Encapsulation of Transforming Growth Factor-β3 in Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cartilage Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
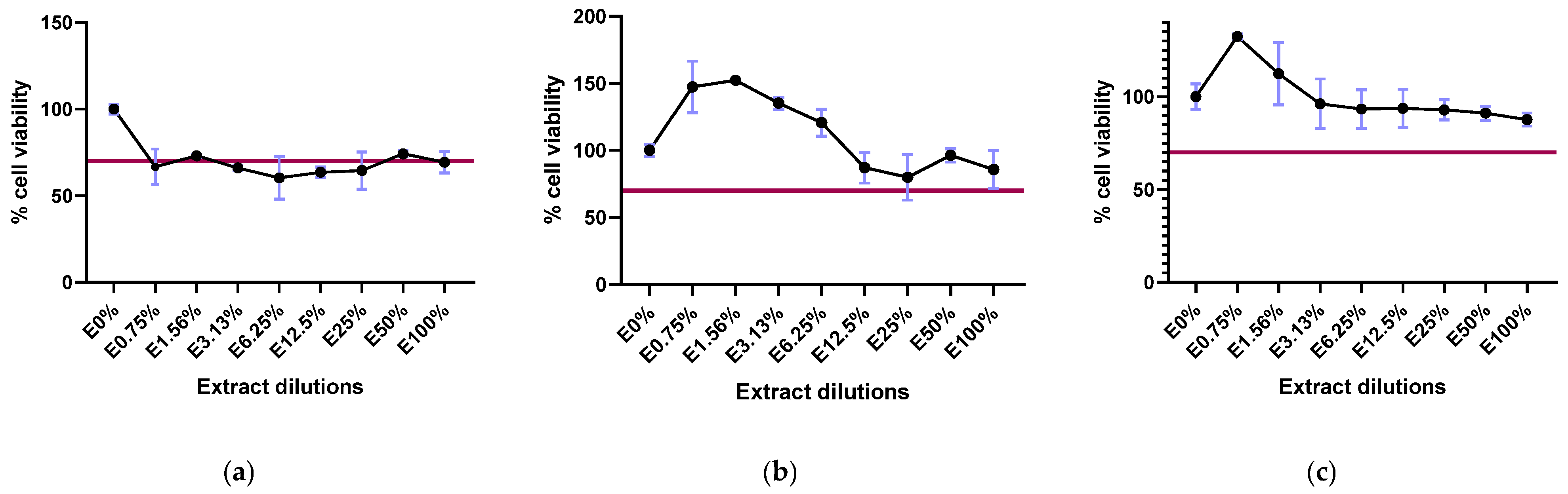
2.1. Biopolymer Cytotoxicity
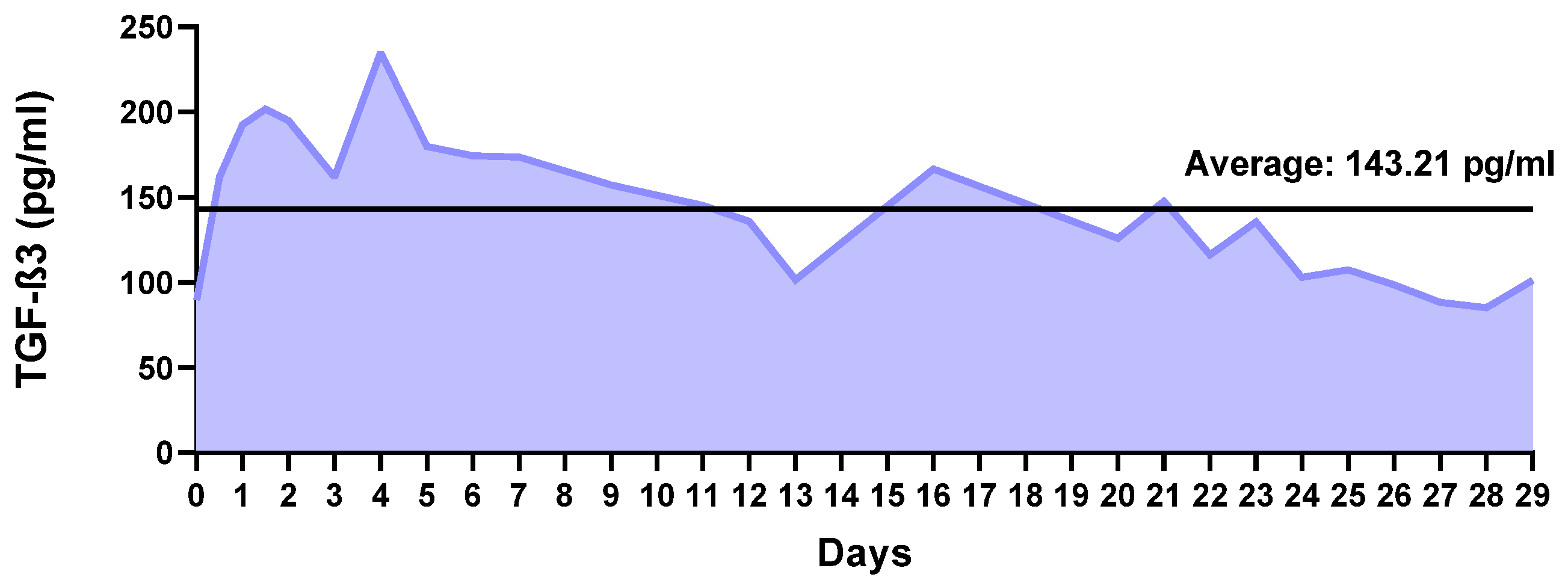
2.2. Factor Release Study
2.3. Biocompatibility of the Nanoparticles
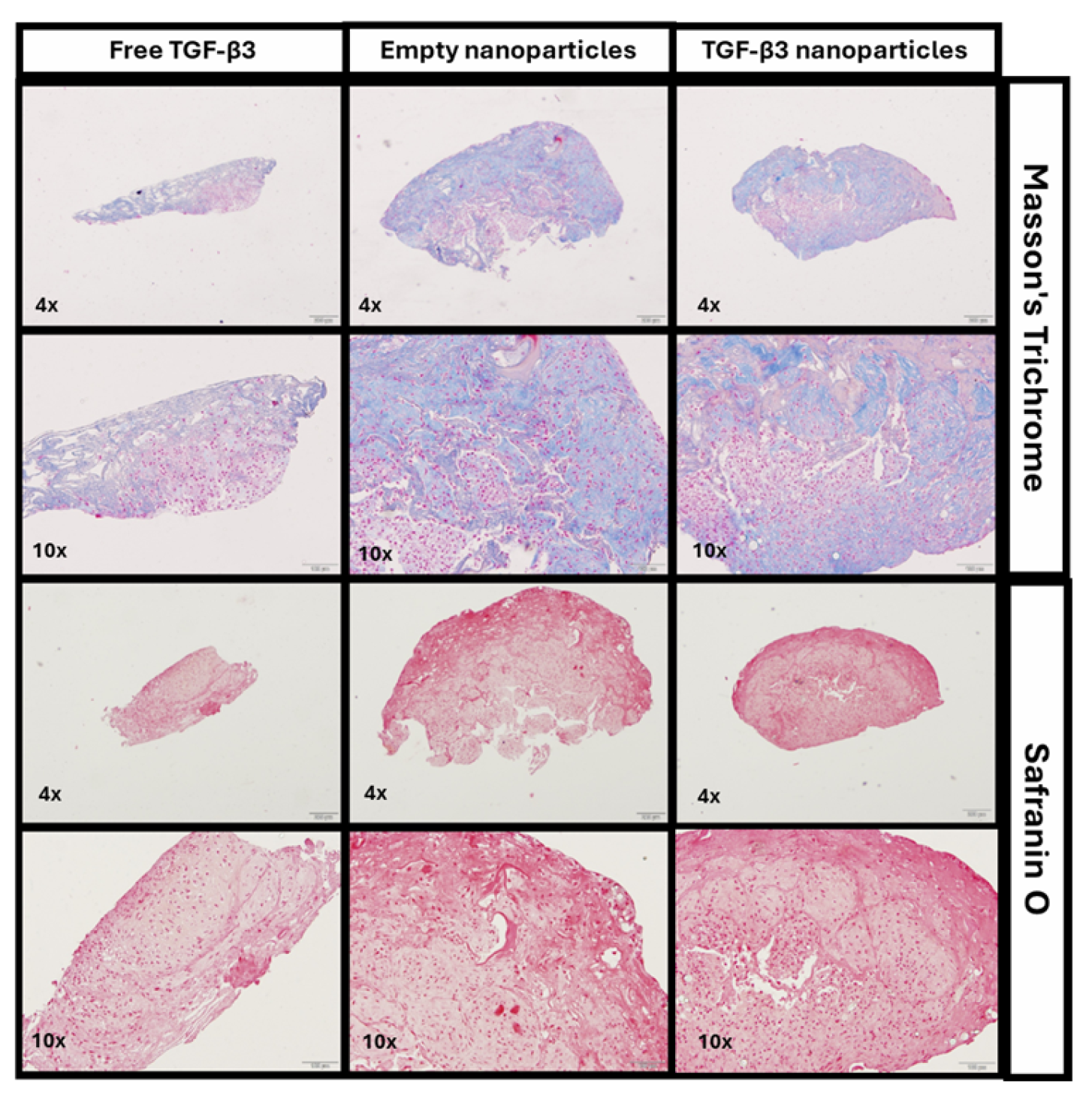
2.4. Generation of Chondrogenic Constructs
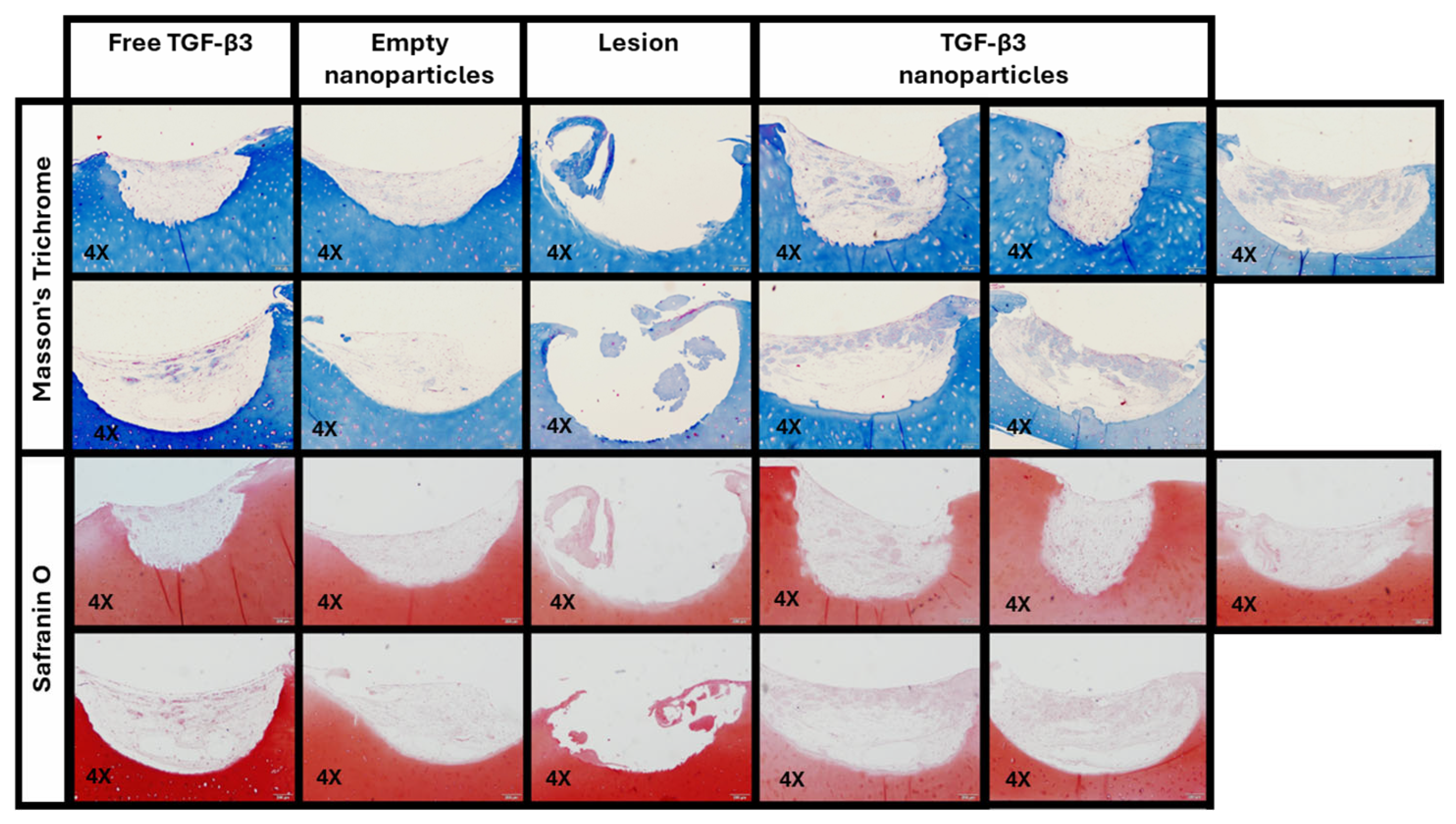
2.5. Ex Vivo Repair Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) and Nanoparticle Formation
4.2. Isolation and Extraction of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
4.3. Biopolymer Cytotoxicity
4.4. Factor Release Study
4.5. Biocompatibility of the Nanoparticles
4.6. Generation of Chondrogenic Constructs
4.7. Ex Vivo Repair Model
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| ACAN | Aggrecan |
| BM | Bone marrow |
| CO2 | Carbon dioxide |
| Col I | Collagen I (biomaterial) |
| COL I | Collagen I (protein) |
| COL II | Collagen II (protein) |
| CHUAC | Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de A Coruña |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase 2 |
| DDS | Drug delivery system |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunoassay |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| HB | Hydroxybutyrate |
| HV | Hydroxyvalerate |
| PCNA | Proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
| IL-1 | Interleukin 1 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1-beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| MT | Masson’s Trichrome |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stem cells |
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappaB |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| P/S | Penicillin/Streptomycin |
| PHBV | Poly (hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) |
| PHA | Polyhydroxyalkanoate |
| PHB | Polyhydroxybutyrate |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| SO | Safranin O |
| SED | Sociedad Española del Dolor |
| SEMDOR | Sociedad Española Multidisciplinar de Dolor |
| 3D | Three dimensions |
| TGF-β3 | Transforming growth factor β3 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor |
| 2D | Two dimensions |
References
- Englund, M. Osteoarthritis, part of life or a curable disease? A bird’s-eye view. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 293, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Li, Z.; Alexander, P.G.; Ocasio-Nieves, B.D.; Yocum, L.; Lin, H.; Tuan, R.S. Pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Risk factors, regulatory pathways in chondrocytes, and experimental models. Biology 2020, 9, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, J.N.; Arant, K.R.; Loeser, R.F. Diagnosis and treatment of hip and knee osteoarthritis: A review. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2021, 325, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschon, M.; Sensi, L.; Perticarini, L.; Massari, L.; Tigani, D.; Fini, M. Gender and sex are key determinants in osteoarthritis, not only confounding variables: A systematic review of clinical data. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.D.; Thoma, L.M.; Golightly, Y.M. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.J.; Fernández-López, J.C.; Villaverde, V.; Montilla, C.; Carmona, L.; Batlle-Gualda, E.; Lajas, C.; Loza, E.; EPISER2016 Working Group. Prevalencia de artrosis sintomática en España: Estudio EPISER2016. Reumatol. Clin. 2021, 17, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, S.; Dunstan, D.W.; Sugiyama, T.; Stathi, A.; Gardiner, P.A.; Owen, N. Active aging and public health: Evidence, implications, and opportunities. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2022, 43, 439–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ageing and Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (accessed on 11 July 2024).
- Savvari, P.; Skiadas, I.; Barmpouni, M.; Papadakis, S.A.; Psychogios, V.; Pastroudis, A.P.; Skarpas, G.A.; Tsoutsanis, A.; Garofalakis, A.; Katsifis, G.; et al. Moderate to severe osteoarthritis: What is the economic burden for patients and the health care system? Insights from the “PONOS” study. Cartilage 2024, 15, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loza, E.; Lopez-Gomez, J.M.; Batlle-Gualda, E.; Blanco, F.J.; Duruoz, T.; Carmona, L.; EPISER Study Group. Economic burden of knee and hip osteoarthritis in Spain. Arthritis Care Res. 2009, 61, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Domínguez, F.; Castrejón, I.; Ramos, M.; Mateo, J.; García-Vivar, M.; Balsa, A. Unmet needs in the osteoarthritis chronic moderate to severe pain management in Spain: A real-world data study. Rheumatol. Ther. 2021, 8, 1113–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, A.; Tenti, S.; Cheleschi, S. Year 2020: New trends in pharmacological treatments for osteoarthritis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 892934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J. Recent advances in hydrogel technology in delivering mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis therapy. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashruf, O.S.; Ansari, M.Y. Natural compounds: Potential therapeutics for the inhibition of cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Life 2023, 13, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, R.H.; Im, G.I.; Park, J.W. Inflammation-modulating hydrogels for osteoarthritis cartilage tissue engineering. Cells 2020, 9, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, V.; Matta, C.; Petho, D.; Szepesi, B.; Nyiri, B.; Toth-Soma, L.; Pinter, E.; Toth, K.; Katona, R. Cytokines and chemokines involved in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.M.; Xu, Q.L.; Zheng, W.J.; Chen, G.Y. The role of TGF-β3 in cartilage development and osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 2023, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozhokin, M.S.; Medvedeva, E.V.; Murashko, M.N.; Lutsenko, S.V.; Bolgova, E.V. Mechanisms of TGFβ3 action as a therapeutic agent for promoting the synthesis of extracellular matrix proteins in hyaline cartilage. Biochem.-Mosc. 2020, 85, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, Y.; Andre, C.; Charbonnier, B.; Rouillon, T.; Regnier, V. Sustained release of TGF-β3 from polysaccharide nanoparticles induces chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 189, 110843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Du, Y. A comprehensive review of advanced drug delivery systems for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tang, H.F.; Wang, Y.J. Polymeric biomaterials: Advanced drug delivery systems in osteoarthritis treatment. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, Z.; Hu, J. Stimuli-sensitive nanotherapies for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 21, e2100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, A.P.; Souza, M.T.; Silva, T.B.; Barros, W.M. Polymeric nanoparticles for drug delivery in osteoarthritis. Polymers 2022, 14, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, V.C.; Patel, S.K.S.; Lee, J.-K. Exploiting polyhydroxyalkanoates for biomedical applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, P.; Lee, W.-H.; Loo, C.-Y.; Wong, H.S.J.; Parumasivam, T. Advances in polyhydroxyalkanoate nanocarriers for effective drug delivery: An overview and challenges. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemoigne, M. Products of dehydration and of polymerization of β-hydroxybutyric acid. Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol. 1926, 8, 770–782. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, G.-Y.A.; Chen, C.-L.; Li, L.; Ge, L.; Wang, L.; Razaad, I.M.N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Mo, Y.; Wang, J.-Y. Start a Research on Biopolymer Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA): A Review. Polymers 2014, 6, 706–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, B.L. Producción de Polihidroxialcanoatos a Partir de Suero Lácteo y Otras Fuentes de Carbono Usando Cultivos Microbianos Mixtos. Master’s Thesis, Universidad de A Coruña, A Coruña, Spain, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Anjum, A.; Zuber, M.; Zia, K.M.; Hussain, A. Microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and its copolymers: A review of recent advancements. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 89, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigore, M.E.; Grigorescu, R.M.; Iancu, L.; Voicu, G. Methods of synthesis, properties and biomedical applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates: A review. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2019, 30, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Cendal, A.I.; Gómez-Seoane, I.; de Toro-Santos, F.J.; Fuentes-Boquete, I.M.; Señarís-Rodríguez, J.; Díaz-Prado, S.M. Biomedical Applications of the Biopolymer Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV): Drug Encapsulation and Scaffold Fabrication. Int. J. Mol. Sci 2023, 24, 11674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Guidance for industry: Pyrogen and endotoxins testing—Questions and answers. In FDA Guidance Document; Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rezaie Shirmard, L.; Bahari Javan, N.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Kebriaee-Zadeh, A.; Dinarvand, R.; Dorkoosh, F.A. Nanoparticulate fingolimod delivery system based on biodegradable poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV): Design, optimization, characterization and in-vitro evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2017, 22, 860–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otroji, M.; Taymouri, S.; Varshosaz, J.; Mirian, M. Preparation and characterization of dry powder containing sunitinib-loaded PHBV nanoparticles for enhanced pulmonary delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 56, 101570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñaloza, J.P.; Márquez-Miranda, V.; Cabaña-Brunod, M.; Reyes-Ramírez, R.; Llancalahuen, F.M.; Vilos, C.; Maldonado-Biermann, F.; Velásquez, L.A.; Fuentes, J.A.; González-Nilo, F.D.; et al. Intracellular trafficking and cellular uptake mechanism of PHBV nanoparticles for targeted delivery in epithelial cell lines. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2017, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masood, F.; Chen, P.; Yasin, T.; Hasan, F.; Ahmad, B.; Hameed, A. Synthesis of poly-(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-12 mol % 3-hydroxyvalerate) by Bacillus cereus FB11: Its characterization and application as a drug carrier. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2013, 24, 1927–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamundeeswari, M.; Jeslin, J.G.; Verma, M.L. Nanocarriers for drug delivery applications. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 17, 849–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawthorne, D.; Pannala, A.; Sandeman, S.; Lloyd, A. Sustained and targeted delivery of hydrophilic drug compounds: A review of existing and novel technologies from bench to bedside. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 78, 103936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrami, S.; Esmaili, Z.; SeyedAlinaghi, S.; Jamali Moghadam, S.R.; Bayrami, S.; Akbari Javar, H.; Rafiee Tehrani, M.; Dorkoosh, F.A. Fabrication of long-acting insulin formulation based on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) nanoparticles: Preparation, optimization, characterization, and in vitro evaluation. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2019, 24, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lightfoot Vidal, S.; Rojas, C.; Bouza Padín, R.; Pérez -Rivera, M.A.; Haensgen, A.; González, M.; Rodríguez-Llamazares, S. Synthesis and characterization of polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate nanoparticles for encapsulation of quercetin. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2016, 31, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Su, P.; Xu, C.; Yang, J.; Yu, W.; Huang, D. Chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells: A comparison between micromass and pellet culture systems. Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 32, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, L.; Zhai, D.Y.; Tous, E.; Rai, R.; Mauck, R.L.; Burdick, J.A. Enhanced MSC chondrogenesis following delivery of TGF-β3 from alginate microspheres within hyaluronic acid hydrogels in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 6425–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- ISO 10993-12:2021; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 12: Sample Preparation and Reference Materials. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Mainil-Varlet, P.; Van Damme, B.; Nesic, D.; Knutsen, G.; Kandel, R. A new histology scoring system for the assessment of the quality of human cartilage repair: ICRS II. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

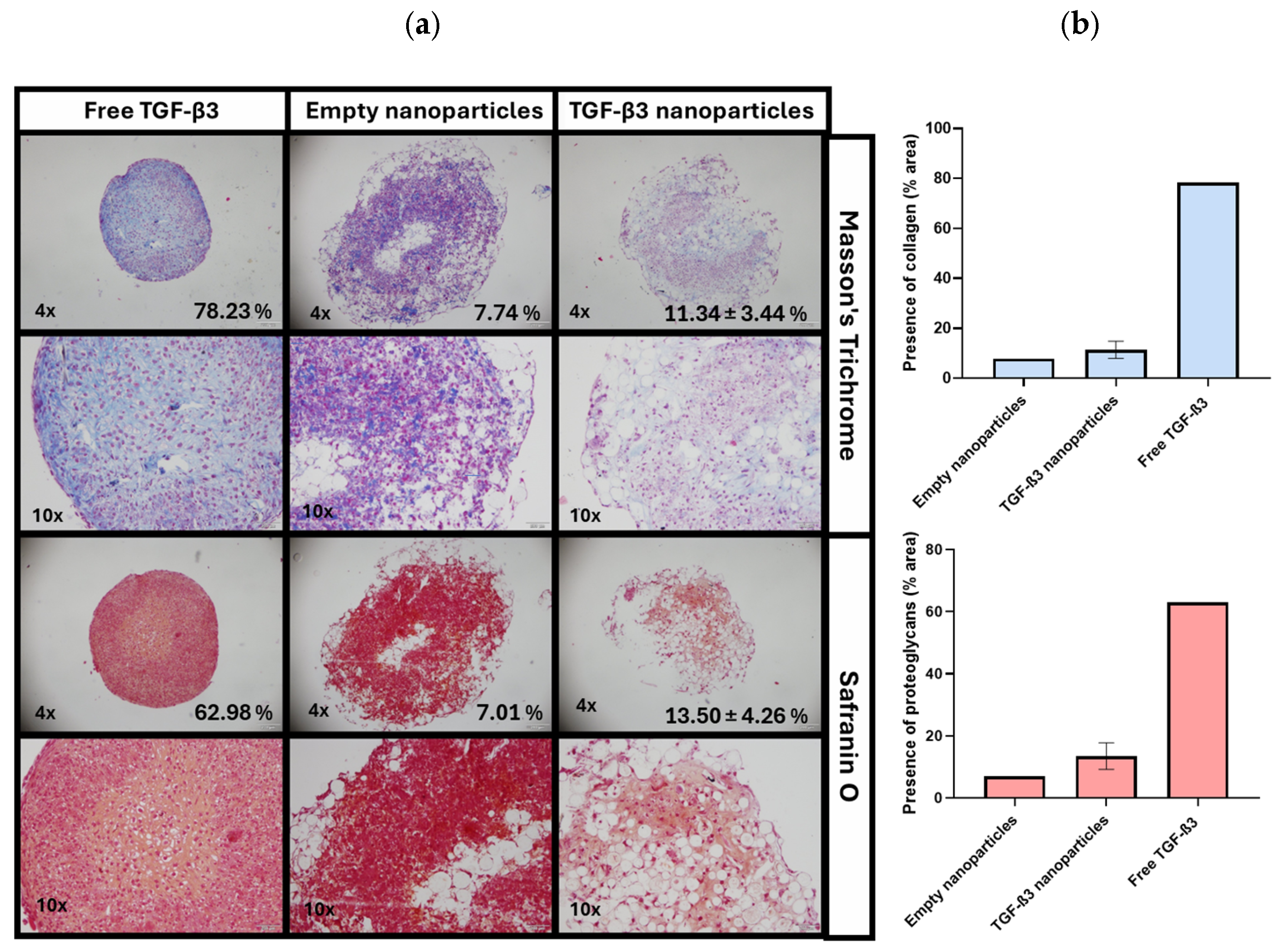
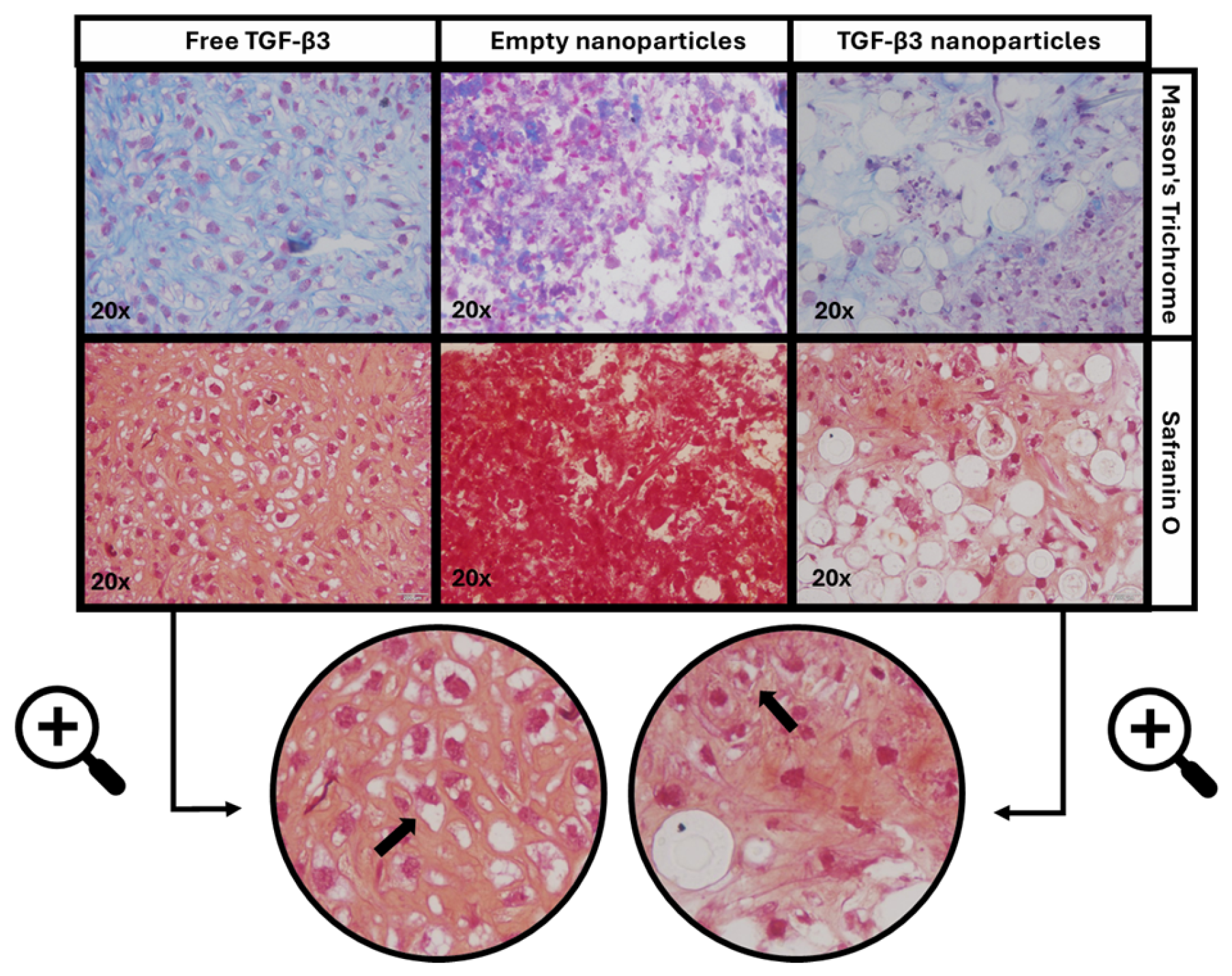
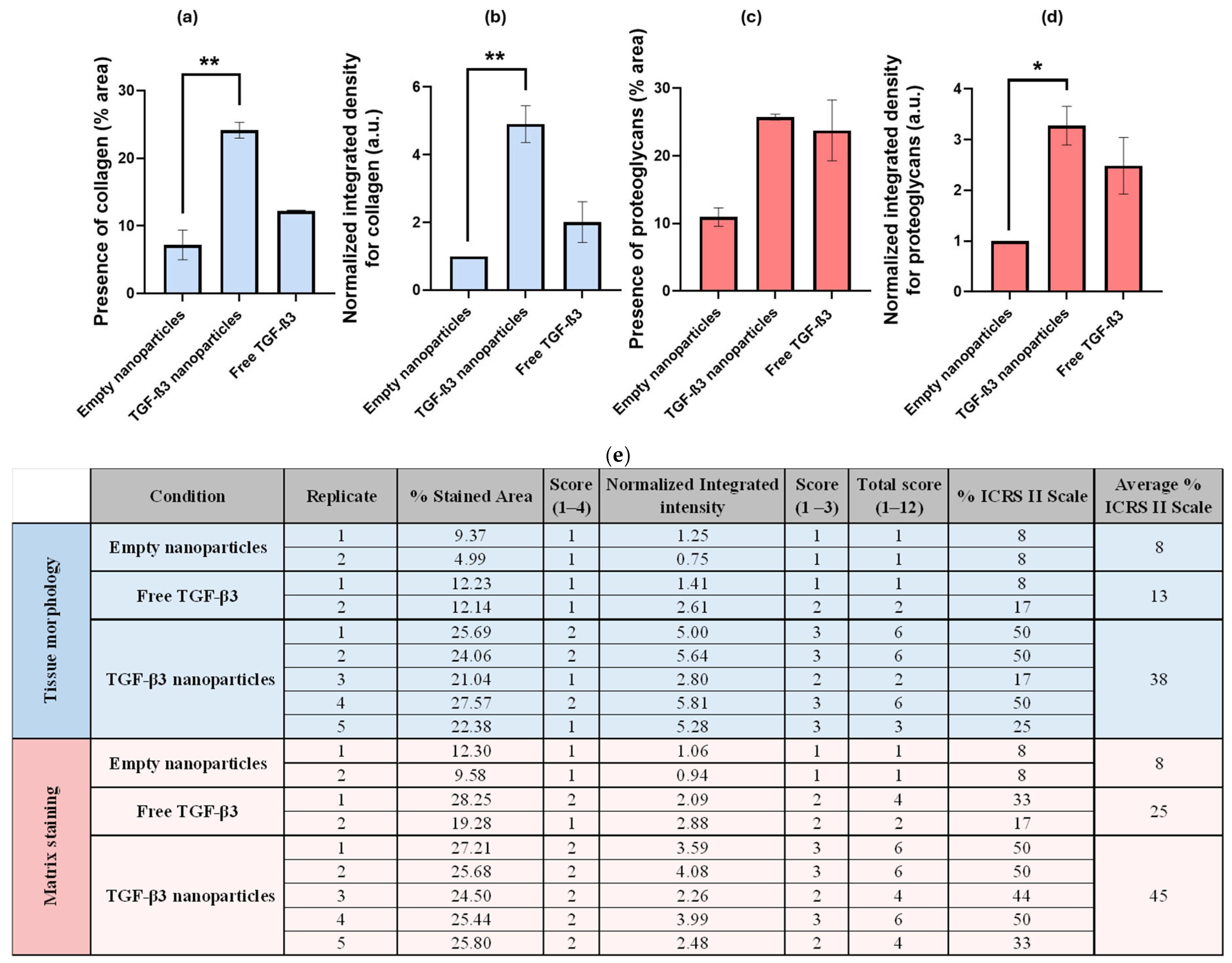
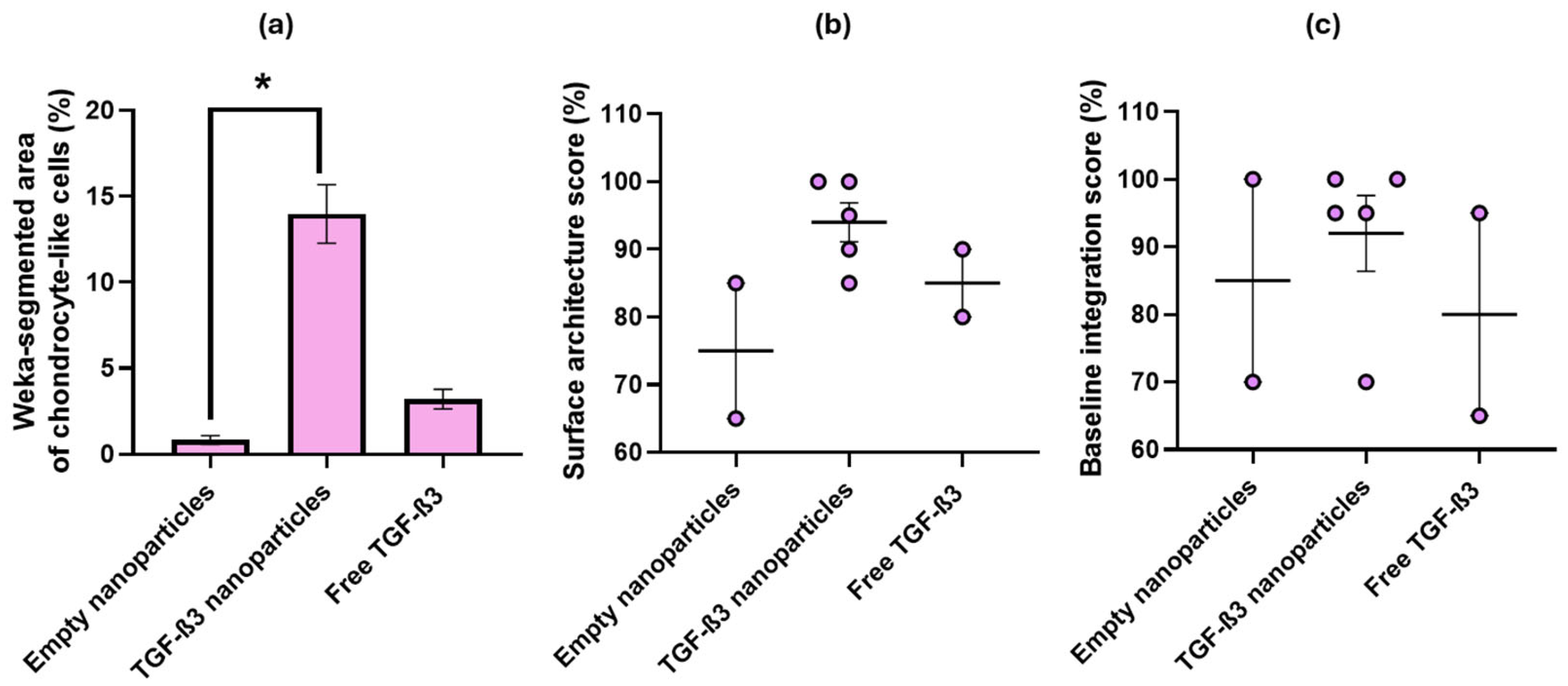
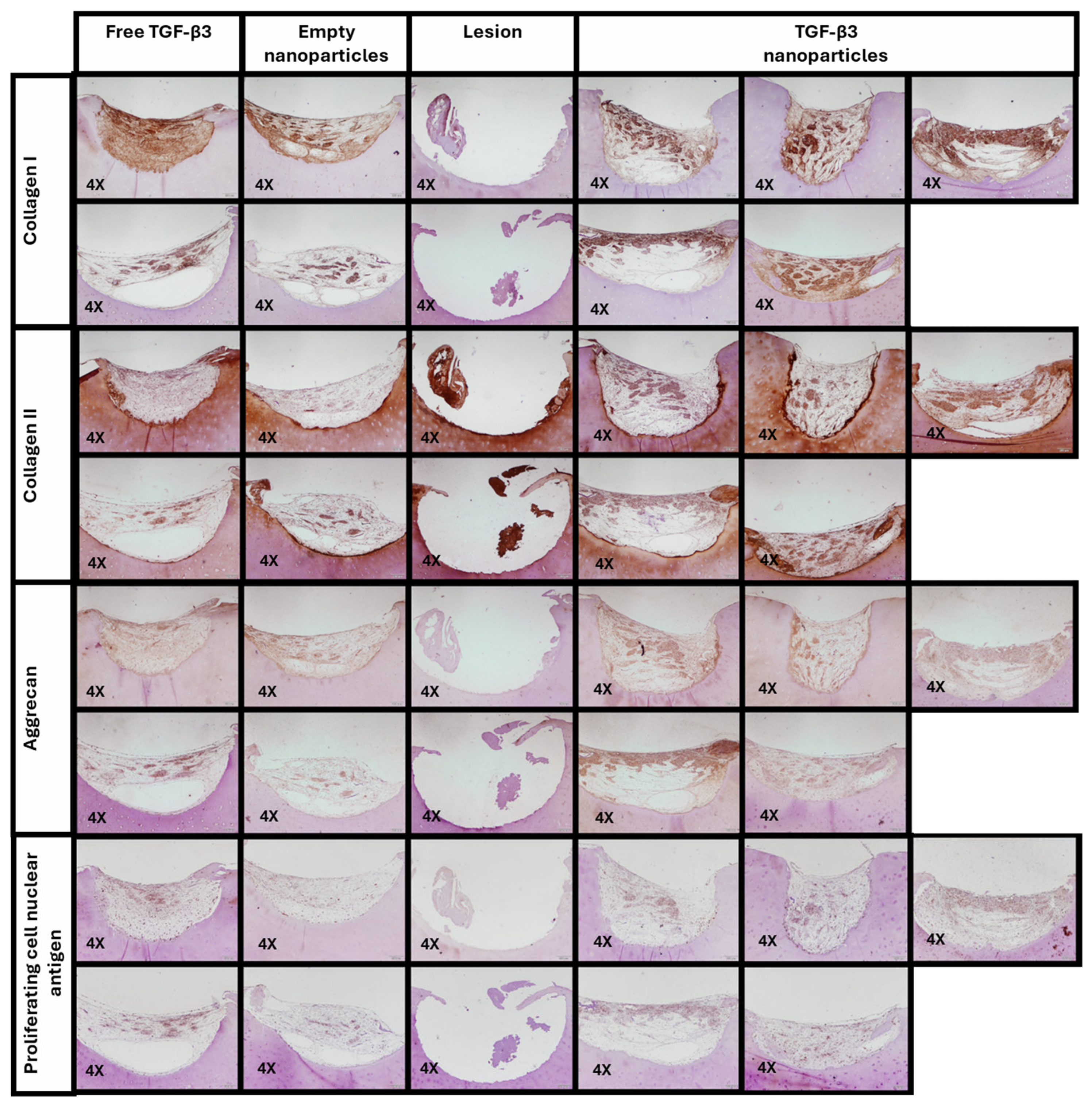
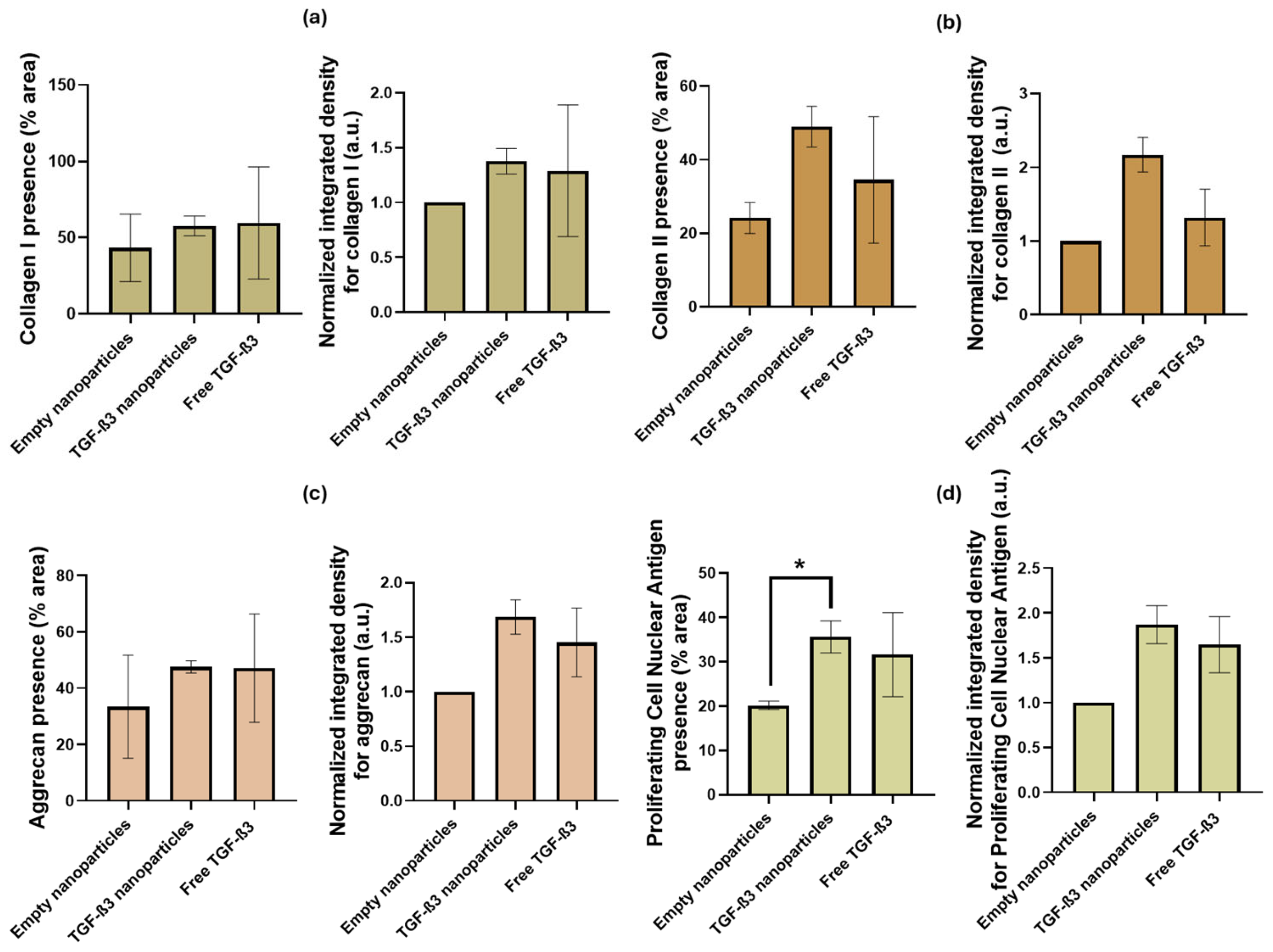
| Parameters | Empty Nanoparticles | TGF-β3 Nanoparticles | Free TGF-β3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tissue morphology | 8% | 38% | 13% |
| Matrix staining | 8% | 45% | 25% |
| Cell morphology | 1% | 14% | 3% |
| Chondrocyte clustering | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Surface architecture | 75% | 95% | 85% |
| Baseline integration | 85% | 93% | 80% |
| Total score | 46% | 64% | 51% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Cendal, A.I.; Señarís-Rodríguez, J.; Piñeiro-Ramil, M.; Cabarcos-Mouzo, L.; Veiga-Barbazán, M.d.C.; Mejide-Faílde, R.M.; de Toro-Santos, F.J.; Fuentes-Boquete, I.M.; Díaz-Prado, S.M. Encapsulation of Transforming Growth Factor-β3 in Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114997
Rodríguez-Cendal AI, Señarís-Rodríguez J, Piñeiro-Ramil M, Cabarcos-Mouzo L, Veiga-Barbazán MdC, Mejide-Faílde RM, de Toro-Santos FJ, Fuentes-Boquete IM, Díaz-Prado SM. Encapsulation of Transforming Growth Factor-β3 in Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cartilage Tissue Engineering. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):4997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114997
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Cendal, Ana Isabel, José Señarís-Rodríguez, María Piñeiro-Ramil, Loreto Cabarcos-Mouzo, María del Carmen Veiga-Barbazán, Rosa María Mejide-Faílde, Francisco Javier de Toro-Santos, Isaac Manuel Fuentes-Boquete, and Silvia María Díaz-Prado. 2025. "Encapsulation of Transforming Growth Factor-β3 in Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cartilage Tissue Engineering" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 4997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114997
APA StyleRodríguez-Cendal, A. I., Señarís-Rodríguez, J., Piñeiro-Ramil, M., Cabarcos-Mouzo, L., Veiga-Barbazán, M. d. C., Mejide-Faílde, R. M., de Toro-Santos, F. J., Fuentes-Boquete, I. M., & Díaz-Prado, S. M. (2025). Encapsulation of Transforming Growth Factor-β3 in Poly(hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate) Nanoparticles for Enhanced Cartilage Tissue Engineering. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 4997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114997








