The Role of microRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
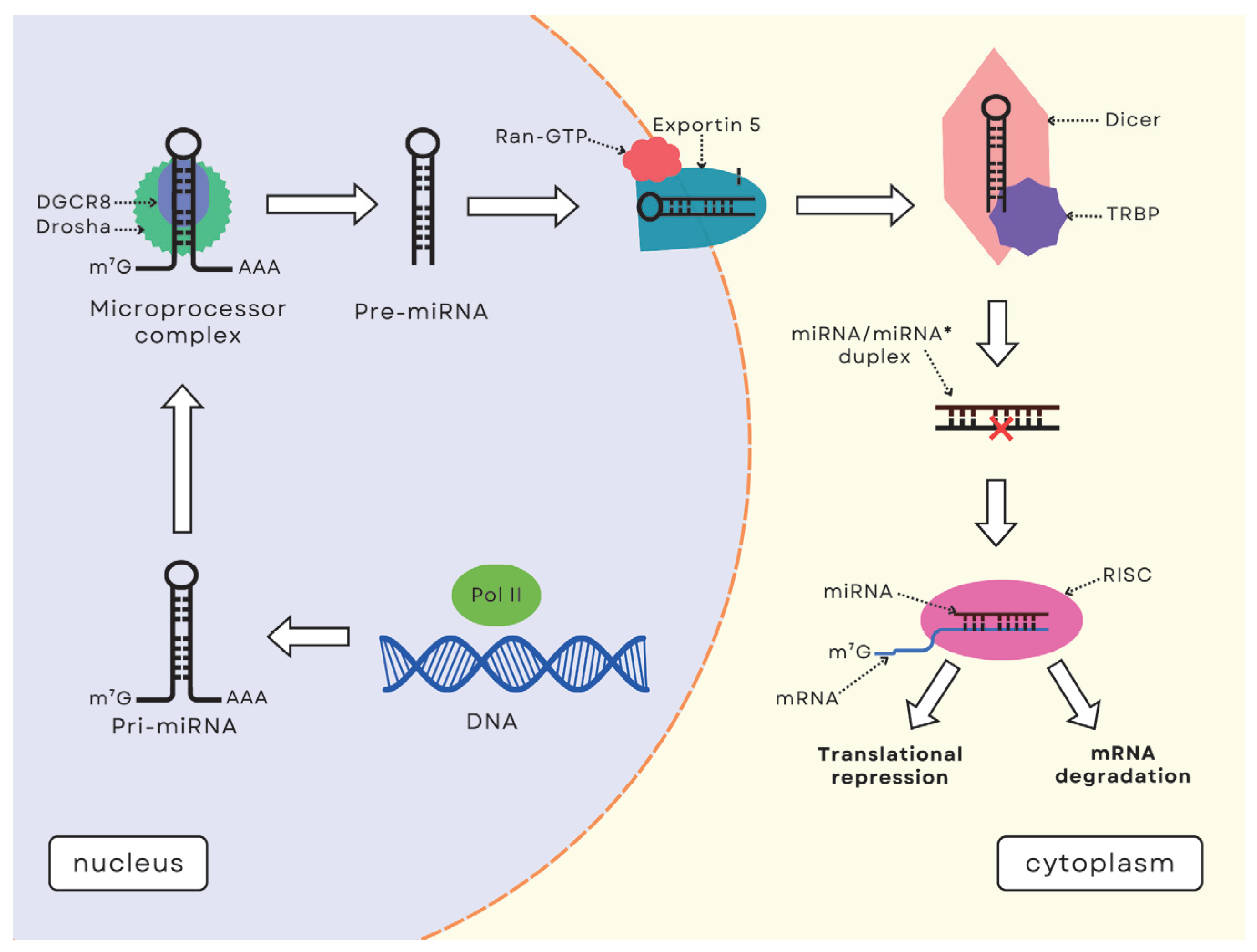
3. MicroRNA Function and Synthesis
4. The Role of miRNAs in the Immunological Response and Regulation of Inflammation in IBD
4.1. microRNAs in Th1/Th17 Regulation
4.2. miRNAs in Ferroptosis and Its Impact on Cell Death in IBD
4.3. miRNAs in Modulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome and Alleviation of IBD
4.4. miRNAs in the Regulation of the NF-κB Pathway
4.5. miRNAs in the Regulation of Intestinal Microbiota and Epithelial Barrier Function
4.6. miRNAs in the Regulation of Fibrosis and Intestinal Homeostasis
5. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
6. Micro-RNAs as Therapy and Predictors of Response to Applied Treatment in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
7. Potential Directions for Research and Clinical Applications
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agrawal, M.; Spencer, E.A.; Colombel, J.F.; Ungaro, R.C. Approach to the Management of Recently Diagnosed Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: A User’s Guide for Adult and Pediatric Gastroenterologists. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Bernstein, C. Environmental Risk Factors for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2022, 10, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, G.; Papadakis, K. Mechanisms of Disease: Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza, H.S.; Fiocchi, C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: Current state of the art. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvez, V.; Puca, P.; Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Bartocci, B.; Murgiano, M.; Iaccarino, J.; Parand, E.; Napolitano, D.; Pugliese, D.; et al. Novel Insights into the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarani, R.; Shojaeian, A.; Palasca, O.; Doncheva, N.T.; Jensen, L.J.; Gorodkin, J.; Pociot, F. Differentially Expressed miRNAs in Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn’s Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 865777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, L.; MacRae, I. Regulation of microRNA Function in Animals. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Bedmar, M.; Viennois, E. MicroRNA and Gut Microbiota: Tiny but Mighty-Novel Insights into Their Cross-Talk in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathogenesis and Therapeutics. J. Crohns Colitis 2022, 16, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakase, H.; Uchino, M.; Shinzaki, S.; Matsuura, M.; Matsuoka, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Saruta, M.; Hirai, F.; Hata, K.; Hiraoka, S.; et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Inflammatory Bowel Disease 2020. Gastroenterol 2021, 56, 489–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, J.; LeBlanc, J.; Hart, A. Ulcerative Colitis: An Update. Clin. Med. Clin. Med. (Lond.) 2021, 21, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushing, K.; Higgins, P. Management of Crohn Disease: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, H.; Biancone, L.; Fiorino, G.; Katsanos, K.; Kopylov, U.; Al Sulais, E.; Axelrad, J.; Balendran, K.; Burisch, J.; de Ridder, L.E.A.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Malignancies. J. Crohns Colitis 2023, 17, 827–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stidham, R.; Higgins, P. Colorectal Cancer in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Colon. Rectal Surg. 2018, 31, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowlus, C.; Arrivé, L.; Bergquist, A.; Deneau, M.; Forman, L.; Ilyas, S.; Lunsford, K.; Martinez, M.; Sapisochin, G.; Shroff, R.E.A.; et al. AASLD Practice Guidance on Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2023, 77, 659–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Pan, K.; Wei, H. Mechanisms and Therapeutic Research Progress in Intestinal Fibrosis. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2024, 11, 1368977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamias, G.; Pizarro, T.; Cominelli, F. Immunological Regulation of Intestinal Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2022, 28, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessio, S.; Ungaro, F.; Noviello, D.; Lovisa, S.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Revisiting Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: The Gut Thickens. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, S.; Eisenstein, S. Inflammatory Bowel Disease Presentation and Diagnosis. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 99, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Fibrosis. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, S.; Sokal, A.; Ferenc, K.; Motyka, E.; Helma, K.; Filip, R. The Role of Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation in Intestinal Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Descending Process or a Programmed Consequence? Genes 2023, 14, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Gönczi, L.; Lakatos, P.; Burisch, J. The Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Europe in 2020. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.; Parlett, L.; Jonsson, F.M.; Brensinger, C.; Pate, V.; Wu, Q.; Dawwas, G.; Weiss, A.C.B.; McCauley, M. Incidence, Prevalence, and Racial and Ethnic Distribution of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the United States. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 1197–1205.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.; Jin, Y.; Shao, X.; Xu, Y.; Ma, G.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, D. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease, 1990-2021: Insights from the Global Burden of Disease 2021. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2024, 39, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.; Feinbaum, R.; Ambros, V. The C. elegans Heterochronic Gene lin-4 Encodes Small RNAs with Antisense Complementarity to lin-14. Cell 1993, 75, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P.; Chakraborty, A.; Sarkar, D.; Langthasa, M.; Rahman, M.; Bari, M.; Singha, R.; Malakar, A.; Chakraborty, S. Interplay Between miRNAs and Human Diseases. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 2007–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnoi, A.; Rani, S. MiRNA Biogenesis and Regulation of Diseases: An Overview. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1509, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R. MicroRNA Biogenesis Pathways in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergani-Junior, C.; Tonon-da-Silva, G.; Inan, M.; Mori, M. DICER: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Biophys. Rev. 2021, 13, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, V.; Sengar, R. Biogenesis and Mechanisms of microRNA-Mediated Gene Regulation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Síbia, C.; Quaglio, A.; Oliveira, E.; Pereira, J.; Ariede, J.; Lapa, R.; Severino, F.; Reis, P.; Sassaki, L.; Saad-Hossne, R. microRNA–mRNA Networks Linked to Inflammation and Immune System Regulation in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, E.; Ptak, W.; Bryniarski, K. Immunoregulacja poprzez interferencyjny RNA-mechanizmy, rola, perspektywy [Immunoregulation by interference RNA (iRNA)–mechanisms, role, perspective]. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2011, 65, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Kim, J. Roles of microRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2112–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Engers, J.; Abdulqadir, R. Talk About Micromanaging! Role of microRNAs in Intestinal Barrier Function. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G170–G174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, P.; Zheng, C. The Involvement of TH17 Cells in the Pathogenesis of IBD. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2023, 69, 28–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Bris, R.; Saez, A.; Herrero-Fernandez, B.; Rius, C.; Sanchez-Martinez, H.; Gonzalez-Granado, J. CD4 T-Cell Subsets and the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, L.; Du, X.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Piao, W. MiRNA-374b-5p and miRNA-106a-5p are Related to Inflammatory Bowel Disease via Regulating IL-10 and STAT3 Signaling Pathways. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y. MicroRNA-219a-5p Suppresses Intestinal Inflammation Through Inhibiting Th1/Th17-Mediated Immune Responses in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Mucosal Immunol. 2020, 13, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Hang, S. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Exosome Shuttling mir-129-5p Attenuates Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Inhibiting Ferroptosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Cao, C.; Shu, D.; Liu, T.; Zhang, T. The Important Role of Ferroptosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2024, 11, 1449037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foerster, E. How Autophagy Controls the Intestinal Epithelial Barrier. Autophagy 2022, 18, 86–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, T.; Onodera, K.; Nakase, H. Role of Autophagy in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 1944–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.L. How Autophagy, a Potential Therapeutic Target, Regulates Intestinal Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1087677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, P.; Zhou, K. Revitalizing Gut Barrier Integrity: Role of miR-192-5p in Enhancing Autophagy via Rictor in Enteritis. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2024, 327, G317–G332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, O. Potential Target for the Treatment of Microbial Infections, Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, and Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Martinez, F. Rictor/Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 2 Signaling Protects Colonocytes from Apoptosis and Prevents Epithelial Barrier Breakdown. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1537–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Peng, J.; Wang, N.; Ocansey, D.; Zhang, X.; Mao, F. hucMSC-Ex Alleviates Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Mice by Enhancing M2-Type Macrophage Polarization via the METTL3-Slc37a2-YTHDF1 Axis. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2024, 40, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, Z. hucMSC-Derived Exosomes Attenuate Colitis by Regulating Macrophage Pyroptosis via the miR-378a-5p/NLRP3 Axis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Zhang, H. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourkochristou, E.; Aggeletopoulou, I.; Konstantakis, C.; Triantos, C. Role of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 4796–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatri, V.; Kalyanasundaram, R. Therapeutic Implications of Inflammasome in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalavino, V.; Piccinno, E.; Valentini, A. miR-369-3p Modulates Intestinal Inflammatory Response via BRCC3/NLRP3 Inflammasome Axis. Cells 2023, 12, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Mao, X.; Chen, D.; Yu, B.; He, J. miRNAs Can Affect Intestinal Epithelial Barrier in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 868229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Gu, L. miR-148a Inhibits Colitis and Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis in Mice. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Li, Y. Deficiency of miRNA-149-3p Shaped Gut Microbiota and Enhanced Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2022, 30, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Yang, D.; Yu, H.; Li, Q. MicroRNA-497 Inhibits Inflammation in DSS-Induced IBD Model Mice and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced RAW264.7 Cells via Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101 Pt B, 108318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnachaitanya, S.; Liu, M.; Fujise, K.; Li, Q. MicroRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Its Complications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, Y.; Li, J. Human Amniotic Epithelial Stem Cells Promote Colonic Recovery in Experimental Colitis via Exosomal MiR-23a-TNFR1-NF-κB Signaling. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 2024, 11, e2401429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldars-García, L.; Marin, A.; Chaparro, M.; Gisbert, J. The Interplay Between Immune System and Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y. Profiles and Interactions of Gut Microbiome and Intestinal MicroRNAs in Pediatric Crohn’s Disease. mSystems 2024, 9, e0078324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, C.; Pekow, J. The Emerging Role of miRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review. Therap Adv. Gastroenterol. 2015, 8, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.; Nijhuis, A.; Mehta, S.; Kumagai, T.; Feakins, R.; Lindsay, J.; Silver, A. Intestinal Fibrosis in Crohn’s Disease: Role of microRNAs as Fibrogenic Modulators, Serum Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Targets. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Ouyang, Y.; Xu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Z. MiR-155 Promotes Colitis-Associated Intestinal Fibrosis by Targeting HBP1/Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling Pathway. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 4765–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Chen, X. Tissue and Serum miR-149-3p/5p in Hospitalized Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Correlation with Disease Severity and Inflammatory Markers. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2024, 40, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, H.; Pan, K. Akkermansia muciniphila and Its Membrane Protein Ameliorates Intestinal Inflammatory Stress and Promotes Epithelial Wound Healing via CREBH and miR-143/145. J. Biomed. Sci. 2023, 30, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magro, D.; Sassaki, L.; Chebli, J. Interaction Between Diet and Genetics in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 1644–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggeletopoulou, I.; Kalafateli, M.; Tsounis, E.; Triantos, C. Exploring the Role of IL-1β in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Pathogenesis. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2024, 11, 1307394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado-Bedmar, M.; Roy, M. Fecal let-7b and miR-21 Directly Modulate the Intestinal Microbiota, Driving Chronic Inflammation. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2394249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Ding, J. Alleviation of Colitis by Honeysuckle MIR2911 via Direct Regulation of Gut Microbiota. J. Control Release 2024, 376, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanassova, A.; Georgieva, A. Circulating miRNA-16 in Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Some Clinical Correlations—A Cohort Study in Bulgarian Patients. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 6310–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, F.; Demmig, C.; Bokemeyer, A.; Brückner, M.; Lenze, F.; Lenz, P.; Nowacki, T.; Tepasse, P.; Schmidt, H.H.; Schmidt, M.A.; et al. MicroRNA-320a Monitors Intestinal Disease Activity in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, e00134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Q.; Yang, G.; Guo, J.; Li, M.; Zeng, Z.; He, Y.; Chen, B.; Chen, M. Circulating MicroRNA223 is a New Biomarker for Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Medicine (Baltimore) 2016, 95, e2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Zhang, S.; Dassopoulos, T.; Harris, M.L.; Bayless, T.M.; Meltzer, S.J.; Brant, S.R.; Kwon, J.H. Identification of MicroRNAs Associated with Ileal and Colonic Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasseu, M.; Tréton, X.; Guichard, C.; Pedruzzi, E.; Cazals-Hatem, D.; Richard, C.; Aparicio, T.; Daniel, F.; Soulé, J.C.; Moreau, R.; et al. Identification of Restricted Subsets of Mature MicroRNA Abnormally Expressed in Inactive Colonic Mucosa of Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, S.R.; Kwon, J.H. The Role of MicroRNA in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 6, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Hu, X.; Du, Y.; Du, J. The Role of miRNAs in Colorectal Cancer Progression and Chemoradiotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 134, 111099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Morishita, A.; Kobara, H.; Masaki, T. The Role of microRNAs in Cholangiocarcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiong, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zheng, B.; Liu, T.; Xie, W. Association of Three Polymorphisms rs11614913, rs2910146, and rs3746444 in miRNA-196a2, miRNA-146a, and miRNA-499 with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 7295131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iborra, M.; Bernuzzi, F.; Correale, C.; Vetrano, S.; Fiorino, G.; Beltrán, B.; Marabita, F.; Locati, M.; Spinelli, A.; Nos, P.; et al. Identification of Serum and Tissue Micro-RNA Expression Profiles in Different Stages of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2013, 173, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahm, A.M.; Thayu, M.; Hand, N.J.; Horner, A.; Leonard, M.B.; Friedman, J.R. Circulating MicroRNA Is a Biomarker of Pediatric Crohn Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 53, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccon, T.D.; Dhahbi, J.M.; Schneider, A.; Nunez Lopez, Y.O.; Qasem, A.; Cavalcante, M.B.; Sing, L.K.; Naser, S.A.; Masternak, M.M. Plasma miRNA Profile of Crohn’s Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Biology 2022, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.; Kelly, O.B.; Smith, M.I.; Kabakchiev, B.; Silverberg, M.S. Differential miRNA Expression in Ileal and Colonic Tissues Reveals an Altered Immunoregulatory Molecular Profile in Individuals with Crohn’s Disease versus Healthy Subjects. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Salem, M.; Boyd, M.; Bornholdt, J.; Li, Y.; Coskun, M.; Seidelin, J.B.; Sandelin, A.; Nielsen, O.H. Relation Between NOD2 Genotype and Changes in Innate Signaling in Crohn’s Disease on mRNA and miRNA Levels. NPJ Genom. Med. 2017, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caparrós, E.; García-Martinez, I.; Zapater, P.; Madero, L.; Valverde, Á.M.; Gutiérrez, A.; Francés, R. An Altered Expression of miR-376a-3p and miR-20a-5p in Peripheral Blood Exosomes Regulates the Autophagy and Inflammatory Systemic Substrates, and Relates to the Smoking Habit and Age in Crohn’s Disease. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e23418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, D.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y.; Gong, H.; Ma, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, D. Focusing on Non-Responders to Infliximab with Ulcerative Colitis, What Can We Do First and Next? Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 141, 112943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casertano, M.; Trotta, M.C.; Cenni, S.; Creoli, M.; Miele, E.; Martinelli, M.; Lepre, C.C.; Russo, M.; Alfano, R.; D’Amico, M.; et al. Infliximab Therapy Decreases the Expression of Serum and Faecal miR-126 and miR-20a in Paediatric Crohn’s Disease: A Pilot Study. Acta Paediatr. 2024, 113, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera-Seco, L.; Baldán-Martín, M.; Fernández-Tomé, S.; Ortega Moreno, L.; Lozano, J.J.; Aransay, A.M.; Chaparro, M.; Gisbert, J.P.; Marigorta, U.M. Characterization of the Regulatory Landscape in Crohn’s Disease Reveals MicroRNA-Associated Alterations that Shape Anti-TNF Response. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2025, izaf029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, G.; Crucitta, S.; Bertani, L.; Ruglioni, M.; Baiano Svizzero, G.; Ceccarelli, L.; Del Re, M.; Danesi, R.; Costa, F.; Fogli, S. Expression of Circulating let-7e and miR-126 May Predict Clinical Remission in Patients with Crohn’s Disease Treated with Anti-TNF-α Biologics. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heier, C.R.; Fiorillo, A.A.; Chaisson, E.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Hathout, Y.; Damsker, J.M.; Hoffman, E.P.; Conklin, L.S. Identification of Pathway-Specific Serum Biomarkers of Response to Glucocorticoid and Infliximab Treatment in Children with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, S.K.; Heier, C.R.; Diaz-Calderon, L.; Tully, C.B.; Fiorillo, A.A.; van den Anker, J.; Conklin, L.S. Serum miRNAs Are Pharmacodynamic Biomarkers Associated with Therapeutic Response in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2020, 26, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Lan, D.; Niu, J.; Miao, J.; Dong, X.; Yang, G.; Zhang, F.; Cao, Y.; Wang, K.; et al. Differential Expression of Serum MicroRNAs in Glucocorticoid-Resistant Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 936–946. [Google Scholar]
- Sáez-González, E.; Moret-Tatay, I.; Bastida, G.; Aguas, M.; Iborra, M.; Nos, P.; Beltrán, B. MicroRNA and Granulocyte-Monocyte Adsorption Apheresis Combotherapy after Inadequate Response to Anti-TNF Agents in Ulcerative Colitis. J. Clin. Apher. 2024, 39, e22101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, P.T.B.; Clark, I.M.; Le, L.T.T. MicroRNA-Based Diagnosis and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brain, O.; Owens, B.M.; Pichulik, T.; Allan, P.; Khatamzas, E.; Leslie, A.; Steevels, T.; Sharma, S.; Mayer, A.; Catuneanu, A.M.; et al. The Intracellular Sensor NOD2 Induces MicroRNA-29 Expression in Human Dendritic Cells to Limit IL-23 Release. Immunity 2013, 39, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza Lahimchi, M.; Eslami, M.; Yousefi, B. Interleukin-35 and Interleukin-37 Anti-Inflammatory Effect on Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Application of Non-Coding RNAs in IBD Therapy. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 117, 109932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Law, I.K.M.; Padua, D.; Sideri, A.; Huang, V.; Kevil, C.G.; Iliopoulos, D.; Pothoulakis, C. MicroRNA-31-3p Is Involved in Substance P (SP)-Associated Inflammation in Human Colonic Epithelial Cells and Experimental Colitis. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Lu, X.; Dong, W. Exosomes Derived from T Regulatory Cells Relieve Inflammatory Bowel Disease by Transferring miR-195a-3p. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggeletopoulou, I.; Mouzaki, A.; Thomopoulos, K.; Triantos, C. miRNA Molecules-Late Breaking Treatment for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, T.; Bigagli, E.; Lynch, E.N.; Galli, A.; Dragoni, G. miRNA-Based Therapies for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: What Are We Still Missing? Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2023, 29, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhu, L.; Feng, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.D.; Hu, Y.C.; Shen, H. MicroRNA-602 prevents the development of inflammatory bowel diseases in a microbiota-dependent manner. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, F.; He, S.; Cui, S.; Shi, Y.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Liu, D.; Zhi, F.; Peng, L. A Molecular Targeted Immunotherapeutic Strategy for Ulcerative Colitis via Dual-targeting Nanoparticles Delivering miR-146b to Intestinal Macrophages. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Cao, Y.; Hou, L.; Luo, T.; Li, M.; Gao, S.; Wang, L.; Sheng, K.; Zheng, L. Ginger exosome-like nanoparticle-derived miRNA therapeutics: A strategic inhibitor of intestinal inflammation. J. Adv. Res. 2025, 69, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Fu, X.; Xie, J.; Pan, H.; Han, W.; Huang, W. miR-26a attenuates colitis and colitis-associated cancer by targeting the multiple intestinal inflammatory pathways. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2021, 24, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.; Danesh, F.R. Promises and challenges of miRNA therapeutics. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2022, 323, F673–F674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masi, L.; Capobianco, I.; Magrì, C.; Marafini, I.; Petito, V.; Scaldaferri, F. MicroRNAs as Innovative Biomarkers for Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Prediction of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeire, S.; Sands, B.E.; Tilg, H.; Tulassay, Z.; Kempinski, R.; Danese, S.; Bunganič, I.; Nitcheu, J.; Santo, J.; Scherrer, D.; et al. ABX464 (obefazimod) for moderate-to-severe, active ulcerative colitis: A phase 2b, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled induction trial and 48 week, open-label extension. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| miRNA | Potential Action in IBD | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| miR-129-5p |
| [37] |
| [38] | |
| miR-378a-5p |
| [64] |
| miR-374b-5p |
| [36] |
| miR-106a-5p |
| [36] |
| miR-149 |
| [48] |
| miR-149-5p |
| [48] |
| miR-143/145 |
| [64] |
| miR-369-3p |
| [45] |
| let-7b and miR-21 |
| [67] |
| let-7b |
| |
| miR-21 |
| |
| miR-23a |
| [51] |
| miR-497 |
| [49] |
| miR149-3p/5p |
| [63] |
| miR-192-5p |
| [60] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sokal-Dembowska, A.; Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, S.; Helma, K.; Filip, R. The Role of microRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104750
Sokal-Dembowska A, Jarmakiewicz-Czaja S, Helma K, Filip R. The Role of microRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104750
Chicago/Turabian StyleSokal-Dembowska, Aneta, Sara Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, Kacper Helma, and Rafał Filip. 2025. "The Role of microRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104750
APA StyleSokal-Dembowska, A., Jarmakiewicz-Czaja, S., Helma, K., & Filip, R. (2025). The Role of microRNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4750. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104750





