Effects of Phenosanic Acid in Rat Seizure Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
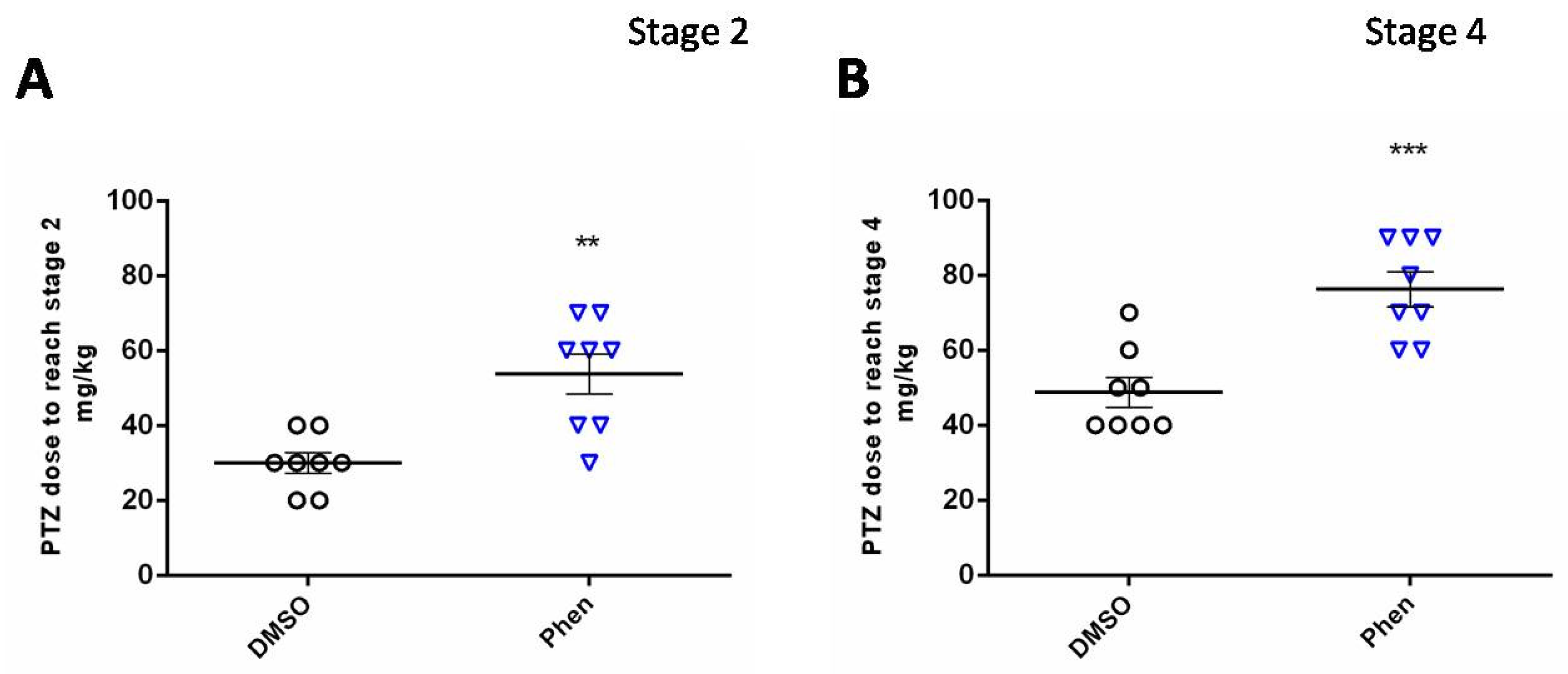
2.1. Acute Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) Model
2.2. Chronic Lithium–Pilocarpine Model
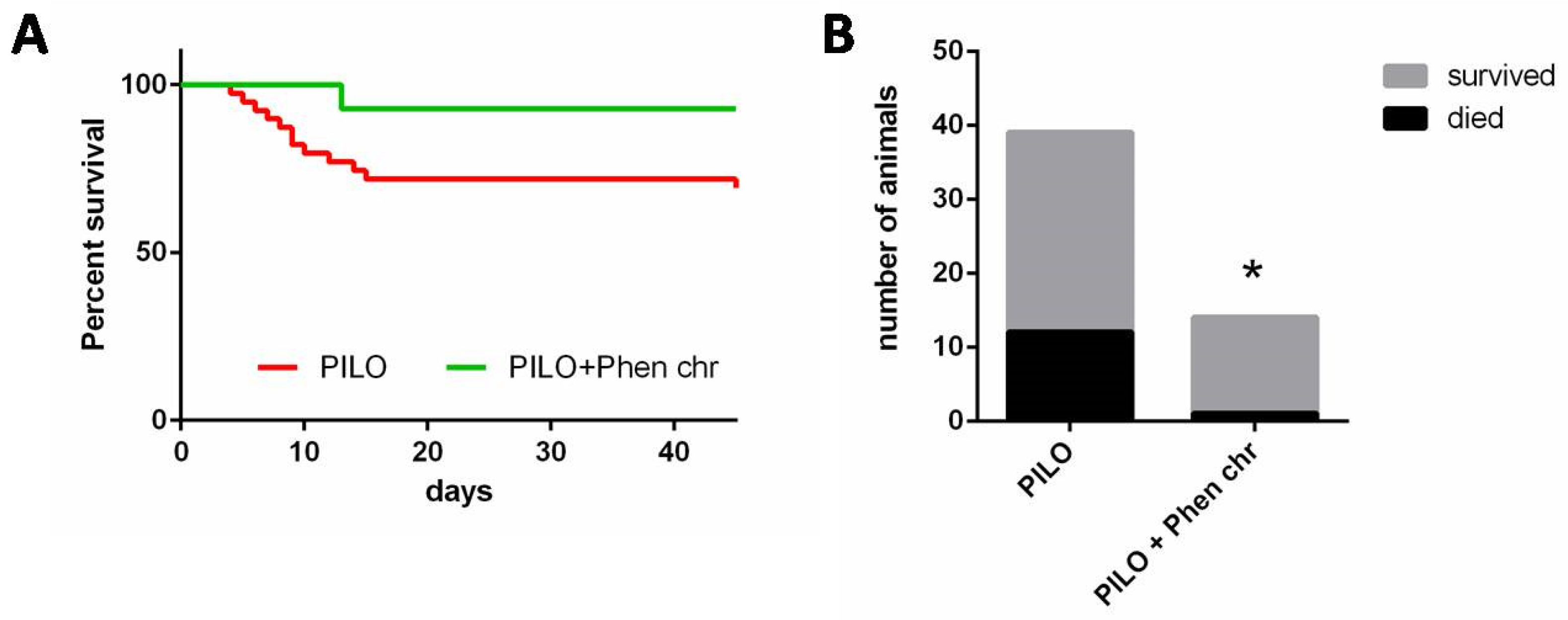
2.2.1. Seizures
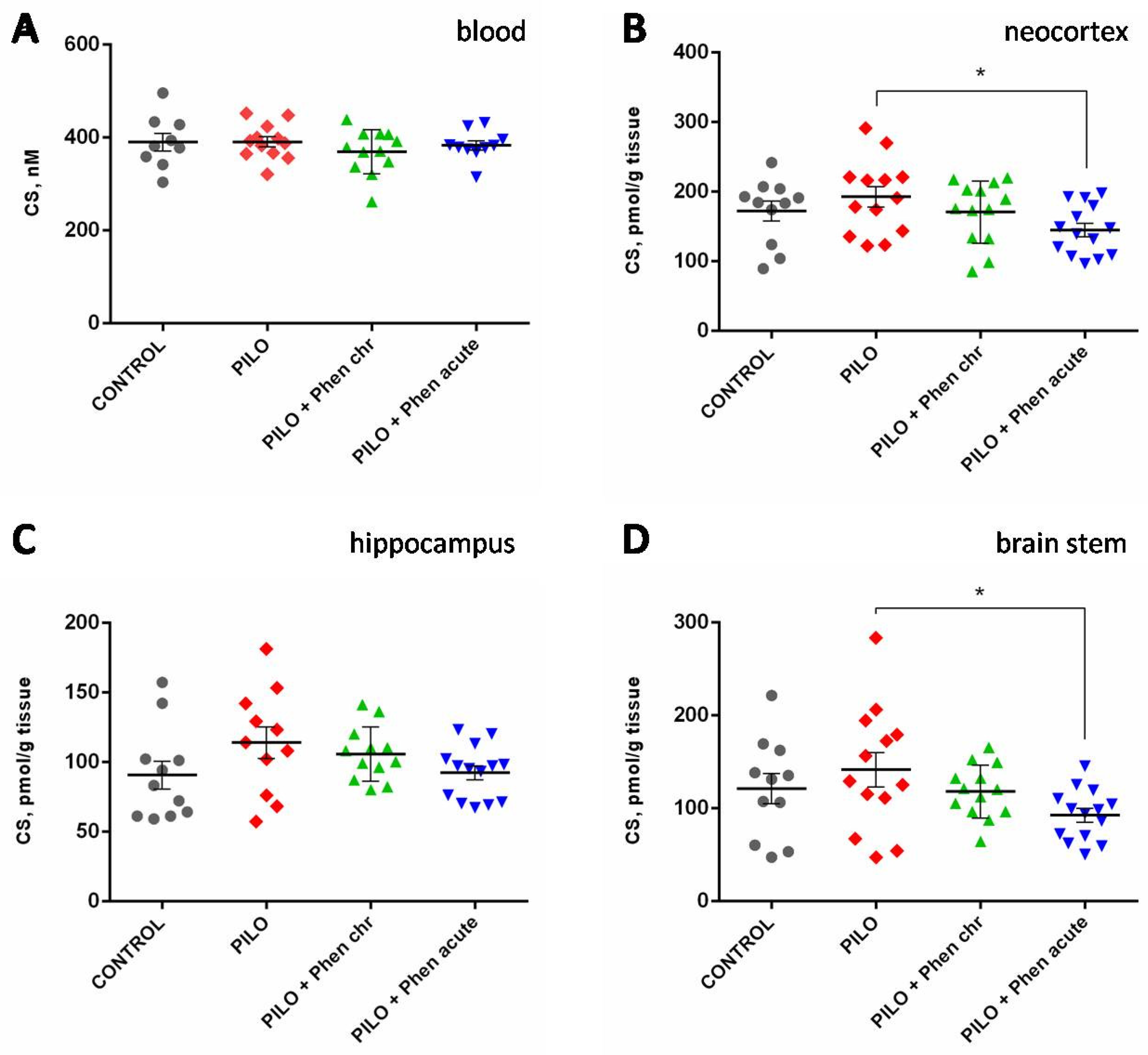
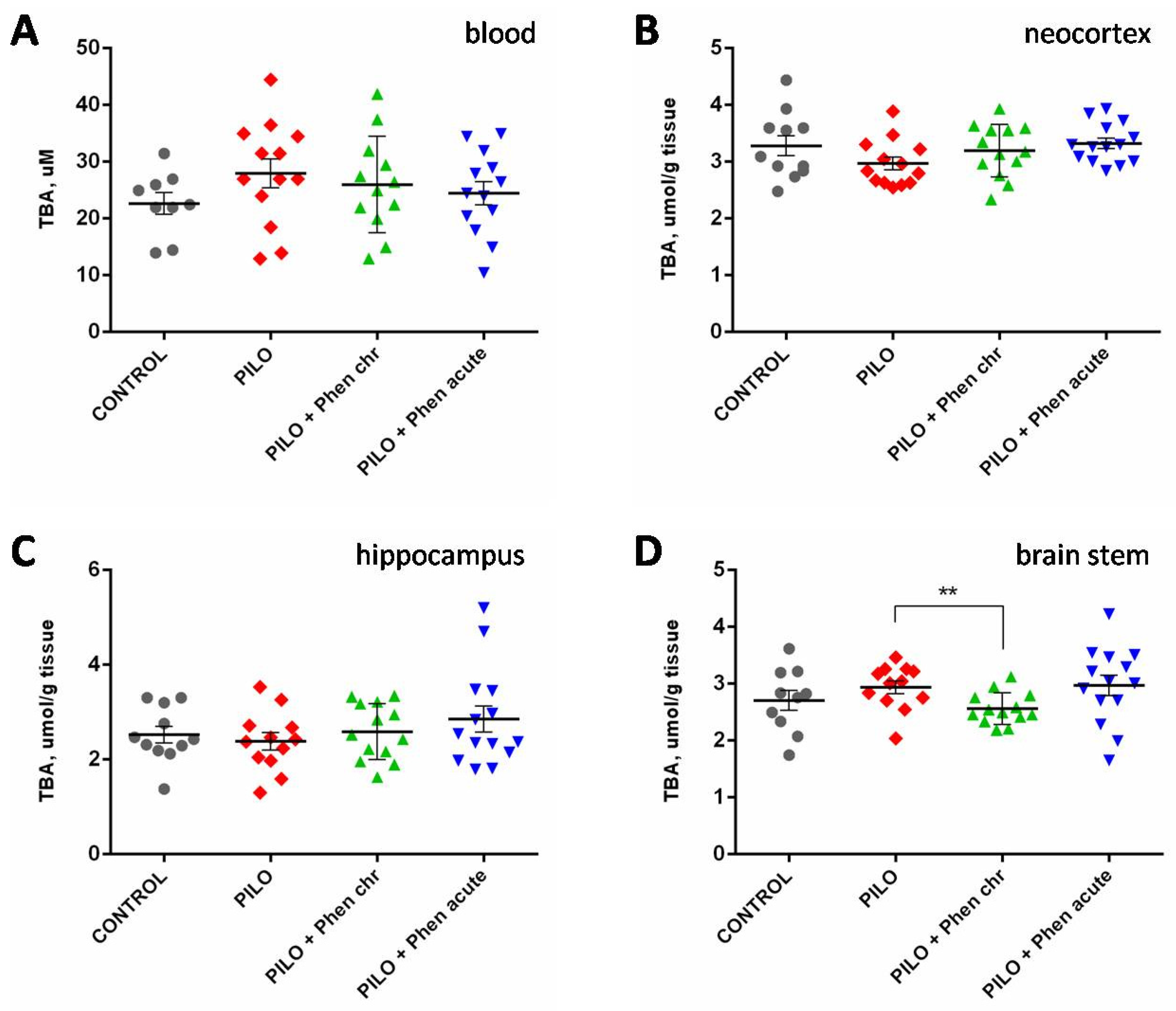
2.2.2. Biochemical Assays
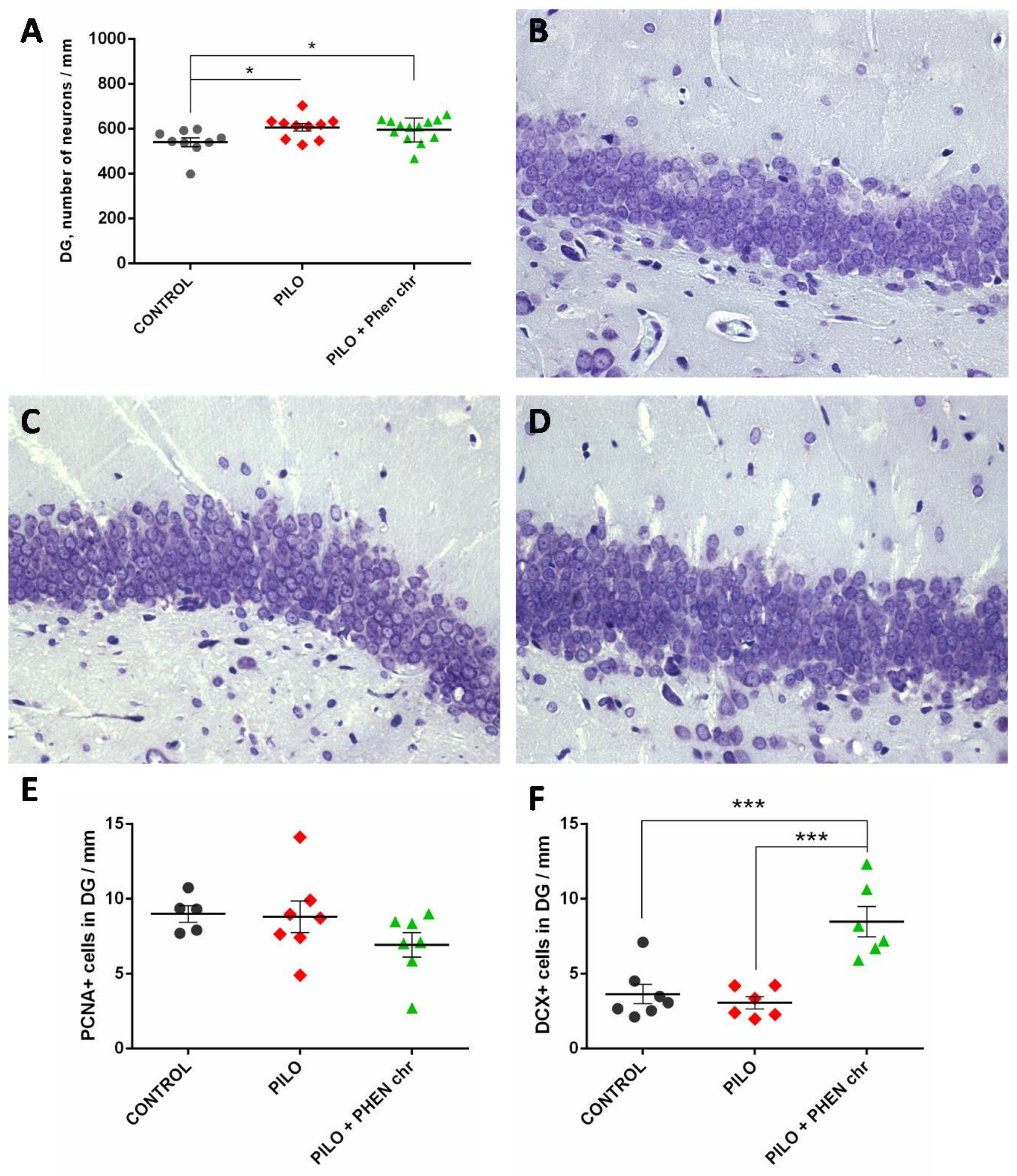
2.2.3. Morphological Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Seizure Models
4.2.1. Acute PTZ-Model
4.2.2. Chronic Lithium–Pilocarpine Model
- Control group (n = 11): Rats of this group were not subjected to lithium–pilocarpine seizures and received a vehicle (peanut butter) per os throughout the whole experiment.
- Pilocarpine SE group (n = 23): These rats were subjected to a lithium–pilocarpine SE model and received a vehicle (peanut butter) per os throughout the whole experiment.
- Pilocarpine SE group with chronic PA administration (n = 21): Rats of this group were subjected to lithium–pilocarpine SE, similarly to animals of the previous group, but received PA in the peanut butter per os (80 mg/kg daily) for 5 weeks after the SE, followed by a one-week period of vehicle administration (during week 6).
- Pilocarpine SE group with acute PA administration (n = 24): Rats of this group were subjected to lithium–pilocarpine SE, similarly to animals of the two previous groups, but received a vehicle (peanut butter) per os throughout the whole experiment except for the last day, when PA (120 mg/kg) was administered.
4.3. Biochemical Assays
4.4. Brain Morphological Analysis
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| AEDs | Antiepileptic drugs |
| DCX+ cells | Doublecortin positive cells |
| DG | Dentate gyrus |
| NOx | Total amount of nitrates and nitrites |
| PA | Phenosanic acid |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PCNA+ cells | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen positive cells |
| PTZ | Pentylenetetrazole |
| SE | Status epilepticus |
| SGZ | Subgranular zone |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TBARPS | Substances reacting with 2-thiobarbituric acid |
References
- Gulyaeva, N.V. Stress-associated molecular and cellular hippocampal mechanisms common for epilepsy and comorbid depressive disorders. Biochemistry 2021, 86, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyvaert, L. Are antiseizure medications disease modifiers? Rev. Neurol. 2025, 181, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löscher, W.; Klein, P. The pharmacology and clinical efficacy of antiseizure medications: From bromide salts to cenobamate and beyond. CNS Drugs 2021, 35, 935–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geronzi, U.; Lotti, F.; Grosso, S. Oxidative stress in epilepsy. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2018, 18, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bespalov, V.G.; Alexandrov, V.A.; Korman, D.B.; Baranenko, D.A. Phenozan, a synthetic phenolic antioxidant, inhibits the development of spontaneous tumors in rats and mice. Drug Res. 2016, 66, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burd, S.G.; Lebedeva, A.V.; Pantina, N.V.; Rubleva, Y.V.; Pizova, N.V.; Vasil’ev, S.V.; Belova, A.N.; Vorob’eva, O.V.; Emel’yanova, V.V.; Zhadnov, V.A.; et al. Clinical results and prospects for the use of phenosanic acid in patients with focal epilepsy. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S.S. Korsakova 2021, 121, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turski, W.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A.; Schwarz, M.; Czuczwar, S.J.; Kleinrok, Z.; Turski, L. Limbic seizures produced by pilocarpine in rats: Behavioural, electroencephalographic and neuropathological study. Behav. Brain Res. 1983, 9, 315–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curia, G.; Longo, D.; Biagini, G.; Jones, R.S.; Avoli, M. The pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J. Neurosci. Methods 2008, 172, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Musto, A.E. The role of inflammation in the development of epilepsy. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guliaeva, N.V.; Levshina, I.P.; Levina, O.L.; Plekhanova, L.G. Corrective action of an antioxidant in chronic emotional-pain stress in rats. Biull. Eksp. Biol. Med. 1984, 98, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pogoretskaia, I.L.; Arkhipova, G.V.; Baĭder, L.M.; Burlakova, E.B. Effect of the antioxidant phenozan and neuropeptide adrenocorticotropic hormone on the structure of the liquid crystalline state of the lipid bilayer and thickness of the phosphatidylcholine membrane. Biofizika 1999, 44, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Treshchenkova, I.A.; Goloshchapov, A.N.; Burlakova, E.B. Effect of low doses of phenozan on lactate dehydrogenase and microviscosity of microsomal membranes of brain cells in mice. Radiats. Biol. Radioecol. 2003, 43, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palmina, N.P.; Chasovskaya, T.E.; Belov, V.V.; Maltseva, E.L. Dose dependences of lipid microviscosity of biological membranes induced by synthetic antioxidant potassium phenosan salt. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 443, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhizhina, G.P.; Zavarykina, T.M.; Mil’, E.M.; Burlakova, E.B. The effects of low doses of low-level gamma-radiation and phenozan injection on structural characteristics of mice spleen DNA. Radiats. Biol. Radioecol. 2007, 47, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palmina, N.P.; Chasovskaya, T.E.; Ryzhkina, I.S.; Murtasina, L.I.; Konovalov, A.I. Water solutions of phenosan potassium salt: Influence on biological membrane structure and conductivity. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 429, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhlov, A.P. Mechanisms of the regulation of membrane receptor activity by synthetic antioxidants of the screened phenol class. Biull. Eksp. Biol. Med. 1988, 106, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlov, S.S.; Chasovskaya, T.E.; Semenova, M.G.; Palmina, N.P. Effects of low concentrations of synthetic antioxidant phenosan potassium salt on the thermoinduced structural transitions in the protein component of plasma membranes. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 459, 190–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedotova, I.B.; Semiokhina, A.F.; Arkhipova, G.V.; Burlakova, E.B. The possibilities of correcting some complex behavioral reactions in KM rats by using an antioxidant. Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deiat. Im. I P Pavlova. 1990, 40, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arkhipova, G.V.; Burlakova, E.B.; Semiokhina, A.F.; Fedotova, I.B.; Krushinskiĭ, L.V. Antiradical mechanism of the protective action of synthetic antioxidants in epileptiform seizures in rats and their subsequent death from hemorrhage into the brain. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 1982, 267, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yakovleva, A.A.; Litvinova, S.A.; Gladysheva, N.A.; Radontseva, V.V.; Voronina, T.A. Experimental study of the influence of phenozanic acid and its combination with valproic acid on the development of the epileptic system. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S.S. Korsakova 2024, 124, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebedeva, A.V.; Burd, S.G.; Rubleva, Y.V.; Pantina, N.V.; Yurchenko, A.V.; Bogomazova, M.A.; Kovaleva, I.I. Study of the practice of prescribing phenosanic acid in epilepsy accompanied by asthenic disorders. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S.S. Korsakova 2024, 124, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voronkova, K.V.; Alieva, A.M.; Nikitin, I.G.; Musina, G.M.; Surskaya, E.V.; Zaitseva, O.S.; Mashkevich, N.G.; Gomonova, L.V.; Petrukhin, A.S. The role of the phenosanic acid in the combined treatment of patients with epilepsy. Zh. Nevrol. Psikhiatr. Im. S.S. Korsakova 2023, 123, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turski, L.; Ikonomidou, C.; Turski, W.A.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A. Review: Cholinergic mechanisms and epileptogenesis. The seizures induced by pilocarpine: A novel experimental model of intractable epilepsy. Synapse 1989, 3, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Choi, B.; Suh, S. Unexpected effects of acetylcholine precursors on pilocarpine seizure-induced neuronal death. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalheiro, E.A.; Leite, J.P.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Turski, W.A.; Ikonomidou, C.; Turski, L. Long-term effects of pilocarpine in rats: Structural damage of the brain triggers kindling and spontaneous recurrent seizures. Epilepsia 1991, 32, 778–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Larionov, S.; Pitsch, J.; Hoerold, N.; Ullmann, C.; Elger, C.E.; Schramm, J.; Becker, A.J. Expression analysis of metabotropic glutamate receptors I and III in mouse strains with different susceptibility to experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 375, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portelli, J.; Aourz, N.; De Bundel, D.; Meurs, A.; Smolders, I.; Michotte, Y.; Clinckers, R. Intrastrain differences in seizure susceptibility, pharmacological response and basal neurochemistry of Wistar rats. Epilepsy Res. 2009, 87, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaeva, N.V. Glucocorticoids Orchestrate Adult Hippocampal Plasticity: Growth Points and Translational Aspects. Biochemistry 2023, 88, 565–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossler, D.G.; Bainbridge, J.L.; Boggs, J.G.; Novotny, E.J.; Loddenkemper, T.; Faught, E.; Amengual-Gual, M.; Fischer, S.N.; Gloss, D.S.; Olson, D.M.; et al. Treatment of refractory convulsive status epilepticus: A comprehensive review by the American Epilepsy Society Treatments Committee. Epilepsy Curr. 2020, 20, 245–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joëls, M.; de Kloet, E.R. Effect of corticosteroid hormones on electrical activity in rat hippocampus. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1991, 40, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, O.W.; Santos, V.R.; Pun, R.Y.K.; McKlveen, J.M.; Batie, M.; Holland, K.D.; Gardner, M.; Garcia-Cairasco, N.; Herman, J.P.; Danzer, S.C. Impact of corticosterone treatment on spontaneous seizure frequency and epileptiform activity in mice with chronic epilepsy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarati, A.M.; Shin, D.; Kwon, Y.S.; Bragin, A.; Pineda, E.; Tio, D.; Taylor, A.N.; Sankar, R. Elevated plasma corticosterone level and depressive behavior in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 34, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulsin, A.C.; Herman, J.P.; Danzer, S.C. RU486 mitigates hippocampal pathology following status epilepticus. Front. Neurol. 2016, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Puttachary, S.; Thippeswamy, T. Glial source of nitric oxide in epileptogenesis: A target for disease modification in epilepsy. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 97, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, P.S.; Perfilieva, E.; Björk-Eriksson, T.; Alborn, A.M.; Nordborg, C.; Peterson, D.A.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the adult human hippocampus. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldrini, M.; Fulmore, C.A.; Tartt, A.N.; Simeon, L.R.; Pavlova, I.; Poposka, V.; Rosoklija, G.B.; Stankov, A.; Arango, V.; Dwork, A.J.; et al. Human hippocampal neurogenesis persists throughout aging. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 589–599.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G.; Gage, F.H.; Aigner, L.; Song, H.; Curtis, M.A.; Thuret, S.; Kuhn, H.G.; Jessberger, S.; Frankland, P.W.; Cameron, H.A.; et al. Human adult neurogenesis: Evidence and remaining questions. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 23, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrells, S.F.; Paredes, M.F.; Cebrian-Silla, A.; Sandoval, K.; Qi, D.; Kelley, K.W.; James, D.; Mayer, S.; Chang, J.; Auguste, K.I.; et al. Human hippocampal neurogenesis drops sharply in children to undetectable levels in adults. Nature 2018, 555, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, H.A.; Woolley, C.S.; McEwen, B.S.; Gould, E. Differentiation of newly born neurons and glia in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Neuroscience 1993, 56, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, F.H. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 2000, 287, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, R.; Shin, D.; Liu, H.; Katsumori, H.; Wasterlain, C.G. Granule cell neurogenesis after status epilepticus in the immature rat brain. Epilepsia 2000, 41 (Suppl. S6), 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parent, J.M.; Valentin, V.V.; Lowenstein, D.H. Prolonged seizures increase proliferating neuroblasts in the adult rat subventricular zone-olfactory bulb pathway. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 3174–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radley, J.J.; Jacobs, B.L. Pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus increases cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus of adult rats via a 5-HT1A receptor-dependent mechanism. Brain Res. 2003, 966, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.P.; Sundstrom, L.E. Kainic acid increases the proliferation of granule cell progenitors in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Brain. Res. 1998, 790, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüttmann, K.; Sadgrove, M.; Wallraff, A.; Hinterkeuser, S.; Kirchhoff, F.; Steinhäuser, C.; Gray, W.P. Seizures preferentially stimulate proliferation of radial glia-like astrocytes in the adult dentate gyrus: Functional and immunocytochemical analysis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, E.; Aimi, Y.; Yasuhara, O.; Tooyama, I.; Shimada, M.; McGeer, P.L. Enhancement of progenitor cell division in the dentate gyrus triggered by initial limbic seizures in rat models of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.D.; McLean, K.J.; Murphy, M.A.; Turnley, A.M.; Cook, M.J. Seizures, not hippocampal neuronal death, provoke neurogenesis in a mouse rapid electrical amygdala kindling model of seizures. Neuroscience 2005, 136, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayin, U.; Osting, S.; Hagen, J.; Rutecki, P.; Sutula, T. Spontaneous seizures and loss of axo-axonic and axo-somatic inhibition induced by repeated brief seizures in kindled rats. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 2759–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Cho, H.; Kim, H.; Kim, K. Repeated brief epileptic seizures by pentylenetetrazole cause neurodegeneration and promote neurogenesis in discrete brain regions of freely moving adult rats. Neuroscience 2006, 140, 673–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniol, V.A.; Ivanova-Dyatlova, A.Y.; Keren, O.; Guekht, A.B.; Sarne, Y.; Gulyaeva, N.V. A single pentylenetetrazole-induced clonic-tonic seizure episode is accompanied by a slowly developing cognitive decline in rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2013, 26, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komoltsev, I.; Shalneva, D.; Kostyunina, O.; Volkova, A.; Frankevich, S.; Shirobokova, N.; Belikova, A.; Balan, S.; Chizhova, O.; Salyp, O.; et al. Delayed TBI-Induced Neuronal Death in the Ipsilateral Hippocampus and Behavioral Deficits in Rats: Influence of Corticosterone-Dependent Survivorship Bias? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aniol, V.A.; Lazareva, N.A.; Moiseeva, Y.V.; Nedogreeva, O.A.; Novikova, M.R.; Kostryukov, P.A.; Onufriev, M.V.; Gulyaeva, N.V. Effects of Phenosanic Acid in Rat Seizure Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125668
Aniol VA, Lazareva NA, Moiseeva YV, Nedogreeva OA, Novikova MR, Kostryukov PA, Onufriev MV, Gulyaeva NV. Effects of Phenosanic Acid in Rat Seizure Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125668
Chicago/Turabian StyleAniol, Victor A., Natalia A. Lazareva, Yulia V. Moiseeva, Olga A. Nedogreeva, Margarita R. Novikova, Pavel A. Kostryukov, Mikhail V. Onufriev, and Natalia V. Gulyaeva. 2025. "Effects of Phenosanic Acid in Rat Seizure Models" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125668
APA StyleAniol, V. A., Lazareva, N. A., Moiseeva, Y. V., Nedogreeva, O. A., Novikova, M. R., Kostryukov, P. A., Onufriev, M. V., & Gulyaeva, N. V. (2025). Effects of Phenosanic Acid in Rat Seizure Models. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125668





