Adrenomedullin in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression
Abstract
1. Introduction
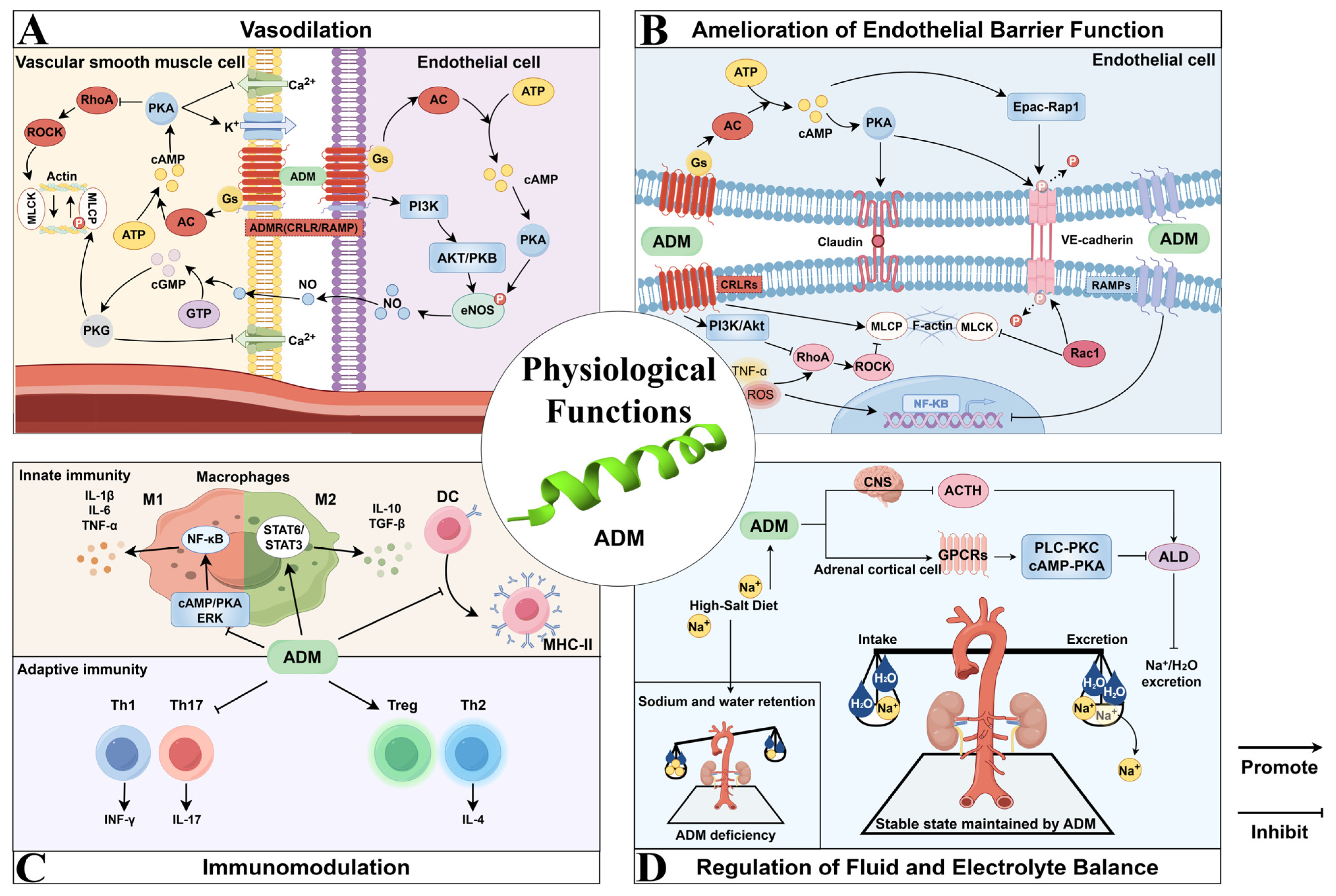
2. Physiological Functions of ADM
2.1. Vasodilation
2.2. Amelioration of Endothelial Barrier Function
2.3. Immunomodulation
2.4. Regulation of Fluid and Electrolyte Balance
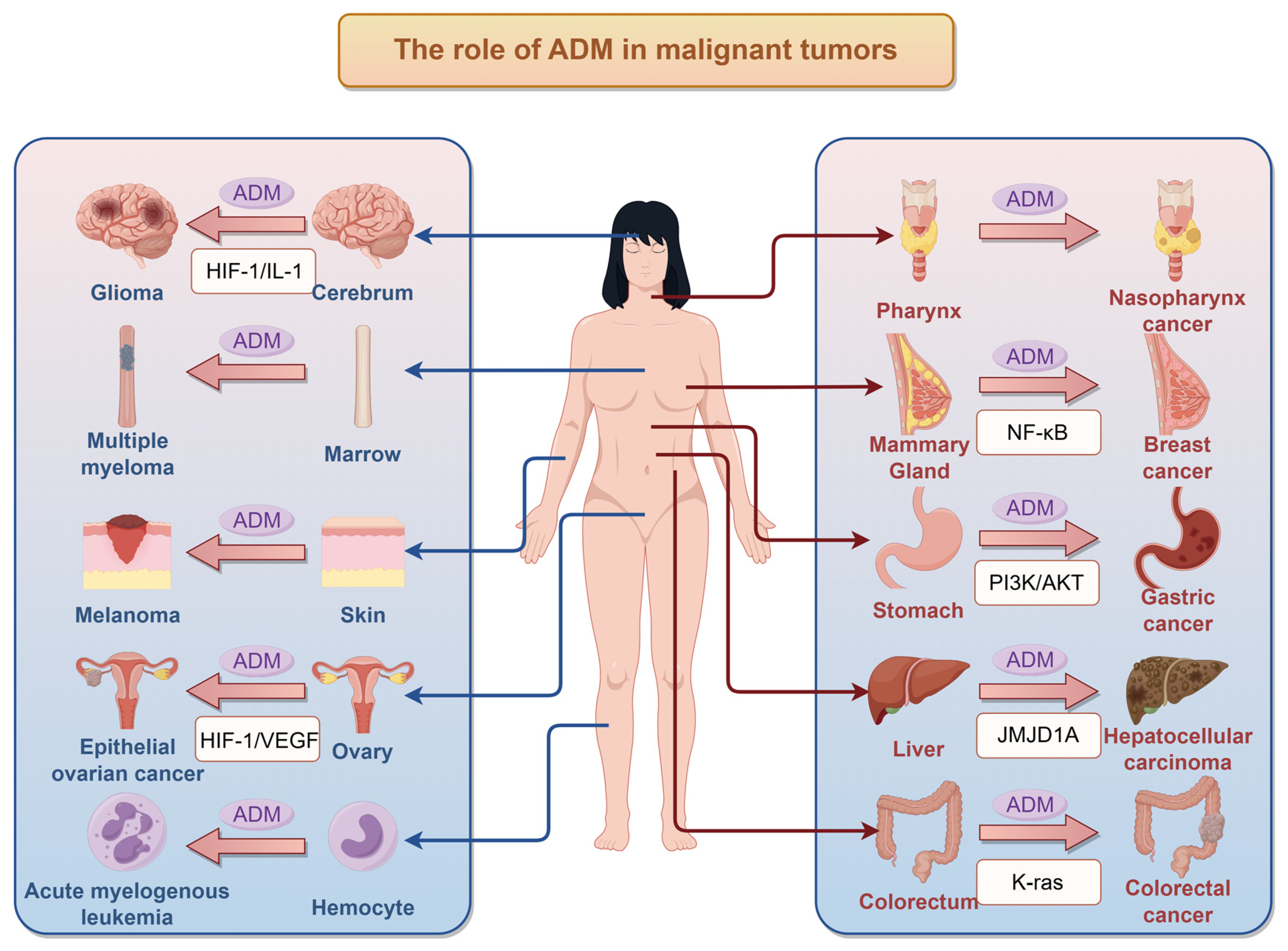
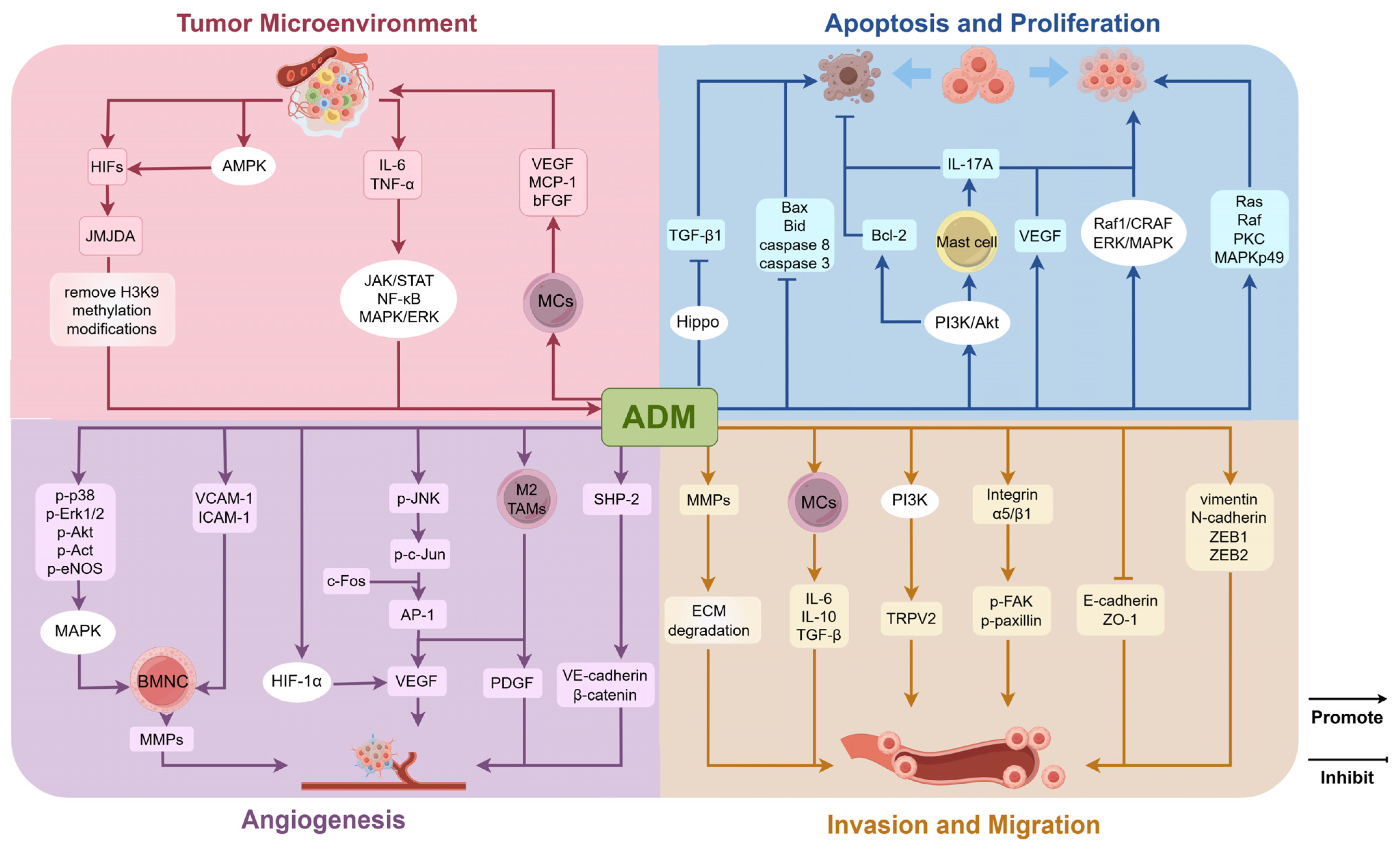
3. Impact of ADM on Tumors
3.1. Role of ADM in the Tumor Microenvironment
3.2. Regulation of Tumor Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis
3.3. Regulation of Angiogenesis in Tumor Tissues
3.4. Regulation of Invasion and Migration Capabilities
4. Drug Resistance and ADM-Targeted Therapies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AAR | adipose afferent reflex |
| AC | adenylyl cyclase |
| ACTH | adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| ADM | adrenomedullin |
| ADMR | adrenomedullin receptor |
| AKT (PKB) | protein kinase B |
| ALDOA | aldolase A |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| AP-1 | activator protein 1 |
| ARDS | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| bFGF | basic fibroblast growth factor |
| CAFs | cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| cGMP | cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| CGRP | calcitonin gene-related peptide |
| CLR | calcitonin receptor-like receptor |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CO | cardiac output |
| CRLR | calcitonin receptor-like receptor |
| DC | dendritic cell |
| E-cadherin | epithelial cadherin |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| EOC | epithelial ovarian cancer |
| Epac-Rap1 | exchange protein directly activated by Rap1 |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| ESCC | esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| FAK | focal adhesion kinase |
| GABA-A receptor | γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor |
| GC | gastric cancer |
| GPCRs | G protein-coupled receptors |
| GSK3β | glycogen synthase kinase 3β |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HIF | hypoxia-inducible factor |
| HSL | hormone-sensitive lipase |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| IFN-γ | interferon-γ |
| IL-1 | interleukin-1 |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MCs | macrophages |
| MDSCs | myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| MMPs | matrix metalloproteinases |
| MR-proADM | mid-regional pro-ADM |
| MVD | microvessel density |
| N-cadherin | neural cadherin |
| NLRP3 | NOD−, LRR− and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| OH | obese hypertensive |
| PDGF | platelet-derived growth factor |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PKA | protein kinase A |
| PLC-PKC | phospholipase C-protein kinase C |
| PVN | paraventricular nucleus |
| RAMP | receptor activity-modifying protein |
| RANKL | receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand |
| RCC | renal cell carcinoma |
| SHP-2 | Src homology phosphotyrosyl phosphatase 2 |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TAMs | tumor-associated macrophages |
| TGF-β1 | transforming growth factor-β1 |
| Th1 | T-helper 1 |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| TMZ | temozolomide |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| Treg | regulatory T cells |
| TRPV2 | transient receptor potential vanilloid 2 |
| TSCC | tongue squamous cell carcinoma |
| UCP1 | uncoupling protein 1 |
| VCAM-1 | vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VE-cadherin | vascular endothelial cadherin |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
References
- Kangawa, K.; Kitamura, K.; Minamino, N.; Eto, T.; Matsuo, H. Adrenomedullin: A new hypotensive peptide. J. Hypertens. Suppl. 1996, 14, S105–S110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, K.; Kangawa, K.; Kawamoto, M.; Ichiki, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Matsuo, H.; Eto, T. Adrenomedullin: A novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 192, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, Y.; Nagata, S.; Akashi, E.; Yamasaki, M.; Kitamura, K. Thrombin rapidly digests adrenomedullin: Synthesis of adrenomedullin analogs resistant to thrombin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 529, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Tanaka, M.; Sakurai, T.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Kawate, H.; Cui, N.; Kakihara, S.; Zhao, Y.; Aruga, K.; et al. Adrenomedullin Ameliorates Pulmonary Fibrosis by Regulating TGF-ß-Smads Signaling and Myofibroblast Differentiation. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirişci, M.; Gunes, H.; Kocarslan, A.; Metin, T.O.; Aykan, D.A.; Seyithanoglu, M.; Doganer, A.; Bayrak, G.; Aksu, E. Protective Effects of Adrenomedullin on Rat Cerebral Tissue After Transient Bilateral Common Carotid Artery Occlusion and Reperfusion. Braz. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 35, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikimi, T.; Nakagawa, Y. Adrenomedullin as a Biomarker of Heart Failure. Heart Fail. Clin. 2018, 14, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otao, G.; Maruta, T.; Yonaha, T.; Igarashi, K.; Nagata, S.; Kitamura, K.; Tsuneyoshi, I. The usefulness of plasma levels of mature and total adrenomedullin as biomarkers indicating the magnitude of surgical stress responses: A single-center, prospective, observational study. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2021, 7, 302–310. [Google Scholar]
- Ihara, M.; Washida, K.; Yoshimoto, T.; Saito, S. Adrenomedullin: A vasoactive agent for sporadic and hereditary vascular cognitive impairment. Cereb. Circ. Cogn. Behav. 2021, 2, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Chen, G.; Rodriguez, E.L.; Klein, J.D.; Sands, J.M.; Wang, Y. Adrenomedullin Inhibits Osmotic Water Permeability in Rat Inner Medullary Collecting Ducts. Cells 2020, 9, 2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoto, S.; Basili, S.; Cangemi, R.; Yuste, J.R.; Lucena, F.; Romiti, G.F.; Raparelli, V.; Argemi, J.; D’Avanzo, G.; Locorriere, L.; et al. A Focus on the Pathophysiology of Adrenomedullin Expression: Endothelitis and Organ Damage in Severe Viral and Bacterial Infections. Cells 2024, 13, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyahia, Z.; Gaudy-Marqueste, C.; Berenguer-Daizé, C.; Chabane, N.; Dussault, N.; Cayol, M.; Vellutini, C.; Djemli, A.; Nanni, I.; Beaufils, N.; et al. Adrenomedullin Secreted by Melanoma Cells Promotes Melanoma Tumor Growth through Angiogenesis and Lymphangiogenesis. Cancers 2022, 14, 5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solé-Ribalta, A.; Bobillo-Pérez, S.; Jordan-García, I. A Review of Adrenomedullin in Pediatric Patients: A Useful Biomarker. Children 2022, 9, 1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.; Wang, Q.; Wang, F.-Z.; Dai, H.-B.; Wang, H.-Y.; Gao, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhou, Y.-B. Adrenomedullin Improves Cardiac Remodeling and Function in Obese Rats with Hypertension. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojan, G.; Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Grzeszczuk, A.; Czupryna, P. Adrenomedullin as a New Prosperous Biomarker in Infections: Current and Future Perspectives. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashizuka, S.; Kita, T.; Inatsu, H.; Kitamura, K. Adrenomedullin: A Novel Therapeutic for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Lier, D.; Kox, M.; Pickkers, P. Promotion of vascular integrity in sepsis through modulation of bioactive adrenomedullin and dipeptidyl peptidase 3. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 289, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetomi, R.; Ohta, Y.; Akiyama, M.; Matsumura, T.; Taguchi, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Kamatani, T.; Tanizawa, Y. Adrenomedullin has a cytoprotective role against endoplasmic reticulum stress for pancreatic β-cells in autocrine and paracrine manners. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 823–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xiong, X.; Wang, X. HIF1α/miR-199a/ADM feedback loop modulates the proliferation of human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMECs) under hypoxic condition. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 2998–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benyahia, Z.; Dussault, N.; Cayol, M.; Sigaud, R.; Berenguer-Daizé, C.; Delfino, C.; Tounsi, A.; Garcia, S.; Martin, P.-M.; Mabrouk, K.; et al. Stromal fibroblasts present in breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through adrenomedullin secretion. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15744–15762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, A.; Roquid, K.A.; Iring, A.; Strilic, B.; Günther, S.; Chen, M.; Weinstein, L.S.; Offermanns, S. Suppression of CCL2 angiocrine function by adrenomedullin promotes tumor growth. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20211628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Wang, X.; Gong, Z.; Yu, M.; Wu, H.; Zhang, D. Exosome-mediated metabolic reprogramming: The emerging role in tumor microenvironment remodeling and its influence on cancer progression. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velard, F.; Chatron-Colliet, A.; Côme, D.; Ah-Kioon, M.-D.; Lin, H.; Hafsia, N.; Cohen-Solal, M.; Ea, H.-K.; Lioté, F. Adrenomedullin and truncated peptide adrenomedullin(22-52) affect chondrocyte response to apoptotis in vitro: Downregulation of FAS protects chondrocyte from cell death. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Wan, Q.; Seo, G.-Y.; Kim, K.; El Baghdady, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kronenberg, M.; Liu, Y.-C. Hypoxia induces adrenomedullin from lung epithelia, stimulating ILC2 inflammation and immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20211985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Kong, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Q. The Immune Regulatory Mechanism of Adrenomedullin on Promoting the Proliferation and Differentiation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Int. Dent. J. 2024, 74, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuerle, J.; Farouque, O.; Vasanthakumar, S.; Patel, S.K.; Burrell, L.M.; Clark, D.J.; Al-Fiadh, A.H. Plasma endothelin-1 and adrenomedullin are associated with coronary artery function and cardiovascular outcomes in humans. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 291, 168–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonura, A.; Brunelli, N.; Marcosano, M.; Iaccarino, G.; Fofi, L.; Vernieri, F.; Altamura, C. Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Systemic Effects: Embracing the Complexity of Its Biological Roles—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cognet, G.; Muir, A. Identifying metabolic limitations in the tumor microenvironment. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadq7305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaglia, P.; Gonzaga, N.A.; Tirapelli, D.P.C.; Tirapelli, L.F.; Tirapelli, C.R. Pharmacological characterisation of the mechanisms underlying the relaxant effect of adrenomedullin in the rat carotid artery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 1734–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Zappa, C.; Ferraresi, A.; Santiemma, V. Adrenomedullin inhibits angiotensin II-induced contraction in human aortic smooth muscle cells. Regul. Pept. 2006, 133, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terata, K.; Miura, H.; Liu, Y.; Loberiza, F.; Gutterman, D.D. Human coronary arteriolar dilation to adrenomedullin: Role of nitric oxide and K(+) channels. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 279, H2620–H2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, G.R.; Yallampalli, U.; Gangula, P.R.R.; Reed, L.; Sathishkumar, K.; Gao, H.; Chauhan, M.; Yallampalli, C. Adrenomedullin relaxes rat uterine artery: Mechanisms and influence of pregnancy and estradiol. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 4485–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimatsu, H.; Suzuki, E.; Nagata, D.; Moriyama, N.; Satonaka, H.; Walsh, K.; Sata, M.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H.; Goto, A.; et al. Adrenomedullin induces endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway in rat aorta. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, R.; Mitsui-Saito, M.; Ozaki, H.; Karaki, H. Effects of adrenomedullin and calcitonin gene-related peptide on contractions of the rat aorta and porcine coronary artery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimekake, Y.; Nagata, K.; Ohta, S.; Kambayashi, Y.; Teraoka, H.; Kitamura, K.; Eto, T.; Kangawa, K.; Matsuo, H. Adrenomedullin stimulates two signal transduction pathways, cAMP accumulation and Ca2+ mobilization, in bovine aortic endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 4412–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-Z.; Qian, P.; Liu, M.-Y.; Ding, L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Z.-Y.; Jin, F.-Y.; Li, R.-G.; Zhou, Y.-B. Adrenomedullin in paraventricular nucleus attenuates adipose afferent reflex and sympathoexcitation via receptors mediated nitric oxide-gamma-aminobutyric acid A type receptor pathway in rats with obesity-related hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2023, 41, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hupf, J.; Mustroph, J.; Hanses, F.; Evert, K.; Maier, L.S.; Jungbauer, C.G. RNA-expression of adrenomedullin is increased in patients with severe COVID-19. Crit. Care 2020, 24, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, A.; Toriyama, Y.; Iesato, Y.; Hirabayashi, K.; Sakurai, T.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Kawate, H.; Tanaka, M.; Liu, T.; et al. Adrenomedullin Suppresses Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-Induced Vascular Hyperpermeability and Inflammation in Retinopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 999–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajith Kumar, A.K. Adrenomedullin in Sepsis: Finally, a Friend or an Enemy? Indian. J. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 24, 1151–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interdonato, L.; D’Amico, R.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Fusco, R.; Peritore, A.F.; Gugliandolo, E.; Crupi, R.; Coaccioli, S.; Genovese, T.; et al. Aerosol-Administered Adelmidrol Attenuates Lung Inflammation in a Murine Model of Acute Lung Injury. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Ponce, A.; Chánez Paredes, S.; Castro Ochoa, K.F.; Schnoor, M. Regulation of endothelial and epithelial barrier functions by peptide hormones of the adrenomedullin family. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1228439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.-B.; Wang, F.-Z.; Kang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhou, H.; Gao, Q.; Li, Z.-Z.; Qian, P.; Zhu, G.-Q.; Zhou, Y.-B. Adrenomedullin Attenuates Inflammation in White Adipose Tissue of Obese Rats Through Receptor-Mediated PKA Pathway. Obesity 2021, 29, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, G.; Angeli, D.; Petracci, E.; Fonzi, E.; Vedovato, S.; Sperotto, A.; Padella, A.; Ghetti, M.; Ferrari, A.; Robustelli, V.; et al. Adrenomedullin Expression Characterizes Leukemia Stem Cells and Associates with an Inflammatory Signature in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 684396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasahara, T.; Tanaka, M.; Zhao, Y.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Sakurai, T.; Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Kawate, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Q.; et al. Receptor activity-modifying proteins of adrenomedullin (RAMP2/3): Roles in the pathogenesis of ARDS. Peptides 2024, 171, 171118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, N.; Sakurai, T.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Kawate, H.; Tanaka, M.; Tanaka, M.; Wei, Y.; Kakihara, S.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Adrenomedullin-RAMP2 and -RAMP3 Systems Regulate Cardiac Homeostasis during Cardiovascular Stress. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqab001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A. Significance of adrenomedullin and the role of adrecizumab in sepsis. Saudi J. Anaesth. 2021, 15, 228–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Kong, L.; Wang, W.; Shi, L.; Wang, M.; Chai, Y.; Xu, J.; Kang, Q. Adrenomedullin 2 improves bone regeneration in type 1 diabetic rats by restoring imbalanced macrophage polarization and impaired osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Ji, C.; Liu, X.; Gu, B.; Dong, T. Macrophage polarization in the tumor microenvironment: Emerging roles and therapeutic potentials. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 116930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhou, P.-h.; Rao, T.; Zhang, X.-b.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.-j. Adrenomedullin attenuates interleukin-1β-induced inflammation and apoptosis in rat Leydig cells via inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 339, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, A.; Lunding, L.P.; Zissler, U.M.; Vock, C.; Webering, S.; Ehlers, J.C.; Orinska, Z.; Chaker, A.; Schmidt-Weber, C.B.; Lang, N.J.; et al. IL-37 regulates allergic inflammation by counterbalancing pro-inflammatory IL-1 and IL-33. Allergy 2022, 77, 856–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, E.; Kantharidis, P.; Cooper, M.E.; Godson, C. Pro-resolving lipid mediators: Regulators of inflammation, metabolism and kidney function. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 725–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palit, S.; Shrestha, A.K.; Thapa, S.; L Grimm, S.; Coarfa, C.; Theis, F.; Simon, L.M.; Shivanna, B. Leveraging Integrated RNA Sequencing to Decipher Adrenomedullin’s Protective Mechanisms in Experimental Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Genes 2024, 15, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.-N.; Kitamura, K.; Kato, J.; Kuwasako, K.; Ito, K.; Onitsuka, H.; Nagoshi, Y.; Uemura, T.; Kita, T.; Eto, T. Chronic salt loading upregulates expression of adrenomedullin and its receptors in adrenal glands and kidneys of the rat. Hypertension 2003, 42, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, H.M.; Krilis, G.; Grenier, C.; Severs, D.; Czopek, A.; Ivy, J.R.; Nixon, M.; Holmes, M.C.; Livingstone, D.E.W.; Hoorn, E.J.; et al. High salt intake activates the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, amplifies the stress response, and alters tissue glucocorticoid exposure in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2023, 119, 1740–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogbe-Díaz, M.E.; Díaz-López, E.E. Adrenomedullin in the kidney: Physiology and pathophysiology. Invest. Clin. 2016, 57, 66–76. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.-L.; Chen, S.-L.; Huang, Y.-H.; Yang, X.; Wang, C.-H.; He, J.-H.; Yun, J.-P.; Luo, R.-Z. Adrenomedullin inhibits tumor metastasis and is associated with good prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 773–786. [Google Scholar]
- Giannakoulas, A.; Stoikos, P.; Kouvata, E.; Kontouli, K.M.; Fotiadis, G.; Stefani, G.; Amoutzias, G.D.; Vassilopoulos, G.; Giannakoulas, N. Angiogenesis and multiple myeloma: Exploring prognostic potential of adrenomedullin. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e70250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Lin, D.-W.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Z.-X.; Wang, Y.-S. Relationship Between Serum Concentration of Adrenomedullin and Myocardial Ischemic T Wave Changes in Patients with Lung Cancer. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 836993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezelius, E.; Bendahl, P.-O.; Gallo, W.; de Oliveira, K.G.; Ek, L.; Bergman, B.; Sundberg, J.; Melander, O.; Belting, M. Circulating Levels of the Cardiovascular Biomarkers ST2 and Adrenomedullin Predict Outcome within a Randomized Phase III Lung Cancer Trial (RASTEN). Cancers 2022, 14, 1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardero, M.; Kovacs, K.; Horvath, E.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Rotondo, F.; Salehi, F.; Lloyd, R.V. Adrenomedullin expression in pituitary adenomas and nontumoral adenohypophyses. Histol. Histopathol. 2008, 23, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic microenvironment in cancer: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, K.; Hana, D.; Chou, J.T.-T.; Singh, C.; Mackiewicz, A.; Kaczmarek, M. Aspects of the Tumor Microenvironment Involved in Immune Resistance and Drug Resistance. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 656364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maia, L.d.L.; Peterle, G.T.; Dos Santos, M.; Trivilin, L.O.; Mendes, S.O.; de Oliveira, M.M.; Dos Santos, J.G.; Stur, E.; Agostini, L.P.; Couto, C.V.M.d.S.; et al. JMJD1A, H3K9me1, H3K9me2 and ADM expression as prognostic markers in oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldogazieva, N.T.; Mokhosoev, I.M.; Terentiev, A.A. Metabolic Heterogeneity of Cancer Cells: An Interplay between HIF-1, GLUTs, and AMPK. Cancers 2020, 12, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Huang, Y.; Bong, R.; Ding, Y.; Song, N.; Wang, X.; Song, X.; Luo, Y. Tumor-associated macrophages promote angiogenesis and melanoma growth via adrenomedullin in a paracrine and autocrine manner. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 7230–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paré, M.; Darini, C.Y.; Yao, X.; Chignon-Sicard, B.; Rekima, S.; Lachambre, S.; Virolle, V.; Aguilar-Mahecha, A.; Basik, M.; Dani, C.; et al. Breast cancer mammospheres secrete Adrenomedullin to induce lipolysis and browning of adjacent adipocytes. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.-g.; Zhang, X.-z.; Li, F.-b.; Zhao, Y.-l.; Guo, Y.-c.; Yang, R.-m. RNA interference targeting adrenomedullin induces apoptosis and reduces the growth of human bladder urothelial cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, J.; Pang, X.; Dong, M. Adrenomedullin promotes angiogenesis in epithelial ovarian cancer through upregulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, A.; Vos, M.; Guédez, L.; Kaur, G.; Chen, Z.; Garayoa, M.; Pío, R.; Moody, T.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G.; Kleinman, H.K.; et al. The effects of adrenomedullin overexpression in breast tumor cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, K.K.; Yalçın, Y.; Erdemoğlu, E.; Tatar, B.; Erdemoğlu, E.; Çerçi, S.S.; Çiriş, İ.M.; Başpınar, Ş.; Uğuz, A.; Kapucuoğlu, N. The role of immunohistochemical adrenomedullin and Bcl-2 expression in development of type-1 endometrial adenocarcinoma: Adrenomedullin expression in endometrium. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2016, 212, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Tao, J.; Yang, X.; Ye, L.; Wu, Y.; He, Q.; Duan, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhu, J. HVEM/HIF-1α promoted proliferation and inhibited apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells under hypoxic microenvironment conditions. J. Ovarian Res. 2020, 13, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, F.; Fang, J.; Xu, J.; Zhao, W.; Ni, Y.; Akuo, B.A.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Ding, F.; Li, G.; et al. The role of adrenomedullin in the pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88464–88474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.-P.; Peng, L.-S.; Wang, Q.-H.; Chen, N.; Teng, Y.-S.; Wang, T.-T.; Mao, F.-Y.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Cheng, P.; Liu, Y.-G.; et al. Degranulation of mast cells induced by gastric cancer-derived adrenomedullin prompts gastric cancer progression. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Han, X.; He, X.; Dai, X. Downregulation of Adrenomedullin Leads to the Inhibition of the Tumorigenesis via VEGF Pathway in Human and Nude Mice Osteosarcoma Models. Arch. Med. Res. 2019, 50, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Qiao, N.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Jia, J.; Yang, S.; Qu, C.; Li, W.; et al. Adrenomedullin blockade suppresses sunitinib-resistant renal cell carcinoma growth by targeting the ERK/MAPK pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63374–63387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greillier, L.; Tounsi, A.; Berenguer-Daizé, C.; Dussault, N.; Delfino, C.; Benyahia, Z.; Cayol, M.; Mabrouk, K.; Garcia, S.; Martin, P.-M.; et al. Functional Analysis of the Adrenomedullin Pathway in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.-W.; Zhu, X.-L.; Li, M.-Y.; Zhou, J.-H.; Yang, Z.-M.; Tong, T.; Chen, B.-H.; Qin, S.-L.; Liu, B.-L.; Hu, W. Anti-apoptotic effect of adrenomedullin gene delivery on Leydig cells by suppressing TGF-β1 via the Hippo signaling pathway. Reprod. Toxicol. 2023, 119, 108418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, S.W.; Ong, C.; Hong, W. The recent advances and implications in cancer therapy for the hippo pathway. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2025, 93, 102476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.D.; Seano, G.; Jain, R.K. Normalizing Function of Tumor Vessels: Progress, Opportunities, and Challenges. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2019, 81, 505–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Qi, F.; Zhang, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Fu, Y.; Luo, Y. Adrenomedullin promotes the growth of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through recruitment of myelomonocytic cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55043–55056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Tian, X.; Yuan, J.; Jin, Y.; Tan, Y. Relationship of adrenomedullin expression and microvessel density and prognosis in smooth muscle tumor of uterus. Front. Med. China 2007, 1, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, P.; Pang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Adrenomedullin Up-regulates the Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma Cells via JNK/AP-1 Pathway. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2015, 25, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shen, M.; Wu, L.; Yang, H.; Yao, Y.; Yang, Q.; Du, J.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y. Stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment: Accomplices of tumor progression? Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussard, K.M.; Mutkus, L.; Stumpf, K.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Marini, F.C. Tumor-associated stromal cells as key contributors to the tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallavalasa, S.; Beeraka, N.M.; Basavaraju, C.G.; Tulimilli, S.V.; Sadhu, S.P.; Rajesh, K.; Aliev, G.; Madhunapantula, S.V. The Role of Tumor Associated Macrophages (TAMs) in Cancer Progression, Chemoresistance, Angiogenesis and Metastasis—Current Status. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 8203–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, K.; Lin, J.; Li, J.; Bi, J. Macrophage M2 Co-expression Factors Correlate with the Immune Microenvironment and Predict Outcome of Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 615655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, K.; Wang, J.; Lin, J.; Bi, J. M2 Macrophage Co-Expression Factors Correlate with Immune Phenotype and Predict Prognosis of Bladder Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 609334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, C.; Liang, Y.; Yang, C.; Xiao, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Shu, J.; Tian, X.; et al. Exosomal miR-301a-3p from esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells promotes angiogenesis by inducing M2 polarization of macrophages via the PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, C.; Xie, H.; Fan, Y.; Yang, Z.; Ma, J.; He, D.; Li, L. Infiltrating mast cells promote renal cell carcinoma angiogenesis by modulating PI3K→︀AKT→︀GSK3β→︀AM signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, T.; Tanaka, M.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Kawate, H.; Sakurai, T. Receptor Activity Modifying Protein RAMP Sub-Isoforms and Their Functional Differentiation, Which Regulates Functional Diversity of Adrenomedullin. Biology 2022, 11, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, T.; Tanaka, M.; Kamiyoshi, A.; Ichikawa-Shindo, Y.; Kawate, H.; Yamauchi, A.; Sakurai, T. Regulation of cardiovascular development and homeostasis by the adrenomedullin-RAMP system. Peptides 2019, 111, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigaud, R.; Dussault, N.; Berenguer-Daizé, C.; Vellutini, C.; Benyahia, Z.; Cayol, M.; Parat, F.; Mabrouk, K.; Vázquez, R.; Riveiro, M.E.; et al. Role of the Tyrosine Phosphatase SHP-2 in Mediating Adrenomedullin Proangiogenic Activity in Solid Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 753244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfaoui-Bendriss, G.; Dussault, N.; Fernandez-Sauze, S.; Berenguer-Daizé, C.; Sigaud, R.; Delfino, C.; Cayol, M.; Metellus, P.; Chinot, O.; Mabrouk, K.; et al. Adrenomedullin blockade induces regression of tumor neovessels through interference with vascular endothelial-cadherin signalling. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7536–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, R.; Riveiro, M.E.; Berenguer-Daizé, C.; O’Kane, A.; Gormley, J.; Touzelet, O.; Rezai, K.; Bekradda, M.; Ouafik, L.H. Targeting Adrenomedullin in Oncology: A Feasible Strategy with Potential as Much More Than an Alternative Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 589218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, L.; Lu, E.; Tian, D.; Li, F.; Deng, L.; Zhang, Y. Adrenomedullin induces cisplatin chemoresistance in ovarian cancer through reprogramming of glucose metabolism. J. Transl. Int. Med. 2023, 11, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepizhko, O.; Armengol-Collado, J.-M.; Alexander, S.; Wagena, E.; Weigelin, B.; Giomi, L.; Friedl, P.; Zapperi, S.; La Porta, C.A.M. Confined cell migration along extracellular matrix space in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2025, 122, e2414009121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikosaka, T.; Tsuruda, T.; Nagata, S.; Kuwasako, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Hoshiko, S.; Inatsu, H.; Chijiiwa, K.; Kitamura, K. Adrenomedullin production is increased in colorectal adenocarcinomas; its relation to matrix metalloproteinase-9. Peptides 2011, 32, 1825–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulidi, A.; Bokhobza, A.; Gkika, D.; Vanden Abeele, F.; Lehen’kyi, V.y.; Ouafik, L.h.; Mauroy, B.; Prevarskaya, N. TRPV2 mediates adrenomedullin stimulation of prostate and urothelial cancer cell adhesion, migration and invasion. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zheng, Y.; Li, L.; Zhai, W.; Li, R.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, L. Adrenomedullin promotes intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma metastasis and invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Cheng, M.; Hu, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, P.; Chen, L.; Cao, D.; Tang, J. miR-1297 sensitizes glioma cells to temozolomide (TMZ) treatment through targeting adrenomedullin (ADM). J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouafik, L.H.; Sauze, S.; Boudouresque, F.; Chinot, O.; Delfino, C.; Fina, F.; Vuaroqueaux, V.; Dussert, C.; Palmari, J.; Dufour, H.; et al. Neutralization of adrenomedullin inhibits the growth of human glioblastoma cell lines in vitro and suppresses tumor xenograft growth in vivo. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 1279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jailani, A.B.A.; Bigos, K.J.A.; Avgoustou, P.; Egan, J.L.; Hathway, R.A.; Skerry, T.M.; Richards, G.O. Targeting the adrenomedullin-2 receptor for the discovery and development of novel anti-cancer agents. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov. 2022, 17, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.L.; Hsu, S.Y.T. Development of chimeric and bifunctional antagonists for CLR/RAMP receptors. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avgoustou, P.; Jailani, A.B.A.; Zirimwabagabo, J.-O.; Tozer, M.J.; Gibson, K.R.; Glossop, P.A.; Mills, J.E.J.; Porter, R.A.; Blaney, P.; Bungay, P.J.; et al. Discovery of a First-in-Class Potent Small Molecule Antagonist against the Adrenomedullin-2 Receptor. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Geng, Y.-H.; Wang, P.; Zhang, H.-Q.; Fang, W.-G.; Tian, X.-X. Extracellular ATP promotes breast cancer chemoresistance via HIF-1α signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, W.; Shi, M.; Li, Y. Adrenomedullin in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125552
Li H, Yang W, Wang S, Zhao Z, Wang W, Shi M, Li Y. Adrenomedullin in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125552
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hanyi, Weijia Yang, Shiqi Wang, Zhihe Zhao, Wangyang Wang, Mingxuan Shi, and Yi Li. 2025. "Adrenomedullin in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125552
APA StyleLi, H., Yang, W., Wang, S., Zhao, Z., Wang, W., Shi, M., & Li, Y. (2025). Adrenomedullin in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125552




