Exploring Salivary Biomarkers in Pediatric Obesity: A Scoping Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
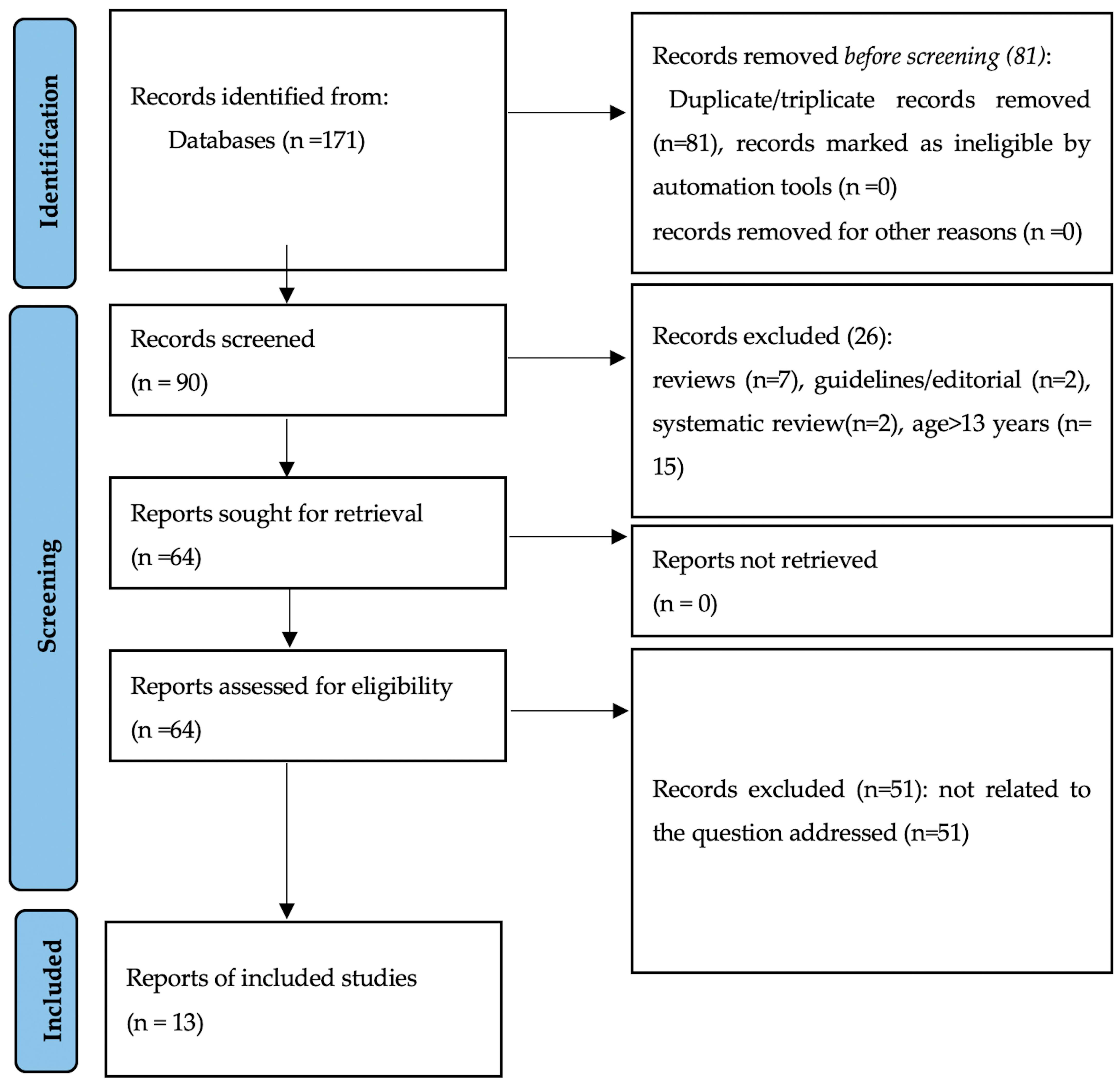
2. Materials and Methods
The Literature Search
3. Results
| First Author | Selection | Comparability | Outcome/Exposure | Design | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Goodson [12] | *** | * | ** | Random selection from a cohort | High quality |
| Hartman [16] | *** | * | ** | Random selection from a cohort | High quality |
| Shi [17] | *** | * | ** | Random selection from a cohort | High quality |
| Alqaderi [13] | ** | * | ** | Subsample of a cohort | Moderate |
| Riis [18] | ** | * | ** | Subsample of a cohort | Moderate |
| Vitale [26] | * | * | ** | Case–control | Low quality |
| Naidoo [22] | * | * | ** | Cross-sectional | Low quality |
| Hartman [25] | * | * | Cross-sectional | Low quality | |
| Starzak [19] | * | * | ** | Cross-sectional | Low quality |
| Tvarijonaviciute [24] | * | * | ** | Cross-sectional | Low quality |
| Selvaraju [20] | * | * | ** | Cross-sectional | Low quality |
| Selvaraju [21] | * | * | ** | Cross-sectional | Low quality |
| Leme [23] | * | * | ** | Cross-sectional | Low quality |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feretzakis, G.; Harokopou, A.; Fafoula, O.; Balaska, A.; Koulountzou, A.; Katoikou, E.; Anastasiou, A.; Zagkavieros, G.; Dalainas, I.; Gkritzelas, G. The Impact of Psychological Health on Childhood Obesity: A Cross-Developmental Stage Analysis. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- World Obesity. Economic Impact of Overweight and Obesity to Surpass $4 Trillion by 2035. Available online: https://www.worldobesity.org/news/economic-impact-of-overweight-and-obesity-to-surpass-4-trillion-by-2035#:~:text=The%20majority%20of%20the%20global,2035%20(from%202020%20levels) (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Johnson, W.; Pereira, S.M.P.; Costa, S.; Baker, J.L.; Norris, T. The associations of maternal and paternal obesity with latent patterns of offspring BMI development between 7 and 17 years of age: Pooled analyses of cohorts born in 1958 and 2001 in the United Kingdom. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 47, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lister, N.B.; Baur, L.A.; Felix, J.F.; Hill, A.J.; Marcus, C.; Reinehr, T.; Summerbell, C.; Wabitsch, M. Child and adolescent obesity. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2023, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shores, D.R.; Everett, A.D. Children as Biomarker Orphans: Progress in the Field of Pediatric Biomarkers. J. Pediatr. 2017, 193, 14–20.e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skevaki, C.; Van den Berg, J.; Jones, N.; Garssen, J.; Vuillermin, P.; Levin, M.; Landay, A.; Renz, H.; Calder, P.C.; Thornton, C.A. Immune biomarkers in the spectrum of childhood noncommunicable diseases. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 137, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.L.; Latimer, M.; Rice, M. Biomarkers of Stress and Inflammation in Children. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2023, 25, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratapwar, M.P.; Sheth, H.J.; Ravi, A.K.; Block, M.L.; Korber, K.A.; Kepsel, A.; Leimanis-Laurens, M.; Comstock, S.S. Use of Biomarkers in Nutrition Intervention Studies of Children: A Scoping Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, F.S.; Michiels, S.; Shyr, Y.; Adjei, A.A.; Oberg, A.L. Biomarker Discovery and Validation: Statistical Considerations. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempini, N.; Leonelli, S. Actionable data for precision oncology: Framing trustworthy evidence for exploratory research and clinical diagnostics. Soc. Sci. Med. 2021, 272, 113760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodson, J.M.; Kantarci, A.; Hartman, M.L.; Denis, G.V.; Stephens, D.; Hasturk, H.; Yaskell, T.; Vargas, J.; Wang, X.; Cugini, M.; et al. Metabolic Disease Risk in Children by Salivary Biomarker Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqaderi, H.; Hegazi, F.; Al-Mulla, F.; Chiu, C.J.; Kantarci, A.; Al-Ozairi, E.; Abu-Farha, M.; Bin-Hasan, S.; Alsumait, A.; Abubaker, J.; et al. Salivary Biomarkers as Predictors of Obesity and Intermediate Hyperglycemia in Adolescents. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 800373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, M.; Roland, S.; Edgar, M.; Thornhill, M. Saliva A review of its role in maintaining oral health and preventing dental disease. BDJ Team 2015, 2, 15123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.A.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Hartman, M.L.; Goodson, J.M.; Shi, P.; Vargas, J.; Yaskell, T.; Stephens, D.; Cugini, M.; Hasturk, H.; Barake, R.; Alsmadi, O.; et al. Unhealthy Phenotype as Indicated by Salivary Biomarkers: Glucose, Insulin, VEGF-A, and IL-12p70 in Obese Kuwaiti Adolescents. J. Obes. 2016, 2016, 6860240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Goodson, J.M. A Data Mining Approach Identified Salivary Biomarkers That Discriminate between Two Obesity Measures. J. Obes. 2019, 2019, 9570218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riis, J.L.; Dent, A.L.; Silke, O.; Granger, D.A. Salivary uric acid across child development and associations with weight, height, and body mass index. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1235143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starzak, D.; Konkol, K.; McKune, A. Effects of Cardiorespiratory Fitness and Obesity on Salivary Secretory IgA and Alpha-Amylase in South African Children. Children 2016, 3, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, V.; Babu, J.R.; Geetha, T. Association of salivary C-reactive protein with the obesity measures and markers in children. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 1239–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, V.; Babu, J.R.; Geetha, T. Multiplexed measurements of salivary fetuin-A, insulin, and adiponectin as potential non-invasive biomarkers in childhood obesity. Cytokine 2022, 153, 155843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, T.; Konkol, K.; Biccard, B.; Dubose, K.; McKune, A. Elevated salivary C-reactive protein predicted by low cardio-respiratory fitness and being overweight in African children: Cardiovascular topic. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2012, 23, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leme, L.A.F.P.; Santos, I.B.; Rizzardi, K.F.; Parisotto, T.M. Exploring the Relationship between Salivary Levels of TNF-α, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus gasseri, Obesity, and Caries in Early Childhood. Pathogens 2022, 11, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tvarijonaviciute, A.; Martinez-Lozano, N.; Rios, R.; de Teruel, M.C.M.; Garaulet, M.; Cerón, J.J. Saliva as a non-invasive tool for assessment of metabolic and inflammatory biomarkers in children. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2471–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartman, M.L.; Groppo, F.; Ohnishi, M.; Goodson, J.M.; Hasturk, H.; Tavares, M.; Yaskell, T.; Floros, C.; Behbehani, K.; Razzaque, M.S. Can Salivary Phosphate Levels Be an Early Biomarker to Monitor the Evolvement of Obesity. Contrib. Nephrol. 2013, 180, 138–148. [Google Scholar]
- Vitale, E.; Magrone, T.; Jirillo, E. Correlations between the Youth Healthy Eating Index, Body Mass Index and the Salivary Nitric Oxide Concentration in Overweight/Obese Children. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord.—Drug Targets 2014, 14, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What Are Biomarkers? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 463–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pletcher, M.J.; Pignone, M. Evaluating the Clinical Utility of a Biomarker. Circulation 2011, 123, 1116–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouellet-Morin, I.; Williams, B.; Arseneault, L.; Danese, A. Validation of a high-sensitivity assay for C-reactive protein in human saliva. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil, A.R.; Norton, R.C.; Rossetti, M.B.; Leão, E.; Mendes, R.P. C-reactive protein as an indicator of low intensity inflammation in children and adolescents with and without obesity. J. Pediatr. 2007, 83, 477–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.S.; Galuska, D.A.; Gillespie, C.; Will, J.C.; Giles, W.H.; Dietz, W.H. C-reactive protein and body mass index in children: Findings from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. J. Pediatr. 2001, 138, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frithioff-Bøjsøe, C.; Lund, M.A.V.; Lausten-Thomsen, U.; Hedley, P.L.; Pedersen, O.; Christiansen, M.; Baker, J.L.; Hansen, T.; Holm, J. Leptin, adiponectin, and their ratio as markers of insulin resistance and cardiometabolic risk in childhood obesity. Pediatr. Diabetes 2019, 21, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Després, J.P.; Lemieux, I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006, 444, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupérez, F.J.; Chamoso-Sánchez, D.; Barbas, C.; Argente, J.; Martos-Moreno, G.Á. Insulin Resistance in Obese Children: What Can Metabolomics and Adipokine Modelling Contribute? Nutrients 2020, 12, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrou, I.; Tsigos, C. Stress hormones: Physiological stress and regulation of metabolism. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.; Nater, U.M. Salivary Alpha-Amylase as a Biomarker of Stress in Behavioral Medicine. Int. J. Behav. Med. 2020, 27, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jin, L.; Chen, T. The Effects of Secretory IgA in the Mucosal Immune System. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 2032057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanavari, T.; Giannogonas, P.; Karalis, K.P. TNF-alpha and obesity. Curr. Dir. Autoimmun. 2010, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, K.T.; Wiesbrock, S.M.; Marino, M.W.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature 1997, 389, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffles, L.F.; Abreu, L.G.; Silva, T.A.; Pordeus, I.A.; Hermont, A.P. Association between obesity and adipokines levels in saliva and gingival crevicular fluid: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Evidence-Based Med. 2019, 12, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, K.; Baffy, N.; Falus, A.; Fulop, A.K. The major inflammatory mediator interleukin-6 and obesity. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, D.A.; Shapiro, R.A.; Nussler, A.K.; Nguyen, D.; Simmons, R.L.; Di Silvio, M.; Freeswick, P.D.; Wang, S.C.; Billiar, T.R. Differential Induction of Nitric Oxide Synthase in Hepatocytes During Endotoxemia and the Acute-Phase Response. Arch. Surg. 1994, 129, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voest, E.E.; Kenyon, B.M.; Truitt, G.; Folkman, J.; O’Reilly, M.S.; D’Amato, R.J. Inhibition of Angiogenesis In Vivo by Interleukin 12. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1995, 87, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeben, A.; Landuyt, B.; Highley, M.S.; Wildiers, H.; Van Oosterom, A.T.; De Bruijn, E.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiogenesis. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 549–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bays, H.E.; Taub, P.R.; Epstein, E.; Michos, E.D.; Ferraro, R.A.; Bailey, A.L.; Kelli, H.M.; Ferdinand, K.C.; Echols, M.R.; Weintraub, H.; et al. Ten things to know about ten cardiovascular disease risk factors. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2021, 5, 100149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Momen Maragheh, S.; Aghazadeh, A.; Mehrjuyan, S.R.; Hussen, B.M.; Abdoli Shadbad, M.; Dastmalchi, N.; Safaralizadeh, R. Interleukin-1 in Obesity-Related Low-Grade Inflammation: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 96, 107765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1): An Overview. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askin, L.; Abus, S.; Tanriverdi, O. Resistin and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review of the Current Literature Regarding Clinical and Pathological Relationships. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2022, 18, e290721195114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Cristo Rodríguez Pérez, M.; González, D.A.; Rodríguez, I.M.; Coello, S.D.; Fernández, F.J.C.; Díaz, B.B.; de León, A.C. Resistin as a risk factor for all-cause (and cardiovascular) death in the general population. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, K.; Miller, Y.I.; Hedrick, C.C. Monocyte and Macrophage Dynamics During Atherogenesis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1506–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trepanowski, J.F.; Mey, J.; Varady, K.A. Fetuin-A: A novel link between obesity and related complications. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 39, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.A.S.; Brenzikofer, R.; Macedo, D.V. Reference intervals for saliva analytes collected by a standardized method in a physically active population. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 1440–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riis, J.L.; Bryce, C.I.; Matin, M.J.; Stebbins, J.L.; Kornienko, O.; van Huisstede, L.; Granger, D.A. The Validity, Stability, and Utility of Measuring Uric Acid in Saliva. Biomarkers Med. 2018, 12, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; He, Q.; Yang, J.; Jia, L.; Xu, G. Relationship between gout, hyperuricemia, and obesity—Does central obesity play a significant role?—A study based on the NHANES database. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2024, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Ridi, R.; Tallima, H. Physiological functions and pathogenic potential of uric acid: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Obesity–NCD Risk Factor Collaboration Estimates Ranking (% Obesity by Country), Children. Available online: https://data.worldobesity.org/tables/ranking-obesity-by-country-children-4.pdf? (accessed on 8 June 2025).
- Constantin, V.; Luchian, I.; Goriuc, A.; Budala, D.G.; Bida, F.C.; Cojocaru, C.; Butnaru, O.M.; Virvescu, D.I. Salivary Biomarkers Identification: Advances in Standard and Emerging Technologies. Oral 2025, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
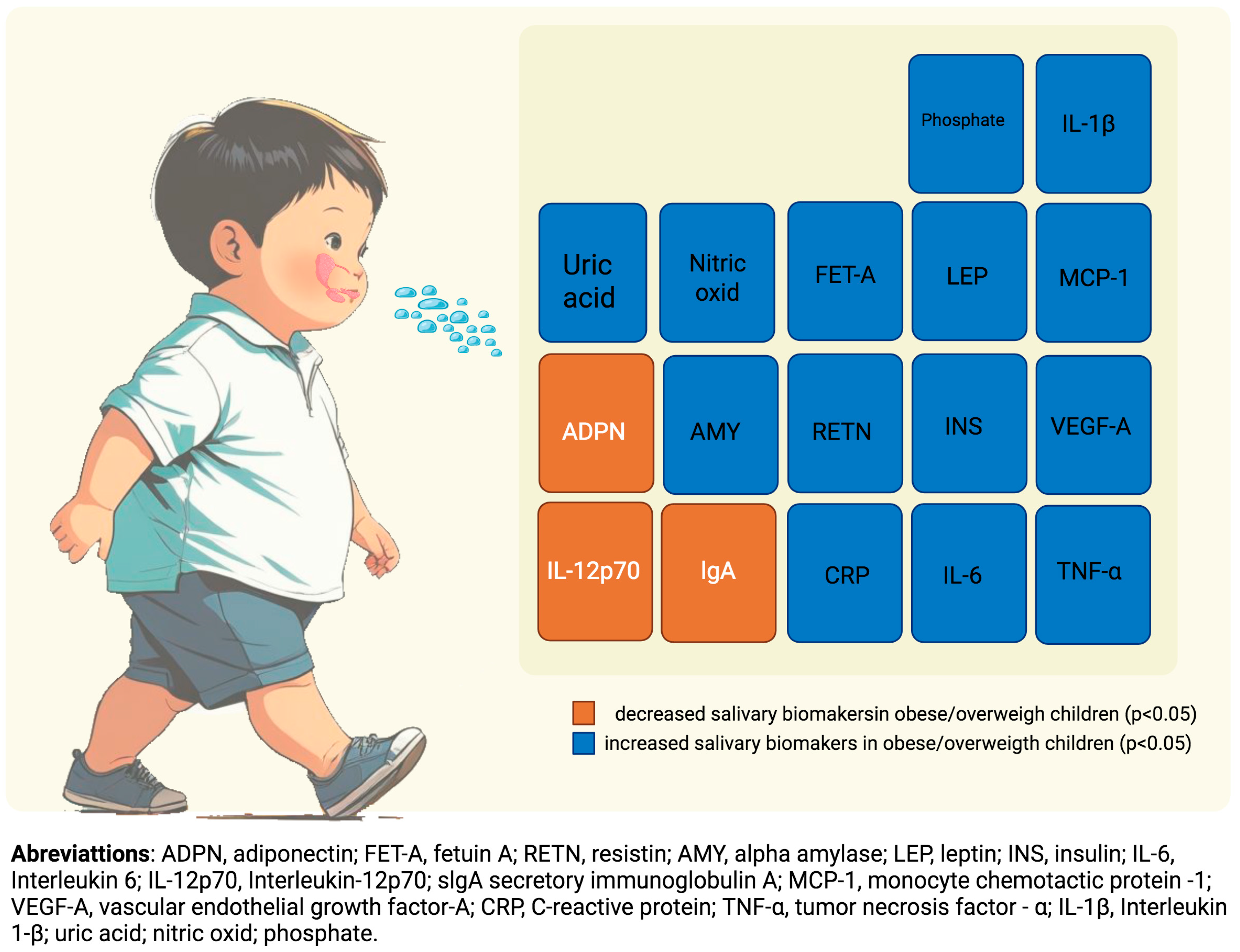
| First Author/Year | Country | Subjects | Age (Years) | Saliva Analysis | Analyzed Markers | Statistically Significant Association Between Salivary Markers in Eutrophic Children and: | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obesity | Overweight | Obesity/Overweight | ||||||
| Naidoo 2012 [22] | Africa | 170 | 9.41 ± 1.55 | ELISA | CRP | ↑ CRP [6.77(0.92) × 7.31(0.93) p < 0.05] a | ||
| Hartman 2013 [25] | USA | 77 | 10.5 ± 1.8 | Chromatography/mass spectrometry | Phosphate | ↑ Phosphate [≈0.9(0.35–1.2) × 1.25(0.45–2.2) p < 0.05] b | ||
| Goodson 2014 [12] | USA Kuwait | 53 + 744 | 10–12 | Luminex System | insulin, IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-1β, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, TNF-α, VEGF-A, ghrelin, leptin, MMP-9, adiponectin, CRP, resistin | ↑ CRP [73.01(153.75)/77.15(186.95) × 429.44(668.52)/443.13(1033.29) p < 0.0001] c ↑ Insulin [39.39(45.38)/44.70(54.38) × 112.98(125.09)/143.50(150.24) p < 0.0001] c ↑ Leptin [1.06(4.77)/0.63(4.61) × 3.16(6.40)/3.70(6.41) p < 0.0001] c ↓ Adiponectin [4220(5303)/3994(5052) × 2548(2779)/3062(3752) p < 0.0001] c | ↑ CRP [73.01(153.75)/77.15(186.95) × 177.46(311.93)/281.39(516.54) p < 0.0001] c ↑ Insulin [39.39(45.38)/44.70(54.38) × 80.39(88.74)/76.25(87.13) p < 0.0001] c ↓ Adiponectin [4220(5303)/3994(5052)x 2402(3785)/3322(3693) p = 0.0001] c | |
| Vitale 2014 [26] | Italy | 45 | 9.4 ± 0.6 | ELISA | Nitric Oxide | ↑ Nitric Oxide [≈226 × 283] p < 0.0001] d | ||
| Starzak 2016 [19] | Africa | 132 | 10.05 ± 1.68 | ELISA | Alpha amylase, IgA | ↑ Alpha amylase [79.83(43.12)/62.13(36.06) × 122.75(46.50) p < 0.001] e ↓ IgA [243.95(119.23) × 158.34(56.03) p < 0.001] e | ↓ IgA [B = −45.737(10.09) p < 0.0001] e | |
| Hartman 2016 [16] | Kuwait | 744 | 10 ± 0.7 | Luminex System | insulin, IFN-γ, IL-10, IL-12p70, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-1β, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, TNF-α, VEGF-A, ghrelin, leptin, MMP-9, adiponectin, CRP, resistin | ↑ VEGF-A [0.10(0.04) p < 0.01] f ↑ Insulin [0.15(0.04) p < 0.0001] f ↓ IL-12p70 [−0.14(0.05) p < 0.0001] f | ↑ Insulin [0.25(0.11) p < 0.02] f | |
| Tvarijonaviciute 2019 [24] | Spain | 129 | 8–12 | Luminex System | Glucose, triglycerides, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, insulin, leptin, MCP-1, NGF, HGF, TNF-α, CRP | ↑ Insulin [6.41(3.8–19) × 17(5.94–62) p = 0.003] g ↑ CRP [2.04(0.51–7.01) × 5.79(2.37–12) p ≤ 0.001] g ↑IL-1β [6.52(2.33–23) × 17(8.32–36) p ≤ 0.028] g | ||
| Shi 2019 [17] | Kuwait | 744 | 10 ± 0.67 | Luminex System | insulin, C-reactive protein (CRP), adiponectin, leptin, IL-1β, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12P70, IL-13, IL-17A, resistin, MMP-9, MPO, MCP-1, TNF-α, VEGF-A, IFN-C, ghrelin, IL-17A, IFN-γ | ↑ CRP ↑ Insulin ↓ Adiponectin [AUC 0.820 (0.782–0.862)] h | ||
| Selvaraju 2019 [20] | USA | 76 | 6–10 | Luminex System | CRP, resistin, MCP-1, TNF-α, IL-6, complement factor D, IL-10 | ↑ CRP [AUC 0.866(0.780–0.952) p = 0.0001] h ↑ IL-6 [AUC 0.673(0.554–0.801) p = 0.01] h ↑ MCP-1 [AUC 0.715(0.554–0.801) p = 0.002] h ↑ Resistin [AUC 0.731(0.606–0.855) p = 0.001] h ↑ TNF-α [AUC 0.694(0.564–0.825) p = 0.005] h | ||
| Selvaraju 2022 [21] | USA | 76 | 6–10 | Luminex System | Fetuin A, insulin, adiponectin | ↑ Fetuin A [≈50 × 400 p < 0.01] i ↑ Insulin [≈100 × 400 p < 0.001] i ↓ Adiponectin [≈25 × 8 p < 0.003] i | ↑ Fetuin A [≈50 × 407 p < 0.004] i | |
| Leme 2022 [23] | Brazil | 94 | 4–5 | Luminex System | TNF-α | ↑ TNF-α [1.13(1.09–1.61) p < 0.001] j | ||
| Alqaderi 2022 [13] | Kuwait | 353 | 10–17 | Luminex System | Insulin, CRP, adiponectin, leptin, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, MCP-1, VEGF | ↑ CRP [4.53(2.4–8.50) p ≤ 0.001] k ↑ Insulin [3.29(1.82–5.97) p ≤ 0.001] k ↓ Adiponectin [0.54(0.3–0.9) p ≤ 0.044] k | ||
| Riis 2023 [18] | USA | 217 | 0–12 | Colorimetric enzymatic assay | Uric acid | ↑ Uric acid [0.13/0.17 p ≤ 0.01/p < 0.0001] l | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sabella, F.M.; Katzenelson, R.T.; de Carvalho, F.G.; Duque, C.; Darrieux, M.; Marson, F.A.L.; Parisotto, T.M. Exploring Salivary Biomarkers in Pediatric Obesity: A Scoping Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125789
Sabella FM, Katzenelson RT, de Carvalho FG, Duque C, Darrieux M, Marson FAL, Parisotto TM. Exploring Salivary Biomarkers in Pediatric Obesity: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125789
Chicago/Turabian StyleSabella, Fernanda Maria, Renata Thomaz Katzenelson, Fabíola Galbiatti de Carvalho, Cristiane Duque, Michelle Darrieux, Fernando Augusto Lima Marson, and Thaís Manzano Parisotto. 2025. "Exploring Salivary Biomarkers in Pediatric Obesity: A Scoping Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125789
APA StyleSabella, F. M., Katzenelson, R. T., de Carvalho, F. G., Duque, C., Darrieux, M., Marson, F. A. L., & Parisotto, T. M. (2025). Exploring Salivary Biomarkers in Pediatric Obesity: A Scoping Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5789. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125789






