Arhgap29 Deficiency Directly Leads to Systemic and Craniofacial Skeletal Abnormalities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
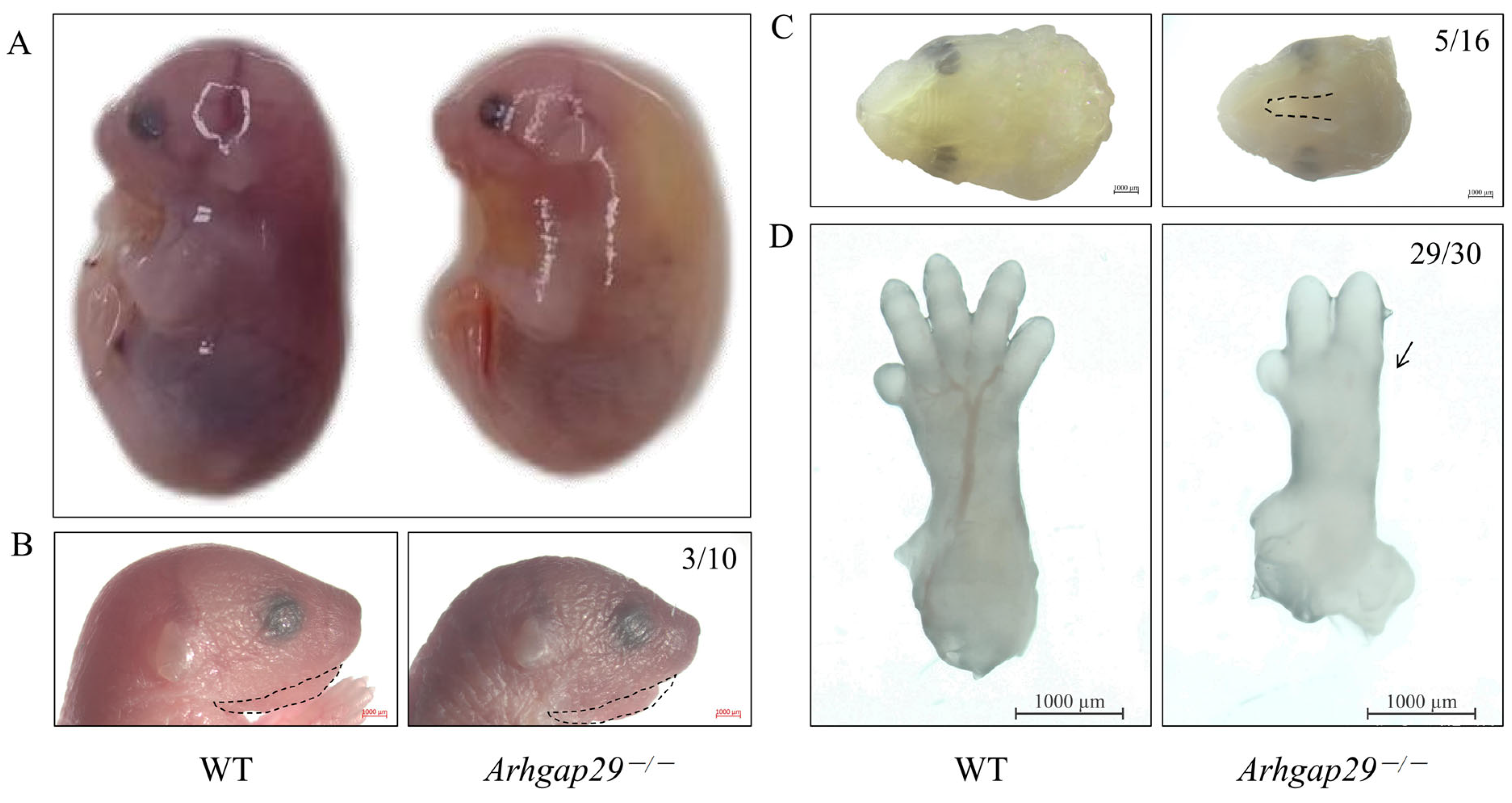
2.1. General Characteristics of Arhgap29 Knockout Mice
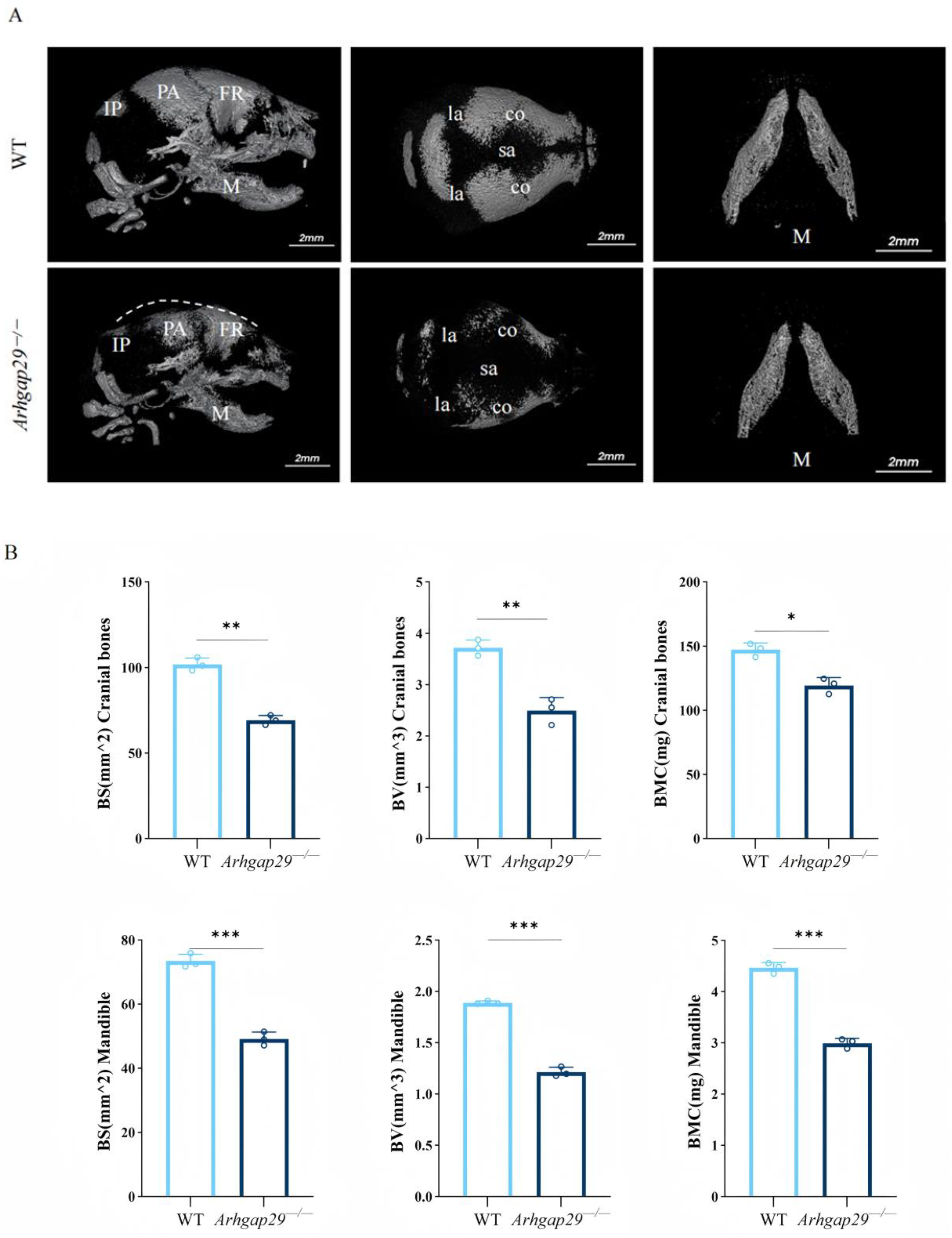
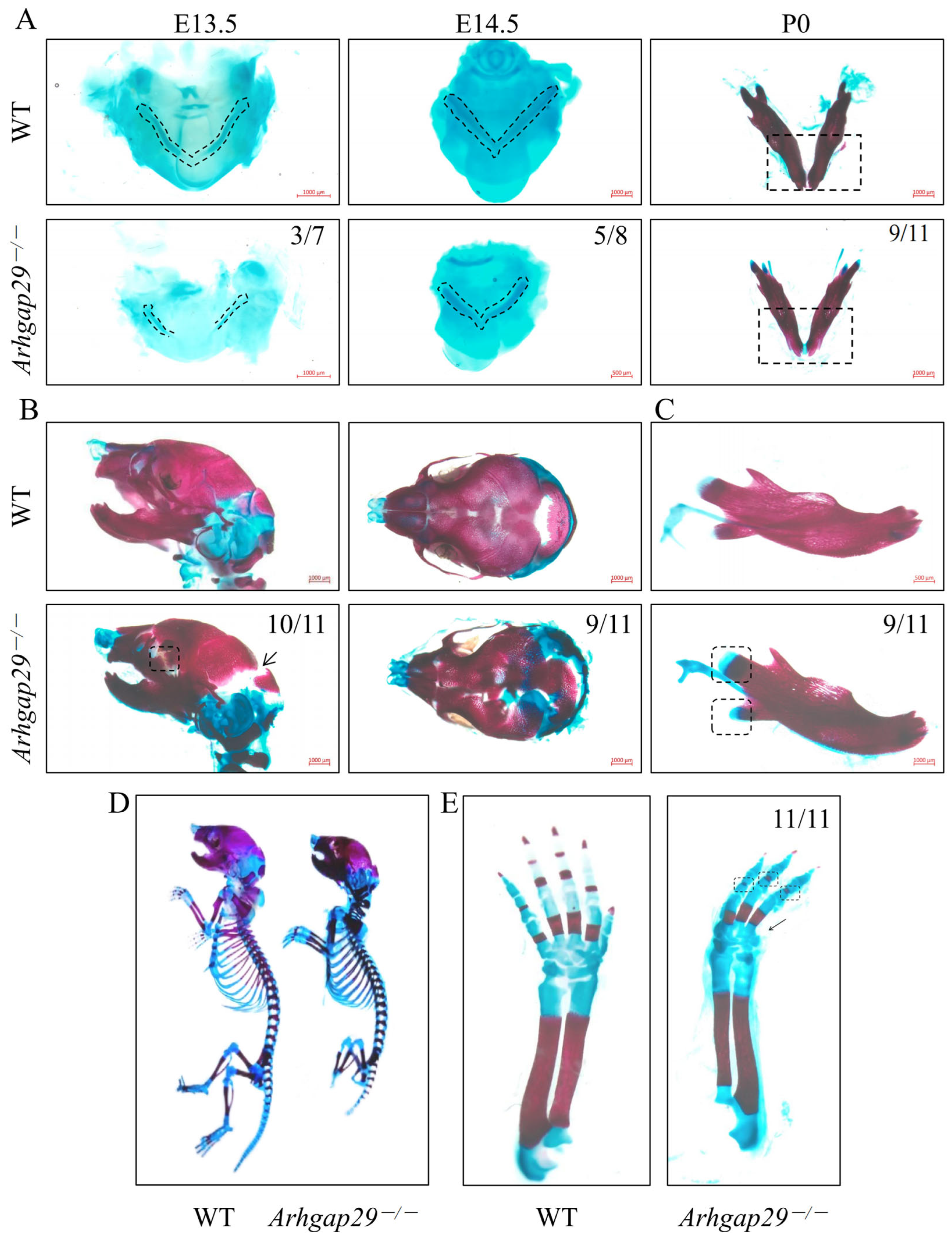
2.2. The Impact of Arhgap29 on Cranial, Maxillofacial Cartilage Bones, and Digits
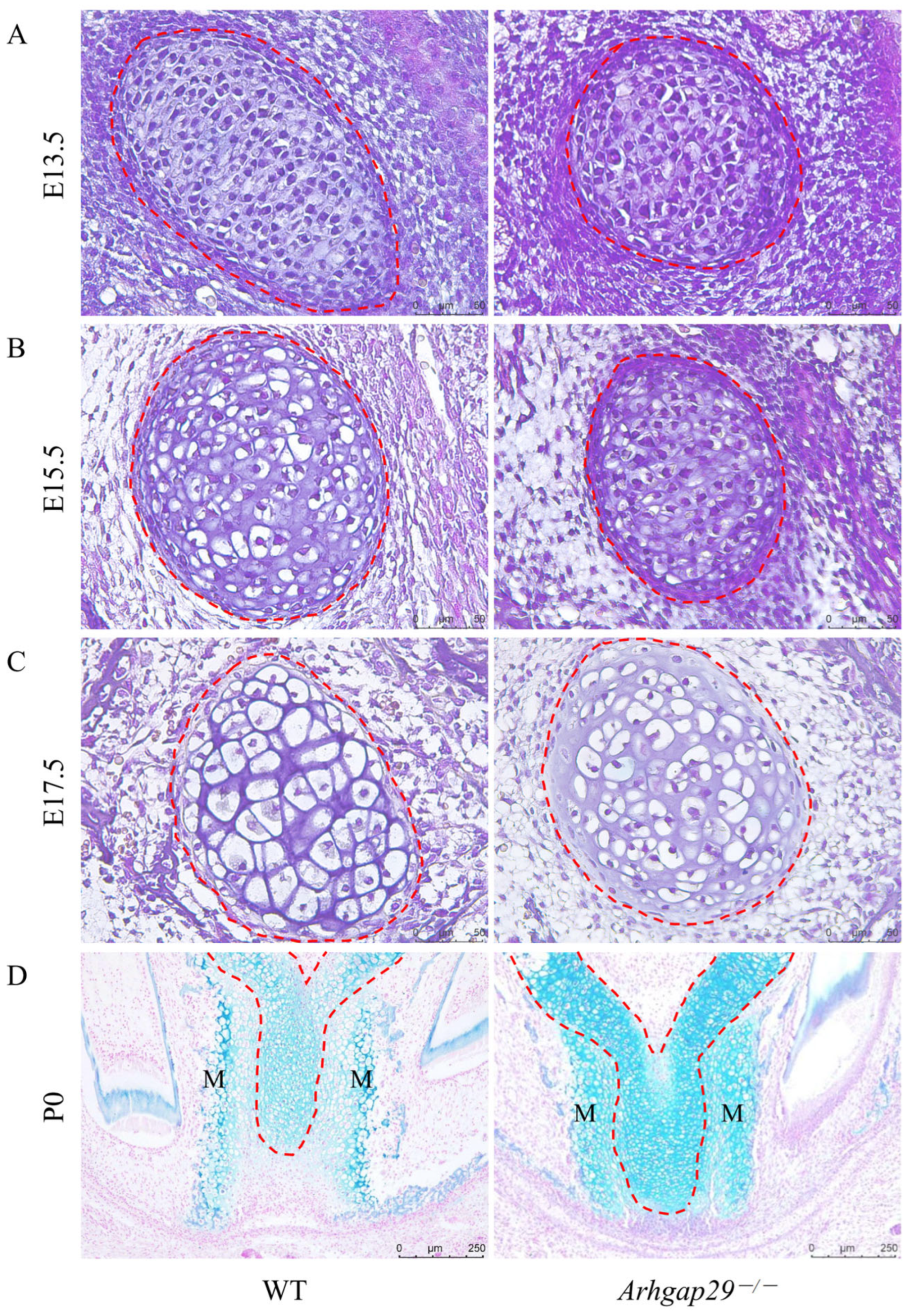
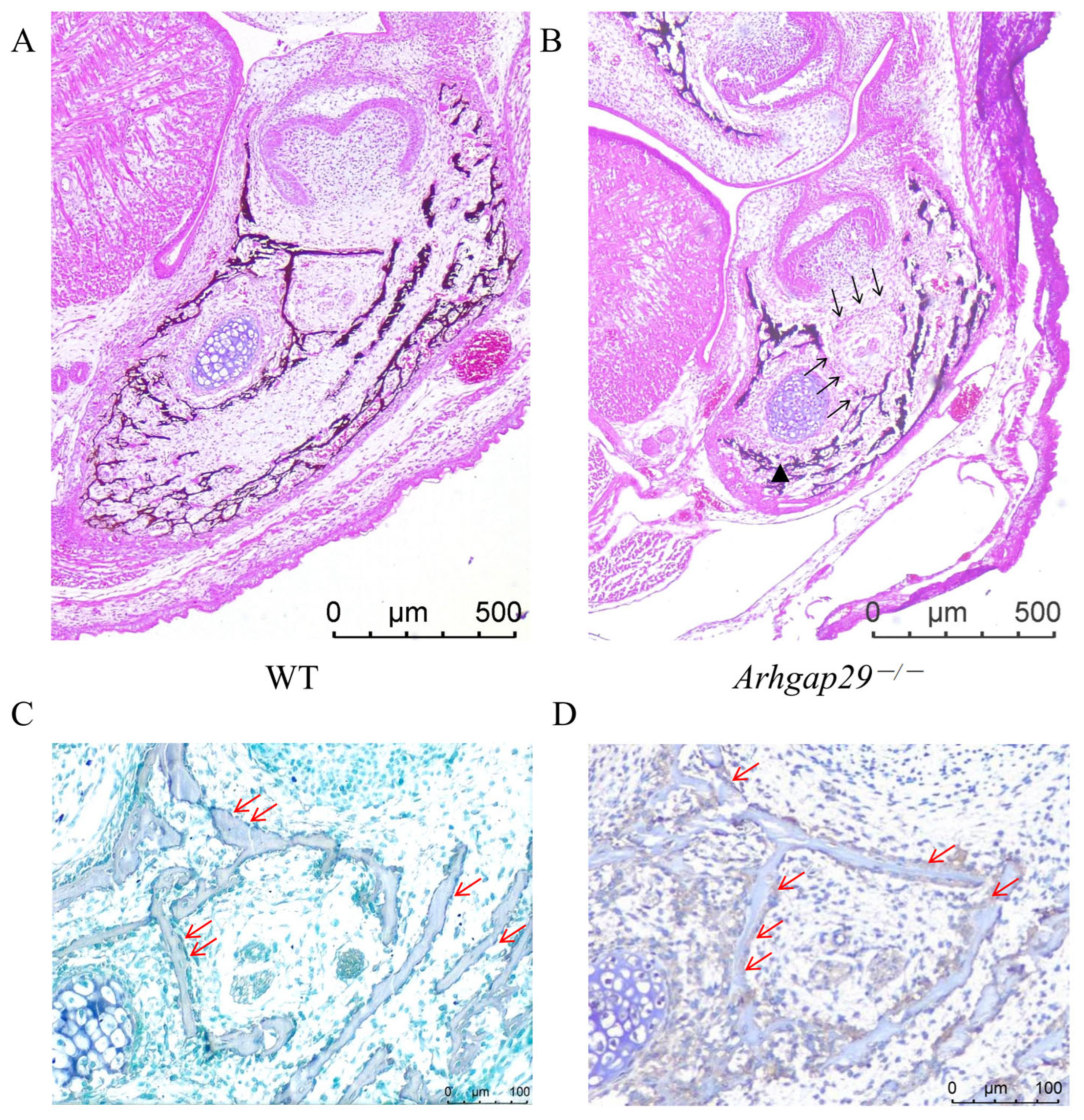
2.3. Histomorphological Phenotypes in Meckel’s Cartilage and Mandible of Arhgap29−/− Mice
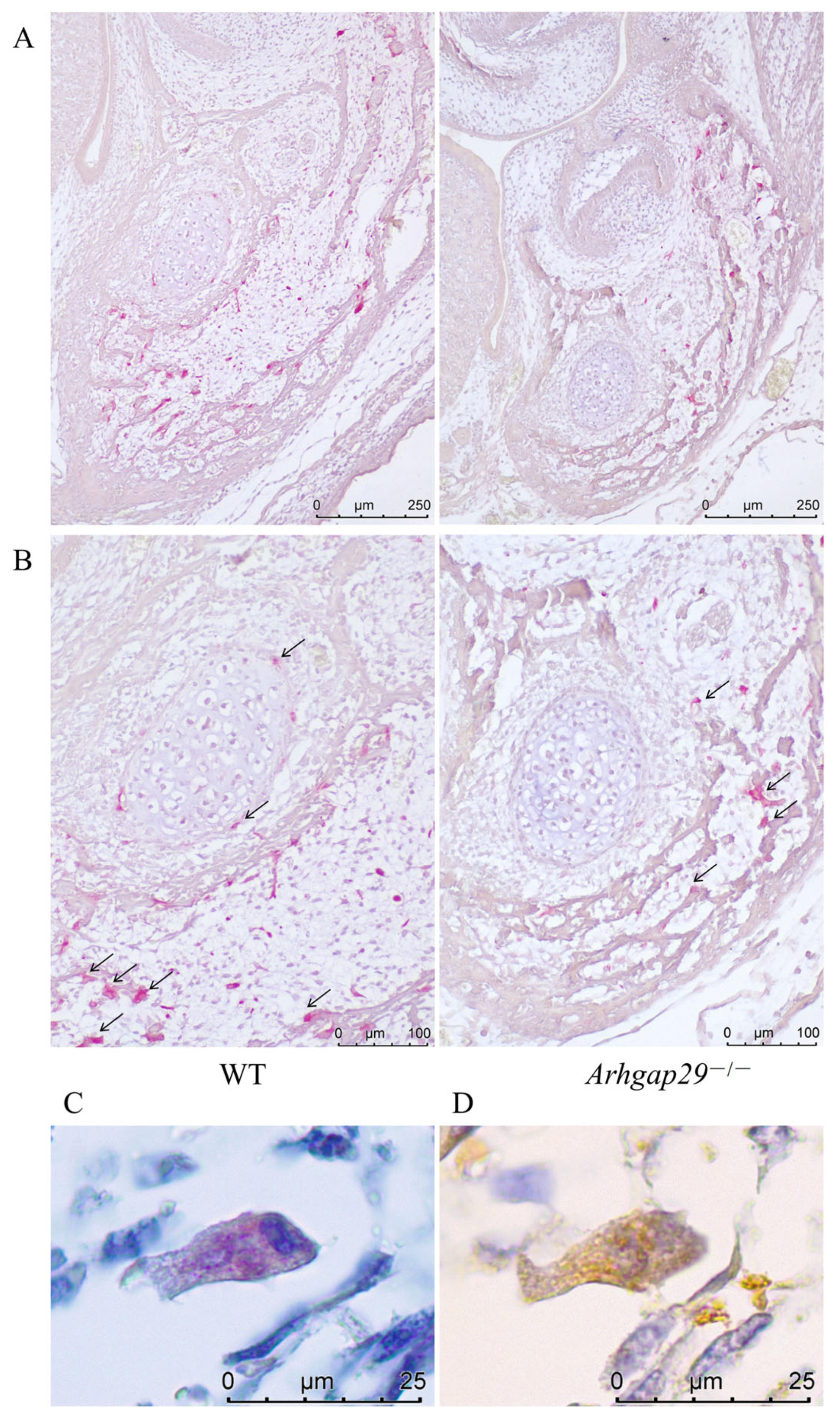
2.4. Level of Bone Resorption in Arhgap29−/− Mice Decreased
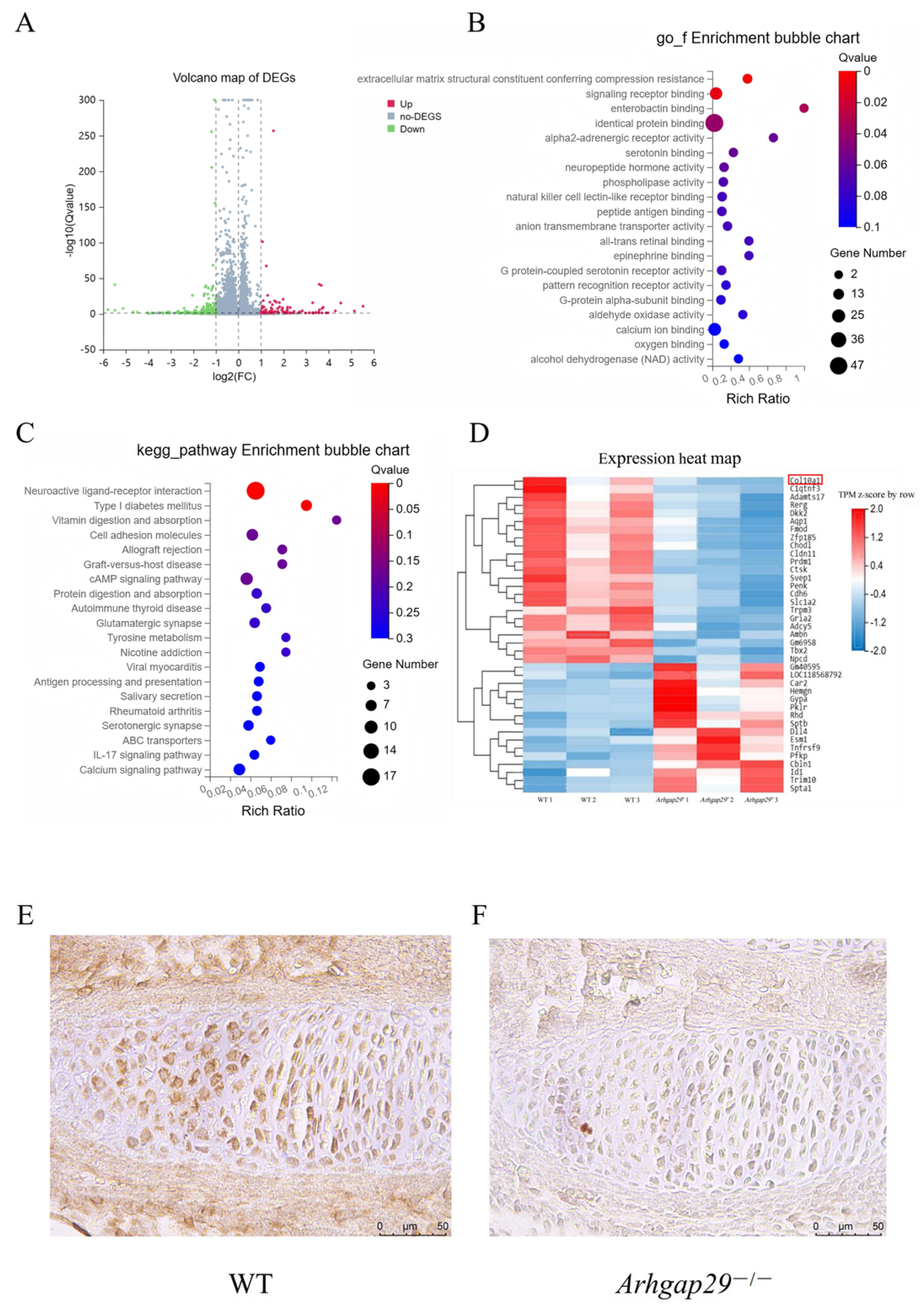
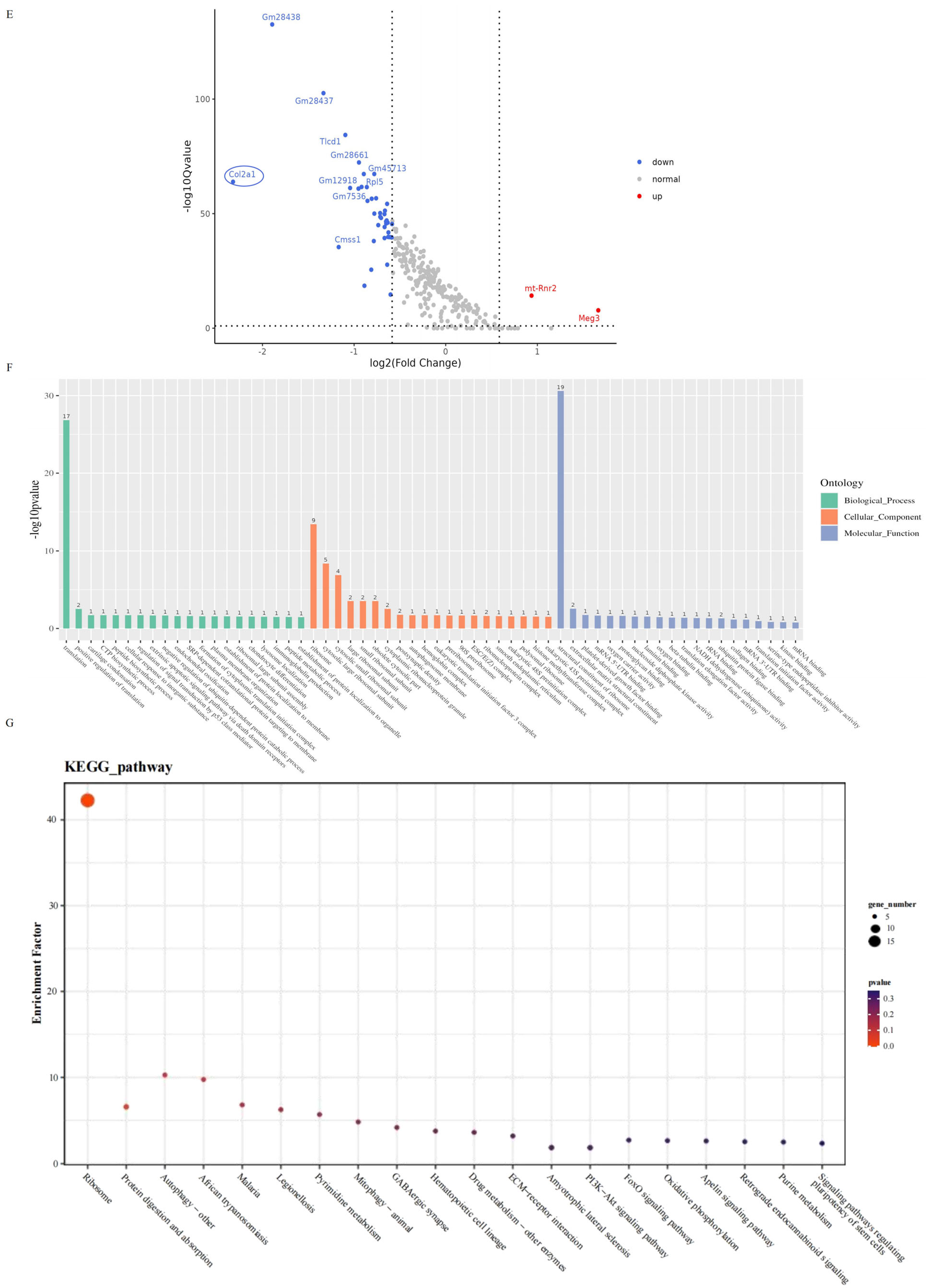
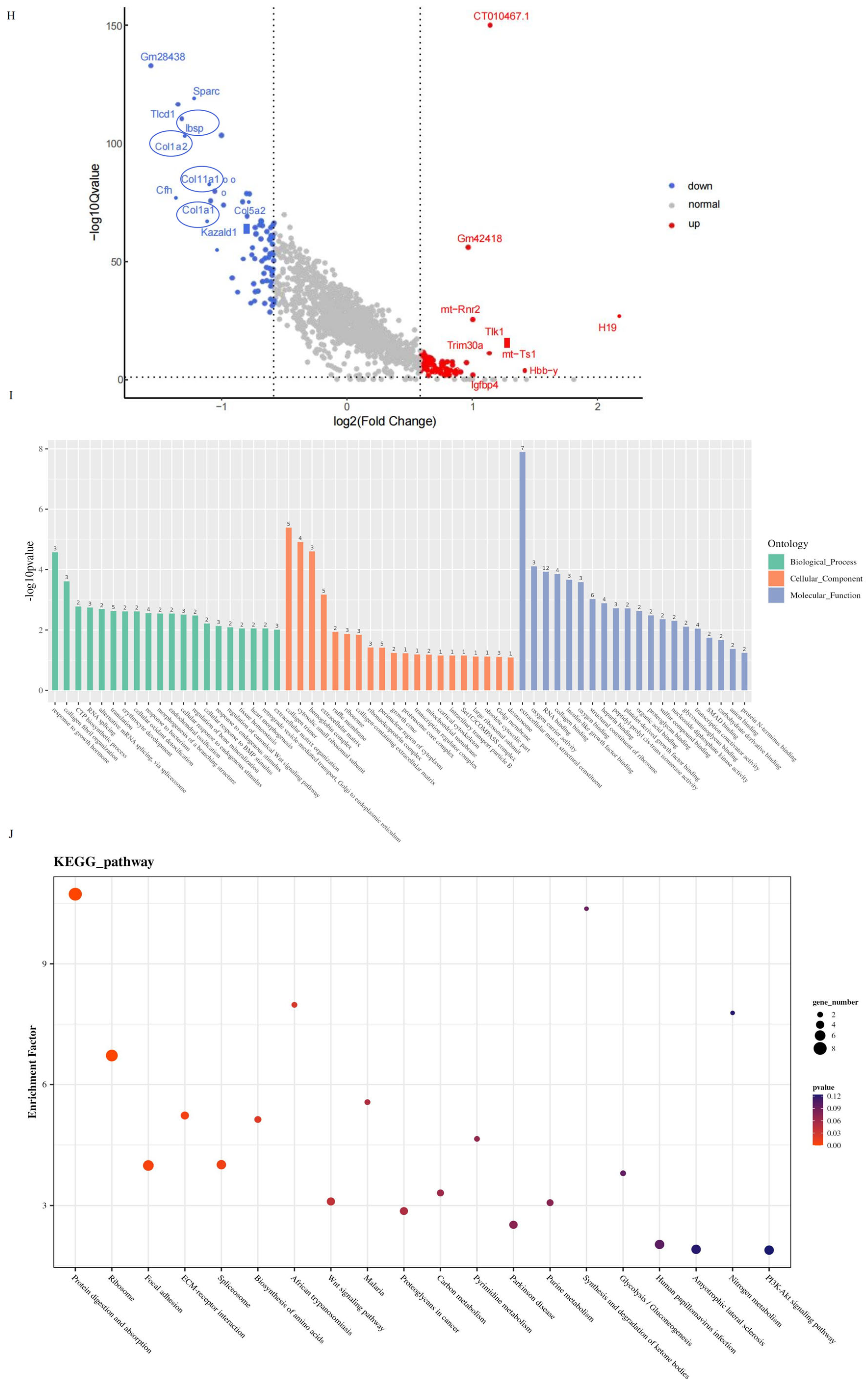
2.5. Impaired Mandibular Mineralization in Arhgap29−/− Mice: Gene Expression and Pathway Alterations
2.6. Decreased Transcriptional Levels of Bone Development-Related Molecules in Digits of Arhgap29−/− Mice
2.7. Knocking out Arhgap29 in Calvarial Cells Decreases Osteoblast Differentiation and Mineralization
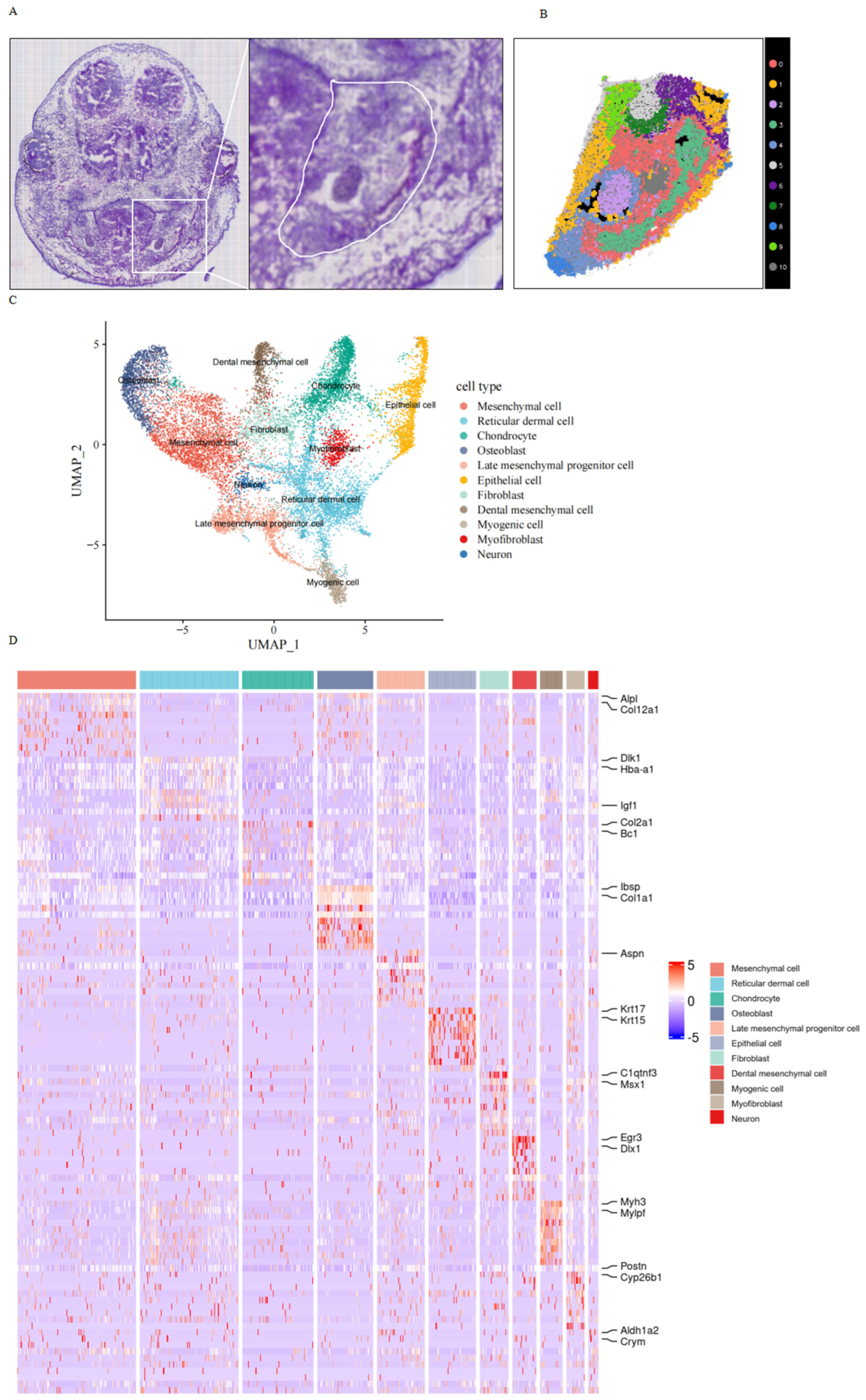
2.8. Impact of Arhgap29 Knockout on Early Mandibular Development in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Model Establishment
4.2. Micro-CT Scanning and Analysis
4.3. Mouse Skeletal Staining
4.3.1. Alcian Blue Staining
4.3.2. Alcian Blue/Alizarin Red Staining
4.4. H&E Staining
4.5. Immunohistochemical Staining
4.6. Von Kossa Staining
4.7. TRAP Staining
4.8. RNA Sequencing Analysis
4.9. Spatial Transcriptome Sequencing
4.10. Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR
4.11. Isolation of Osteoblasts and In Vitro Differentiation
4.12. ALP and Alizarin Red Staining
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mossey, P.A.; Little, J.; Munger, R.G.; Dixon, M.J.; Shaw, W.C. Cleft lip and palate. Lancet 2009, 374, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimov, F.; Nieminen, P.; Kumari, P.; Juuri, E.; Nikopensius, T.; Paraiso, K.; German, J.; Karvanen, A.; Kals, M.; Elnahas, A.G.; et al. High incidence and geographic distribution of cleft palate in Finland are associated with the IRF6 gene. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Cui, R.; Chi, H.; Wan, T.; Ma, D.; Zhang, J.; Cai, M. A novel IRF6 gene mutation impacting the regulation of TGFbeta2-AS1 in the TGFbeta pathway: A mechanism in the development of Van der Woude syndrome. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1397410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruojing, L.; Ruizhi, L.; Zhuo, C.; Shujuan, Z.; Jingtao, L.; Xing, Y. Cephalometric analyses of the correlation between nasal and maxilla morphology among adult patients with cleft. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2025, 103, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, A.; Spinner, A. Hemifacial Microsomia. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, K.; Hellinger, J.; Kansy, M.; Wegwitz, F.; Bauerschmitz, G.; Emons, G.; Grundker, C. Influence of Arhgap29 on the Invasion of Mesenchymal-Transformed Breast Cancer Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranji, P.; Pairet, E.; Helaers, R.; Bayet, B.; Gerdom, A.; Gil-da-Silva-Lopes, V.L.; Revencu, N.; Vikkula, M. Four putative pathogenic Arhgap29 variants in patients with non-syndromic orofacial clefts (NsOFC). Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2025, 33, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabrowska, J.; Biedziak, B.; Szponar-Zurowska, A.; Budner, M.; Jagodzinski, P.P.; Ploski, R.; Mostowska, A. Identification of novel susceptibility genes for non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate using NGS-based multigene panel testing. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2022, 297, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, L.C.; Naridze, R.L.; DeMali, K.A.; Lusche, D.F.; Kuhl, S.; Soll, D.R.; Schutte, B.C.; Dunnwald, M. Interferon regulatory factor 6 regulates keratinocyte migration. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 2840–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, B.J.; Palmer, K.; Sharp, J.C.; Pratt, C.H.; Murray, S.A.; Dunnwald, M. Arhgap29 Mutation Is Associated with Abnormal Oral Epithelial Adhesions. J. Dent. Res. 2017, 96, 1298–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, D.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Ruan, W.; Zhang, B.; Ma, J.; Duan, X.; Huang, Y. Arhgap29 deficiency causes EEC like syndrome in mice. Genes Dis. 2024, 12, 101404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diewert, V.M. Correlation between alterations in Meckel’s cartilage and induction of cleft palate with beta-aminoproprionitrile in the rat. Teratology 1981, 24, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seegmiller, R.E.; Fraser, F.C. Mandibular growth retardation as a cause of cleft palate in mice homozygous for the chondrodysplasia gene. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 1977, 38, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, N.; Singh, A. Anesthetic Consideration in Pierre Robin Sequence. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Huo, S.; He, W.; Huang, C.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, X.; Qian, Y.; Chen, C.; Dai, Z.; Yang, X.; et al. Fine-tuning of Wnt signaling by RNA surveillance factor Smg5 in the mouse craniofacial development. iScience 2025, 28, 111972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiais-Thibaud, M.; Simion, P.; Venteo, S.; Munoz, D.; Marcellini, S.; Mazan, S.; Haitina, T. Skeletal Mineralization in Association with Type X Collagen Expression Is an Ancestral Feature for Jawed Vertebrates. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2265–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govaerts, D.; Kalantary, S.; Van de Casteele, E.; Nadjmi, N. Mandibular distraction osteogenesis in children with Pierre Robin sequence: Long-term analysis of teeth and jaw growth. Br. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 62, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Maxson, R.E.J. Recent advances in craniofacial morphogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 2006, 235, 2353–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldatov, R.; Kaucka, M.; Kastriti, M.E.; Petersen, J.; Chontorotzea, T.; Englmaier, L.; Akkuratova, N.; Yang, Y.; Haring, M.; Dyachuk, V.; et al. Spatiotemporal structure of cell fate decisions in murine neural crest. Science 2019, 364, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, E.; Bonelli, F.; Bievel-Radulescu, R.; Decastello, N.; Ferrari, S.; Barbaro, V.; Ponzin, D. Ocular Manifestations in Patients Affected by p63-Associated Disorders: Ectrodactyly-Ectodermal Dysplasia-Clefting (EEC) and Ankyloblepharon-Ectodermal Defects-Cleft Lip Palate (AEC) Syndromes. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katoh, Y.; Katoh, M. Identification and characterization of ARHGAP27 gene in silico. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2004, 14, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, C.C.; Taylor, S.H.; Garva, R.; Holmes, D.F. Zeef, L.A.; Soininen, R.; Boot-Handford, R.P.; Kadler, K.E. Arhgap28 is a RhoGAP that inactivates RhoA and downregulates stress fibers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, B.K.; Miyake, T. The membranous skeleton: The role of cell condensations in vertebrate skeletogenesis. Anat. Embryol. 1992, 186, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, A.D.; Olsen, B.R. Bone development. Bone 2015, 80, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, C.; Anderson, P.; Schwarz, Q.; Wiszniak, S. Vessel-derived angiocrine IGF1 promotes Meckel’s cartilage proliferation to drive jaw growth during embryogenesis. Development 2020, 147, dev190488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chai, Y. Regulatory mechanisms of jaw bone and tooth development. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2019, 133, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, F.; Ornitz, D.M. Development of the endochondral skeleton. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, J.P.; Bordoni, B. Histology, Osteoblasts. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Svandova, E.; Anthwal, N.; Tucker, A.S.; Matalova, E. Diverse Fate of an Enigmatic Structure: 200 Years of Meckel’s Cartilage. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, K.; Oka, S.; Hosokawa, R.; Bringas, P.J.; Brockhoff, H.C.N.; Nonaka, K.; Chai, Y. TGF-beta mediated Dlx5 signaling plays a crucial role in osteo-chondroprogenitor cell lineage determination during mandible development. Dev. Biol. 2008, 321, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjidakis, D.J. Androulakis, I.I. Bone remodeling. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1092, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florencio-Silva, R.; Sasso, G.R.D.S.; Sasso-Cerri, E.; Simoes, M.J.; Cerri, P.S. Biology of Bone Tissue: Structure, Function, and Factors That Influence Bone Cells. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 421746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrack, D.S.; Thul, R.; Owen, M.R. Modelling the coupling between intracellular calcium release and the cell cycle during cortical brain development. J. Theor. Biol. 2014, 347, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kito, H.; Ohya, S. Role of K+ and Ca2+-Permeable Channels in Osteoblast Functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winslow, M.M.; Pan, M.; Starbucks, M.; Gallo, E.M.; Deng, L.; Karsenty, G.; Crabtree, G.R. Calcineurin/NFAT signaling in osteoblasts regulates bone mass. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilquil, C.; Alvandi, Z.; Opas, M. Calreticulin regulates a switch between osteoblast and chondrocyte lineages derived from murine embryonic stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 6861–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daino, K.; Ugolin, N.; Altmeyer-Morel, S.; Guilly, M.; Chevillard, S. Gene expression profiling of alpha-radiation-induced rat osteosarcomas: Identification of dysregulated genes involved in radiation-induced tumorigenesis of bone. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Chen, M.; Chen, P.; Chen, C.; Tsai, S.; Cheng, C.; Sun, J. A mutation of the Col2a1 gene (G1170S) alters the transgenic murine phenotype and cartilage matrix homeostasis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trainor, P.A.; Merrill, A.E. Ribosome biogenesis in skeletal development and the pathogenesis of skeletal disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014, 1842, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, G.; Montanaro, L. How Altered Ribosome Production Can Cause or Contribute to Human Disease: The Spectrum of Ribosomopathies. Cells 2020, 9, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Tan, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Rong, X.; Lu, L.; Li, Y. The ribosome biogenesis protein Esf1 is essential for pharyngeal cartilage formation in zebrafish. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 3464–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto, E.; Ebe, Y.; Kanaya, S.; Tsuchiya, M.; Nakamura, T.; Tamura, M.; Shimauchi, H. Wnt5a signaling is a substantial constituent in bone morphogenetic protein-2-mediated osteoblastogenesis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnell, L.M.; Jonason, J.H.; Loiselle, A.E.; Kohn, A.; Schwarz, E.M.; Hilton, M.J.; O’Keefe, R.J. TAK1 regulates cartilage and joint development via the MAPK and BMP signaling pathways. J. Bone. Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 1784–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thouverey, C.; Caverzasio, J. Suppression of p38alpha MAPK Signaling in Osteoblast Lineage Cells Impairs Bone Anabolic Action of Parathyroid Hormone. J. Bone. Miner. Res. 2016, 31, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlMuraikhi, N.; Binhamdan, S.; Alaskar, H.; Alotaibi, A.; Tareen, S.; Muthurangan, M.; Alfayez, M. Inhibition of GSK-3beta Enhances Osteoblast Differentiation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells through Wnt Signalling Overexpressing Runx2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, K.Z.; Cozzone, A.; Caetano-Lopes, J.; Harris, M.P.; Fisher, S. Osteoclast activity sculpts craniofacial form to permit sensorineural patterning in the zebrafish skull. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 969481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Name | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | CATGTTCCAGTATGACTCCACTC | GGCCTCACCCCATTTGATGT |
| Cacnb1 | TCACCTTTGAGCCCAAGGAC | GGCACGTGCTCTGTCGATTT |
| Srl | TTTCAGGACAAGCAGAGGTGG | GATTTGCCAACACTCCACGG |
| Dhrs7c | TCAGTGTGAAGACGTGAGCA | TGGCATAGAGGCTCTCCAGT |
| Stac3 | TCTCAGCTGTCCACTGTCCT | CTTCAGTCGCTGTAGCCCAC |
| Cav3 | TCAATGAGGACATTGTGAAGGTAGA | CAGTGTAGACAACAGGCGGT |
| Camk1 | AGCAGGCGGAAGACATTAGG | TTGGGGTGCTTGATCTTGTGTGT |
| Mustn1 | ATGCGGGACTACGAGCAAG | GGTTGGGGACATTGGGCATA |
| Fgf18 | GATGTATTCAGCGCCCTCCG | TCCACTAGGAGCTGGGCATAC |
| Rassf2 | GCACCTTATTCCCTCCACCC | CTCGTCTTCCTCCTCTCGGT |
| Trp53inp2 | TCTGCTATTACTGCTCTGGCA | AGGAGCTGTATAGCTGTCCTGT |
| Prkaca | TGCAGCAGATCTTATGAGGC | TGCTTTAGCTTCACCACCTTCT |
| Gab2 | CCGACTCCATCGAGCTTCTT | TGGGCTCATGGGGATGTAGA |
| Col1a1 | TTCTGCCCGGAAGAATACGTATC | GGACATCTGGGAAGCAAAGTTTC |
| Ibsp | CGGCCACGCTACTTTCTTTATAA | AGTGTGGAAAGTGTGGAGTTCTC |
| Alpl | AGCTTCCTTCTGTTCGTGCT | TTGACGTTCCGATCCTGAGT |
| Ocn | GGAGGGCAATAAGGTAGTGAACA | TAGGGCAGCACAGGTCCTAAATA |
| Opn | GCCGCCTGATCAAGTTCTCC | GCTGCTGCCCACAGTAGAAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Chi, D.; Wang, Y.; Ruan, W.; Ma, J.; Duan, X.; Huang, Y. Arhgap29 Deficiency Directly Leads to Systemic and Craniofacial Skeletal Abnormalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104647
Zhang B, Pan X, Chi D, Wang Y, Ruan W, Ma J, Duan X, Huang Y. Arhgap29 Deficiency Directly Leads to Systemic and Craniofacial Skeletal Abnormalities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104647
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Beibei, Xiaoyun Pan, Dandan Chi, Yumeng Wang, Wenyan Ruan, Jian Ma, Xiaohong Duan, and Yongqing Huang. 2025. "Arhgap29 Deficiency Directly Leads to Systemic and Craniofacial Skeletal Abnormalities" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104647
APA StyleZhang, B., Pan, X., Chi, D., Wang, Y., Ruan, W., Ma, J., Duan, X., & Huang, Y. (2025). Arhgap29 Deficiency Directly Leads to Systemic and Craniofacial Skeletal Abnormalities. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104647







