Proteomics-Based Exploration of the Hepatoprotective Mechanism of α-Lipoic Acid in Rats with Iron Overload-Induced Liver Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
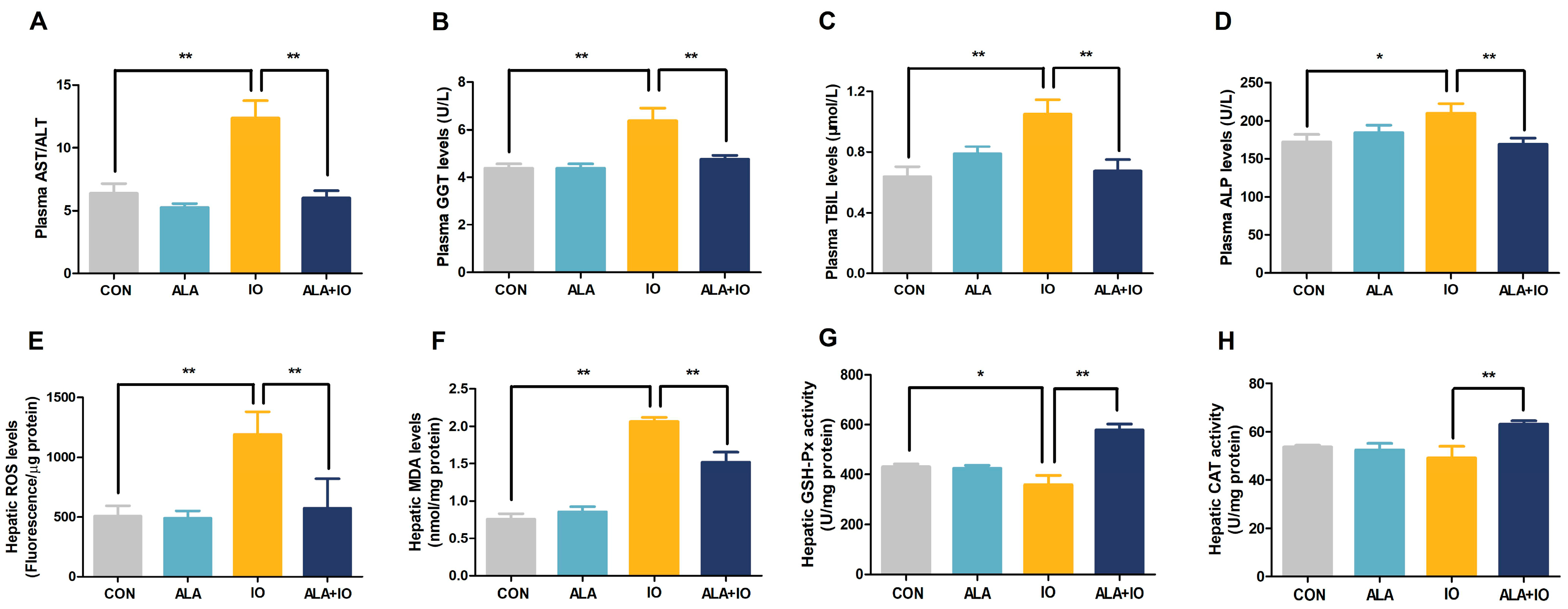
2.1. α-Lipoic Acid Alleviates Hepatic Iron Toxicity in Iron-Overloaded Rats
2.2. ALA Reduces Oxidative Stress and Enhances Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Iron-Overloaded Rats
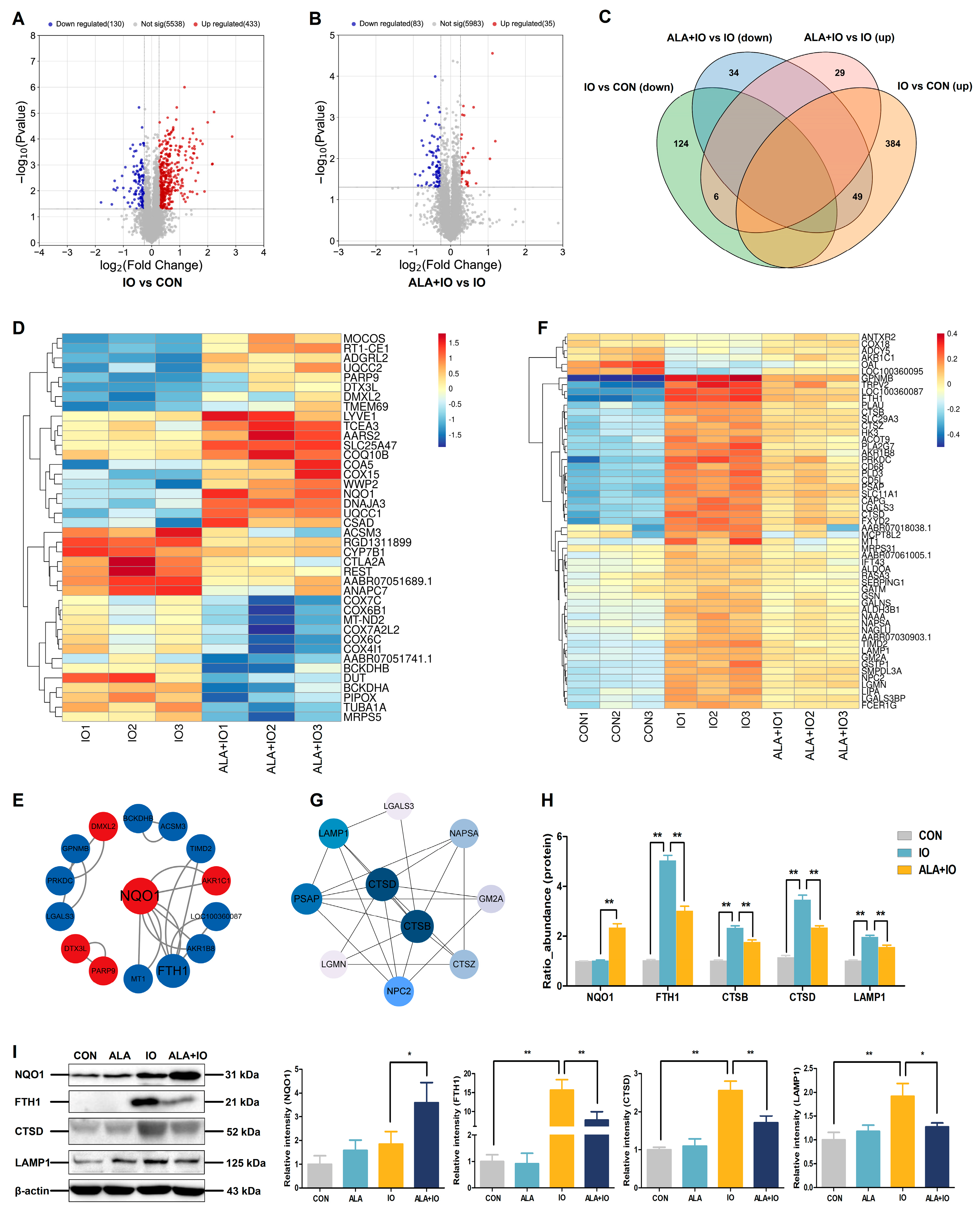
2.3. Proteomics Reveals NQO1 and Autophagy-Related Protein Modulation by ALA in Hepatic Iron Overload
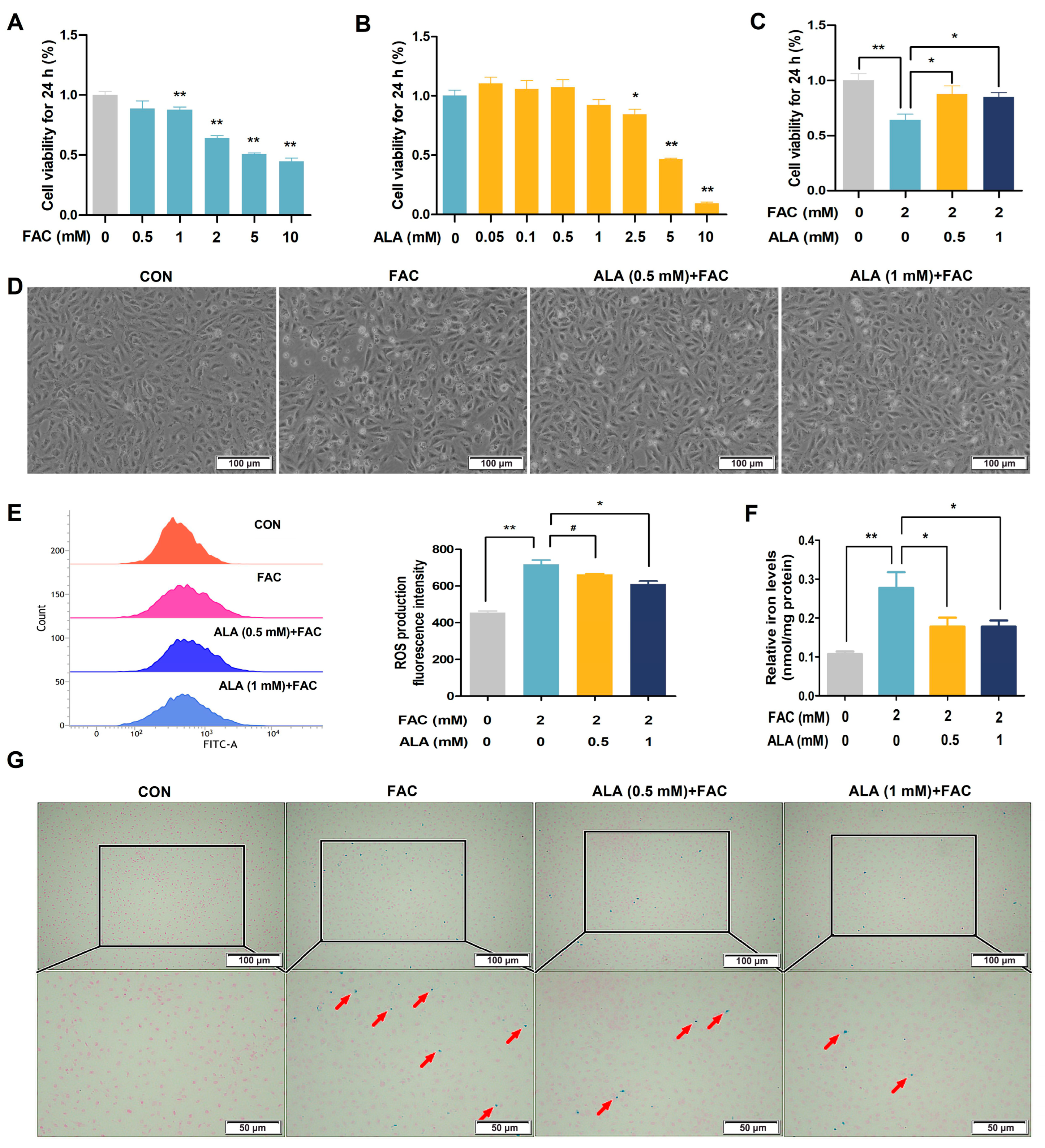
2.4. ALA Enhances Cell Viability and Reduces ROS in Iron-Overloaded BRL-3A Cells
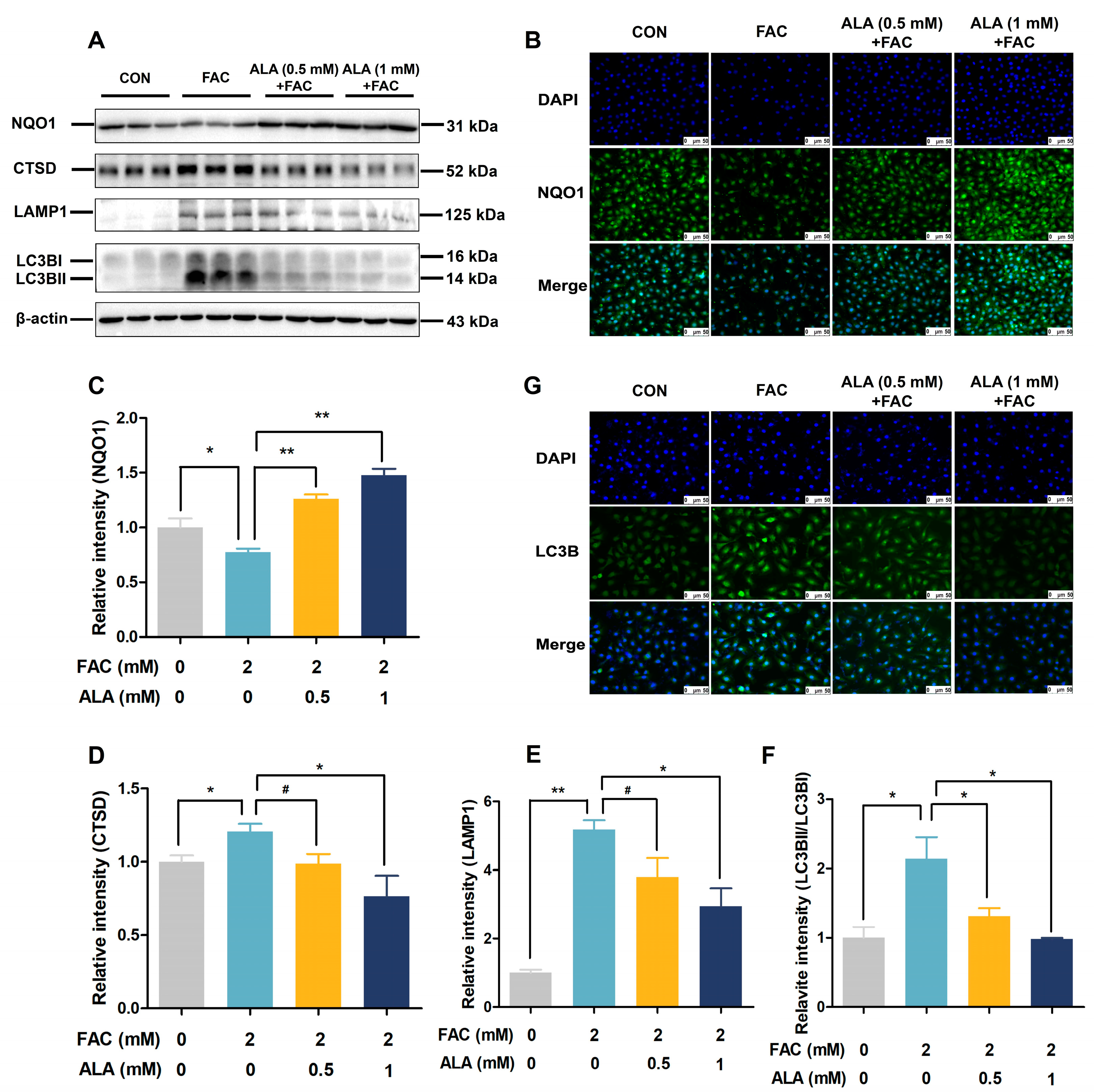
2.5. ALA Improves NQO1 and Autophagy Protein Expression in Iron-Overloaded BRL-3A Cells
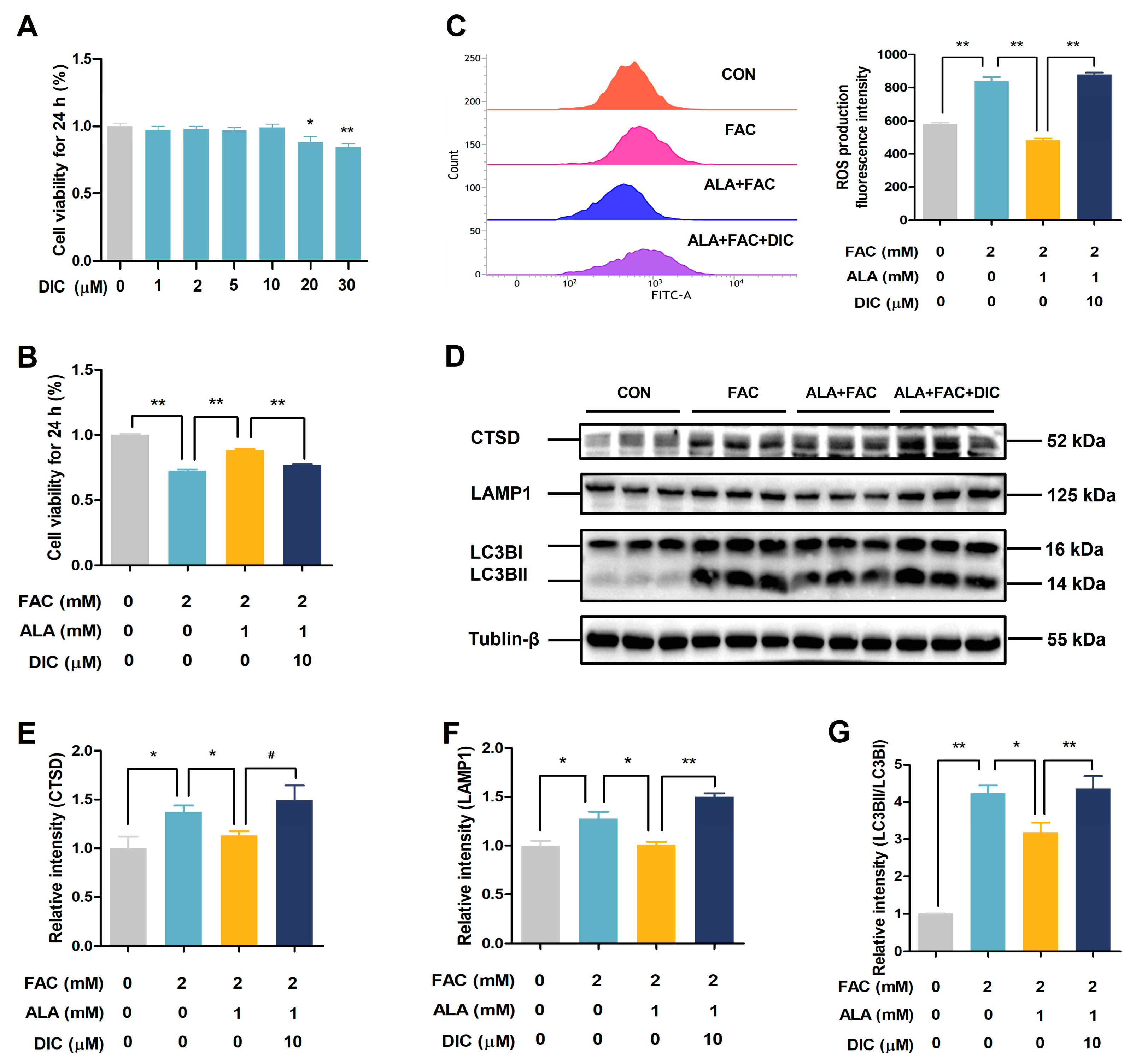
2.6. DIC Reverses the Protective Effects of ALA in Iron-Overloaded BRL-3A Cells
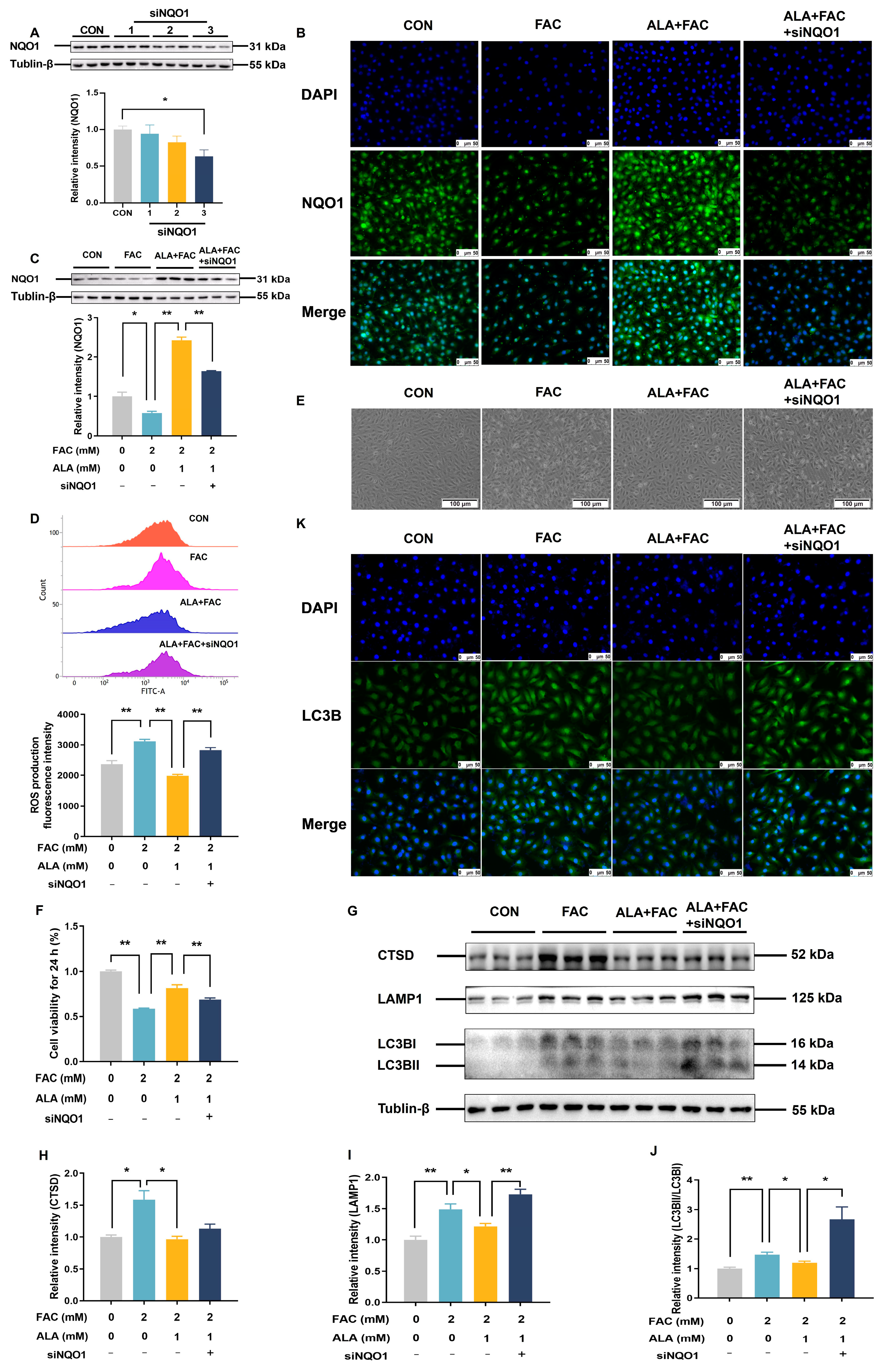
2.7. Silencing NQO1 Reverses the Protective Effects of α-Lipoic Acid in Iron-Overloaded BRL-3A Cells
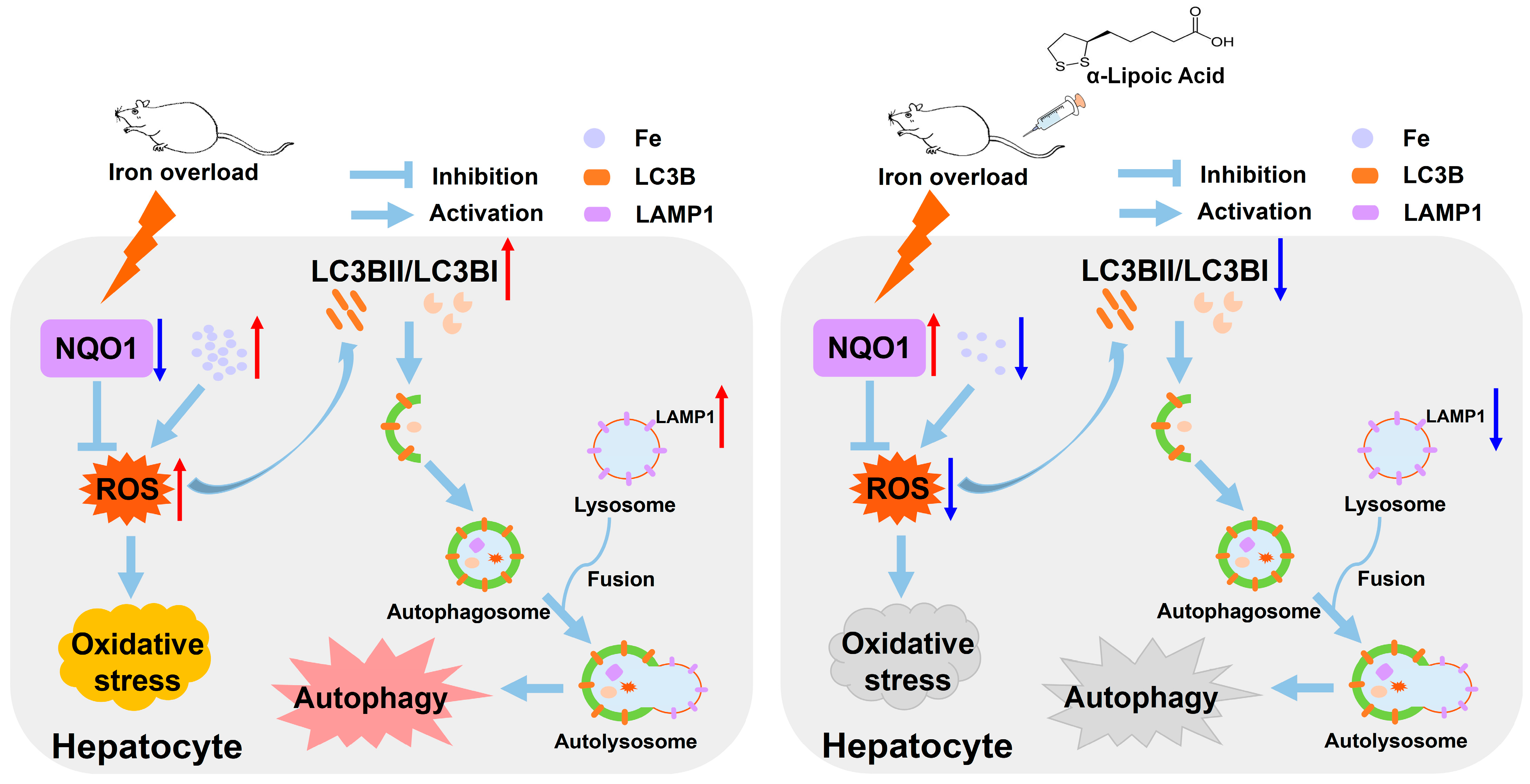
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Experimental Design
4.2. Measurement of Plasma Biochemical Parameters
4.3. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
4.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy
4.5. Perl’s Prussian Blue Staining
4.6. Determination of Liver Iron Content
4.7. Measurement of Hepatic ROS Levels
4.8. Measurement of Hepatic Malondialdehyde (MDA) and the Antioxidant Enzyme Activities
4.9. TMT-Based Quantitative Proteomics
4.9.1. Protein Extraction
4.9.2. TMT-Based Quantitative Proteomics Analysis
4.9.3. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.10. Western Blotting
4.11. Cell Culture and Cell Viability
4.12. Measurement of ROS in BRL-3A Cells
4.13. Measurement of Total Iron Levels in BRL-3A Cells
4.14. Immunofluorescence
4.15. Cell Transfection
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALA | α-lipoic acid |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| CTSB | Cathepsin B |
| CTSD | Cathepsin D |
| DIC | Dicoumarol |
| DMT1 | Divalent metal transporter 1 |
| FAC | Ferric ammonium citrate |
| FTH1 | Ferritin heavy chain 1 |
| FTL | Ferritin light chain |
| FPN | Ferroportin |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyltransferase |
| GSH-Px | Glutathione peroxidase |
| LAMP1 | Lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 |
| LC3B | Light chain 3B |
| LIP | Labile iron pool |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| NOQ1 | NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1 |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TBIL | Total bilirubin |
| STEAP3 | Prostate transmembrane epithelial antigen 3 |
| TF | Transferrin |
| TFR | Transferrin receptor protein |
References
- Mehta, K.J.; Farnaud, S.J.; Sharp, P.A. Iron and liver fibrosis: Mechanistic and clinical aspects. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 521–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Yuan, J.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Huang, K.; Zhan, J.; Dong, G.P.; Fu, J. Iron overload is related to elevated blood glucose levels in obese children and aggravates high glucose-induced endothelial cell dysfunction in vitro. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2020, 8, e001426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontoghiorghes, G.J. The importance and essentiality of natural and synthetic chelators in medicine: Increased prospects for the effective treatment of iron overload and iron deficiency. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlebois, E.; Pantopoulos, K. Nutritional aspects of iron in health and disease. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Jin, Z.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Wang, G.; Zhang, D.; Rocha, K.C.E.; Liu, X.; Zhao, H.; Kisseleva, T.; Brenner, D.A.; et al. Aberrant iron distribution via hepatocyte-stellate cell axis drives liver lipogenesis and fibrosis. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1201–1213.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Guo, Z.; Li, G.; He, L.; Liu, H.; Cai, S.; Huo, T. Diammonium glycyrrhizinate alleviates iron overload-induced liver injury in mice via regulating the gut-liver axis. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Ferrao, K.; Mehta, K.J. Liver iron loading in alcohol-associated liver disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 193, 1427–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, F.; Tang, Y.; Shen, H.; Wu, L.; Liu, Q.; Nie, S.; Li, M.; Ling, C. HIF1alpha/miR-146alpha/TRAF6/NF-kappaB axis modulates hepatic iron overload-induced inflammation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2024, 125, 109499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinyopornpanish, K.; Tantiworawit, A.; Leerapun, A.; Soontornpun, A.; Thongsawat, S. Secondary iron overload and the liver: A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2023, 11, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, L.F.; Santos, F.P.S.; Perini, G.F.; Nascimento, C.M.B.; Silva, L.P.; Wroclawski, C.K.; Esposito, B.P.; Ribeiro, M.S.S.; Velloso, E.D.R.P.; Nomura, C.H.; et al. Hepatic and cardiac and iron overload detected by T2* magnetic resonance (MRI) in patients with myelodisplastic syndrome: A cross-sectional study. Leuk. Res. 2019, 76, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyna-Bolaños, I.; Solís-García, E.P.; Vargas-Vargas, M.A.; Peña-Montes, D.J.; Saavedra-Molina, A.; Cortés-Rojo, C.; Calderón-Cortés, E. Polydatin prevents electron transport chain dysfunction and ROS overproduction paralleled by an improvement in lipid peroxidation and cardiolipin levels in iron-overloaded rat liver mitochondria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, C.; Ma, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Liu, C.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Li, W. Oleanolic acid inhibits mercury chloride induced-liver ferroptosis by regulating ROS/iron overload. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 258, 114973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Fang, Y.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, J.; Kuang, J. Therapeutic potential and mechanisms of Rifaximin in ameliorating iron overload-induced ferroptosis and liver fibrosis in vivo and in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2024, 484, 116845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teschke, R. Hemochromatosis: Ferroptosis, ROS, Gut microbiome, and clinical challenges with alcohol as confounding variable. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Lai, J.Y. Synthesis, bioactive properties, and biomedical applications of intrinsically therapeutic nanoparticles for disease treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Huang, L.; Sun, K.; Li, J.; Han, S.; Gao, X.; Wang, Q.Q.; Yang, S.; Sun, W.; Gao, H. Oleuropein alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by suppressing oxidative stress and excessive autophagy via TLR4/MAPK signaling pathway. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, A.D.; Dudek, A.M.; Ferreira, G.B.; Verfaillie, T.; Vandenabeele, P.; Krysko, D.V.; Mathieu, C.; Agostinis, P. ROS-induced autophagy in cancer cells assists in evasion from determinants of immunogenic cell death. Autophagy 2013, 9, 1292–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, L.; Yang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zheng, M. 5-FU promotes HBV replication through oxidative stress-induced autophagy dysfunction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2024, 213, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Hua, C.; Ci, X. Melatonin alleviates particulate matter-induced liver fibrosis by inhibiting ROS-mediated mitophagy and inflammation via Nrf2 activation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.Y.; He, S.; Ling, X.L.; Wang, Y.Q.; Huang, C.; Long, J.R.; Wang, J.Q.; Qin, Y.; Wei, H.; Yu, C.Y. Review of lipoic acid: From a clinical therapeutic agent to various emerging biomaterials. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 627, 122201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camiolo, G.; Tibullo, D.; Giallongo, C.; Romano, A.; Parrinello, N.L.; Musumeci, G.; Di Rosa, M.; Vicario, N.; Brundo, M.V.; Amenta, F.; et al. α-Lipoic acid reduces iron-induced toxicity and oxidative stress in a model of iron overload. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, S.; Zheng, Q.; Zhai, S.; Cai, T.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Jiao, L.; Zhang, C. Alpha-lipoic acid mediates clearance of iron accumulation by regulating iron metabolism in a parkinson’s disease model induced by 6-OHDA. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carota, G.; Distefano, A.; Spampinato, M.; Giallongo, C.; Broggi, G.; Longhitano, L.; Palumbo, G.A.; Parenti, R.; Caltabiano, R.; Giallongo, S.; et al. Neuroprotective role of α-lipoic acid in iron-overload-mediated toxicity and inflammation in in vitro and in vivo models. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavdar, Z.; Oktan, M.A.; Ural, C.; Calisir, M.; Kocak, A.; Heybeli, C.; Yildiz, S.; Arici, A.; Ellidokuz, H.; Celik, A.; et al. Renoprotective effects of alpha lipoic acid on iron overload-induced kidney injury in rats by suppressing NADPH oxidase 4 and p38 MAPK signaling. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2020, 193, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, S.; Lu, J.; Chen, B.; Yuan, L.; Chen, L.; Ju, L.; Cai, W.; Wu, J. The multifaceted role of alpha-lipoic acid in cancer prevention, occurrence, and treatment. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Liang, C.; Pei, T.; Guo, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. α-Lipoic acid alleviated fluoride-induced hepatocyte injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 15962–15971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawen, A.; Lane, D.J.R. Mammalian iron homeostasis in health and disease: Uptake, storage, transport, and molecular mechanisms of action. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 2473–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, H. Transferrin and transferrin receptors update. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillebeen, C.; Charlebois, E.; Wagner, J.; Katsarou, A.; Mui, J.; Vali, H.; Garcia-Santos, D.; Ponka, P.; Presley, J.; Pantopoulos, K. Transferrin receptor 1 controls systemic iron homeostasis by fine-tuning hepcidin expression to hepatocellular iron load. Blood 2019, 133, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casale, M.; Borriello, A.; Scianguetta, S.; Roberti, D.; Caiazza, M.; Bencivenga, D.; Tartaglione, I.; Ladogana, S.; Maruzzi, M.; Della Ragione, F.; et al. Hereditary hypochromic microcytic anemia associated with loss-of-function DMT1 gene mutations and absence of liver iron overload. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, E58–E60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Qin, M.C.; Zhong, W.C.; Liu, C.; Deng, G.H.; Yang, M.H.; Li, J.J.; Ye, H.X.; Shi, H.; Wu, C.F.; et al. RAGE promotes dysregulation of iron and lipid metabolism in alcoholic liver disease. Redox Biol. 2023, 59, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camaschella, C.; Nai, A.; Silvestri, L. Iron metabolism and iron disorders revisited in the hepcidin era. Haematologica 2020, 105, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauf, A.; Khalil, A.A.; Awadallah, S.; Khan, S.A.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Kamran, M.; Hemeg, H.A.; Mubarak, M.S.; Khalid, A.; Wilairatana, P. Reactive oxygen species in biological systems: Pathways, associated diseases, and potential inhibitors-a review. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salete-Granado, D.; Carbonell, C.; Puertas-Miranda, D.; Vega-Rodríguez, V.J.; García-Macia, M.; Herrero, A.B.; Marcos, M. Autophagy, oxidative stress, and alcoholic liver disease: A systematic review and potential clinical applications. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.N.; Wang, G.H.; Zhou, F.; Hao, J.J.; Tian, L.; Guan, L.F.; Geng, X.K.; Ding, Y.C.; Wu, H.W.; Zhang, K.Z. PM2.5 induces liver fibrosis via triggering ROS-mediated mitophagy. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 167, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gensluckner, S.; Wernly, B.; Datz, C.; Aigner, E. Iron, oxidative stress, and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Zeng, X.; Xing, H. AMPK/PPAR-γ/NF-κB axis participates in ROS-mediated apoptosis and autophagy caused by cadmium in pig liver. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; McMillan-Ward, E.; Kong, J.; Israels, S.J.; Gibson, S.B. Oxidative stress induces autophagic cell death independent of apoptosis in transformed and cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 2008, 15, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, D.; Song, S.; Wang, Y.; Bian, Y.; Wu, M.; Wu, H.; Shi, Y.; Duan, H. NAD(P)H: Quinone oxidoreductase 1 attenuates oxidative stress and apoptosis by regulating Sirt1 in diabetic nephropathy. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, X.; Yan, D.; Ren, C.; Zhang, J.; Gu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, Z.; Kong, L.; et al. PROTAC nanoplatform with targeted degradation of NAD(P)H:Quinone oxidoreductase 1 to enhance reactive oxygen species-mediated apoptosis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 8946–8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Ding, L.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Z. Alleviating effect of quercetin on cadmium-induced oxidative damage and apoptosis by activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway in BRL-3A cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 969892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ding, J.; Feng, L.; Wu, H.; Xu, Z.; Tao, W.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Ling, Y.; Zhu, P. Development of novel nitric oxide-releasing quinolinedione/furoxan hybrids as NQO1 inhibitors for intervention of drug-resistant hepatocellular cancer. Bioorg. Chem. 2022, 129, 106174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Superti, F.; Russo, R. Alpha-lipoic acid: Biological mechanisms and health benefits. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaqub, F.; Latief, N.; Butt, H.; Naseer, N.; Riazuddin, S. Alpha lipoic acid priming enhances the hepatoprotective effect of adipose derived stem cells in CCl4 induced hepatic injury in-vitro. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 906, 174201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.C.; Choi, H.; Oh, J.M.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, B.G.; Cho, J.H.; Lee, J. Protective effects of α-lipoic acid on cultured human nasal fibroblasts exposed to urban particulate matter. Int. Forum. Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 638–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasnicka, A.; Lastuvkova, H.; Alaei Faradonbeh, F.; Cermanova, J.; Hroch, M.; Mokry, J.; Dolezelova, E.; Pavek, P.; Zizalova, K.; Vitek, L.; et al. Iron overload reduces synthesis and elimination of bile acids in rat liver. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güvendi, G.F.; Eroğlu, H.A.; Makav, M.; Güvendi, B.; Adalı, Y. Selenium or ozone: Effects on liver injury caused by experimental iron overload. Life Sci. 2020, 262, 118558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, C.M.; Nunes, E.; Louro, T.; Proença, T.; Fernandes, R.; Boarder, M.R.; Seiça, R.M. Effects of alpha-lipoic acid on endothelial function in aged diabetic and high-fat fed rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Guo, T.; Guo, S.; Gao, J.; Ni, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhao, R. Chronic variable stress induces hepatic Fe(II) deposition by up-regulating ZIP14 expression via miR-181 family pathway in rats. Biology 2021, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Yan, K.; Sun, B.; Gao, S.; Yang, X.; Ni, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhao, R. Long-term high-fat diet decreases hepatic iron storage associated with suppressing TFR2 and ZIP14 expression in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 11612–11621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, S.; Yang, C.; Yang, S.; He, B.; Ma, W.; Zhao, R. Long-term dexamethasone exposure down-regulates hepatic TFR1 and reduces liver iron concentration in rats. Nutrients 2017, 9, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, M.; Xu, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Xu, A.; Pouladi, M.A.; Xu, X. Neuroprotective role of CHCHD2 in parkinson’s disease: Insights into the GPX4-related ferroptosis pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2025, 226, 348–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Li, C.; Yang, S.; Ma, Y.; Wang, H.L. Liver proteomics analysis reveals the differentiation of lipid mechanism and antioxidant enzyme activity during chicken embryonic development. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirpara, J.; Thuya, W.L.; Cheow, S.H.; Fernando, K.; Eu, J.Q.; Wang, L.; Wong, A.L.A.; Fong, E.L.S.; Ali, A.B.; Ding, L.W.; et al. Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles convey solute transporters to induce bioenergetic dependence shift contributing to treatment resistance. Theranostics 2024, 14, 6350–6369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, N.A.; Desai, T.R.; Tirgar, P.R. Investigation into iron chelating and antioxidant potential of melilotus officinalis in iron dextran induced iron overloaded sprague dawley Rat Model. Drug Res. 2016, 66, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, S.; Shu, Y.; Guo, S.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, R.; Shan, H.; Ma, W. Proteomics-Based Exploration of the Hepatoprotective Mechanism of α-Lipoic Acid in Rats with Iron Overload-Induced Liver Injury. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104774
Jiang S, Shu Y, Guo S, Ni Y, Zhao R, Shan H, Ma W. Proteomics-Based Exploration of the Hepatoprotective Mechanism of α-Lipoic Acid in Rats with Iron Overload-Induced Liver Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104774
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Shuxia, Yujia Shu, Shihui Guo, Yingdong Ni, Ruqian Zhao, Hongli Shan, and Wenqiang Ma. 2025. "Proteomics-Based Exploration of the Hepatoprotective Mechanism of α-Lipoic Acid in Rats with Iron Overload-Induced Liver Injury" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104774
APA StyleJiang, S., Shu, Y., Guo, S., Ni, Y., Zhao, R., Shan, H., & Ma, W. (2025). Proteomics-Based Exploration of the Hepatoprotective Mechanism of α-Lipoic Acid in Rats with Iron Overload-Induced Liver Injury. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4774. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104774





