RIPK1 in Diffuse Glioma Pathology: From Prognosis Marker to Potential Therapeutic Target
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. RIPK1 Expression and Survival
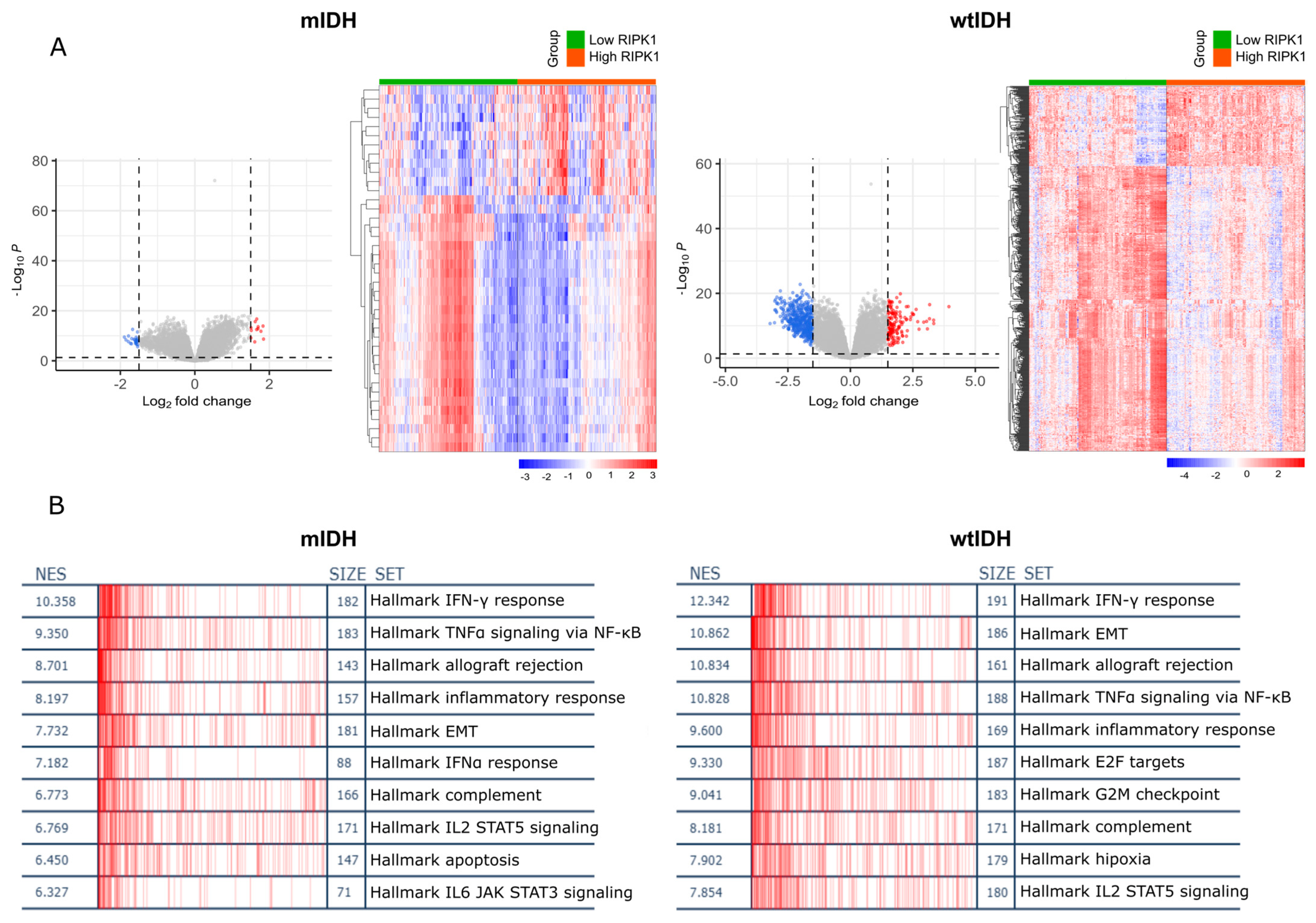
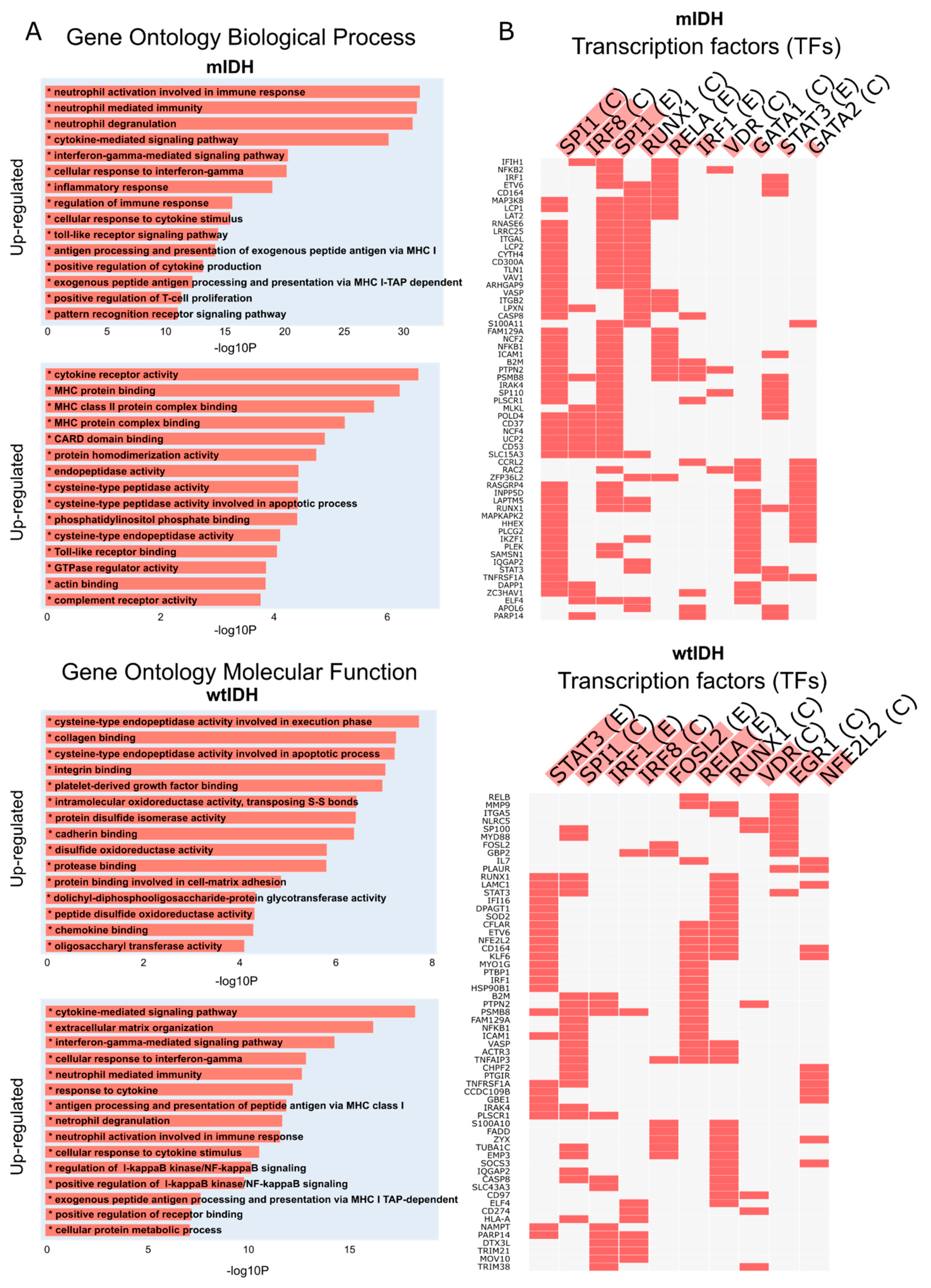
2.2. RIPK1 Differential Expression Analysis
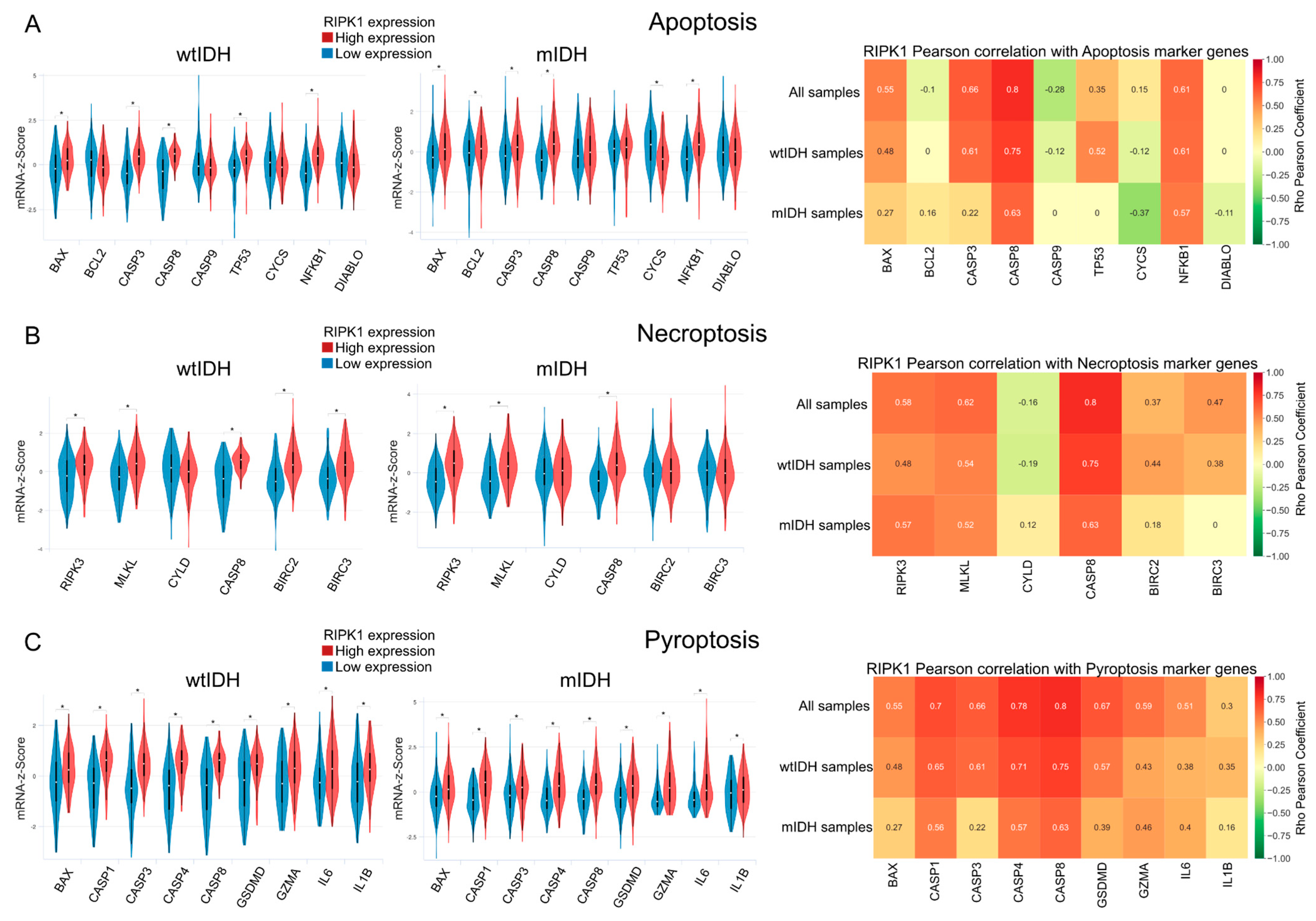
2.3. Apoptosis
2.4. Necroptosis and Pyroptosis
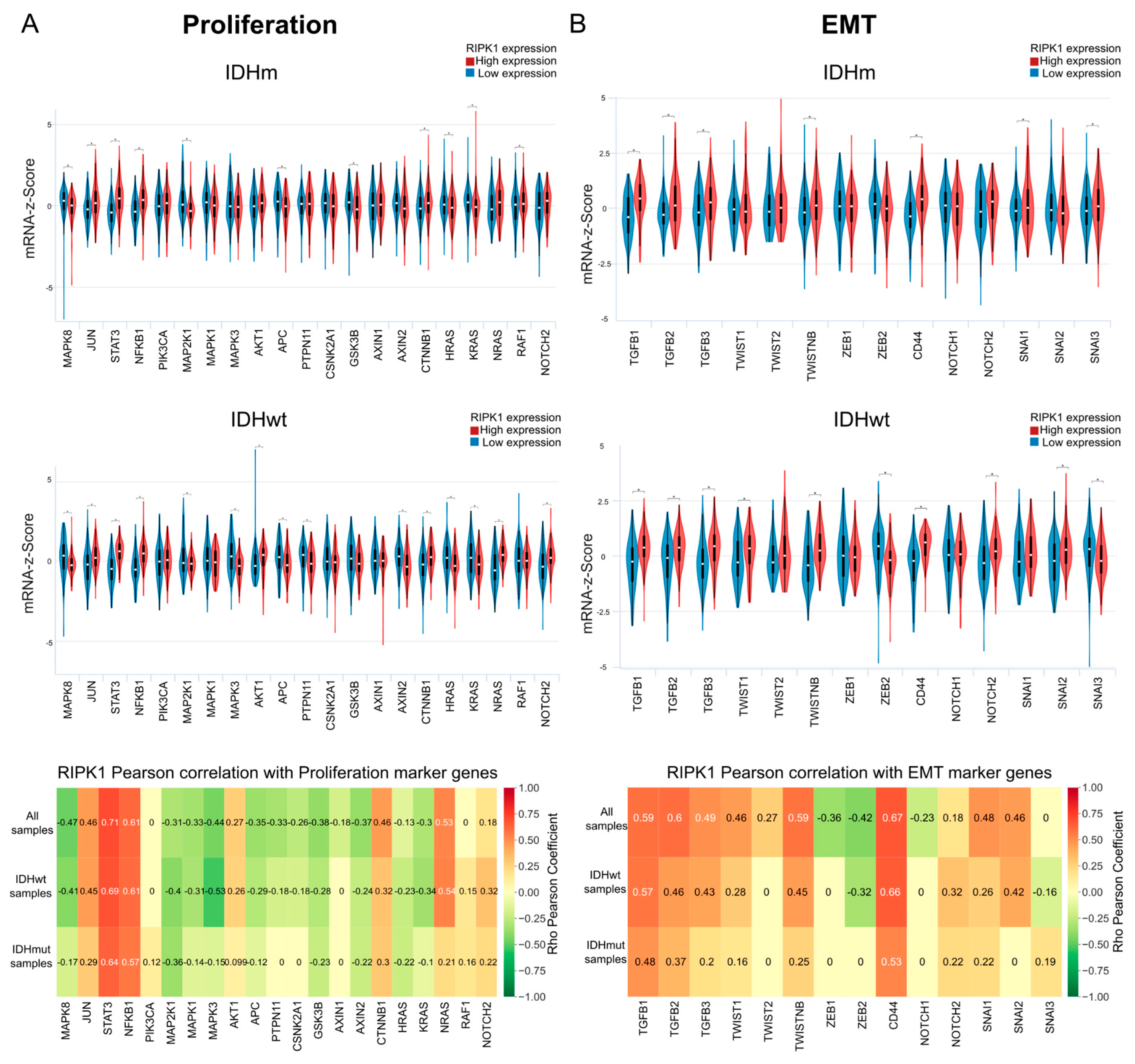
2.5. Proliferation
2.6. RIPK1 and EMT
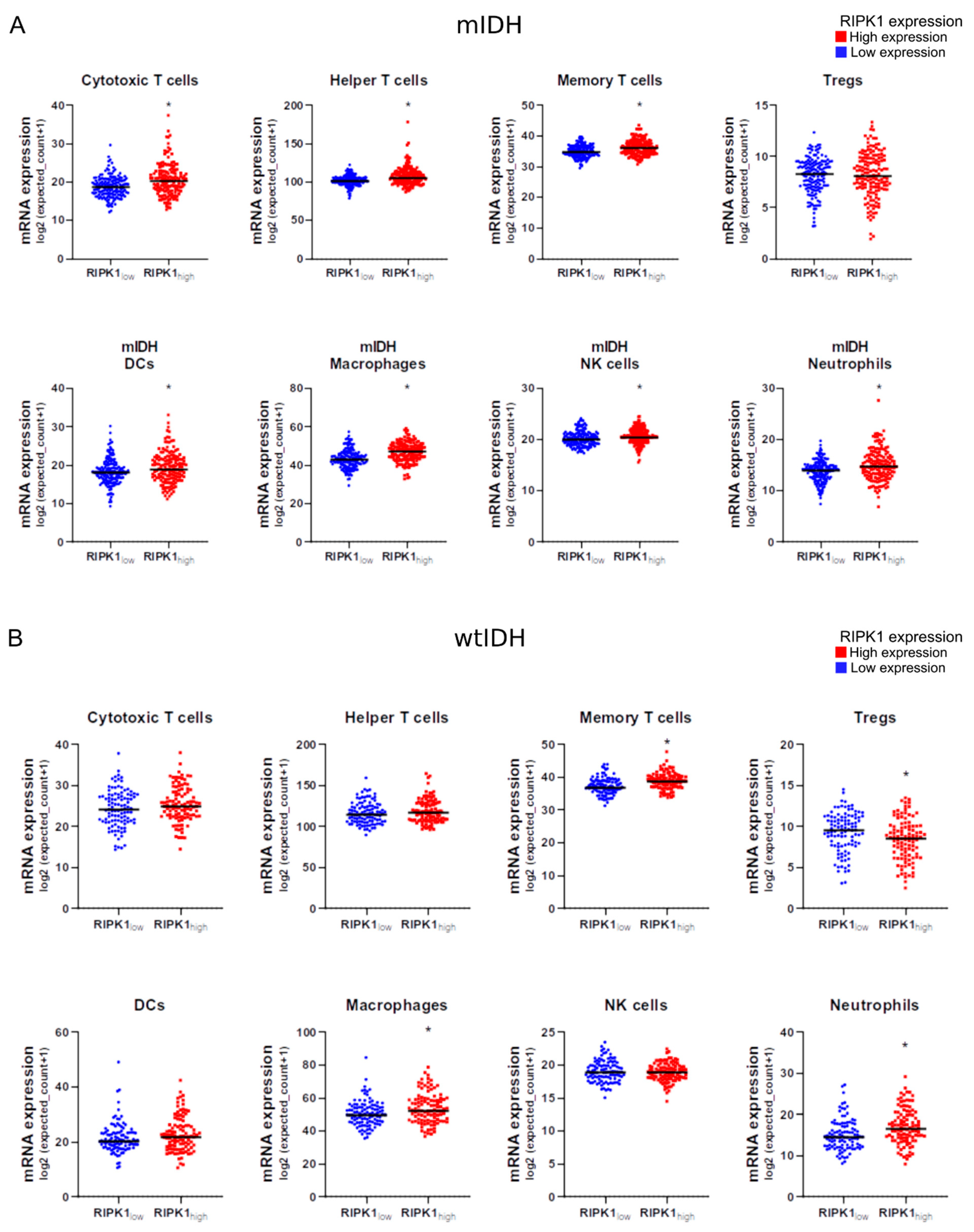
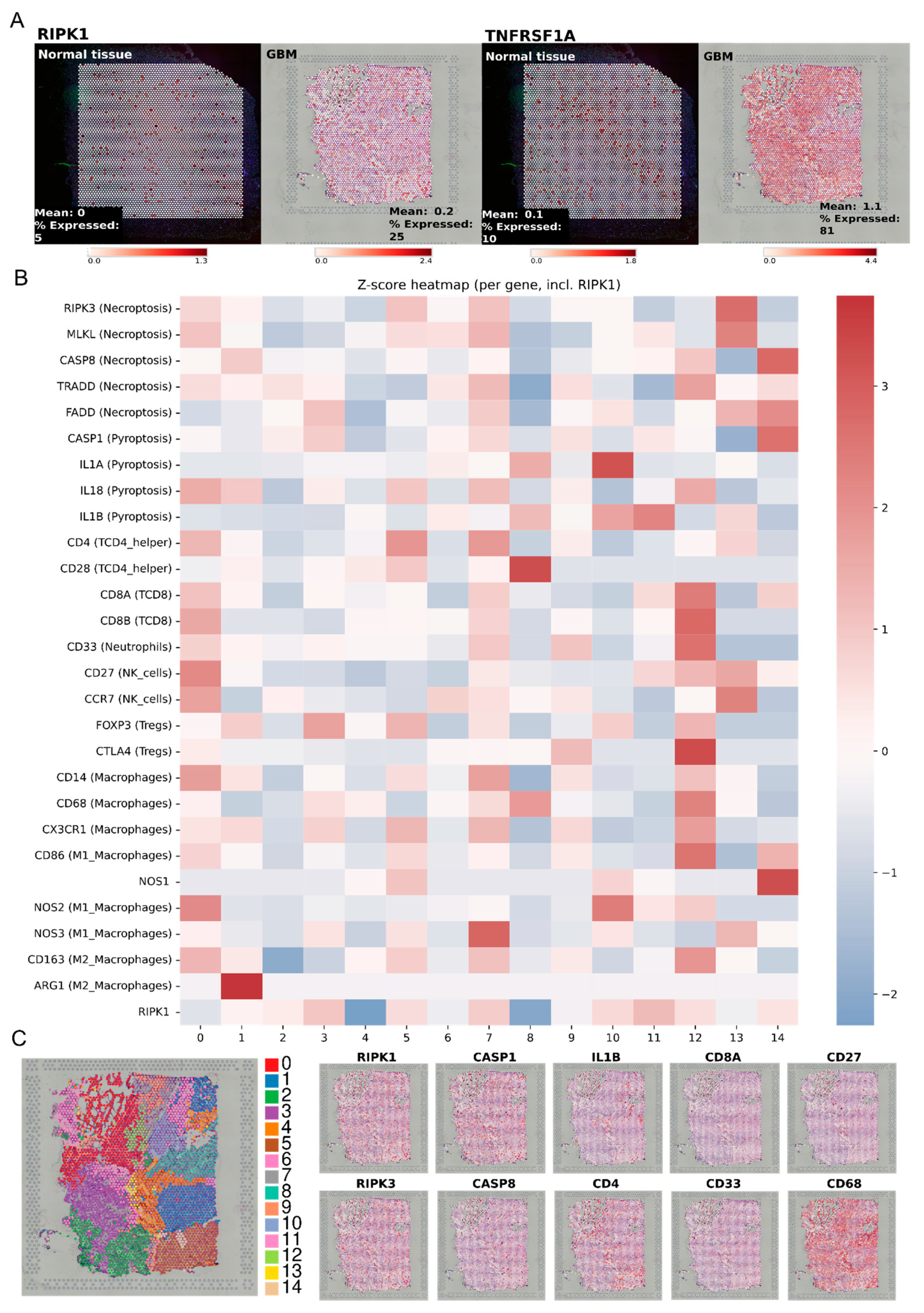
2.7. RIPK1 Expression and Immune Cell Infiltration
2.8. RIPK1 Inhibition Combined with Chemotherapy Reduces Cell Growth and Induces Apoptosis In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Cohort
4.2. Glioma Patient Samples
4.3. RIPK1 Expression and Clinical Attributes
4.4. Survival Plots
4.5. Transcriptomic Analysis
4.6. Enrichment and Functional Analysis
4.7. Meta-Analysis of Immune Gene Signatures in mIDH and wtIDH Glioma Biopsies
4.8. Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM) Cells
4.9. Tumor Cell Growth
4.10. Apoptosis by TUNEL
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DG | Diffuse glioma |
| GBM | Glioblastoma multiforme |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| 2-HG | 2-hydroxyglutarate |
| mIDH | Mutated isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| wtIDH | Wild type isocitrate dehydrogenase |
| PCD | Programmed cell death |
| RIPK1 | Receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 |
| Nec-1 | Necrostatin-1 |
| KO | Knockout |
| TIME | Tumor immune microenvironment |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| LGGGBM | Low-Grade Glioma and Glioblastoma Multiforme |
| GSEA | Gene set enrichment analysis |
| EMT | Epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| NES | Normalized enrichment score |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| TF | Transcription factor |
| DEG | Differentially expressed gene |
| FET | Fisher’s exact test |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| NK | Natural killer |
| Tregs | Regulatory T cells |
| CDDP | cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) (cisplatin) |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling |
| TMZ | Temozolomide |
| AATx | Anti-angiogenic therapy |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| GAMs | Glioma-associated macrophages |
| IFN | Interferon |
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Truitt, G.; Boscia, A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2011–2015. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 20, iv1–iv86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Patil, N.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. Corrigendum to: CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2013–2017. Neuro-Oncol. 2022, 24, 1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, N.; Asad, A.S.; Gómez Escalante, J.; Peña Agudelo, J.A.; Nicola Candia, A.J.; García Fallit, M.; Seilicovich, A.; Candolfi, M. Potential of IDH Mutations as Immunotherapeutic Targets in Gliomas: A Review and Meta-Analysis. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2021, 25, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Klockow, J.L.; Zhang, M.; Lafortune, F.; Chang, E.; Jin, L.; Wu, Y.; Daldrup-Link, H.E. Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM): An Overview of Current Therapies and Mechanisms of Resistance. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 171, 105780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reifenberger, G.; Wirsching, H.-G.; Knobbe-Thomsen, C.B.; Weller, M. Advances in the Molecular Genetics of Gliomas—Implications for Classification and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, K.; Mischel, P.S.; Reifenberger, G. Molecular Classification of Gliomas. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; Volume 134, pp. 97–120. ISBN 978-0-12-802997-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wesseling, P.; Capper, D. WHO 2016 Classification of Gliomas. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobio 2018, 44, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.R.; Wen, P.Y.; Lang-Orsini, M.; Chukwueke, U.N. World Health Organization 2021 Classification of Central Nervous System Tumors and Implications for Therapy for Adult-Type Gliomas: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, L.; White, D.W.; Gross, S.; Bennett, B.D.; Bittinger, M.A.; Driggers, E.M.; Fantin, V.R.; Jang, H.G.; Jin, S.; Keenan, M.C.; et al. Cancer-Associated IDH1 Mutations Produce 2-Hydroxyglutarate. Nature 2009, 462, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, R.; Yeoh, K.K.; Tian, Y.; Hillringhaus, L.; Bagg, E.A.; Rose, N.R.; Leung, I.K.H.; Li, X.S.; Woon, E.C.Y.; Yang, M.; et al. The Oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate Inhibits Histone Lysine Demethylases. EMBO Rep. 2011, 12, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Kim, S.-H.; Ito, S.; Yang, C.; Wang, P.; Xiao, M.-T.; et al. Oncometabolite 2-Hydroxyglutarate Is a Competitive Inhibitor of α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases. Cancer Cell 2011, 19, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschka, P.; Schlenk, R.F.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Habdank, M.; Krönke, J.; Bullinger, L.; Späth, D.; Kayser, S.; Zucknick, M.; Götze, K.; et al. IDH1 and IDH2 Mutations Are Frequent Genetic Alterations in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Confer Adverse Prognosis in Cytogenetically Normal Acute Myeloid Leukemia With NPM1 Mutation Without FLT3 Internal Tandem Duplication. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3636–3643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.C.-H.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Siu, I.-M.; Gallia, G.L.; et al. An Integrated Genomic Analysis of Human Glioblastoma Multiforme. Science 2008, 321, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noushmehr, H.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Diefes, K.; Phillips, H.S.; Pujara, K.; Berman, B.P.; Pan, F.; Pelloski, C.E.; Sulman, E.P.; Bhat, K.P.; et al. Identification of a CpG Island Methylator Phenotype That Defines a Distinct Subgroup of Glioma. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Liao, M.; Qin, R.; Zhu, S.; Peng, C.; Fu, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, B. Regulated Cell Death (RCD) in Cancer: Key Pathways and Targeted Therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, X.; Liu, N.; Tang, L.; Peng, C.; Chen, X. Pyroptosis: Mechanisms and Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S. Therapeutic Exploitation of Necroptosis for Cancer Therapy. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 35, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Fan, Z.; Luo, G.; Yang, C.; Huang, Q.; Fan, K.; Cheng, H.; Jin, K.; Ni, Q.; Yu, X.; et al. The Role of Necroptosis in Cancer Biology and Therapy. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mifflin, L.; Ofengeim, D.; Yuan, J. Receptor-Interacting Protein Kinase 1 (RIPK1) as a Therapeutic Target. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 553–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samir, P.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kanneganti, T.-D. The PANoptosome: A Deadly Protein Complex Driving Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PANoptosis). Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Dwarakanath, B.; Kong, L.; Lu, J.J. Upregulated Necroptosis-Pathway-Associated Genes Are Unfavorable Prognostic Markers in Low-Grade Glioma and Glioblastoma Multiforme. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, J.; Huang, N.; Tang, J.; Ma, P.; Cheng, Y. Clinical and Biological Significance of a Necroptosis-Related Gene Signature in Glioma. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 855434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Mu, W. Necrostatin-1 and Necroptosis Inhibition: Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Implications. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 163, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, E.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Small-Molecule Receptor-Interacting Protein 1 (RIP1) Inhibitors as Therapeutic Agents for Multifaceted Diseases: Current Medicinal Chemistry Insights and Emerging Opportunities. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 14971–14999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, S.; Harris, P.; Nagilla, R.; Kasparcova, V.; Hoffman, S.; Swift, B.; Dare, L.; Schaeffer, M.; Capriotti, C.; Ouellette, M.; et al. Characterization of GSK′963: A Structurally Distinct, Potent and Selective Inhibitor of RIP1 Kinase. Cell Death Discov. 2015, 1, 15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, G.; Han, G.; Feng, S.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, C.; Zhao, L.; Jin, F. Emodin induced necroptosis in the glioma cell line U251 via the TNF-α/RIP1/RIP3 Pathway. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Lima, S.; Lopes, M.C.; Mollinedo, F. Necroptosis Is Associated with Low Procaspase-8 and Active RIPK1 and -3 in Human Glioma Cells. Oncoscience 2014, 1, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Duan, X.; Peng, W.; Lv, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. RIPK1 Contributes to Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells via Activation of JNK Pathway. Life Sci. 2021, 269, 119064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Song, Y.; Su, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Zhou, B.; et al. RIP1 Promotes Proliferation through G2/M Checkpoint Progression and Mediates Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis and Necroptosis in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, J.G.; Checcoli, A.; Lizarralde-Guerrero, M.; Kroemer, G. RIPK1 Inhibition in Malignant Cells Potentiates Immunotherapy and Radiotherapy Outcome. OncoImmunology 2024, 13, 2425465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannion, J.; Gifford, V.; Bellenie, B.; Fernando, W.; Ramos Garcia, L.; Wilson, R.; John, S.W.; Udainiya, S.; Patin, E.C.; Tiu, C.; et al. A RIPK1-Specific PROTAC Degrader Achieves Potent Antitumor Activity by Enhancing Immunogenic Cell Death. Immunity 2024, 57, 1514–1532.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastushenko, I.; Blanpain, C. EMT Transition States during Tumor Progression and Metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaiu, O.; Chierici, M.; Lucarini, V.; Jurman, G.; Conti, L.A.; De Vito, R.; Boldrini, R.; Cifaldi, L.; Castellano, A.; Furlanello, C.; et al. Cellular and Gene Signatures of Tumor-Infiltrating Dendritic Cells and Natural-Killer Cells Predict Prognosis of Neuroblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Waldner, M.; Obenauf, A.C.; Angell, H.; Fredriksen, T.; Lafontaine, L.; Berger, A.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Intratumoral Immune Cells Reveal the Immune Landscape in Human Cancer. Immunity 2013, 39, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, K.; Scott, N.; Berger, S.; Wang, S.; Brown, K.; Powell, M.; Broer, M.; Watts, C.; Tompson, D.J.; Burriss, S.W.; et al. A Randomised, Placebo-Controlled Study of RIPK1 Inhibitor GSK2982772 in Patients with Active Ulcerative Colitis. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021, 8, e000680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisel, K.; Berger, S.; Thorn, K.; Taylor, P.C.; Peterfy, C.; Siddall, H.; Tompson, D.; Wang, S.; Quattrocchi, E.; Burriss, S.W.; et al. A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Experimental Medicine Study of RIPK1 Inhibitor GSK2982772 in Patients with Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelland, L. The Resurgence of Platinum-Based Cancer Chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, E.; Tosoni, A.; Bartolini, S.; Minichillo, S.; Mura, A.; Asioli, S.; Bartolini, D.; Gardiman, M.; Gessi, M.; Ghimenton, C.; et al. Histopathological Grading Affects Survival in Patients with IDH-Mutant Grade II and Grade III Diffuse Gliomas. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 137, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.G.; Fine, H.A. Diffuse Glioma Heterogeneity and Its Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 575–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabaei, P.; Visse, E.; Bergström, P.; Brännström, T.; Siesjö, P.; Bergenheim, A.T. Radiotherapy Induces an Immediate Inflammatory Reaction in Malignant Glioma: A Clinical Microdialysis Study. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 131, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Singh, O.; Ekinci, C.; Gill, J.; Li, M.; Mamatjan, Y.; Karimi, S.; Bunda, S.; Mansouri, S.; Aldape, K.; et al. TNFα Secreted by Glioma Associated Macrophages Promotes Endothelial Activation and Resistance against Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lai, X.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.; Wu, C. Pyroptosis in Glioblastoma: A Crucial Regulator of the Tumour Immune Microenvironment and a Predictor of Prognosis. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 1579–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Chen, G.; Wu, L.; Yu, K.N.; Sun, M.; Yang, M.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Peng, S.; et al. Ionizing Radiation Triggers the Antitumor Immunity by Inducing Gasdermin E-Mediated Pyroptosis in Tumor Cells. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2023, 115, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aasland, D.; Reich, T.R.; Tomicic, M.T.; Switzeny, O.J.; Kaina, B.; Christmann, M. Repair Gene O6-methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase Is Controlled by SP1 and Up-regulated by Glucocorticoids, but Not by Temozolomide and Radiation. J. Neurochem. 2018, 144, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandes, A.A.; Basso, U.; Reni, M.; Vastola, F.; Tosoni, A.; Cavallo, G.; Scopece, L.; Ferreri, A.J.; Panucci, M.G.; Monfardini, S.; et al. First-Line Chemotherapy With Cisplatin Plus Fractionated Temozolomide in Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Phase II Study of the Gruppo Italiano Cooperativo Di Neuro-Oncologia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1598–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; Yin, J.; Lovejoy, D.B.; Zheng, M.; Liang, X.; Park, J.B.; Efremov, Y.M.; et al. Brain Co-Delivery of Temozolomide and Cisplatin for Combinatorial Glioblastoma Chemotherapy. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2203958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoto, S.; Hermelo, I.; Vuorinen, E.M.; Hannus, P.; Kesseli, J.; Nykter, M.; Granberg, K.J. Computational Characterization of Suppressive Immune Microenvironments in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5574–5585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sørensen, M.D.; Dahlrot, R.H.; Boldt, H.B.; Hansen, S.; Kristensen, B.W. Tumour-Associated Microglia/Macrophages Predict Poor Prognosis in High-Grade Gliomas and Correlate with an Aggressive Tumour Subtype. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2018, 44, 185–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, F.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; He, Q.; Zhang, C.; Li, F.; Maimela, N.R.; Sun, Z.; et al. The R132H Mutation in IDH 1 Promotes the Recruitment of NK Cells through CX3CL1/CX3CR1 Chemotaxis and Is Correlated with a Better Prognosis in Gliomas. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2019, 97, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, H.; Pala, A.; Högel, J.; Hlavac, M.; Dietrich, E.; Westhoff, M.A.; Nonnenmacher, L.; Burster, T.; Georgieff, M.; Wirtz, C.R.; et al. Immune Phenotypes Predict Survival in Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chimal-Ramírez, G.K.; Espinoza-Sánchez, N.A.; Fuentes-Pananá, E.M. Protumor Activities of the Immune Response: Insights in the Mechanisms of Immunological Shift, Oncotraining, and Oncopromotion. J. Oncol. 2013, 2013, 835956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Ren, X.; Zhang, C.; Cai, J.; Liu, Y.; Han, S.; Wu, A. Bioinformatic Profiling Identifies an Immune-Related Risk Signature for Glioblastoma. Neurology 2016, 86, 2226–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinari, E.; Allard, M.; Gustave, R.; Widmer, V.; Philippin, G.; Merkler, D.; Tsantoulis, P.; Dutoit, V.; Dietrich, P.-Y. Inflammation and Lymphocyte Infiltration Are Associated with Shorter Survival in Patients with High-Grade Glioma. Oncoimmunology 2020, 9, 1779990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Boire, A.; Jin, X.; Valiente, M.; Er, E.E.; Lopez-Soto, A.; Jacob, L.S.; Patwa, R.; Shah, H.; Xu, K.; et al. Carcinoma–Astrocyte Gap Junctions Promote Brain Metastasis by cGAMP Transfer. Nature 2016, 533, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzu, M.; Sin, W.; Shimizu, A.; Sato, H. Conflicting Roles of Connexin43 in Tumor Invasion and Growth in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouan-Lanhouet, S.; Riquet, F.; Duprez, L.; Vanden Berghe, T.; Takahashi, N.; Vandenabeele, P. Necroptosis, in Vivo Detection in Experimental Disease Models. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 35, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Zhou, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X. A Pyroptosis-Related Gene Prognostic Index Correlated with Survival and Immune Microenvironment in Glioma. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and Interpreting Cancer Genomics Data via the Xena Platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, W.; Yang, T.; Li, L.; Ma, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Gould, J.; Lu, H.; et al. STOmicsDB: A Comprehensive Database for Spatial Transcriptomics Data Sharing, Analysis and Visualization. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, D1053–D1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Clinical Attribute | Database: TCGA—LGGGBM | |
|---|---|---|
| Total of Patients | 670 | |
| RIPK1 | High expression | 335 |
| Low expression | 335 | |
| IDH status | wtIDH | 257 |
| mIDH | 404 | |
| Undefined | 9 | |
| Age at initial pathologic diagnosis | ≤50 | 393 |
| >50 | 275 | |
| Undefined | 2 | |
| Histological classification | Oligoastrocytoma | 130 |
| Oligodendroglioma | 191 | |
| Astrocytoma | 324 | |
| GBM | 153 | |
| Radiotherapy | Yes | 408 |
| No | 200 | |
| Discrepancy | 1 | |
| Undefined | 61 | |
| Additional pharmaceutical therapy | Yes | 134 |
| No | 102 | |
| Undefined | 434 | |
| Additional surgery | Yes | 56 |
| No | 62 | |
| Undefined | 552 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amorós Morales, L.C.; Gómez Bergna, S.M.; Marchesini, A.; Scalise, M.L.; Gonzalez, N.; Ferrelli, M.L.; Candolfi, M.; Romanowski, V.; Pidre, M.L. RIPK1 in Diffuse Glioma Pathology: From Prognosis Marker to Potential Therapeutic Target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125555
Amorós Morales LC, Gómez Bergna SM, Marchesini A, Scalise ML, Gonzalez N, Ferrelli ML, Candolfi M, Romanowski V, Pidre ML. RIPK1 in Diffuse Glioma Pathology: From Prognosis Marker to Potential Therapeutic Target. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125555
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmorós Morales, Leslie C., Santiago M. Gómez Bergna, Abril Marchesini, María Luján Scalise, Nazareno Gonzalez, M. Leticia Ferrelli, Marianela Candolfi, Víctor Romanowski, and Matias L. Pidre. 2025. "RIPK1 in Diffuse Glioma Pathology: From Prognosis Marker to Potential Therapeutic Target" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125555
APA StyleAmorós Morales, L. C., Gómez Bergna, S. M., Marchesini, A., Scalise, M. L., Gonzalez, N., Ferrelli, M. L., Candolfi, M., Romanowski, V., & Pidre, M. L. (2025). RIPK1 in Diffuse Glioma Pathology: From Prognosis Marker to Potential Therapeutic Target. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5555. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125555






