Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the YTH Domain-Containing Protein Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The YTH Gene Family in S. miltiorrhiza
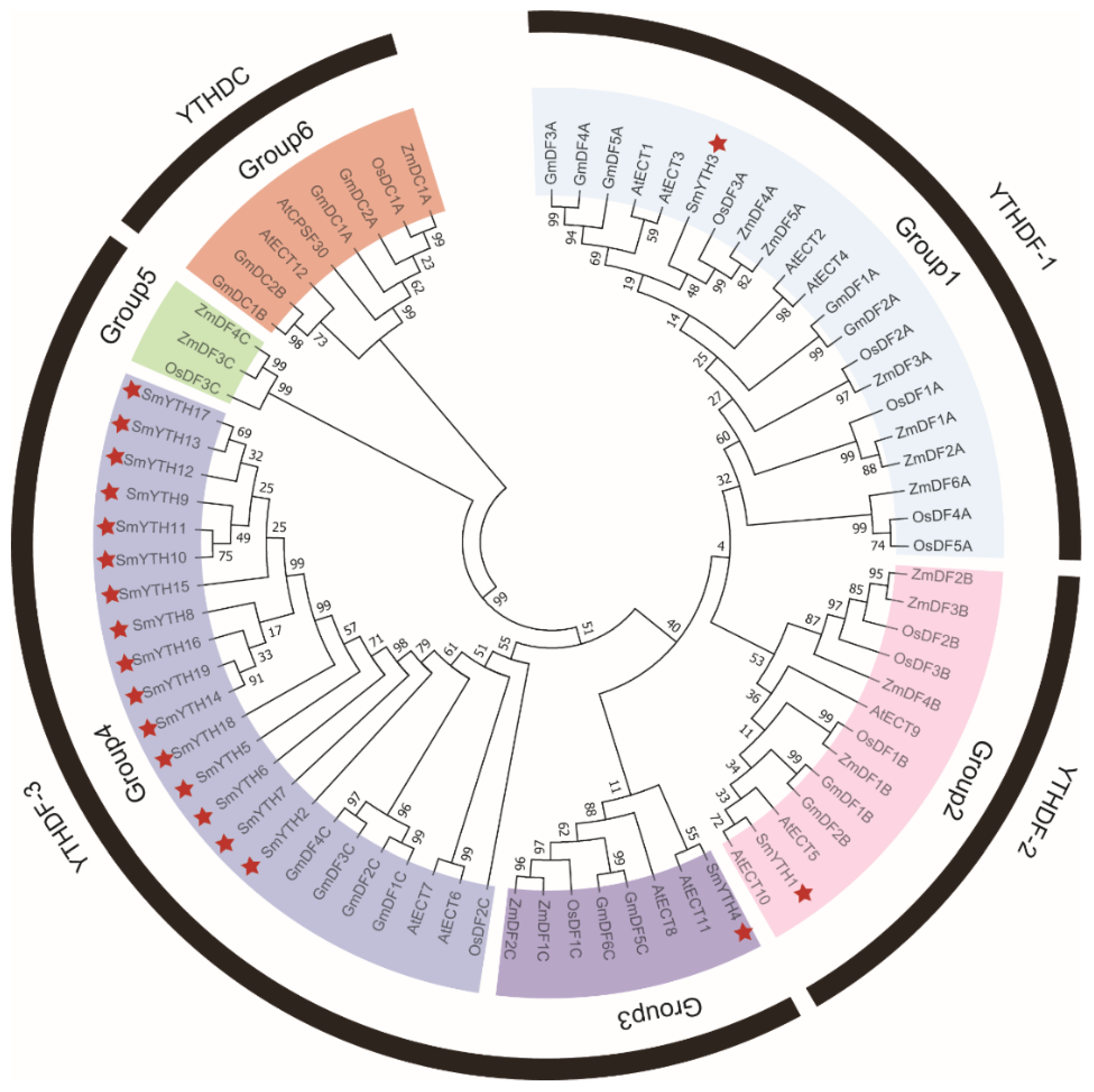
2.2. Evolutionary Relationship of SmYTH Proteins
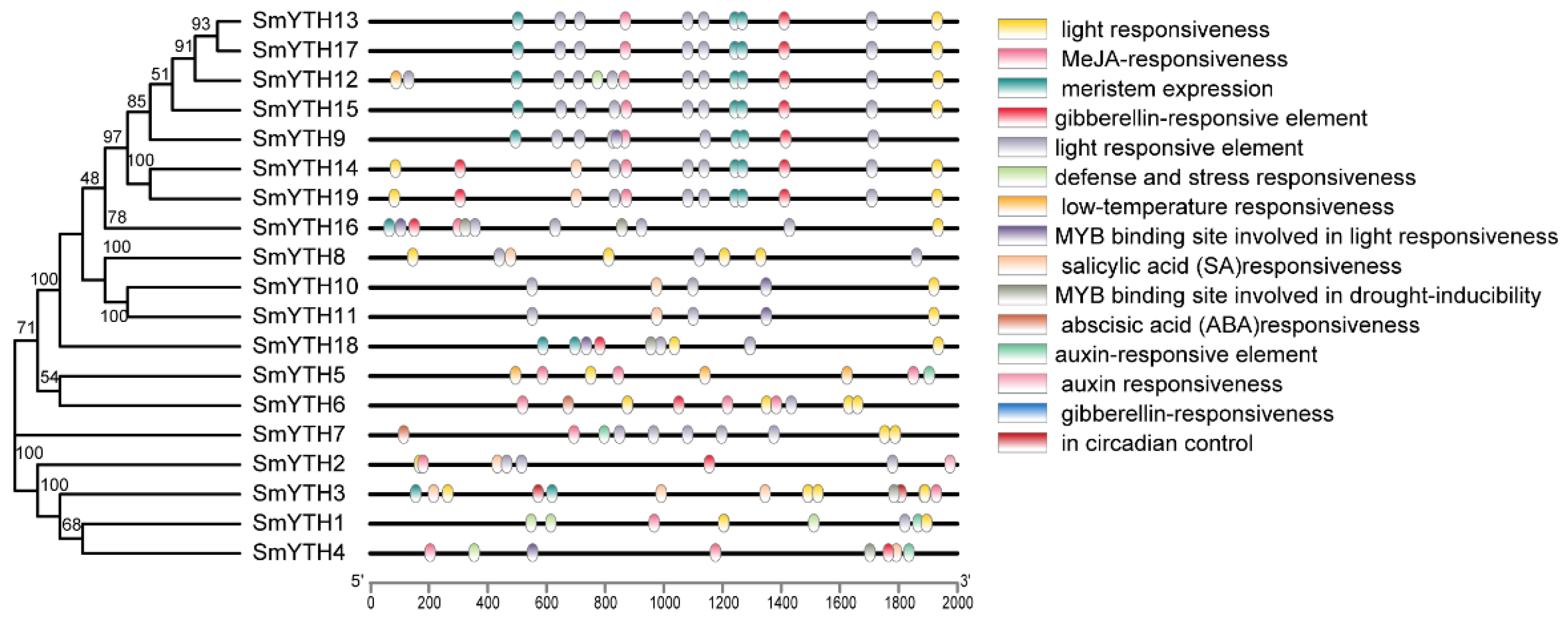
2.3. Gene Structure, Conserved Domain, and Conserved Motif of SmYTHs
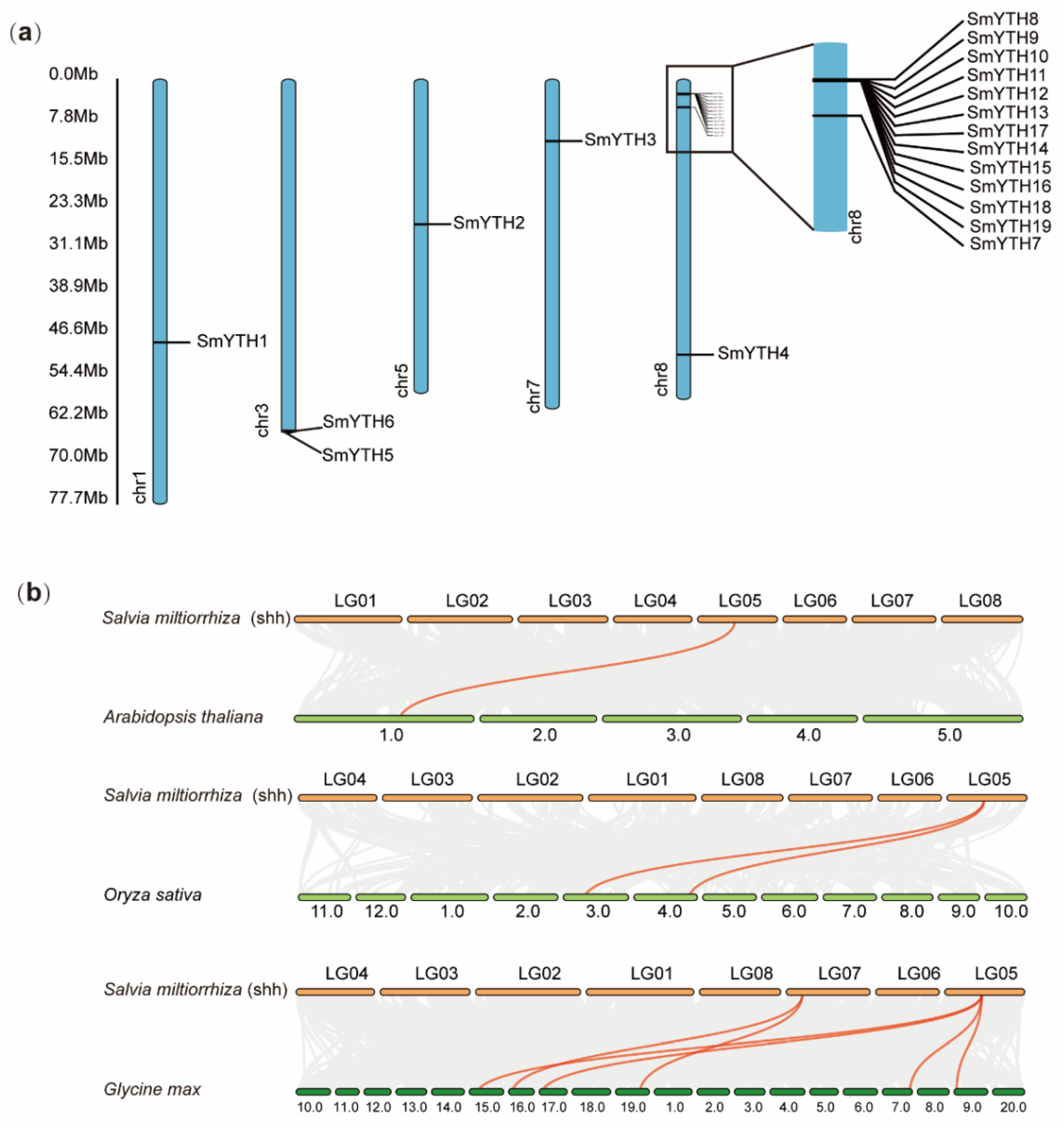
2.4. Chromosome Location of SmYTH Genes and Collinear Relationships
2.5. Cis-Acting Elements in the Promoter Region of SmYTH Genes
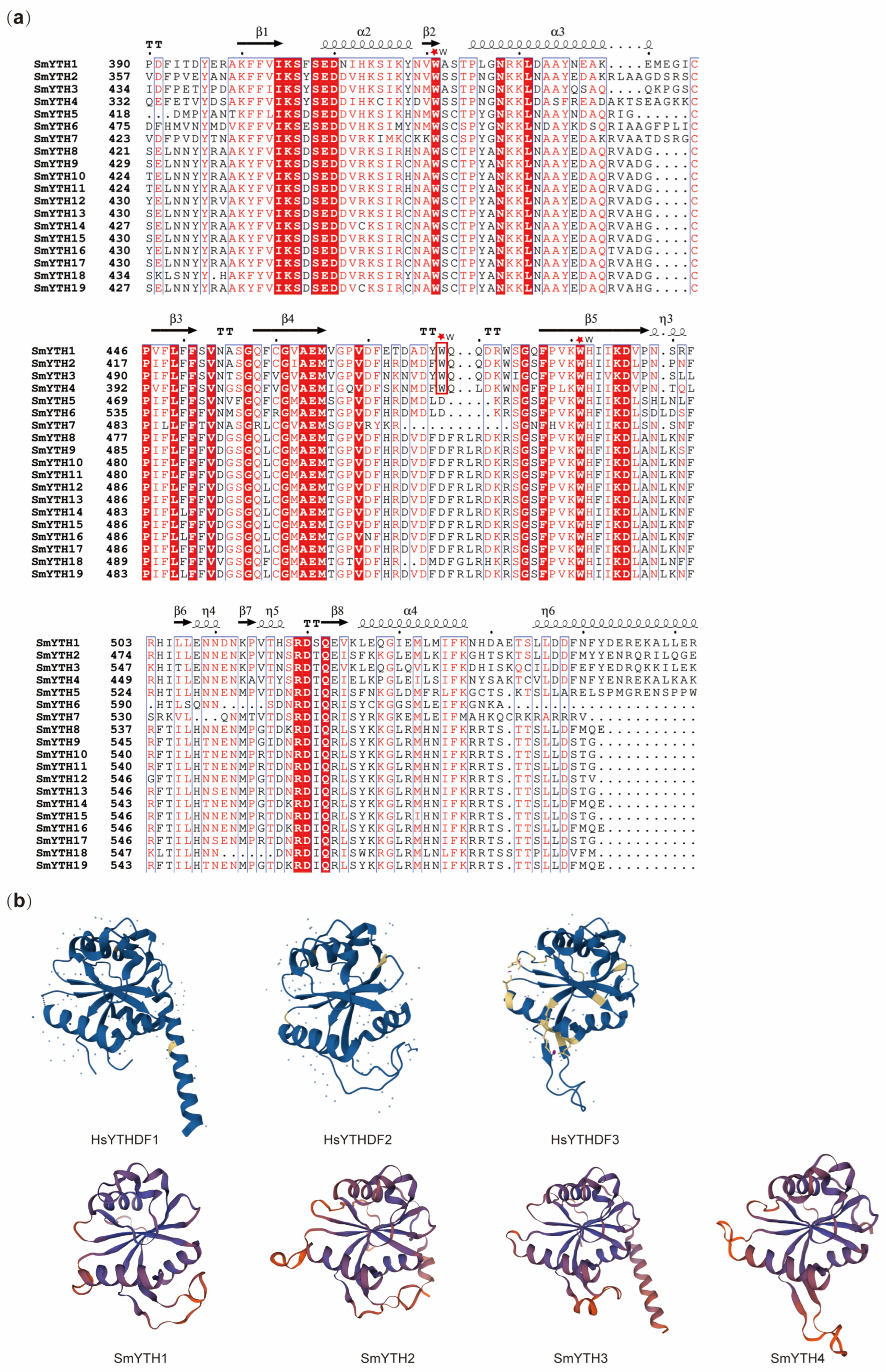
2.6. The Structure of SmYTH Proteins
2.7. SmYTH1–SmYTH4 in Phase Separation
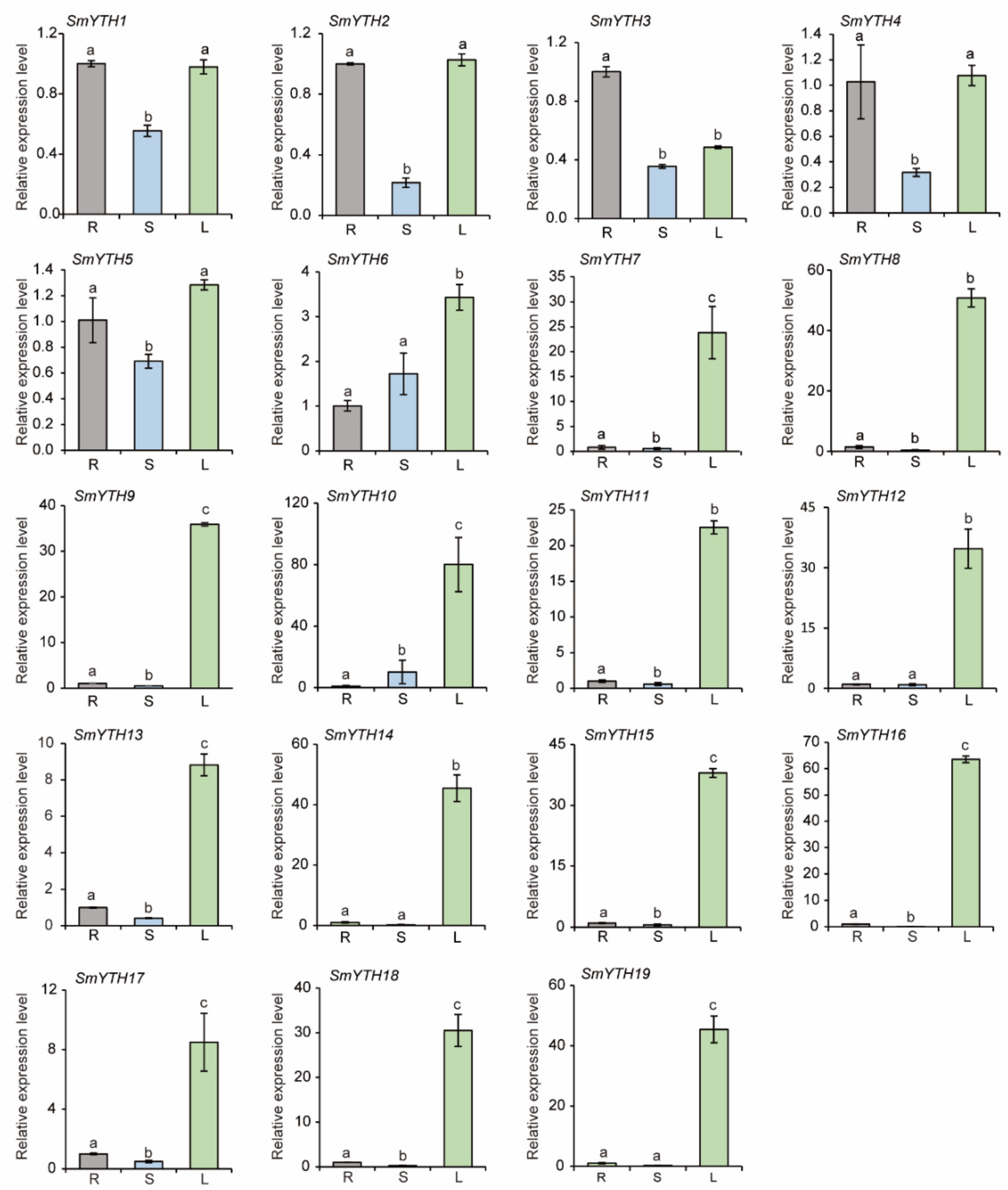
2.8. Differential Expression of SmYTH Genes in S. miltiorrhiza
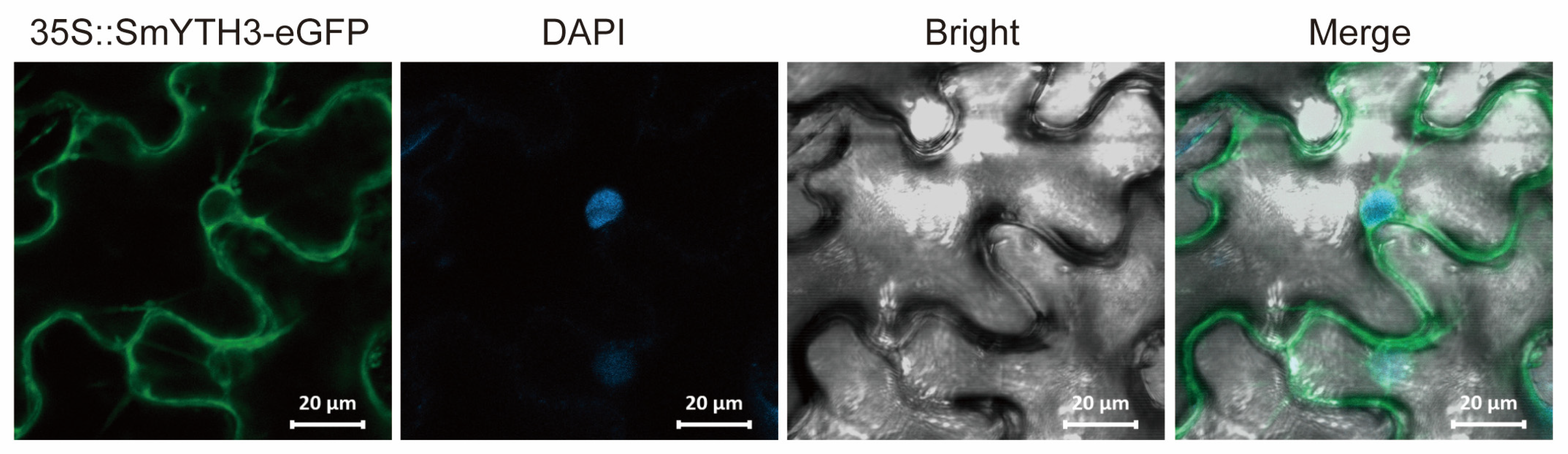
2.9. Subcellular Localization of SmYTH3
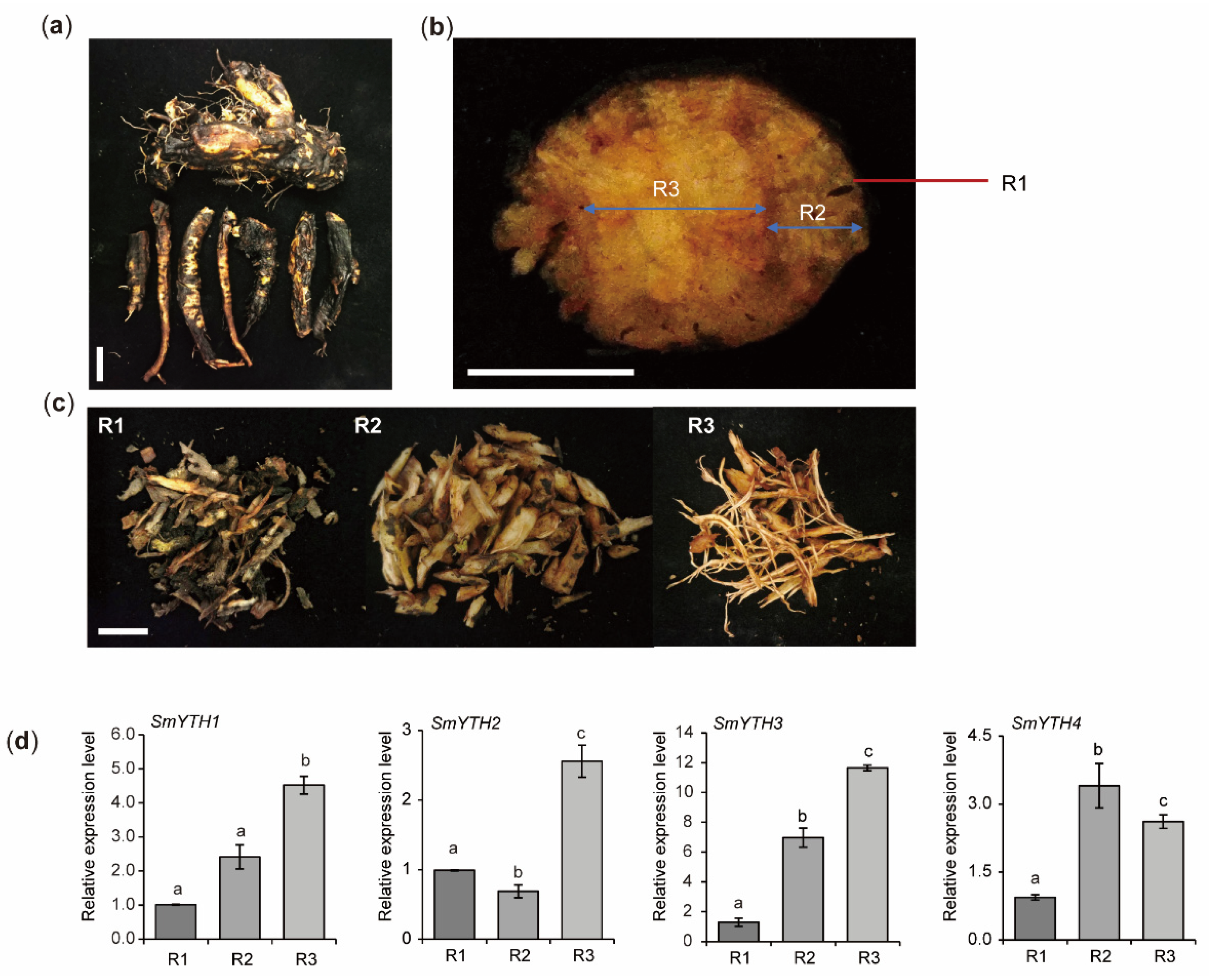
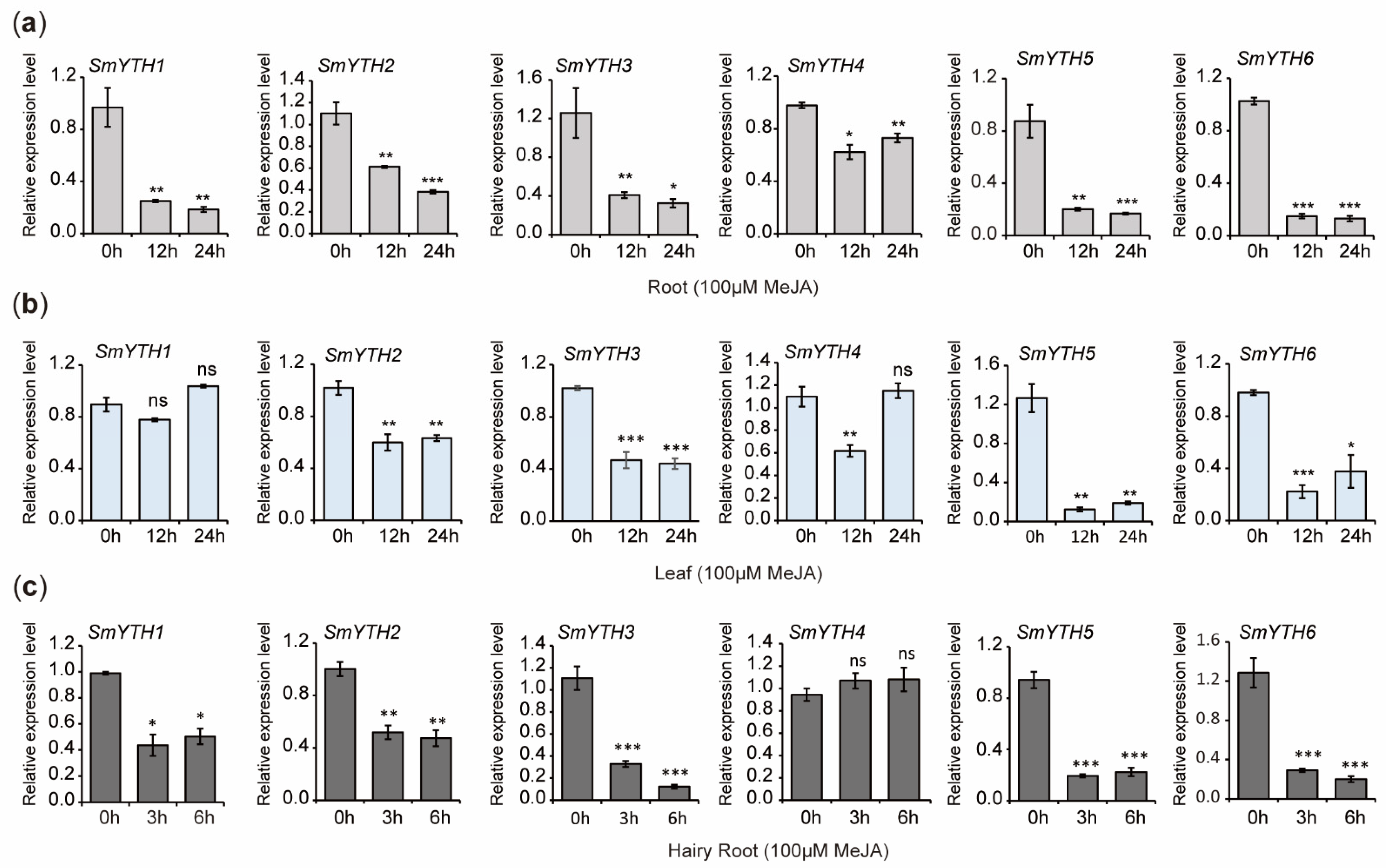
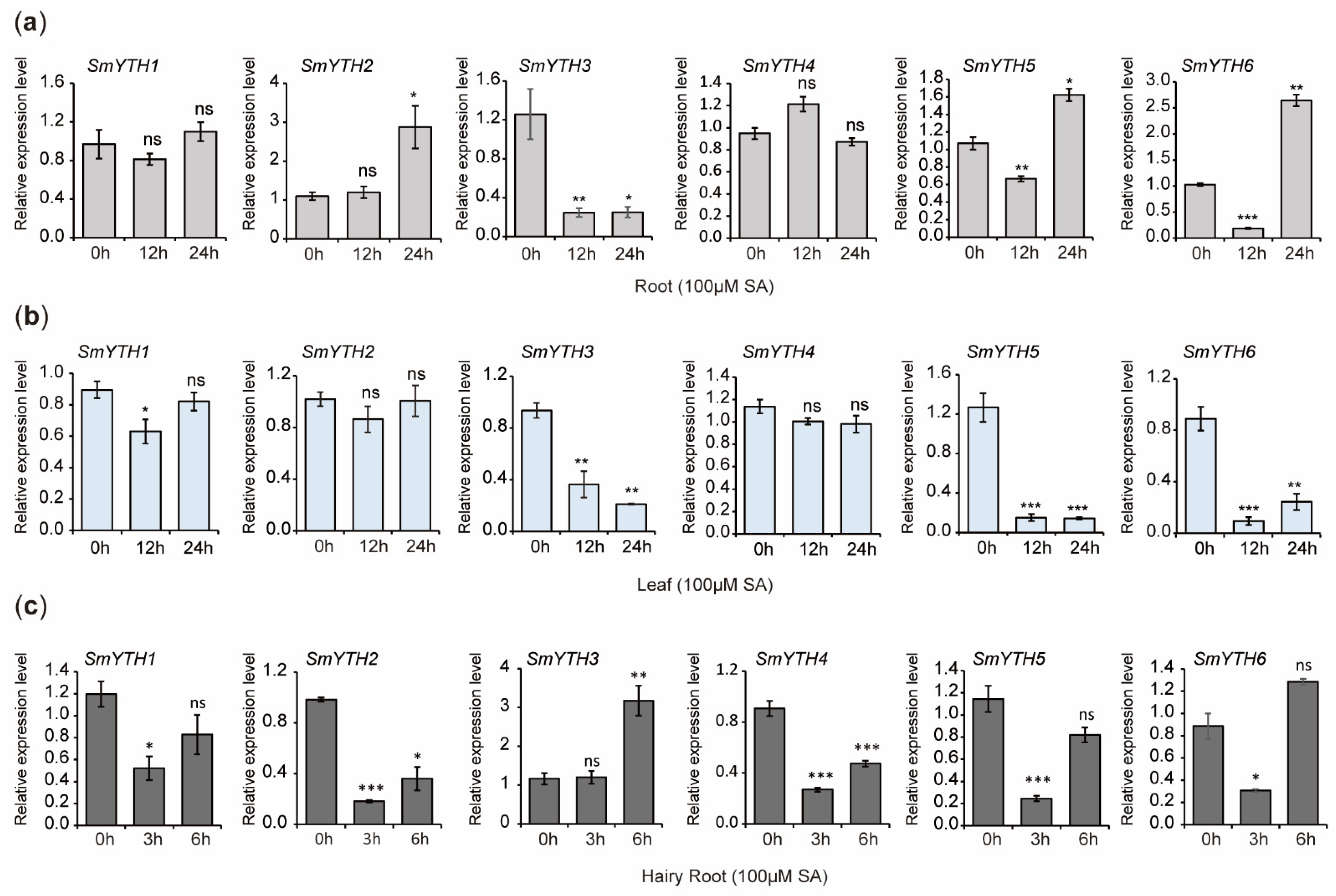
2.10. PGR Responses of SmYTHs in S. miltiorrhiza Plantlets and Hairy Roots
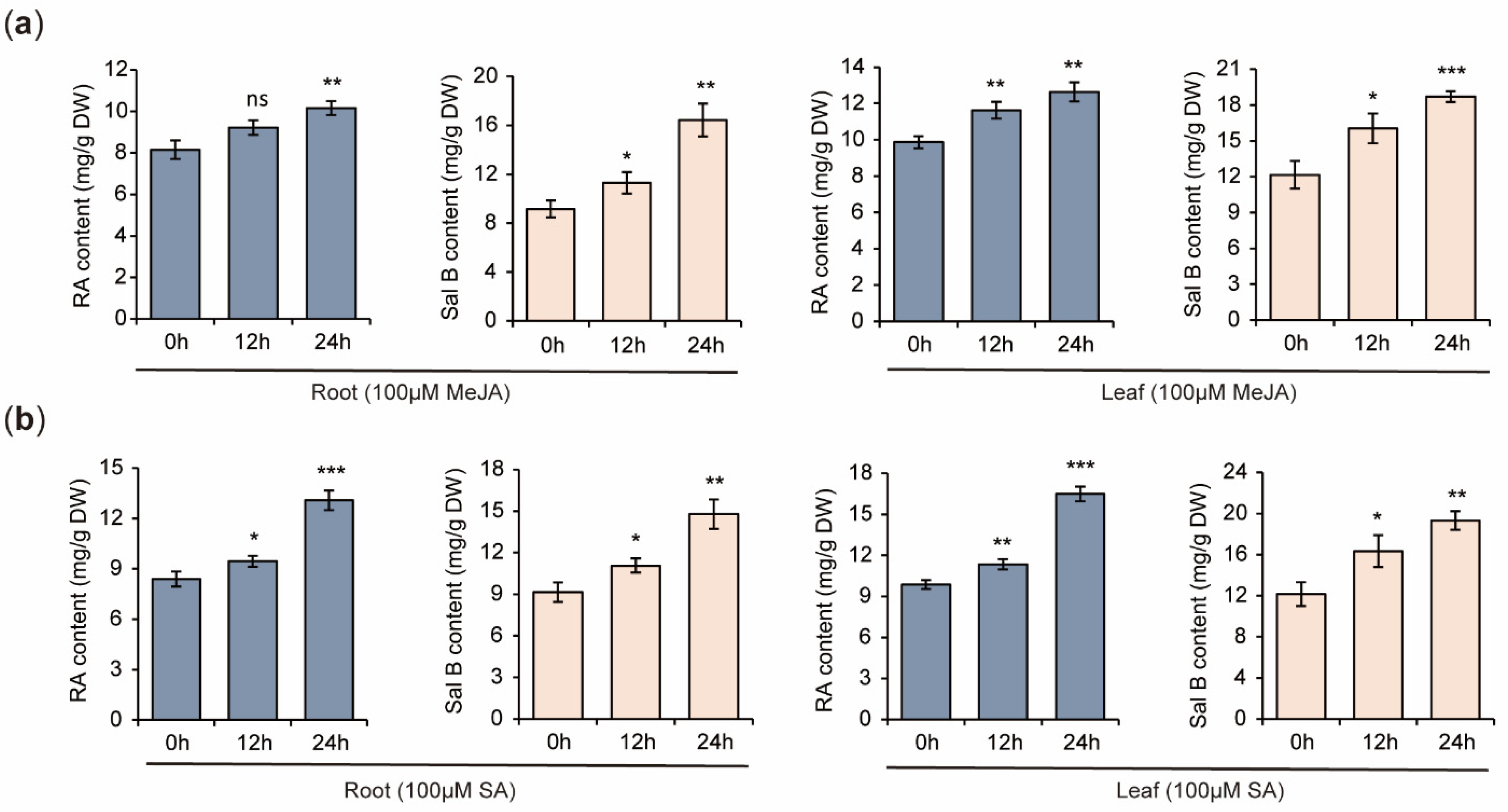
2.11. Increases of RA and Sal B Contents in S. miltiorrhiza Plantlets Treated with MeJA and SA
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Growth Conditions, Hairy Root Cultivation, and Hormone/PGR Treatments
4.2. Identification of the SmYTH Gene Family
4.3. Analyses of Phylogenetic Tree, Gene Structure, Conserved Motif, Conserved Domain, and Cis-Acting Element
4.4. Chromosome Localization and Synteny Relationship Analysis
4.5. Structure Construction and Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation (LLPS) Prediction
4.6. Subcellular Localization of SmYTH3 Protein
4.7. Gene Expression Analysis by Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.8. HPLC Determination of Phenolic Acids
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boccaletto, P.; Stefaniak, F.; Ray, A.; Cappannini, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Purta, E.; Kurkowska, M.; Shirvanizadeh, N.; Destefanis, E.; Groza, P.; et al. MODOMICS: A database of RNA modification pathways. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Li, H.; Bodi, Z.; Button, J.; Vespa, L.; Herzog, M.; Fray, R.G. MTA is an Arabidopsis messenger RNA adenosine methylase and interacts with a homolog of a sex-specific splicing factor. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Růžička, K.; Zhang, M.; Campilho, A.; Bodi, Z.; Kashif, M.; Saleh, M.; Eeckhout, D.; El-Showk, S.; Li, H.; Zhong, S.; et al. Identification of factors required for m6A mRNA methylation in Arabidopsis reveals a role for the conserved E3 ubiquitin ligase HAKAI. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Liang, Z.; Gu, X.; Chen, Y.; Teo, Z.W.; Hou, X.; Cai, W.M.; Dedon, P.C.; Liu, L.; Yu, H. N6-methyladenosine RNA modification regulates shoot stem cell fate in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2016, 38, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bodi, Z.; Mackinnon, K.; Zhong, S.; Archer, N.; Mongan, N.P.; Simpson, G.G.; Fray, R.G. Two zinc finger proteins with functions in m6A writing interact with HAKAI. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L. Functional interdependence of N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase complex subunits in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2023, 35, 1901–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, J.; Song, P.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Q.; Yu, Q.; Jia, G. FIONA1 is an RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase affecting Arabidopsis photomorphogenesis and flowering. Genome Biol. 2022, 23, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pérez, M.; Aparicio, F.; López-Gresa, M.P.; Bellés, J.M.; Sánchez-Navarro, J.A.; Pallás, V. Arabidopsis m6A demethylase activity modulates viral infection of a plant virus and the m6A abundance in its genomic RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10755–10760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, Q.; Tang, Q.; Chen, S.; Jia, G. The RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase ALKBH9B modulates ABA responses in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 2361–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.C.; Wei, L.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, Z.; Chen, P.R.; He, C.; Jia, G. ALKBH10B is an RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase affecting Arabidopsis floral transition. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2995–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Wen, H.; Sun, W.; Qin, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, H.; Zhao, B.S.; Mesquita, A.; Liu, C.; Yuan, C.L.; et al. Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2013, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Kasowitz, S.D.; Ma, J.; Anderson, S.J.; Leu, N.A.; Xu, Y.; Gregory, B.D.; Schultz, R.M.; Wang, P.J. Nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 regulates alternative polyadenylation and splicing during mouse oocyte development. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007412. [Google Scholar]
- Song, P.; Yang, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, Q.; Shi, L.; Tayier, S.; Jia, G. Arabidopsis N6-methyladenosine reader CPSF30-L recognizes FUE signals to control polyadenylation site choice in liquid-like nuclear bodies. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fustin, J.M.; Doi, M.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Hida, H.; Nishimura, S.; Yoshida, M.; Isagawa, T.; Morioka, M.S.; Kakeya, H.; Manabe, I.; et al. RNA-methylation-dependent RNA processing controls the speed of the circadian clock. Cell 2013, 155, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Zhuang, X. m6A-binding YTHDF proteins promote stress granule formation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2020, 16, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, H.; Hsu, P.J.; Liu, C.; He, C. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, R.J.; Zaccara, S.; Klein, P.; Olarerin-George, A.; Namkoong, S.; Pickering, B.F.; Patil, D.P.; Kwak, H.; Lee, J.H.; Jaffrey, S.R. m6A enhances the phase separation potential of mRNA. Nature 2019, 571, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.; Roundtree, I.A.; Lu, Z.; Han, D.; Ma, H.; Weng, X.; Chen, K.; Shi, H.; He, C. N6-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell 2015, 161, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Wei, L.; Chen, Z.; Cai, Z.; Lu, Q.; Wang, C.; Tian, E.; Jia, G. m6A readers ECT2/ECT3/ECT4 enhance mRNA stability through direct recruitment of the poly(A) binding proteins in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Tang, R.; Li, X.; Tian, S.; Li, B.; Qin, G. N6-methyladenosine RNA modification regulates strawberry fruit ripening in an ABA-dependent manner. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, S.; Yu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; et al. RNA demethylation increases the yield and biomass of rice and potato plants in field trials. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1581–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Cai, J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, K.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yun, J.Y.; Xu, T.; Kang, H. N6-methyladenosine mRNA methylation is important for salt stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2021, 106, 1759–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scutenaire, J.; Deragon, J.M.; Jean, V.; Benhamed, M.; Raynaud, C.; Favory, J.J.; Merret, R.; Bousquet-Antonelli, C. The YTH domain protein ECT2 is an m6A reader required for normal trichome branching in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 986–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.H.; Song, P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Tang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Duan, H.C.; Jia, G. The m6A reader ECT2 controls trichome morphology by affecting mRNA stability in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Peled-Zehavi, H.; Galili, G. The m6A reader ECT2 post-transcriptionally regulates proteasome activity in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2020, 228, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas-Hernández, L.; Bressendorff, S.; Hansen, M.H.; Poulsen, C.; Erdmann, S.; Brodersen, P. An m6A-YTH module controls developmental timing and morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 952–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arribas-Hernández, L.; Simonini, S.; Hansen, M.H.; Paredes, E.B.; Bressendorff, S.; Dong, Y.; Østergaard, L.; Brodersen, P. Recurrent requirement for the m6A-ECT2/ECT3/ECT4 axis in the control of cell proliferation during plant organogenesis. Development 2020, 147, dev189134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Liu, C.; Meng, F.; Hu, L.; Fu, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, N.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Ma, F. The m6A reader MhYTP2 regulates MdMLO19 mRNA stability and antioxidant genes translation efficiency conferring powdery mildew resistance in apple. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 20, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Roundtree, I.A.; Tempel, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; He, C.; Min, J. Structural basis for selective binding of m6A RNA by the YTHDC1 YTH domain. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, D.P.; Pickering, B.F.; Jaffrey, S.R. Reading m6A in the transcriptome: m6A-binding proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Ying, S.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. Linking the YTH domain to cancer: The importance of YTH family proteins in epigenetics. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.; Sun, H.; Xu, C. YTH domain: A family of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) readers. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Pei, G.; Li, D.; Li, R.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, Q.C.; Li, P. Multivalent m6A motifs promote phase separation of YTHDF proteins. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Hong, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ouyang, Z.; Song, F. Genome-wide identification, biochemical characterization, and expression analyses of the YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 32, 1169–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Sun, J.; Wu, B.; Gao, Y.; Nie, H.; Nie, Z.; Quan, S.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Li, S. CPSF30-L-mediated recognition of mRNA m6A modification controls alternative polyadenylation of nitrate signaling-related gene transcripts in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Liu, K.; Kim, E.Y.; Medina-Puche, L.; Dong, H.; Di, M.; Singh, R.M.; Li, M.; Qi, S.; Meng, Z.; et al. The m6A reader ECT1 drives mRNA sequestration to dampen salicylic acid–dependent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 746–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Tang, Q.; Song, P.; Tian, E.; Yang, J.; Jia, G. The m6A reader ECT8 is an abiotic stress sensor that accelerates mRNA decay in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 2908–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Su, T.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, C.E.; Ma, J.; Shao, Y.; Hua, C.; Shen, L.; Yu, H. N6-methyladenosine-mediated feedback regulation of abscisic acid perception via phase-separated ECT8 condensates in Arabidopsis. Nat. Plants 2024, 10, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amara, U.; Hu, J.; Park, S.J.; Kang, H. ECT12, an YTH-domain protein, is a potential mRNA m6A reader that affects abiotic stress responses by modulating mRNA stability in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 206, 108255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Song, P.; Wang, C.; Chen, S.; Hao, B.; Xu, Z.; Cai, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Gan, X.; et al. The RNA binding protein EHD6 recruits the m6A reader YTH07 and sequesters OsCOL4 mRNA into phase-separated ribonucleoprotein condensates to promote rice flowering. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 935–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Tang, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Diao, X.; Yu, J. The m6A reader SiYTH1 enhances drought tolerance by affecting the messenger RNA stability of genes related to stomatal closure and reactive oxygen species scavenging in Setaria italica. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 2569–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, H.; Song, P.; Gao, Y.; Deng, Z.; Huang, C.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Ye, B.; Cai, Z.; Pan, Y.; et al. The m6A reader SlYTH2 negatively regulates tomato fruit aroma by impeding the translation process. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2405100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S. Biosynthesis and regulatory mechanisms of bioactive compounds in Salvia miltiorrhiza, a model system for medicinal plant biology. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2021, 40, 243–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Jing, L.; Jiang, X.; Pu, C.; Zhao, S.; Yang, J.; Guo, J.; Cui, G.; Tang, J.; Ma, Y.; et al. The ERF-VII transcription factor SmERF73 coordinately regulates tanshinone biosynthesis in response to stress elicitors in Salvia miltiorrhiza. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 1940–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Shi, M.; Deng, C.; Lu, S.; Huang, F.; Wang, Y.; Kai, G. The methyl jasmonate-responsive transcription factor SmMYB1 promotes phenolic acid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Hortic. Res. 2021, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Deng, H.; Wei, J.; Feng, Q.; Liu, B.; Zuo, A.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J.; Dong, J.; Ma, P. SmJAZs-SmbHLH37/SmERF73-SmSAP4 module mediates jasmonic acid signaling to balance biosynthesis of medicinal metabolites and salt tolerance in Salvia miltiorrhiza. New Phytol. 2024, 244, 1450–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qiu, X.; Hou, X.; Li, D.; Jiang, M.; Cui, X.; Pan, X.; Shao, F.; Li, Q.; Xie, D.Y.; et al. Polymerization of proanthocyanidins under the catalysis of miR397a-regulated laccases in Salvia miltiorrhiza and Populus trichocarpa. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, M.; Pang, Y.; Hu, X.; Sun, C.; Zhou, H.; Deng, Y.; Lu, S. The Smi-miR858a-SmMYB module regulates tanshinone and phenolic acid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Peng, L.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Shao, L.; Liu, T.; Shou, M.; Lin, Q.; Wang, B.; Shi, M.; et al. Abscisic acid enhances SmAPK1-mediated phosphorylation of SmbZIP4 to positively regulate tanshinone biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. New Phytol. 2025, 245, 1124–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Bai, Z.; Pei, T.; Ding, K.; Liang, Z.; Gong, Y. The protein kinase SmSnRK2.6 positively regulates phenolic acid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza by interacting with SmAREB1. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S.; Battistuzzi, F.U. MEGA11: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Liu, K.; Ahmed, H.; Loppnau, P.; Schapira, M.; Min, J. Structural basis for the discriminative recognition of N6-methyladenosine RNA by the human YT521-B homology domain family of proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24902–24913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Li, Y. Prion–like proteins in plants: Key regulators of development and environmental adaptation via phase separation. Plants 2024, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Chang, Y.; Li, C.; Qiu, X.; Cui, X.; Meng, F.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Lu, S. Chromosome-level genome assembly of Salvia miltiorrhiza with orange roots uncovers the role of Sm2OGD3 in catalyzing 15,16-dehydrogenation of tanshinones. Hortic. Res. 2023, 10, uhad069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, D.; Zhou, L.; Yu, X.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Cao, X.; et al. JA-responsive transcription factor SmMYB97 promotes phenolic acid and tanshinone accumulation in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 14850–14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Shi, M.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yuan, T.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Kai, G. The biosynthesis of phenolic acids is positively regulated by the JA-responsive transcription factor ERF115 in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Guo, T.; Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Shao, Y.; Jia, X.; Liang, B.; Gong, X.; Ma, F. MhYTP1 and MhYTP2 from apple confer tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.; Ao, Q.; Tan, C.; Yang, Y. Genome-wide identification and characterization of YTH domain-containing genes, encoding the m6A readers, and their expression in tomato. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1229–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Yin, Y.; Zhao, Y. Genome-wide identification, characterization, and expression analysis of m6A readers-YTH domain-containing genes in alfalfa. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Yao, S.; Cheng, X.; Ji, K.; Yu, Q. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of members in the YT521-B homology domain-containing RNA binding protein family in Ginkgo biloba. Plants 2024, 13, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yao, S.; Cheng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, W.; Ren, X.; Ji, K.; Yu, Q. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in Cinnamomum camphora. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, S.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, X.; Wang, D.; Yu, W.; Ji, K.; Yu, Q. Genome-wide identification and characterization of the YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family in Liriodendron chinense. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Li, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, C.; Lin, A.; Lian, H. Comprehensive identification and expression analysis of the YTH family of RNA-binding proteins in strawberry. Plants 2023, 12, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.; Wang, W.; Xiao, X.; Sun, J.; Wu, B.; Zhao, Y.; Pei, S.; Fan, W.; Xu, D.; Qin, T. Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of Gossypium YTH domain-containing RNA-binding protein family and the role of GhYTH8 in response to drought stress. Plants 2023, 12, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Luo, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Xie, Q.; Wu, T.; Chen, G. Genome-wide identification, classification and expression analysis of m6A gene family in Solanum lycopersicum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Hu, B.; Guo, S.; Xue, Z.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C. miR394 and LCR cooperate with TPL to regulate AM initiation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, H.; Negi, H.; Sharma, B. Role of F-box E3-ubiquitin ligases in plant development and stress responses. Plant Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 1133–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorski, V.; Selberg, S.; Lalowski, M.; Karelson, M.; Kankuri, E. The structure and function of YTHDF epitranscriptomic m6A readers. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 44, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, X.; Mashiguchi, K.; Yamaguchi, S.; Lu, S. Biosynthesis and signal transduction of plant growth regulators and their effects on bioactive compound production in Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen). Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Shi, M.; Cui, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Kai, G. Effects of methyl jasmonate and salicylic acid on tanshinone production and biosynthetic gene expression in transgenic Salvia miltiorrhiza hairy roots. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2015, 62, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Yuan, L.; Wu, B.; Li, X.; Chen, S.; Lu, S. Genome-wide identification and characterization of novel genes involved in terpenoid biosynthesis in Salvia miltiorrhiza. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 2809–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; Lu, S.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; Thanki, N.; Yamashita, R.A.; et al. The conserved domain database in 2023. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescot, M.; Déhais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouzé, P.; Rombauts, S. PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: A “one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; De Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, A.K.; Nutter-Upham, A.; Lindquist, S.; King, O.D. PLAAC: A web and command-line application to identify proteins with prion-like amino acid composition. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2501–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene Name | Chromosome | Start | End | ORF (bp) | AA a | Mw b | pI c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SmYTH1 | Chr1 | 48,158,370 | 48,164,782 | 1827 | 608 | 66,859.19 | 5.15 |
| SmYTH2 | Chr5 | 26,492,103 | 26,496,935 | 2103 | 700 | 76,823.39 | 5.92 |
| SmYTH3 | Chr7 | 11,251,622 | 11,255,803 | 2097 | 698 | 76,342.98 | 6.9 |
| SmYTH4 | Chr8 | 50,414,449 | 50,420,087 | 1692 | 563 | 61,918.98 | 7.96 |
| SmYTH5 | Chr3 | 64,499,982 | 64,503,334 | 1785 | 594 | 68,037.9 | 5.17 |
| SmYTH6 | Chr3 | 64,383,621 | 64,386,316 | 1869 | 622 | 71,225.09 | 4.69 |
| SmYTH7 | Chr8 | 5,040,013 | 5,042,279 | 1725 | 574 | 65,632.12 | 5.28 |
| SmYTH8 | Chr8 | 2,540,335 | 2,542,918 | 1785 | 594 | 68,402.62 | 5.15 |
| SmYTH9 | Chr8 | 2,556,826 | 2,558,542 | 1797 | 598 | 69,114.55 | 5.29 |
| SmYTH10 | Chr8 | 2,565,385 | 2,567,524 | 1782 | 593 | 68,542.75 | 5.41 |
| SmYTH11 | Chr8 | 2,587,693 | 2,589,834 | 1782 | 593 | 68,542.75 | 5.41 |
| SmYTH12 | Chr8 | 2,601,514 | 2,603,695 | 1800 | 599 | 69,634.15 | 5.39 |
| SmYTH13 | Chr8 | 2,612,165 | 2,614,350 | 1800 | 599 | 69,678.27 | 5.56 |
| SmYTH14 | Chr8 | 2,628,473 | 2,630,842 | 1803 | 600 | 69,720.34 | 5.33 |
| SmYTH15 | Chr8 | 2,634,422 | 2,636,603 | 1800 | 599 | 69,531.02 | 5.37 |
| SmYTH16 | Chr8 | 2,638,250 | 2,640,615 | 1812 | 603 | 69,615.04 | 5.26 |
| SmYTH17 | Chr8 | 2,656,711 | 2,658,896 | 1800 | 599 | 69,678.27 | 5.56 |
| SmYTH18 | Chr8 | 2,659,911 | 2,662,254 | 1788 | 595 | 68,603.27 | 6.17 |
| SmYTH19 | Chr8 | 2,668,109 | 2,670,480 | 1803 | 600 | 69,720.34 | 5.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Peng, Y.; Pan, X.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, B.; Niu, L.; Lu, S. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the YTH Domain-Containing Protein Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104645
Wang C, Peng Y, Pan X, Zhang S, Xu Y, Li C, Zhu B, Niu L, Lu S. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the YTH Domain-Containing Protein Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104645
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chunling, Yunliang Peng, Xian Pan, Sixuan Zhang, Yayun Xu, Caili Li, Butuo Zhu, Lili Niu, and Shanfa Lu. 2025. "Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the YTH Domain-Containing Protein Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104645
APA StyleWang, C., Peng, Y., Pan, X., Zhang, S., Xu, Y., Li, C., Zhu, B., Niu, L., & Lu, S. (2025). Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of the YTH Domain-Containing Protein Gene Family in Salvia miltiorrhiza. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104645







