Liquid Biopsy: The Challenges of a Revolutionary Approach in Oncology
Abstract
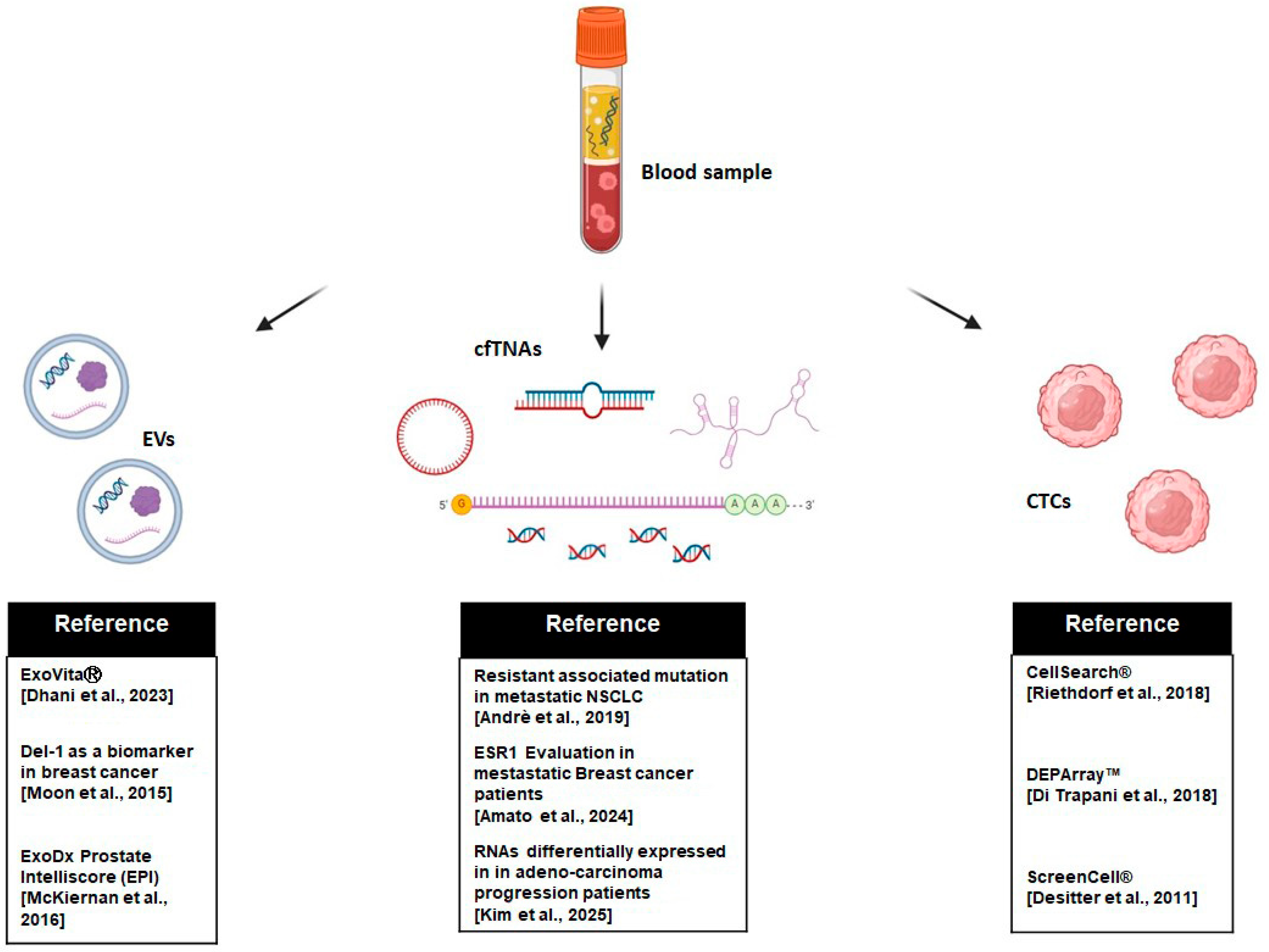
1. Introduction
2. Analytes in Liquid Biopsy
2.1. Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs)
2.2. Cell-Free TNAs: cfDNA and cfRNA
2.3. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs)
2.4. Tumor-Educated Platelets (TEPs)
2.5. Comparative Clinical Performance: Liquid vs. Tissue Biopsy
3. Challenges in Liquid Biopsy
4. Future Prospects
4.1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Liquid Biopsy
4.2. Multyanalyte and Multimodal Approaches
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, P.L.; Parker, L.S. The Precision Medicine Initiative’s All of Us Research Program: An agenda for research on its ethical, legal, and social issues. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morganti, S.; Tarantino, P.; Ferraro, E.; D’amico, P.; Duso, B.A.; Curigliano, G. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS): A Revolutionary Technology in Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Medicine in Cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1168, 9–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Campbell, P.J.; Stephens, P.J.; Pleasance, E.D.; O’Meara, S.; Li, H.; Santarius, T.; A Stebbings, L.; Leroy, C.; Edkins, S.; Hardy, C.; et al. Identification of somatically acquired rearrangements in cancer using genome-wide massively parallel paired-end sequencing. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022, 12, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikanjam, M.; Kato, S.; Kurzrock, R. Liquid biopsy: Current technology and clinical applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wulandari, L.; Soegiarto, G.; Febriani, A.; Fatmawati, F.; Sahrun. Comparison of Detection of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EFGR) Gene Mutation in Peripheral Blood Plasma (Liquid Biopsy) with Cytological Specimens in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 12, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rolfo, C.; Mack, P.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Aggarwal, C.; Arcila, M.E.; Barlesi, F.; Bivona, T.; Diehn, M.; Dive, C.; Dziadziuszko, R.; et al. Liquid Biopsy for Advanced NSCLC: A Consensus Statement From the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1647–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofman, P. Implementation of the clinical practice of liquid biopsies for thoracic oncology the experience of the RespirERA university hospital institute (Nice, France). J. Liq. Biopsy 2023, 1, 100004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malapelle, U.; Rolfo, C. The first issue of the official journal of the International Society of Liquid Biopsy: The Journal of Liquid Biopsy. J. Liq. Biopsy 2023, 1, 100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Shen, L.; Luo, M.; Zhang, K.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhou, D.; Zheng, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Circulating tumor cells: Biology and clinical significance. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Sledge, G.W.; Jeffrey, S.S. Liquid biopsy enters the clinic—Implementation issues and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midha, A.; Dearden, S.; McCormack, R. EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: A systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMapII). Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2892–2911. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Joshi, J.; Raval, A.; Desai, U.; Upadhyay, V.; Bhavsar, M.; Shah, K.; Rawal, R.; Panchal, H.; Shah, F. EGFR Mutation Analysis in Non-small Cell Lung Carcinoma Patients: A Liquid Biopsy Approach. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2021, 36, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Uemura, T.; Kenmotsu, H.; Hazama, D.; Teraoka, S.; Kobe, H.; Azuma, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Masuda, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Otsubo, K.; et al. Liquid biopsy detects genomic drivers in NSCLC without EGFR mutations by single-plex testing: WJOG13620L. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 21097–21110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bohaumilitzky, L.; Gebert, J.; Doeberitz, M.V.K.; Kloor, M.; Ahadova, A. Liquid biopsy-based early tumor and minimal residual disease detection: New perspectives for cancer predisposition syndromes. Med. Genet. 2023, 35, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ashworth, T.R. A Case of Cancer in Which Cells Similar to Those in the Tumors Were Seen in the Blood after Death. Med. J. Aust. 1869, 14, 146–147. [Google Scholar]
- Szostakowska-Rodzos, M.; Fabisiewicz, A.; Wakula, M.; Tabor, S.; Szafron, L.; Jagiello-Gruszfeld, A.; Grzybowska, E.A. Longitudinal analysis of circulating tumor cell numbers improves tracking metastatic breast cancer progression. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Donato, C.; Kunz, L.; Castro-Giner, F.; Paasinen-Sohns, A.; Strittmatter, K.; Szczerba, B.M.; Scherrer, R.; Di Maggio, N.; Heusermann, W.; Biehlmaier, O.; et al. Hypoxia Triggers the Intravasation of Clustered Circulating Tumor Cells. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pantel, K.; Alix-Panabières, C. Real-time liquid biopsy in cancer patients: Fact or fiction? Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6384–6388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riethdorf, S.; O’Flaherty, L.; Hille, C.; Pantel, K. Clinical applications of the CellSearch platform in cancer patients. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 125, 102–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W. Tumor cells circulate in the peripheral blood of all major carcinomas but not in healthy subjects or patients with nonmalignant diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.F.; Guo, W.; Xu, Y.; Shi, Y.-H.; Gong, Z.J.; Ji, Y.; Du, M.; Zhang, X.; Hu, B.; Huang, A.; et al. Circulating Tumor Cells from Different Vascular Sites Exhibit Spatial Heterogeneity in Epithelial and Mesenchymal Composition and Distinct Clinical Significance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, K.; Mao, Y.; Yu, Y.; Yi, Q.; Wu, Y. Controllable Environment Protein Corona-Disguised Immunomagnetic Beads for High-Performance Circulating Tumor Cell Enrichment. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 4650–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, S.L.; Graf, R.P.; Landers, M.; Valenta, D.T.; Schroeder, M.; Greene, S.B.; Bales, N.; Dittamore, R.; Marrinucci, D. Analytical Validation and Capabilities of the Epic CTC Platform: Enrichment-Free Circulating Tumour Cell Detection and Characterization. J. Circ. Biomarkers 2015, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, J.F.; Ho, H.; Lichterman, J.; Lu, Y.T.; Zhang, Y.; Garcia, M.A.; Chen, S.F.; Liang, A.J.; Hodara, E.; Zhau, H.E.; et al. Subclassification of prostate cancer circulating tumor cells by nuclear size reveals very small nuclear circulating tumor cells in patients with visceral metastases. Cancer 2015, 121, 3240–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Desitter, I.; Guerrouahen, B.S.; Benali-Furet, N.; Wechsler, J.; Jänne, P.A.; Kuang, Y.; Yanagita, M.; Wang, L.; Berkowitz, J.A.; Distel, R.J.; et al. A new device for rapid isolation by size and characterization of rare circulating tumor cells. Anticancer. Res. 2011, 31, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.J.; Padmanaban, V.; Silvestri, V.; Schipper, K.; Cohen, J.D.; Fairchild, A.N.; Gorin, M.A.; Verdone, J.E.; Pienta, K.J.; Bader, J.S.; et al. Polyclonal breast cancer metastases arise from collective dissemination of keratin 14-expressing tumor cell clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E854–E863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mutlu, B.R.; Dubash, T.; Dietsche, C.; Mishra, A.; Ozbey, A.; Keim, K.; Edd, J.F.; Haber, D.A.; Maheswaran, S.; Toner, M. In-flow measurement of cell–cell adhesion using oscillatory inertial microfluidics. Lab. Chip 2020, 20, 1612–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kojima, M.; Harada, T.; Fukazawa, T.; Kurihara, S.; Saeki, I.; Takahashi, S.; Hiyama, E. Single-cell DNA and RNA sequencing of circulating tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Di Trapani, M.; Manaresi, N.; Medoro, G. DEPArray™ system: An automatic image-based sorter for isolation of pure circulating tumor cells. Cytom. Part A 2018, 93, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mandel, P.; Metais, P. Les acides nucléiques du plasma sanguin chez l’homme [Nuclear Acids In Human Blood Plasma]. C. R. Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 1948, 142, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hudecova, I.; Smith, C.G.; Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Chilamakuri, C.S.; Morris, J.A.; Vijayaraghavan, A.; Heider, K.; Chandrananda, D.; Cooper, W.N.; Gale, D.; et al. Characteristics, origin, and potential for cancer diagnostics of ultrashort plasma cell-free DNA. Genome Res. 2022, 32, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Choy, L.Y.L.; Peng, W.; Jiang, P.; Cheng, S.H.; Yu, S.C.Y.; Shang, H.; Olivia Tse, O.; Wong, J.; Wong, V.W.S.; Wong, G.L.; et al. Single-Molecule Sequencing Enables Long Cell-Free DNA Detection and Direct Methylation Analysis for Cancer Patients. Clin. Chem. 2022, 68, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattox, A.K.; Douville, C.; Wang, Y.; Popoli, M.; Ptak, J.; Silliman, N.; Dobbyn, L.; Schaefer, J.; Lu, S.; Pearlman, A.H.; et al. The Origin of Highly Elevated Cell-Free DNA in Healthy Individuals and Patients with Pancreatic, Colorectal, Lung, or Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 2166–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Hoon, D.S.B.; Pantel, K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; O’Keefe, C.M.; Hsieh, K.; Cope, L.; Joyce, S.C.; Pisanic, T.R.; Herman, J.G.; Wang, T.H. Multiplex Digital Methylation-Specific PCR for Noninvasive Screening of Lung Cancer. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pott, C.; Kotrova, M.; Darzentas, N.; Brüggemann, M.; Khouja, M.; EuroClonality-NGS Working Group. cfDNA-Based NGS IG Analysis in Lymphoma. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2453, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pascual, J.; Attard, G.; Bidard, F.-C.; Curigliano, G.; De Mattos-Arruda, L.; Diehn, M.; Italiano, A.; Lindberg, J.; Merker, J.D.; Montagut, C.; et al. ESMO recommendations on the use of circulating tumour DNA assays for patients with cancer: A report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 750–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, K.L.; Ptashkin, R.N.; Gao, T.; Braunstein, L.; Devlin, S.M.; Kelly, D.; Patel, M.; Berthon, A.; Syed, A.; Yabe, M.; et al. Cancer therapy shapes the fitness landscape of clonal hematopoiesis. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Niroula, A.; Sekar, A.; Murakami, M.A.; Trinder, M.; Agrawal, M.; Wong, W.J.; Bick, A.G.; Uddin, M.M.; Gibson, C.J.; Griffin, G.K.; et al. Distinction of lymphoid and myeloid clonal hematopoiesis. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Olsson, E.; Winter, C.; George, A.; Chen, Y.; Howlin, J.; Tang, M.E.; Dahlgren, M.; Schulz, R.; Grabau, D.; van Westen, D.; et al. Serial monitoring of circulating tumor DNA in patients with primary breast cancer for detection of occult metastatic disease. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Riva, F.; Bidard, F.C.; Houy, A.; Saliou, A.; Madic, J.; Rampanou, A.; Hego, C.; Milder, M.; Cottu, P.; Sablin, M.P.; et al. Patient-Specific Circulating Tumor DNA Detection during Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Hancock, B.A.; Solzak, J.P.; Brinza, D.; Scafe, C.; Miller, K.D.; Radovich, M. Next-generation sequencing of circulating tumor DNA to predict recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer patients with residual disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. NPJ Breast Cancer 2017, 3, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Garcia-Murillas, I.; Chopra, N.; Comino-Méndez, I.; Beaney, M.; Tovey, H.; Cutts, R.J.; Swift, C.; Kriplani, D.; Afentakis, M.; Hrebien, S.; et al. Assessment of Molecular Relapse Detection in Early-Stage Breast Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 1473–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rothé, F.; Silva, M.J.; Venet, D.; Campbell, C.; Bradburry, I.; Rouas, G.; de Azambuja, E.; Maetens, M.; Fumagalli, D.; Rodrik-Outmezguine, V.; et al. Circulating Tumor DNA in HER2-Amplified Breast Cancer: A Translational Research Substudy of the NeoALTTO Phase III Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3581–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombes, R.C.; Page, K.; Salari, R.; Hastings, R.K.; Armstrong, A.C.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, S.; Cleator, S.J.; Kenny, L.M.; Stebbing, J.; et al. Personalized Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA Antedates Breast Cancer Metastatic Recurrence. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 4255–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, B.R.; Contente-Cuomo, T.; Sammut, S.J.; Odenheimer-Bergman, A.; Ernst, B.; Perdigones, N.; Chin, S.F.; Farooq, M.; Mejia, R.; Cronin, P.A.; et al. Personalized circulating tumor DNA analysis to detect residual disease after neoadjuvant therapy in breast cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaax7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Wei, W.; You, Z.; Ou, X.; Sun, M.; Yin, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, C.; et al. Parallel Analyses of Somatic Mutations in Plasma Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA) and Matched Tumor Tissues in Early-Stage Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6546–6553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovich, M.; Jiang, G.; Hancock, B.A.; Chitambar, C.; Nanda, R.; Falkson, C.; Lynce, F.C.; Gallagher, C.; Isaacs, C.; Blaya, M.; et al. Association of Circulating Tumor DNA and Circulating Tumor Cells After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy With Disease Recurrence in Patients With Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Preplanned Secondary Analysis of the BRE12-158 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bratman, S.V.; Yang, S.Y.C.; Iafolla, M.A.J.; Liu, Z.; Hansen, A.R.; Bedard, P.L.; Lheureux, S.; Spreafico, A.; Razak, A.A.; Shchegrova, S.; et al. Personalized circulating tumor DNA analysis as a predictive biomarker in solid tumor patients treated with pembrolizumab. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- André, F.; Ciruelos, E.; Rubovszky, G.; Campone, M.; Loibl, S.; Rugo, H.S.; Iwata, H.; Conte, P.; Mayer, I.A.; Kaufman, B.; et al. Alpelisib for PIK3CA-Mutated, Hormone Receptor–Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1929–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidard, F.C.; Kaklamani, V.G.; Neven, P.; Streich, G.; Montero, A.J.; Forget, F.; Mouret-Reynier, M.A.; Sohn, J.H.; Taylor, D.; Harnden, K.K.; et al. Elacestrant (oral selective estrogen receptor degrader) Versus Standard Endocrine Therapy for Estrogen Receptor–Positive, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2–Negative Advanced Breast Cancer: Results From the Randomized Phase III EMERALD Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3246–3256, Erratum in J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3962. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.23.01239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Amato, O.; Giannopoulou, N.; Ignatiadis, M. Circulating tumor DNA validity and potential uses in metastatic breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2024, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Available online: https://investors.guardanthealth.com/press-releases/press-releases/2023/Guardant-Health-receives-FDA-approval-for-Guardant360-CDx-as-companion-diagnostic-for-Menarini-Groups-ORSERDU-for-treatment-of-patients-with-ESR1-mutations-in-ER-HER2--advanced-or-metastatic-breast-cancer/default.aspx (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Moy, B.; Rumble, R.B.; Carey, L.A.; Chemotherapy, F.T.; Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy for Endocrine-Pretreated or Hormone Receptor–Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer Expert Panel. Chemotherapy and Targeted Therapy for Endocrine-Pretreated or Hormone Receptor–Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer: ASCO Guideline Rapid Recommendation Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1318–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosele, M.F.; Westphalen, C.B.; Stenzinger, A.; Barlesi, F.; Bayle, A.; Bièche, I.; Bonastre, J.; Castro, E.; Dienstmann, R.; Krämer, A.; et al. Recommendations for the use of next-generation sequencing (NGS) for patients with advanced cancer in 2024: A report from the ESMO Precision Medicine Working Group. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 588–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyfer, N.; Magenheim, J.; Peretz, A.; Cann, G.; Bredno, J.; Klochendler, A.; Fox-Fisher, I.; Shabi-Porat, S.; Hecht, M.; Pelet, T.; et al. A DNA methylation atlas of normal human cell types. Nature 2023, 613, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Heeke, S.; Gay, C.M.; Estecio, M.R.; Tran, H.; Morris, B.B.; Zhang, B.; Tang, X.; Raso, M.G.; Rocha, P.; Lai, S.; et al. Tumor- and circulating-free DNA methylation identifies clinically relevant small cell lung cancer subtypes. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 225–237.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Katsman, E.; Orlanski, S.; Martignano, F.; Fox-Fisher, I.; Shemer, R.; Dor, Y.; Zick, A.; Eden, A.; Petrini, I.; Conticello, S.G.; et al. Detecting cell-of-origin and cancer-specific methylation features of cell-free DNA from Nanopore sequencing. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lo, K.W.; Lo, Y.D.; Leung, S.F.; Tsang, Y.S.; Chan, L.Y.; Johnson, P.J.; Hjelm, N.M.; Lee, J.C.; Huang, D.P. Analysis of cell-free Epstein-Barr virus-associated RNA in the plasma of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin. Chem. 1999, 45, 1292–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Wang, P.; Lin, W. The Value of Circulating Circular RNA in Cancer Diagnosis, Monitoring, Prognosis, and Guiding Treatment. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 736546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Freedman, J.E.; Gerstein, M.; Mick, E.; Rozowsky, J.; Levy, D.; Kitchen, R.; Das, S.; Shah, R.; Danielson, K.; Beaulieu, L.; et al. Diverse human extracellular RNAs are widely detected in human plasma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11106, Erratum in Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11902. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Evans, L.W.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Sutton, K.J.; Yam, P.; Bouzid, Y.Y.; Cervantes, E.; Bonnel, E.; Stephenson, C.B.; Bennett, B.J. Specific circulating miRNAs are associated with plasma lipids in a healthy American cohort. Physiol. Genom. 2024, 56, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuji, T.; Umeda, Y.; Nyuya, A.; Taniguchi, F.; Kawai, T.; Yasui, K.; Toshima, T.; Yoshida, K.; Fujiwara, T.; Goel, A.; et al. Detection of circulating microRNAs with Ago2 complexes to monitor the tumor dynamics of colorectal cancer patients during chemotherapy. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 2169–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Géczi, D.; Nagy, B.; Szilágyi, M.; Penyige, A.; Klekner, Á.; Jenei, A.; Virga, J.; Birkó, Z. Analysis of Circulating miRNA Profile in Plasma Samples of Glioblastoma Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Batool, S.M.; Muralidharan, K.; Hsia, T.; Falotico, S.; Gamblin, A.S.; Rosenfeld, Y.B.; Khanna, S.K.; Balaj, L.; Carter, B.S. Highly Sensitive EGFRvIII Detection in Circulating Extracellular Vesicle RNA of Glioma Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4070–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gao, Y.; Shang, S.; Guo, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhi, H.; et al. Lnc2Cancer 3.0: An updated resource for experimentally supported lncRNA/circRNA cancer associations and web tools based on RNA-seq and scRNA-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1251–D1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Buermans, H.P.; Waasdorp, M.; Stoorvogel, W.; Wauben, M.H.; ’t Hoen, P.A. Deep sequencing of RNA from immune cell-derived vesicles uncovers the selective incorporation of small non-coding RNA biotypes with potential regulatory functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 9272–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ratajczak, J.; Miękus, K.; Kucia, M.; Zhang, J.; Reca, R.; Dvorak, P.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: Evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia 2006, 20, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koi, Y.; Tsutani, Y.; Nishiyama, Y.; Ueda, D.; Ibuki, Y.; Sasada, S.; Akita, T.; Masumoto, N.; Kadoya, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; et al. Predicting the presence of breast cancer using circulating small RNAs, including those in the extracellular vesicles. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2104–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kim, L.A.; Han, J.; Kim, T.I.; Park, J.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.; Lee, H. Circulating RNA Markers Associated with Adenoma–Carcinoma Sequence in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Zhang, Q.; Franklin, J.L.; Coffey, R.J. Extracellular vesicles and nanoparticles: Emerging complexities. Trends Cell Biol. 2023, 33, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zheng, R.; Zhang, K.; Tan, S.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Gu, D.; Zhu, L.; Li, S.; et al. Exosomal circLPAR1 functions in colorectal cancer diagnosis and tumorigenesis through suppressing BRD4 via METTL3–eIF3h interaction. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yu, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Gu, J.; Xu, W.; Cai, H.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X. Exosomes as a new frontier of cancer liquid biopsy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rezabakhsh, A.; Sokullu, E.; Rahbarghazi, R. Applications, challenges and prospects of mesenchymal stem cell exosomes in regenerative medicine. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, M.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Tsai, H.M.; He, P.L.; Lin, Y.C.; Herschman, H.; Li, H.J. PGE2/EP4 Signaling Controls the Transfer of the Mammary Stem Cell State by Lipid Rafts in Extracellular Vesicles. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 425–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Lin, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Wang, T.; Cui, Y. Establishment of a simplified dichotomic size-exclusion chromatography for isolating extracellular vesicles toward clinical applications. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Casadei, L.; Choudhury, A.; Sarchet, P.; Mohana Sundaram, P.; Lopez, G.; Braggio, D.; Balakirsky, G.; Pollock, R.; Prakash, S. Cross-flow microfiltration for isolation, selective capture and release of liposarcoma extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dhani, H.; Hinestrosa, J.P.; Izaguirre-Carbonell, J.; Balcer, H.I.; Kurzrock, R.; Billings, P.R. Case Report: Early detection of pancreatic pre-cancer lesion in multimodal approach with exosome liquid biopsy. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1170513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Moon, P.G.; Lee, J.E.; Cho, Y.E.; Lee, S.J.; Jung, J.H.; Chae, Y.S.; Bae, H.I.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, I.S.; Park, H.Y.; et al. Identification of Developmental Endothelial Locus-1 on Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Biomarker for Early Breast Cancer Detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1757–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Wei, S.N.; Geng, N.; Qin, W.W.; He, X.; Wang, X.H.; Qi, Y.P.; Song, S.; Wang, P. Evaluation of circulating small extracellular vesicle-derived miRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for differentiating between different pathological types of early lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- McKiernan, J.; Donovan, M.J.; O’Neill, V.; Bentink, S.; Noerholm, M.; Belzer, S.; Skog, J.; Kattan, M.W.; Partin, A.; Andriole, G.; et al. A Novel Urine Exosome Gene Expression Assay to Predict High-grade Prostate Cancer at Initial Biopsy. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, E.; Brown, G.; Partin, A.; Carter, B.; McKiernan, J.; Tutrone, R.; Torkler, P.; Fischer, C.; Tadigotla, V.; Noerholm, M.; et al. Predicting high-grade prostate cancer at initial biopsy: Clinical performance of the ExoDx (EPI) Prostate Intelliscore test in three independent prospective studies. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Serratì, S.; Di Fonte, R.; Porcelli, L.; De Summa, S.; De Risi, I.; Fucci, L.; Ruggieri, E.; Marvulli, T.M.; Strippoli, S.; Fasano, R.; et al. Circulating extracellular vesicles are monitoring biomarkers of anti-PD1 response and enhancer of tumor progression and immunosuppression in metastatic melanoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Denis, M.M.; Tolley, N.D.; Bunting, M.; Schwertz, H.; Jiang, H.; Lindemann, S.; Yost, C.C.; Rubner, F.J.; Albertine, K.H.; Swoboda, K.J.; et al. Escaping the nuclear confines: Signal-dependent pre-mrna splicing in anucleate platelets. Cell 2005, 122, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Metharom, P.; Falasca, M.; Berndt, M.C. The History of Armand Trousseau and Cancer-Associated Thrombosis. Cancers 2019, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Liefaard, M.C.; Moore, K.S.; Mulder, L.; van den Broek, D.; Wesseling, J.; Sonke, G.S.; Wessels, L.F.A.; Rookus, M.; Lips, E.H. Tumour-educated platelets for breast cancer detection: Biological and technical insights. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 1572–1581, Erratum in Br. J. Cancer 2023, 129, 734. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-023-02371-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ren, J.; He, J.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y.; Hu, Z.; Loughran, P.; Billiar, T.; Huang, H.; Tsung, A. Platelet TLR4-ERK5 Axis Facilitates NET-Mediated Capturing of Circulating Tumor Cells and Distant Metastasis after Surgical Stress. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2373–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, X.; Chen, X.; Gong, S.; Zhao, J.; Yao, C.; Zhu, H.; Xiao, R.; Qin, Y.; Li, R.; Sun, N.; et al. Platelets promote CRC by activating the C5a/C5aR1 axis via PSGL-1/JNK/STAT1 signaling in tumor-associated macrophages. Theranostics 2023, 13, 2040–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cho, M.S.; Noh, K.; Haemmerle, M.; Li, D.; Park, H.; Hu, Q.; Hisamatsu, T.; Mitamura, T.; Mak, S.L.C.; Kunapuli, S.; et al. Role of ADP receptors on platelets in the growth of ovarian cancer. Blood 2017, 130, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Raez, L.E.; Brice, K.; Dumais, K.; Lopez-Cohen, A.; Wietecha, D.; Izquierdo, P.A.; Santos, E.S.; Powery, H.W. Liquid Biopsy Versus Tissue Biopsy to Determine Front Line Therapy in Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 24, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shong, L.Y.; Deng, J.Y.; Kwok, H.H.; Lee, N.C.; Tseng, S.C.; Ng, L.Y.; Yee, W.K.; Lam, D.C. Detection of EGFR mutations in patients with suspected lung cancer using paired tissue-plasma testing: A prospective comparative study with plasma ddPCR assay. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ezeife, D.A.; Spackman, E.; Juergens, R.A.; Laskin, J.J.; Agulnik, J.S.; Hao, D.; Laurie, S.A.; Law, J.H.; Le, L.W.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; et al. The economic value of liquid biopsy for genomic profiling in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2022, 14, 17588359221112696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Englmeier, F.; Bleckmann, A.; Brückl, W.; Griesinger, F.; Fleitz, A.; Nagels, K. Clinical benefit and cost-effectiveness analysis of liquid biopsy application in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A modelling approach. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 1495–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bachet, J.; Bouché, O.; Taieb, J.; Dubreuil, O.; Garcia, M.; Meurisse, A.; Normand, C.; Gornet, J.; Artru, P.; Louafi, S.; et al. RAS mutation analysis in circulating tumor DNA from patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: The AGEO RASANC prospective multicenter study. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, A.; Greuter, M.J.E.; Schraa, S.J.; Vink, G.R.; Phallen, J.; Velculescu, V.E.; Meijer, G.A.; van den, D.; Koopman, M.; Roodhart, J.M.L.; et al. Early evaluation of the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of ctDNA-guided selection for adjuvant chemotherapy in stage II colon cancer. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2024, 16, 17588359241266164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor DNA in early- and late-stage human malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhou, X.; Cheng, Z.; Dong, M.; Liu, Q.; Yang, W.; Liu, M.; Tian, J.; Cheng, W. Publisher Correction: Tumor fractions deciphered from circulating cell-free DNA methylation for cancer early diagnosis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 328, Erratum in Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7694. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-35320-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gentzler, R.D.; Guittar, J.; Mitra, A.; Iams, W.T.; Driessen, T.; Schwind, R.; Stein, M.M.; Kaneva, K.; Hyun, S.W.; Liu, Y.; et al. Dynamic Changes in Circulating Tumor Fraction as a Predictor of Real-World Clinical Outcomes in Solid Tumor Malignancy Patients Treated with Immunotherapy. Oncol. Ther. 2024, 12, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abbosh, C.; Frankell, A.M.; Harrison, T.; Kisistok, J.; Garnett, A.; Johnson, L.; Veeriah, S.; Moreau, M.; Chesh, A.; Chaunzwa, T.L.; et al. Tracking early lung cancer metastatic dissemination in TRACERx using ctDNA. Nature 2023, 616, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brown, P. The Cobas® EGFR Mutation Test v2 assay. Future Oncol. 2016, 12, 451–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauml, J.M.; Li, B.T.; Velcheti, V.; Govindan, R.; Curioni-Fontecedro, A.; Dooms, C.; Takahashi, T.; Duda, A.W.; Odegaard, J.I.; Cruz-Guilloty, F.; et al. Clinical validation of Guardant360 CDx as a blood-based companion diagnostic for sotorasib. Lung Cancer 2022, 166, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Woodhouse, R.; Li, M.; Hughes, J.; Delfosse, D.; Skoletsky, J.; Ma, P.; Meng, W.; Dewal, N.; Milbury, C.; Clark, T.; et al. Clinical and analytical validation of FoundationOne Liquid CDx, a novel 324-Gene cfDNA-based comprehensive genomic profiling assay for cancers of solid tumor origin. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Batool, S.M.; Yekula, A.; Khanna, P.; Hsia, T.; Gamblin, A.S.; Ekanayake, E.; Escobedo, A.K.; You, D.G.; Castro, C.M.; Im, H.; et al. The Liquid Biopsy Consortium: Challenges and opportunities for early cancer detection and monitoring. Cell Rep. Med. 2023, 4, 101198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Febbo, P.G.; Martin, A.; Scher, H.I.; Barrett, J.C.; Beaver, J.A.; Beresford, P.J.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Bramlett, K.; Compton, C.; Dittamore, R.; et al. Minimum Technical Data Elements for Liquid Biopsy Data Submitted to Public Databases. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 107, 730–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Heidrich, I.; Deitert, B.; Werner, S.; Pantel, K. Liquid biopsy for monitoring of tumor dormancy and early detection of disease recurrence in solid tumors. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2023, 42, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chi, K.N.; Barnicle, A.; Sibilla, C.; Lai, Z.; Corcoran, C.; Barrett, J.C.; Adelman, C.A.; Qiu, P.; Easter, A.; Dearden, S.; et al. Detection of BRCA1, BRCA2, and ATM Alterations in Matched Tumor Tissue and Circulating Tumor DNA in Patients with Prostate Cancer Screened in PROfound. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Meng, Y.; Pople, C.B.; Suppiah, S.; Llinas, M.; Huang, Y.; Sahgal, A.; Perry, J.; Keith, J.; Davidson, B.; Hamani, C.; et al. MR-guided focused ultrasound liquid biopsy enriches circulating biomarkers in patients with brain tumors. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 23, 1789–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Khier, S.; Lohan, L. Kinetics of circulating cell-free DNA for biomedical applications: Critical appraisal of the literature. Future Sci. OA 2018, 4, FSO295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wong, D.; Tageldein, M.; Luo, P.; Ensminger, E.; Bruce, J.; Oldfield, L.; Gong, H.; Fischer, N.W.; Laverty, B.; Subasri, V.; et al. Cell-free DNA from germline TP53 mutation carriers reflect cancer-like fragmentation patterns. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ramírez-Mena, A.; Andrés-León, E.; Alvarez-Cubero, M.J.; Anguita-Ruiz, A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, L.J.; Alcala-Fdez, J. Explainable artificial intelligence to predict and identify prostate cancer tissue by gene expression. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 240, 107719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Tong, L.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; et al. A Classifier for Improving Early Lung Cancer Diagnosis Incorporating Artificial Intelligence and Liquid Biopsy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 853801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ginghina, O.; Hudita, A.; Zamfir, M.; Spanu, A.; Mardare, M.; Bondoc, I.; Buburuzan, L.; Georgescu, S.E.; Costache, M.; Negrei, C.; et al. Liquid Biopsy and Artificial Intelligence as Tools to Detect Signatures of Colorectal Malignancies: A Modern Approach in Patient’s Stratification. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 856575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Herrgott, G.A.; Snyder, J.M.; She, R.; Malta, T.M.; Sabedot, T.S.; Lee, I.Y.; Pawloski, J.; Podolsky-Gondim, G.G.; Asmaro, K.P.; Zhang, J.; et al. Detection of diagnostic and prognostic methylation-based signatures in liquid biopsy specimens from patients with meningiomas. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Eledkawy, A.; Hamza, T.; El-Metwally, S. Precision cancer classification using liquid biopsy and advanced machine learning techniques. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Liu, F.; Huang, H.; et al. Transformer-based AI technology improves early ovarian cancer diagnosis using cfDNA methylation markers. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Modlin, I.M.; Kidd, M.; Drozdov, I.A.; Boegemann, M.; Bodei, L.; Kunikowska, J.; Malczewska, A.; Bernemann, C.; Koduru, S.V.; Rahbar, K. Development of a multigenomic liquid biopsy (PROSTest) for prostate cancer in whole blood. Prostate 2024, 84, 850–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimzadeh, M.; Momen-Roknabadi, A.; Cavazos, T.B.; Fang, Y.; Chen, N.C.; Multhaup, M.; Yen, J.; Ku, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.; et al. Deep generative AI models analyzing circulating orphan non-coding RNAs enable detection of early-stage lung cancer. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hofmann, L.; Sallinger, K.; Haudum, C.; Smolle, M.; Heitzer, E.; Moser, T.; Novy, M.; Gesson, K.; Kroneis, T.; Bauernhofer, T.; et al. A Multi-Analyte Approach for Improved Sensitivity of Liquid Biopsies in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bortolini Silveira, A.; Bidard, F.C.; Tanguy, M.L.; Girard, E.; Trédan, O.; Dubot, C.; Jacot, W.; Goncalves, A.; Debled, M.; Levy, C.; et al. Multimodal liquid biopsy for early monitoring and outcome prediction of chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Stoecklein, N.H.; Fluegen, G.; Guglielmi, R.; Neves, R.P.L.; Hackert, T.; Birgin, E.; Cieslik, S.A.; Sudarsanam, M.; Driemel, C.; van Dalum, G.; et al. Ultra-sensitive CTC-based liquid biopsy for pancreatic cancer enabled by large blood volume analysis. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Frilling, A.; Clift, A.K.; Frampton, A.E.; Bomanji, J.; Kaemmerer, D.; Al-Nahhas, A.; Alsafi, A.; Kidd, M.; Modlin, I.M.; Hoersch, D.; et al. A combination of surgery, theranostics, and liquid biopsy-a personalised oncologic approach to treatment of patients with advanced metastatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 2166–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Keup, C.; Suryaprakash, V.; Hauch, S.; Storbeck, M.; Hahn, P.; Sprenger-Haussels, M.; Kolberg, H.C.; Tewes, M.; Hoffmann, O.; Kimmig, R.; et al. Integrative statistical analyses of multiple liquid biopsy analytes in metastatic breast cancer. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, W.; Ye, B.; Song, Y.; Yang, P.; Si, W.; Jing, H.; Yang, F.; Yuan, D.; Wu, Z.; Lyu, J.; et al. Integrating multi-omics features enables non-invasive early diagnosis and treatment response prediction of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Clin. Transl. Med. 2025, 15, e70174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Malapelle, U.; Leighl, N.; Addeo, A.; Hershkovitz, D.; Hochmair, M.J.; Khorshid, O.; Länger, F.; de Marinis, F.; Peled, N.; Sheffield, B.S.; et al. Recommendations for reporting tissue and circulating tumour (ct)DNA next-generation sequencing results in non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 131, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Daamen, L.A.; Molenaar, I.Q.; Groot, V.P. Recent Advances and Future Challenges in Pancreatic Cancer Care: Early Detection, Liquid Biopsies, Precision Medicine and Artificial Intelligence. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sijithra, P.C.; Santhi, N.; Ramasamy, N. A review study on early detection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using artificial intelligence assisted diagnostic methods. Eur. J. Radiol. 2023, 166, 110972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Type of Mutation | Cancer Type | ctDNA Analysis Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | All pathogenic mutations | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Recommended for cancer patients who have not responded to treatment and for individuals who have established resistance mutations to TKIs where tissue is unavailable or cannot be evaluated |
| ALK | Amplifications and fusions | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Recommended only when tissue is unavailable or cannot be evaluated |
| MET | |||
| ROS1 | |||
| NTRK1-2-3 | Amplification, instability and fusions | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Recommended only when tissue biopsy is not feasible or where prompt therapeutic decision-making is required |
| Breast Cancer | |||
| Gastric Cancer | |||
| Pancreatic Cancer Hepatocellular Carcinoma | |||
| Cholangiocarcinoma | |||
| Urothelial Cancer | |||
| Soft Tissue Sarcoma | |||
| Thyroid Cancer | |||
| ERBB2 | Amplification, instability and fusions | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Recommended only when tissue is unavailable or cannot be evaluated |
| Breast Cancer | |||
| Gastric Cancer | |||
| PIK3CA | All pathogenic mutations | Breast Cancer | Recommended for treatment monitoring in patients with progressing cancer |
| BRCA1-2 | All pathogenic mutations | Breast Cancer | Recommended only when tissue is unavailable or cannot be evaluated and for treatment monitoring |
| Ovarian Cancer | |||
| Prostate Cancer | |||
| ESR1 | All pathogenic mutations | Breast Cancer | Recommended for treatment monitoring |
| MSI | Instability | Breast Cancer | Recommended only when tissue is unavailable or cannot be evaluated |
| Gastric Cancer | |||
| Pancreatic Cancer | |||
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma | |||
| Cholangiocarcinoma | |||
| Metastatic Colorectal Cancer | |||
| Ovarian Cancer | |||
| Endometrial Cancer | |||
| Prostate Cancer | |||
| IDH1 | All pathogenic mutations and fusions | Cholangiocarcinoma | Recommended only when tissue biopsy is not feasible or where prompt therapeutic decision-making is required |
| FGFR2 | |||
| EGFR-ECD | S492, G465, S464, V441 | Metastatic Colorectal Cancer | Recommended for pre-treated patients with EGFR mutations |
| KRAS/NRAS | G12C | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Recommended for patients who are naive to chemotherapy when a tissue biopsy is not available or when prompt treatment decision-making is required |
| Exon 2, 3, 4 | Metastatic Colorectal Cancer | ||
| BRAF | V600E | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Recommended for patients who are naive to chemotherapy when a tissue biopsy is not available or when prompt treatment decision-making is required |
| Metastatic Colorectal Cancer | |||
| Thyroid Cancer | |||
| ATM | Pathogenic mutations and deletions | Prostate Cancer | Recommended only when tissue is unavailable or cannot be evaluated |
| PTEN | |||
| PALB2 | |||
| FGFR | All pathogenic mutations | Urothelial Cancer | Recommended only when tissue is unavailable or cannot be evaluated |
| FGFR3 | |||
| RET | Amplifications and fusions | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | Recommended only when tissue is unavailable or cannot be evaluated |
| Thyroid Cancer |
| Techniques | Analyte | Main Sources | Applications | Benefits | Limitations | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CellSearch®, DEPAr-ray™, ScreenCell® | CTCs | Blood | Prognosis, treatment monitoring, metastasis detection | Intact cells, allows for phenotypic/molecular analysis | Rare cells, complex enrichment, low yield | Moderate (high cost per result, limited use) |
| dPCR, NGS, Methylation analysis | cfDNA/ctDNA | Plasma/Serum | Mutation profiling for early diagnosis, MRD, resistance mutations | High sensitivity with NGS, widely used | Variable yield, interference from non-tumor DNA | High (approved tests available for certain cancer types, scalable) |
| RT-qPCR, RNA-Seq, ddPCR | cfRNA/ctRNA | Plasma/Urine | Biomarker discovery, early diagnosis, resistance mutations | Reflects active transcription, dynamic changes | RNA instability, technical noise | Moderate (emerging utility, limited protocols) |
| Ultracentrifugation, Immunoaffinity | EVs | Blood/Urine | Tumor cross-talk, early detection | High stability, rich content, present in many biofluids | Heterogeneous population, low specificity | Moderate (technically demanding, not standardized) |
| RNA-seq | TEPs | Blood | Early detection, immune evasion, prognosis | Easily accessible, reflects systemic tumor communication | Mechanisms not fully understood, RNA sequencing required | Low (experimental, no clinical translation yet) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coppola, C.A.; De Summa, S.; Matera, G.; Pilato, B.; Traversa, D.; Tommasi, S. Liquid Biopsy: The Challenges of a Revolutionary Approach in Oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115013
Coppola CA, De Summa S, Matera G, Pilato B, Traversa D, Tommasi S. Liquid Biopsy: The Challenges of a Revolutionary Approach in Oncology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115013
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoppola, Claudio Antonio, Simona De Summa, Giuseppina Matera, Brunella Pilato, Debora Traversa, and Stefania Tommasi. 2025. "Liquid Biopsy: The Challenges of a Revolutionary Approach in Oncology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115013
APA StyleCoppola, C. A., De Summa, S., Matera, G., Pilato, B., Traversa, D., & Tommasi, S. (2025). Liquid Biopsy: The Challenges of a Revolutionary Approach in Oncology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 5013. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26115013





