow Cytometry
4.7. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaul, A.; Gordon, C.; Crow, M.K.; Touma, Z.; Urowitz, M.B.; van Vollenhoven, R.; Ruiz-Irastorza, G.; Hughes, G. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crow, M.K. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: Risks, mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 999–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, C.; Zhang, T.; Putterman, C. Pathogenic cellular and molecular mediators in lupus nephritis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.C.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Saxena, R.; Tanaka, Y. Treatment of lupus nephritis: Consensus, evidence and perspectives. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furie, R.; Rovin, B.H.; Houssiau, F.; Malvar, A.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Contreras, G.; Amoura, Z.; Yu, X.; Mok, C.C.; Santiago, M.B.; et al. Two-Year, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Belimumab in Lupus Nephritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morand, E.F.; Furie, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Bruce, I.N.; Askanase, A.D.; Richez, C.; Bae, S.C.; Brohawn, P.Z.; Pineda, L.; Berglind, A.; et al. Trial of Anifrolumab in Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Teng, Y.K.O.; Ginzler, E.M.; Arriens, C.; Caster, D.J.; Romero-Diaz, J.; Gibson, K.; Kaplan, J.; Lisk, L.; Navarra, S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of voclosporin versus placebo for lupus nephritis (AURORA 1): A double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2070–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhan, X.; Chen, J.; Gao, J.; Gong, Y.; Ren, J.; He, L.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of rebamipide according to Helicobacter pylori status in patients with chronic erosive gastritis: A randomized sucralfate-controlled multicenter trial in China-STARS study. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 2886–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iinuma, S.; Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Takahashi, S.; Takemura, T.; Yoshida, N.; Kondo, M. In vitro studies indicating antioxidative properties of rebamipide. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 35s–39s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohashi, M.; Ishimaru, N.; Arakaki, R.; Hayashi, Y. Effective treatment with oral administration of rebamipide in a mouse model of Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.J.; Park, J.S.; Woo, Y.J.; Lim, M.A.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, E.K.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, W.S.; Park, S.H.; et al. Rebamipide suppresses collagen-induced arthritis through reciprocal regulation of th17/treg cell differentiation and heme oxygenase 1 induction. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, S.J.; Woo, Y.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Park, M.K.; Oh, H.J.; Park, J.S.; Kim, E.K.; Cho, M.L.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; et al. Rebamipide attenuates pain severity and cartilage degeneration in a rat model of osteoarthritis by downregulating oxidative damage and catabolic activity in chondrocytes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2012, 20, 1426–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, T.; Ohno, S.; Hirohata, S.; Miyanaga, Y.; Ujihara, H.; Inaba, G.; Nakamura, S.; Tanaka, S.; Kogure, M.; Mizushima, Y. Efficacy of rebamipide as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of recurrent oral aphthous ulcers in patients with Behçet’s disease: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Drugs R D 2003, 4, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemay, S.; Mao, C.; Singh, A.K. Cytokine gene expression in the MRL/lpr model of lupus nephritis. Kidney Int. 1996, 50, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theofilopoulos, A.N.; Dixon, F.J. Murine models of systemic lupus erythematosus. Adv. Immunol. 1985, 37, 269–390. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Sheng, J.; Han, Y.; Yang, Y.; Pan, H.; Yao, J. CD3(+)CD4(−)CD8(−) (Double-Negative) T Cells in Inflammation, Immune Disorders and Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 816005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poddighe, D.; Dossybayeva, K.; Kozhakhmetov, S.; Rozenson, R.; Assylbekova, M. Double-Negative T (DNT) Cells in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavenstädt, H. Roles of the podocyte in glomerular function. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2000, 278, F173–F179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida-Asanuma, E.; Asanuma, K.; Kim, K.; Donnelly, M.; Young Choi, H.; Hyung Chang, J.; Suetsugu, S.; Tomino, Y.; Takenawa, T.; Faul, C.; et al. Synaptopodin protects against proteinuria by disrupting Cdc42:IRSp53:Mena signaling complexes in kidney podocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, M. Podocyte injury and its consequences. Kidney Int. 2016, 89, 1221–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, X.; Lu, M.; Wu, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Hu, C.; Miao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Hou, F.F.; et al. Wnt/β-catenin links oxidative stress to podocyte injury and proteinuria. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 830–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.H.; Saito, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Sekine, A.; Noguchi, N.; Niki, E. 4-Hydroxynonenal induces adaptive response and enhances PC12 cell tolerance primarily through induction of thioredoxin reductase 1 via activation of Nrf2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 41921–41927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin-Sil, P.; Sun-Hee, H.; SeungCheon, Y.; JeongWon, C.; Kyung-Ah, J.; Mi-La, C.; Sung-Hwan, P. Immune modulation by rebamipide in a mouse model of Sjogren’s syndrome via T and B cell regulation. Immunol. Lett. 2019, 214, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, J.K.; Moon, S.J.; Jhun, J.Y.; Kim, E.K.; Park, J.S.; Youn, J.; Min, J.K.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Cho, M.L. Rebamipide attenuates autoimmune arthritis severity in SKG mice via regulation of B cell and antibody production. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 178, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.T.; Wan, C.; Lin, J.H.; Hammes, H.P.; Zhang, C. Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress and Cell Death in Podocytopathies. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Guo, Q.; Li, X.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Xu, K. Urinary biomarkers associated with podocyte injury in lupus nephritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1324540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Guo, H.; Miao, X.; Xu, J.; Yang, R.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Gao, F.; Zhang, W.; et al. Nestin protects podocyte from injury in lupus nephritis by mitophagy and oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, S.Y.; Najjar, T.A.; Al-Sohaibani, M.O. The effect of rebamipide on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2000, 42, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.C., 3rd; Wyatt, J.E.; Bullins, K.W.; Hanley, A.V.; Hanley, G.A.; Denham, J.W.; Panus, P.C.; Harirforoosh, S. Effects of rebamipide on nephrotoxicity associated with selected NSAIDs in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 720, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmansy, R.A.; Seleem, H.S.; Mahmoud, A.R.; Hassanein, E.H.M.; Ali, F.E.M. Rebamipide potentially mitigates methotrexate-induced nephrotoxicity via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation: A molecular and histochemical study. Anat. Rec. 2021, 304, 647–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaky, H.S.; Abdel-Sattar, S.A.; Allam, A.; Ahmed, H.I. Further insights into the impact of rebamipide on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: Modulation of SIRT1 and β-catenin/cyclin D1 pathways. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2023, 46, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Park, S.H.; Cho, C.S.; Lee, S.T.; Yoo, W.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, Y.M.; Rew, J.S.; Park, Y.W.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Preventive efficacy and safety of rebamipide in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced mucosal toxicity. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su-Jin, M.; Soo Hyun, L.; Byung-Hwa, J.; Jun-Ki, M. Metabolomics Approach to Explore the Effects of Rebamipide on Inflammatory Arthritis Using Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography/Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 24, 192–202. [Google Scholar]
- Kikawada, E.; Lenda, D.M.; Kelley, V.R. IL-12 deficiency in MRL-Fas(lpr) mice delays nephritis and intrarenal IFN-gamma expression, and diminishes systemic pathology. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 3915–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.-S.; Park, Y.; Kim, D.-S.; Jang, S.G.; Kwok, S.-K. Rebamipide Attenuates Lupus Nephritis by Enhancing Antioxidative Defense in Podocytes: Evidence from a Lupus-Prone Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125809
Song Y-S, Park Y, Kim D-S, Jang SG, Kwok S-K. Rebamipide Attenuates Lupus Nephritis by Enhancing Antioxidative Defense in Podocytes: Evidence from a Lupus-Prone Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125809
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Young-Suk, Youngjae Park, Da-Som Kim, Se Gwang Jang, and Seung-Ki Kwok. 2025. "Rebamipide Attenuates Lupus Nephritis by Enhancing Antioxidative Defense in Podocytes: Evidence from a Lupus-Prone Mouse Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125809
APA StyleSong, Y.-S., Park, Y., Kim, D.-S., Jang, S. G., & Kwok, S.-K. (2025). Rebamipide Attenuates Lupus Nephritis by Enhancing Antioxidative Defense in Podocytes: Evidence from a Lupus-Prone Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125809






