Low-Temperature Spine-Specific PMMA Enhances Bone Regeneration via Localized Thermal Necrosis in an Osteoporotic Rat Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Spine-Specific PMMA Promotes Bone Formation in Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis In Vivo
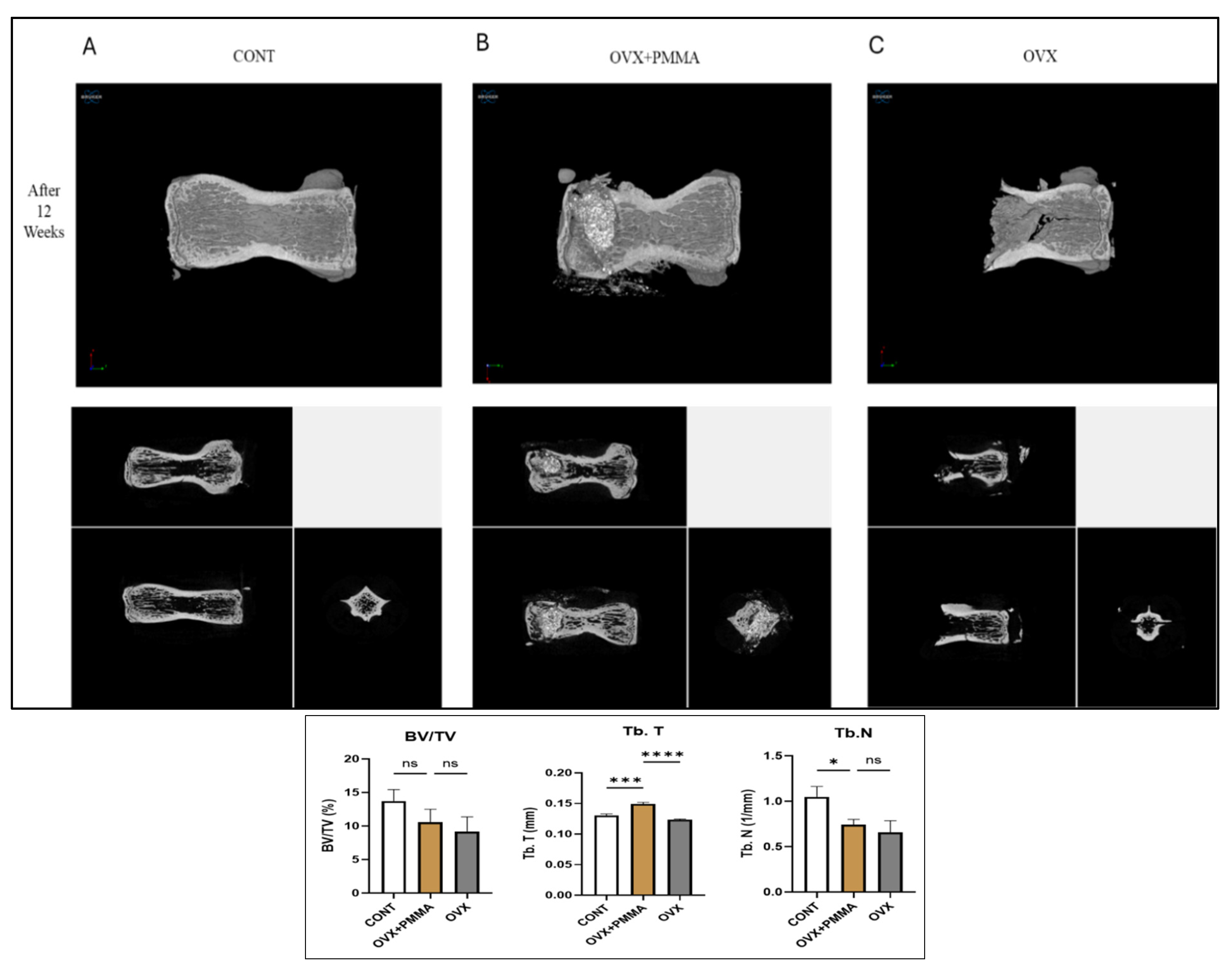
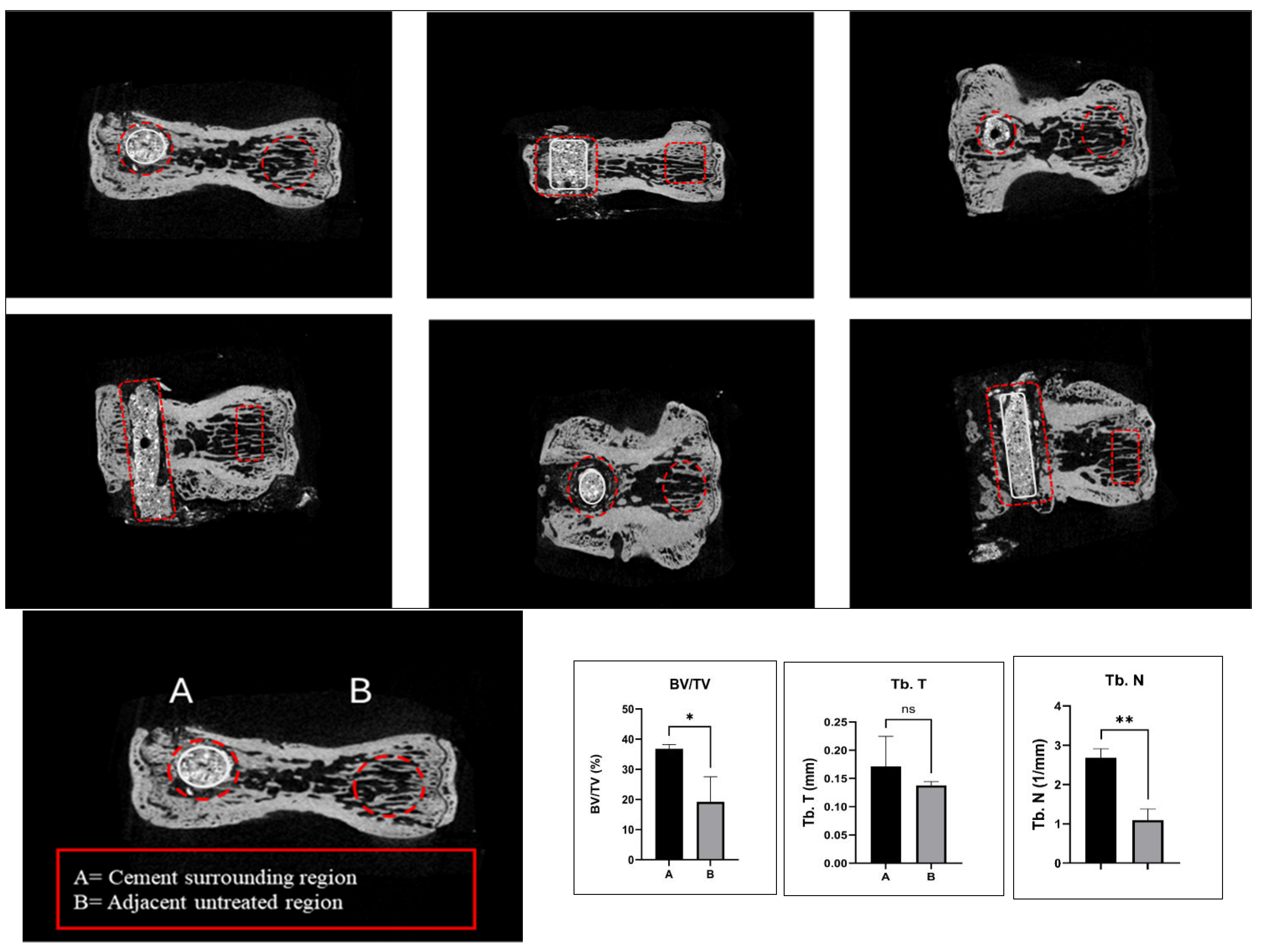
2.2. Spine-Specific PMMA Induces Bone Microarchitecture in OVX Rat
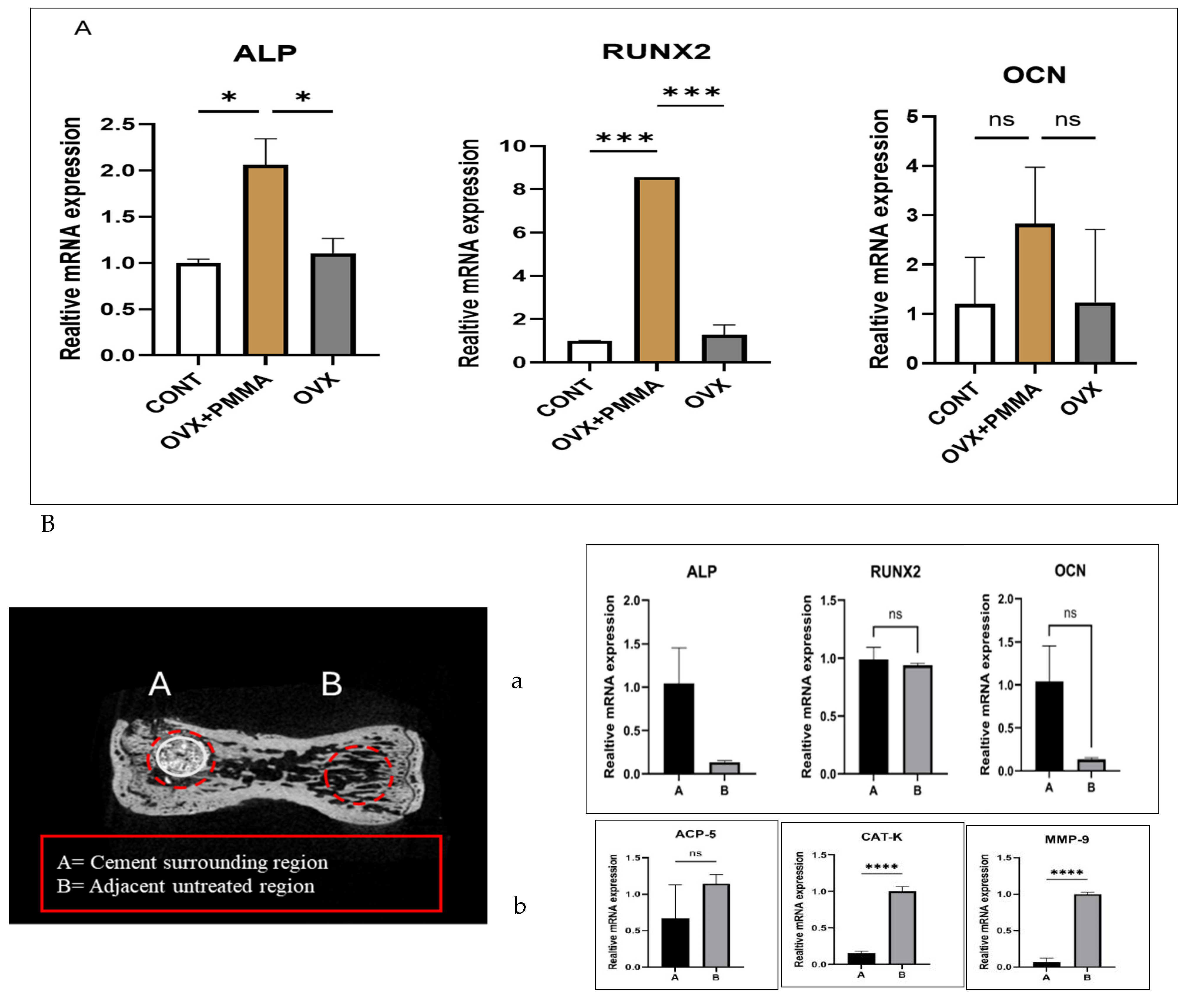
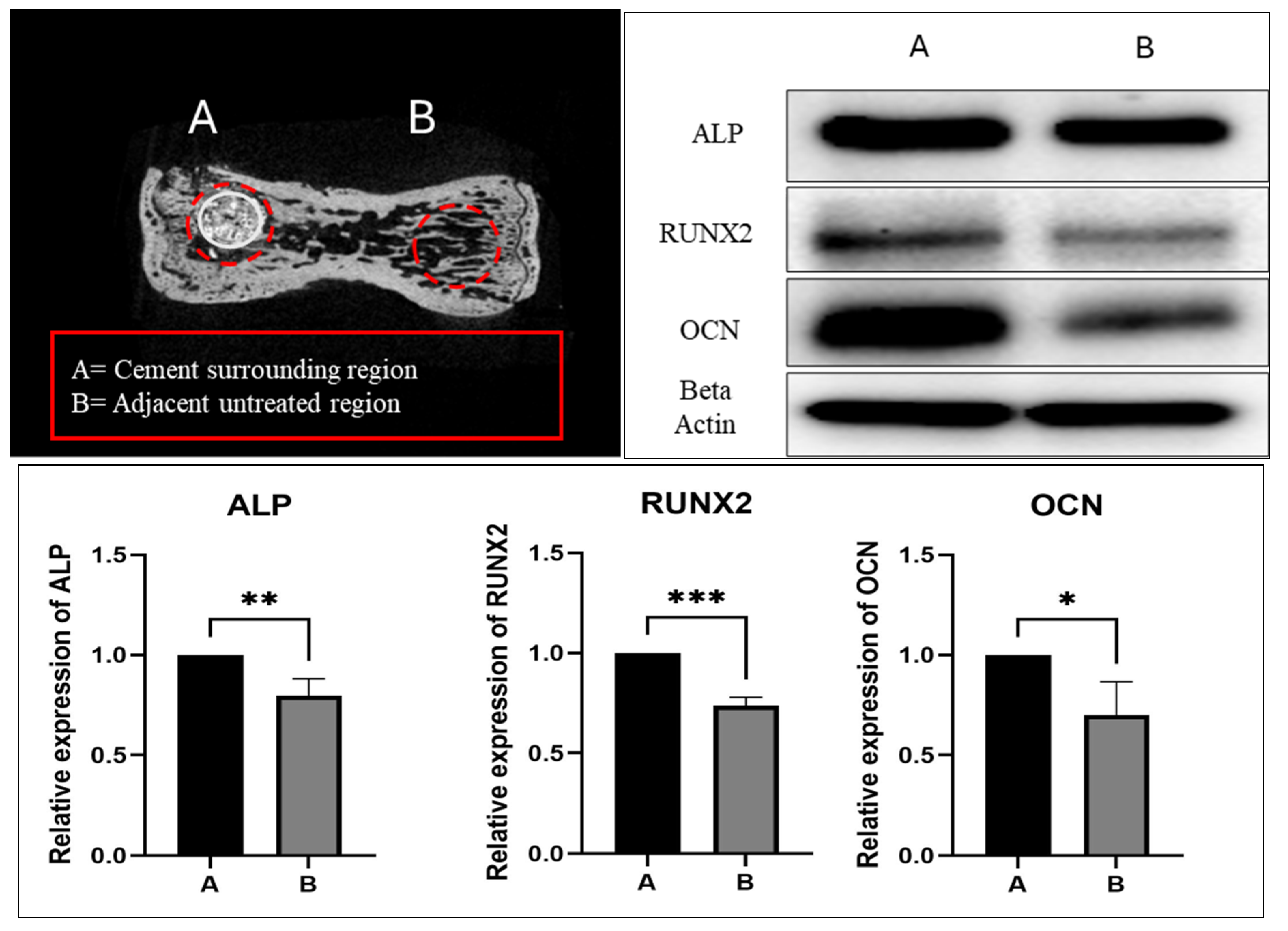
2.3. Spine-Specific PMMA Mitigates OVX-Induced Bone Loss by Enhancing the Expression of Genes Associated with Bone Formation
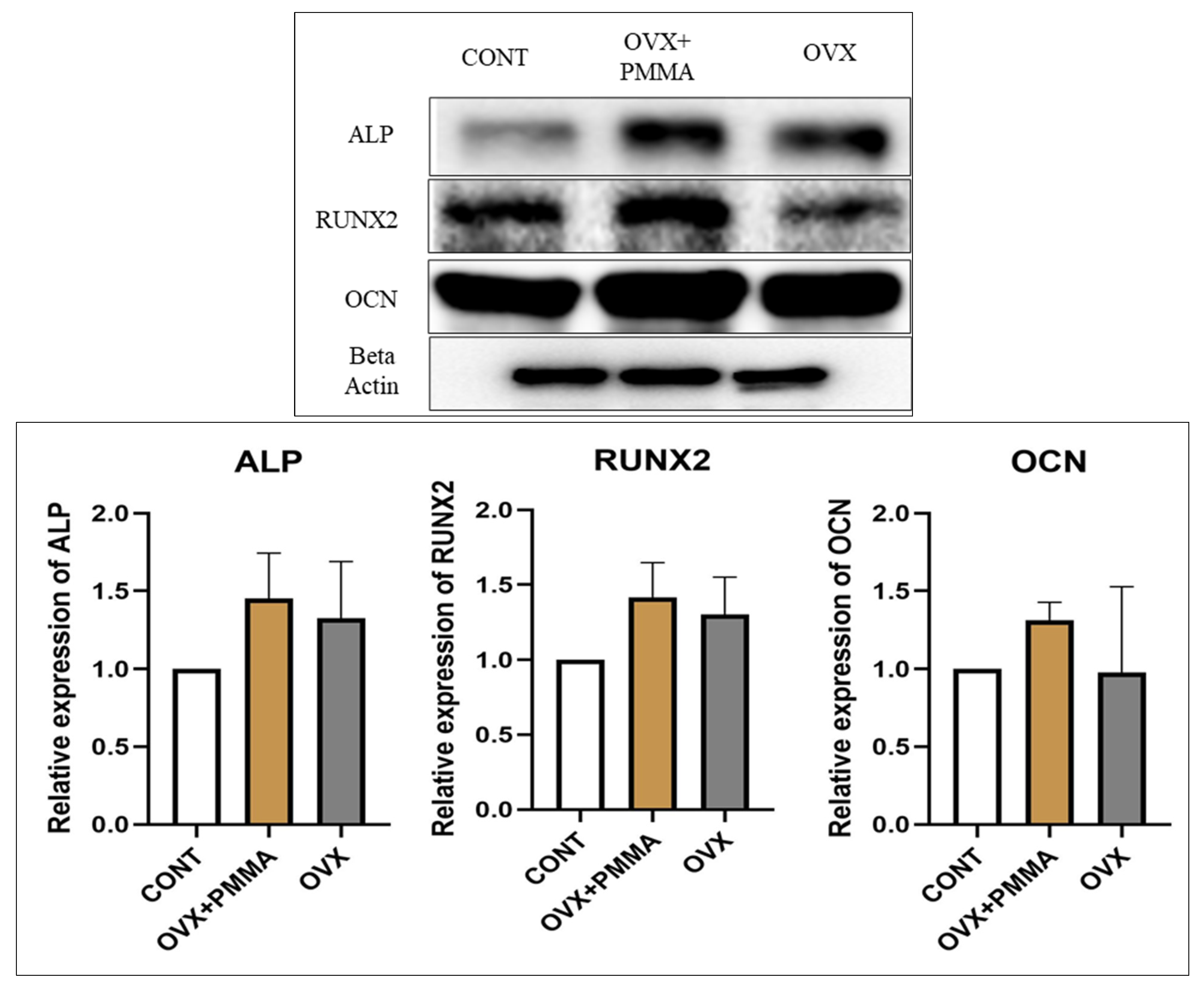
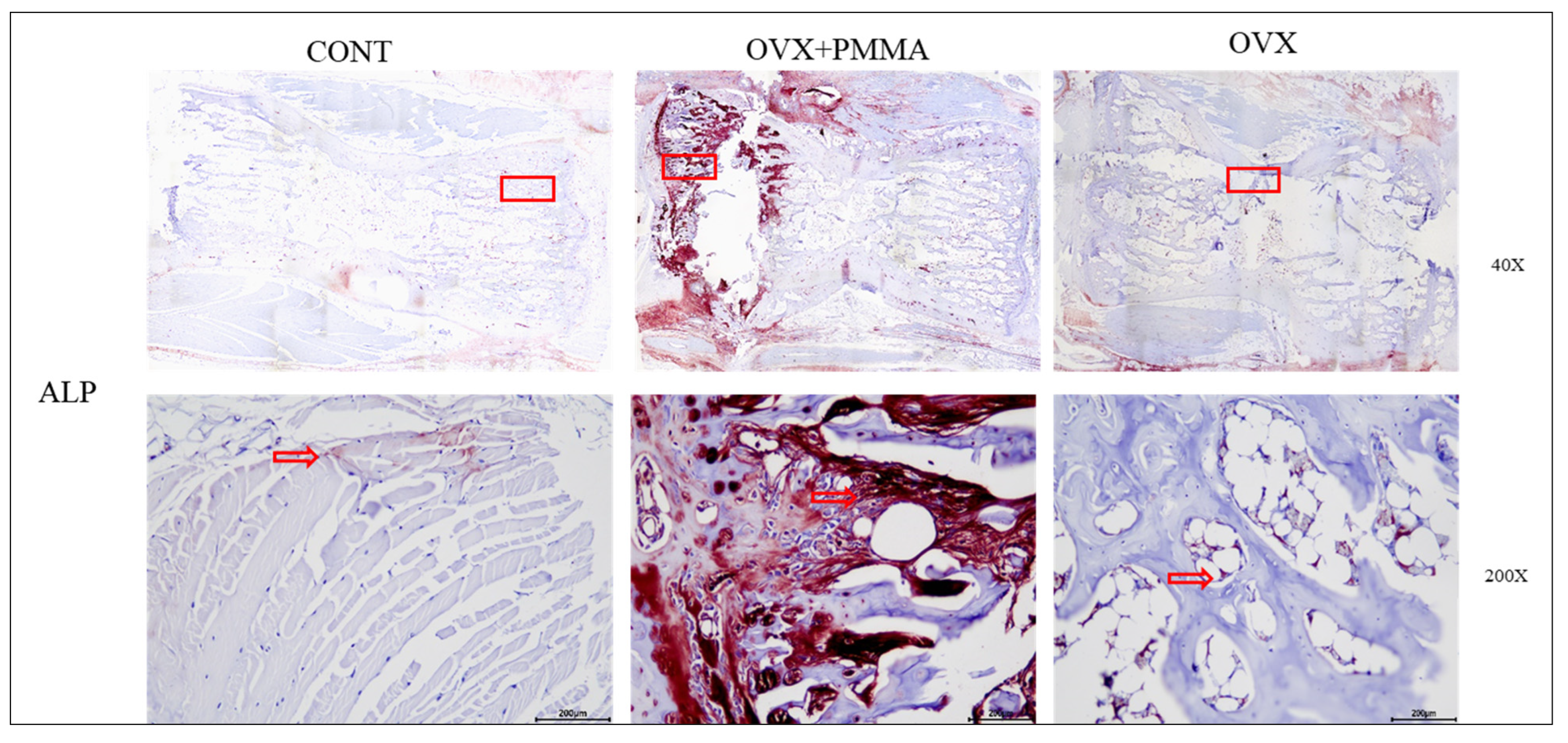
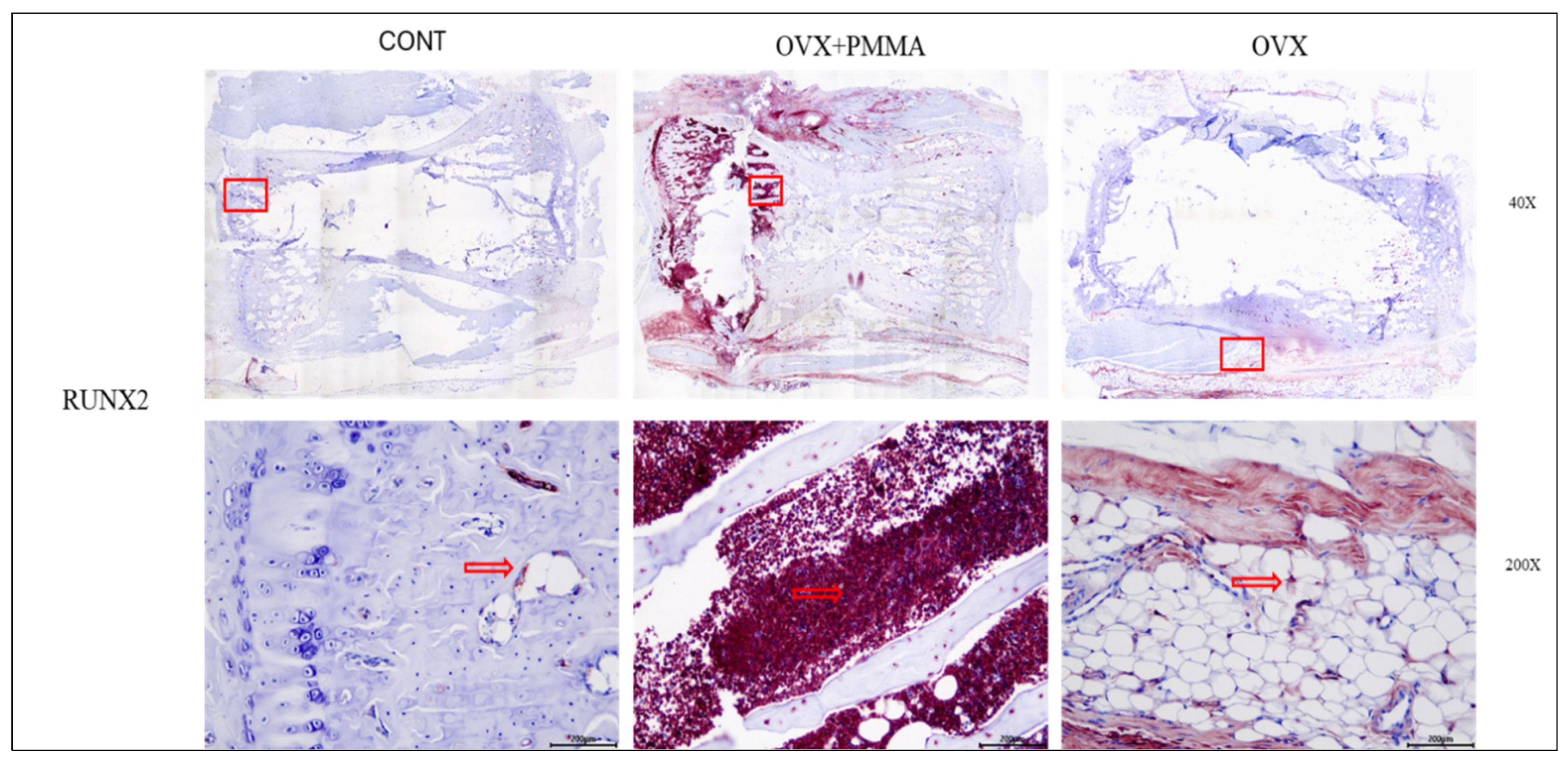
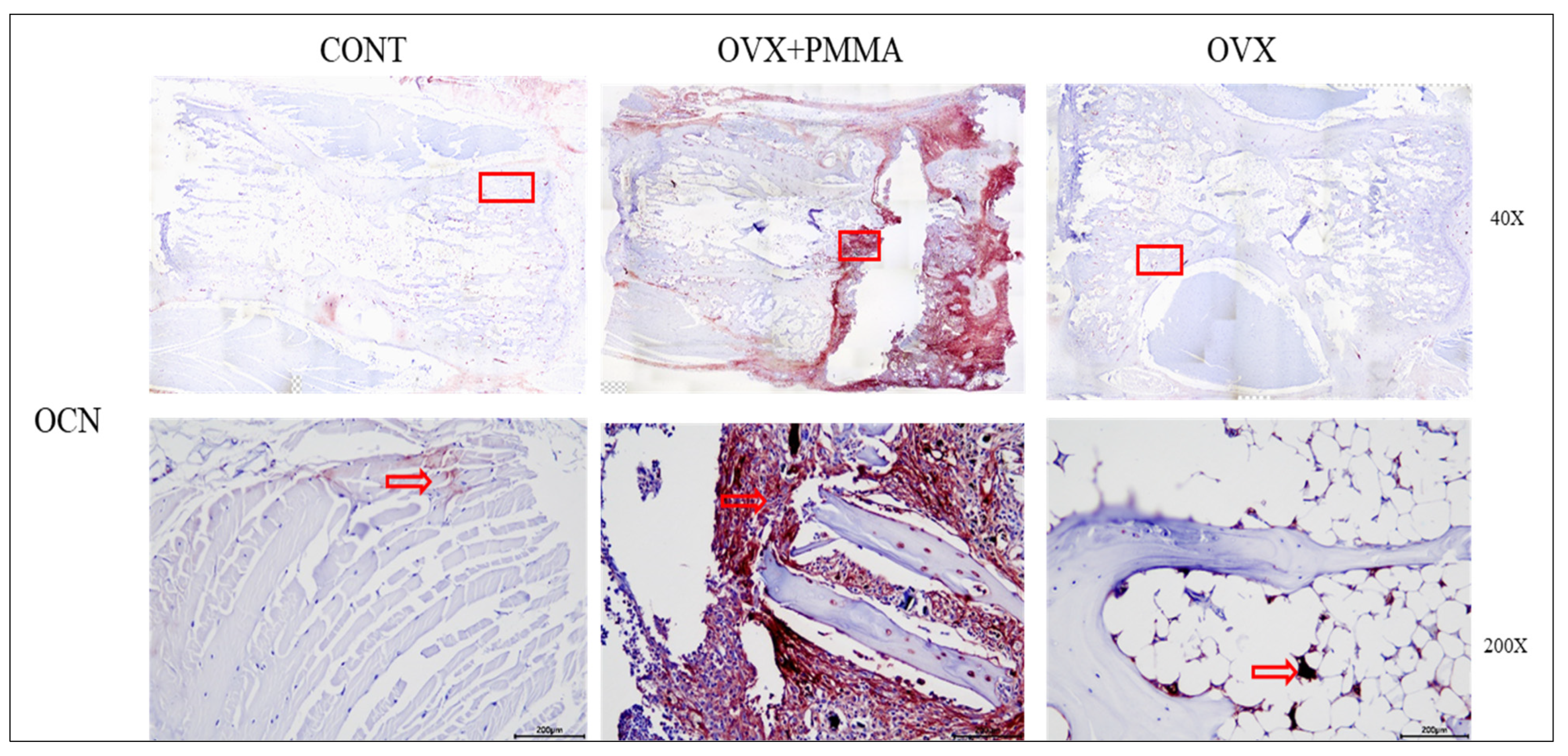
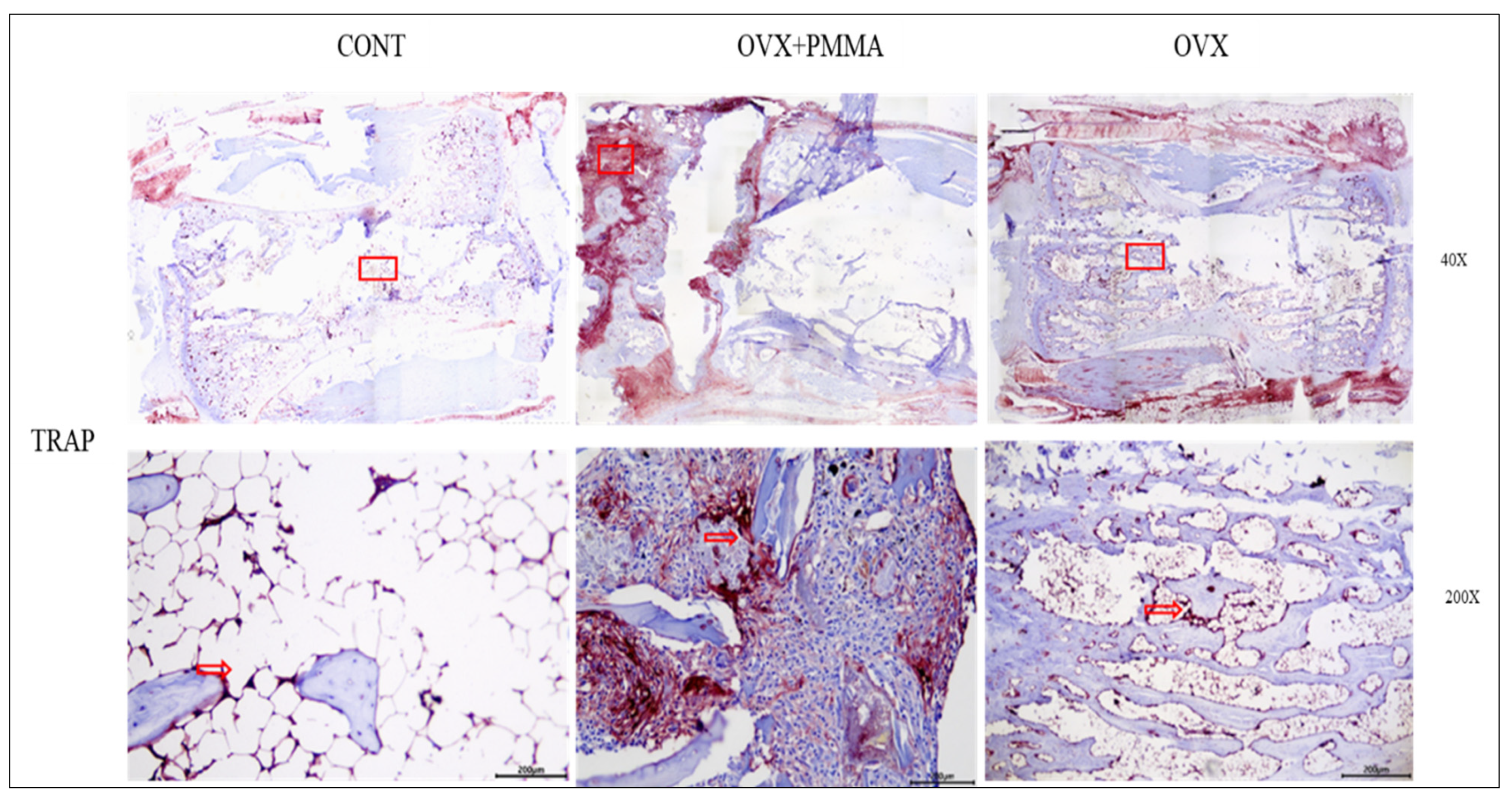
2.4. Spine-Specific PMMA Induces Osteoblast Activity in Rat Caudal Vertebrae
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Preparation of the Rat’s Osteoporosis Model
4.3. Osteoporotic Rat Model
4.4. Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry
4.5. Micro-CT Imaging of the Treated Caudal Vertebral Body
4.6. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)
4.7. Histological Staining and Imaging
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
| Group | Description | n |
|---|---|---|
| Control | No surgery or treatment | 8 |
| OVX | Ovariectomized + Defect, no PMMA | 8 |
| OVX + PMMA | Ovariectomized + Spine-Specific PMMA injection | 8 |
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Catalano, A.; Martino, G.; Morabito, N.; Scarcella, C.; Gaudio, A.; Basile, G.; Lasco, A. Pain in Osteoporosis: From Pathophysiology to Therapeutic Approach. Drugs Aging 2017, 34, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salari, N.; Ghasemi, H.; Mohammadi, L.; Behzadi, M.H.; Rabieenia, E.; Shohaimi, S.; Mohammadi, M. The global prevalence of osteoporosis in the world: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Ren, H.; Shen, G.; Qiu, T.; Liang, D.; Yang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Tang, J.; Jiang, X.; Wei, Q. Animal models for glucocorticoid-induced postmenopausal osteoporosis: An updated review. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdhem, P. Osteoporosis and fragility fractures: Vertebral fractures. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 27, 743–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firanescu, C.E.; de Vries, J.; Lodder, P.; Venmans, A.; Schoemaker, M.C.; Smeets, A.J.; Donga, E.; Juttmann, J.R.; Klazen, C.A.H.; Elgersma, O.E.H.; et al. Vertebroplasty versus sham procedure for painful acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (VERTOS IV): Randomised sham controlled clinical trial. BMJ 2018, 361, k1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, S.; Cai, K.; Wang, S.; Qiu, Z.; Huang, J.; Jiang, G.; Wang, X.; Fang, X. Bioactive poly (methyl methacrylate) bone cement for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Theranostics 2020, 10, 6544–6560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukeoka, T.; Suzuki, M.; Ohtsuki, C.; Sugino, A.; Tsuneizumi, Y.; Miyagi, J.; Kuramoto, K.; Moriya, H. Mechanical and histological evaluation of a PMMA-based bone cement modified with gamma-methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane and calcium acetate. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3897–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanvir, M.A.H.; Khaleque, M.A.; Kim, G.H.; Yoo, W.Y.; Kim, Y.Y. The role of bioceramics for bone regeneration: History, mechanisms, and future perspectives. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, W.; Zeng, Y. Open surgical treatments of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Orthop. Surg. 2023, 15, 2743–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yan, L. A preliminary review of modified polymethyl methacrylate and calcium-based bone cement for improving properties in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 912713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robo, C.; Hulsart-Billström, G.; Nilsson, M.; Persson, C. In vivo response to a low-modulus PMMA bone cement in an ovine model. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, K.; Thiele, J.; Geisler, D.; Boening, K.; Wieckiewicz, M. Effect of Chemical Disinfection on Chitosan Coated PMMA and PETG Surfaces-An In Vitro Study. Polymers 2018, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, M.; Jiang, G.; Zhao, J. Small intestinal submucosa/polymethyl methacrylate composite bone cement for vertebral repair. Mater. Des. 2018, 154, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, R.; Szabelski, J.; Krakowski, P.; Jonak, J.; Falkowicz, K.; Jojczuk, M.; Nogalski, A.; Przekora, A. Effect of various admixtures on selected mechanical properties of medium viscosity bone cements: Part 1—α/β tricalcium phosphate (TCP). Compos. Struct. 2024, 343, 118306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, R.; Szabelski, J.; Krakowski, P.; Jonak, J.; Falkowicz, K.; Jojczuk, M.; Nogalski, A.; Przekora, A. Effect of various admixtures on selected mechanical properties of medium viscosity bone cements: Part 2—Hydroxyapatite. Compos. Struct. 2024, 343, 118308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpiński, R.; Szabelski, J.; Krakowski, P.; Jonak, J.; Falkowicz, K.; Jojczuk, M.; Nogalski, A.; Przekora, A. Effect of various admixtures on selected mechanical properties of medium viscosity bone cements: Part 3—Glassy carbon. Compos. Struct. 2024, 343, 118307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños, M.A.C.; Buttigieg, J.; Triana, J.C.B. Development and characterization of a novel porous small intestine submucosa-hydroxyapatite scaffold for bone regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 72, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Koh, B.T.; Ramruttun, A.; Wang, W. Compression and Flexural Strength of Bone Cement Mixed with Blood. J. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 24, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szoradi, G.T.; Feier, A.M.; Zuh, S.G.; Russu, O.M.; Pop, T.S. Polymethyl Methacrylate Bone Cement Polymerization Induced Thermal Necrosis at the Cement–Bone Interface: A Narrative Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleque, M.A.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, B.J.; Kang, J.K.; Quan, M.; Kim, Y.Y. Role of necroptosis in intervertebral disc degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.A.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, K.N.; Shin, H.C.; Yoon, D.H. Spontaneous Bursting Collapse of a PMMA Augmented Vertebra: A Rare Complication of Vertebroplasty: A Case Report. J. Korean Neurotraumatol. Soc. 2006, 2, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Guan, Q.; Chen, M.; Cao, Y.; Zou, J.; Zhang, L. Effects of Thermal Environment on Bone Microenvironment: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.; Xue, D.; Zhang, W.; Lin, F.; Pan, Z. Extracellular heat shock protein 70 promotes osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells through activation of the ERK signaling pathway. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 4088–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.; Urakawa, H.; Kozawa, E.; Hamada, S.; Ota, T.; Kato, R.; Honda, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Ishiguro, N.; Nishida, Y. In vivo heat-stimulus-triggered osteogenesis. Int. J. Hyperth. 2015, 31, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fuchs, S.; Böse, T.; Schmidt, H.; Hofmann, A.; Tonak, M.; Unger, R.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Mild heat stress enhances angiogenesis in a co-culture system consisting of primary human osteoblasts and outgrowth endothelial cells. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2014, 20, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Ju, S.; Zhang, Z. Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures caused by Cushing’s syndrome in young women: Case report and literature review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2023, 24, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgawaad, A.S.; Ezzati, A.; Govindasamy, R.; Krajnovic, B.; Elnady, B.; Said, G.Z. Kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fractures with posterior wall injury. Spine J. 2018, 18, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.A.; Miller, M.A.; Cleary, R.J.; Janssen, D.; Verdonschot, N. Experimental micromechanics of the cement-bone interface. J. Orthop. Res. 2008, 26, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPisa, J.A.; Sih, G.S.; Berman, A.T. The temperature problem at the bone-acrylic cement interface of the total hip replacement. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1976, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodop, O.; Kiral, A.; Arpacioglu, O.; Akmaz, I.; Solakoglu, C.; Pehlivan, O.; Kaplan, H. Effects of stem design and pre-cooling prostheses on the heat generated by bone cement in an in vitro model. J. Int. Med. Res. 2002, 30, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrat, M.A.; Schlierf, T.J.; Efaw, M.L.; Shuler, F.D.; Godby, J.; Stanko, L.M.; Tamski, H.L. Unilateral heat accelerates bone elongation and lengthens extremities of growing mice. J. Orthop. Res. 2015, 33, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, T.; Nishida, Y.; Ikuta, K.; Kato, R.; Kozawa, E.; Hamada, S.; Sakai, T.; Ishiguro, N. Heat-stimuli-enhanced osteogenesis using clinically available biomaterials. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Shi, Z.D.; Ji, X.; Morales, J.; Zhang, J.; Kaur, N.; Wang, S. Enhanced osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells by periodic heat shock in self-assembling peptide hydrogel. Tissue Eng. Part A 2013, 19, 716–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olkku, A.; Leskinen, J.J.; Lammi, M.J.; Hynynen, K.; Mahonen, A. Ultrasound-induced activation of Wnt signaling in human MG-63 osteoblastic cells. Bone 2010, 47, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, D.K.; Lee, S.; Choi, D.J.; Park, S.Y.; Woo, D.G.; Kim, C.H.; Kim, H.S. Mechanical properties of blood-mixed PMMA in percutaneous vertebroplasty. J. Korean Soc. Spine Surg. 2009, 16, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Powder Components | 20 g Container of Sterile Powder | Liquid Components | 9.2 g Phial of Sterile Liquid |
|---|---|---|---|
| Methyl Methylcrylate Polymer | 66.00% w/w | Methylmethacrylate | 99.10% w/w |
| Barium sulfate | 29.00% w/w | N-N-dimethyl-p-toluidine | 0.90% w/w |
| Benzoyl peroxide | 2.00% w/w | Hydroquinone | 75 ppm |
| Sample | Powder (g) | Liquid (mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poly(methyl methacrylate-co-methyl acrylate) | BaSO4/ZrO2 | Benzoyl peroxide | Methyl methacrylate | N,N-dimethyl-p-toluidine | Hydroquinone | |
| PMMA cement | 13.5 | 6 | 0.5 | 9.91 | 0.09 | 75 ppm |
| Genes | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | 5′GTATCGGACGCCTGGTTAC3′ | 5′CTTGCCGTGGGTAGAGTCAT3′ |
| ACP-5 | 5′TCCCCAATGCCCCATTC3′ | 5′CGGTTCTGGCGATCTCTTTG3′ |
| MMP-9 | 5′AAAGACCTGAAAACCTCCAACCT3′ | 5′GCCCGGGTGTAACCATAGC3′ |
| CAT-K | 5′GGCTGTGGAGGCGGCTAT3′ | 5′AGAGTCAATGCCTCCGTTCTG3′ |
| ALP | 5′ACCTAGACACAAGCACTCC3′ | 5′GCCTCCTTCCACTAGCAAGA3′ |
| RUNX2 | 5′TCCCAGTATGAGAGTAGGTGTCC3′ | 5′GGCTCAGATAAGGGTAAGAC3′ |
| OCN | 5′CAGCCTTCATGTCCAAGCAG3′ | 5′TAGAGACCACCCAGCACAAG3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanvir, M.A.H.; Khaleque, M.A.; Kim, G.-H.; Park, S.-E.; Lee, H.-H.; Kim, Y.-Y. Low-Temperature Spine-Specific PMMA Enhances Bone Regeneration via Localized Thermal Necrosis in an Osteoporotic Rat Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104786
Tanvir MAH, Khaleque MA, Kim G-H, Park S-E, Lee H-H, Kim Y-Y. Low-Temperature Spine-Specific PMMA Enhances Bone Regeneration via Localized Thermal Necrosis in an Osteoporotic Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104786
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanvir, Md Amit Hasan, Md Abdul Khaleque, Ga-Hyun Kim, Sang-Eun Park, Hwan-Hee Lee, and Young-Yul Kim. 2025. "Low-Temperature Spine-Specific PMMA Enhances Bone Regeneration via Localized Thermal Necrosis in an Osteoporotic Rat Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104786
APA StyleTanvir, M. A. H., Khaleque, M. A., Kim, G.-H., Park, S.-E., Lee, H.-H., & Kim, Y.-Y. (2025). Low-Temperature Spine-Specific PMMA Enhances Bone Regeneration via Localized Thermal Necrosis in an Osteoporotic Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104786









