Swt21p Is Required for Nam8p-U1 snRNP Association and Efficient Pre-mRNA Splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
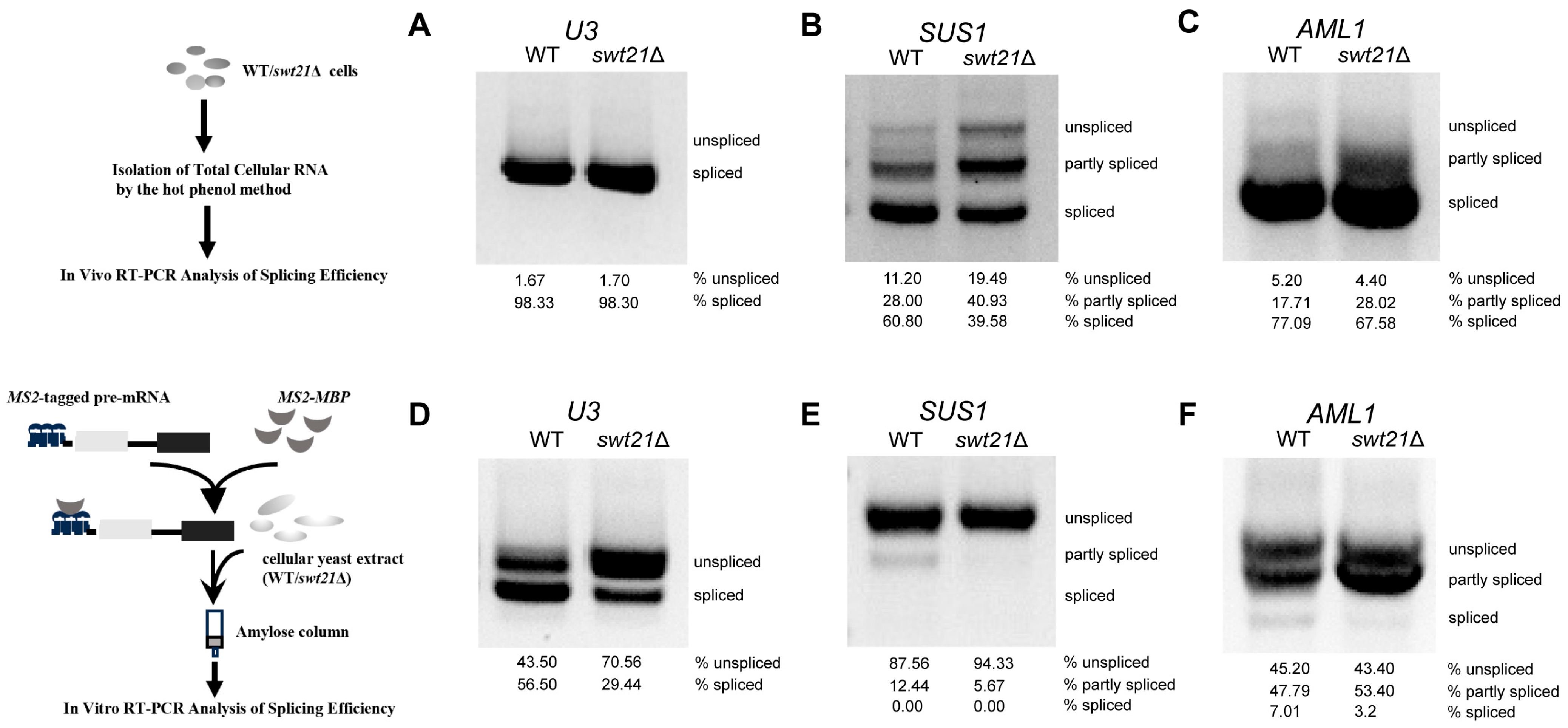
2.1. Swt21p Affects the Efficiency of Pre-mRNA Splicing In Vivo and In Vitro
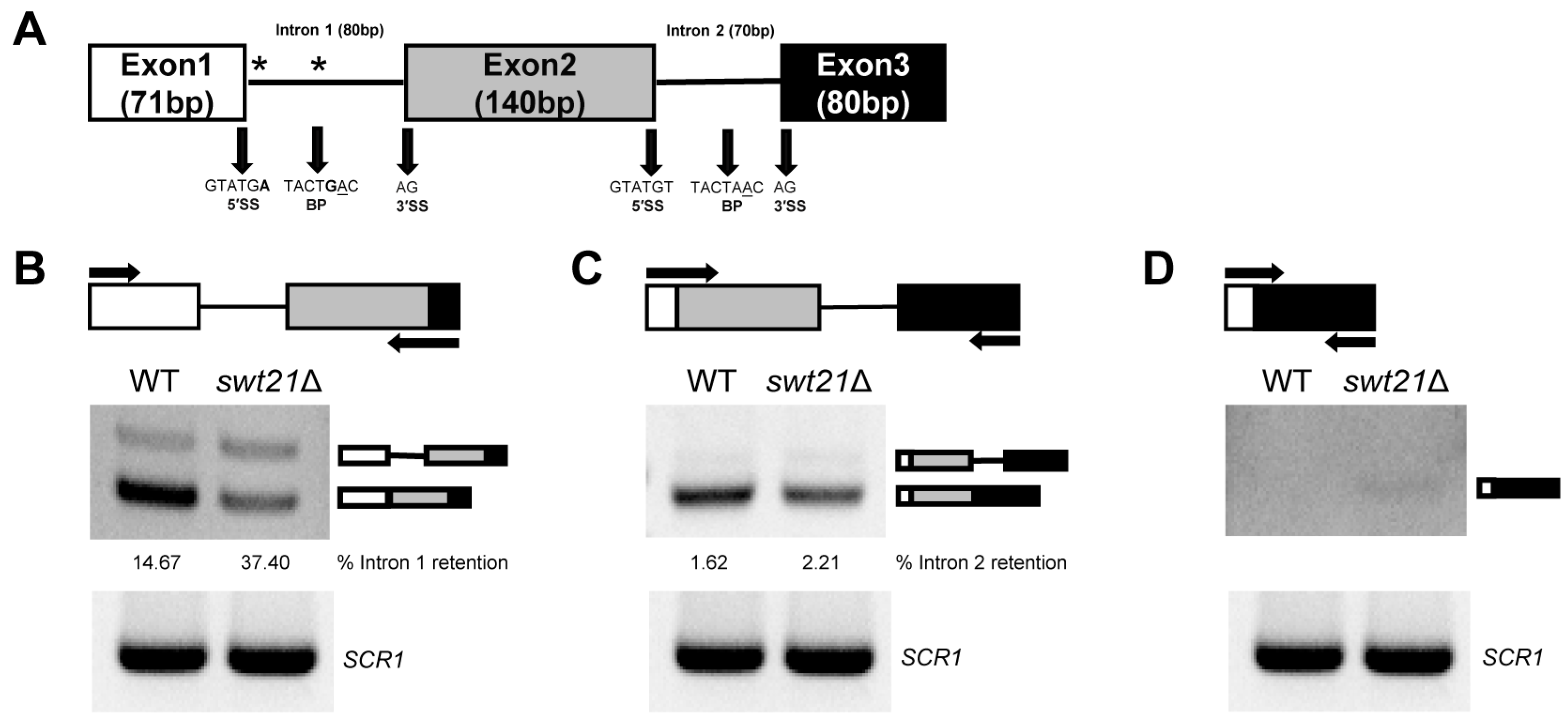
2.2. The Pattern of SUS1 Splicing Is Altered upon swt21Δ
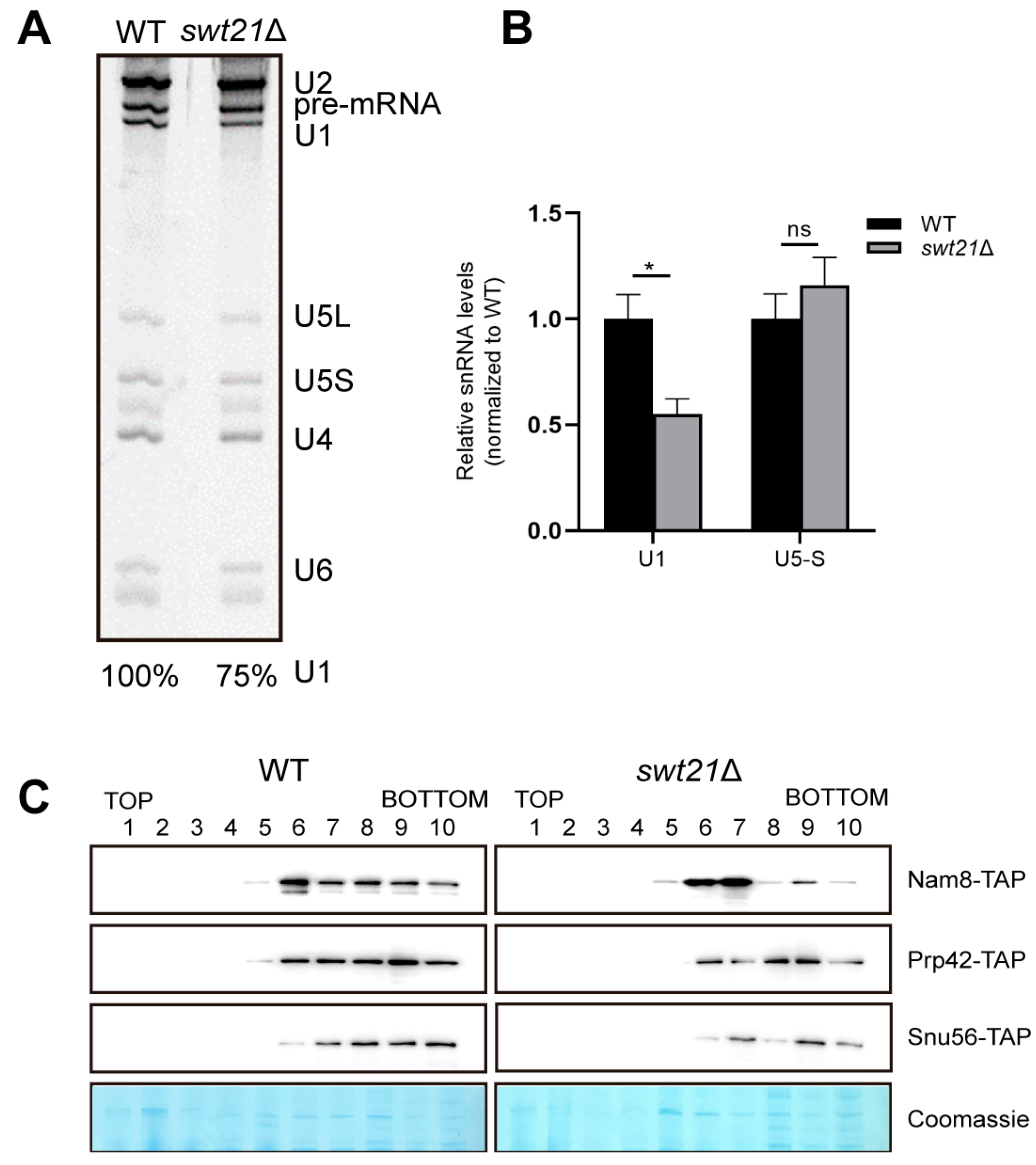
2.3. SWT21 Deletion Reduces U1 snRNP Levels in the Pre-B Complex
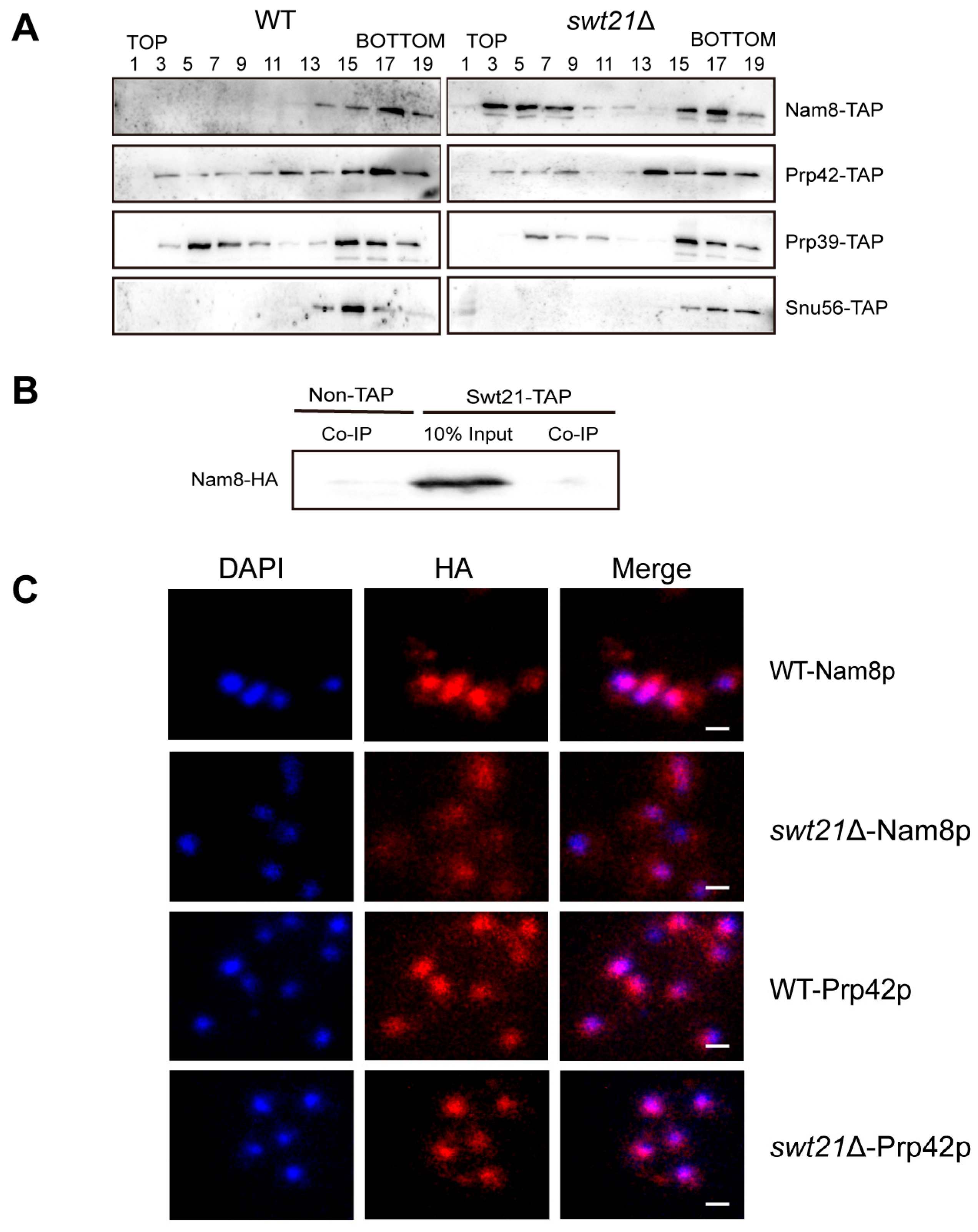
2.4. SWT21 Deletion Alters the Stability and Localization of the U1 Component Nam8p
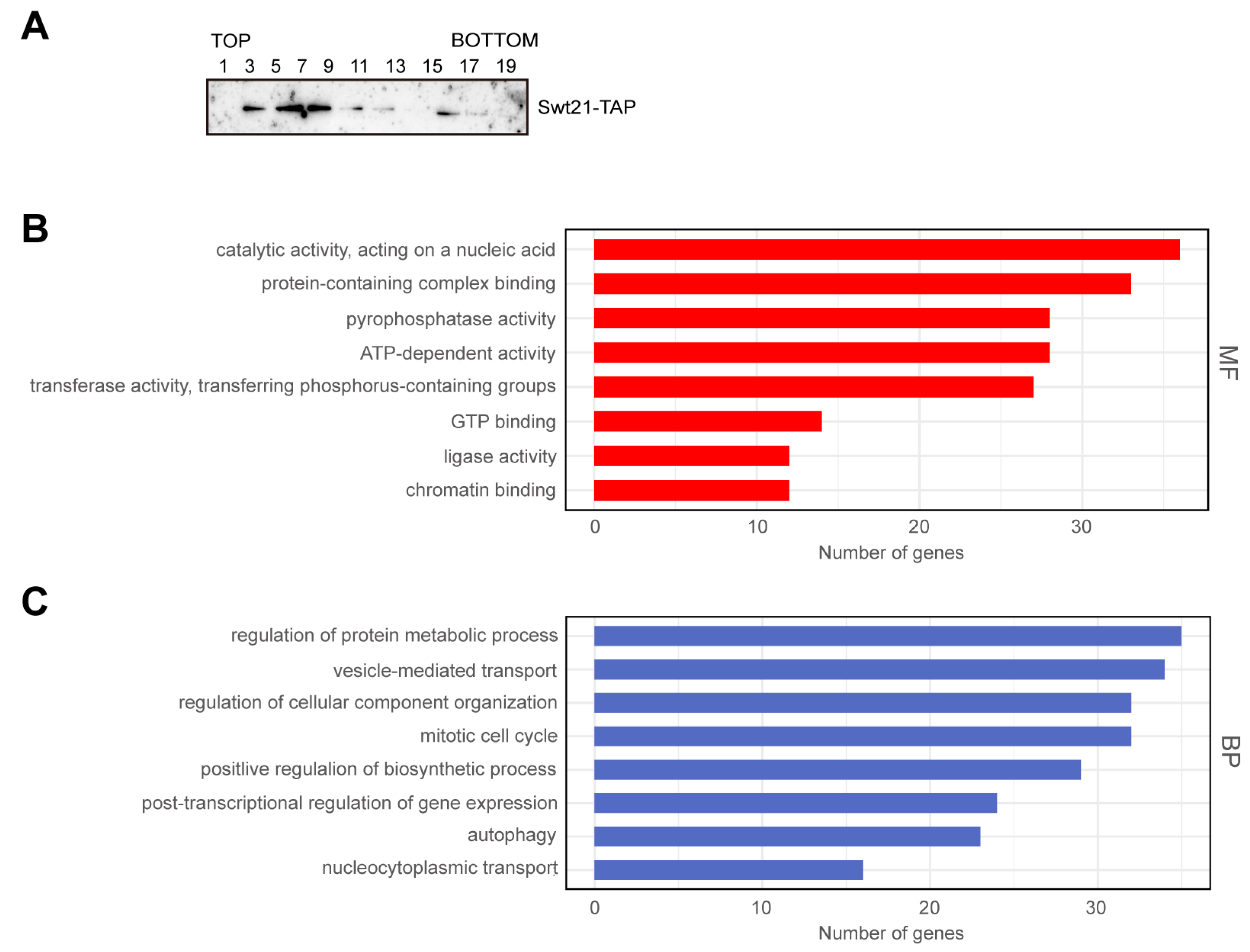
2.5. Swt21p Acts as a Regulatory Factor in Spliceosome Assembly
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Yeast Strains, Plasmids, and Primers
4.2. Splicing Extracts and In Vivo and In Vitro Splicing
4.3. Affinity Purification of Yeast Pre-B Complex
4.4. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.5. Protein Sample Preparation and Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Glycerol Gradient Analysis for the Distribution of Spliceosome Components
4.7. Immunoprecipitation Assay and Immunofluorescence Microscopy
4.8. TAP Purification of Swt21p/Nam8p Complexes
4.9. Mass Spectrometry and Gene Ontology Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gilbert, W. Why genes in pieces? Nature 1978, 271, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Will, C.L.; Lührmann, R. Spliceosome structure and function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.E.; Charenton, C.; Nagai, K. RNA Splicing by the Spliceosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boesler, C.; Rigo, N.; Anokhina, M.M.; Tauchert, M.J.; Agafonov, D.E.; Kastner, B.; Urlaub, H.; Ficner, R.; Will, C.L.; Lührmann, R. A spliceosome intermediate with loosely associated tri-snRNP accumulates in the absence of Prp28 ATPase activity. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, A.J.; Norman, C. U5 snRNA interacts with exon sequences at 5′ and 3′ splice sites. Cell 1992, 68, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandels-Lewis, S.; Séraphin, B. Involvement of U6 snRNA in 5′ splice site selection. Science 1993, 262, 2035–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staley, J.P.; Guthrie, C. Mechanical devices of the spliceosome: Motors, clocks, springs, and things. Cell 1998, 92, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wan, R.; Shi, Y. Molecular Mechanisms of pre-mRNA Splicing through Structural Biology of the Spliceosome. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a032409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, X.; Olson, A.J.; Rao, A.R.; Enerly, E.; Kristensen, V.N.; Børresen-Dale, A.L.; Andresen, B.S.; Krainer, A.R.; Sachidanandam, R. Features of 5′-splice-site efficiency derived from disease-causing mutations and comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, O.; Gottschalk, A.; Fabrizio, P.; Séraphin, B. Interaction of the U1 snRNP with nonconserved intronic sequences affects 5′ splice site selection. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, A.; Tang, J.; Puig, O.; Salgado, J.; Neubauer, G.; Colot, H.V.; Mann, M.; Séraphin, B.; Rosbash, M.; Lührmann, R.; et al. A comprehensive biochemical and genetic analysis of the yeast U1 snRNP reveals five novel proteins. Rna 1998, 4, 374–393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fortes, P.; Bilbao-Cortés, D.; Fornerod, M.; Rigaut, G.; Raymond, W.; Séraphin, B.; Mattaj, I.W. Luc7p, a novel yeast U1 snRNP protein with a role in 5′ splice site recognition. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 2425–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwer, B.; Shuman, S. Structure-function analysis of the Yhc1 subunit of yeast U1 snRNP and genetic interactions of Yhc1 with Mud2, Nam8, Mud1, Tgs1, U1 snRNA, SmD3 and Prp28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 4697–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Schwer, B.; Shuman, S. Mutational analyses of trimethylguanosine synthase (Tgs1) and Mud2: Proteins implicated in pre-mRNA splicing. Rna 2010, 16, 1018–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubol, B.E.; Wozniak, J.M.; Fattet, L.; Gonzalez, D.J.; Adams, J.A. CLK1 reorganizes the splicing factor U1-70K for early spliceosomal protein assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2018251118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, T.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Fargason, T.; De Silva, N.I.U.; Powell, E.; Ekpenyong, E.; Jamal, S.; Yu, Y.; Prevelige, P.; et al. The U1-70K and SRSF1 interaction is modulated by phosphorylation during the early stages of spliceosome assembly. Protein Sci. 2024, 33, e5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tong, C.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Shen, X.; Li, X.; Yin, Y. Condensation of ZFP207 and U1 snRNP promotes spliceosome assembly. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, R.; Tung, L.; Du, H.; Stands, L.; Rosbash, M.; Chang, T.H. A targeted bypass screen identifies Ynl187p, Prp42p, Snu71p, and Cbp80p for stable U1 snRNP/Pre-mRNA interaction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 3941–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromont-Racine, M.; Mayes, A.E.; Brunet-Simon, A.; Rain, J.C.; Colley, A.; Dix, I.; Decourty, L.; Joly, N.; Ricard, F.; Beggs, J.D.; et al. Genome-wide protein interaction screens reveal functional networks involving Sm-like proteins. Yeast 2000, 17, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, M.W.; Olson, B.L.; Siliciano, P.G. The yeast splicing factor Prp40p contains functional leucine-rich nuclear export signals that are essential for splicing. Genetics 2004, 166, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decourty, L.; Saveanu, C.; Zemam, K.; Hantraye, F.; Frachon, E.; Rousselle, J.C.; Fromont-Racine, M.; Jacquier, A. Linking functionally related genes by sensitive and quantitative characterization of genetic interaction profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5821–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.A.; Grate, L.; Spingola, M.; Ares, M., Jr. Test of intron predictions reveals novel splice sites, alternatively spliced mRNAs and new introns in meiotically regulated genes of yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.A.; Claggett, J.M.; Nguyen, T.; Johnson, T.L. The cap binding complex influences H2B ubiquitination by facilitating splicing of the SUS1 pre-mRNA. Rna 2009, 15, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbuQattam, A.; Gallego, J.; Rodríguez-Navarro, S. An intronic RNA structure modulates expression of the mRNA biogenesis factor Sus1. Rna 2016, 22, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Navarro, S.; Fischer, T.; Luo, M.J.; Antúnez, O.; Brettschneider, S.; Lechner, J.; Pérez-Ortín, J.E.; Reed, R.; Hurt, E. Sus1, a functional component of the SAGA histone acetylase complex and the nuclear pore-associated mRNA export machinery. Cell 2004, 116, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Rodriguez, C.M.; Johnson, T.L. Key features of the two-intron Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene SUS1 contribute to its alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 8612–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabrizio, P.; Dannenberg, J.; Dube, P.; Kastner, B.; Stark, H.; Urlaub, H.; Lührmann, R. The evolutionarily conserved core design of the catalytic activation step of the yeast spliceosome. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 593–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, P.; Will, C.L.; Urlaub, H.; Boon, K.L.; Lührmann, R. The RES complex is required for efficient transformation of the precatalytic B spliceosome into an activated B(act) complex. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 2416–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boon, K.L.; Auchynnikava, T.; Edwalds-Gilbert, G.; Barrass, J.D.; Droop, A.P.; Dez, C.; Beggs, J.D. Yeast ntr1/spp382 mediates prp43 function in postspliceosomes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 6016–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, W.K.; Falvo, J.V.; Gerke, L.C.; Carroll, A.S.; Howson, R.W.; Weissman, J.S.; O’Shea, E.K. Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature 2003, 425, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigaut, G.; Shevchenko, A.; Rutz, B.; Wilm, M.; Mann, M.; Séraphin, B. A generic protein purification method for protein complex characterization and proteome exploration. Nat. Biotechnol. 1999, 17, 1030–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavin, A.C.; Bösche, M.; Krause, R.; Grandi, P.; Marzioch, M.; Bauer, A.; Schultz, J.; Rick, J.M.; Michon, A.M.; Cruciat, C.M.; et al. Functional organization of the yeast proteome by systematic analysis of protein complexes. Nature 2002, 415, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-García, P.; Rodríguez-Navarro, S. A tale of coupling, Sus1 function in transcription and mRNA export. RNA Biol. 2009, 6, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engebrecht, J.A.; Voelkel-Meiman, K.; Roeder, G.S. Meiosis-specific RNA splicing in yeast. Cell 1991, 66, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardell, J.; Warner, J.R. Regulation of splicing at an intermediate step in the formation of the spliceosome. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preker, P.J.; Kim, K.S.; Guthrie, C. Expression of the essential mRNA export factor Yra1p is autoregulated by a splicing-dependent mechanism. Rna 2002, 8, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juneau, K.; Nislow, C.; Davis, R.W. Alternative splicing of PTC7 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae determines protein localization. Genetics 2009, 183, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merens, H.E.; Choquet, K.; Baxter-Koenigs, A.R.; Churchman, L.S. Timing is everything: Advances in quantifying splicing kinetics. Trends Cell Biol. 2024, 34, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enders, M.; Neumann, P.; Dickmanns, A.; Ficner, R. Structure and function of spliceosomal DEAH-box ATPases. Biol. Chem. 2023, 404, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Wan, R.; Yan, C.; Lei, J.; Shi, Y. Structures of the fully assembled Saccharomyces cerevisiae spliceosome before activation. Science 2018, 360, 1423–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaschka, C.; Lin, P.C.; Charenton, C.; Nagai, K. Prespliceosome structure provides insights into spliceosome assembly and regulation. Nature 2018, 559, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Issaian, A.; Hill, R.C.; Espinosa, S.; Shi, S.; Cui, Y.; Kappel, K.; Das, R.; et al. A unified mechanism for intron and exon definition and back-splicing. Nature 2019, 573, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Rosbash, M. Identification of eight proteins that cross-link to pre-mRNA in the yeast commitment complex. Genes Dev. 1999, 13, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo, J.M.; Valcárcel, J. Fas-activated serine/threonine kinase (FAST K) synergizes with TIA-1/TIAR proteins to regulate Fas alternative splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 1539–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipak, L.; Spirek, M.; Novatchkova, M.; Chen, Z.; Rumpf, C.; Lugmayr, W.; Mechtler, K.; Ammerer, G.; Csaszar, E.; Gregan, J. An improved strategy for tandem affinity purification-tagging of Schizosaccharomyces pombe genes. Proteomics 2009, 9, 4825–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longtine, M.S.; McKenzie, A., 3rd; Demarini, D.J.; Shah, N.G.; Wach, A.; Brachat, A.; Philippsen, P.; Pringle, J.R. Additional modules for versatile and economical PCR-based gene deletion and modification in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 1998, 14, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umen, J.G.; Guthrie, C. A novel role for a U5 snRNP protein in 3′ splice site selection. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volland, C.; Urban-Grimal, D.; Géraud, G.; Haguenauer-Tsapis, R. Endocytosis and degradation of the yeast uracil permease under adverse conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 9833–9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, C.; Urlaub, H.; Luhrmann, R.; Fabrizio, P. Mutagenesis suggests several roles of Snu114p in pre-mRNA splicing. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28324–28334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teigelkamp, S.; Newman, A.J.; Beggs, J.D. Extensive interactions of PRP8 protein with the 5′ and 3′ splice sites during splicing suggest a role in stabilization of exon alignment by U5 snRNA. Embo J. 1995, 14, 2602–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, K.; Fu, X.; Wang, L.; Xiao, S.; Wang, S.; Fan, Y.; An, X.; Boon, K.-L.; Bao, P. Swt21p Is Required for Nam8p-U1 snRNP Association and Efficient Pre-mRNA Splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125440
Lin K, Fu X, Wang L, Xiao S, Wang S, Fan Y, An X, Boon K-L, Bao P. Swt21p Is Required for Nam8p-U1 snRNP Association and Efficient Pre-mRNA Splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(12):5440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125440
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Ke, Xiuhu Fu, Lulu Wang, Sa Xiao, Shenxin Wang, Yingjie Fan, Xinyu An, Kum-Loong Boon, and Penghui Bao. 2025. "Swt21p Is Required for Nam8p-U1 snRNP Association and Efficient Pre-mRNA Splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 12: 5440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125440
APA StyleLin, K., Fu, X., Wang, L., Xiao, S., Wang, S., Fan, Y., An, X., Boon, K.-L., & Bao, P. (2025). Swt21p Is Required for Nam8p-U1 snRNP Association and Efficient Pre-mRNA Splicing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(12), 5440. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26125440





