Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)-Associated Colorectal Cancer (CRC): Is cGAS-STING Pathway Targeting the Key to Chemoprevention?
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. IBD Epidemiology, Therapy, and Colitis-Associated Cancer Risk
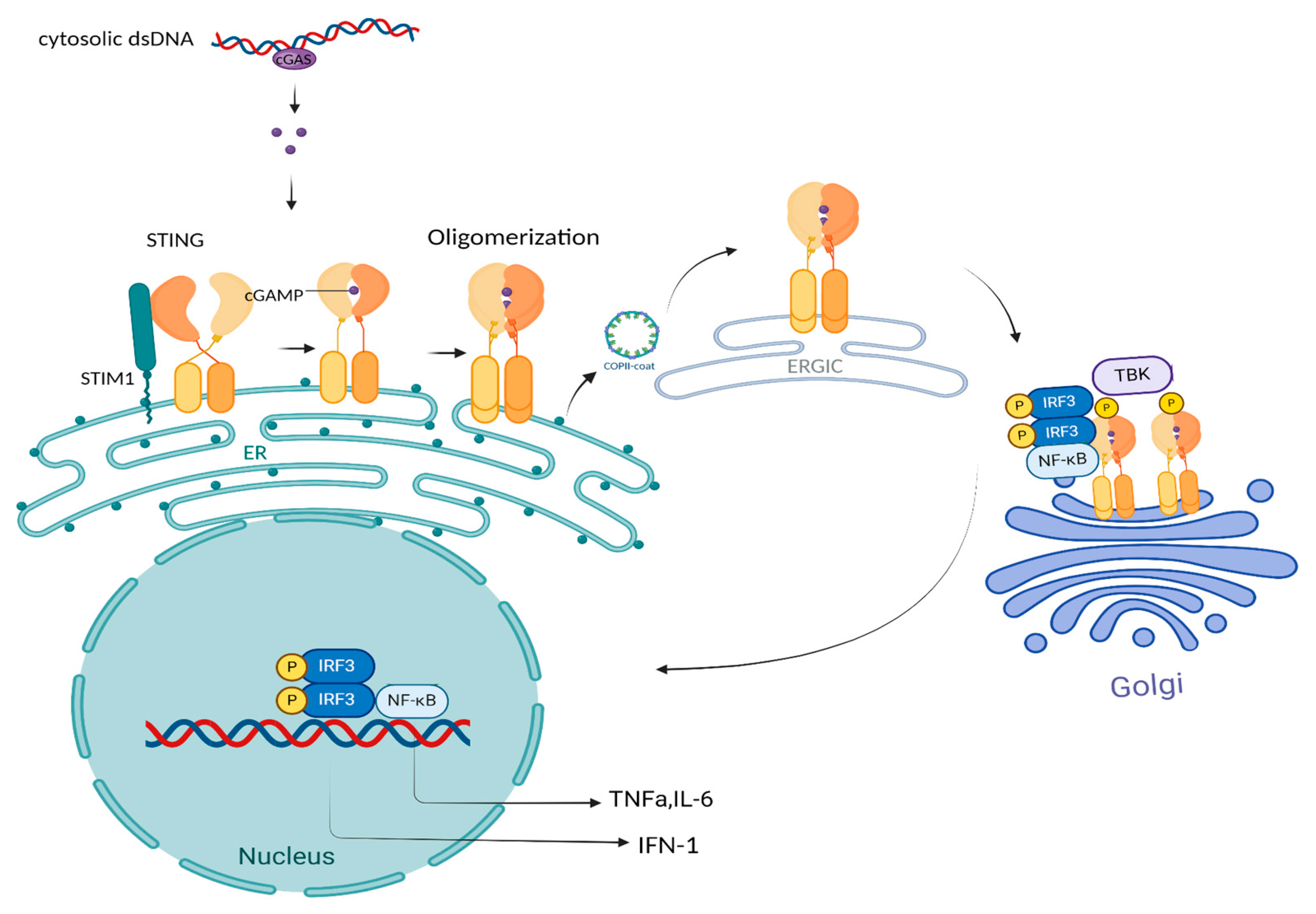
1.2. The cGAS-STING: Linking DNA Sensing to Immune Signaling and Function
2. The cGAS-STING Pathway: Bridging Innate Immunity and Chronic Diseases
3. The cGAS-STING Pathway in IBD: Integrating Innate Immunity, Inflammation, and Gut Homeostasis
3.1. Effect of the cGAS-STING Pathway in Epithelial Cells in IBD
3.2. Effect of the STING Pathway in Macrophages and Dendritic Cells in IBD
3.3. Effect of the STING Pathway in B and T Lymphocytes in IBD
3.4. Role of Sting in Neuroinflammation in IBD
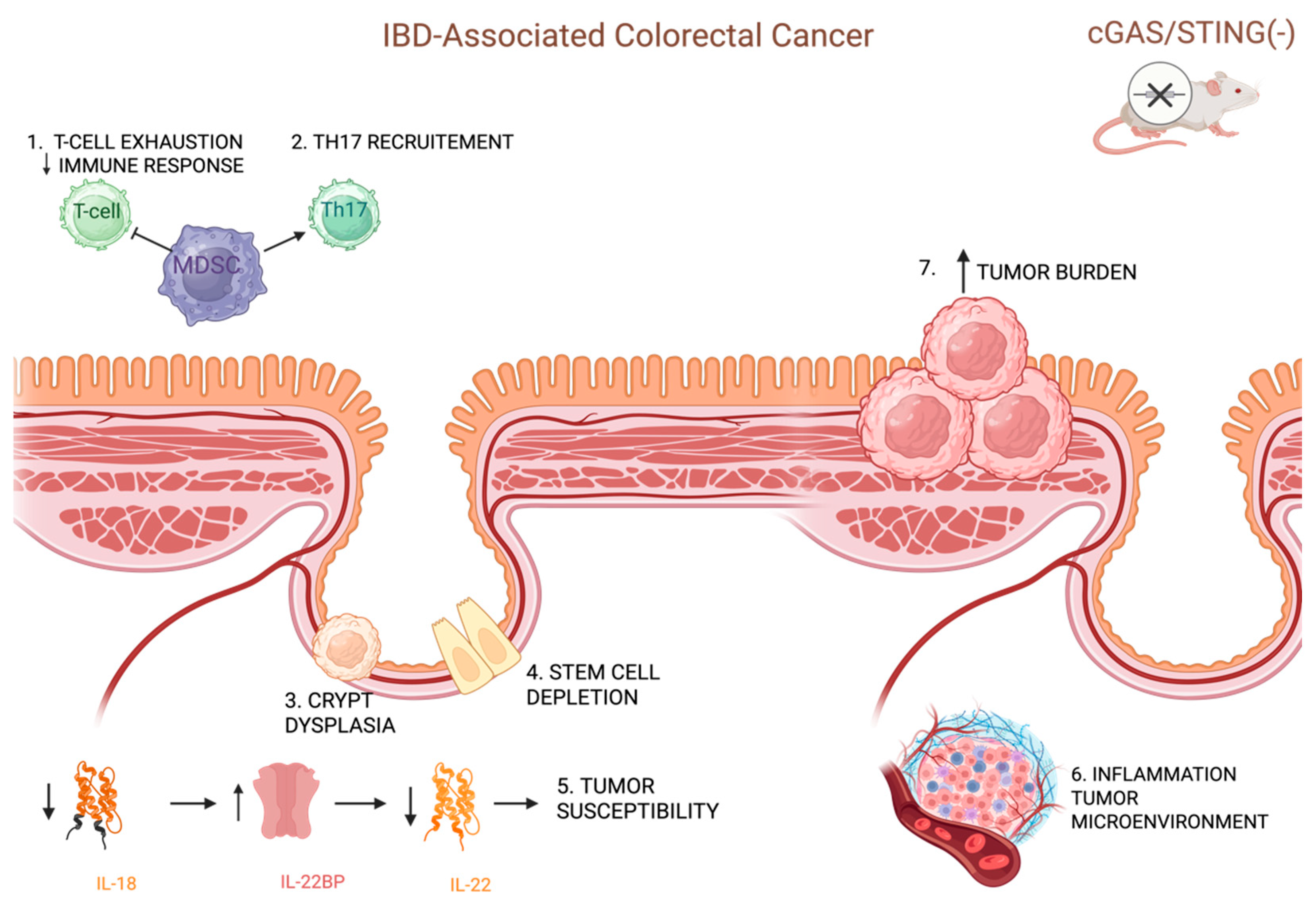
4. The cGAS-STING Pathway in Colitis-Associated Carcinogenesis: From Pathogenesis to Treatment
4.1. Epithelial Protection and Immune Surveillance: cGAS-STING’s Role in CAC Pathogenesis
4.2. The cGAS-STING Signaling in CAC: A Therapeutic Focus on Inflammation Control
4.3. Pyroptosis and Immune Regulation: Unlocking STING’s Role in CAC Immunotherapy
4.4. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting the cGAS-STING Pathway
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torres, J.; Bonovas, S.; Doherty, G.; Kucharzik, T.; Gisbert, J.P.; Raine, T.; Adamina, M.; Armuzzi, A.; Bachmann, O.; Bager, P.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Medical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2020, 14, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raine, T.; Bonovas, S.; Burisch, J.; Kucharzik, T.; Adamina, M.; Annese, V.; Bachmann, O.; Bettenworth, D.; Chaparro, M.; Czuber-Dochan, W.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Ulcerative Colitis: Medical Treatment. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2022, 16, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alatab, S.; Sepanlou, S.G.; Ikuta, K.; Vahedi, H.; Bisignano, C.; Safiri, S.; Sadeghi, A.; Nixon, M.R.; Abdoli, A.; Abolhassani, H.; et al. The Global, Regional, and National Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in 195 Countries and Territories, 1990–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Kaplan, G.G.; Ng, S.C. Changing Global Epidemiology of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Sustaining Health Care Delivery Into the 21st Century. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, C.A.; Bernstein, C.N. Identifying Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases at High vs. Low Risk of Complications. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 18, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagnini, C.; Siakavellas, S.I.; Bamias, G. Systematic Review with Network Meta-Analysis: Efficacy of Induction Therapy with a Second Biological Agent in Anti-TNF-Experienced Crohn’s Disease Patients. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 6317057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekbom, A.; Helmick, C.; Zack, M.; Adami, H.-O. Ulcerative Colitis and Colorectal Cancer: A Population-Based Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 1228–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnands, A.M.; De Jong, M.E.; Lutgens, M.W.M.D.; Hoentjen, F.; Elias, S.G.; Oldenburg, B. Prognostic Factors for Advanced Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1584–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Tsujinaka, S.; Miura, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Shibata, C. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Etiology, Surveillance, and Management. Cancers 2023, 15, 4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño-Milla, C.; Chaparro, M.; Gisbert, J.P. Systematic Review with Meta-analysis: The Declining Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Ulcerative Colitis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Schardey, J.; Zhang, T.; Crispin, A.; Wirth, U.; Karcz, K.W.; Bazhin, A.V.; Andrassy, J.; Werner, J.; Kühn, F. Survival Outcomes and Clinicopathological Features in Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Associated Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Surg. 2022, 276, e319–e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olén, O.; Erichsen, R.; Sachs, M.C.; Pedersen, L.; Halfvarson, J.; Askling, J.; Ekbom, A.; Sørensen, H.T.; Ludvigsson, J.F. Colorectal Cancer in Ulcerative Colitis: A Scandinavian Population-Based Cohort Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadakos, S.P.; Petrogiannopoulos, L.; Pergaris, A.; Theocharis, S. The EPH/Ephrin System in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Peugnet-González, I.; Parada-Venegas, D.; Dijkstra, G.; Faber, K.N. cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway in Intestinal Homeostasis and Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1239142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decout, A.; Katz, J.D.; Venkatraman, S.; Ablasser, A. The cGAS–STING Pathway as a Therapeutic Target in Inflammatory Diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 548–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yao, N.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Jiang, Z. Research Progress of cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway in Intestinal Diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 135, 112271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Kawai, T. Discrimination Between Self and Non-Self-Nucleic Acids by the Innate Immune System. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2019, 344, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, J.; Feng, Z. Significance of the cGAS-STING Pathway in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Lama, L.; Adura, C.; Tomita, D.; Glickman, J.F.; Tuschl, T.; Patel, D.J. Human cGAS Catalytic Domain Has an Additional DNA-Binding Interface That Enhances Enzymatic Activity and Liquid-Phase Condensation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11946–11955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Ishii, R.; Goto, E.; Ishitani, R.; Tokunaga, F.; Nureki, O. Structural and Functional Analyses of DNA-Sensing and Immune Activation by Human cGAS. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Zhao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, H. cGAS: Action in the Nucleus. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1380517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Fei, C.-J.; Hu, Y.; Wu, X.-Y.; Nie, L.; Chen, J. Current Understanding of the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway: Structure, Regulatory Mechanisms, and Related Diseases. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 183–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanth, S.; Woo, J.S.; Wu, B.; El-Sherbiny, Y.M.; Leung, J.; Chupradit, K.; Rice, L.; Seo, G.J.; Calmettes, G.; Ramakrishna, C.; et al. The Ca2+ Sensor STIM1 Regulates the Type I Interferon Response by Retaining the Signaling Adaptor STING at the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shang, G.; Gui, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.; Chen, Z.J. Structural Basis of STING Binding with and Phosphorylation by TBK1. Nature 2019, 567, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of Type I Interferon Responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, H.; Ouyang, X.; Dong, Y.; Sarapultsev, A.; Luo, S.; Hu, D. Multifaceted Functions of STING in Human Health and Disease: From Molecular Mechanism to Targeted Strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonugunta, V.K.; Sakai, T.; Pokatayev, V.; Yang, K.; Wu, J.; Dobbs, N.; Yan, N. Trafficking-Mediated STING Degradation Requires Sorting to Acidified Endolysosomes and Can Be Targeted to Enhance Anti-Tumor Response. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3234–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konno, H.; Konno, K.; Barber, G.N. Cyclic Dinucleotides Trigger ULK1 (ATG1) Phosphorylation of STING to Prevent Sustained Innate Immune Signaling. Cell 2013, 155, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z.J. Regulation and Function of the cGAS–STING Pathway of Cytosolic DNA Sensing. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Zheng, D.; Luo, Y.; Mou, T.; Chen, Q.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Z. MicroRNA-24-3p Alleviates Hepatic Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury in Mice through the Repression of STING Signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 522, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.U.; Cao, Y.; Siddique, N.; Lin, J.; Yang, Q. miR29a and miR378b Influence CpG-Stimulated Dendritic Cells and Regulate cGAS/STING Pathway. Vaccines 2019, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Cong, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, T.; Du, F.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y.-T.; Grishin, N.V.; et al. Phosphorylation of Innate Immune Adaptor Proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF Induces IRF3 Activation. Science 2015, 347, aaa2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skopelja-Gardner, S.; An, J.; Elkon, K.B. Role of the cGAS-STING Pathway in Systemic and Organ-Specific Diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2022, 18, 558–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, V.E.; Skarlis, C.; Evangelopoulos, M.-E.; Mavragani, C.P. Type I Interferon Detection in Autoimmune Diseases: Challenges and Clinical Applications. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 17, 883–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavragani, C.P.; Kirou, K.A.; Seshan, S.V.; Crow, M.K. Type I Interferon and Neutrophil Transcripts in Lupus Nephritis Renal Biopsies: Clinical and Histopathological Associations. Rheumatology 2023, 62, 2534–2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavragani, C.P.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Sjögren’s Syndrome: Old and New Therapeutic Targets. J. Autoimmun. 2020, 110, 102364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzis, L.; Goules, A.V.; Stergiou, I.E.; Voulgarelis, M.; Tzioufas, A.G.; Kapsogeorgou, E.K. Serum, but Not Saliva, CXCL13 Levels Associate with Infiltrating CXCL13+ Cells in the Minor Salivary Gland Lesions and Other Histologic Parameters in Patients with Sjögren’s Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 705079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauro, D.; Lin, X.; Pontarini, E.; Wehr, P.; Guggino, G.; Tang, Y.; Deng, C.; Gandolfo, S.; Xiao, F.; Rui, K.; et al. CD8+ Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells Are Expanded in Primary Sjögren’s Disease and Can Be Therapeutically Targeted by CD103 Blockade. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1345–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachogiannis, N.I.; Tual-Chalot, S.; Zormpas, E.; Bonini, F.; Ntouros, P.A.; Pappa, M.; Bournia, V.-K.; Tektonidou, M.G.; Souliotis, V.L.; Mavragani, C.P.; et al. Adenosine-to-Inosine RNA Editing Contributes to Type I Interferon Responses in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 125, 102755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jesus, A.A.; Marrero, B.; Yang, D.; Ramsey, S.E.; Montealegre Sanchez, G.A.; Tenbrock, K.; Wittkowski, H.; Jones, O.Y.; Kuehn, H.S.; et al. Activated STING in a Vascular and Pulmonary Syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepelley, A.; Martin-Niclós, M.J.; Le Bihan, M.; Marsh, J.A.; Uggenti, C.; Rice, G.I.; Bondet, V.; Duffy, D.; Hertzog, J.; Rehwinkel, J.; et al. Mutations in COPA Lead to Abnormal Trafficking of STING to the Golgi and Interferon Signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20200600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, E.E.; Treuting, P.M.; Woodward, J.J.; Stetson, D.B. cGAS Is Required for Lethal Autoimmune Disease in the Trex1-Deficient Mouse Model of Aicardi–Goutières Syndrome. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1939–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, M.K.; Nandakumar, R.; Stadler, D.; Malo, A.; Valls, R.M.; Wang, F.; Reinert, L.S.; Dagnæs-Hansen, F.; Hollensen, A.K.; Mikkelsen, J.G.; et al. Lack of Immunological DNA Sensing in Hepatocytes Facilitates Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Hepatology 2016, 64, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domizio, J.D.; Gulen, M.F.; Saidoune, F.; Thacker, V.V.; Yatim, A.; Sharma, K.; Nass, T.; Guenova, E.; Schaller, M.; Conrad, C.; et al. The cGAS–STING Pathway Drives Type I IFN Immunopathology in COVID-19. Nature 2022, 603, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzner, A.-M.; Hagmann, C.A.; Goldeck, M.; Wolter, S.; Kübler, K.; Wittmann, S.; Gramberg, T.; Andreeva, L.; Hopfner, K.-P.; Mertens, C.; et al. Sequence-Specific Activation of the DNA Sensor cGAS by Y-Form DNA Structures as Found in Primary HIV-1 cDNA. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.T.; Cui, C.; Qing, L.; Wang, L.S.; He, T.Y.; Yan, F.; Liu, F.Q.; Shen, Y.H.; Hou, X.G.; Chen, L. Activation of the STING-IRF3 Pathway Promotes Hepatocyte Inflammation, Apoptosis and Induces Metabolic Disorders in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Metabolism 2018, 81, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Bakhoum, S.F. The Pleiotropic Roles of cGAS–STING Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 14, mjac019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, B.; Aitken, J.D.; Malleshappa, M.; Vijay-Kumar, M. Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS)-Induced Colitis in Mice. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2014, 104, 15.25.1–15.25.14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parang, B.; Barrett, C.W.; Williams, C.S. AOM/DSS Model of Colitis-Associated Cancer. In Gastrointestinal Physiology and Diseases; Ivanov, A.I., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1422, pp. 297–307. ISBN 978-1-4939-3601-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, T.; Wang, D.; Mei, Q.; Flavell, R.A.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; Pan, W.; et al. DHX9 Maintains Epithelial Homeostasis by Restraining R-Loop-Mediated Genomic Instability in Intestinal Stem Cells. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flood, P.; Fanning, A.; Woznicki, J.A.; Crowley, T.; Christopher, A.; Vaccaro, A.; Houston, A.; McSweeney, S.; Ross, S.; Hogan, A.; et al. DNA Sensor-Associated Type I Interferon Signaling Is Increased in Ulcerative Colitis and Induces JAK-Dependent Inflammatory Cell Death in Colonic Organoids. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2022, 323, G439–G460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhong, X.; Cao, W.; Mao, M.; Liu, D.; Liu, W.; Zu, X.; Liu, J. IGF2/IGF2R/Sting Signaling as a Therapeutic Target in DSS-Induced Ulcerative Colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 960, 176122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y. Epoxy Triglyceride Enhances Intestinal Permeability via Caspase-1/NLRP3/GSDMD and cGAS-STING Pathways in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 4371–4381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, C.; Zeh, H.J.; Wang, H.; Kroemer, G.; Klionsky, D.J.; Billiar, T.R.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Nuclear Localization of STING1 Competes with Canonical Signaling to Activate AHR for Commensal and Intestinal Homeostasis. Immunity 2023, 56, 2736–2754.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, G.R.; Blomquist, C.M.; Henare, K.L.; Jirik, F.R. Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) Activation Exacerbates Experimental Colitis in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Bilotta, A.J.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, S.; Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Dann, S.M.; et al. STING Controls Intestinal Homeostasis through Promoting Antimicrobial Peptide Expression in Epithelial Cells. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 15417–15430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canesso, M.C.C.; Lemos, L.; Neves, T.C.; Marim, F.M.; Castro, T.B.R.; Veloso, É.; Queiroz, C.P.; Ahn, J.; Santiago, H.C.; Martins, F.S.; et al. The Cytosolic Sensor STING Is Required for Intestinal Homeostasis and Control of Inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 820–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Duan, S.; Fan, G.; Bai, J.; Zheng, Q.; Gu, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, R. Intestinal Epithelial Damage-Derived mtDNA Activates STING-IL12 Axis in Dendritic Cells to Promote Colitis. Theranostics 2024, 14, 4393–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmuel-Galia, L.; Humphries, F.; Lei, X.; Ceglia, S.; Wilson, R.; Jiang, Z.; Ketelut-Carneiro, N.; Foley, S.E.; Pechhold, S.; Houghton, J.; et al. Dysbiosis Exacerbates Colitis by Promoting Ubiquitination and Accumulation of the Innate Immune Adaptor STING in Myeloid Cells. Immunity 2021, 54, 1137–1153.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Son, S.; Oliveira, S.C.; Barber, G.N. STING-Dependent Signaling Underlies IL-10 Controlled Inflammatory Colitis. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3873–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Zheng, T.; Gong, W.; Wu, J.; Xie, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, R.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles Package dsDNA to Aggravate Crohn’s Disease by Activating the STING Pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Ding, Q.; Gong, J.; Xiao, F.; Chen, L.; Tian, D.; Liu, M.; Luo, Z. CRIg+ Macrophages Deficiency Enhanced Inflammation Damage in IBD Due to Gut Extracellular Vesicles Containing Microbial DNA. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2379633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yu, T.; Zhou, G.; Yao, S.; Wakamiya, M.; Hu, H.; Paessler, S.; Sun, J.; Cong, Y. Intrinsic STING Switches off Pathogenetic Programs of Th1 Cells to Inhibit Colitis. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 15, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasceno, L.E.A.; Cunha, T.M.; Cunha, F.Q.; Sparwasser, T.; Alves-Filho, J.C. A Clinically-Relevant STING Agonist Restrains Human TH17 Cell Inflammatory Profile. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 111007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B. The Enteric Nervous System and Neurogastroenterology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubišić, V.; McClain, J.L.; Fried, D.E.; Grants, I.; Rajasekhar, P.; Csizmadia, E.; Ajijola, O.A.; Watson, R.E.; Poole, D.P.; Robson, S.C.; et al. Enteric Glia Modulate Macrophage Phenotype and Visceral Sensitivity Following Inflammation. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 108100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A.; Zhang, M.; Frugier, T.; Bedoui, S.; Taylor, J.M.; Crack, P.J. STING-Mediated Type-I Interferons Contribute to the Neuroinflammatory Process and Detrimental Effects Following Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharshika, C.; Gonzales, J.; Chow, A.; Morales-Soto, W.; Gulbransen, B.D. Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) Expression in the Enteric Nervous System and Contributions of Glial STING in Disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2023, 35, e14553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Deng, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, D.; Fan, K.; Chang, J.; Ma, Y. Neuropeptide Substance P Attenuates Colitis by Suppressing Inflammation and Ferroptosis via the cGAS-STING Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 2507–2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Ma, Z.; Sun, D.; Liang, X.; Zhang, X. A Molecular Subtyping Associated with the cGAS-STING Pathway Provides Novel Perspectives on the Treatment of Ulcerative Colitis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Fang, Y.; Chen, X.; Cheng, T.; Zhao, M.; Du, M.; Li, T.; Li, M.; Zeng, Z.; Wei, Y.; et al. cGAS Restricts Colon Cancer Development by Protecting Intestinal Barrier Integrity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2105747118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Man, S.M.; Gurung, P.; Liu, Z.; Vogel, P.; Lamkanfi, M.; Kanneganti, T.-D. STING Mediates Protection against Colorectal Tumorigenesis by Governing the Magnitude of Intestinal Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 4779–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Konno, H.; Barber, G.N. Diverse Roles of STING-Dependent Signaling on the Development of Cancer. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5302–5308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mühl, H.; Bachmann, M. IL-18/IL-18BP and IL-22/IL-22BP: Two Interrelated Couples with Therapeutic Potential. Cell. Signal. 2019, 63, 109388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghonim, M.A.; Ibba, S.V.; Tarhuni, A.F.; Errami, Y.; Luu, H.H.; Dean, M.J.; El-Bahrawy, A.H.; Wyczechowska, D.; Benslimane, I.A.; Del Valle, L.; et al. Targeting PARP-1 with Metronomic Therapy Modulates MDSC Suppressive Function and Enhances Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Colon Cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e001643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Perez, E.A.; Wu, Y.; Guo, T.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y. Protective Effects of Palbociclib on Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 14, 2436–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Liu, P.; Zhao, F.; Liu, J.; Hong, Z.; Ren, H.; Gu, G.; Wang, G.; Wu, X.; Zheng, T.; et al. STING-Mediated Syk Signaling Attenuates Tumorigenesis of Colitis-associated Colorectal Cancer Through Enhancing Intestinal Epithelium Pyroptosis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Shapira, S.D. Negative Regulation of Cytosolic Sensing of DNA. In International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 344, pp. 91–115. ISBN 978-0-12-815979-8. [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevan, S.O.; Behl, B.; Rathinam, V.A. Pyroptosis-Induced Inflammation and Tissue Damage. Semin. Immunol. 2023, 69, 101781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkuri, T.; Kosaka, A.; Ishibashi, K.; Kumai, T.; Hirata, Y.; Ohara, K.; Nagato, T.; Oikawa, K.; Aoki, N.; Harabuchi, Y.; et al. Intratumoral Administration of cGAMP Transiently Accumulates Potent Macrophages for Anti-Tumor Immunity at a Mouse Tumor Site. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lee, W.S.; Kong, S.J.; Kim, C.G.; Kim, J.H.; Chang, S.K.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.; Chon, H.J.; Kim, C. STING Activation Reprograms Tumor Vasculatures and Synergizes with VEGFR2 Blockade. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4350–4364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Liu, C.; Luo, S.; Cao, T.; Lin, B.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Zheng, T.; Li, X. STING Agonist and IDO Inhibitor Combination Therapy Inhibits Tumor Progression in Murine Models of Colorectal Cancer. Cell. Immunol. 2021, 366, 104384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, S.M.; Gulen, M.F.; Reymond, L.; Gibelin, A.; Abrami, L.; Decout, A.; Heymann, M.; Van Der Goot, F.G.; Turcatti, G.; Behrendt, R.; et al. Targeting STING with Covalent Small-Molecule Inhibitors. Nature 2018, 559, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Guo, W.; Guo, L.; Gu, Y.; Cai, P.; Xie, N.; Yang, X.; Shu, Y.; Wu, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. Andrographolide Sulfonate Ameliorates Experimental Colitis in Mice by Inhibiting Th1/Th17 Response. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2014, 20, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, B.; Wang, D.; Wu, J.; Gao, J.; Zhong, H.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liu, W.; Gu, Y.; et al. DNA Damage Repair Promotion in Colonic Epithelial Cells by Andrographolide Downregulated cGAS–STING Pathway Activation and Contributed to the Relief of CPT-11-Induced Intestinal Mucositis. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 262–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Chen, Q.; Mao, W.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J. Combination of Irinotecan Silicasome Nanoparticles with Radiation Therapy Sensitizes Immunotherapy by Modulating the Activation of the cGAS/STING Pathway for Colorectal Cancer. Mater. Today Bio 2023, 23, 100809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orel, V.B.; Papazoglou, A.S.; Tsagkaris, C.; Moysidis, D.V.; Papadakos, S.; Galkin, O.Y.; Orel, V.E.; Syvak, L.A. Nanotherapy Based on Magneto-mechanochemical Modulation of Tumor Redox State. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 15, e1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Y.; Ren, Y.; Sayed, M.; Hu, X.; Lei, C.; Kumar, A.; Hutchins, E.; Mu, J.; Deng, Z.; Luo, C.; et al. Plant-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Shape the Gut Microbiota. Cell Host Microbe 2018, 24, 637–652.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.; Biancone, L.; Fiorino, G.; Katsanos, K.H.; Kopylov, U.; Al Sulais, E.; Axelrad, J.E.; Balendran, K.; Burisch, J.; De Ridder, L.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Malignancies. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2023, 17, 827–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jess, T.; Rungoe, C.; Peyrin–Biroulet, L. Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Cohort Studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgens, M.W.M.D.; Van Oijen, M.G.H.; Van Der Heijden, G.J.M.G.; Vleggaar, F.P.; Siersema, P.D.; Oldenburg, B. Declining Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: An Updated Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Cohort Studies. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2013, 19, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jess, T.; Gamborg, M.; Matzen, P.; Munkholm, P.; Sorensen, T.I.A. Increased Risk of Intestinal Cancer in Crohn’s Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Cohort Studies. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 100, 2724–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutgens, M.W.M.D.; Vleggaar, F.P.; Schipper, M.E.I.; Stokkers, P.C.F.; Van Der Woude, C.J.; Hommes, D.W.; De Jong, D.J.; Dijkstra, G.; Van Bodegraven, A.A.; Oldenburg, B.; et al. High Frequency of Early Colorectal Cancer in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut 2008, 57, 1246–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, W.-Y.; Zhou, G.-Z.; Peng, L.-H.; Pan, F. Update and Latest Advances in Mechanisms and Management of Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2023, 15, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, I.; Bujanda, L.; Castro, J.; Merino, O.; Tosca, J.; Camps, B.; Gutiérrez, A.; Gordillo Ábalos, J.; De Castro, L.; Iborra, M.; et al. Clinical Characteristics, Associated Malignancies and Management of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: A Multicentre Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2019, 13, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayos, F.S.; Loftus, E.V.; Jess, T.; Harmsen, W.S.; Bida, J.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Tremaine, W.J.; Sandborn, W.J. Predictive and Protective Factors Associated with Colorectal Cancer in Ulcerative Colitis: A Case-Control Study. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, X.; Ma, J.; Wang, K.; Zhang, H. Chemopreventive Effects of 5-Aminosalicylic Acid on Inflammatory Bowel Disease-Associated Colorectal Cancer and Dysplasia: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1031–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonovas, S.; Fiorino, G.; Lytras, T.; Nikolopoulos, G.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Systematic Review with Meta-analysis: Use of 5-aminosalicylates and Risk of Colorectal Neoplasia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 45, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, F.; Gionchetti, P.; Eliakim, R.; Ardizzone, S.; Armuzzi, A.; Barreiro-de Acosta, M.; Burisch, J.; Gecse, K.B.; Hart, A.L.; Hindryckx, P.; et al. Third European Evidence-Based Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Ulcerative Colitis. Part 1: Definitions, Diagnosis, Extra-Intestinal Manifestations, Pregnancy, Cancer Surveillance, Surgery, and Ileo-Anal Pouch Disorders. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2017, 11, 649–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schaik, F.D.M.; Van Oijen, M.G.H.; Smeets, H.M.; Van Der Heijden, G.J.M.G.; Siersema, P.D.; Oldenburg, B. Thiopurines Prevent Advanced Colorectal Neoplasia in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut 2012, 61, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study/Reference | Key Findings | Mechanisms | Therapeutic Insights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghonim et al. (2023)/ [75] | Partial inhibition of PARP-1 (via heterozygosity or low-dose olaparib) reduced tumor burden, colitis severity, and systemic inflammation; full inhibition less effective. | Modulated MDSC function; reduced TNF-α, MCP-1; enhanced mucosal integrity. Excess inhibition impaired immune homeostasis. | Partial PARP-1 inhibition shows robust protective effect against CAC; excessive inhibition may be counterproductive. |
| Ahn et al. (2017)/ [60] | STING-deficient mice had increased polyps, dysbiosis, and disrupted cytokine balance. Antibiotics reduced polyp load. | STING regulated IL-10, IL-1β, and IL-18 via MyD88-dependent pathways; microbial CDNs were dominant STING activators over self-DNA. | STING controls tumor-promoting inflammation; microbial modulation and STING targeting may suppress CAC progression. |
| Yang et al. (2023)/ [76] | Palbociclib reduced inflammation, epithelial damage, and tumor load in AOM/DSS mice; suppressed pro-inflammatory cytokines (Ifnb1, Il6, Il1b) | Inhibited STING activation by interfering with its dimerization and signaling cascade. | Palbociclib modulates STING to curb inflammation-driven CRC; further studies needed to confirm clinical potential. |
| Study/Reference | Key Findings | Mechanisms | Therapeutic Insights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cai et al. (2023)/ [58] | STING activation in early CAC exacerbates inflammation; myeloid-specific STING deletion reduces tumor formation. In advanced tumors, STING is essential for anti-tumor immunity. | STING promotes inflammation and tumor initiation via TFAM-mtDNA activation but supports CD8+ T cell responses in advanced disease. | Timing of STING-targeted therapy is critical. Early inhibition may prevent CAC, while later activation enhances anti-tumor responses. |
| Vasudevan et al. (2023)/ [79] | STING interacts with Syk to induce pyroptosis via GSDMD cleavage. STING deficiency promotes tumor growth and suppresses anti-tumor cytokine production. | STING–Syk interaction triggers pyroptosis and enhances type-I IFN production via TBK1-IRF3; regulates tumor cytokine balance. | STING agonists like DMXAA may enhance pyroptosis and immune responses. STING–Syk axis is a potential therapeutic target in CAC. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papadakos, S.P.; Georgiadou, C.; Argyrou, A.; Michailidou, E.; Thanos, C.; Vogli, S.; Siakavellas, S.I.; Manolakopoulos, S.; Theocharis, S. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)-Associated Colorectal Cancer (CRC): Is cGAS-STING Pathway Targeting the Key to Chemoprevention? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114979
Papadakos SP, Georgiadou C, Argyrou A, Michailidou E, Thanos C, Vogli S, Siakavellas SI, Manolakopoulos S, Theocharis S. Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)-Associated Colorectal Cancer (CRC): Is cGAS-STING Pathway Targeting the Key to Chemoprevention? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(11):4979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114979
Chicago/Turabian StylePapadakos, Stavros P., Chara Georgiadou, Alexandra Argyrou, Elisavet Michailidou, Charalampos Thanos, Stamatina Vogli, Spyros I. Siakavellas, Spillios Manolakopoulos, and Stamatios Theocharis. 2025. "Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)-Associated Colorectal Cancer (CRC): Is cGAS-STING Pathway Targeting the Key to Chemoprevention?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 11: 4979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114979
APA StylePapadakos, S. P., Georgiadou, C., Argyrou, A., Michailidou, E., Thanos, C., Vogli, S., Siakavellas, S. I., Manolakopoulos, S., & Theocharis, S. (2025). Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)-Associated Colorectal Cancer (CRC): Is cGAS-STING Pathway Targeting the Key to Chemoprevention? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(11), 4979. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26114979








