Challenges in Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
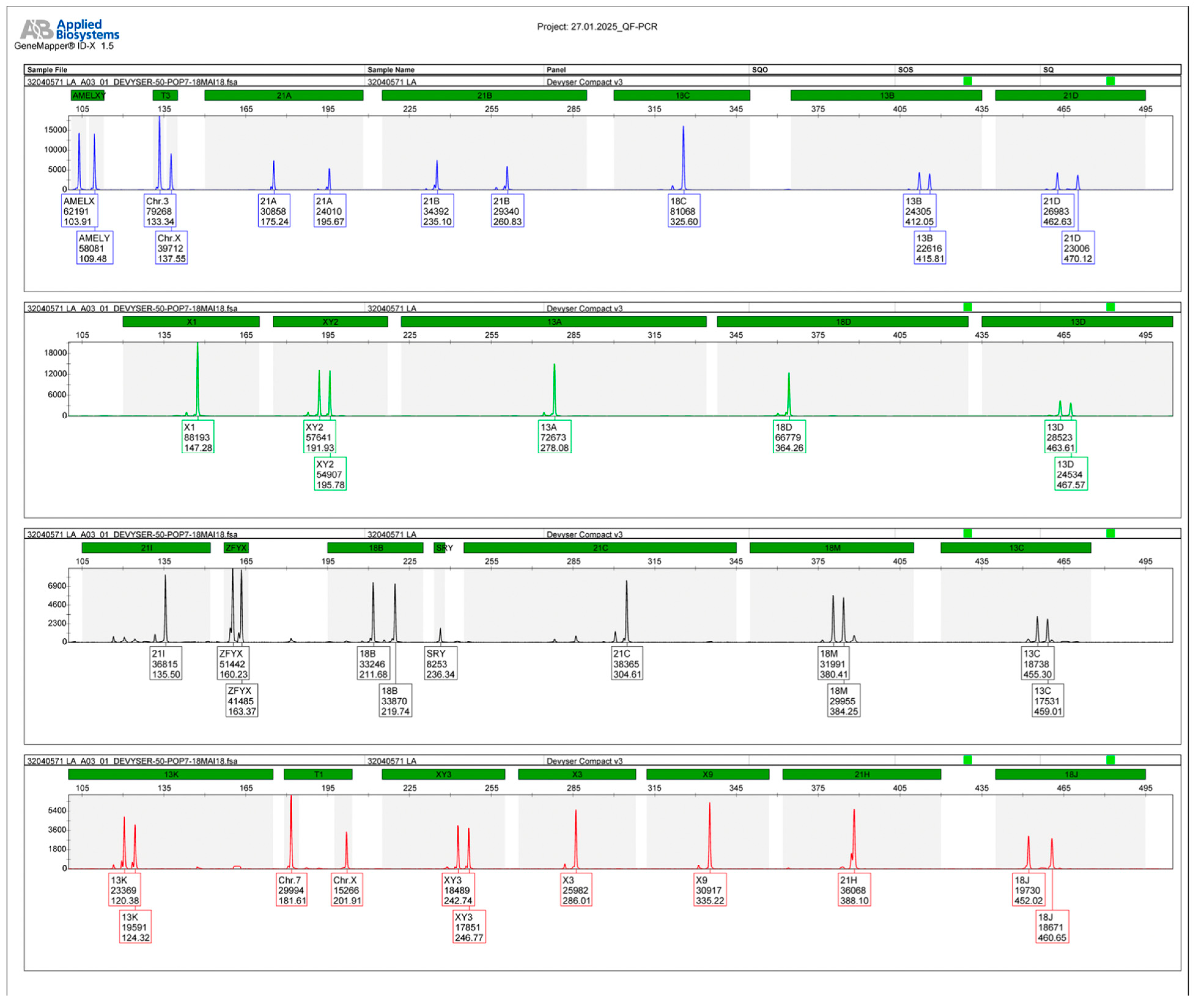
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Presentation
2.2. Case Management
3. Literature Search: Methodology and Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Manifestations
4.2. Genetics of the Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome (RSTS)
4.3. Prenatal Diagnosis and Differential Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome (RSTS)
- Diagnostic Challenges
- Differential diagnosis
4.4. Complications
4.5. Management
4.6. Ethical Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADHD | Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder |
| ASD | Autistic spectrum disorders |
| βHCG | Β human chorionic gonadotropin |
| HPA | Hypoplasia of the pulmonary artery |
| IUGR | Intrauterine growth restriction |
| MoM | Multiple of the median |
| MTHFR | Methylenetetrahydropholate reductase |
| PAPP-A | Pregnancy-associated plasma protein A |
| RSTS | Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome |
| SNP array | Single-nucleotide polymorphism array |
| TF | Tetralogy of Fallot |
References
- Huang, F.R.; Zhang, A.M.; Xu, J.; Huang, L. A clinical characteristics and genetic analysis of a case of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome with glaucoma. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, C.A. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome. In GeneReviews® [Internet]; Adam, M.P., Feldman, J., Mirzaa, G.M., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Gripp, K.W., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Van-Gils, J.; Naudion, S.; Toutain, J.; Lancelot, G.; Attié-Bitach, T.; Blesson, S.; Demeer, B.; Doray, B.; Gonzales, M.; Martinovic, J.; et al. Fetal phenotype of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome caused by CREBBP mutations. Clin. Genet. 2019, 95, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ambrosi, F.; Ronzoni, L.; Villa, R.; De Marinis, S.; Cetera, G.E.; Soldavini, C.M.; Ferrazzi, E. Ultrasound 2-D and 3-D diagnosis of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in a 21-week-old fetus. J. Ultrasound 2022, 25, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennekam, R.C. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 14, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Aggarwal, R.; Kabra, M.; Deorari, A.K. Dandy-Walker malformation in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: A rare association. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2002, 11, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, C.C.; Pedroso, J.L.; Souza, P.V.; Pinto, W.B.; Barsottini, O.G. Broad thumbs and broad hallux: The hallmarks for the Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatria 2014, 72, 81–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, M.J.; Newbury-Ecob, R.; Holder-Espinasse, M.; Yau, S.; Lillis, S.; Hurst, J.A.; Clement, E.; Reardon, W.; Joss, S.; Hobson, E.; et al. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome type 2: Report of nine new cases that extend the phenotypic and genotypic spectrum. Clin. Dysmorphol. 2016, 25, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Suthar, R.; Panigrahi, I.; Marwaha, R.K. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: Clinical profile of 11 patients and review of literature. Indian J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 18, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosek, J.; Borková, A. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrom nebo-li syndrom sirokých palců [The Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome or a broad thumb-hallux syndrome]. Cas. Lek. Ceskych 2008, 147, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Milani, D.; Manzoni, F.M.; Pezzani, L.; Ajmone, P.; Gervasini, C.; Menni, F.; Esposito, S. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: Clinical features, genetic basis, diagnosis, and management. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2015, 41, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, G.; Milani, D.; Colapietro, P.; Forzano, F.; Della Monica, M.; Rusconi, D.; Consonni, L.; Caffi, L.G.; Finelli, P.; Scarano, G.; et al. Clinical and molecular characterization of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome patients carrying distinct novel mutations of the EP300 gene. Clin. Genet. 2015, 87, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, O.; Kress, W.; Kempf, O.; Lechno, S.; Haaf, T.; Zechner, U. Inheritance and variable expression in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2010, 152A, 2254–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, E.; Sglavo, G.; Paladini, D. Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. J. Ultrasound Med. 2009, 28, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedeschi, M.F.; Crippa, B.L.; Colombo, L.; Guez, S.; Cerruti, M.; Fogliani, R.; Gervasini, C.; Lalatta, F. Unusual prenatal presentation of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: A case report. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164A, 2663–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelfsema, J.H.; White, S.J.; Ariyürek, Y.; Bartholdi, D.; Niedrist, D.; Papadia, F.; Bacino, C.A.; den Dunnen, J.T.; van Ommen, G.J.; Breuning, M.H.; et al. Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome: Mutations in both the CBP and EP300 genes cause disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 76, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Kort, E.; Conneman, N.; Diderich, K. A case of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome and congenital neuroblastoma. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2014, 164A, 1332–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardalliac, C.; Vincent, M.; Joubert, M.; Le Vaillant, C. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome in a Fetus: Contribution of 2- and 3-Dimensional Ultrasonography. J. Ultrasound Med. 2017, 37, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Li, P.; Qu, H.Q.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zheng, M.; Tian, L.; Wu, Z.; et al. Role of the ADCY9 gene in cardiac abnormalities of the Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zloto, K.; Weissbach, T.; Messing, B.; Birnbaum, R.; Gindes, L.; Levy, M.; Lerman-Sagie, T.; Hadi, E.; Eliyahu, A.; Feinstein-Goren, N.; et al. Prenatal Sonographic Features of Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome-A Small Case Series of a Rare Syndrome. Prenat. Diagn. 2024, 44, 1502–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qattan, M.M.; Jarman, A.; Rafique, A.; Al-Hassnan, Z.N.; Al-Qattan, H.M. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in a Saudi boy with distinct features and variants in both the CREBBP and EP300 genes: A case report. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagilova, O.R.; Adyan, T.A.; Beskorovainaya, T.S.; Polyakov, A.V. Molecular genetic analysis of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in Russian patients. Front. Genet. 2025, 16, 1516565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotsirilos, P.; Taylor, J.C.; Matalon, R.; Opitz, J.M.; Reynolds, J.F. Dominant inheritance of a syndrome similar to Rubinstein-Taybi. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1987, 26, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumul, R.C.R.; Chiong, M.A.D. Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome in a Filipino Infant with a Novel CREBBP Gene Pathogenic Variant. Case Rep. Genet. 2022, 2022, 3388879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawky, R.M.; Elsayed, N.S.; Seifeldin, N.S. Facial dysmorphism, skeletal anomalies, congenital glucoma, dysplastic nails: Mild Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome. Egypt. J. Med. Hum. Genet. 2012, 13, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Seidel, V.; Santibáñez, P.; Cervera-Acedo, C.; Castro-de Castro, P.; Domínguez-Garrido, E. First case report of inherited Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome associated with a novel EP300 variant. BMC Med. Genet. 2016, 17, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Bourdeaut, F.; Miquel, C.; Richer, W.; Grill, J.; Zerah, M.; Grison, C.; Pierron, G.; Amiel, J.; Krucker, C.; Radvanyi, F.; et al. Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome predisposing to non-WNT, non-SHH, group 3 medulloblastoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2014, 61, 383–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, Y.H.; Huang, H.Y.; Hong, Y.K.; Aala, W.F., Jr.; Tu, W.T.; Tsai, M.C.; Chou, Y.Y.; Hsu, C.-K. Genetic Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome With Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) and Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES): Case Series with a Novel CREBBP Variant. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 848879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, H.M.H.; Rößling, R.I.; Geithe, C.; Khan, M.M.; Dinter, F.; Hanack, K.; Prüß, H.; Husse, B.; Roggenbuck, D.; Schierack, P.; et al. MicroRNA biomarkers as next-generation diagnostic tools for neurodegenerative diseases: A comprehensive review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 17, 1386735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, M.; Zampetaki, A.; Willeit, P.; Willeit, J.; Kiechl, S. MicroRNAs within the continuum of postgenomics biomarker discovery. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spena, S.; Gervasini, C.; Milani, D. Ultra-Rare Syndromes: The Example of Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome. J. Pediatr. Genet. 2015, 4, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chima, S.C.; Mamdoo, F. Ethical and legal dilemmas around termination of pregnancy for severe fetal anomalies: A review of two African neonates presenting with ventriculomegaly and holoprosencephaly. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2015, 18, S31–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
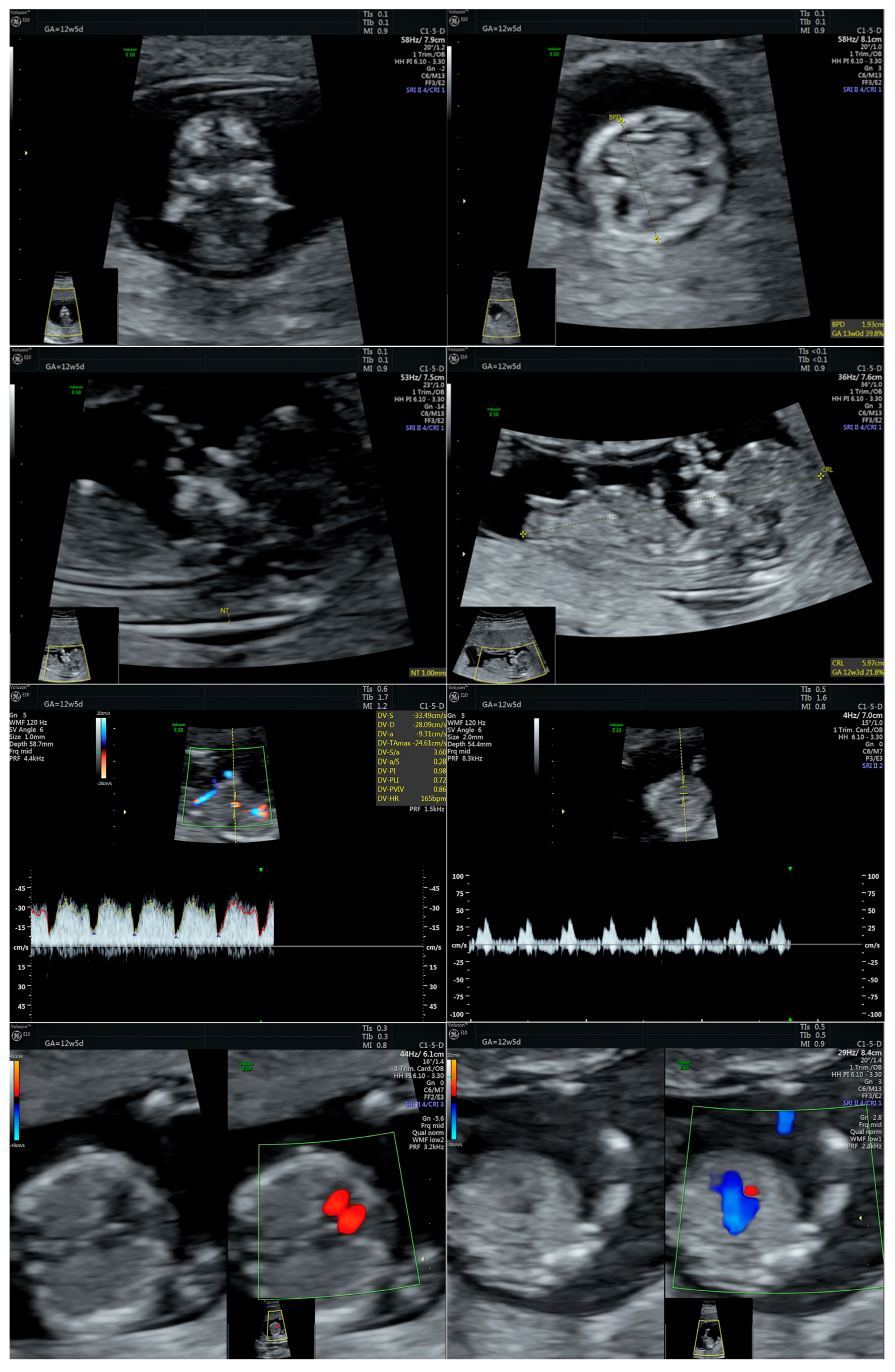
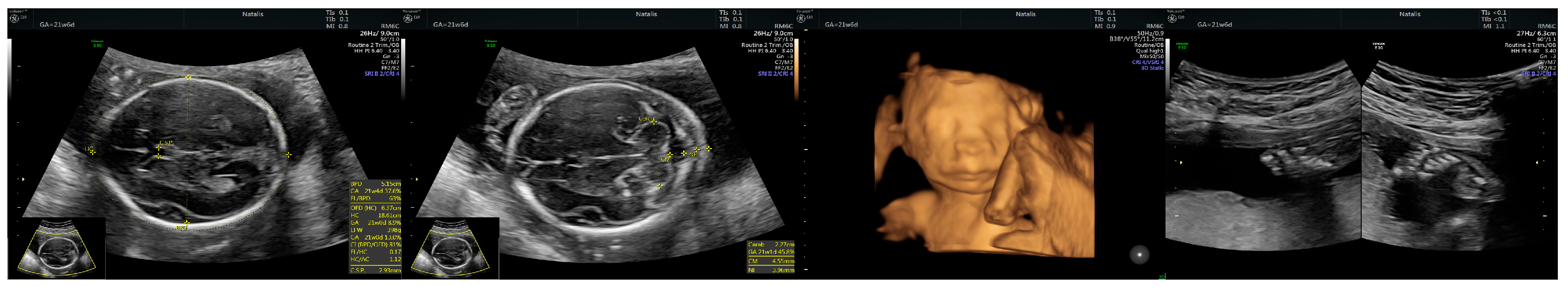
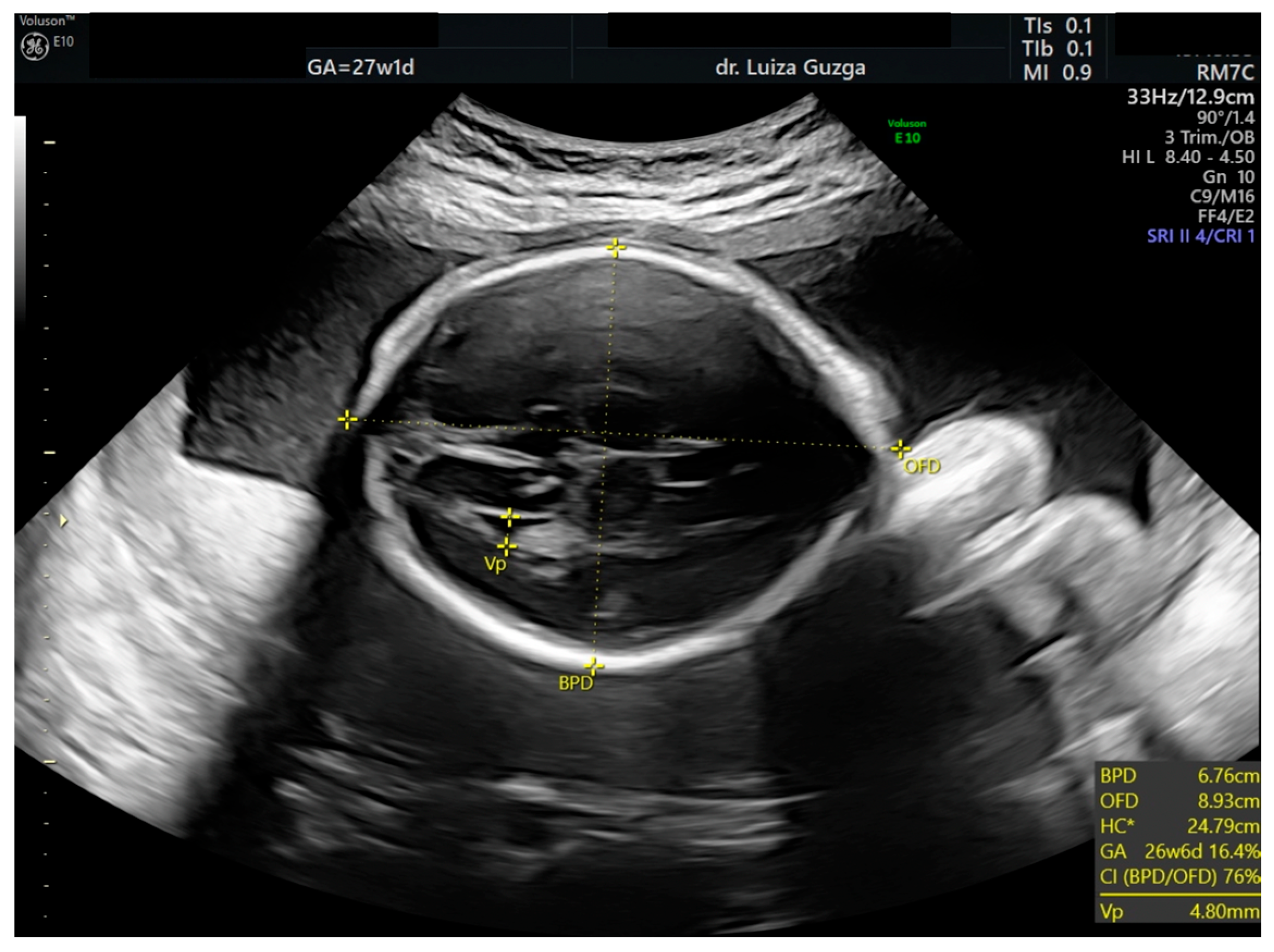
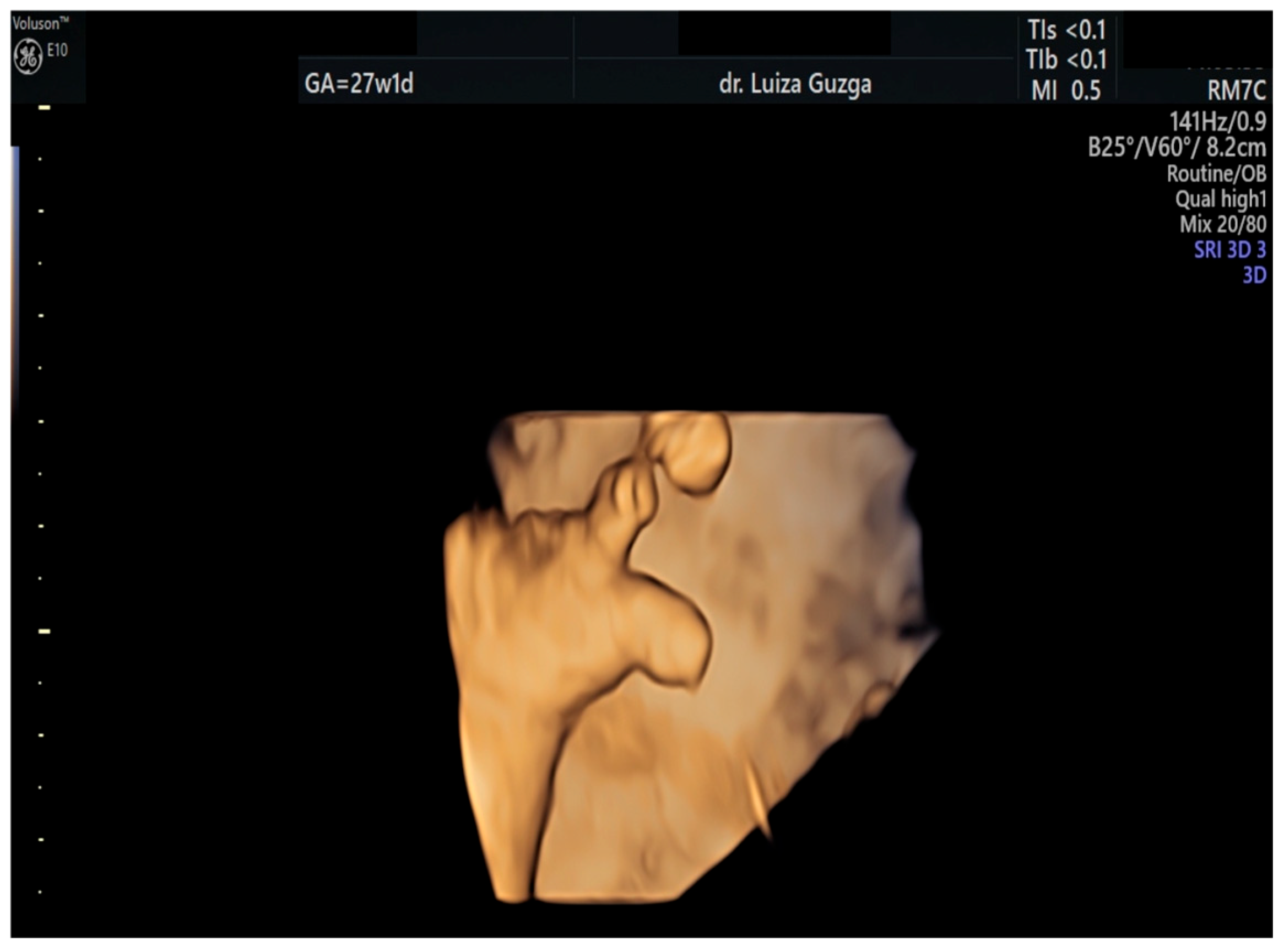
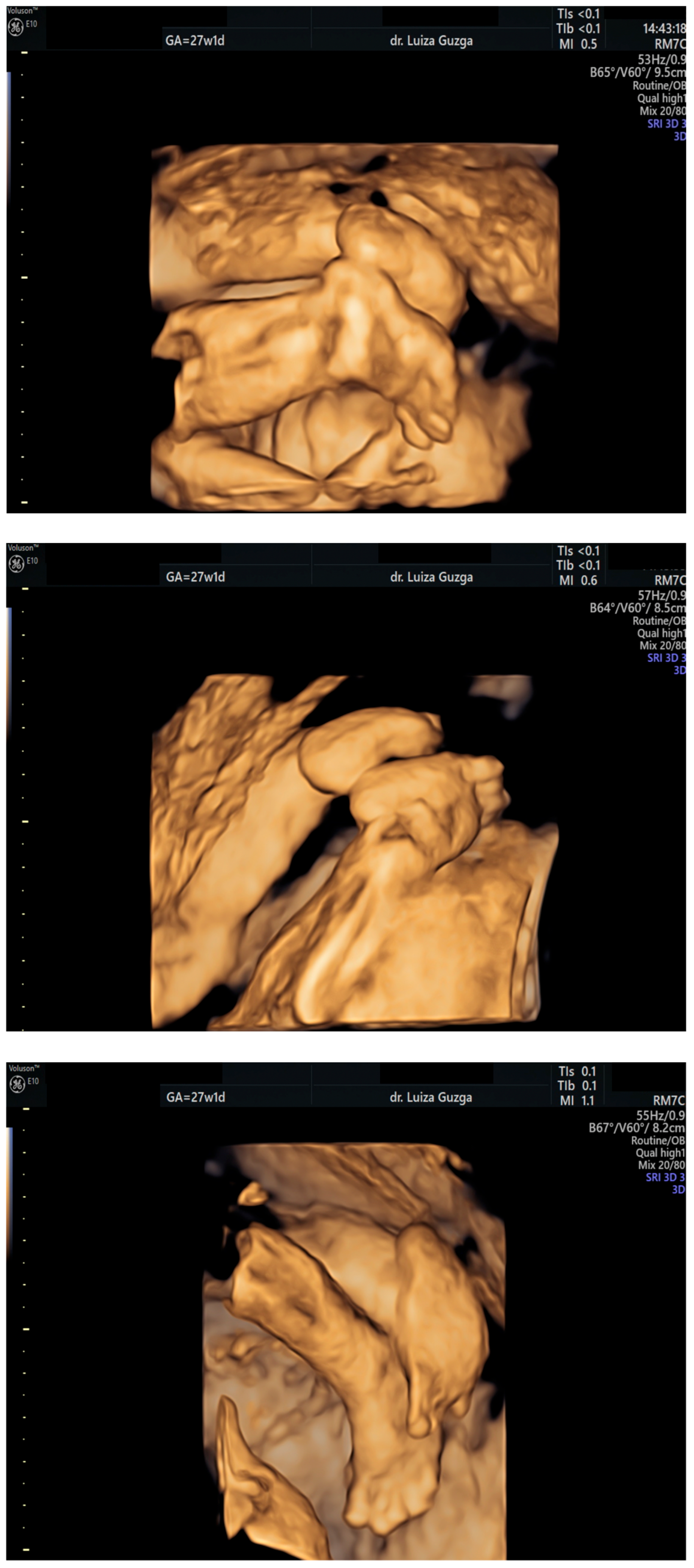
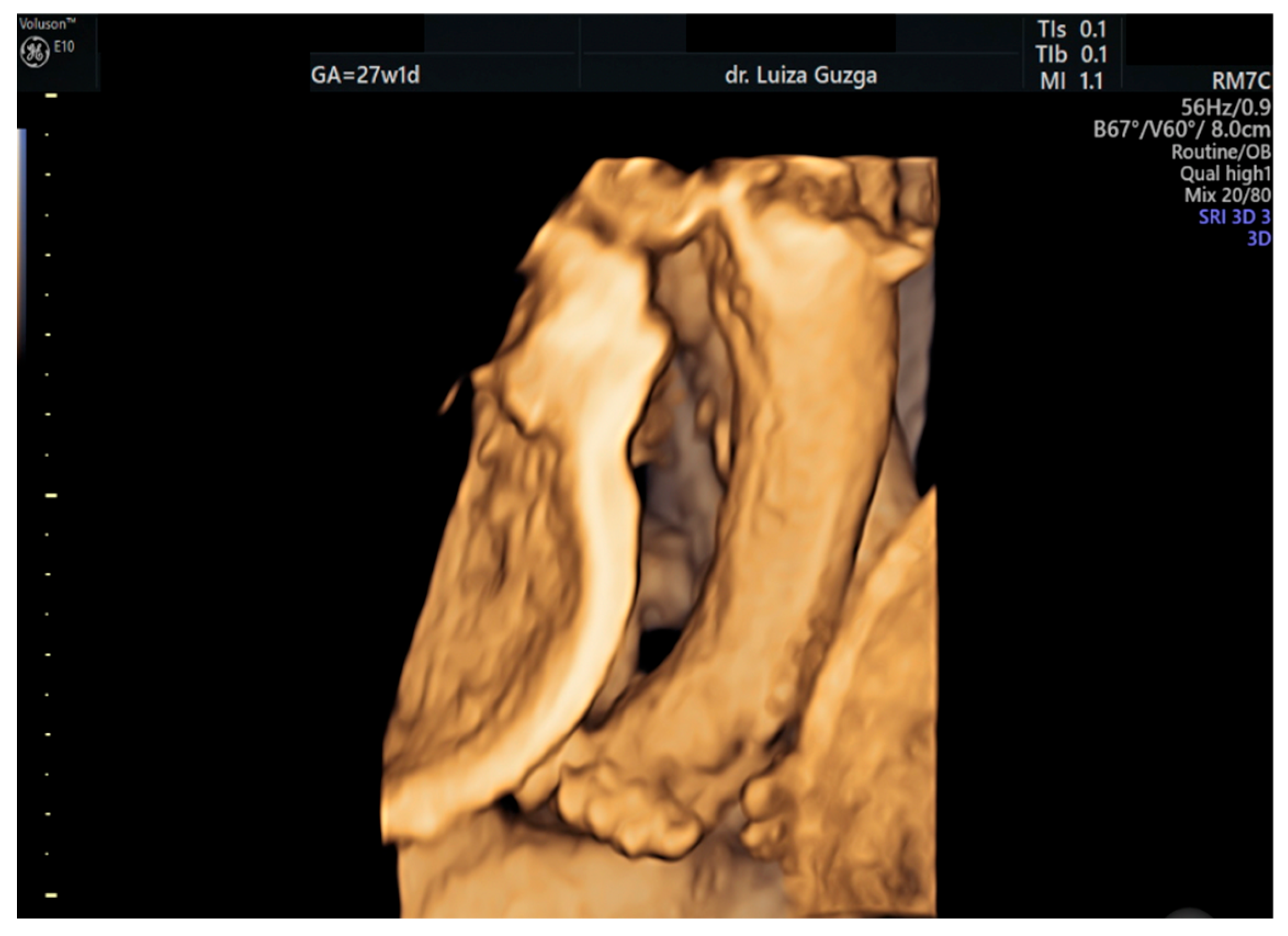
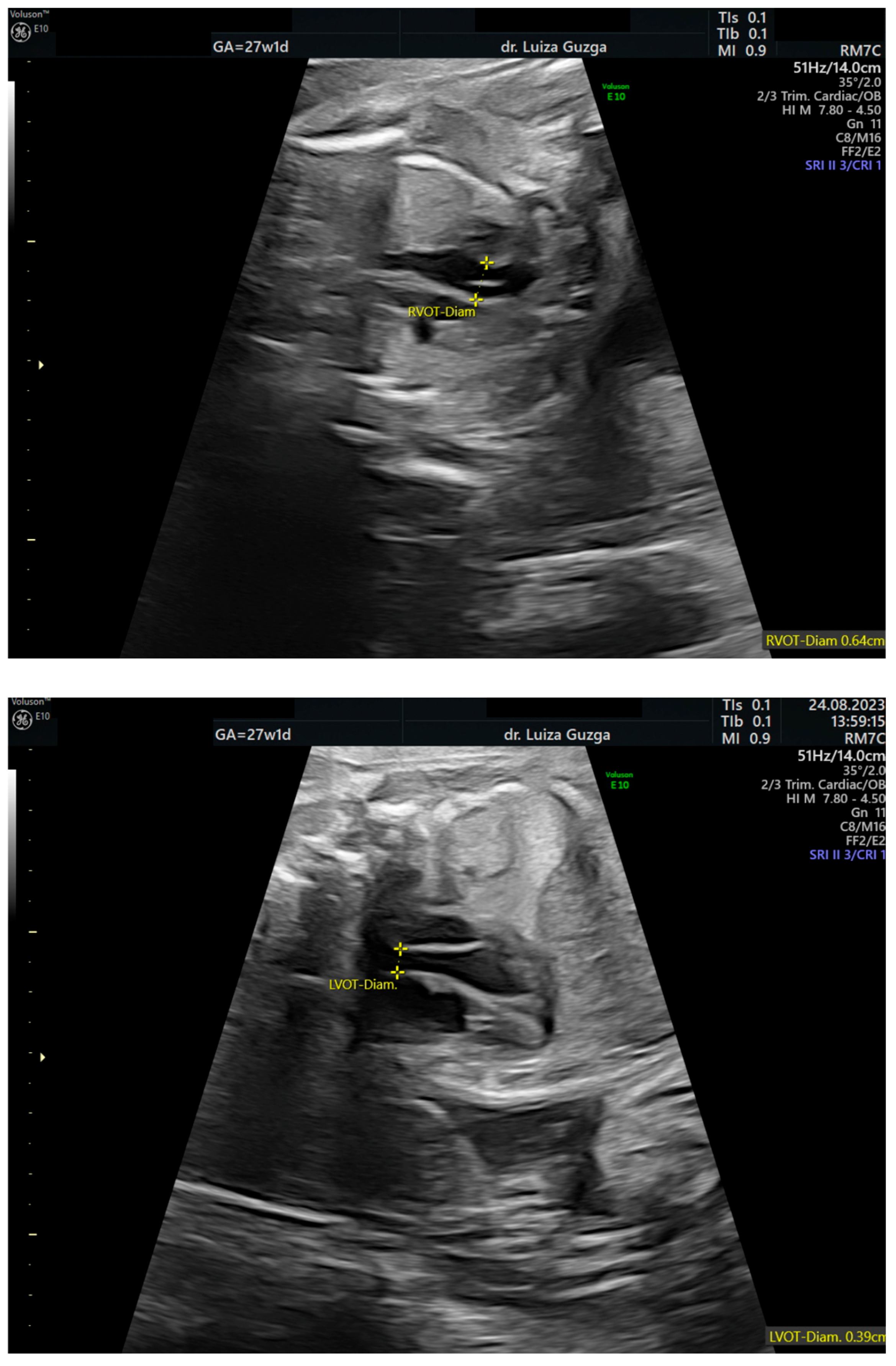
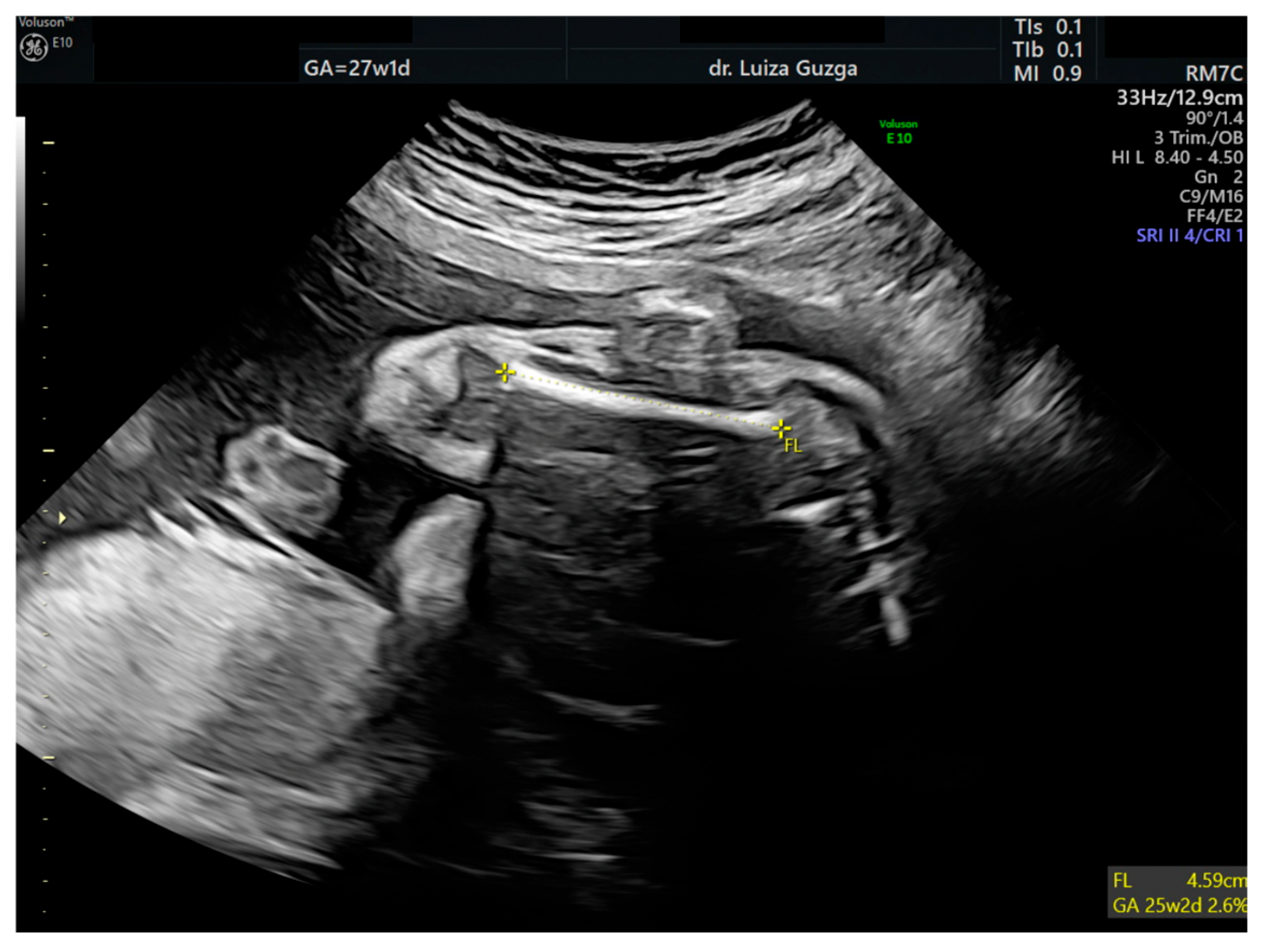

| Prenatal Ultrasound Findings | 21 + 6 | 26 + 6 | 28 + 6 | Frequency of Postnatal Findings in the Literature |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pointed forehead/premature closure of the metopic suture | - | + | +++ | ? |
| Hypotelorism | - | + | +++ | Rather hypertelorism |
| Micrognathia/small chin size | - | + | +++ | +++ |
| Low-set ears | - | - | + | +++ |
| Corpus callosum hypoplasia | - 19.9 mm > 5% (19.54 mm) | + 27.7 mm < 5% (29.91 mm = 5%) | Difficult to visualize—premature metopic suture closure | ++ |
| Broad thumb | - | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Rocker-bottom feet | - | +++ | +++ | +++ |
| Short femur | - | + | ++ | +++ |
| Fetal growth—SGA-like | - | - | - | + |
| Low-lying conus medullaris | - | + | + | + |
| Increased pulmonary valve echogenicity with normal PSV | - | + | + | ++ |
| Bilateral cryptorchidism Shawl scrotum with excessive rugae | - | ++ | ++ | ++ |
| Findings | Report (Author and Year of Publications) | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greco et al. (2009) [14] | Bedeschi et al. (2014) [15] | Cardalliac et al. (2017) [18] | Van-Gils et al. (2019) [3] | D’Ambrosi et al. (2022) [4] | Wu et al. (2020) [19] | Zloto et al. (2024) [20] | |||||||||
| The gestational age (weeks) at detection of abnormal ultrasound findings | 23 | 28 | 26 | 33 | 26 | 35 | 24 | 37 | 35 | 21 | 27 | 38 | 19 | 38 | 24 |
| Gene(s) | |||||||||||||||
| Prenatal | |||||||||||||||
| CREBBP | x | x | ND | x | |||||||||||
| EP300 | x | ND | |||||||||||||
| Postnatal diagnosis (CREBBP) | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ND | x | x | x | x | |||
| Abnormal ultrasound | |||||||||||||||
| Central nervous system (CNS) | |||||||||||||||
| Microcephaly | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| Brachiacephalic head | x | ||||||||||||||
| Cerebellar vermis hypoplasia/agenesis | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||
| Corpus callosum dysgenesis | x | x | x | ||||||||||||
| Face and neck | |||||||||||||||
| Moderate micrognathia | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| Broad nasal bridge/short/absent nasal bone | x | x | x | x | x | x | |||||||||
| Low set ears | x | ||||||||||||||
| Cleft lip and palate | x | ||||||||||||||
| Thickened nuchal fold | x | x | |||||||||||||
| Extremities and skeletal system | |||||||||||||||
| Broad, abducted thumbs and halluces/prominent broad big first toe/bifid thumb | x | x | x | x | x | x | x | ||||||||
| Short long bones | x | x | |||||||||||||
| Cardiovascular system | |||||||||||||||
| Abnormal course of the ductus venosus | x | ||||||||||||||
| Hypoplasia of the pulmonary artery (HPA) | x | ||||||||||||||
| Tetralogy of Fallot | x | ||||||||||||||
| Ascending aorta and aortic arch—thin, narrow aorta and large oval hole | x | ||||||||||||||
| Genitourinary system | |||||||||||||||
| Unilateral/Bilateral renal hydronephrosis | x | x | |||||||||||||
| Duplication of the gallbladder | x | x | |||||||||||||
| Bilateral cryptorchidism Shawl scrotum with excessive rugae | x | ||||||||||||||
| Gastrointestinal system | |||||||||||||||
| Absent splenium | x | ||||||||||||||
| Fetal annexes | |||||||||||||||
| Polyhydramnios | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
| Fetal biometry | |||||||||||||||
| Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) | x | x | x | x | |||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matasariu, D.R.; Bujor, I.-E.; Gireada, R.M.; Guzga, L.M.; Nedelea, F.M.; Titianu, M.; Ursache, A. Challenges in Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115142
Matasariu DR, Bujor I-E, Gireada RM, Guzga LM, Nedelea FM, Titianu M, Ursache A. Challenges in Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115142
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatasariu, Daniela Roxana, Iuliana-Elena Bujor, Roxana Maria Gireada, Luiza Maria Guzga, Florina Mihaela Nedelea, Monica Titianu, and Alexandra Ursache. 2025. "Challenges in Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115142
APA StyleMatasariu, D. R., Bujor, I.-E., Gireada, R. M., Guzga, L. M., Nedelea, F. M., Titianu, M., & Ursache, A. (2025). Challenges in Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome: A Case Report and Comprehensive Literature Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115142





