Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with a Genetic Defect: A Report of Two Cases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Type 2 diabetes (30–50%);
- Type 1 diabetes (3.9%);
- Hypertension (27.2%);
- Primary glomerulonephritis (8.2%);
- Chronic tubulointerstitial nephritis (3.6%);
- Hereditary or cystic diseases (3.1%);
- Secondary glomerulonephritis or vasculitis (2.1%);
- Plasma cell dyscrasias or neoplasm (2.1%).
2. Results
2.1. Patient with CKD
2.1.1. Medical History and Complaints at Presentation
2.1.2. Results at Admission
2.1.3. Patient Management During Hospitalization
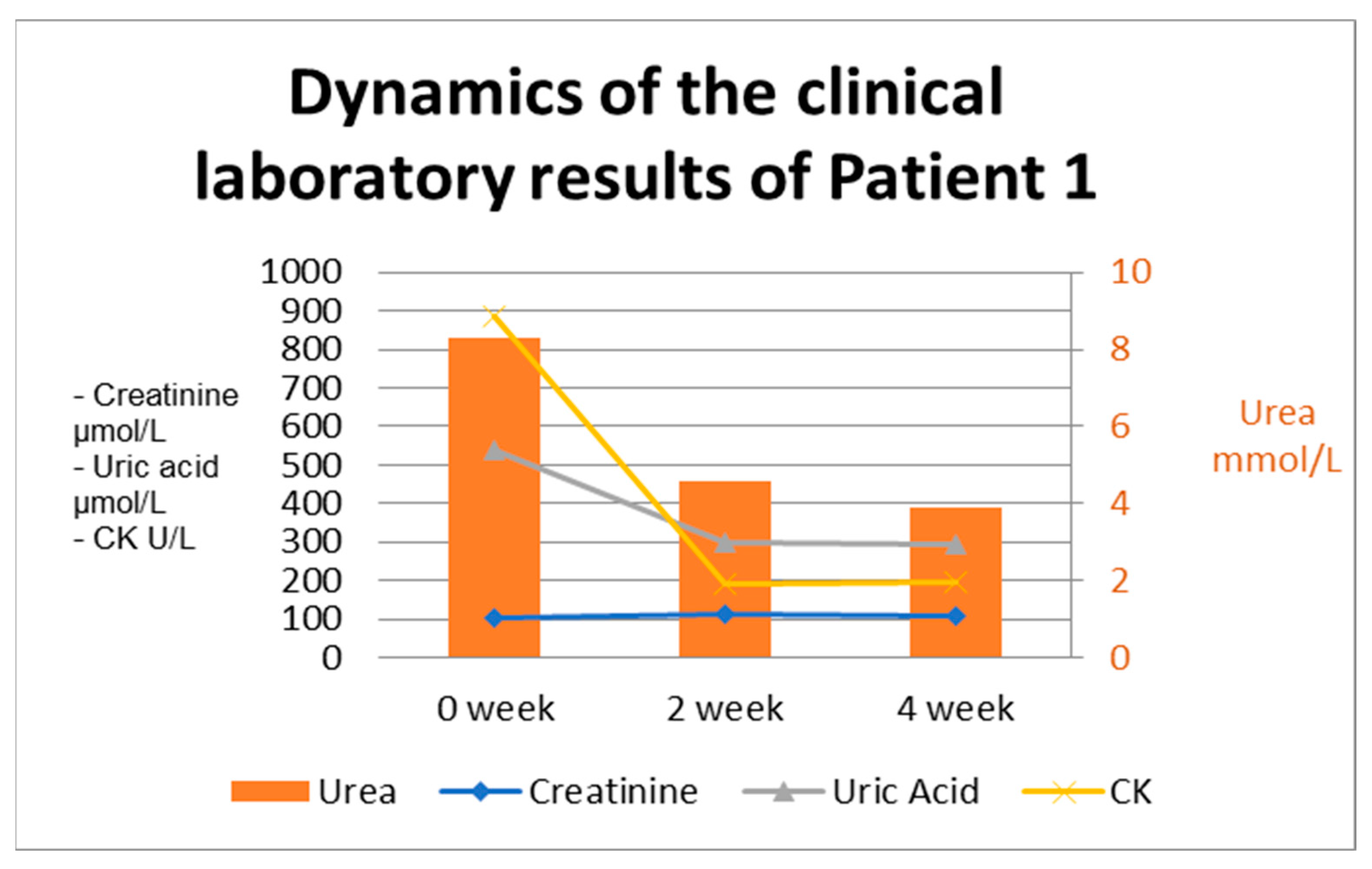
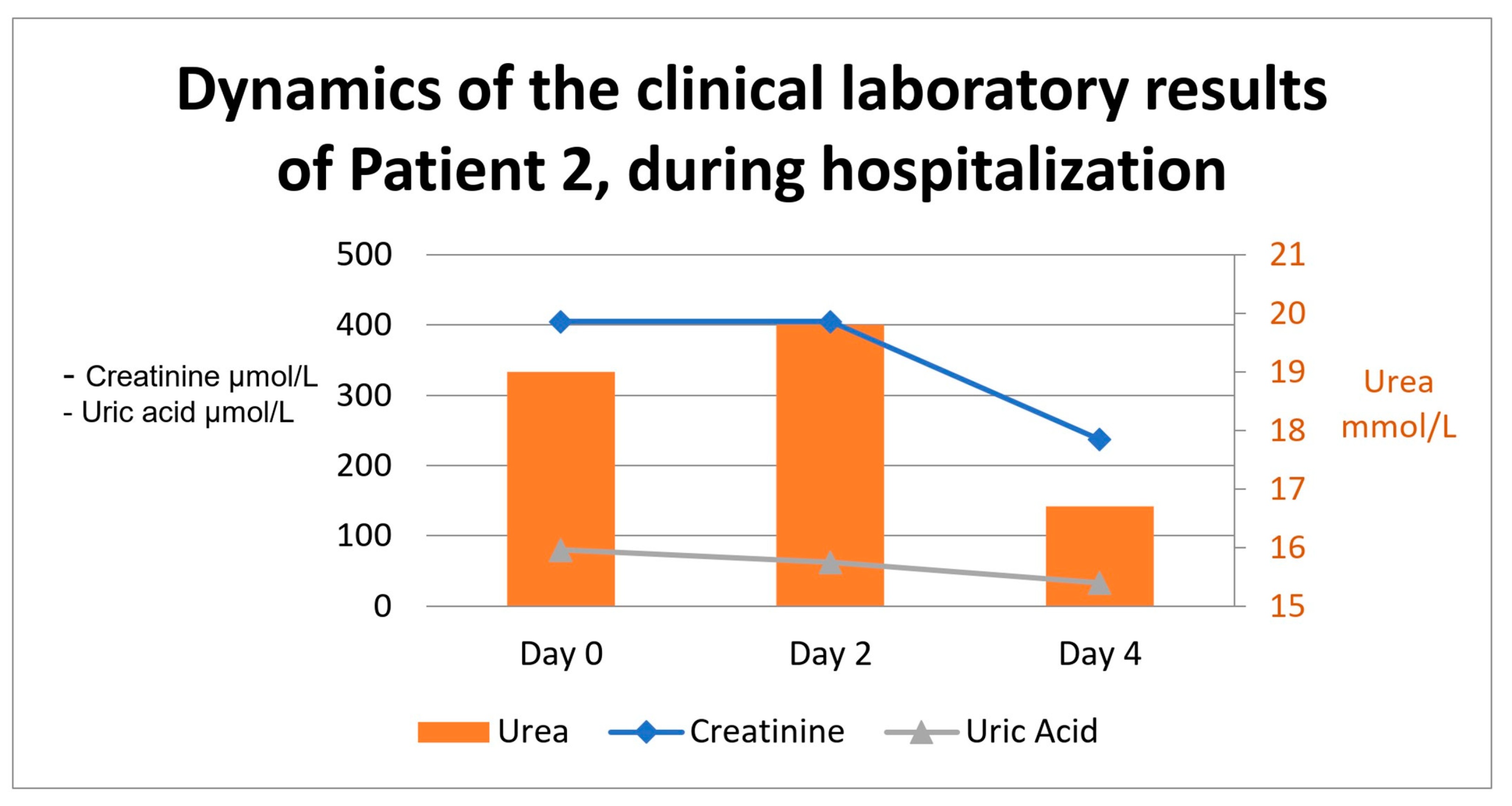
2.1.4. Case Approach and Results
2.2. Patient with AKI
2.2.1. Medical History and Complaints at Presentation
2.2.2. Results at Admission
2.2.3. Patient Management During Hospitalization
2.2.4. Case Approach and Results
3. Discussion
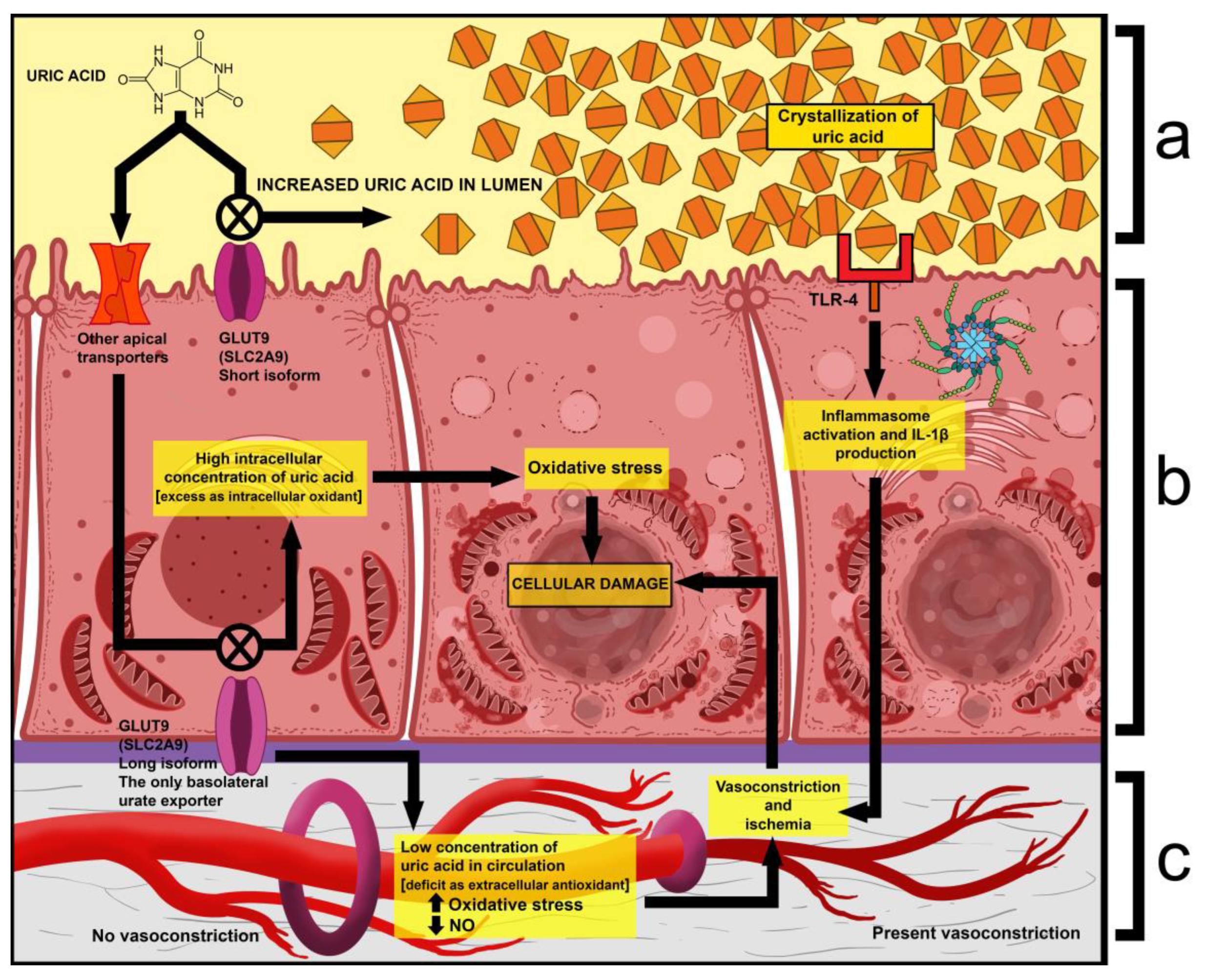
- One is that exercise causes an increase in uric acid production and a spike in serum levels. Given that the latter already has abnormally high excretion, its tubular concentration increases even more, which leads to the precipitation and deposition of crystals within the tubules. Due to this, nephrons may become obstructed, and the production of primary urine is impaired [35].
- Another is that extraordinarily high tubular concentrations of uric acid have been shown to activate Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR-4) on the apical surface of renal cells, which then leads to the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome complex. This results in the induced production of interleukin 1β (IL-1β), which then acts as an activator of sympathetic fibers. The result of this is the vasoconstriction of glomerular arterioles, which further decreases filtration and interstitial blood flow [36].
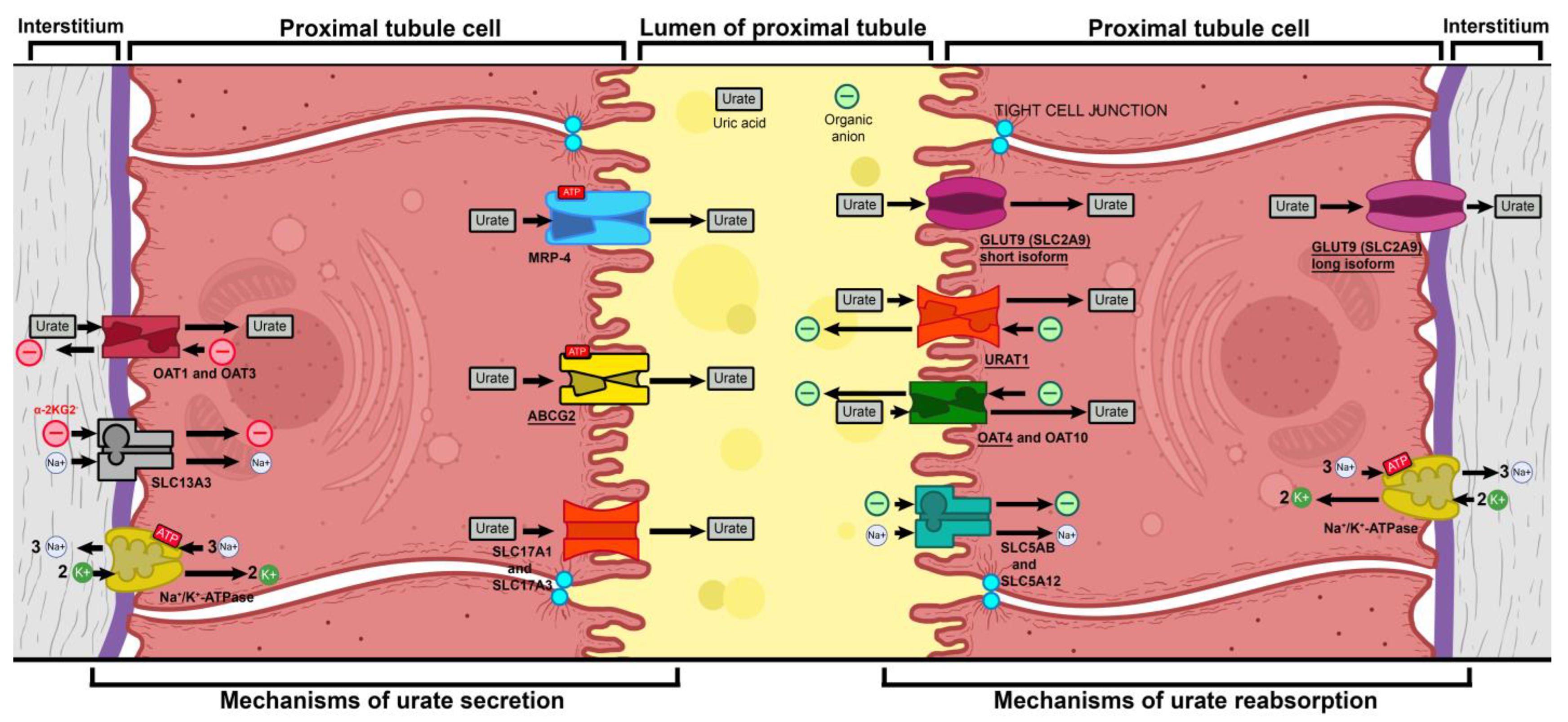
- Mutations in GLUT9 lead to a partial (yet substantial) decrease in luminal urate reuptake because other apical transporters continue to function. The basolateral efflux of uric acid, however, is severely diminished due to GLUT9 being the sole basolateral exporter. Therefore, there is an increase in the uric acid concentration within tubular cells, which leads to the production of ROS and oxidative stress (due to its property of being an intracellular oxidant) [37].
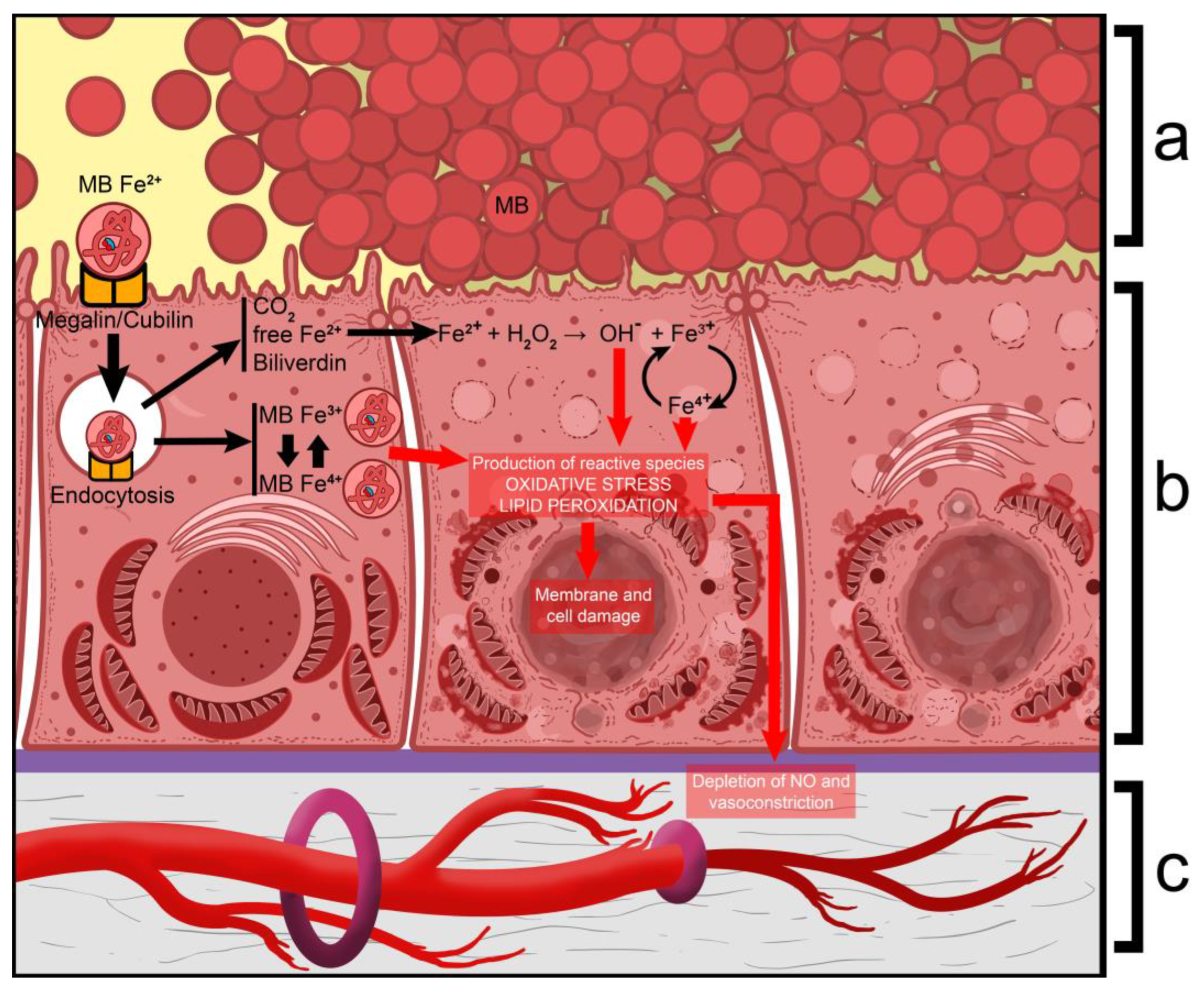
- A fourth mechanism is that during physical exercise, the body is subjected to elevated levels of oxidative stress, which, in the absence of sufficient amounts of antioxidants (i.e., uric acid), leads to oxidative damage, renal vasoconstriction, and ischemia, resulting in tubular cell damage (acute tubular damage) [35].
Future Research Directions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Genetic Testing
4.2.1. Patient with CKD
4.2.2. Patient with AKI
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease. |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate. |
| ESRD | End-Stage Renal Disease. |
| CKDs | Chronic kidney diseases. |
| ARPKD | Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. |
| INF2 | Inverted formin-2. |
| PAX2 | Paired box 2. |
| WT1 | Wilms tumor suppression gene. |
| AS | Alport syndrome. |
| COL4A5 | Collagen type IV alpha 5 chain. |
| CKDu | CKD of unknown etiology. |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury. |
| ARF | Acute renal failure. |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate. |
| CK | Creatine kinase |
| RYR1 | Ryanodine receptor 1. |
| MH | Malignant hyperthermia. |
| CCD | Central core disease. |
| ER | Exertional rhabdomyolysis. |
| SERCA | Ca2+-ATPase. |
| GLUT9 | Glucose transporter 9. |
| SLC2A9 | Solute Carrier 2A9. |
| URAT1 | Urate Transporter 1. |
| OAT1 | Organic anion transporter 1. |
| OAT3 | Organic anion transporter 3. |
| OAT4 | Organic anion transporter 4. |
| OAT10 | Organic anion transporter 10. |
| SLC5AB | Solute Carrier 5AB. |
| SLC5A12 | Solute Carrier 5A12. |
| SLC13A3 | Solute Carrier 13A3. |
| SLC17A1 | Solute Carrier 17A1. |
| SLC17A3 | Solute Carrier 17A3. |
| MRP1 | Multi-drug Resistance Protein 1. |
| ABCG2 | ATP-binding cassette superfamily G member 2. |
| Na+/K+-ATPase | Sodium/potassium active transport antiporter. |
| RHUC2 | Renal hypouricemia type 2. |
| RHUC1 | Renal hypouricemia type 1. |
References
- Vaidya, S.R.; Aeddula, N.R. Chronic Kidney Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Webster, A.C.; Nagler, E.V.; Morton, R.L.; Masson, P. Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, F. Genetic Kidney Diseases. Lancet 2010, 375, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottlewski, I.; Münch, J.; Wagner, T.; Schönauer, R.; Bachmann, A.; Weimann, A.; Hentschel, J.; Lindner, T.H.; Seehofer, D.; Bergmann, C.; et al. Value of Renal Gene Panel Diagnostics in Adults Waiting for Kidney Transplantation Due to Undetermined End-Stage Renal Disease. Kidney Int. 2019, 96, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Titze, S.; Schmid, M.; Kottgen, A.; Busch, M.; Floege, J.; Wanner, C.; Kronenberg, F.; Eckardt, K.-U.; for the GCKD study investigators; Titze, S.; et al. Disease Burden and Risk Profile in Referred Patients with Moderate Chronic Kidney Disease: Composition of the German Chronic Kidney Disease (GCKD) Cohort. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2015, 30, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saran, R.; Li, Y.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Ayanian, J.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Chen, J.L.T.; Cope, E.; et al. US Renal Data System 2015 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2016, 67, A7–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, A.; Pippias, M.; Noordzij, M.; Stel, V.S.; Afentakis, N.; Ambühl, P.M.; Andrusev, A.M.; Fuster, E.A.; Arribas Monzón, F.E.; Åsberg, A.; et al. The European Renal Association—European Dialysis and Transplant Association (ERA-EDTA) Registry Annual Report 2015: A Summary. Clin. Kidney J. 2018, 11, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimaru, T.; Mori, T.; Chiga, M.; Mandai, S.; Kikuchi, H.; Ando, F.; Mori, Y.; Susa, K.; Nakano, Y.; Shoji, T.; et al. Genetic Diagnosis of Adult Hemodialysis Patients with Unknown Etiology. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paidi, G.; Iroshani Jayarathna, A.I.; Salibindla, D.B.A.M.R.; Amirthalingam, J.; Karpinska-Leydier, K.; Alshowaikh, K.; Ergin, H.E. Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Origin: A Mysterious Epidemic. Cureus 2021, 13, e17132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gifford, F.J.; Gifford, R.M.; Eddleston, M.; Dhaun, N. Endemic Nephropathy Around the World. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasumana, C.; Paranagama, P.; Agampodi, S.; Wijewardane, C.; Gunatilake, S.; Siribaddana, S. Drinking Well Water and Occupational Exposure to Herbicides Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease, in Padavi-Sripura, Sri Lanka. Environ. Health 2015, 14, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.H.; Elledge, M.F.; Womack, D.S.; Wickremashinghe, R.; Wanigasuriya, K.P.; Peiris-John, R.J.; Lunyera, J.; Smith, K.; Raymer, J.H.; Levine, K.E. Additional Perspectives on Chronic Kidney Disease of Unknown Aetiology (CKDu) in Sri Lanka—Lessons Learned from the WHO CKDu Population Prevalence Study. BMC Nephrol. 2014, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Daneshpajouhnejad, P.; Hashmi, M.F.; Bashir, K. Acute Kidney Injury. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Muroya, Y.; He, X.; Fan, L.; Wang, S.; Xu, R.; Fan, F.; Roman, R.J. Enhanced Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Aging and Diabetes. Am. J. Physiol.-Ren. Physiol. 2018, 315, F1843–F1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palevsky, P.M. Endpoints for Clinical Trials of Acute Kidney Injury. Nephron 2018, 140, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuber, K.; Davis, J. The ABCs of Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Acad. Physician Assist. 2018, 31, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawhney, S.; Bell, S.; Black, C.; Christiansen, C.F.; Heide-Jørgensen, U.; Jensen, S.K.; Ronksley, P.E.; Tan, Z.; Tonelli, M.; Walker, H.; et al. Harmonization of Epidemiology of Acute Kidney Injury and Acute Kidney Disease Produces Comparable Findings across Four Geographic Populations. Kidney Int. 2022, 101, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susantitaphong, P.; Cruz, D.N.; Cerda, J.; Abulfaraj, M.; Alqahtani, F.; Koulouridis, I.; Jaber, B.L. World Incidence of AKI: A Meta-Analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- See, E.J.; Jayasinghe, K.; Glassford, N.; Bailey, M.; Johnson, D.W.; Polkinghorne, K.R.; Toussaint, N.D.; Bellomo, R. Long-Term Risk of Adverse Outcomes after Acute Kidney Injury: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies Using Consensus Definitions of Exposure. Kidney Int. 2019, 95, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Loubon, C.; Martínez-Paz, P.; García-Morán, E.; Tamayo-Velasco, Á.; López-Hernández, F.J.; Jorge-Monjas, P.; Tamayo, E. Genetic Susceptibility to Acute Kidney Injury. JCM 2021, 10, 3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.M.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer Analysis Project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Wilson, C.J.; Lehár, J.; Kryukov, G.V.; Sonkin, D.; et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia Enables Predictive Modelling of Anticancer Drug Sensitivity. Nature 2012, 483, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnett, M.J.; Edelman, E.J.; Heidorn, S.J.; Greenman, C.D.; Dastur, A.; Lau, K.W.; Greninger, P.; Thompson, I.R.; Luo, X.; Soares, J.; et al. Systematic Identification of Genomic Markers of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer Cells. Nature 2012, 483, 570–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zibar, L.; Wagner, J.; Pavlinić, D.; Galić, J.; Pasini, J.; Juras, K.; Barbić, J. The Relationship Between Interferon-γ Gene Polymorphism and Acute Kidney Allograft Rejection. Scand. J. Immunol. 2011, 73, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.H.; Daneshmandi, S.; Pourfathollah, A.A.; Geramizadeh, B.; Yaghobi, R.; Rais-Jalali, G.A.; Roozbeh, J.; Bolandparvaz, S. A Study of the Impact of Cytokine Gene Polymorphism in Acute Rejection of Renal Transplant Recipients. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schott, C.; Lebedeva, V.; Taylor, C.; Abumelha, S.; Roshanov, P.S.; Connaughton, D.M. Utility of Genetic Testing in Adults with CKD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2025, 20, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capacchione, J.F.; Sambuughin, N.; Bina, S.; Mulligan, L.P.; Lawson, T.D.; Muldoon, S.M. Exertional Rhabdomyolysis and Malignant Hyperthermia in a Patient with Ryanodine Receptor Type 1 Gene, L-Type Calcium Channel α-1 Subunit Gene, and Calsequestrin-1 Gene Polymorphisms. Anesthesiology 2010, 112, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J.; Schiemann, A.H.; Roesl, C.; Miller, D.; Massey, S.; Pollock, N.; Bulger, T.; Stowell, K. Functional Analysis of RYR1 Variants Linked to Malignant Hyperthermia. Temperature 2016, 3, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petejova, N.; Martinek, A. Acute Kidney Injury Due to Rhabdomyolysis and Renal Replacement Therapy: A Critical Review. Crit. Care 2014, 18, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafian, B.; Fogo, A.B.; Lusco, M.A.; Alpers, C.E. AJKD Atlas of Renal Pathology: Myoglobin Cast Nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 69, e7–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikov, E.Y.; Chupyrkina, A.A.; Pevzner, I.B.; Isaev, N.K.; Zorov, D.B. Myoglobin Causes Oxidative Stress, Increase of NO Production and Dysfunction of Kidney’s Mitochondria. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2009, 1792, 796–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valaitienė, J.; Laučytė-Cibulskienė, A. Oxidative Stress and Its Biomarkers in Cardiovascular Diseases. Artery Res. 2024, 30, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sautin, Y.Y.; Johnson, R.J. Uric Acid: The Oxidant-Antioxidant Paradox. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2008, 27, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitart, V.; Rudan, I.; Hayward, C.; Gray, N.K.; Floyd, J.; Palmer, C.N.; Knott, S.A.; Kolcic, I.; Polasek, O.; Graessler, J.; et al. SLC2A9 Is a Newly Identified Urate Transporter Influencing Serum Urate Concentration, Urate Excretion and Gout. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 437–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Liang, X.; Song, Y.; Feng, L.; Zhong, L.; Guo, X. Idiopathic Renal Hypouricemia: A Case Report and Literature Review. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 5118–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosoyamada, M. Hypothetical Mechanism of Exercise-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Associated with Renal Hypouricemia. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paladugu, N.R.; Vukkadala, M. Renal Hypouricemia Type 2 with SLC2A9 Compound Heterozygous Variants: A Case Report of Recurrent Acute Kidney Injury Triggered by Low-Intensity Exercise. Front. Nephrol. 2024, 4, 1463913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caulfield, M.J.; Munroe, P.B.; O’Neill, D.; Witkowska, K.; Charchar, F.J.; Doblado, M.; Evans, S.; Eyheramendy, S.; Onipinla, A.; Howard, P.; et al. SLC2A9 Is a High-Capacity Urate Transporter in Humans. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlivan, R.; Murphy, E.; Pula, S.; Pain, A.; Brain, H.; Scopes, G.; Gjika, F.; Ahmadouk, N.; Manole, A.; Houlden, H. Raised CK and Acute Kidney Injury Following Intense Exercise in Three Patients with a History of Exercise Intolerance Due to Homozygous Mutations in SLC2A9. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2024, 34, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoers, N.; Antignac, C.; Bergmann, C.; Dahan, K.; Giglio, S.; Heidet, L.; Lipska-Ziętkiewicz, B.S.; Noris, M.; Remuzzi, G.; Vargas-Poussou, R.; et al. Genetic Testing in the Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease: Recommendations for Clinical Practice. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallawaarachchi, A.; McCarthy, H.; Forbes, T.A.; Jayasinghe, K.; Patel, C.; Alexander, S.I.; Boughtwood, T.; Braithwaite, J.; Chakera, A.; Crafter, S.; et al. Enhancing Diagnostic Outcomes in Kidney Genetic Disorders: The KidGen National Kidney Genomics Study Protocol. BMC Nephrol. 2025, 26, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNI EN ISO 15189:2013; Medical laboratories—Requirements for Quality and Competence. Ente Nazionale Italiano di Unificazione (UNI): Milton Keynes, UK, 2013.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdravkova, I.; Tilkiyan, E.; Ivanov, H.; Lambrev, A.; Dzhongarova, V.; Kraleva, G.; Kirilov, B. Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with a Genetic Defect: A Report of Two Cases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104681
Zdravkova I, Tilkiyan E, Ivanov H, Lambrev A, Dzhongarova V, Kraleva G, Kirilov B. Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with a Genetic Defect: A Report of Two Cases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104681
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdravkova, Irina, Eduard Tilkiyan, Hristo Ivanov, Atanas Lambrev, Violeta Dzhongarova, Gergana Kraleva, and Boris Kirilov. 2025. "Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with a Genetic Defect: A Report of Two Cases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104681
APA StyleZdravkova, I., Tilkiyan, E., Ivanov, H., Lambrev, A., Dzhongarova, V., Kraleva, G., & Kirilov, B. (2025). Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with a Genetic Defect: A Report of Two Cases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104681







