The Rab18/Ras/ERK/FosB/MMP3 Signaling Pathway Mediates Cell Migration Regulation by 2′3′-cGAMP
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
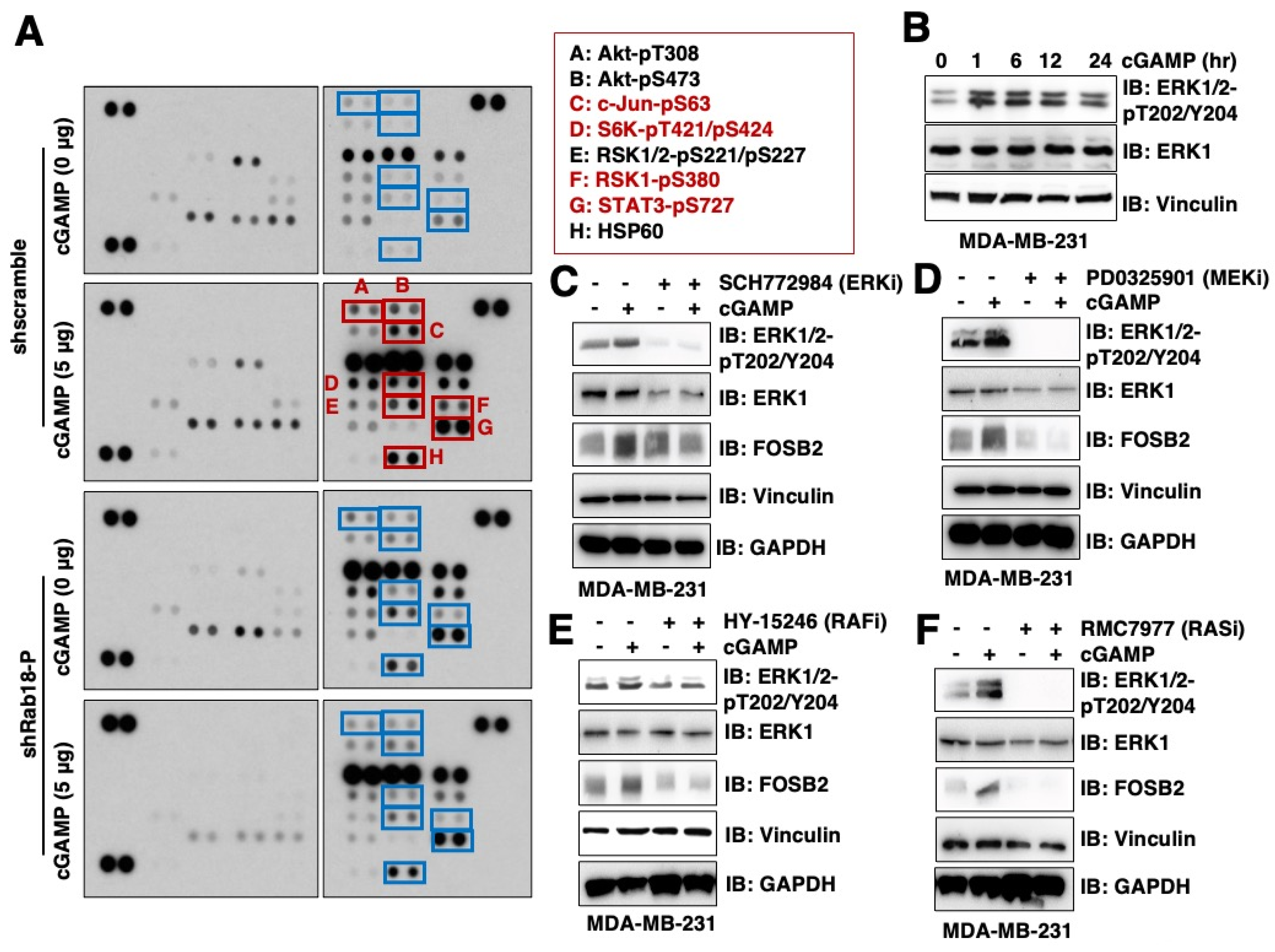
2.1. Phospho-Profiling Reveals That 2′3′-cGAMP Induces ERK Activation in a Rab18-Dependent Manner
2.2. 2′3′-cGAMP/Rab18-Induced ERK Activation Is Dependent on the RAS/RAF/MEK Pathway
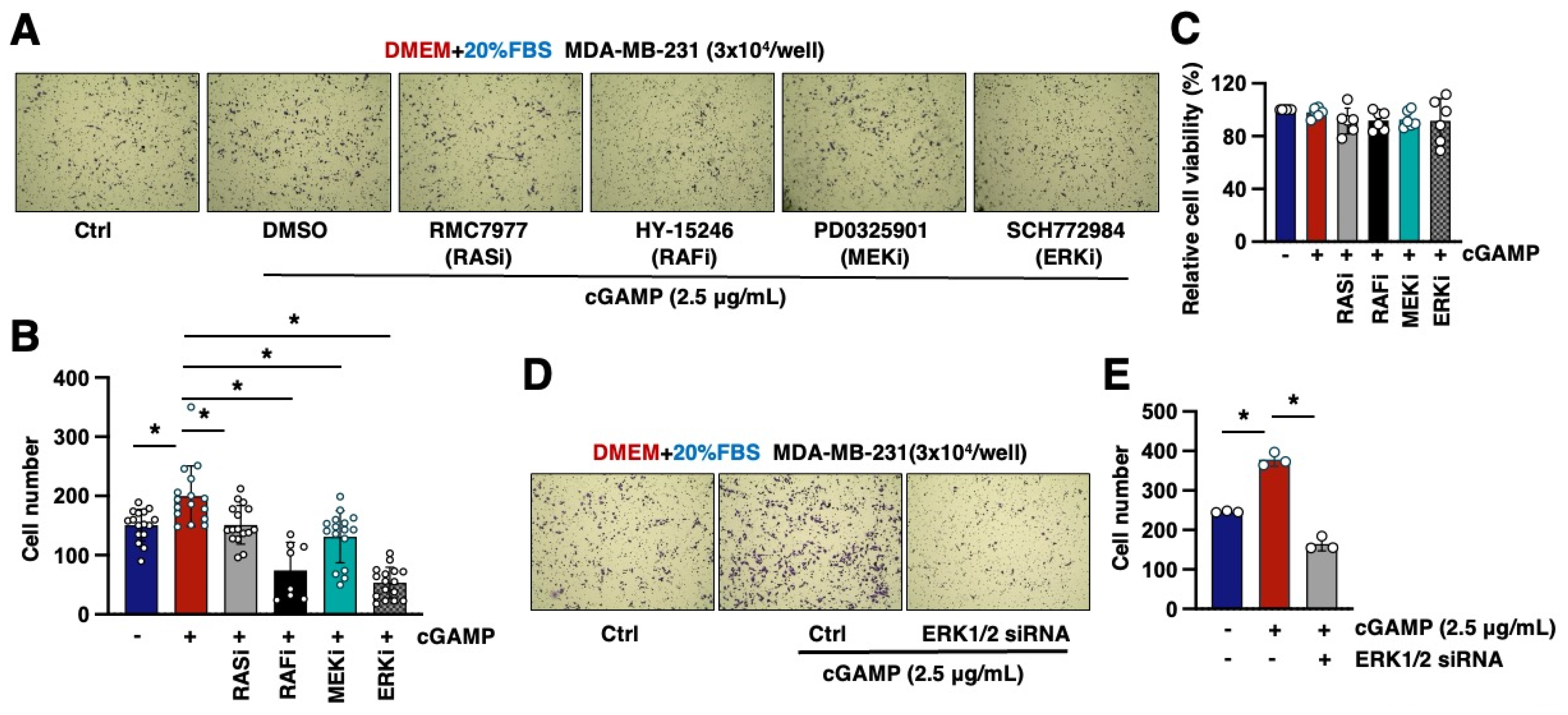
2.3. The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK Pathway Mediates 2′3′-cGAMP-Induced Cell Migration
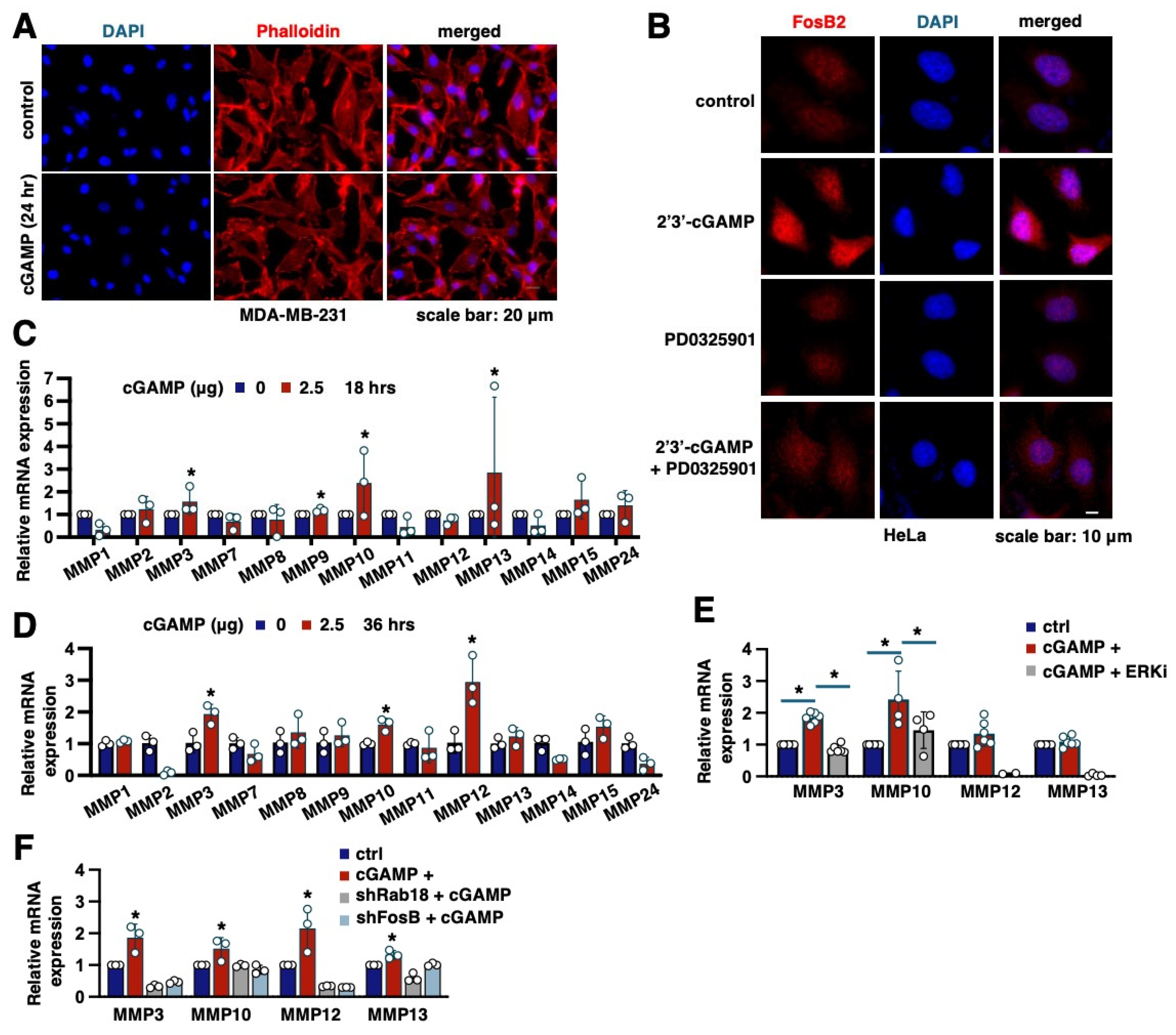
2.4. MMPs Are Key Transcriptional Targets of FosB2 That Mediate Cell Migration Induced by 2′3′-cGAMP
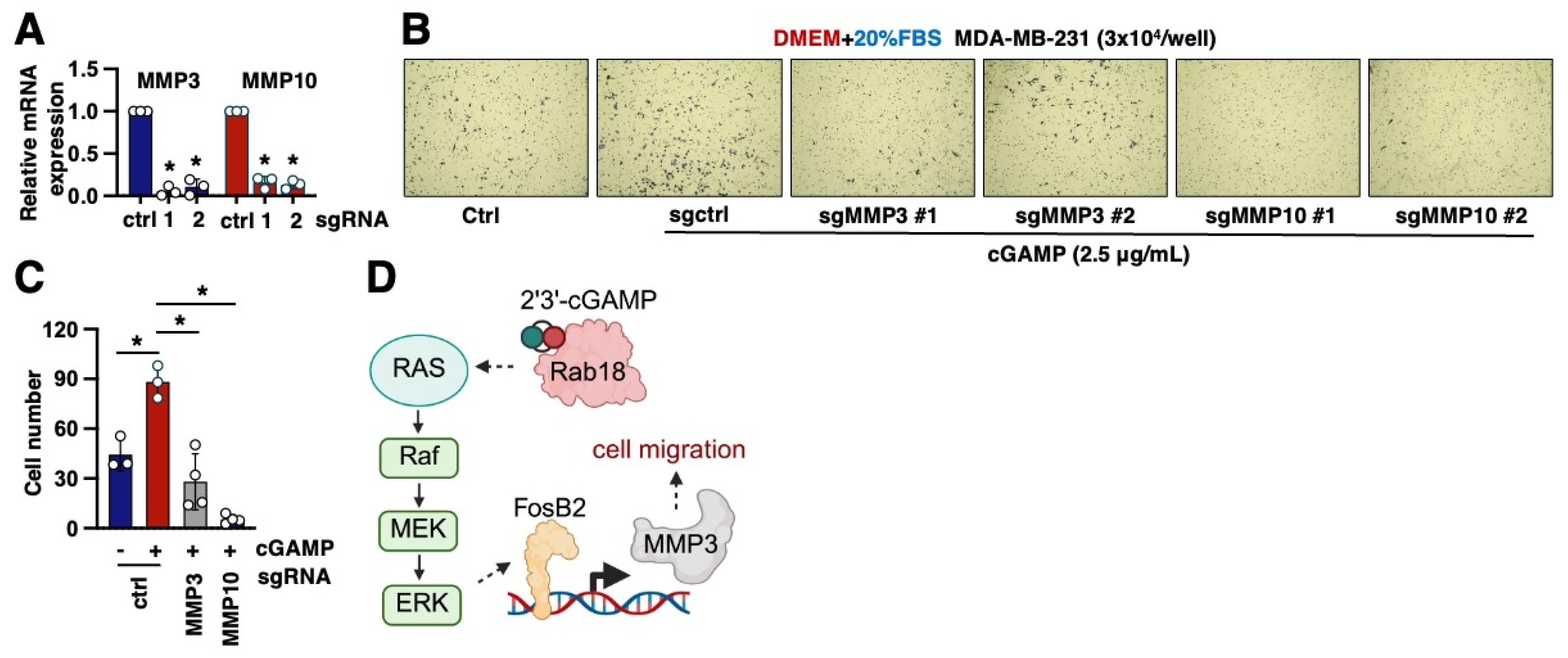
2.5. MMP3 Is a Key Downstream Effector to Mediate 2′3′-cGAMP-Induced Cell Migration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Transfection
4.2. Reagents
4.3. Antibodies
4.4. Primers
4.5. siRNA, shRNAs and sgRNAs
4.6. RT-PCR Quantifications
4.7. Transwell Assays
4.8. Immunoblot Analyses
4.9. Immunofluorescence Assays
4.10. MTT Cell Viability Assay
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| FosB2 | FosB proto-oncogene |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| RAS | rat sarcoma virus |
| RAF | RAF protein-serine/threonine kinase |
| MEK | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| ICB | immune checkpoint blockade |
| STING | stimulator of interferon genes |
| cGAS | cyclic GAMP synthase |
References
- Zhang, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP containing mixed phosphodiester linkages is an endogenous high-affinity ligand for STING. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrales, L.; McWhirter, S.M.; Dubensky, T.W., Jr.; Gajewski, T.F. The host STING pathway at the interface of cancer and immunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2404–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, G.N. STING: Infection, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltbaek, J.H.; Cambier, S.; Snyder, J.M.; Stetson, D.B. ABCC1 transporter exports the immunostimulatory cyclic dinucleotide cGAMP. Immunity 2022, 55, 1799–1812.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Chen, X.; Planells-Cases, R.; Chu, J.; Wang, L.; Cao, L.; Li, Z.; Lopez-Cayuqueo, K.I.; Xie, Y.; Ye, S.; et al. Transfer of cGAMP into Bystander Cells via LRRC8 Volume-Regulated Anion Channels Augments STING-Mediated Interferon Responses and Anti-viral Immunity. Immunity 2020, 52, 767–781.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahey, L.J.; Mardjuki, R.E.; Wen, X.; Hess, G.T.; Ritchie, C.; Carozza, J.A.; Bohnert, V.; Maduke, M.; Bassik, M.C.; Li, L. LRRC8A:C/E Heteromeric Channels Are Ubiquitous Transporters of cGAMP. Mol. Cell 2020, 80, 578–591.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordova, A.F.; Ritchie, C.; Bohnert, V.; Li, L. Human SLC46A2 Is the Dominant cGAMP Importer in Extracellular cGAMP-Sensing Macrophages and Monocytes. ACS Cent. Sci. 2021, 7, 1073–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, C.; Cordova, A.F.; Hess, G.T.; Bassik, M.C.; Li, L. SLC19A1 Is an Importer of the Immunotransmitter cGAMP. Mol. Cell 2019, 75, 372–381.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luteijn, R.D.; Zaver, S.A.; Gowen, B.G.; Wyman, S.K.; Garelis, N.E.; Onia, L.; McWhirter, S.M.; Katibah, G.E.; Corn, J.E.; Woodward, J.J.; et al. SLC19A1 transports immunoreactive cyclic dinucleotides. Nature 2019, 573, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepin, G.; De Nardo, D.; Rootes, C.L.; Ullah, T.R.; Al-Asmari, S.S.; Balka, K.R.; Li, H.M.; Quinn, K.M.; Moghaddas, F.; Chappaz, S.; et al. Connexin-Dependent Transfer of cGAMP to Phagocytes Modulates Antiviral Responses. mBio 2020, 11, 10-1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Guan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.; Yin, C.; Sun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, H. A photoaffinity labeling strategy identified EF1A1 as a binding protein of cyclic dinucleotide 2′3′-cGAMP. Cell Chem. Biol. 2022, 29, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Hahn, Q.; Yu, L.; Zhu, Z.; Boyer, J.A.; Wang, J.; Kong, D.; Carey, L.M.; Hepperla, A.J.; Simon, J.M.; et al. 2′3′-cGAMP interactome identifies 2′3′-cGAMP/Rab18/FosB signaling in cell migration control independent of innate immunity. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eado7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelinek, T.; Dent, P.; Sturgill, T.W.; Weber, M.J. Ras-induced activation of Raf-1 is dependent on tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.H.; Guan, K.L. Activation of B-Raf kinase requires phosphorylation of the conserved residues Thr598 and Ser601. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 5429–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Jiang, X.; Li, B.; Yang, H.J.; Miller, M.; Yang, A.; Dhar, A.; Pavletich, N.P. Mechanisms of mTORC1 activation by RHEB and inhibition by PRAS40. Nature 2017, 552, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancak, Y.; Bar-Peled, L.; Zoncu, R.; Markhard, A.L.; Nada, S.; Sabatini, D.M. Ragulator-Rag complex targets mTORC1 to the lysosomal surface and is necessary for its activation by amino acids. Cell 2010, 141, 290–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waudby, C.A.; Alvarez-Teijeiro, S.; Josue Ruiz, E.; Suppinger, S.; Pinotsis, N.; Brown, P.R.; Behrens, A.; Christodoulou, J.; Mylona, A. An intrinsic temporal order of c-JUN N-terminal phosphorylation regulates its activity by orchestrating co-factor recruitment. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.A.; Fu, J.; Romanelli, A.; Shimamura, A.; Blenis, J. Ribosomal S6 kinase 1 (RSK1) activation requires signals dependent on and independent of the MAP kinase ERK. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Uchida, E.; Grammer, T.C.; Blenis, J. STAT3 serine phosphorylation by ERK-dependent and -independent pathways negatively modulates its tyrosine phosphorylation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 6508–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Liu, Z.; Zandi, E. AP-1 function and regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renaud, S.J.; Kubota, K.; Rumi, M.A.; Soares, M.J. The FOS transcription factor family differentially controls trophoblast migration and invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 5025–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wobma, H.; Shin, D.S.; Chou, J.; Dedeoglu, F. Dysregulation of the cGAS-STING Pathway in Monogenic Autoinflammation and Lupus. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 905109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Li, T.; Li, X.D.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.Z.; Wight-Carter, M.; Chen, Z.J. Activation of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase by self-DNA causes autoimmune diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5699–E5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falahat, R.; Berglund, A.; Putney, R.M.; Perez-Villarroel, P.; Aoyama, S.; Pilon-Thomas, S.; Barber, G.N.; Mule, J.J. Epigenetic reprogramming of tumor cell-intrinsic STING function sculpts antigenicity and T cell recognition of melanoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2013598118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, P. cGAS/STING signalling pathway in senescence and oncogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2024, 106–107, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.M.; Zhao, D.C.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.N.; Du, T.; Zhou, L.; Chen, Y.H.; Yu, Q.C.; Chen, Q.S.; et al. Inactivated cGAS-STING Signaling Facilitates Endocrine Resistance by Forming a Positive Feedback Loop with AKT Kinase in ER+HER2- Breast Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2403592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hu, S.; Chen, X.; Shi, H.; Chen, C.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. cGAS is essential for the antitumor effect of immune checkpoint blockade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1637–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, W.; Jiang, H.; Meng, X.; Tang, D.; Liu, D. Clinical applications of STING agonists in cancer immunotherapy: Current progress and future prospects. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1485546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, Z.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, G.; Dai, R.Z.; Ni, N.; Tao, J.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, Q.L.; et al. Rab2A-mediated Golgi-lipid droplet interactions support very-low-density lipoprotein secretion in hepatocytes. EMBO J. 2024, 43, 6383–6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, X.; Qiu, X.; Ouyang, J.; Dai, J.; Min, S. Matrix Metalloproteinase 3: A Promoting and Destabilizing Factor in the Pathogenesis of Disease and Cell Differentiation. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 663978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Santos, C.; Davis, I.J.; Earp, H.S.; Liu, P. Co-targeting JAK1/STAT6/GAS6/TAM signaling improves chemotherapy efficacy in Ewing sarcoma. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Su, S.; Pickar-Oliver, A.; Chiarella, A.M.; Hahn, Q.; Goldfarb, D.; Cloer, E.W.; Small, G.W.; Sivashankar, S.; Ramsden, D.A.; et al. Engineered Cas9 variants bypass Keap1-mediated degradation in human cells and enhance epigenome editing efficiency. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 11536–11551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Du, H.; Cloer, E.W.; Zhang, J.; Mei, L.; Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Hepperla, A.J.; Simon, J.M.; et al. STING Suppresses Mitochondrial VDAC2 to Govern RCC Growth Independent of Innate Immunity. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2203718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deng, Y.; Yuan, R.; Liu, P. The Rab18/Ras/ERK/FosB/MMP3 Signaling Pathway Mediates Cell Migration Regulation by 2′3′-cGAMP. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125758
Deng Y, Yuan R, Liu P. The Rab18/Ras/ERK/FosB/MMP3 Signaling Pathway Mediates Cell Migration Regulation by 2′3′-cGAMP. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125758
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeng, Yu, Runjie Yuan, and Pengda Liu. 2025. "The Rab18/Ras/ERK/FosB/MMP3 Signaling Pathway Mediates Cell Migration Regulation by 2′3′-cGAMP" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125758
APA StyleDeng, Y., Yuan, R., & Liu, P. (2025). The Rab18/Ras/ERK/FosB/MMP3 Signaling Pathway Mediates Cell Migration Regulation by 2′3′-cGAMP. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125758






