Ionizing Radiation Increases Death Receptor 5 (DR5)-Mediated Cell Death, but Not Death Receptor 4 (DR4)-Mediated Cell Death in 3D Tumor Spheroids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. TRAIL-Induced Cell Death in 2D Monolayer H460 and DLD-1 Cells
2.2. IR Enhances TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in 2D Monolayer Cancer Cells
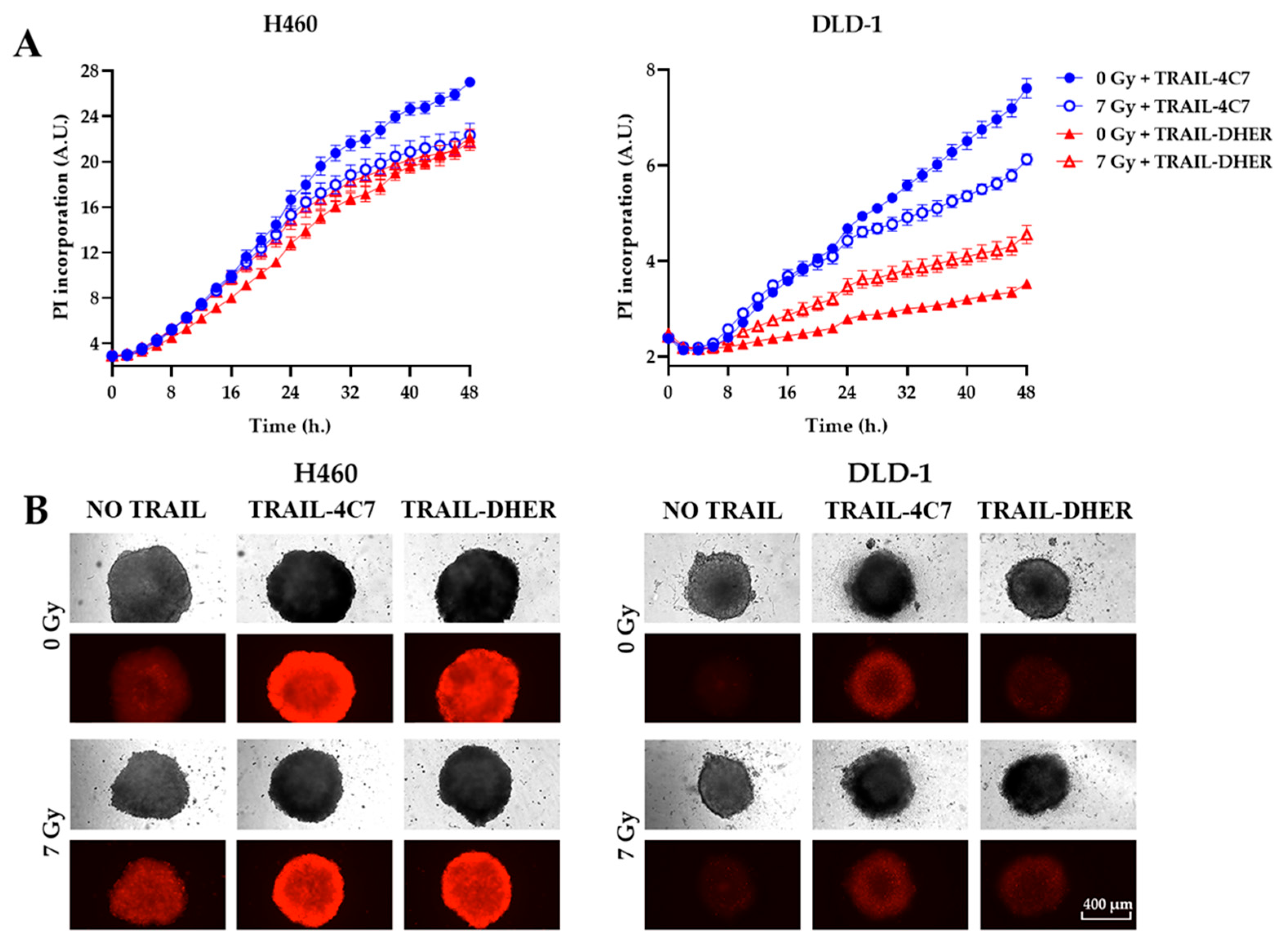
2.3. IR Inhibits DR4-Mediated Cell Death in 3D Cancer Spheroids
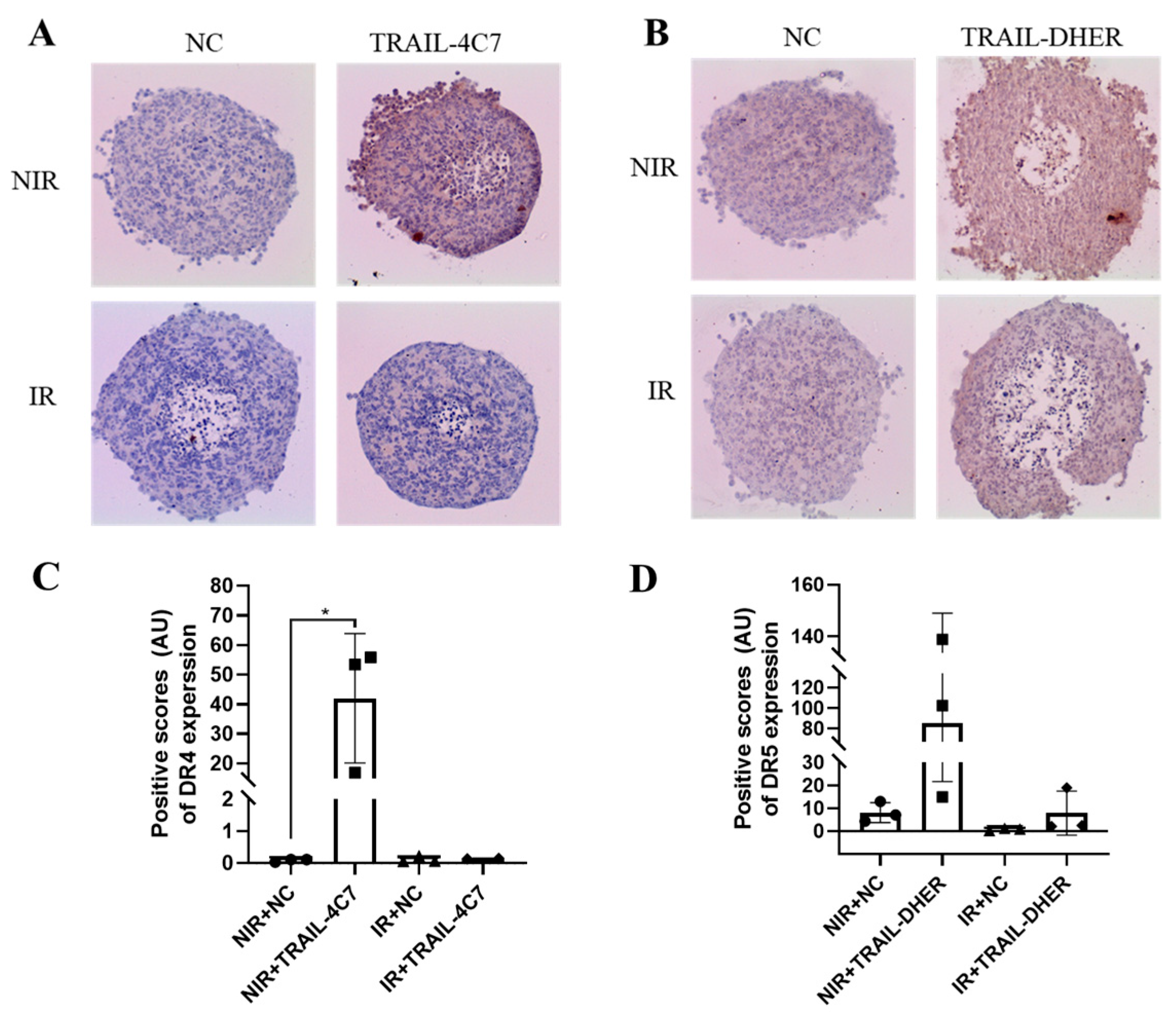
2.4. IR Upregulates the Expression of DR5, but Not DR4 in 3D Spheroids
2.5. Ionizing Radiation Only Inhibits the Upregulation of DR4 in 3D Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Reagents
4.2. Cell Viability Assay for 2D
4.3. D Spheroid Construction and Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Incucyte ® ZOOM Time-Resolved Assays
4.5. Flow Cytometry of Death Receptor Expression
4.6. Spheroid Embedding and Sections
4.7. Immunohistochemistry for 3D Spheroid Sections
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thariat, J.; Hannoun-Levi, J.-M.; Sun Myint, A.; Vuong, T.; Gérard, J.-P. Past, Present, and Future of Radiotherapy for the Benefit of Patients. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, M.; Halpin-McCormick, A.; Sessler, T.; Samali, A.; Szegezdi, E. Resistance to TRAIL in Non-Transformed Cells Is Due to Multiple Redundant Pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, F.; Zhou, X.; Setroikromo, R.; Quax, W.J. Receptor Specificity Engineering of TNF Superfamily Ligands. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snajdauf, M.; Havlova, K.; Vachtenheim, J.; Ozaniak, A.; Lischke, R.; Bartunkova, J.; Smrz, D.; Strizova, Z. The TRAIL in the Treatment of Human Cancer: An Update on Clinical Trials. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Gajan, A.; Chu, Q.; Xiong, H.; Wu, K.; Wu, G.S. Developing TRAIL/TRAIL Death Receptor-Based Cancer Therapies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 733–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orning, P.; Lien, E. Multiple Roles of Caspase-8 in Cell Death, Inflammation, and Innate Immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021, 109, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A Review of Programmed Cell Death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, B. Mechanisms of Resistance to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetschko, H.; Voss, V.; Horn, S.; Seifert, V.; Prehn, J.H.M.; Kögel, D. Pharmacological Inhibition of Bcl-2 Family Members Reactivates TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Malignant Glioma. J. Neurooncol. 2008, 86, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, C.; Bin, L.; Thorburn, J.; Behbakht, K.; Ford, H.L.; Thorburn, A. Distinct TRAIL Resistance Mechanisms Can Be Overcome by Proteasome Inhibition but Not Generally by Synergizing Agents. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1883–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, T.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Wang, G.; Chang, K.J. Overcoming Resistance to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Solid Tumor Cells by Simultaneously Targeting Death Receptors, c-FLIP and IAPs. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimberg, L.Y.; Anderson, C.K.; Camidge, R.; Behbakht, K.; Thorburn, A.; Ford, H.L. On the TRAIL to Successful Cancer Therapy? Predicting and Counteracting Resistance against TRAIL-Based Therapeutics. Oncogene 2013, 32, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imamura, Y.; Mukohara, T.; Shimono, Y.; Funakoshi, Y.; Chayahara, N.; Toyoda, M.; Kiyota, N.; Takao, S.; Kono, S.; Nakatsura, T.; et al. Comparison of 2D- and 3D-Culture Models as Drug-Testing Platforms in Breast Cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1837–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, S.A. Three-Dimensional in Vitro Cell Culture Models in Drug Discovery and Drug Repositioning. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöhr, D.; Schmid, J.O.; Beigl, T.B.; Mack, A.; Maichl, D.S.; Cao, K.; Budai, B.; Fullstone, G.; Kontermann, R.E.; Mürdter, T.E.; et al. Stress-Induced TRAILR2 Expression Overcomes TRAIL Resistance in Cancer Cell Spheroids. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 3037–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rückert, M.; Flohr, A.-S.; Hecht, M.; Gaipl, U.S. Radiotherapy and the Immune System: More than Just Immune Suppression. Stem Cells 2021, 39, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, V.N.; Hei, T.K. A Role for TRAIL/TRAIL-R2 in Radiation-Induced Apoptosis and Radiation-Induced Bystander Response of Human Neural Stem Cells. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellinger, H.; Stangl, S.; Schnelzer, A.H.; Schwab, M.; Di Genio, T.; Pieper, M.; Werner, C.; Shevtsov, M.; Haller, B.; Multhoff, G. Time- and Dose-Dependent Effects of Ionizing Irradiation on the Membrane Expression of Hsp70 on Glioma Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Prasad, U.; Shankar, S.; Hamstra, D.A.; Shanaiah, M.; Chenevert, T.L.; Ross, B.D.; Rehemtulla, A. Combined Effect of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand and Ionizing Radiation in Breast Cancer Therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belka, C.; Schmid, B.; Marini, P.; Durand, E.; Rudner, J.; Faltin, H.; Bamberg, M.; Schulze-Osthoff, K.; Budach, W. Sensitization of Resistant Lymphoma Cells to Irradiation-Induced Apoptosis by the Death Ligand TRAIL. Oncogene 2001, 20, 2190–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shankar, S.; Singh, T.R.; Chen, X.; Thakkar, H.; Firnin, J.; Srivastava, R.K. The Sequential Treatment with Ionizing Radiation Followed by TRAIL/Apo-2L Reduces Tumor Growth and Induces Apoptosis of Breast Tumor Xenografts in Nude Mice. Int. J. Oncol. 2004, 24, 1133–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, S.; Singh, T.R.; Srivastava, R.K. Ionizing Radiation Enhances the Therapeutic Potential of TRAIL in Prostate Cancer in Vitro and in Vivo: Intracellular Mechanisms. Prostate 2004, 61, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemoeller, O.M.; Belka, C. Radiotherapy and TRAIL for Cancer Therapy. Cancer Lett. 2013, 332, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, M.S.; Huang, Y.; Fernandez-Salas, E.A.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Friess, H.; Amundson, S.; Yin, J.; Meltzer, S.J.; Holbrook, N.J.; Fornace, A.J. The Antiapoptotic Decoy Receptor TRID/TRAIL-R3 Is a P53-Regulated DNA Damage-Inducible Gene That Is Overexpressed in Primary Tumors of the Gastrointestinal Tract. Oncogene 1999, 18, 4153–4159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yue, P.; Khuri, F.R.; Sun, S.Y. Decoy Receptor 2 (DcR2) Is a P53 Target Gene and Regulates Chemosensitivity. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9169–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. Targeted Nanosystems: Advances in Targeted Dendrimers for Cancer Therapy. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2016, 12, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougis, P.; Moreau Bachelard, C.; Kamal, M.; Gan, H.K.; Borcoman, E.; Torossian, N.; Bièche, I.; Le Tourneau, C. Clinical Development of Molecular Targeted Therapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2019, 3, pkz055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, S.R.; Schooley, K.; Smolak, P.J.; Din, W.S.; Huang, C.P.; Nicholl, J.K.; Sutherland, G.R.; Smith, T.D.; Rauch, C.; Smith, C.A.; et al. Identification and Characterization of a New Member of the TNF Family That Induces Apoptosis. Immunity 1995, 3, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flakus, F.N. Radiation Detection Detecting and Measuring Ionizing Radiation-a Short History. IAEA Bull. 1982, 23, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Cuttler, J.M. Application of Low Doses of Ionizing Radiation in Medical Therapies. Dose-Response 2020, 18, 1559325819895739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduro, J.H.; de Vries, E.G.E.; Meersma, G.J.; Hougardy, B.M.T.; van der Zee, A.G.J.; de Jong, S. Targeting Pro-Apoptotic TRAIL Receptors Sensitizes HeLa Cervical Cancer Cells to Irradiation-Induced Apoptosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2008, 72, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Gamez, A.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Seras, L.; Quax, W.; Demaria, M. Enhanced Extrinsic Apoptosis of Therapy-Induced Senescent Cancer Cells Using a Death Receptor 5 (DR5) Selective Agonist. Cancer Lett. 2022, 525, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerp, S.F.; Bibi, Z.; Verbrugge, I.; Voest, E.E.; Verheij, M. Enhancing Radiation Response by a Second-Generation TRAIL Receptor Agonist Using a New in Vitro Organoid Model System. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, P.; Denzinger, S.; Schiller, D.; Kauder, S.; Welz, S.; Humphreys, R.; Daniel, P.T.; Jendrossek, V.; Budach, W.; Belka, C. Combined Treatment of Colorectal Tumours with Agonistic TRAIL Receptor Antibodies HGS-ETR1 and HGS-ETR2 and Radiotherapy: Enhanced Effects in Vitro and Dose-Dependent Growth Delay in Vivo. Oncogene 2006, 25, 5145–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Yasui, H.; Ogura, A.; Asanuma, T.; Kubota, N.; Tsujitani, M.; Kuwabara, M.; Inanami, O. X Irradiation Combined with TNF α-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL) Reduces Hypoxic Regions of Human Gastric Adenocarcinoma Xenografts in SCID Mice. J. Radiat. Res. 2008, 49, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Di Pietro, R.; Secchiero, P.; Rana, R.; Gibellini, D.; Visani, G.; Bemis, K.; Zamai, L.; Miscia, S.; Zauli, G. Ionizing Radiation Sensitizes Erythroleukemic Cells but Not Normal Erythroblasts to Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand (TRAIL)-Mediated Cytotoxicity by Selective up-Regulation of TRAIL-R1. Blood 2001, 97, 2596–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifeadi, V.; Garnett-Benson, C. Sub-Lethal Irradiation of Human Colorectal Tumor Cells Imparts Enhanced and Sustained Susceptibility to Multiple Death Receptor Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.J.; Chen, D.; Dekker, F.J.; Quax, W.J. Improving TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Cancers by Interfering with Histone Modifications. Cancer Drug Resist. 2020, 3, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Liu, B.; Chen, D.; Setroikromo, R.; Haisma, H.J.; Quax, W.J. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Sensitize TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells. Cancers 2019, 11, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacan, E.; Greer, S.F.; Garnett-Benson, C. Radiation-Induced Modulation of Immunogenic Genes in Tumor Cells Is Regulated by Both Histone Deacetylases and DNA Methyltransferases. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 2264–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, A.K.; Verma, A.; Singh, A.; Arya, R.K.; Maheshwari, S.; Chaturvedi, P.; Nengroo, M.A.; Saini, K.K.; Vishwakarma, A.L.; Singh, K.; et al. Salinomycin Inhibits Epigenetic Modulator EZH2 to Enhance Death Receptors in Colon Cancer Stem Cells. Epigenetics 2020, 16, 144–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, R.; Srivastava, N.; Chopra, R.; Gochhait, S.; Gupta, P.; Prakash, N.; Agarwal, G.; Bamezai, R.N.K. Investigation of DNA Damage Response and Apoptotic Gene Methylation Pattern in Sporadic Breast Tumors Using High Throughput Quantitative DNA Methylation Analysis Technology. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, D.G.; Das, C.M.; Sinnappah-Kang, N.D.; Joyce, C.; Taylor, P.H.; Wen, S.; Hasselblatt, M.; Paulus, W.; Fuller, G.; Wolff, J.E.; et al. Reactivation of Death Receptor 4 (DR4) Expression Sensitizes Medulloblastoma Cell Lines to TRAIL. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 93, 303–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sallam, M.; Mysara, M.; Benotmane, M.A.; Crijns, A.P.G.; Spoor, D.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Deforce, D.; Baatout, S.; Guns, P.J.; Aerts, A.; et al. DNA Methylation Alterations in Fractionally Irradiated Rats and Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Radiotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwih, D.A.; Gabbara, K.M.; Lancaster, W.D.; Ruden, D.M.; Zielske, S.P. Radiation-Induced Epigenetic DNA Methylation Modification of Radiation-Response Pathways. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, C.R.; Van Der Sloot, A.M.; Natoni, A.; Szegezdi, E.; Setroikromo, R.; Meijer, M.; Sjollema, K.; Stricher, F.; Cool, R.H.; Samali, A.; et al. Rapid and Efficient Cancer Cell Killing Mediated by High-Affinity Death Receptor Homotrimerizing TRAIL Variants. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Sloot, A.M.; Tur, V.; Szegezdi, E.; Mullally, M.M.; Cool, R.H.; Samali, A.; Serrano, L.; Quax, W.J. Designed Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand Variants Initiating Apoptosis Exclusively via the DR5 Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8634–8639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suo, F.; Zhou, X.; Soto-Gamez, A.; Nijdam, F.B.; Setroikromo, R.; Quax, W.J. Ionizing Radiation Increases Death Receptor 5 (DR5)-Mediated Cell Death, but Not Death Receptor 4 (DR4)-Mediated Cell Death in 3D Tumor Spheroids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104635
Suo F, Zhou X, Soto-Gamez A, Nijdam FB, Setroikromo R, Quax WJ. Ionizing Radiation Increases Death Receptor 5 (DR5)-Mediated Cell Death, but Not Death Receptor 4 (DR4)-Mediated Cell Death in 3D Tumor Spheroids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104635
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuo, Fengzhi, Xinyu Zhou, Abel Soto-Gamez, Fleur B. Nijdam, Rita Setroikromo, and Wim J. Quax. 2025. "Ionizing Radiation Increases Death Receptor 5 (DR5)-Mediated Cell Death, but Not Death Receptor 4 (DR4)-Mediated Cell Death in 3D Tumor Spheroids" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104635
APA StyleSuo, F., Zhou, X., Soto-Gamez, A., Nijdam, F. B., Setroikromo, R., & Quax, W. J. (2025). Ionizing Radiation Increases Death Receptor 5 (DR5)-Mediated Cell Death, but Not Death Receptor 4 (DR4)-Mediated Cell Death in 3D Tumor Spheroids. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104635







