Biphasic CAPA-IVM Improves Equine Oocyte Quality and Subsequent Embryo Development Without Inducing Genetic Aberrations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Long CAPA-IVM Increases Maturation Rates While Showing a Trend of Compromised Developmental Competency
2.2. Short CAPA-IVM Significantly Improved Maturation Rates and Embryo Development
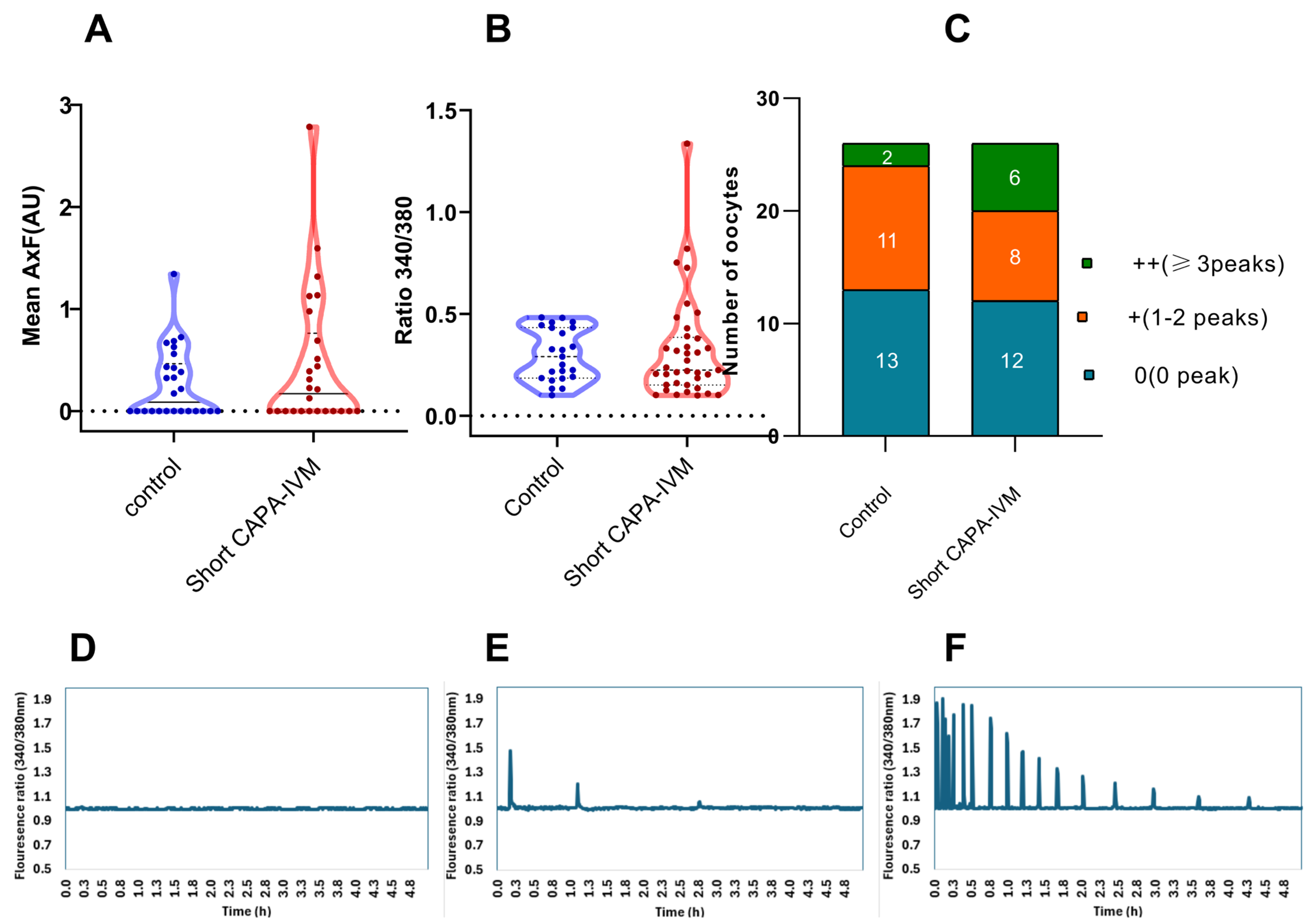
2.3. Equine Oocytes Demonstrate an Irregular Calcium-Releasing Pattern
2.4. Genetic Analysis of Developed Embryos Shows Higher Euploidy Rates Across the Groups
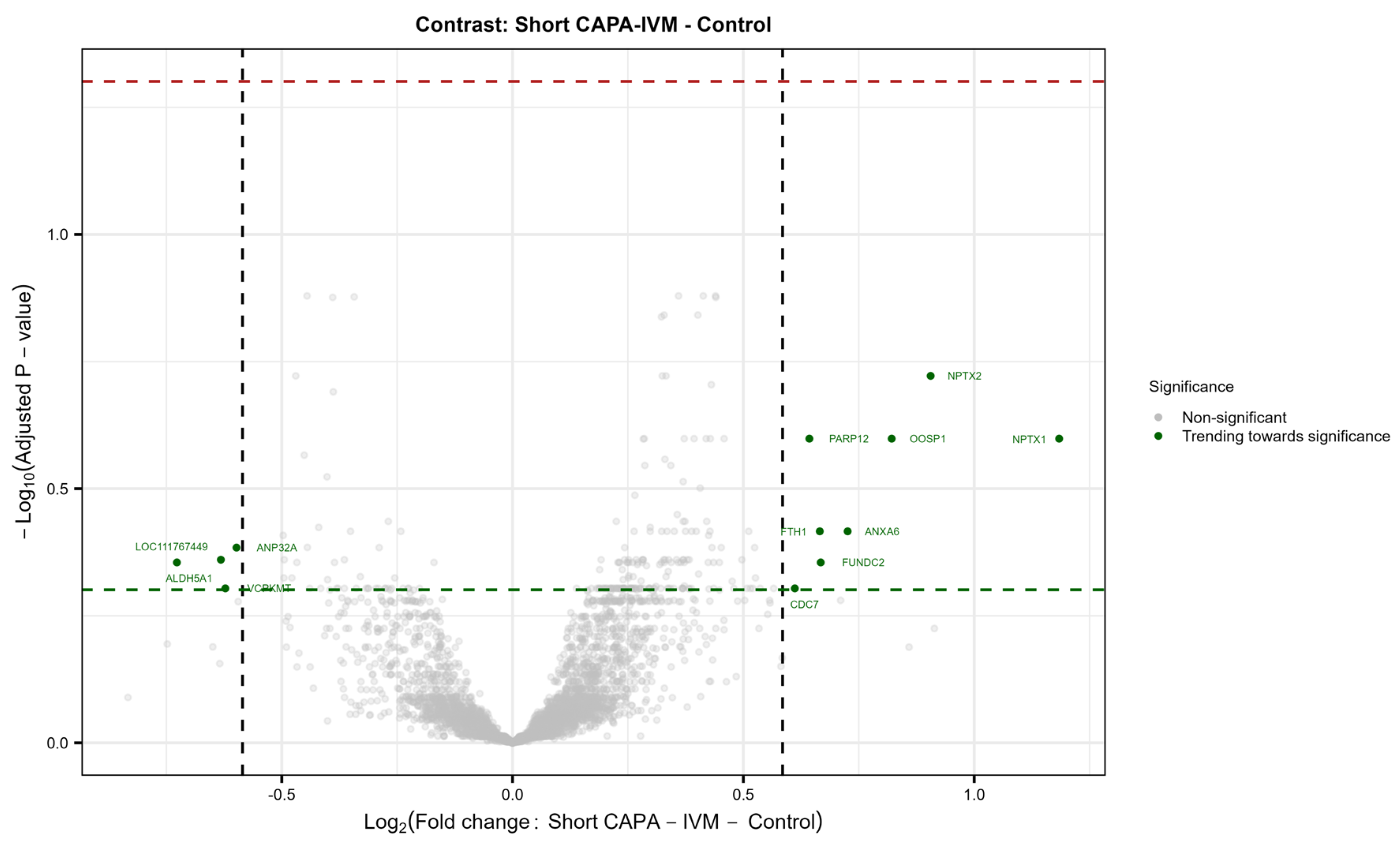
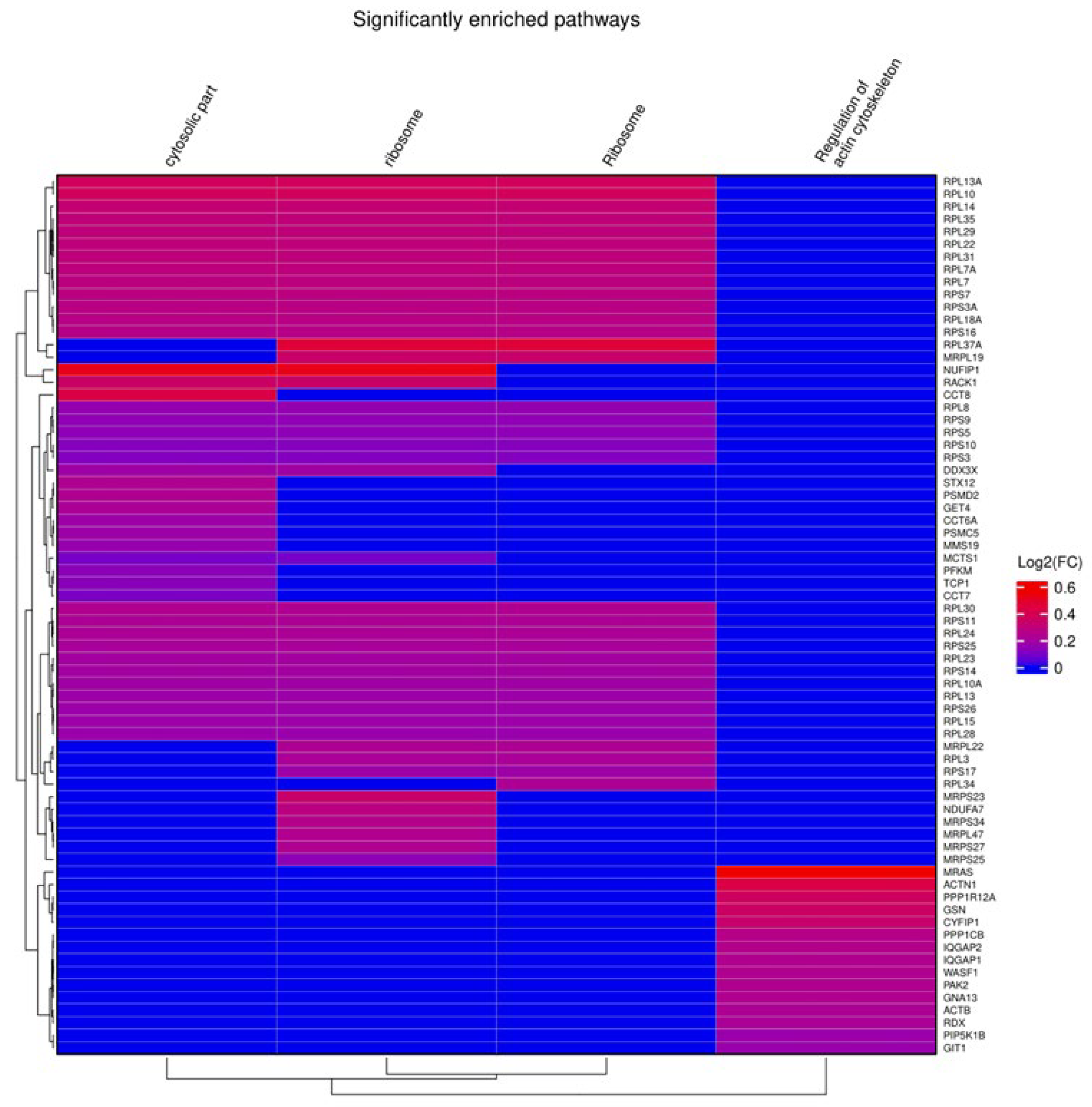
2.5. The Proteome Is Maintained in In Vitro-Matured Oocytes Regardless of In Vitro Maturation Conditions
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection of Equine COCs
4.2. In Vitro Maturation and Fertilization
4.3. Calcium Imaging of In Vitro-Matured Oocytes
4.4. Genetic Analysis of Developed Embryos
4.5. Single-Oocyte Proteome Sample Preparation
4.6. Proteomics Data Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, Y. The Improvement and Clinical Application of Human Oocyte In Vitro Maturation (IVM). Reprod. Sci. 2022, 29, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maclellan, L.; Carnevale, E.; Da Silva, M.C.; Scoggin, C.; Bruemmer, J.; Squires, E. Pregnancies from vitrified equine oocytes collected from super-stimulated and non-stimulated mares. Theriogenology 2002, 58, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinrichs, K. Immature oocyte collection and maturation. In Equine Reproduction, 2nd ed.; McKinnon, A.O., Squires, E.L., Vaala, W.E., Varner, D.D., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 2931–2935. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. Mechanisms of Oocyte Maturation and Related Epigenetic Regulation. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 654028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, T.J.; Carnevale, E.; Maclellan, L.; Scoggin, C.; Squires, E. Embryo development rates after transfer of oocytes matured in vivo, in vitro, or within oviducts of mares. Theriogenology 2001, 55, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foss, R.; Ortis, H.; Hinrichs, K. Effect of potential oocyte transport protocols on blastocyst rates after intracytoplasmic sperm injection in the horse. Equine Vet. J. 2013, 45, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyttel, P.; Fair, T.; Callesen, H.; Greve, T. Oocyte growth, capacitation and final maturation in cattle. Theriogenology 1997, 47, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriksen, P.; Vos, P.; Steenweg, W.; Bevers, M.; Dieleman, S. Bovine follicular development and its effect on the in vitro competence of oocytes. Theriogenology 2000, 53, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.-Y.; Gong, S.; Kong, Q.-Q.; Li, Z.-B.; Wang, J.; Xu, M.-T.; Luo, M.-J.; Tan, J.-H. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase during postovulatory aging of mouse oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2020, 103, 534–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, R.P.; Ratzan, W.J.; Freudzon, M.; Mehlmann, L.M.; Krall, J.; Movsesian, M.A.; Wang, H.; Ke, H.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Jaffe, L.A. Cyclic GMP from the surrounding somatic cells regulates cyclic AMP and meiosis in the mouse oocyte. Development 2009, 136, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, S.; Weeks, J.L.; Hsieh, M.; Menniti, F.S.; Conti, M. Cyclic GMP signaling is involved in the luteinizing hormone-dependent meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyttel, P.; Greve, T.; Callesen, H. Ultrastructural aspects of oocyte maturation and fertilization in cattle. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1989, 38, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Q. Metabolic control of oocyte development. Biol. Reprod. 2022, 107, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, G.R.; Monteiro, C.A.S.; Souza-Fabjan, J.M.G.; de Paula Vasconcelos, C.O.; Nogueira, L.A.G.; Ferreira, A.M.R.; Serapião, R.V. Role of cAMP modulator supplementations during oocyte in vitro maturation in domestic animals. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2018, 199, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Ho, T.M.; De Vos, M.; Sanchez, F.; Romero, S.; Ledger, W.L.; Anckaert, E.; Vuong, L.N.; Smitz, J. A fresh start for IVM: Capacitating the oocyte for development using pre-IVM. Hum. Reprod. Update 2023, 30, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuccotti, M.; Giorgi Rossi, P.; Martinez, A.; Garagna, S.; Forabosco, A.; Redi, C.A. Meiotic and developmental competence of mouse antral oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 1998, 58, 700–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, H.; Cantley, T.C.; Day, B.N. Synchronization of meiosis in porcine oocytes by exposure to dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate improves developmental competence following in vitro fertilization. Biol. Reprod. 1997, 57, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, A.M.; Franciosi, F.; Modina, S.C.; Lodde, V. Gap junction-mediated communications regulate chromatin remodeling during bovine oocyte growth and differentiation through cAMP-dependent mechanism (s). Biol. Reprod. 2011, 85, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, D.; Cortvrindt, R.; De Matos, D.; Vanhoutte, L.; Smitz, J. Effect of phosphodiesterase type 3 inhibitor on developmental competence of immature mouse oocytes in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 69, 2045–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Somfai, T.; Kikuchi, K.; Onishi, A.; Iwamoto, M.; Fuchimoto, D.-I.; Papp, Á.B.; Sato, E.; Nagai, T. Meiotic arrest maintained by cAMP during the initiation of maturation enhances meiotic potential and developmental competence and reduces polyspermy of IVM/IVF porcine oocytes. Zygote 2003, 11, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuz, F.; Sasseville, M.; Lane, M.; Armstrong, D.; Thompson, J.; Gilchrist, R. Simulated physiological oocyte maturation (SPOM): A novel in vitro maturation system that substantially improves embryo yield and pregnancy outcomes. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 2999–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guixue, Z.; Luciano, A.; Coenen, K.; Gandolfi, F.; Sirard, M. The influence of cAMP before or during bovine oocyte maturation on embryonic developmental competence. Theriogenology 2001, 55, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Su, Y.-Q.; Sugiura, K.; Xia, G.; Eppig, J.J. Granulosa cell ligand NPPC and its receptor NPR2 maintain meiotic arrest in mouse oocytes. Science 2010, 330, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franciosi, F.; Coticchio, G.; Lodde, V.; Tessaro, I.; Modina, S.C.; Fadini, R.; Dal Canto, M.; Renzini, M.M.; Albertini, D.F.; Luciano, A.M. Natriuretic peptide precursor C delays meiotic resumption and sustains gap junction-mediated communication in bovine cumulus-enclosed oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 91, 61, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirillova, A.; Bunyaeva, E.; Van Ranst, H.; Khabas, G.; Farmakovskaya, M.; Kamaletdinov, N.; Nazarenko, T.; Abubakirov, A.; Sukhikh, G.; Smitz, J.E.J. Improved maturation competence of ovarian tissue oocytes using a biphasic in vitro maturation system for patients with gynecological malignancy: A study on sibling oocytes. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2021, 38, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.; Le, A.H.; Ho, V.N.A.; Romero, S.; Van Ranst, H.; De Vos, M.; Gilchrist, R.B.; Ho, T.M.; Vuong, L.N.; Smitz, J. Biphasic in vitro maturation (CAPA-IVM) specifically improves the developmental capacity of oocytes from small antral follicles. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2019, 36, 2135–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, F.; Lolicato, F.; Romero, S.; De Vos, M.; Van Ranst, H.; Verheyen, G.; Anckaert, E.; Smitz, J.E.J. An improved IVM method for cumulus-oocyte complexes from small follicles in polycystic ovary syndrome patients enhances oocyte competence and embryo yield. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 32, 2056–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, N.; Le, A.H.; Ha, U.D.T.; Romero, S.; Sanchez, F.; Pham, T.D.; Nguyen, M.H.N.; Anckaert, E.; Ho, T.M.; Smitz, J.; et al. Positive effects of amphiregulin on human oocyte maturation and its molecular drivers in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum. Reprod. 2022, 37, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, L.N.; Ho, V.N.; Ho, T.M.; Dang, V.Q.; Phung, T.H.; Giang, N.H.; Le, A.H.; Pham, T.D.; Wang, R.; Smitz, J. In-vitro maturation of oocytes versus conventional IVF in women with infertility and a high antral follicle count: A randomized non-inferiority controlled trial. Hum. Reprod. 2020, 35, 2537–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, L.N.; Le, A.H.; Ho, V.N.; Pham, T.D.; Sanchez, F.; Romero, S.; De Vos, M.; Ho, T.M.; Gilchrist, R.B.; Smitz, J. Live births after oocyte in vitro maturation with a prematuration step in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2020, 37, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuong, L.N.; Nguyen, L.K.; Le, A.H.; Pham, H.H.; Ho, V.N.; Le, H.L.; Pham, T.D.; Dang, V.Q.; Phung, T.H.; Smitz, J. Fresh embryo transfer versus freeze-only after in vitro maturation with a pre-maturation step in women with high antral follicle count: A randomized controlled pilot study. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2021, 38, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.; Albertini, D.; Wallace, W.; Anderson, R.; Telfer, E. Metaphase II oocytes from human unilaminar follicles grown in a multi-step culture system. MHR Basic Sci. Reprod. Med. 2018, 24, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Lawson, M.S.; Bean, Y.; Ting, A.Y.; Pejovic, T.; De Geest, K.; Moffitt, M.; Mitalipov, S.M.; Xu, J. Matrix-free 3D culture supports human follicular development from the unilaminar to the antral stage in vitro yielding morphologically normal metaphase II oocytes. Hum. Reprod. 2021, 36, 1326–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Jia, L.; Zeng, H.; Sun, P.; Su, W.; Li, T.; Liang, X.; Fang, C. Neurotrophin-4 promotes in vitro development and maturation of human secondary follicles yielding metaphase II oocytes and successful blastocyst formation. Hum. Reprod. Open 2024, 2024, hoae005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuervo-Arango, J.; Claes, A.N.; Stout, T.A. Mare and stallion effects on blastocyst production in a commercial equine ovum pick-up–intracytoplasmic sperm injection program. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2019, 31, 1894–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Love, L.B.; Varner, D.D.; Hinrichs, K. Blastocyst development in equine oocytes with low meiotic competence after suppression of meiosis with roscovitine prior to in vitro maturation. Zygote 2006, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Love, L.B.; Varner, D.D.; Hinrichs, K. Holding immature equine oocytes in the absence of meiotic inhibitors: Effect on germinal vesicle chromatin and blastocyst development after intracytoplasmic sperm injection. Theriogenology 2006, 66, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broothaers, K.; Pascottini, O.B.; Hedia, M.; Angel-Velez, D.; De Coster, T.; Peere, S.; Polfliet, E.; Van den Branden, E.; Govaere, J.; Van Soom, A.; et al. Oocyte holding and in vitro maturation duration between 28 and 34 hours do not affect equine OPU-ICSI outcomes. Theriogenology 2025, 233, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, E.S.; Masterson, K.R.; Battaglia, D.; Thompson, J.G.; Foss, R.; Beck, R.; Cook, N.L.; O’Leary, T. Conditions to optimise the developmental competence of immature equine oocytes. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2020, 32, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodde, V.; Colleoni, S.; Tessaro, I.; Corbani, D.; Lazzari, G.; Luciano, A.M.; Galli, C.; Franciosi, F. A prematuration approach to equine IVM: Considering cumulus morphology, seasonality, follicle of origin, gap junction coupling and large-scale chromatin configuration in the germinal vesicle. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2019, 31, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benammar, A.; Derisoud, E.; Vialard, F.; Palmer, E.; Ayoubi, J.M.; Poulain, M.; Chavatte-Palmer, P. The Mare: A Pertinent Model for Human Assisted Reproductive Technologies? Animals 2021, 11, 2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnevale, E.M.; Catandi, G.D.; Fresa, K. Equine Aging and the Oocyte: A Potential Model for Reproductive Aging in Women. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2020, 89, 103022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, D.; Ron-El, R.; Friedler, S.; Schachter, M.; Raziel, A.; Cortvrindt, R.; Smitz, J. Meiotic Arrest In Vitro by Phosphodiesterase 3-Inhibitor Enhances Maturation Capacity of Human Oocytes and Allows Subsequent Embryonic Development1. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 74, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiquet, N.W.; Greene, A.F.; Becker, J.; Barfield, J.P.; Schoolcraft, W.B.; Krisher, R.L. A pre-in vitro maturation medium containing cumulus oocyte complex ligand-receptor signaling molecules maintains meiotic arrest, supports the cumulus oocyte complex and improves oocyte developmental competence. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2017, 23, 594–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morishita, N.; Shibata, K.; Matsunaga, R.; Ochi, M.; Horiuchi, T. Novel CAPA-IVM using dibutyryl-cAMP (DBCAMP) and C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP): Bovine model study for human IVM of oocytes. Fertil. Steril. 2020, 114, e353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghaly, T.; Khalifa, E.; Mostafa, S.; Hussein, M.; Bedaiwy, M.; Ahmady, A. The effect of temporary meiotic attenuation on the in vitro maturation outcome of bovine oocytes. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biology. Anim. 2015, 51, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghani, M.A.; Sakaguchi, K.; Kanno, C.; Yanagawa, Y.; Katagiri, S.; Nagano, M. Effects of pre-maturational culture duration on developmental competence of bovine small-sized oocytes. J. Reprod. Dev. 2018, 64, 365–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galatidou, S.; Petelski, A.A.; Pujol, A.; Lattes, K.; Latorraca, L.B.; Fair, T.; Popovic, M.; Vassena, R.; Slavov, N.; Barragán, M. Single-cell proteomics reveals decreased abundance of proteostasis and meiosis proteins in advanced maternal age oocytes. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2024, 30, gaae023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Zeng, Q.; Tian, C.; He, F.; Yang, Y. Simple One-step Vial-based Pretreatment for Deep Single-cell Proteomics and Its Application to Oocyte Aging. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Heras, S.; Paramio, M.-T.; Thompson, J.G. Effect of pre-maturation with C-type natriuretic peptide and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine on cumulus-oocyte communication and oocyte developmental competence in cattle. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 202, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Shen, L.; Zhang, H.; Ai, J.; Gilchrist, R.B.; Zhao, Y. CAPA-IVM improves the cytoplasmic quality of in vitro-matured oocytes from unstimulated mice. Theriogenology 2023, 212, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelman, V.; Patrizio, P. The oocyte. In A Color Atlas for Human Assisted Reproduction; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T.; Igarashi, H.; Amita, M.; Hara, S.; Kurachi, H. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of various types of oocyte aging. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2011, 10, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, X.; Miao, D.; Chang, Z.; Luo, M.; Tan, J. Fate of the first polar bodies in mouse oocytes. Mol. Reprod. Dev. Inc. Gamete Res. 2004, 69, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilula, N.B.; Epstein, M.L.; Beers, W.H. Cell-to-cell communication and ovulation. A study of the cumulus-oocyte complex. J. Cell Biol. 1978, 78, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colonna, R.; Mangia, F. Mechanisms of amino acid uptake in cumulus-enclosed mouse oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 1983, 28, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, A.M.; Franciosi, F.; Dieci, C.; Lodde, V. Changes in large-scale chromatin structure and function during oogenesis: A journey in company with follicular cells. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 2014, 149, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibi, S.; Hajian, M.; Ostadhosseini, S.; Hosseini, S.; Forouzanfar, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M. Effect of phosphodiesterase type 3 inhibitor on nuclear maturation and in vitro development of ovine oocytes. Theriogenology 2013, 80, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sutton-McDowall, M.; Wang, X.; Sugimura, S.; Thompson, J.; Gilchrist, R. Extending prematuration with cAMP modulators enhances the cumulus contribution to oocyte antioxidant defence and oocyte quality via gap junctions. Hum. Reprod. 2016, 31, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, S.; Sánchez, F.; Lolicato, F.; Van Ranst, H.; Smitz, J. Immature oocytes from unprimed juvenile mice become a valuable source for embryo production when using C-type natriuretic peptide as essential component of culture medium. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 95, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Lee, J.E.; Kang, J.W.; Oqani, R.K.; Cho, E.S.; Kim, S.B.; Il Jin, D. Melatonin supplementation during prolonged in vitro maturation improves the quality and development of poor-quality porcine oocytes via anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic effects. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2018, 85, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altermatt, J.L.; Suh, T.K.; Stokes, J.E.; Carnevale, E.M. Effects of age and equine follicle-stimulating hormone (eFSH) on collection and viability of equine oocytes assessed by morphology and developmental competency after intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2009, 21, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mu, Y.; Elshewy, N.; Ding, D.; Zou, H.; Chen, B.; Wei, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Z. Comparison of IVF and IVM outcomes in the same patient treated with a modified IVM protocol along with an oocytes-maturing system containing melatonin: A pilot study. Life Sci. 2021, 264, 118706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, G.; An, L.; Jia, Z.; Tan, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Miao, K.; Wu, Z.; Tian, J. Natriuretic peptide receptor 2 (NPR2) localized in bovine oocyte underlies a unique mechanism for C-type natriuretic peptide (CNP)-induced meiotic arrest. Theriogenology 2018, 106, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Nisio, V.; Antonouli, S.; Damdimopoulou, P.; Salumets, A.; Cecconi, S. on behalf of SIERR. In vivo and in vitro postovulatory aging: When time works against oocyte quality? J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2022, 39, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, W.-Y.; Lee, S.-Y.; Lim, J.-H. Fertilization, cleavage and blastocyst development according to the maturation timing of oocytes in in vitro maturation cycles. Hum. Reprod. 2005, 20, 3204–3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yan, J.; Liu, Z.C.; Yan, L.Y.; Li, M.; Zhou, Q.; Qiao, J. Optimal timing of oocyte maturation and its relationship with the spindle assembly and developmental competence of in vitro matured human oocytes. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 96, 73–78.e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Ata, B.; Son, W.-Y.; Buckett, W.M.; Tan, S.-L.; Ao, A. Chromosome abnormality rates in human embryos obtained from in-vitro maturation and IVF treatment cycles. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2010, 21, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, C.A.; González, C.; Díaz, R.M.; Gutierrez, A.M.; Hinrichs, K. Prolonged maturation reduces cleavage and blastocyst rates after ICSI. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2023, 125, 104637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, Q.; Cai, J.; Zhao, X.; Ma, B. Effect of C-Type Natriuretic Peptide on Maturation and Developmental Competence of Goat Oocytes Matured In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, S.J.; Kurokawa, M.; Hinrichs, K.; Fissore, R.A. Intracellular calcium oscillations and activation in horse oocytes injected with stallion sperm extracts or spermatozoa. Reproduction 2003, 126, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedford, S.J.; Kurokawa, M.; Hinrichs, K.; Fissore, R.A. Patterns of Intracellular Calcium Oscillations in Horse Oocytes Fertilized by Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection: Possible Explanations for the Low Success of This Assisted Reproduction Technique in the Horse1. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 70, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeste, M.; Jones, C.; Amdani, S.N.; Coward, K. Oocyte activation and fertilisation: Crucial contributors from the sperm and oocyte. Signal.-Mediat. Control Cell Div. Oogenesis Oocyte-Embryo Dev. 2017, 59, 213–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar, M.I.; Lu, S.; Li, H. Sperm-oocyte interplay: An overview of spermatozoon’s role in oocyte activation and current perspectives in diagnosis and fertility treatment. Cell Biosci. 2021, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, M.; Fissore, R.A. ICSI-generated mouse zygotes exhibit altered calcium oscillations, inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-1 down-regulation, and embryo development. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2003, 9, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dozortsev, D.; Rybouchkin, A.; De Sutter, P.; Dhont, M. Sperm plasma membrane damage prior to intracytoplasmic sperm injection: A necessary condition for sperm nucleus decondensation. Hum. Reprod. 1995, 10, 2960–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagida, K.; Katayose, H.; Hirata, S.; Yazawa, H.; Hayashi, S.; Sato, A. Influence of sperm immobilization on onset of Ca2+ oscillations after ICSI. Hum. Reprod. 2001, 16, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, T.; Zhao, Y.; Tšuiko, O.; Demyda-Peyrás, S.; Van Soom, A.; Vermeesch, J.; Smits, K. Genome-wide equine preimplantation genetic testing enabled by simultaneous haplotyping and copy number detection. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Li, K.; Li, R.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Dai, X.; He, Y. Chromosomal aneuploidy associated with clinical characteristics of pregnancy loss. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 667697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilton, C.A.; Kahler, A.; Davis, B.W.; Crabtree, J.R.; Crowhurst, J.; McGladdery, A.J.; Wathes, D.C.; Raudsepp, T.; de Mestre, A.M. Whole genome analysis reveals aneuploidies in early pregnancy loss in the horse. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claes, A.; Stout, T.A.E. Success rate in a clinical equine in vitro embryo production program. Theriogenology 2022, 187, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkley, S.; Scheffler, K.; Mogessie, B. Cytoskeletal form and function in mammalian oocytes and zygotes. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2022, 75, 102073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egbert, J.R.; Silbern, I.; Uliasz, T.F.; Lowther, K.M.; Yee, S.-P.; Urlaub, H.; Jaffe, L.A. Phosphatases modified by LH signaling in ovarian follicles: Testing their role in regulating the NPR2 guanylyl cyclase†. Biol. Reprod. 2023, 110, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lin, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Z. Research Progress of Ribosomal Proteins in Reproductive Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angel-Velez, D.; De Coster, T.; Azari-Dolatabad, N.; Fernandez-Montoro, A.; Benedetti, C.; Bogado Pascottini, O.; Woelders, H.; Van Soom, A.; Smits, K. New alternative mixtures of cryoprotectants for equine immature oocyte vitrification. Animals 2021, 11, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, B.; Gadella, B.M.; Stout, T.A.E.; Heras, S.; Smits, K.; Ferrer-Buitrago, M.; Claes, E.; Heindryckx, B.; De Vos, W.H.; Nelis, H.; et al. Procaine Induces Cytokinesis in Horse Oocytes via a pH-Dependent Mechanism1. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 93, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, M.; Dheedene, A.; Christodoulou, C.; Taelman, J.; Dhaenens, L.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Deforce, D.; Van den Abbeel, E.; De Sutter, P.; Menten, B. Chromosomal mosaicism in human blastocysts: The ultimate challenge of preimplantation genetic testing? Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1342–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sante, T.; Vergult, S.; Volders, P.-J.; Kloosterman, W.P.; Trooskens, G.; De Preter, K.; Dheedene, A.; Speleman, F.; De Meyer, T.; Menten, B. ViVar: A comprehensive platform for the analysis and visualization of structural genomic variation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, L.; Dheedene, A.; De Smet, M.; Van Dorpe, J.; Menten, B. WisecondorX: Improved copy number detection for routine shallow whole-genome sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Montoro, A.; Araftpoor, E.; De Coster, T.; Angel-Velez, D.; Bühler, M.; Hedia, M.; Gevaert, K.; Van Soom, A.; Pavani, K.C.; Smits, K. Decoding bull fertility in vitro: A proteomics exploration from sperm to blastocyst. Reproduction 2025, 169, e240296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Matsuura, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M. KEGG: Biological systems database as a model of the real world. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 53, D672–D677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Control | Long CAPA-IVM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COCs | 138 | 61 | |
| Survival rate (%) | 83/138 (60%) | 43/61 (70%) | 0.163 |
| Maturation rate (%) | 70/138 (51%) | 42/61 (69%) * | 0.017 |
| Oocytes injected | 63 | 34 | |
| Cleavage rate (%) | 39/63 (62%) | 14/34 (41%) | 0.050 |
| Blastocyst rate (%) | 8/63 (13%) | 1 (3%) | 0.114 |
| Control | Short CAPA-IVM | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| COCs | 280 | 266 | |
| Survival rate (%) | 158/280 (56%) | 167/266 (63%) | 0.131 |
| Maturation rate (%) | 141/280 (50%) | 162/266 (61%) * | 0.013 |
| Oocytes injected | 63 | 69 | |
| Cleavage rate (%) | 40/63 (63%) | 56/69 (81%) * | 0.022 |
| Blastocyst rate (%) | 9/63 (14%) | 20/69 (29%) * | 0.041 |
| Control | Short CAPA-IVM | Long CAPA-IVM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Euploidy rate (%) | 21/23 (91%) | 16/16 (100%) | 1/1 (100%) |
| Inconclusive profiles | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fakhar-I-Adil, M.; Angel-Velez, D.; Araftpoor, E.; Amin, Q.A.; Hedia, M.; Bühler, M.; Gevaert, K.; Menten, B.; Van Soom, A.; Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S.M.; et al. Biphasic CAPA-IVM Improves Equine Oocyte Quality and Subsequent Embryo Development Without Inducing Genetic Aberrations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125495
Fakhar-I-Adil M, Angel-Velez D, Araftpoor E, Amin QA, Hedia M, Bühler M, Gevaert K, Menten B, Van Soom A, Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM, et al. Biphasic CAPA-IVM Improves Equine Oocyte Quality and Subsequent Embryo Development Without Inducing Genetic Aberrations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125495
Chicago/Turabian StyleFakhar-I-Adil, Muhammad, Daniel Angel-Velez, Emin Araftpoor, Qurratul Ain Amin, Mohamed Hedia, Marcel Bühler, Kris Gevaert, Björn Menten, Ann Van Soom, Susana Marina Chuva de Sousa Lopes, and et al. 2025. "Biphasic CAPA-IVM Improves Equine Oocyte Quality and Subsequent Embryo Development Without Inducing Genetic Aberrations" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125495
APA StyleFakhar-I-Adil, M., Angel-Velez, D., Araftpoor, E., Amin, Q. A., Hedia, M., Bühler, M., Gevaert, K., Menten, B., Van Soom, A., Chuva de Sousa Lopes, S. M., Stoop, D., De Roo, C., Smits, K., & Heindryckx, B. (2025). Biphasic CAPA-IVM Improves Equine Oocyte Quality and Subsequent Embryo Development Without Inducing Genetic Aberrations. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125495







