Exploring Exosome Contributions to Gouty Arthritis: A Proteomics and Experimental Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
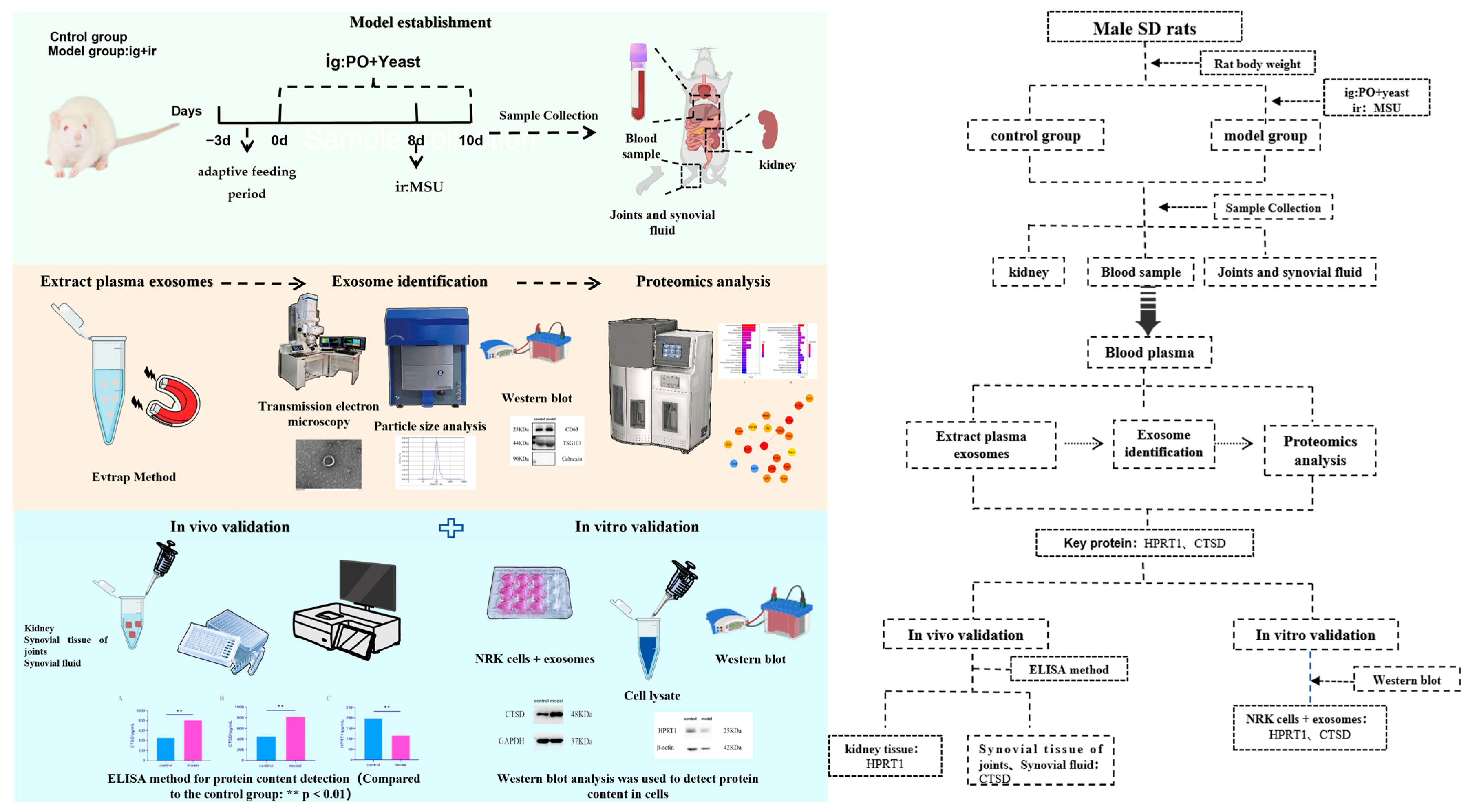
2.1. Establishment of Rat Model with Hyperuricemia and Gouty Arthritis
2.2. Characterization of Plasma Exosomes in Rats
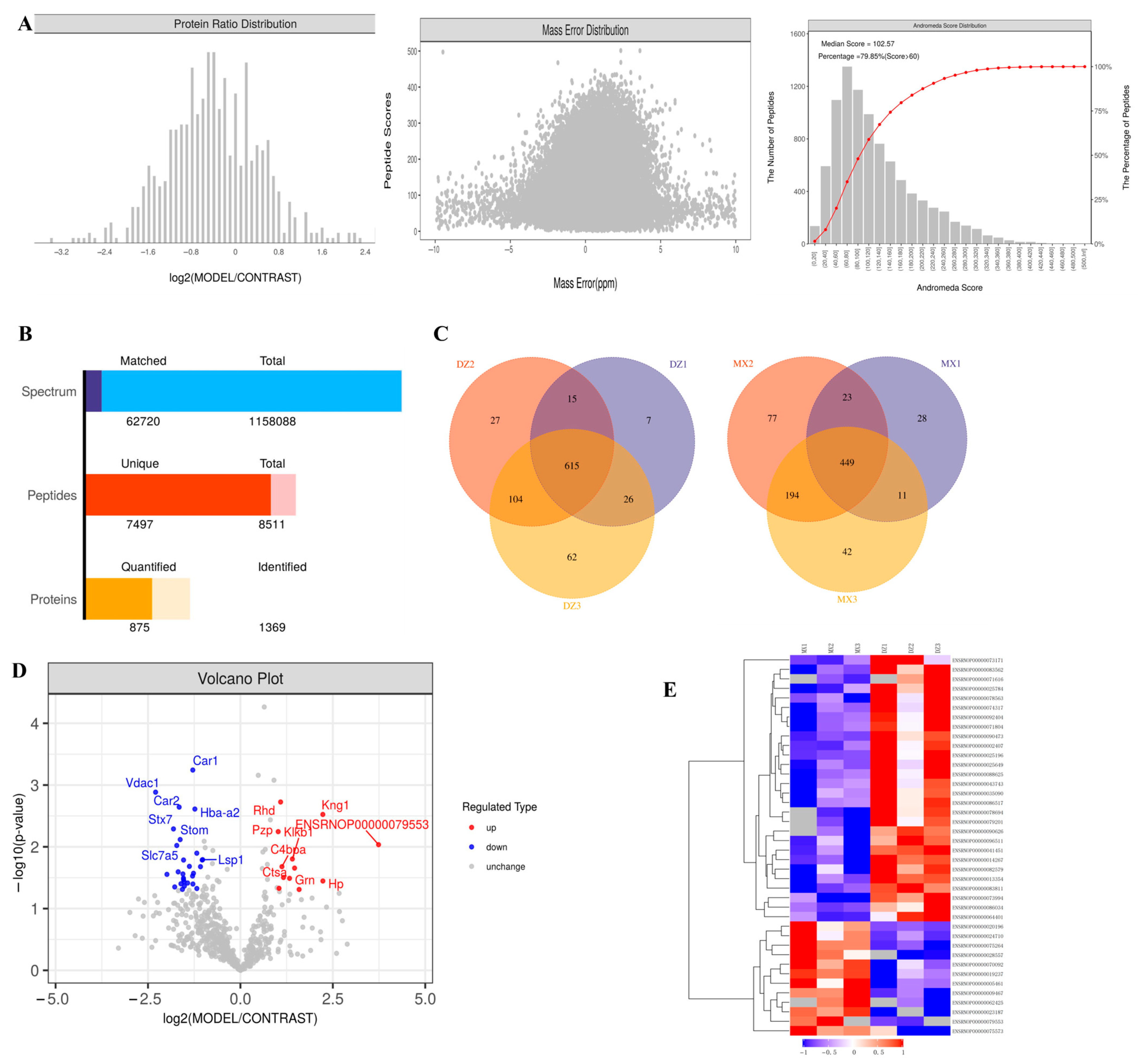
2.3. Proteomics Analysis of Plasma Exosomes in Rats
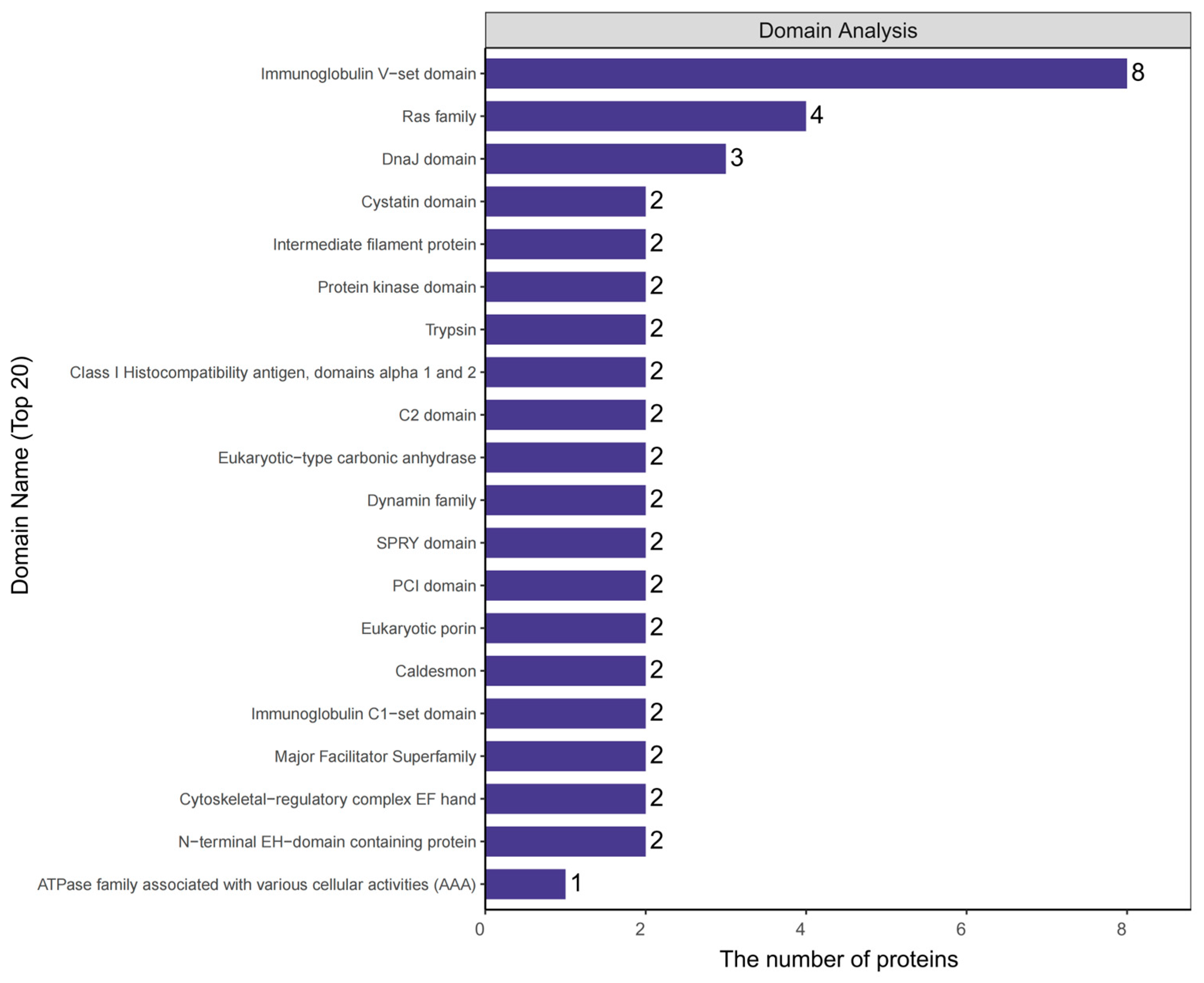
2.4. Analysis of Protein Domains in Plasma Exosomes of Rats
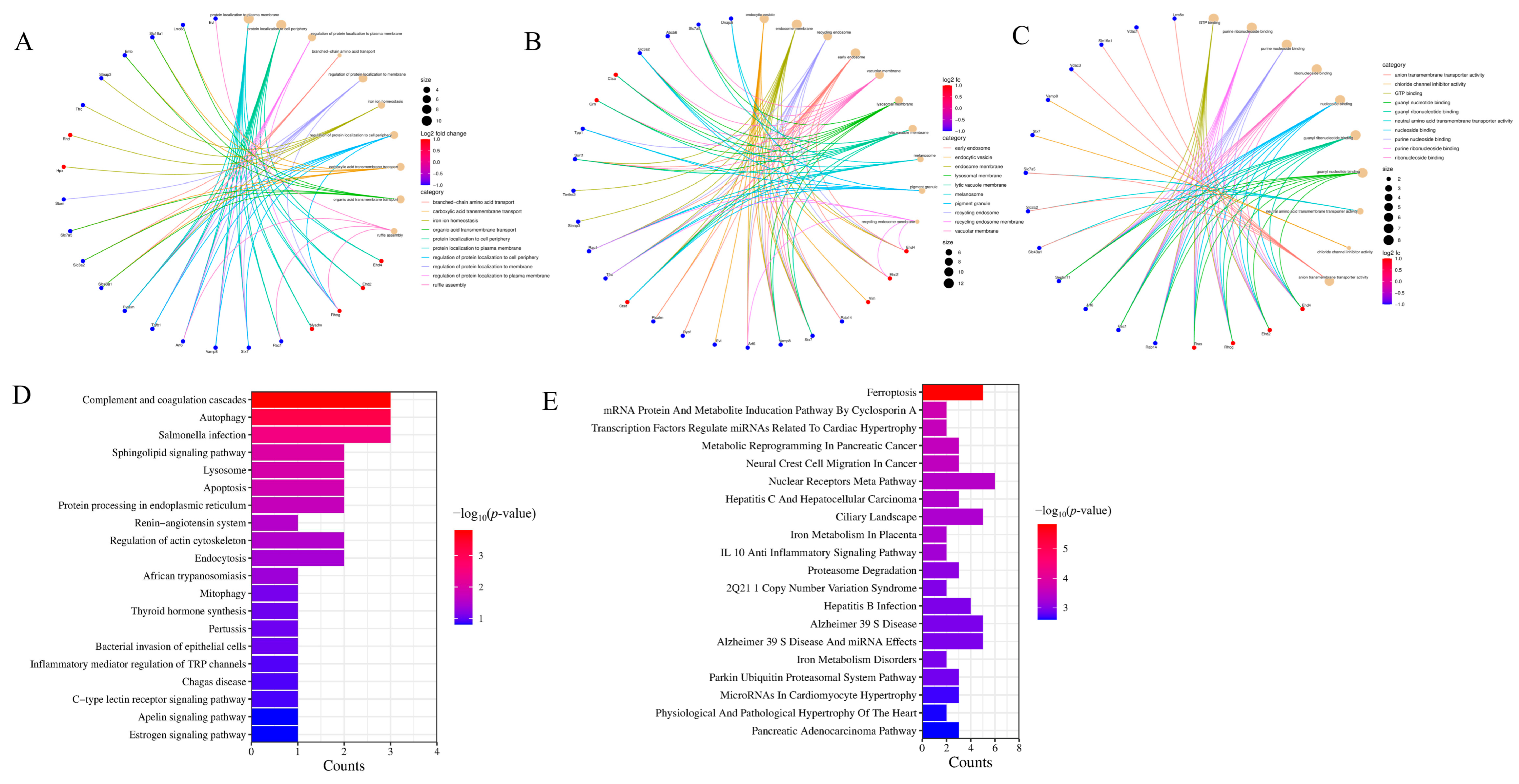
2.5. GO Annotation and KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Exosome Proteins in Rat Plasma
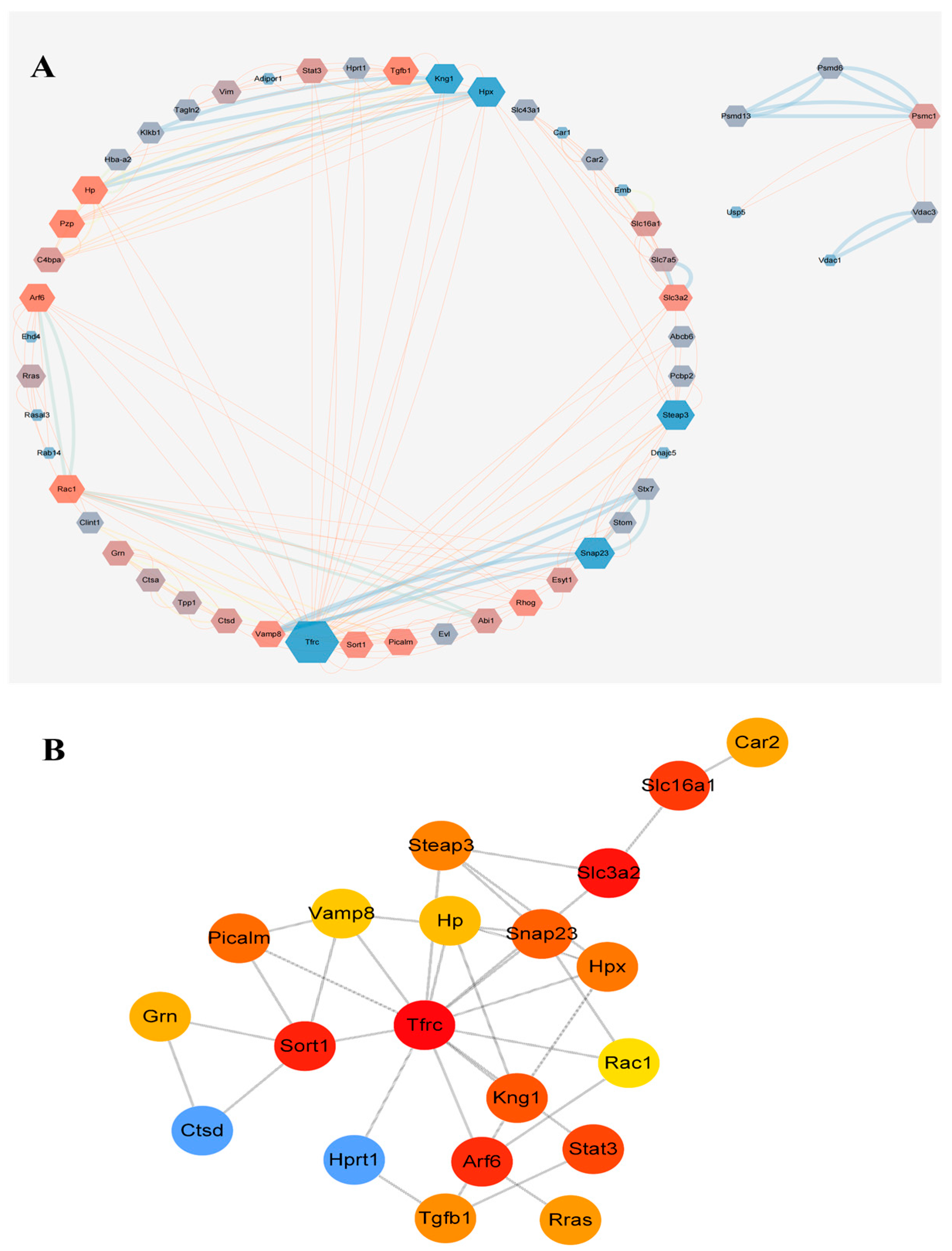
2.6. Protein Interaction Network Analysis of Exosome Proteins in Rat Plasma
2.7. In Vitro and In Vivo Experiments Were Conducted to Verify the Results
2.7.1. In Vivo Experiments
2.7.2. In Vitro Experiments
Cell Morphology
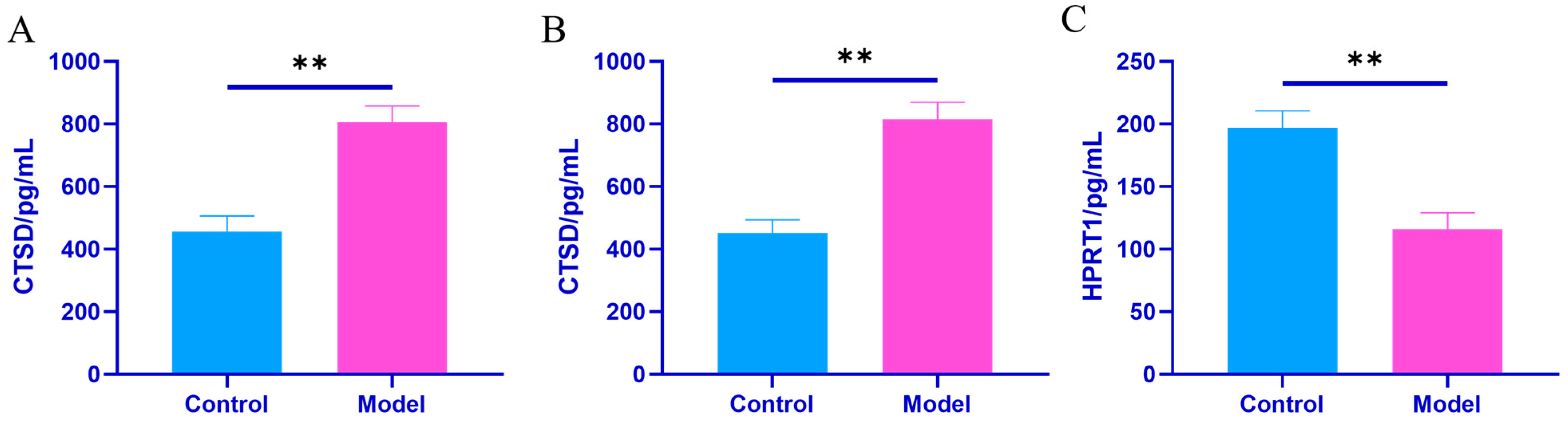
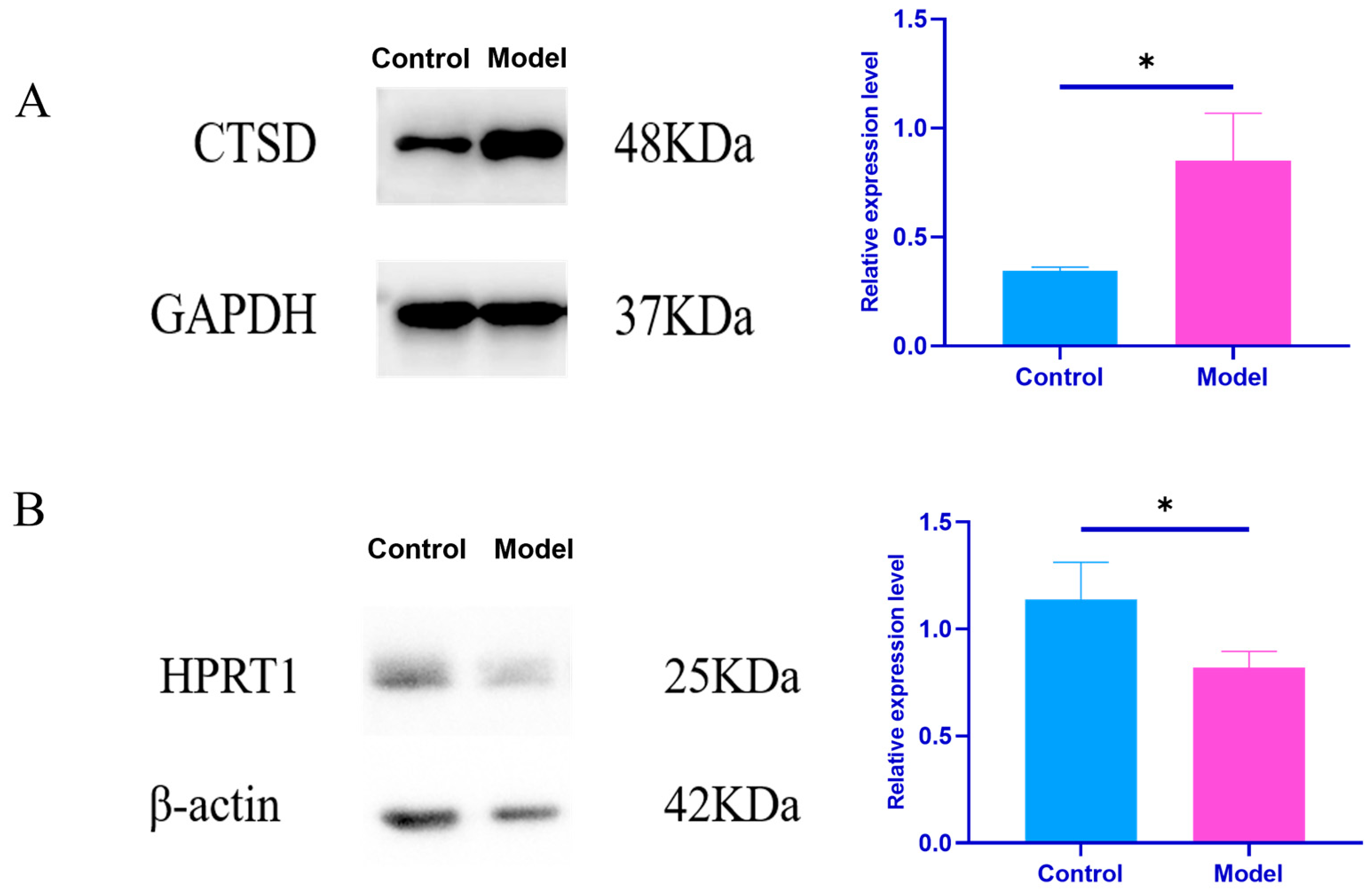
Effects of Plasma Exosomes on the Content of CTSD and HPRT1 Proteins in NRK Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Animals
4.1.2. Cells
4.1.3. Main Reagents
4.1.4. Major Instruments
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Animal Grouping and Model Preparation
4.2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
4.2.3. Detection Indicators and Methods
Indicators of Successful Model Induction
Isolation and Identification of Plasma Exosomes
- Plasma Exosome Separation (EVtrap Method)
- Plasma Exosome Identification
- Proteomics Analysis
- In Vivo Experiments
- In Vivo Experiments
4.2.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, B. Modern cognition and prevention and treatment of uric acid metabolism disorders-related diseases with traditional Chinese medicine. J. Chin. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2024, 49, 3160–3167. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhang, B. Are hyperuricemia and gout different diseases? Comment on the guidelines for the diagnosis and management of hyperuricemia and gout from the healthcare professional perspectives in China. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 26, 1866–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.Z. Why Does Hyperuricemia Not Necessarily Induce Gout? Biomolecules 2021, 11, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; House, M.E.; Aati, O.; Tan, P.; Franklin, C.; Horne, A.; Gamble, G.D.; Stamp, L.K.; Doyle, A.J.; McQueen, F.M. Urate crystal deposition in asymptomatic hyperuricaemia and symptomatic gout: A dual energy CT study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 908–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, S. Biological characteristics and potential application value of exosomes. Adv. Physiol. Sci. 2025, 56, 54–61. [Google Scholar]
- Ritankar, M.; Aidin, T.T.; Carole, A.P. Exosomes Mediate LTB4 Release during Neutrophil Chemotaxis. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, 1002336. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, E.; Zhu, H.; Geng, H.; Zhong, L.; Qiu, X.; Xie, J.; Xiao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. The Inhibition of Osteoblast Viability by Monosodium Urate Crystal-Stimulated Neutrophil-Derived Exosomes. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 809586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, F.; Yuan, Y.; Jin, C.; Chang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, C.; He, F.; Wang, J. Inflammasome-Derived Exosomes Activate NF-κB Signaling in Macrophages. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, M.J.; Yu, H.; Lu, J.J.; Hu, Y.J.; Huang, Q.C.; Huang, R.Y.; Lu, C.J. Novel findings from determination of common expressed plasma exosomal microRNAs in patients with psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis vulgaris, rheumatoid arthritis, and gouty arthritis. Discov. Med. 2019, 28, 47–68. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.E.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, J.H.; Moon, K.W.; Park, J.K.; Park, K.S.; Lee, E.Y. Role of Synovial Exosomes in Osteoclast Differentiation in Inflammatory Arthritis. Cells 2021, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, Q.; Sun, S.; Ji, Z.; Huang, L.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Deng, W.; Li, T. TMT-Based Quantitative Proteomics Analysis of Synovial Fluid-Derived Exosomes in Inflammatory Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 800902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Liu, N.; Hu, M.; Zhang, M. Differential expression of ferroptosis-related proteins in urinary exosomes: Potential indicators for monitoring acute gout attack. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2024, 11, 1476631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zeng, H.; Li, H.; Li, S.; Chen, F.; Wang, W. Research progress on the pathogenesis of gouty arthritis and its treatment with traditional Chinese medicine. J. Chin. Exp. Formula 2022, 28, 256–267. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Yin, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y. Exosomes from mammals: Isolation, purification, clinical application and prospect. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 44, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, W.; Qian, X. Research progress on exosome isolation technology and its clinical application. Chromatography 2019, 37, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Hao, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, W.; Li, W. Preparation of Puerarin plasma exosomes and its effect on the permeability of an in vitro blood-brain barrier model. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lan, M.; Chen, Y. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV): Ten-Year Evolution (2014–2023). Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Wu, Y.; Shen, S.; Xiao, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, J.; Ding, H. Research progress on NLRP3 inflammasome activation in arthritic diseases. Chin. J. Clin. Res. 2025, 38, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, S.; Tang, M.; Zhang, B.; Xiang, D.; Li, F. Ferroptosis in inflammatory arthritis: A promising future. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 955069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gemmis, P.; Anesi, L.; Lorenzetto, E.; Gioachini, I.; Fortunati, E.; Zandonà, G.; Fanin, E.; Fairbanks, L.; Andrighetto, G.; Parmigiani, P. Analysis of the HPRT1 gene in 35 Italian Lesch-Nyhan families:45 patients and 77 potential female carriers. Mutat. Res. 2010, 692, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, S.; Kolobova, I.; Crapper, L.; Ernst, C. Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome: Models, Theories, and Therapies. Mol. Syndromol. 2016, 7, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayat, A.; Christensen, M.; Wibrand, F.; Duno, M.; Lund, A. Mild Lesch-Nyhan Disease in a Boy with a Null Mutation in HPRT1: An Exception to the Known Genotype-Phenotype Correlation. JIMD Rep. 2015, 18, 135–137. [Google Scholar]
- Chavarriaga, J.; Ocampo, M.; Fakih, N.; Herrera, J.S. Kelley-Seegmiller Syndrome: Urolithiasis, Renal Uric Acid Deposits, Gout: What is the Role of the Urologist? Urol. Int. 2019, 102, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima, E.; Mori, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Toyohara, T.; Kikuchi, K.; Oikawa, Y.; Matsuhashi, T.; Maeda, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kudo, M. HPRT-related hyperuricemia with a novel p.V35M mutation in HPRT1 presenting familial juvenile gout. CEN Case Rep. 2020, 9, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Ge, M.; Li, J. Phospholipase A2 regulates autophagy in gouty arthritis: Proteomic and metabolomic studies. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, N.; Hu, M.; Zhang, M. Lysosome-related proteins may have changes in the urinary exosomes of patients with acute gout attack. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaudet-Coopman, E.; Beaujouin, M.; Derocq, D.; Garcia, M.; Glondu-Lassis, M.; Laurent-Matha, V.; Prébois, C.; Rochefort, H.; Vignon, F.; Cathepsin, D. New. Discov. Funct. A Long-Standing Aspartic Protease Cancer apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2006, 237, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.H.; Chen, W.Y.; Yu, C.L.; Tsai, C.Y.; Hsieh, S.C. Gouty arthritis involves impairment of autophagic degradation via cathepsin D inactivation-mediated lysosomal dysfunction that promotes apoptosis in macrophages. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2023, 1869, 166703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coderre, T.J.; Wall, P.D. Ankle joint urate arthritis (AJUA) in rats: An alternative animal model of arthritis to that produced by Freund’s adjuvant. Pain 1987, 28, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
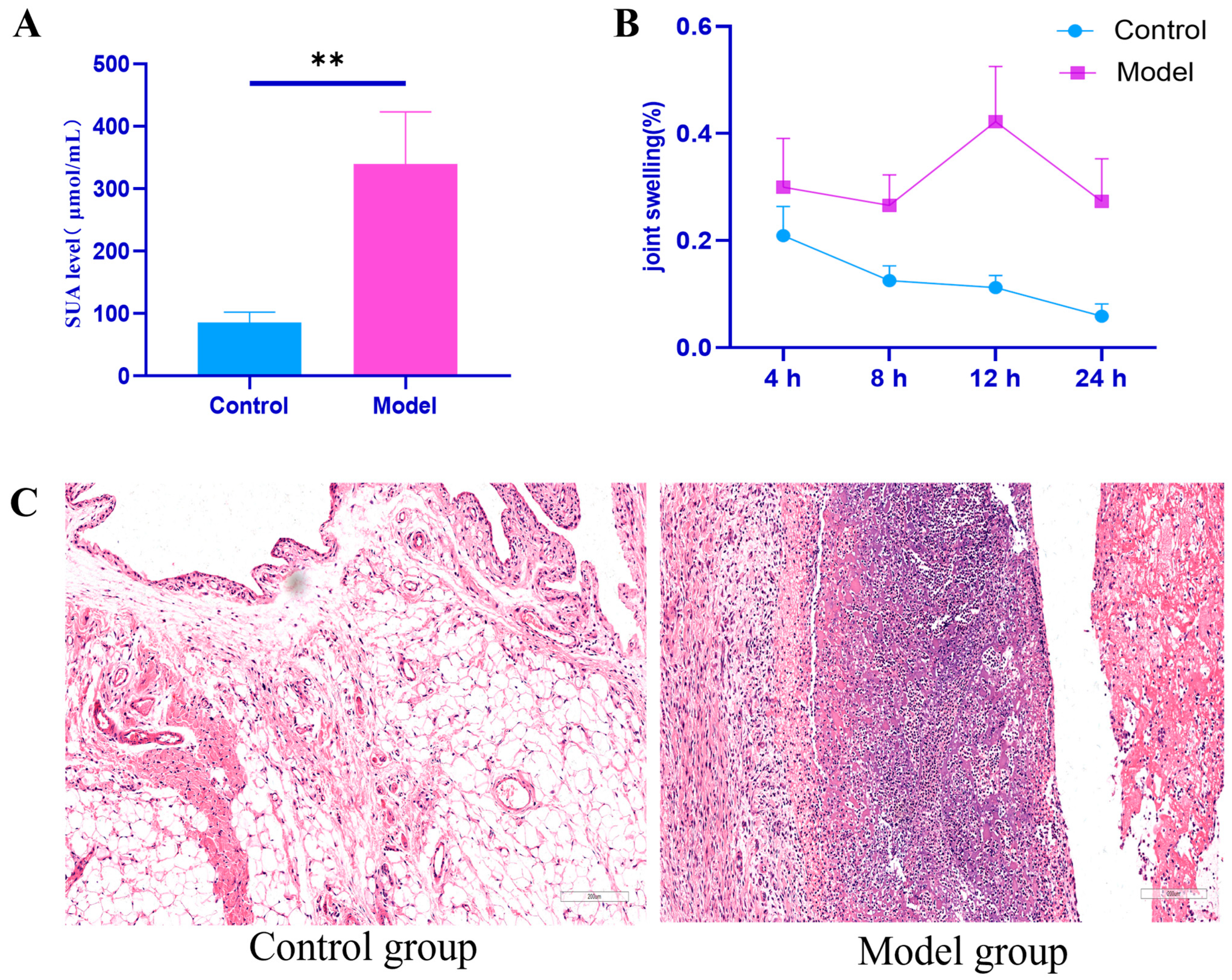

| Group | 4 h | 8 h | 12 h | 24 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 0.21 ± 0.05 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.02 | 0.06 ± 0.02 |
| Model set | 0.30 ± 0.09 ** | 0.27 ± 0.05 ** | 0.42 ± 0.10 ** | 0.27 ± 0.08 ** |
| Group | Average Grain Diameter (nm) | Concentration (Particles/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Control group | 160.1 | 6.8 × 1010 |
| Model set | 118.6 | 2.2 × 1010 |
| Protein ID | Protein Name | Gene Name | p Value | Regulated Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSRNOP00000079553 | 0.009234265 | Up | ||
| ENSRNOP00000020196 | Haptoglobin | Hp | 0.035755848 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000075264 | Kininogen 1 | Kng1 | 0.002991341 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000024710 | Hemopexin | Hpx | 0.049060005 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000070092 | 0.02210595 | Up | ||
| ENSRNOP00000019237 | Kallikrein B1 | Klkb1 | 0.015746642 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000028557 | Granulin precursor | Grn | 0.032365177 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000062425 | Cathepsin A | Ctsa | 0.03134781 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000005461 | Complement component 4 binding | C4bpa | 0.020942102 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000023187 | Rh blood group, D antigen | Rhd | 0.001881085 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000075573 | Kininogen 2 | Kng2l1 | 0.046996226 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000009467 | Pregnancy zone protein | Pzp | 0.005680288 | Up |
| ENSRNOP00000096511 | Lymphocyte-specific protein 1 | Lsp1 | 0.016146578 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000090626 | Voltage-dependent anion channel 3 | Vdac3 | 0.016342616 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000078694 | Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 5 | Usp5 | 0.020973216 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000086034 | Solute carrier family 43 member 1 | Slc43a1 | 0.047359279 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000090473 | Ubiquitin-40S ribosomal protein S27a-like | 0.012683047 | Down | |
| ENSRNOP00000041451 | Hemoglobin alpha, adult chain | Hba-a2 | 0.002447625 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000002407 | Transferrin receptor | Tfrc | 0.026856811 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000025649 | RAB14, member RAS oncogene family | Rab14 | 0.040039527 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000014267 | Carbonic anhydrase 1 | Car1 | 0.000571536 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000071804 | RT1 class Ia, locus A1 | RT1-CE11 | 0.029687156 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000025196 | Solute carrier family 3 member 2 | Slc3a2 | 0.020725478 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000035090 | Biliverdin reductase B | Blvrb | 0.038578949 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000071616 | Rac family small GTPase 1 | Rac1 | 0.043284863 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000074317 | Solute carrier family 44 member 1 | Slc44a1 | 0.036478675 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000082579 | Similar to Tpi1 protein | RGD1563601 | 0.016361424 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000078563 | Embigin | Emb | 0.033908058 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000064401 | Synaptosome associate | AABR07053516.1 | 0.032261476 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000092404 | Solute carrier family 16 member 1 | Slc16a1 | 0.027531761 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000043743 | Butyrophilin like 10 | Btnl10 | 0.048835568 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000073171 | ATP binding cassette subfamily | Abcb6 | 0.039659617 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000083562 | Stomatin | Stom | 0.007628371 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000013354 | Carbonic anhydrase 2 | Car2 | 0.002274499 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000086517 | STEAP3 metalloreductase | Steap3 | 0.02542084 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000025784 | Solute carrier family 7 member 5 | Slc7a5 | 0.009520689 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000079201 | Proline-rich coiled-coil 1 | Prrc1 | 0.044639932 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000073994 | Syntaxin 7 | Stx7 | 0.005132134 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000088625 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 8 | Vamp8 | 0.027923844 | Down |
| ENSRNOP00000083811 | Voltage-dependent anion channel 1 | Vdac1 | 0.001304447 | Down |
| Group | Synovial Tissue CTSD (pg/mL) | Joint Fluid CTSD (pg/mL) | Kidney Tissue HPRT1 (pg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 457.40 ± 46.51 | 451.11 ± 40.60 | 196.74 ± 13.10 |
| Model set | 806.50 ± 49.58 ** | 813.81 ± 53.19 ** | 115.98 ± 12.61 ** |
| Group | CTSD/GAPDH | HPRT1/β-Actin |
|---|---|---|
| Control group | 0.34 ± 0.01 | 1.14 ± 0.15 |
| Model set | 0.85 ± 0.18 * | 0.82 ± 0.07 * |
| Order of Holes | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reagents added | Washing buffer containing magnetic beads | Washing buffer | 1 mL PBS | 1 mL PBS | 200 μL 200 mM TEA solution elution | |
| Drain the liquid 1 | Remove liquid 2 | Drain the liquid 3 | Remove liquid 4 | Merge eluates and store | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lin, Z. Exploring Exosome Contributions to Gouty Arthritis: A Proteomics and Experimental Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115320
Lu C, Yang X, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang B, Lin Z. Exploring Exosome Contributions to Gouty Arthritis: A Proteomics and Experimental Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115320
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Chengjin, Xiaoxiong Yang, Xue Wang, Yu Wang, Bing Zhang, and Zhijian Lin. 2025. "Exploring Exosome Contributions to Gouty Arthritis: A Proteomics and Experimental Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115320
APA StyleLu, C., Yang, X., Wang, X., Wang, Y., Zhang, B., & Lin, Z. (2025). Exploring Exosome Contributions to Gouty Arthritis: A Proteomics and Experimental Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115320






