An Automated and Precise Approach for the Determination of Azide Residue in Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Using In Situ Matrix Elimination Ion Chromatography with Switching Strategy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Development of In Situ Matrix Elimination IC Integration System
2.1.1. Operation Procedure
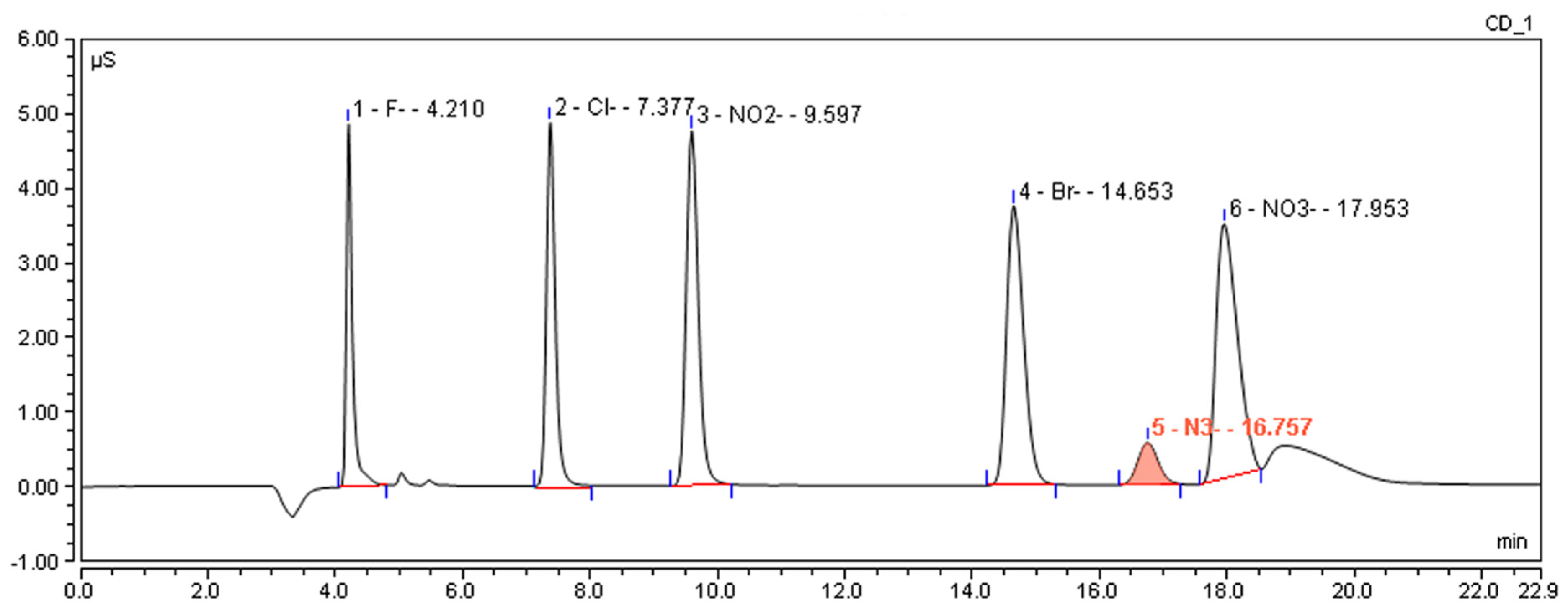
2.1.2. Optimization of Switching Time
2.1.3. Optimization of Ion Chromatography Conditions
2.2. Method Validation
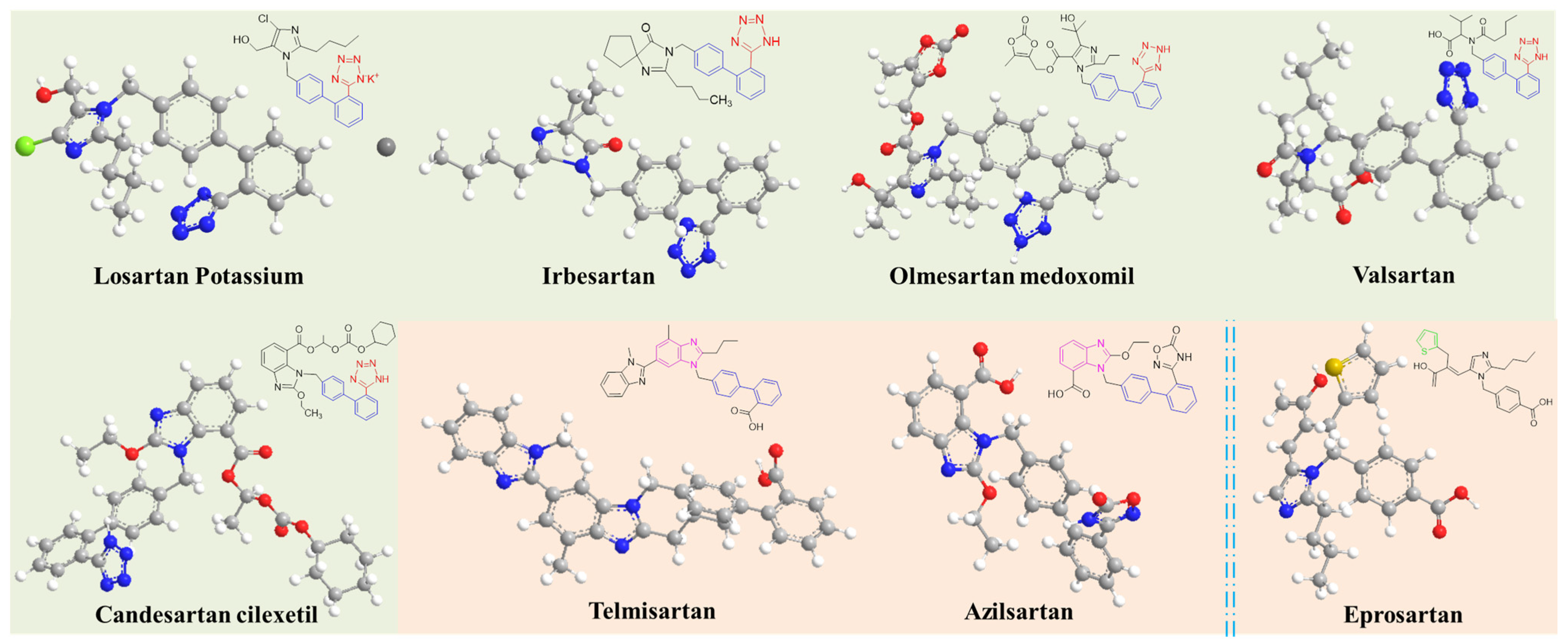
2.3. Analysis of Azide Residues in Sartan-Class Drug Products
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Instrumentation and Equipment
3.3. Preparation of Standard Solutions
3.4. Pretreatment of Real Samples
3.5. Incorporation of In Situ Matrix Elimination IC Integration System
3.6. Chromatographic Conditions
3.7. Validation Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munzel, T.; Hahad, O.; Sorensen, M.; Lelieveld, J.; Duerr, G.D.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.; Daiber, A. Environmental risk factors and cardiovascular diseases: A comprehensive expert review. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 2880–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, H.; Huang, S.; Yin, L.; Wang, F.; Luo, P.; Huang, H. Epigenetic regulation in cardiovascular disease: Mechanisms and advances in clinical trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnier, M.; Damianaki, A. Hypertension as Cardiovascular Risk Factor in Chronic Kidney Disease. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.G.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, L. Hypertension in China: Epidemiology and treatment initiatives. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2023, 20, 531–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutrell, S.; Alhomoud, I.S.; Mehta, A.; Talasaz, A.H.; Van Tassell, B.; Dixon, D.L. ACE-Inhibitors in Hypertension: A Historical Perspective and Current Insights. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2023, 25, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostini, L.D.C.; Silva, N.N.T.; Belo, V.A.; Luizon, M.R.; Lima, A.A.; da Silva, G.N. Pharmacogenetics of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI) and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARB) in cardiovascular diseases. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2024, 981, 176907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D′Silva, E.; Meor Azlan, N.F.; Zhang, J. Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers in the Management of Hypertension in Preventing Cognitive Impairment and Dementia—A Systematic Review. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presta, V.; Figliuzzi, I.; Citoni, B.; Gallo, G.; Battistoni, A.; Tocci, G.; Volpe, M. ARB-Based Combination Therapy for the Clinical Management of Hypertension and Hypertension-Related Comorbidities: A Spotlight on Their Use in COVID-19 Patients. High Blood Press. Cardiovasc. Prev. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Hypertens. 2021, 28, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Orchard, S.G.; Nelson, M.R.; Fravel, M.A.; Ernst, M.E. Angiotensin Receptor Blockers and Cognition: A Scoping Review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2023, 26, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, S.M.; Ihm, S.H.; Yi, J.E.; Jeong, S.H.; Kim, B.S. Comparative efficacy and safety of fimasartan in patients with hypertension: A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2022, 24, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourasiya, S.S.; Kathuria, D.; Kumar, V.; Ranbhan, K.J. Mutagenic Azido Impurities in Drug Substances: A Perspective. Ther. Innov. Regul. Sci. 2024, 58, 1159–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Hu, T. Simultaneous Determination of Nitrite and Azide Ions in Valsartan. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2021, 59, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prihed, H.; Shifrovitch, A.; Shamai Yamin, T.; Madmon, M.; Belay, C.; Blanca, M.; Weissberg, A. Rapid and simple identification of trace amounts of sodium azide in beverages and bodily fluids followed by derivatization and liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. RCM 2023, 37, e9624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serratrice, G.; Béguin, C.; Chautemps, P.; Cogne, C.; Pierre, J.-L. Biomimetic studies related to the azide-inhibited Cu,Zn superoxide dismutases. New J. Chem. 2001, 25, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Luk, H.L.; Eswaran, S.V.; Hadad, C.M.; Platz, M.S. Ultrafast infrared and UV-vis studies of the photochemistry of methoxycarbonylphenyl azides in solution. J. Phys. Chem. A 2012, 116, 5325–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruin, M.A.C.; Dekker, D.; Venekamp, N.; Tibben, M.; Rosing, H.; de Lange, D.W.; Beijnen, J.H.; Huitema, A.D.R. Toxicological analysis of azide and cyanide for azide intoxications using gas chromatography. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 128, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, K.; Usumoto, Y.; Sameshima, N.; Okumura, M.; Tsuji, A.; Ikeda, N. Reliable determination of cyanide, thiocyanate and azide in human whole blood by GC–MS, and its application in NAGINATA–GC–MS screening. Forensic Toxicol. 2017, 36, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, T.; Iwamuro, Y.; Sakamoto, Y.; Minami, E.; Ishimaru, R.; Tsuchihashi, H.; Chinaka, S. Rapid Simultaneous Determination of Cyanide, Azide, and Ethanol in Whole Blood Using Headspace Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Chromatographia 2023, 86, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliano, E.; Campanella, B.; D’Ulivo, A.; Mester, Z. Derivatization chemistries for the determination of inorganic anions and structurally related compounds by gas chromatography—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1025, 12–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachelko, O.; Szpot, P.; Zawadzki, M. A novel simple and precise method for the determination of azide impurity in sartans using headspace gas chromatography with two dissimilar capillary columns and two flame ionization detectors (HS-GC-FID/FID). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 192, 113671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gricar, M.; Andrensek, S. Determination of azide impurity in sartans using reversed-phase HPLC with UV detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 125, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Tang, M.; Xu, D.; Shao, B.; Li, P.L.; Tang, T.S.; Qin, L.; Zhu, B.Z. The critical role of unique azido-substituted chloro-O-semiquinone radical intermediates in the synergistic toxicity between sodium azide and chlorocatecholic carcinogens. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 177, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Xue, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, W.; Shang, M.; Su, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qian, X. Process parameter and kinetic study for the azidation of a zidovudine intermediate with sodium azide in microreactors. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 132207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Páll, B.; Gyenge, Z.; Kormány, R.; Horváth, K. Determination of Genotoxic Azide Impurity in Cilostazol API by Ion Chromatography with Matrix Elimination. Separations 2021, 8, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, P.; Xia, Y. +Facile extraction of azide in sartan drugs using magnetized anion-exchange metal-organic frameworks prior to ion chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1514, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

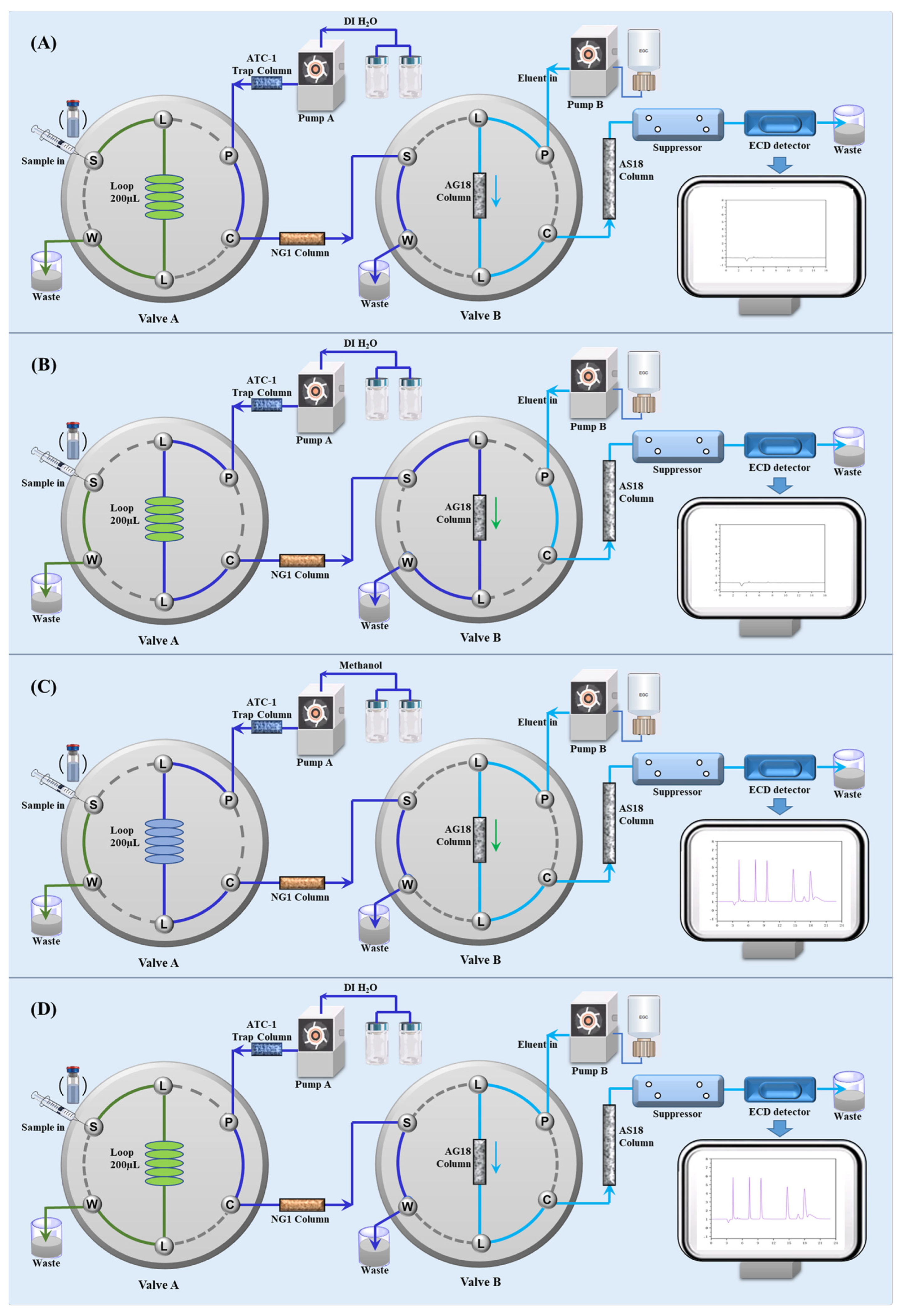


| Steps | A | B | C | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time/min | / | 0.0–0.5 | 0.5–30.0 | 30.0–35.0 |
| Valve A | Load | Inject | Inject | Load |
| Eluent A | Deionized water | Deionized water | Methanol | Deionized water |
| Valve B | Inject | Load | Inject | Inject |
| Eluent B | 12 mM KOH | 12 mM KOH | 12 mM KOH (0.5–25.0 min) 40 mM KOH (25.0–30.0 min) | 12 mM KOH |
| Statement | Sample injection | Matrix elimination and azide enrichment | Analysis and detection | System regeneration |
| Samples | ARBs | Added Levels (ng/mL) | Content of Azide Found a (ng/mL) | Recovery a (%) | Intra-Day RSD b | Inter-Day RSD c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Candesartan cilexetil | 0.0 | 10.0 ± 2.1 | / | 4.3 | 7.1 |
| 10.0 | 20.2 ± 3.0 | 101.8 | 3.5 | 8.3 | ||
| 100.0 | 108.1 ± 4.9 | 98.1 | 4.9 | 6.0 | ||
| B | Candesartan cilexetil | 0.0 | 3.8 ± 1.9 | / | 5.5 | 7.5 |
| 10.0 | 14.4 ± 2.5 | 105.5 | 6.4 | 7.2 | ||
| 100.0 | 100.4 ± 3.4 | 96.6 | 6.7 | 6.8 | ||
| C | Candesartan cilexetil | 0.0 | ND d | / | / | / |
| 10.0 | 10.9 ± 2.7 | 108.7 | 5.3 | 9.7 | ||
| 100.0 | 96.7 ± 5.3 | 96.7 | 6.7 | 7.6 | ||
| D | Valsartan | 0.0 | 7.3 ± 1.5 | / | 4.1 | 5.7 |
| 10.0 | 17.8 ± 2.2 | 105.3 | 3.7 | 5.8 | ||
| 100.0 | 105.8 ± 6.4 | 98.5 | 4.3 | 7.2 | ||
| E | Valsartan | 0.0 | 2.6 ± 1.6 | / | 5.5 | 7.1 |
| 10.0 | 11.9 ± 1.8 | 92.8 | 4.1 | 8.6 | ||
| 100.0 | 103.5 ± 5.2 | 100.9 | 5.9 | 7.9 | ||
| F | Irbesartan | 0.0 | ND | / | / | / |
| 10.0 | 10.7 ± 1.4 | 107.2 | 4.4 | 8.1 | ||
| 100.0 | 97.3 ± 3.5 | 97.3 | 5.8 | 8.3 | ||
| G | Irbesartan | 0.0 | ND | / | / | / |
| 10.0 | 9.5 ± 1.7 | 95.4 | 4.7 | 7.7 | ||
| 100.0 | 102.0 ± 4.2 | 102.3 | 7.2 | 8.6 | ||
| H | Losartan Potassium | 0.0 | ND | / | / | / |
| 10.0 | 9.8 ± 2.4 | 97.8 | 5.3 | 8.2 | ||
| 100.0 | 96.2 ± 4.5 | 96.2 | 6.7 | 7.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lou, C.; Pan, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, K.; Zhu, Y. An Automated and Precise Approach for the Determination of Azide Residue in Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Using In Situ Matrix Elimination Ion Chromatography with Switching Strategy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104895
Lou C, Pan S, Yu X, Zhang K, Zhang K, Zhu Y. An Automated and Precise Approach for the Determination of Azide Residue in Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Using In Situ Matrix Elimination Ion Chromatography with Switching Strategy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104895
Chicago/Turabian StyleLou, Chaoyan, Shaojie Pan, Xiaolin Yu, Kaidi Zhang, Kai Zhang, and Yan Zhu. 2025. "An Automated and Precise Approach for the Determination of Azide Residue in Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Using In Situ Matrix Elimination Ion Chromatography with Switching Strategy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104895
APA StyleLou, C., Pan, S., Yu, X., Zhang, K., Zhang, K., & Zhu, Y. (2025). An Automated and Precise Approach for the Determination of Azide Residue in Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Using In Situ Matrix Elimination Ion Chromatography with Switching Strategy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4895. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104895






