Microneurotrophin BNN27 Exerts Significant Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Murine T-Lymphocytes Following CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
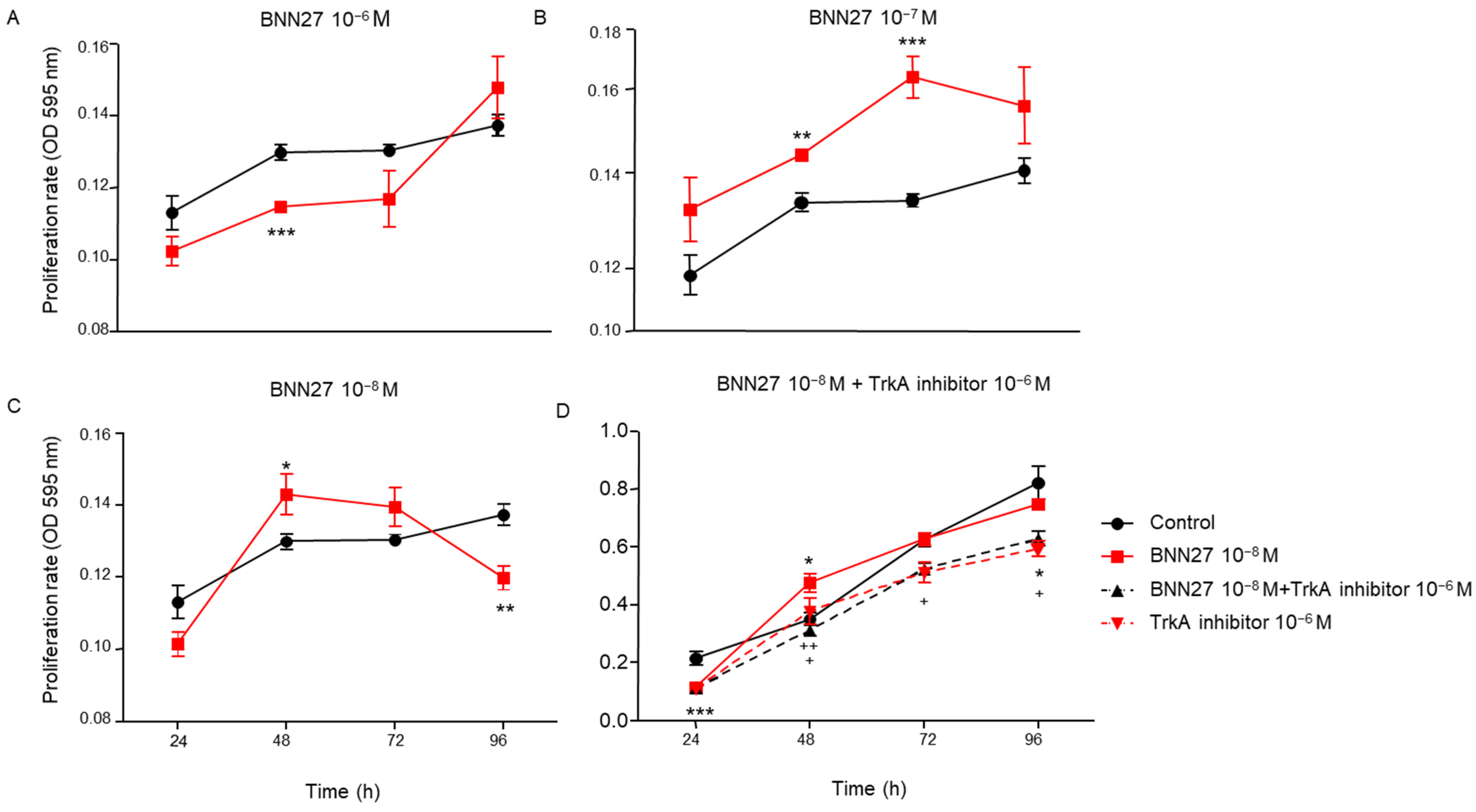
2.1. BNN27 Affected T Lymphocytes Proliferation in a Concentration-Dependent Manner
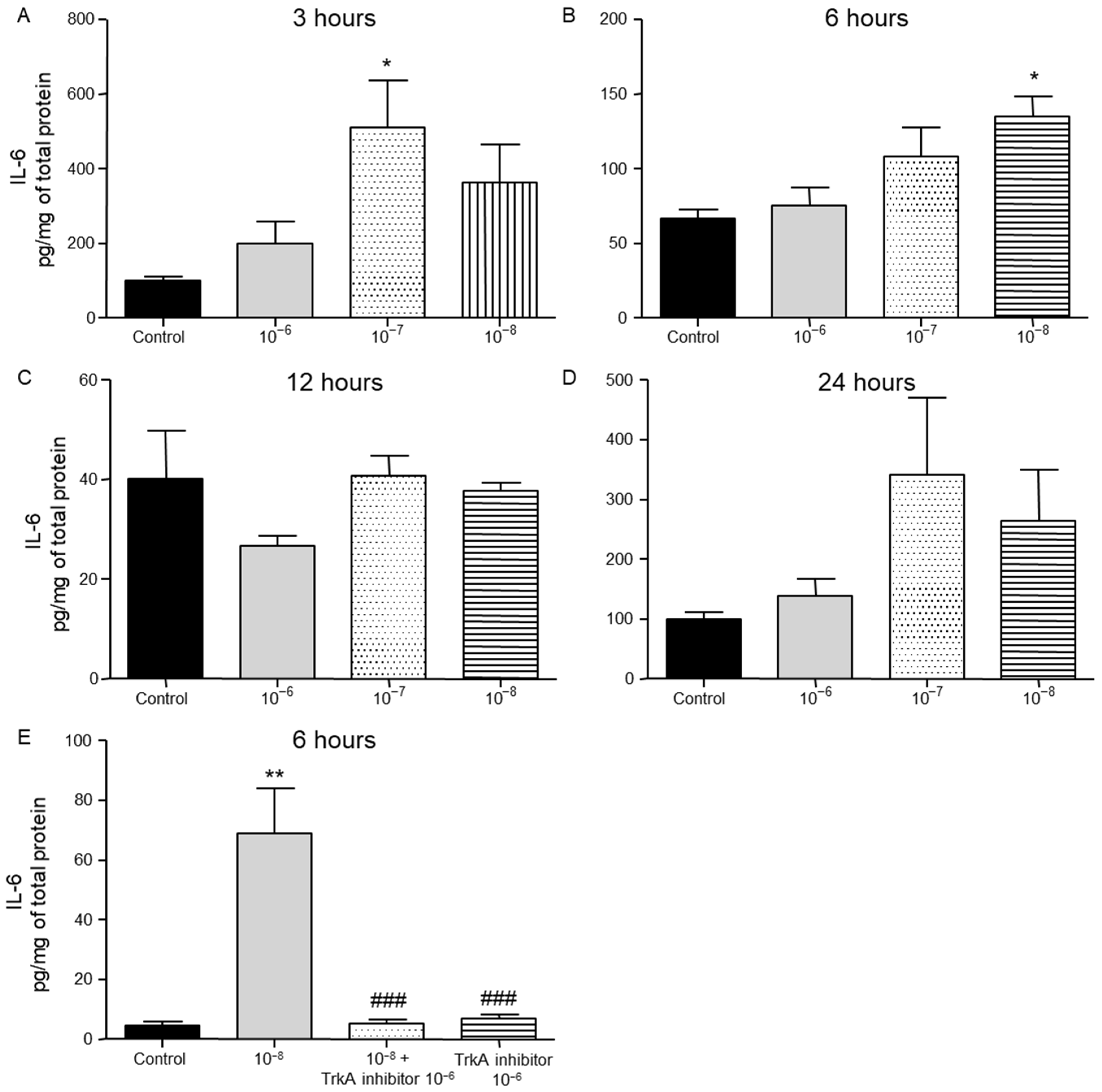
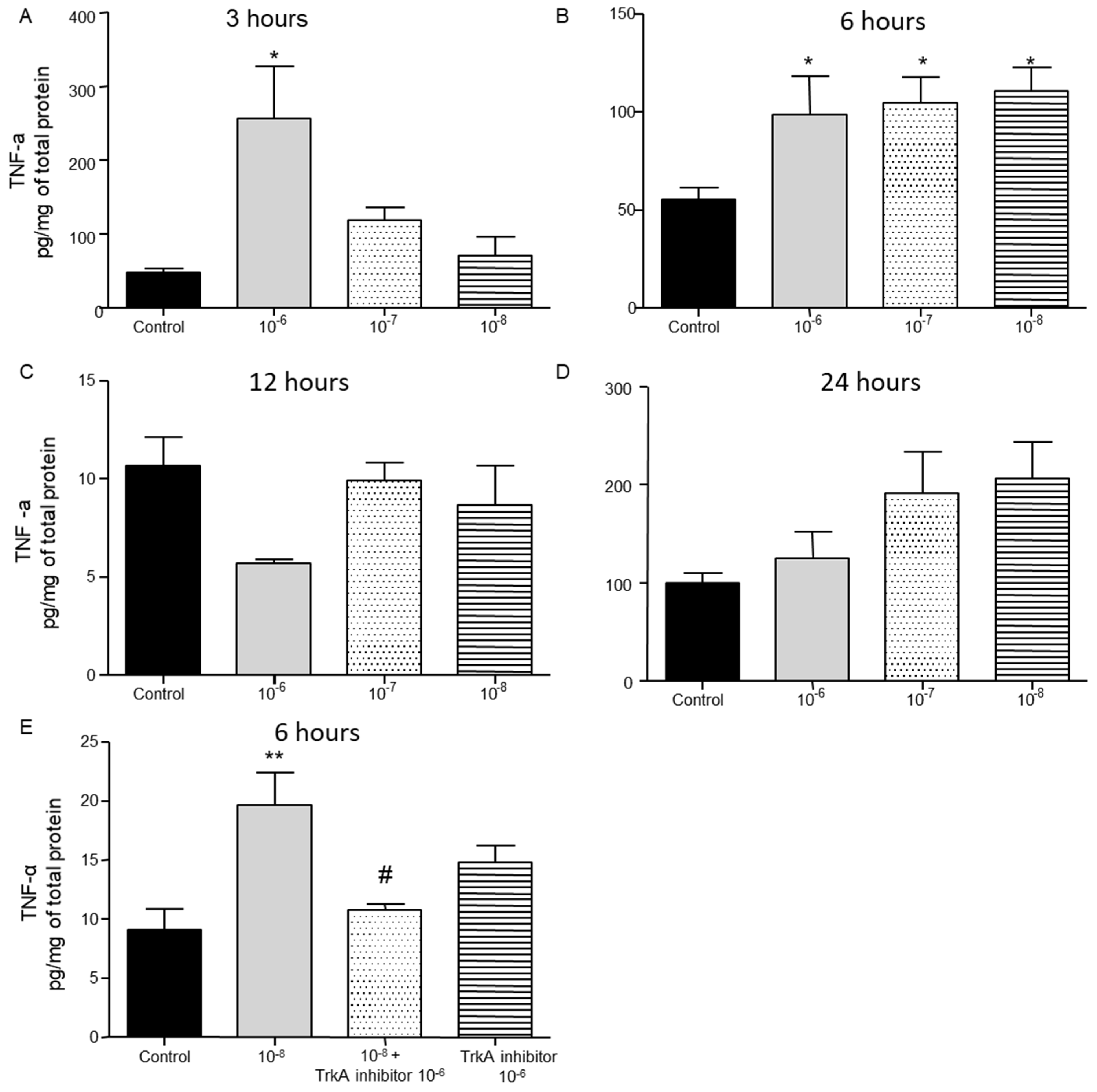
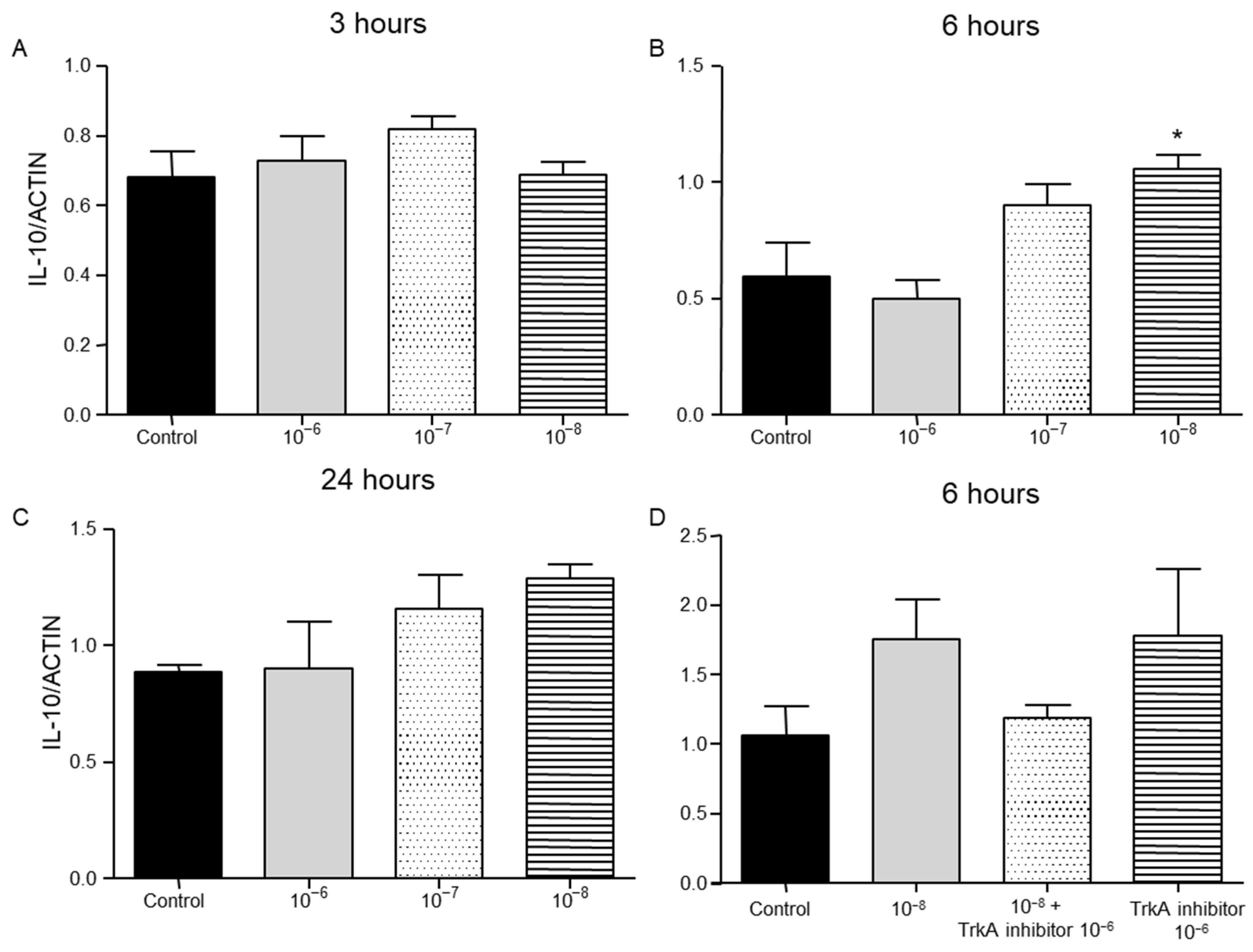
2.2. Effect of BNN27 on T Lymphocyte Secreted Cytokines
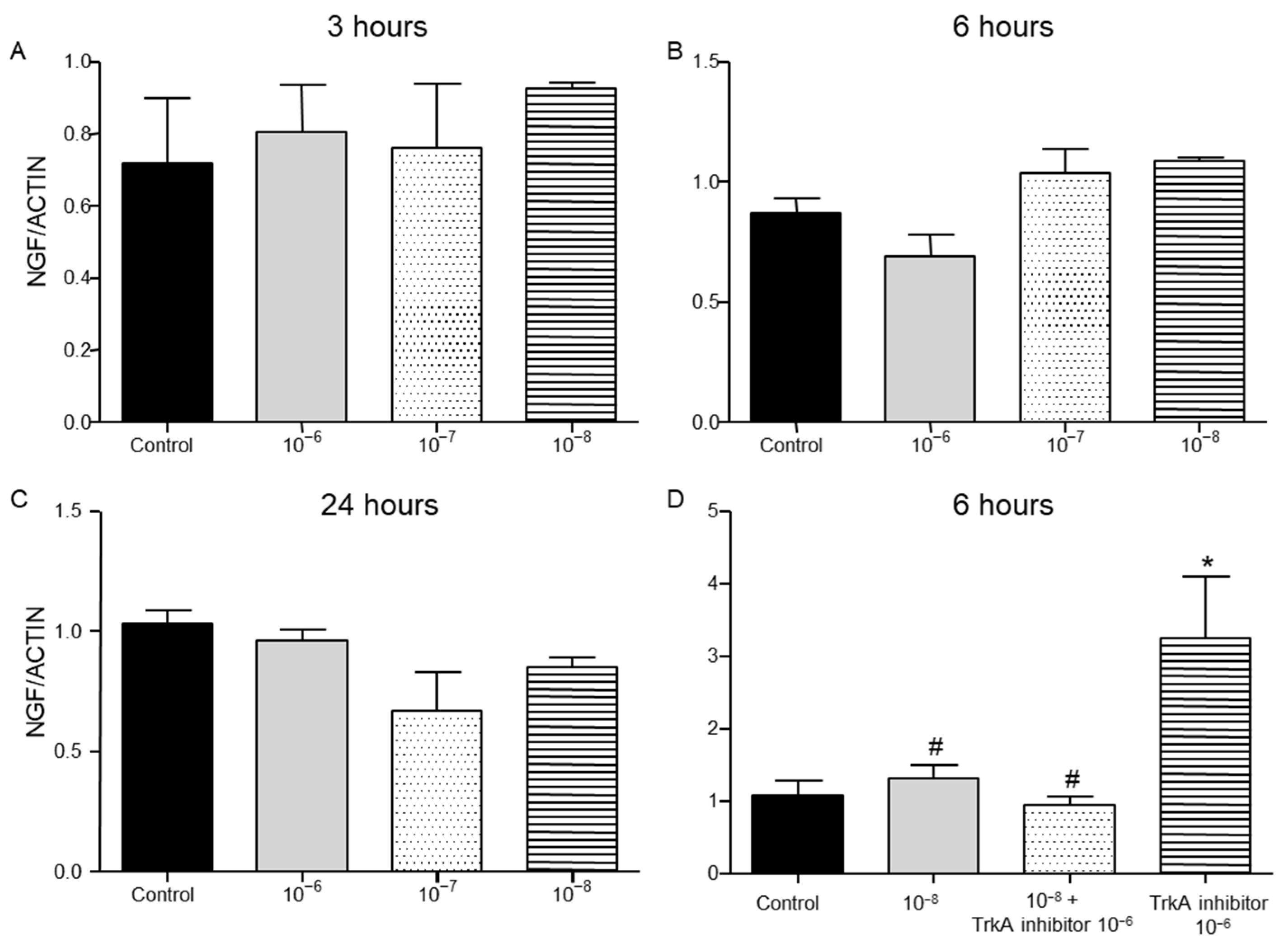
2.3. Effect of BNN27 on NGF and Its Receptor TrkA Synthesis by T Lymphocytes
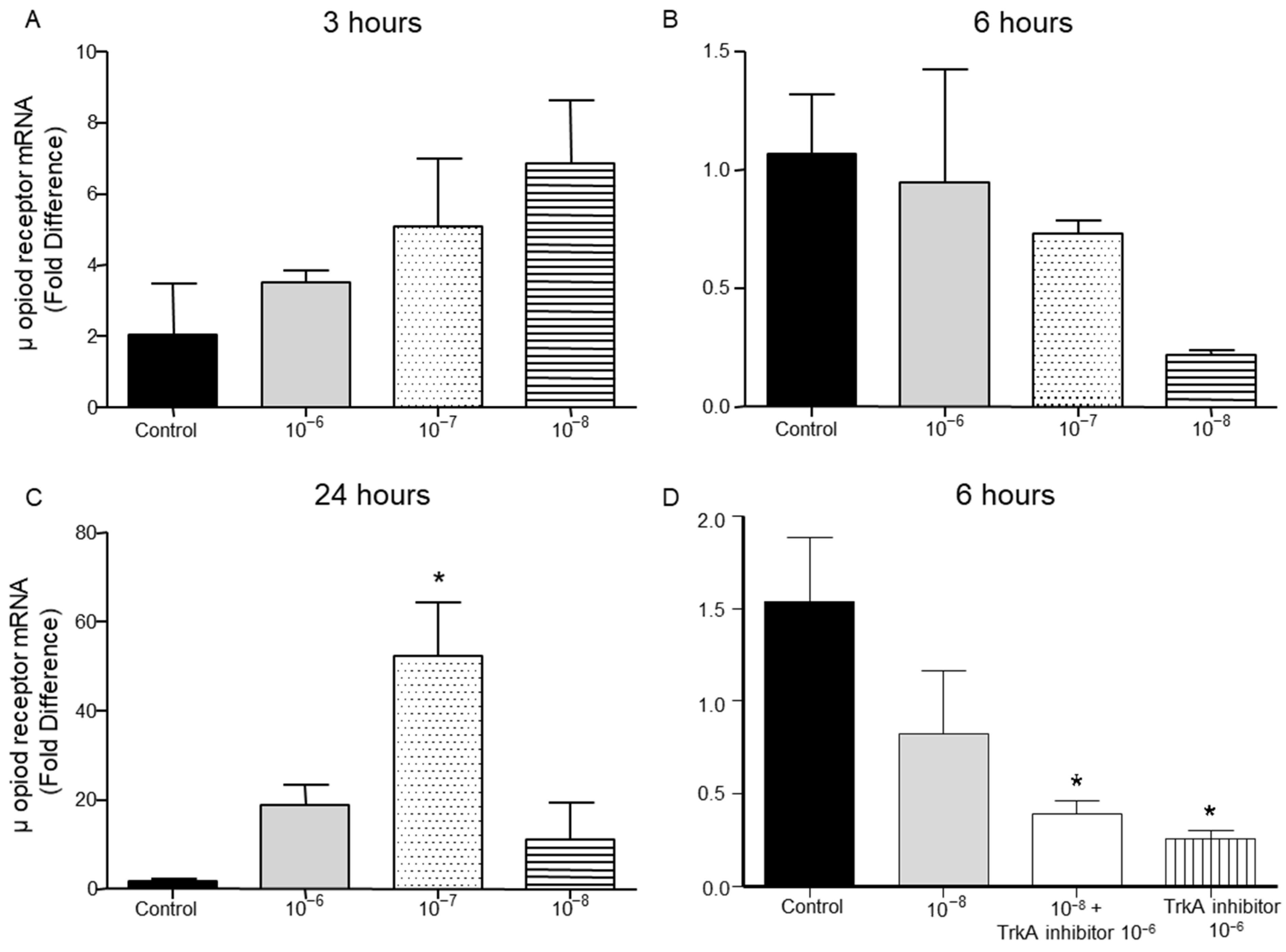
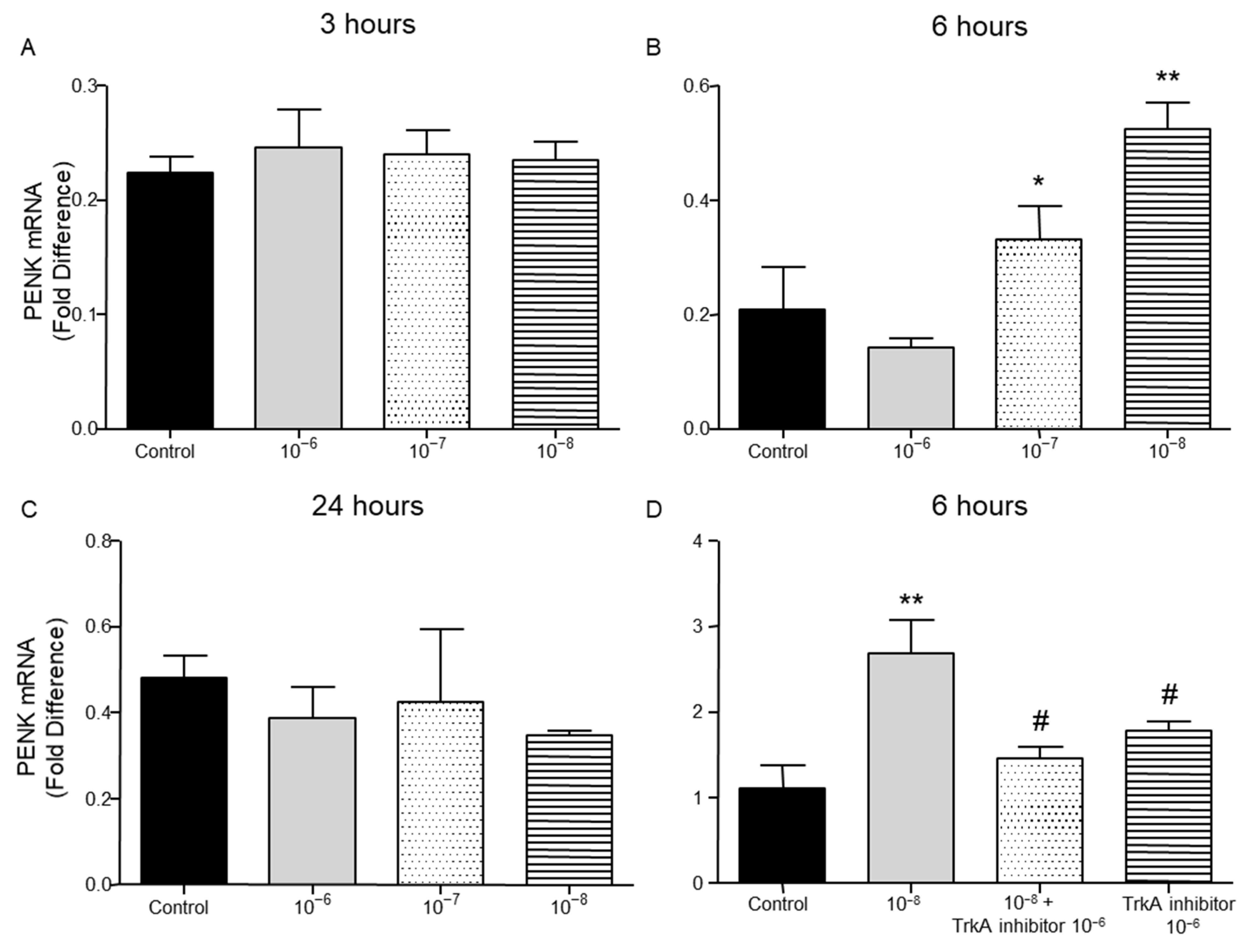
2.4. Effect of BNN27 on Opioids Synthesis by T Lymphocytes
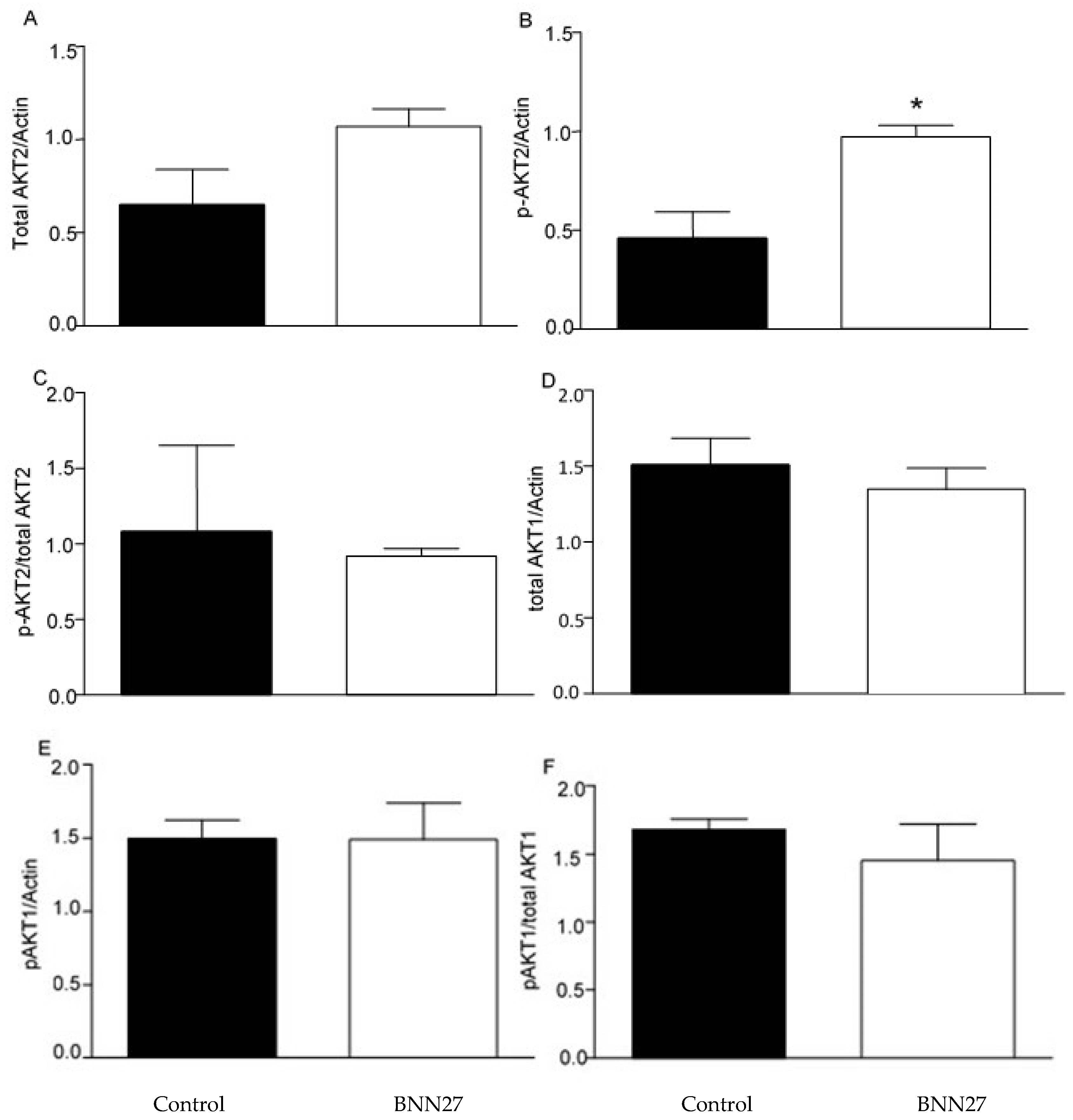
2.5. Effect of BNN27 on AKT Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Laboratory Animals
4.2. Induction of Inflammation and Harvest of Spleen Cells
4.3. Treatment with BNN27 and TrkA Inhibitor
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR, RT-PCR
4.5. Measurement of Cytokines
4.6. MTT and Trypan Blue Assays
4.7. Western Blot
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- LeBien, T.W.; Tedder, T.F. B lymphocytes: How they develop and function. Blood 2008, 112, 1570–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauri, C.; Bosma, A. Immune regulatory function of B cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Ohigashi, I.; Takahama, Y. Thymus machinery for T-cell selection. Int. Immunol. 2019, 31, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corthay, A. How do regulatory T cells work? Scand. J. Immunol. 2009, 70, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Flavell, R.A. Cell fate decision: T-helper 1 and 2 subsets in immune responses. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2000, 2, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigelin, B.; den Boer, A.T.; Wagena, E.; Broen, K.; Dolstra, H.; de Boer, R.J.; Figdor, C.G.; Textor, J.; Friedl, P. Cytotoxic T cells are able to efficiently eliminate cancer cells by additive cytotoxicity. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignali, D.A.; Collison, L.W.; Workman, C.J. How regulatory T cells work. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbach, K.; Vincenti, I.; Merkler, D. Resident-Memory T Cells in Tissue-Restricted Immune Responses: For Better or Worse? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Wing, K.; Onishi, Y.; Prieto-Martin, P.; Yamaguchi, T. Regulatory T cells: How do they suppress immune responses? Int. Immunol. 2009, 21, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro-Garcia, M.A.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; Alonso-Arias, R. Influence of Inflammation in the Process of T Lymphocyte Differentiation: Proliferative, Metabolic, and Oxidative Changes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cope, A.P. Studies of T-cell activation in chronic inflammation. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2002, 4 (Suppl. S3), S197–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, D.; Gross, S.; Harding, J.; Bokhari, S.; Niewiesk, S.; Lairmore, M.; Piwnica-Worms, D.; Ratner, L. T-cell activation promotes tumorigenesis in inflammation-associated cancer. Retrovirology 2009, 6, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmstrom, V.; Trollmo, C.; Klareskog, L. Modulating co-stimulation: A rational strategy in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7 (Suppl. S2), S15–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sakakura, Y.; Nakagawa, Y.; Ohzeki, T. Differential effect of DHEA on mitogen-induced proliferation of T and B lymphocytes. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 99, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T.; Suzuki, N.; Daynes, R.A.; Engleman, E.G. Dehydroepiandrosterone enhances IL2 production and cytotoxic effector function of human T cells. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1991, 61 Pt 1, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratschke, S.; von Dossow-Hanfstingl, V.; Dietz, J.; Schneider, C.P.; Tufman, A.; Albertsmeier, M.; Winter, H.; Angele, M.K. Dehydroepiandrosterone modulates T-cell response after major abdominal surgery. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 189, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, X.; Gui, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L. DHEA promotes osteoblast differentiation by regulating the expression of osteoblast-related genes and Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells. Biosci. Trends 2015, 9, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Dubner, R. Inflammatory Models of Pain and Hyperalgesia. ILAR J. 1999, 40, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittner, H.L.; Brack, A.; Machelska, H.; Mousa, S.A.; Bauer, M.; Schafer, M.; Stein, C. Opioid peptide-expressing leukocytes: Identification, recruitment, and simultaneously increasing inhibition of inflammatory pain. Anesthesiology 2001, 95, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pediaditakis, I.; Kourgiantaki, A.; Prousis, K.C.; Potamitis, C.; Xanthopoulos, K.P.; Zervou, M.; Calogeropoulou, T.; Charalampopoulos, I.; Gravanis, A. BNN27, a 17-Spiroepoxy Steroid Derivative, Interacts With and Activates p75 Neurotrophin Receptor, Rescuing Cerebellar Granule Neurons from Apoptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iban-Arias, R.; Lisa, S.; Mastrodimou, N.; Kokona, D.; Koulakis, E.; Iordanidou, P.; Kouvarakis, A.; Fothiadaki, M.; Papadogkonaki, S.; Sotiriou, A.; et al. The Synthetic Microneurotrophin BNN27 Affects Retinal Function in Rats With Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes. Diabetes 2018, 67, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pediaditakis, I.; Efstathopoulos, P.; Prousis, K.C.; Zervou, M.; Arevalo, J.C.; Alexaki, V.I.; Nikoletopoulou, V.; Karagianni, E.; Potamitis, C.; Tavernarakis, N.; et al. Selective and differential interactions of BNN27, a novel C17-spiroepoxy steroid derivative, with TrkA receptors, regulating neuronal survival and differentiation. Neuropharmacology 2016, 111, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, C.; Guan, Q.; Khalil, M.W.; Sriram, S. Stimulation of Th2 response by high doses of dehydroepiandrosterone in KLH-primed splenocytes. Exp. Biol. Med. 2001, 226, 1051–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daynes, R.A.; Dudley, D.J.; Araneo, B.A. Regulation of murine lymphokine production in vivo. II. Dehydroepiandrosterone is a natural enhancer of interleukin 2 synthesis by helper T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1990, 20, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danenberg, H.D.; Alpert, G.; Lustig, S.; Ben-Nathan, D. Dehydroepiandrosterone protects mice from endotoxin toxicity and reduces tumor necrosis factor production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1992, 36, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.F.; Tseng, J. Regulation of murine interleukin-10 production by dehydroepiandrosterone. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2000, 20, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Chapin, R.B.; Cain, K.J.; Charboneau, R.G.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Barke, R.A. Morphine inhibits transcriptional activation of IL-2 in mouse thymocytes. Cell. Immunol. 1997, 179, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Barke, R.A.; Loh, H.H. MU-opioid receptor-knockout mice: Role of µ-opioid receptor in morphine mediated immune functions. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1998, 61, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Barke, R.A.; Charboneau, R.; Loh, H.H.; Roy, S. Morphine negatively regulates interferon-γ promoter activity in activated murine T cells through two distinct cyclic AMP-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 37622–37631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J.; Borner, C.; Giannini, E.; Hickfang, K.; Braun, H.; Mayer, P.; Hoehe, M.R.; Ambrosch, A.; Konig, W.; Hollt, V. Regulation of µ-opioid receptor gene transcription by interleukin-4 and influence of an allelic variation within a STAT6 transcription factor binding site. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 43901–43908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, J.; Borner, C.; Giannini, E.; Hollt, V. The role of nuclear factor κB in tumor necrosis factor-regulated transcription of the human µ-opioid receptor gene. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulaki, S.; Rassouli, O.; Liapakis, G.; Gravanis, A.; Venihaki, M. Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of the Synthetic Neurosteroid Analogue BNN27 during CFA-Induced Hyperalgesia. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawrylowicz, C.M.; Klaus, G.G. Activation and proliferation signals in mouse B cells. IV. Concanavalin A stimulates B cells to leave G0, but not to proliferate. Immunology 1984, 53, 703–711. [Google Scholar]
- Kalia, V.; Sarkar, S. Regulation of Effector and Memory CD8 T Cell Differentiation by IL-2—A Balancing Act. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, S.H.; Cantrell, D.A. Signaling and Function of Interleukin-2 in T Lymphocytes. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 36, 411–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| GENE | FORWARD | REVERSE |
|---|---|---|
| beta-actin | tctctttgatgtcacgcacg | tcagaaggactcctatgtgg |
| pomc | gctgcttcagacctccatagatgtg | cagcgagaggtcgagtttgc |
| penk | cgacatcaatttcctggcgt | agatccttgcaggtctccca |
| μ-opioid receptor | acgctcagacgttccattct | tccaaagaggcccactacac |
| ngf | cacccacccagtcttcc | ctcggcacttggtctcaaa |
| trka | cctgcaacgcttggagtttg | cactcttcacgatggttaggct |
| Il10 | gcgctgtcatcgatttctcccctg | ggccttgtagacaccttggtcttgg |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poulaki, S.; Kalantidou, A.; Lapi, I.; Gravanis, A.; Venihaki, M. Microneurotrophin BNN27 Exerts Significant Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Murine T-Lymphocytes Following CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125498
Poulaki S, Kalantidou A, Lapi I, Gravanis A, Venihaki M. Microneurotrophin BNN27 Exerts Significant Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Murine T-Lymphocytes Following CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125498
Chicago/Turabian StylePoulaki, Smaragda, Aikaterini Kalantidou, Ioanna Lapi, Achille Gravanis, and Maria Venihaki. 2025. "Microneurotrophin BNN27 Exerts Significant Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Murine T-Lymphocytes Following CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125498
APA StylePoulaki, S., Kalantidou, A., Lapi, I., Gravanis, A., & Venihaki, M. (2025). Microneurotrophin BNN27 Exerts Significant Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Murine T-Lymphocytes Following CFA-Induced Inflammatory Pain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5498. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125498







