Comparative Efficacy of Exosomes Derived from Different Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sources in Osteoarthritis Models: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of BMSC-Exos, ADSC-Exos, and UMSC-Exos Isolated by ATPS
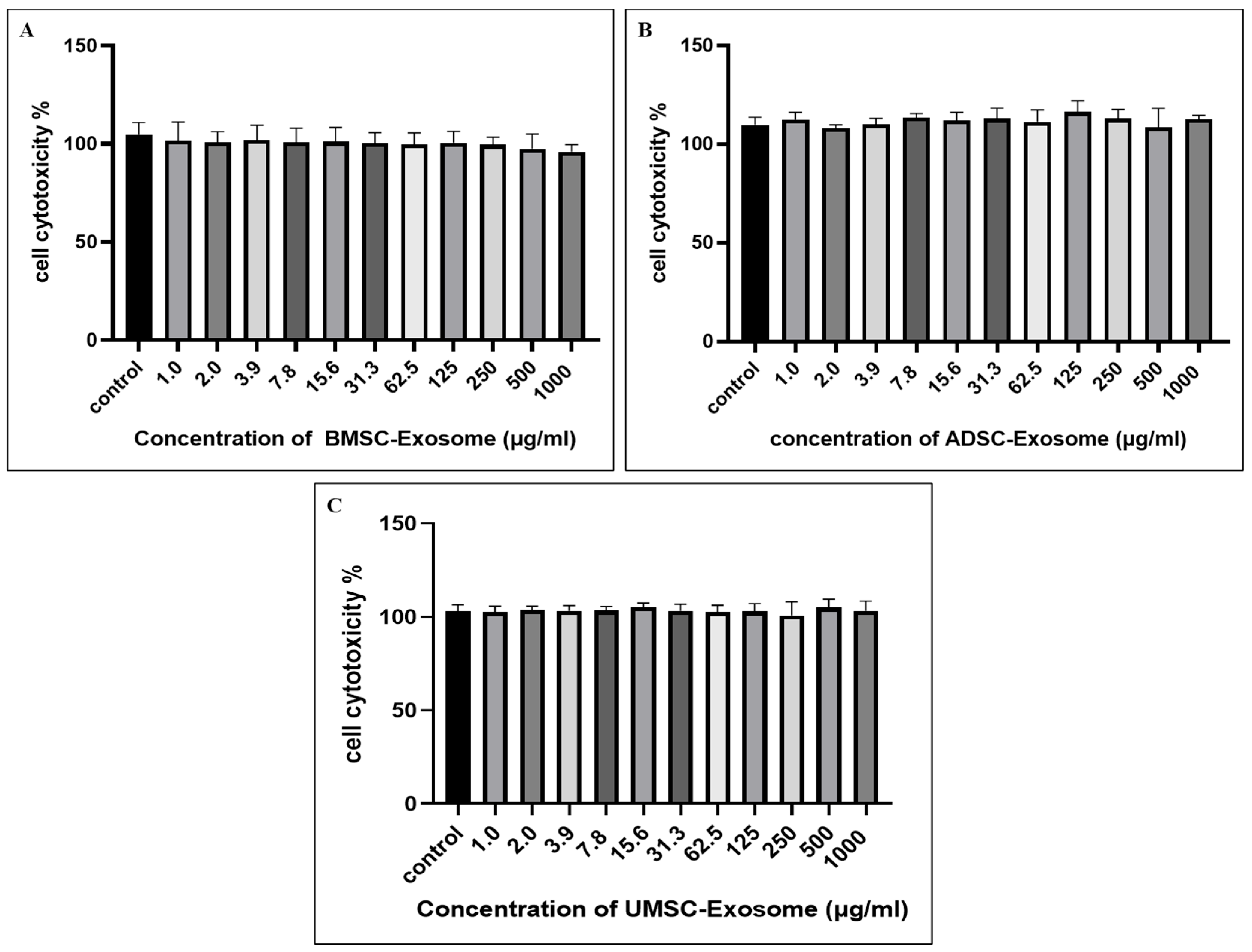
2.2. Cell Cytotoxicity of BMSC-Exos, ADSC-Exos, and UMSC-Exos Using CCK-8 Assay
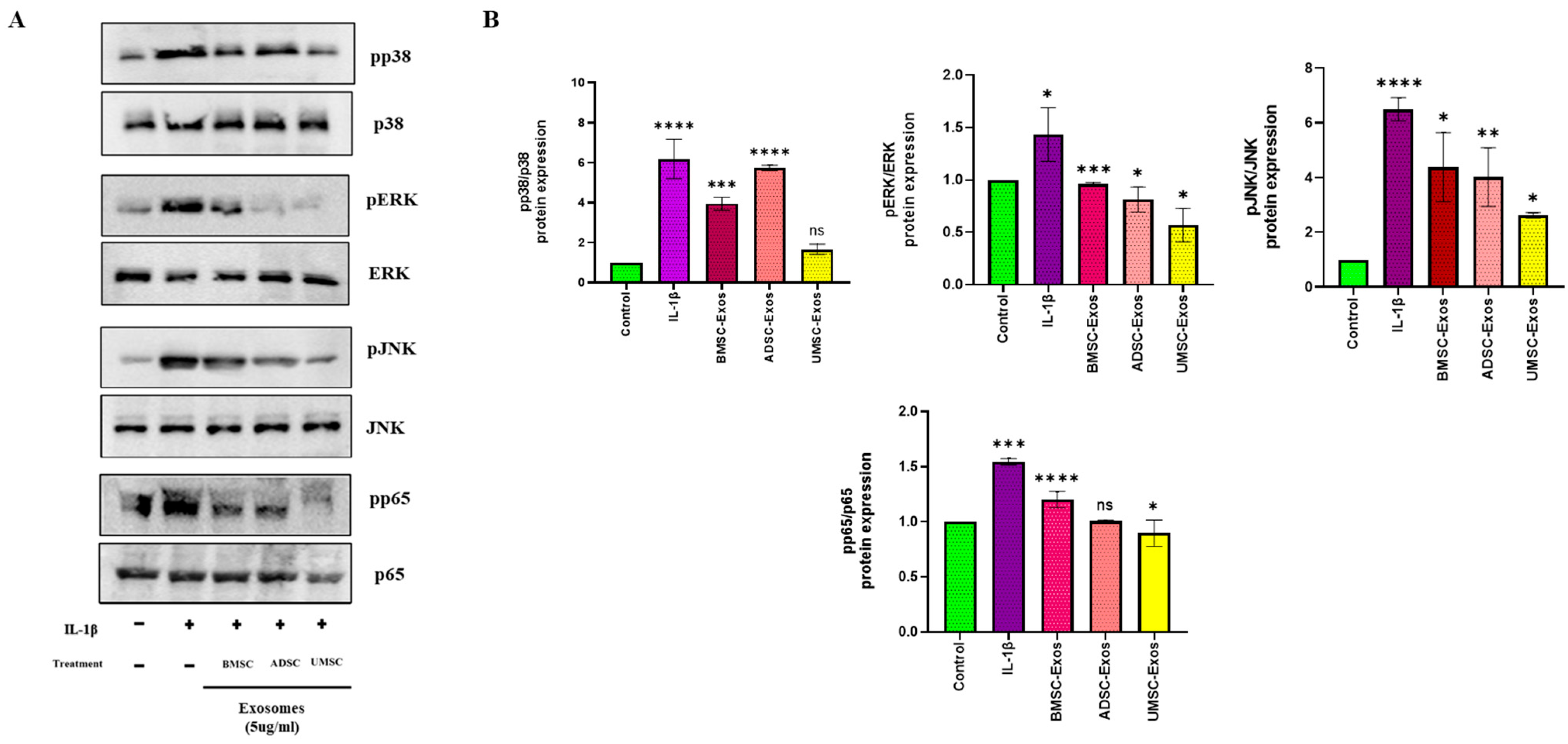
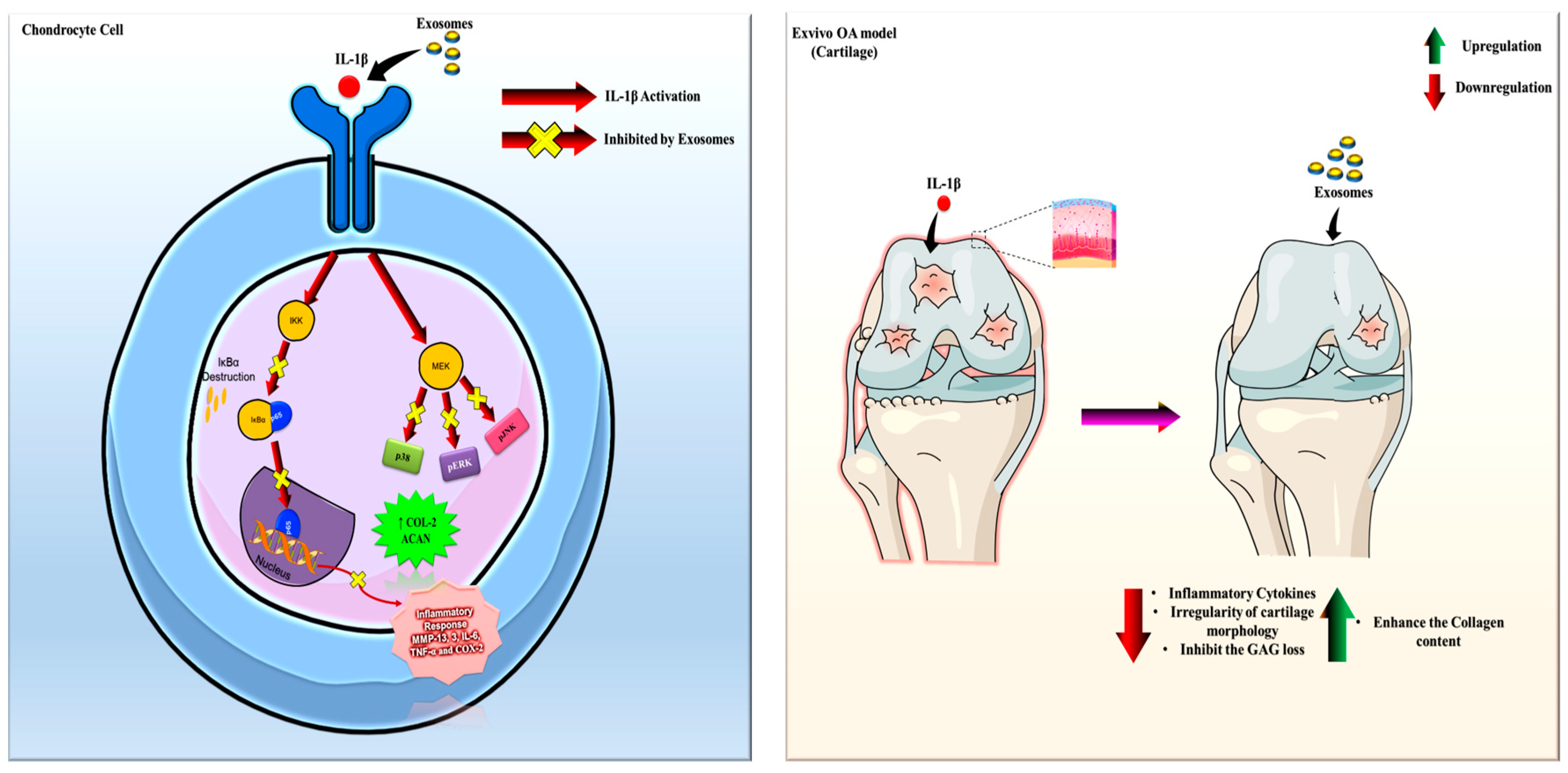
2.3. In Vitro Efficacy of BMSC-Exos, ADSC-Exos, and UMSC-Exos on NF-kB and MAPK Signaling Pathways
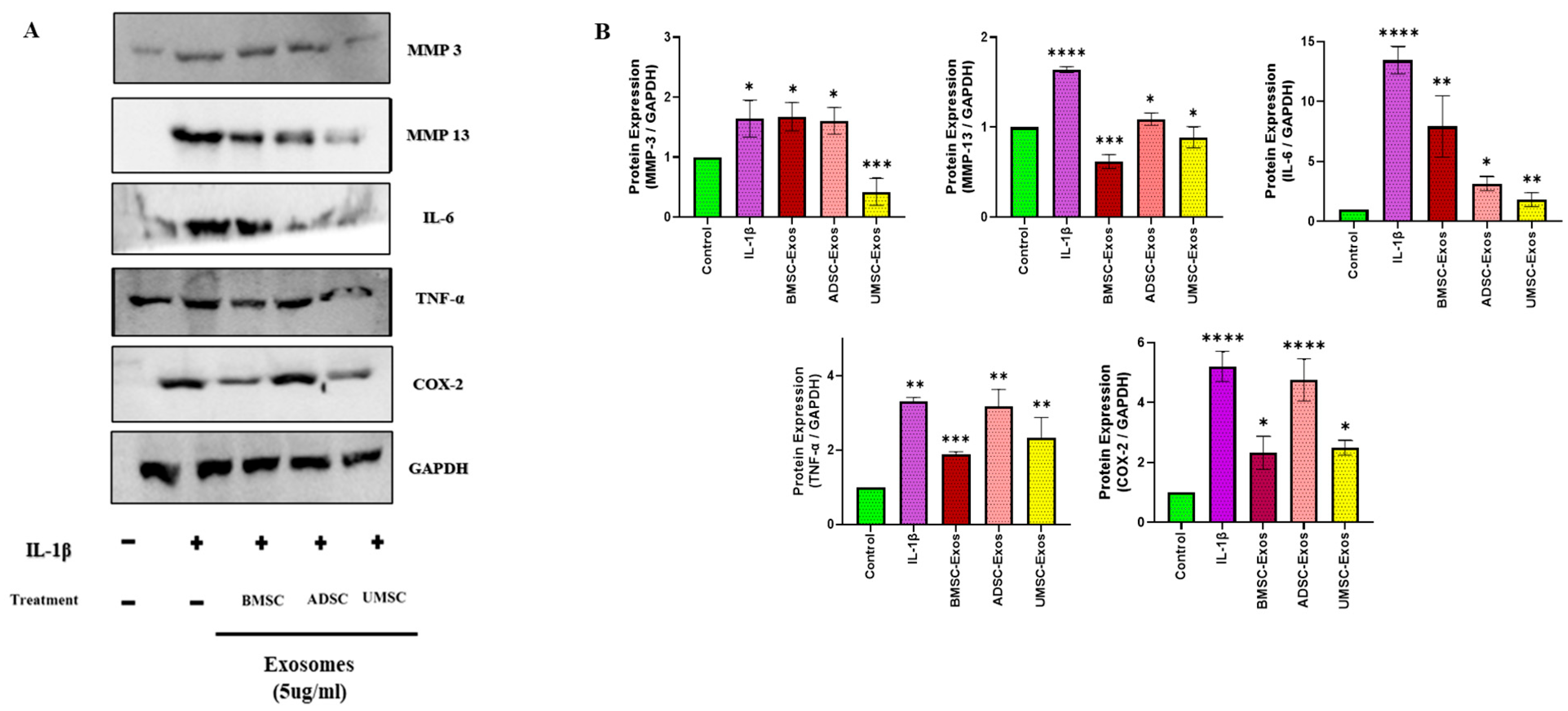
2.4. In Vitro Efficacy of BMSC-Exos, ADSC-Exos, and UMSC-Exos on Inflammatory Markers
2.5. In Vitro Efficacy of BMSC-Exos, ADSC-Exos, and UMSC-Exos on Chondroprotective Markers
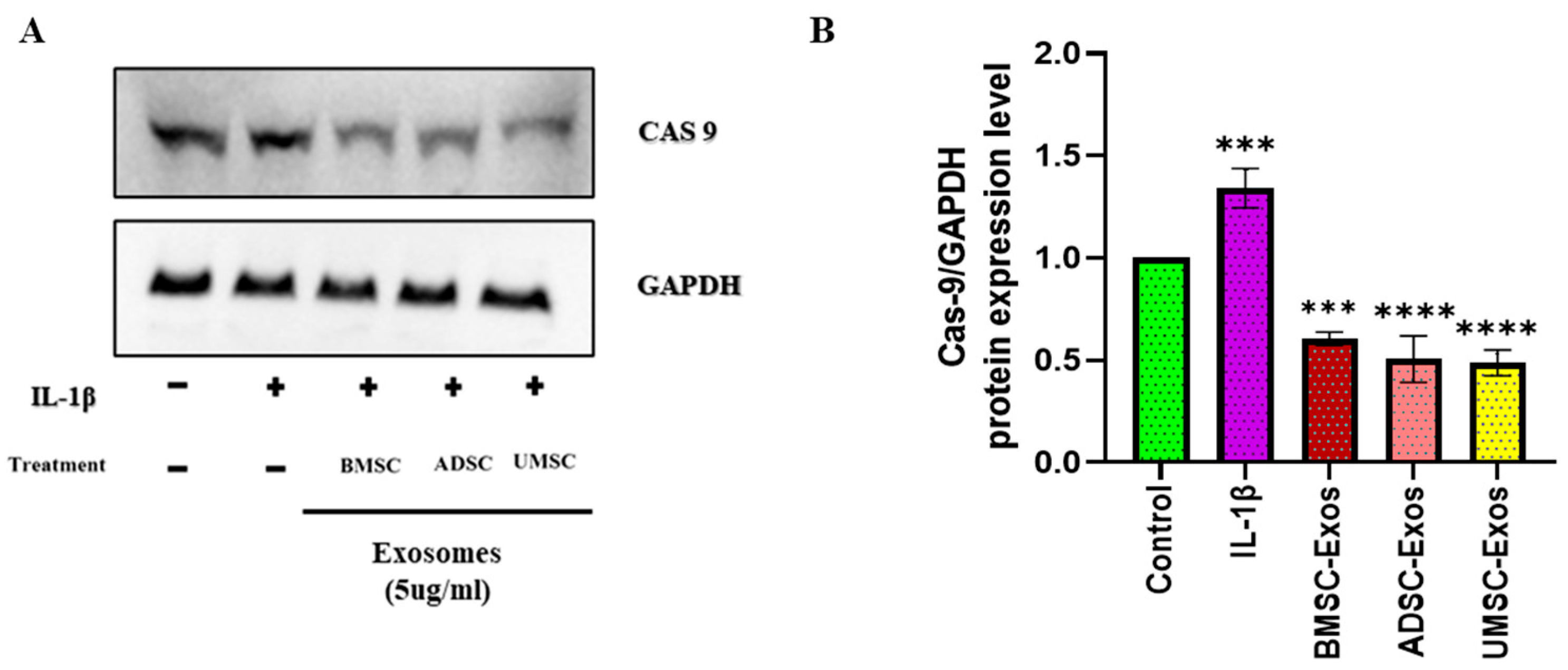
2.6. In Vitro Efficacy of BMSC-Exos, ADSC-Exos, and UMSC-Exos on Apoptotic Marker
2.7. Chondrocyte Migration Efficacy Using Scratch Wound Assay
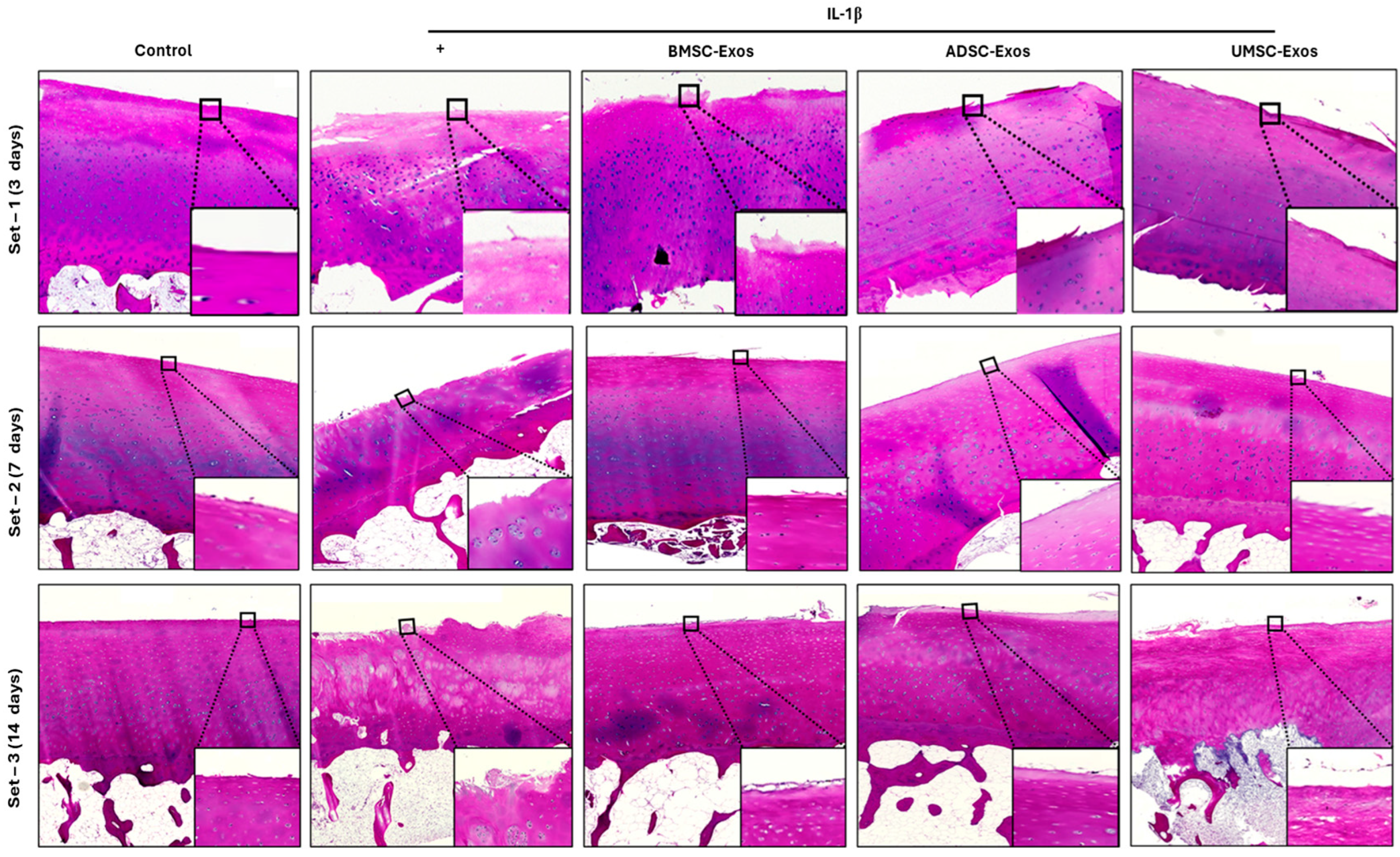
2.8. H&E Staining Reveals Cartilage Histopathology
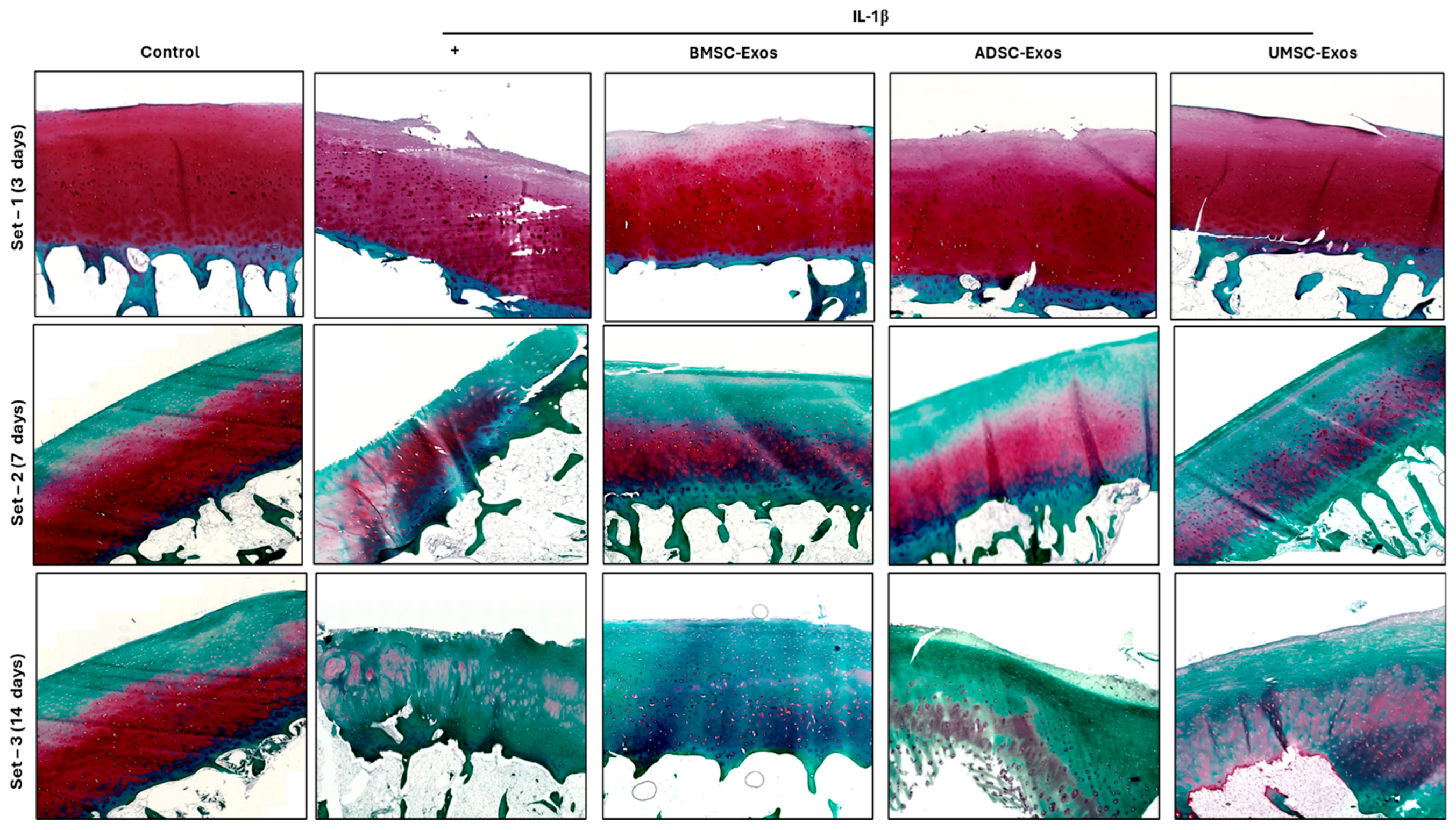
2.9. Safranin O/Fast Green Staining Reveals Proteoglycan Distribution in Cartilage Samples
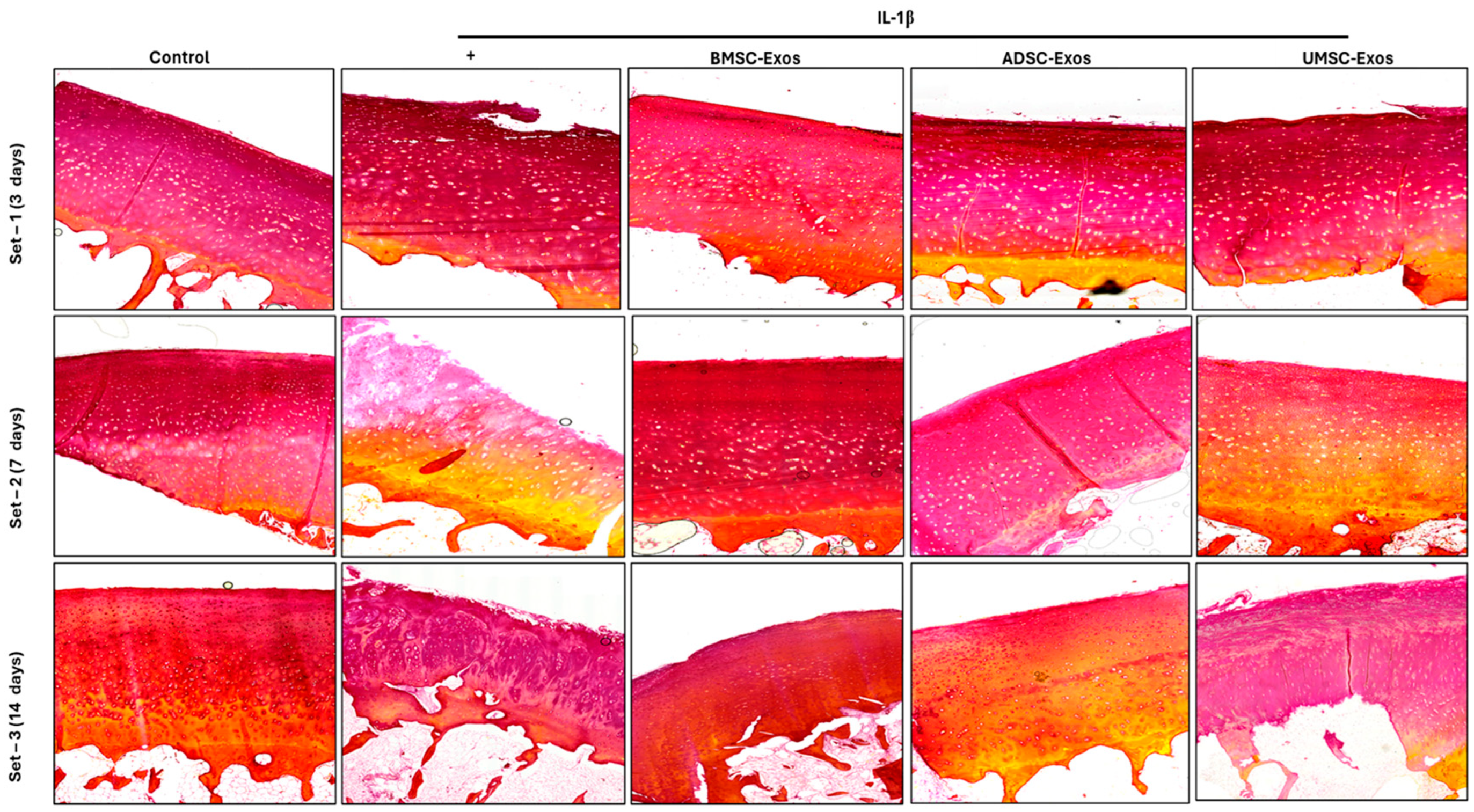
2.10. Picrosirius Red Staining Reveals Collagen Content in Cartilage Samples
3. Discussion
Challenges and Future Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antibodies and Reagents
4.2. Source of Chondrocytes and MSCs Culture
4.3. Exosome Isolation from BMSC, ADSC, and UMSCs
4.4. Characterization of the ATPS and Exosomes
4.5. Role of Exosomes in IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Inflammation In Vitro
4.6. Cellular Cytotoxicity Using the CCK-8 Assay
4.7. Whole-Cell Lysate Preparation and Wesatern Blot Analysis
4.8. Scratch Wound Assay
4.9. Experimental Design for the Establishment of an Ex Vivo OA Model
4.10. Sampling and Tissue Preparation
4.11. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, Y.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H.; Kang, D.; Lee, J.; Kang, S.-B.; Kim, J.-H. Disease-modifying therapeutic strategies in osteoarthritis: Current status and future directions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Y.; Yin, J.M.; Gao, J.J.; Cheng, T.S.; Pavlos, N.J.; Zhang, C.Q.; Zheng, M.H. Subchondral bone in osteoarthritis: Insight into risk factors and microstructural changes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Tian, Y.; Zuo, J.; Yang, J.; Fan, Y. Global, Regional, and National Burdens of Hepatitis E From 1990 to 2021 and Predicted 2030 Incidence: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. J. Med. Virol. 2025, 97, e70279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.-Y. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Osteoarthritis in Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study. Medicina 2024, 60, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.W.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, D.-J. The prevalence of and demographic factors associated with radiographic knee osteoarthritis in Korean adults aged ≥ 50 years: The 2010–2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Weng, W.; Liu, Y.; Aspera-Werz, R.H.; Nüssler, A.K.; Xu, J. Update on Novel Non-Operative Treatment for Osteoarthritis: Current Status and Future Trends. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 755230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Qu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, B. Relative efficacy and safety of mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1366297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najar, M.; Melki, R.; Khalife, F.; Lagneaux, L.; Bouhtit, F.; Agha, D.M.; Fahmi, H.; Lewalle, P.; Fayyad-Kazan, M.; Merimi, M. Therapeutic Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells: Value, Challenges and Optimization. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 9, 716853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, S.; Ruiz, M.; Toupet, K.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes and microparticles protect cartilage and bone from degradation in osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, B.A.A.; Fernandes, L.A.; Fratini, P.; Sogayar, M.C.; Carreira, A.C.O. Role of MSC-derived small extracellular vesicles in tissue repair and regeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 10, 1047094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil You, D.G.; Lim, G.T.; Kwon, S.; Um, W.; Oh, B.H.; Song, S.H.; Lee, J.; Jo, D.-G.; Cho, Y.W.; Park, J.H. Metabolically engineered stem cell–derived exosomes to regulate macrophage heterogeneity in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe0083. [Google Scholar]
- Vadhan, A.; Gupta, T.; Hsu, W.-L. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as a Treatment Option for Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Tian, B.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Kang, X. Potential and challenges of utilizing exosomes in osteoarthritis therapy (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 55, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Qi, L.; Liu, K. Hypoxic ADSCs-derived EVs promote the proliferation and chondrogenic differentiation of cartilage stem/progenitor cells. Adipocyte 2021, 10, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Yang, C.; Bi, H.; Qian, X.; Wu, M.; Ji, K.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Maity, P.; Kapat, K. The Opportunities and Challenges of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes in Theranostics and Regenerative Medicine. Cells 2024, 13, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Rong, Y.; Luo, C.; Cui, W. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes prevent osteoarthritis by regulating synovial macrophage polarization. Aging 2020, 12, 25138–25152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, F.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Shahzad, K.; Zheng, J. Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Chu, W.C.; Lai, R.C.; Lim, S.K.; Hui, J.H.P.; Toh, W.S. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2016, 24, 2135–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, S.R.; Goldring, M.B. The Role of Cytokines in Cartilage Matrix Degeneration in Osteoarthritis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2004, 427, S27–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Miyaki, S.; Ishitobi, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Nakasa, T.; Lotz, M.K.; Ochi, M. Exosomes from IL-1β stimulated synovial fibroblasts induce osteoarthritic changes in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.; Fang, Y.; Xin, W.; You, H. The Application of Extracellular Vesicles Mediated miRNAs in Osteoarthritis: Current Knowledge and Perspective. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, ume 15, 2583–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.-C.; Yuan, T.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Yin, W.-J.; Guo, S.-C.; Zhang, C.-Q. Exosomes derived from miR-140-5p-overexpressing human synovial mesenchymal stem cells enhance cartilage tissue regeneration and prevent osteoarthritis of the knee in a rat model. Theranostics 2017, 7, 180–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zheng, Q.; Xie, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Hu, H.; He, H.; Lu, Q. Role of Exosomal Non-Coding RNAs in Bone-Related Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 811666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Y.; Alini, M.; Grad, S.; Li, Z. Establishment of an Ex Vivo Inflammatory Osteoarthritis Model With Human Osteochondral Explants. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 787020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, J.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, H.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Kuppa, S.S.; Seon, J.K. Exosomes Reshape the Osteoarthritic Defect: Emerging Potential in Regenerative Medicine–A Review. Int. J. Stem Cells 2024, 17, 381–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Cong, M.; Huang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, M.; Gu, X.; Sun, C.; Yang, H. The Effect of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on Cartilage Repair in Rabbits. Stem Cells Int. 2022, 2022, 5760107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Huang, X.; Ma, J.; Zhao, G.; Ma, T.; Chen, K.; Huang, G.; Chen, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, S. Exosomes derived from MSC as drug system in osteoarthritis therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1331218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.M.; Luo, T.; von der Ohe, J.; Mora, B.d.J.; Schmitt, R.; Hass, R. Human MSC-Derived Exosomes Reduce Cellular Senescence in Renal Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.K.; Bons, J.; Rose, J.P.; Chappel, J.R.; Beres, R.L.; Watson, M.A.; Webster, C.; Burton, J.B.; Bruderer, R.; Desprez, P.Y.; et al. Exosomes Released from Senescent Cells and Circulatory Exosomes Isolated from Human Plasma Reveal Aging-associated Proteomic and Lipid Signatures. bioRxiv 2024. Preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Kaushal, D.; Wilson, R.B. Cellular Senescence and Extracellular Vesicles in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of Obesity—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.H.; Kim, H.-K.; Lee, J.; Kwon, H.H.; Park, G.-H.; Yang, S.H.; Jung, J.Y.; Choi, H.; Lee, J.H.; Sung, S.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell-Derived Exosomes for Immunomodulatory Therapeutics and Skin Regeneration. Cells 2020, 9, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.; Koh, D.; Bin Jeon, H.; Kim, K.M. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Senescence. Mol. Cells 2022, 45, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Lin, L.; Zou, R.; Wen, C.; Wang, Z.; Lin, F. MSC-derived exosomes promote proliferation and inhibit apoptosis of chondrocytes via lncRNA-KLF3-AS1/miR-206/GIT1 axis in osteoarthritis. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 2411–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.R.; Phelan, M.M.; Foddy, L.; Clegg, P.D.; Peffers, M.J. Ex Vivo Equine Cartilage Explant Osteoarthritis Model: A Metabolomics and Proteomics Study. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 3652–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, J.; Xiang, W.; Gong, Y.; Feng, D.; Fang, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, R.; et al. Engineering exosomes derived from TNF-α preconditioned IPFP-MSCs enhance both yield and therapeutic efficacy for osteoarthritis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Shin, D.I.; Choi, B.H.; Min, B.H. Exosomes from IL-1beta-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibited IL-1beta- and TNF-alpha-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Osteoarthritic SW982 Cells. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2021, 18, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, W.; Lv, S.; Sun, Z.; Si, L.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y.; Qiu, D.; Liu, X.; Zhu, S.; et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes exert anti-inflammatory effects on osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Aging 2023, 15, 9544–9560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Delen, M.; Derdelinckx, J.; Wouters, K.; Nelissen, I.; Cools, N. A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials assessing safety and efficacy of human extracellular vesicle-based therapy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.-J.; Liu, D.; Pan, L.-Y.; Wang, W.-Y.; Ding, Y.-L.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Ye, R.-X.; Zhou, Y.; An, S.-B.; Xiao, W.-F. Exosomes in osteoarthritis: Updated insights on pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 949690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Zhu, H.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a promising cell-free therapy for knee osteoarthritis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1309946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankaranarayanan, J.; Lee, S.C.; Kim, H.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Kuppa, S.S.; Seon, J.K. Cinnamaldehyde-Treated Bone Marrow Mesenchymal-Stem-Cell-Derived Exosomes via Aqueous Two-Phase System Attenuate IL-1β-Induced Inflammation and Catabolism via Modulation of Proinflammatory Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sankaranarayanan, J.; Kim, H.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Kuppa, S.S.; Yang, H.Y.; Seon, J.K. Comparative Efficacy of Exosomes Derived from Different Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sources in Osteoarthritis Models: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125447
Sankaranarayanan J, Kim HK, Kang JY, Kuppa SS, Yang HY, Seon JK. Comparative Efficacy of Exosomes Derived from Different Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sources in Osteoarthritis Models: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125447
Chicago/Turabian StyleSankaranarayanan, Jaishree, Hyung Keun Kim, Ju Yeon Kang, Sree Samanvitha Kuppa, Hong Yeol Yang, and Jong Keun Seon. 2025. "Comparative Efficacy of Exosomes Derived from Different Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sources in Osteoarthritis Models: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125447
APA StyleSankaranarayanan, J., Kim, H. K., Kang, J. Y., Kuppa, S. S., Yang, H. Y., & Seon, J. K. (2025). Comparative Efficacy of Exosomes Derived from Different Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sources in Osteoarthritis Models: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5447. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125447






