Polyphyllin I Inhibits the Metastasis of Cervical Cancer Through the Regulation of the β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
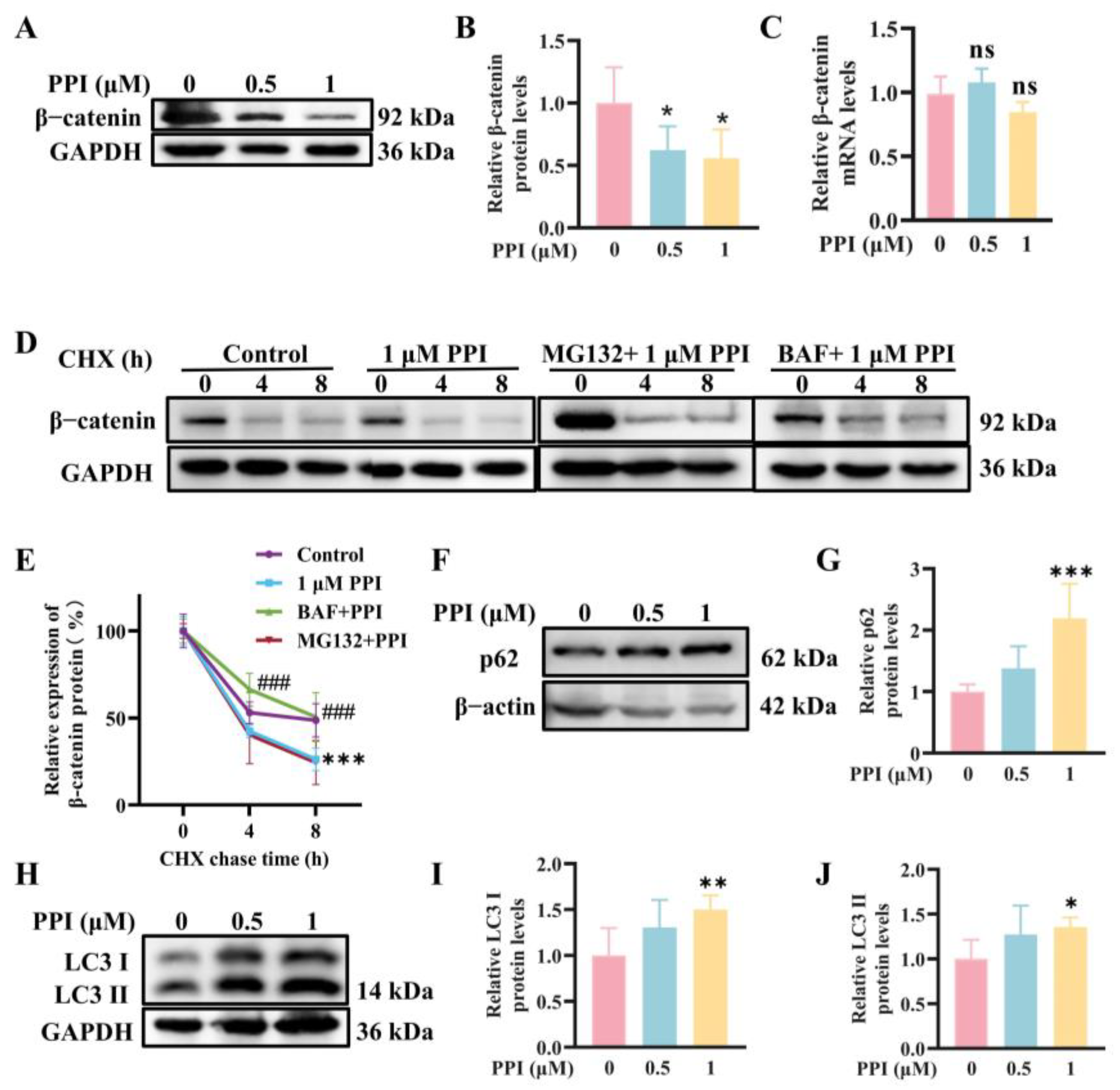
2.1. The Interaction Between PPI and β-Catenin
2.2. The Depletion of β-Catenin Triggered by PPI Is Mediated Through the Process of Autophagy
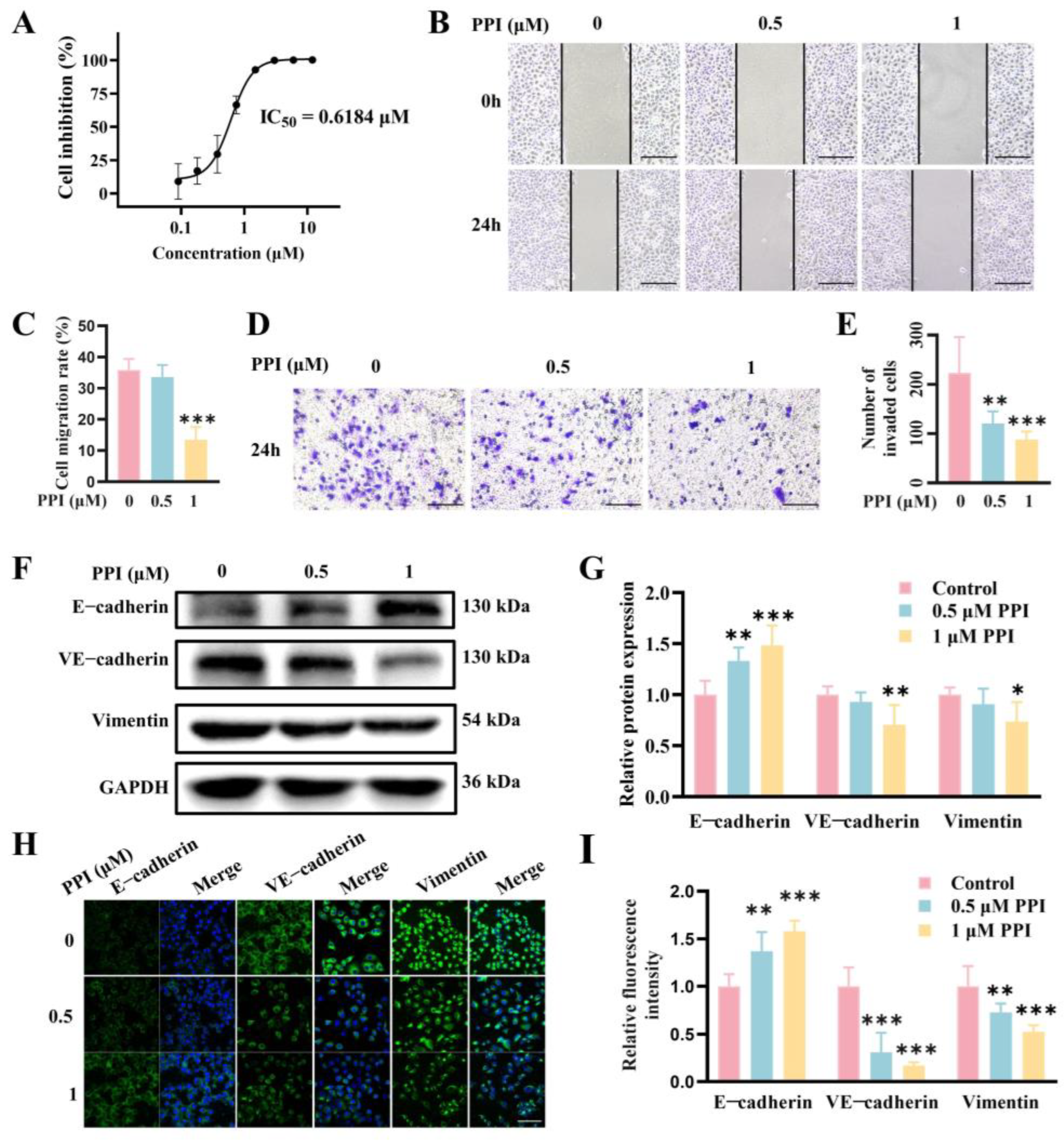
2.3. PPI Regulates the Expression of EMT-TFs by Modulating the β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
2.4. PPI Inhibits the Growth, Migration, and Invasion of HO-8910PM Cells by Reversing the EMT Progress
2.5. PPI Inhibits the Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion of Cervical Cancer Cell Lines SiHa and C33A
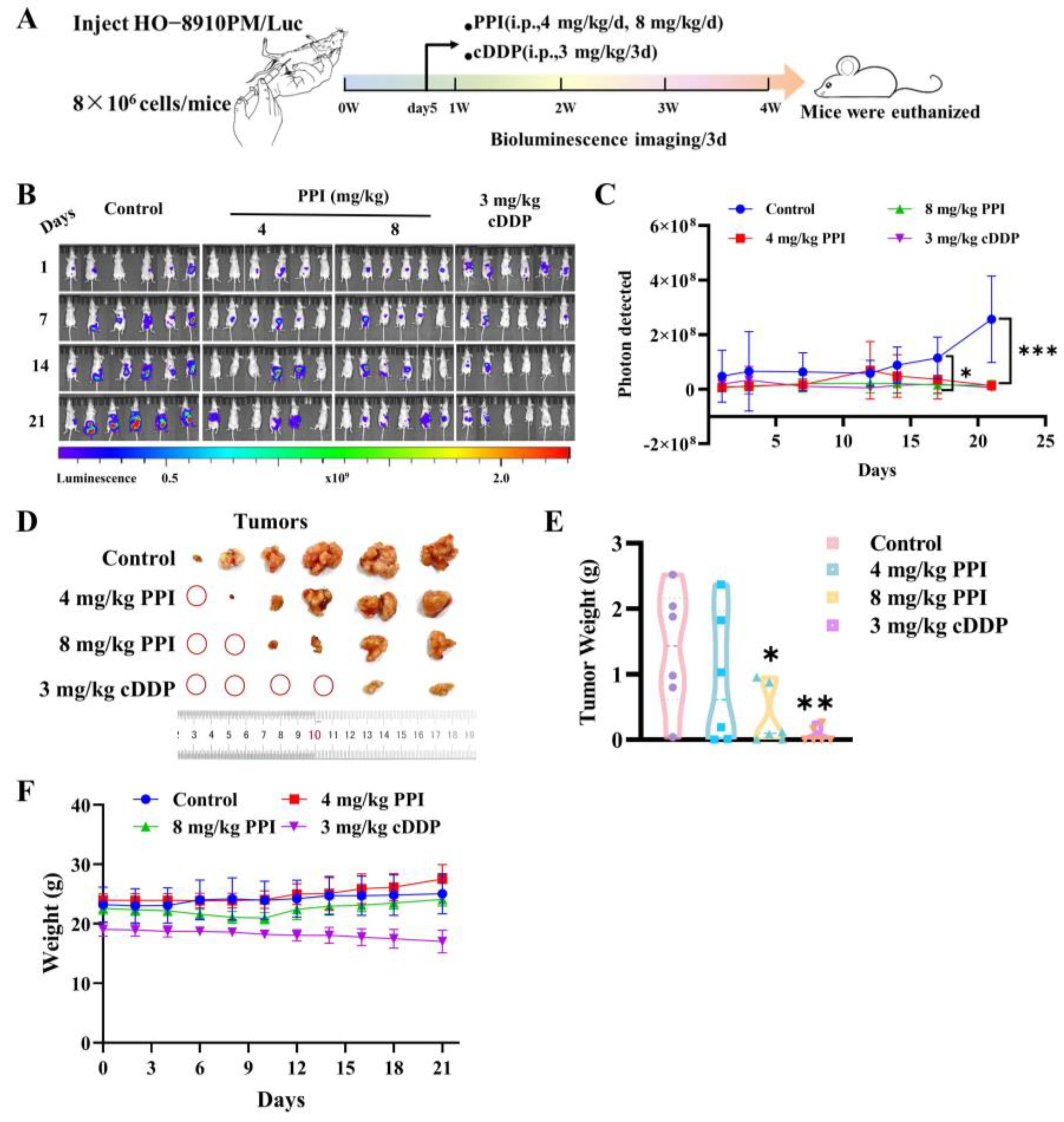
2.6. PPI Inhibits the Growth of Cervical Cancer Cells In Vivo
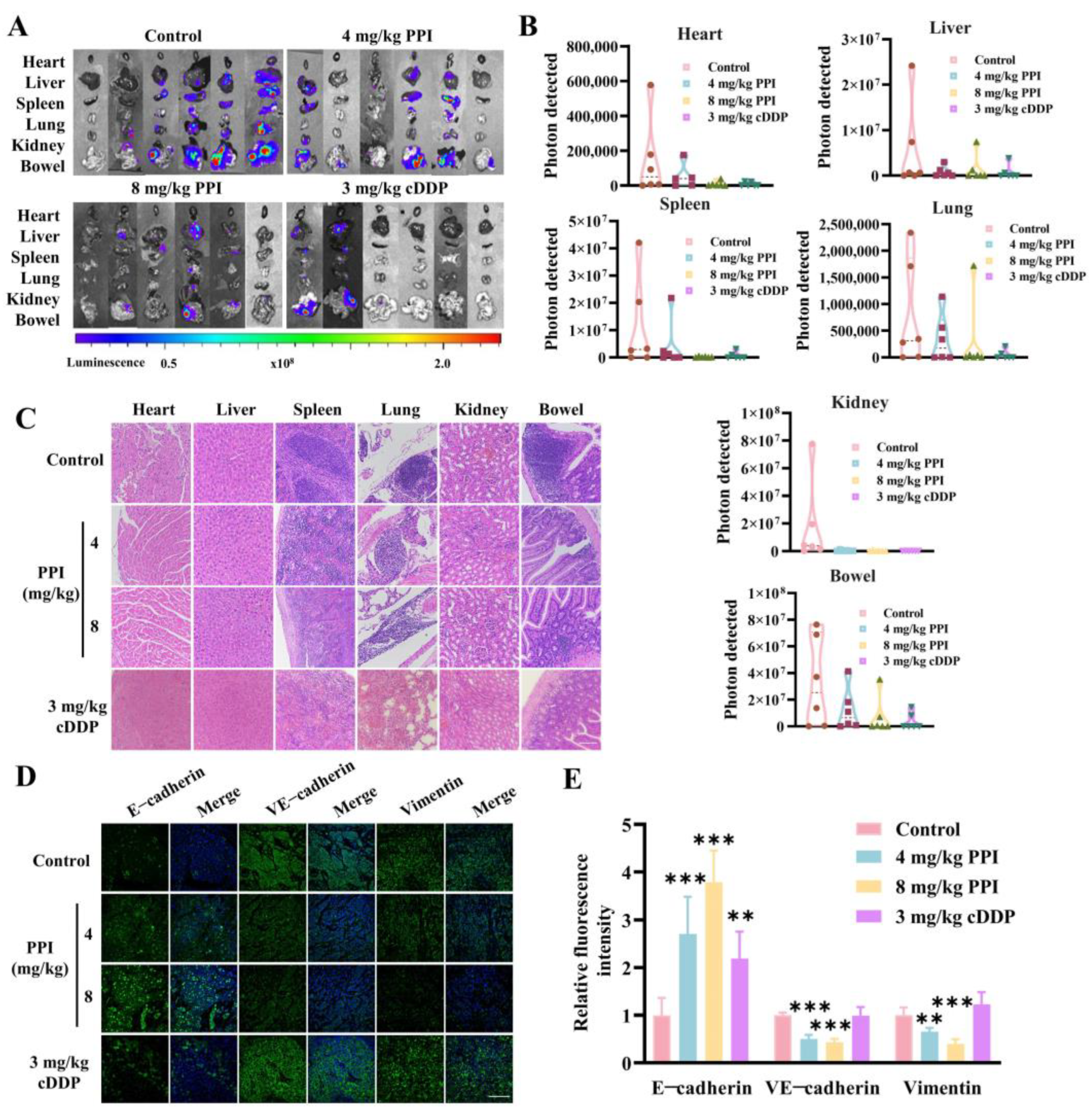
2.7. PPI Inhibits the Metastasis of Cervical Cancer Cells In Vivo
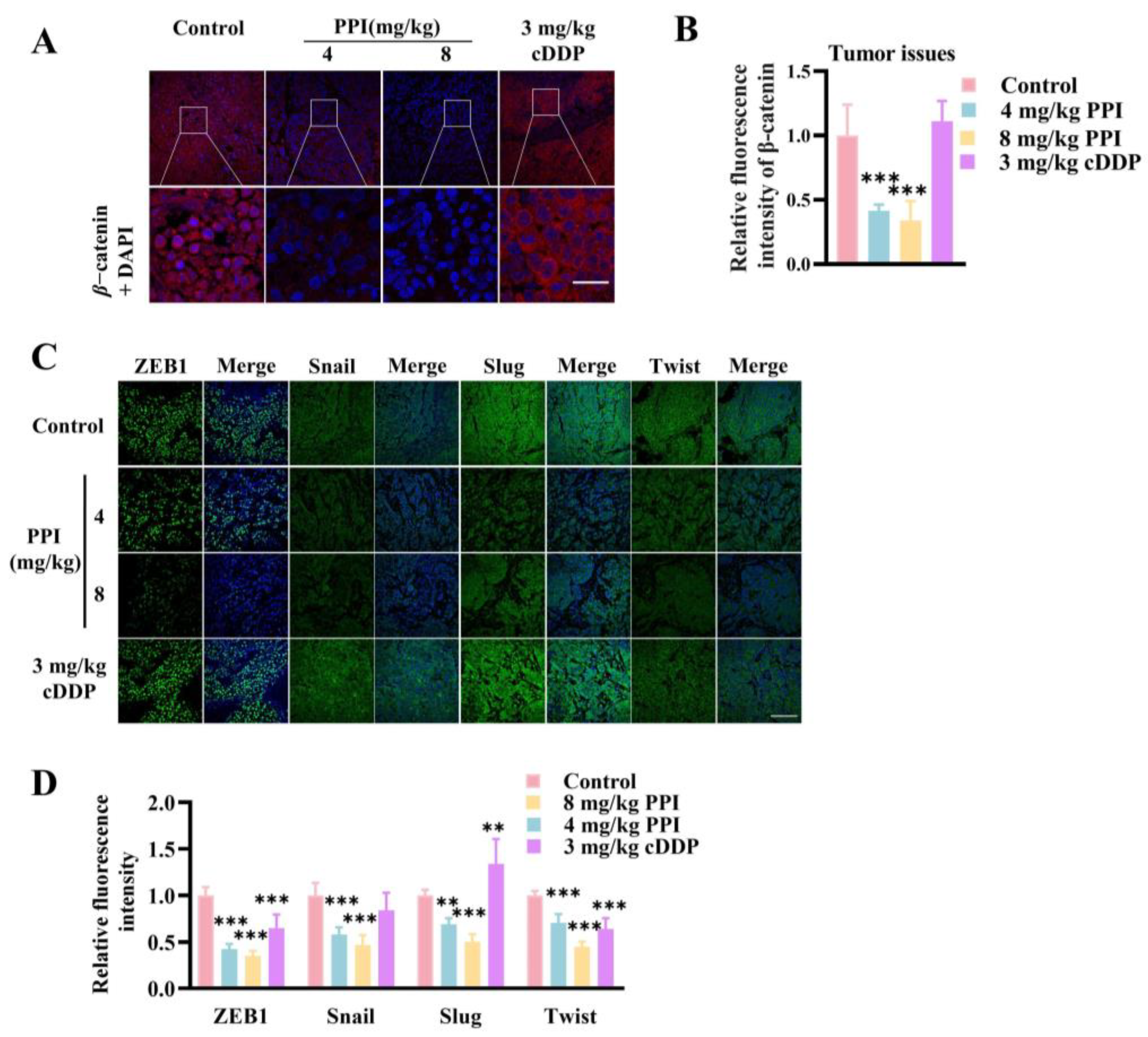
2.8. PPI Suppresses the Growth and Metastasis of Cervical Cancer Through the Modulation of the β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Animals
4.3. Cell Lines and Culture
4.4. Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Wound Healing Assay
4.6. Cell Migration and Invasion Assays
4.7. Quantitative Real Time PCR (qRT–PCR)
4.8. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
4.9. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA)
4.10. Molecular Modeling
4.11. TOPFlash Reporter Gene Assay
4.12. CHX Chase Assay
4.13. Western Blot Analysis
4.14. Immunofluorescent (IF) Staining Analysis
4.15. Hematoxylin–Eosin Staining (HE)
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Volkova, L.V.; Pashov, A.I.; Omelchuk, N.N. Cervical Carcinoma: Oncobiology and Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marret, G.; Borcoman, E.; Le Tourneau, C. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of cervical cancer. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 871–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Tian, J.; Fu, X.; Ren, X.; Hao, Q. Significance of the absolute number and ratio of metastatic lymph nodes in predicting postoperative survival for the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics stage IA2 to IIA cervical cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2013, 23, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Cao, C.; Wu, P.; Huang, X.; Ma, D. Advances in cervical cancer: Current insights and future directions. Cancer Commun. 2025, 45, 77–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormack, M.; Eminowicz, G.; Gallardo, D.; Diez, P.; Farrelly, L.; Kent, C.; Hudson, E.; Panades, M.; Mathew, T.; Anand, A.; et al. Induction chemotherapy followed by standard chemoradiotherapy versus standard chemoradiotherapy alone in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer (GCIG INTERLACE): An international, multicentre, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2024, 404, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Yashar, C.M.; Arend, R.; Barber, E.; Bradley, K.; Brooks, R.; Campos, S.M.; Chino, J.; Chon, H.S.; Crispens, M.A.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Cervical Cancer, Version 1.2024. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2023, 21, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordhuis, M.G.; Fehrmann, R.S.; Wisman, G.B.; Nijhuis, E.R.; van Zanden, J.J.; Moerland, P.D.; Ver Loren van Themaat, E.; Volders, H.H.; Kok, M.; ten Hoor, K.A.; et al. Involvement of the TGF-beta and beta-catenin pathways in pelvic lymph node metastasis in early-stage cervical cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wise, M.L.; Li, F.; Dey, M. Phytochemicals attenuating aberrant activation of β-catenin in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Plasencia, C.; Duenas-Gonzalez, A.; Alatorre-Tavera, B. Second hit in cervical carcinogenesis process: Involvement of wnt/beta catenin pathway. Int. Arch. Med. 2008, 1, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkes, E.E.; Kennedy, R.D. Clinical Application of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors in High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Oncologist 2016, 21, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Xu, G.; Schulman, B.A.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Harper, J.W.; Pavletich, N.P. Structure of a beta-TrCP1-Skp1-beta-catenin complex: Destruction motif binding and lysine specificity of the SCF(beta-TrCP1) ubiquitin ligase. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 1445–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauriello, D.V.; Jordens, I.; Kirchner, K.; Slootstra, J.W.; Kruitwagen, T.; Bouwman, B.A.; Noutsou, M.; Rüdiger, S.G.; Schwamborn, K.; Schambony, A.; et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling requires interaction of the Dishevelled DEP domain and C terminus with a discontinuous motif in Frizzled. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E812–E820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arend, R.C.; Londoño-Joshi, A.I.; Straughn, J.M., Jr.; Buchsbaum, D.J. The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: A review. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 131, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.Y.; Chou, C.Y.; Tang, M.J.; Shen, M.R. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer: Correlation with tumor progression, epidermal growth factor receptor overexpression, and snail up-regulation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 4743–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Spoelstra, N.S.; Jean, A.; Howe, E.; Torkko, K.C.; Clark, H.R.; Darling, D.S.; Shroyer, K.R.; Horwitz, K.B.; Broaddus, R.R.; et al. ZEB1 expression in type I vs type II endometrial cancers: A marker of aggressive disease. Mod. Pathol. 2008, 21, 912–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Hu, T.; Wang, S.; Yang, R.; Jia, Y.; et al. The nuclear protein expression levels of SNAI1 and ZEB1 are involved in the progression and lymph node metastasis of cervical cancer via the epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathway. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 2097–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jia, J.; Zhu, W.; Chen, J.; Zheng, Q.; Li, D. Therapeutic effects on cancer of the active ingredients in rhizoma paridis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1095786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Yu, S.; Guo, C.; Tan, L.; Song, X.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Long, Y.; Gong, D.; Zhang, R.; et al. Polyphyllin I induces autophagy and cell cycle arrest via inhibiting PDK1/Akt/mTOR signal and downregulating cyclin B1 in human gastric carcinoma HGC-27 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Shen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lai, J.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, H. Polyphyllin I reverses the resistance of osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer cell through regulation of PI3K/Akt signaling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 419, 115518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liang, C.L.; Liu, H.; Qiu, F.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H.; Lu, W.; et al. Polyphyllin I suppresses the gastric cancer growth by promoting cancer cell ferroptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1145407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Jia, L.; Huang, C.; Qi, Q.; Jahangir, A.; Xia, Y.; Liu, W.; Shi, R.; Tang, L.; Chen, Z. Polyphyllin I Promotes Autophagic Cell Death and Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells via the ROS-Inhibited AKT/mTOR Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Su, J.J.; Hou, H.J.; Li, Q.L. Effect and mechanism of polyphyllin I on human cervical cancer cell HeLa in vitro. Zhong Yao Cai 2013, 36, 1815–1819. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y.; Xu, C.; Yu, M. Polyphyllin I Sensitizes Cisplatin-Resistant Human Cervical Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Treatment. Nutr. Cancer 2024, 76, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Du, H.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Huang, D.; Tong, G. Anticancer Effect of Polyphyllin I in Suppressing Stem Cell-Like Properties of Hepatocellular Carcinoma via the AKT/GSK-3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2022, 2022, 4031008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Li, X.; He, X.; Qiu, X.; Jin, X.L.; Zhao, X.Y.; Xu, R.Z. Polyphyllin I induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human myeloma cells via modulating β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. J. Haematol. 2016, 97, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Wang, H.; Shi, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y. Polyphyllin I suppresses human osteosarcoma growth by inactivation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, D.; Hawke, D.; Zheng, Y.; Xia, Y.; Meisenhelder, J.; Nika, H.; Mills, G.B.; Kobayashi, R.; Hunter, T.; Lu, Z. Phosphorylation of beta-catenin by AKT promotes beta-catenin transcriptional activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 11221–11229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petherick, K.J.; Williams, A.C.; Lane, J.D.; Ordóñez-Morán, P.; Huelsken, J.; Collard, T.J.; Smartt, H.J.; Batson, J.; Malik, K.; Paraskeva, C.; et al. Autolysosomal β-catenin degradation regulates Wnt-autophagy-p62 crosstalk. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, E.K.; Fukushiro-Lopes, D.; Dalheim, A.; Burnette, M.; Zartman, J.; Kaja, S.; Wells, C.; Campo, L.; Curtis, K.J.; Romero-Moreno, R.; et al. Potassium channel activity controls breast cancer metastasis by affecting β-catenin signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nàger, M.; Sallán, M.C.; Visa, A.; Pushparaj, C.; Santacana, M.; Macià, A.; Yeramian, A.; Cantí, C.; Herreros, J. Inhibition of WNT-CTNNB1 signaling upregulates SQSTM1 and sensitizes glioblastoma cells to autophagy blockers. Autophagy 2018, 14, 619–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, G.Y.; Bierman, R.; Beardsley, L.; Chang, C.J.; Burk, R.D. Natural history of cervicovaginal papillomavirus infection in young women. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, Y.; Enomoto, T.; Miyatake, T.; Ozaki, K.; Yoshizaki, T.; Kanao, H.; Ueno, Y.; Nakashima, R.; Shroyer, K.R.; Murata, Y. Monoclonal expansion with integration of high-risk type human papillomaviruses is an initial step for cervical carcinogenesis: Association of clonal status and human papillomavirus infection with clinical outcome in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Lab. Investig. 2003, 83, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, G.; Fallen, S.; Beauchamp, E.M.; Drebing, L.E.; Sun, J.; Berry, D.L.; Kallakury, B.; Crum, C.P.; Toretsky, J.A.; Schlegel, R.; et al. Beta-catenin accelerates human papilloma virus type-16 mediated cervical carcinogenesis in transgenic mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uren, A.; Fallen, S.; Yuan, H.; Usubütün, A.; Küçükali, T.; Schlegel, R.; Toretsky, J.A. Activation of the canonical Wnt pathway during genital keratinocyte transformation: A model for cervical cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 6199–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, H.; Lyu, Y.Y.; Yang, X.M.; Zhu, L.Y.; Yang, G.D.; Jiang, P.C.; Re, Y.; Song, W.W.; Wang, J.H.; et al. E6/E7-P53-POU2F1-CTHRC1 axis promotes cervical cancer metastasis and activates Wnt/PCP pathway. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzawa, S.I.; Reed, J.C. Siah-1, SIP, and Ebi collaborate in a novel pathway for beta-catenin degradation linked to p53 responses. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pim, D.; Massimi, P.; Dilworth, S.M.; Banks, L. Activation of the protein kinase B pathway by the HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein occurs through a mechanism involving interaction with PP2A. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7830–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wu, H.; Kang, Q.; Liao, M.; Qin, M.; Chen, N.; Huang, H.; Huang, D.; Wang, P.; Tong, G. Polyphyllin I attenuates the invasion and metastasis via downregulating GRP78 in drug-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Aging 2023, 15, 12251–12263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sun, Z.; Deng, J.; Liu, J.; Ma, K.; Si, Y.; Zhang, T.; Feng, T.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Y. Polyphyllin I inhibits invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via CIP2A/PP2A/ERK signaling in prostate cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.X.; Li, J.H.; Cai, J.P.; Hou, X.; Huang, C.S.; Huang, X.T.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, S.J.; Xu, Q.C.; Yin, X.Y. EYA4 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by repressing MYCBP by dephosphorylating β-catenin at Ser552. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 3110–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Xu, J.; Li, H.; Tan, M.; Xiong, X.; Sun, Y. FBXW2 suppresses migration and invasion of lung cancer cells via promoting β-catenin ubiquitylation and degradation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amable, G.; Martínez-León, E.; Picco, M.E.; Di Siervi, N.; Davio, C.; Rozengurt, E.; Rey, O. Metformin inhibits β-catenin phosphorylation on Ser-552 through an AMPK/PI3K/Akt pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2019, 112, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Miao, F.; Huang, R.; Liu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Jiao, T.; Lu, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; et al. RHBDD1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through the Wnt signaling pathway and its downstream target ZEB1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Wang, P.; Zhang, J.; Fu, L.; Ouyang, L.; Wang, J. Deconvoluting the relationships between autophagy and metastasis for potential cancer therapy. Apoptosis 2016, 21, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yi, H.; Liao, S.; He, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lei, Y. LC3B: A microtubule-associated protein influences disease progression and prognosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2025, 81, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakopoulos-Soares, I.; Chartoumpekis, D.V.; Kyriazopoulou, V.; Zaravinos, A. EMT Factors and Metabolic Pathways in Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, G.; Di Caprio, G.; Santangelo, L.; Fimia, G.M.; Cozzolino, A.M.; Komatsu, M.; Ippolito, G.; Tripodi, M.; Alonzi, T. Autophagy regulates hepatocyte identity and epithelial-to-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-to-epithelial transitions promoting Snail degradation. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, M.; D’Alessandro, G.; Lepore, F.; Corazzari, M.; Caldarola, S.; Valacca, C.; Faienza, F.; Esposito, V.; Limatola, C.; Cecconi, F.; et al. Autophagy induction impairs migration and invasion by reversing EMT in glioblastoma cells. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1612–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, A.R.; Kim, S.J.; Park, M.J.; Park, Y.H. CORM-2 reduces cisplatin accumulation in the mouse inner ear and protects against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 64, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of Cell Viability by the MTT Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018, pdb-prot095505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, G.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, Z.; Yao, T. TGF-β signaling promotes cervical cancer metastasis via CDR1as. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.; Li, Z.; Luo, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, J.; Gao, S.; Yang, Y.; Fu, W.; Kong, L.; et al. piRNA-14633 promotes cervical cancer cell malignancy in a METTL14-dependent m6A RNA methylation manner. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, P.; Guo, A.; Wang, L.; Lin, X.; Feng, M. Circular RNA CDK6 suppresses cervical cancer proliferation and metastasis by sponging miR-449a. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 4885–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Devireddy, R.; Gartia, M.R. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Sensor for Cancer Biomarker Detection. Biosensors 2023, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez Molina, D.; Jafari, R.; Ignatushchenko, M.; Seki, T.; Larsson, E.A.; Dan, C.; Sreekumar, L.; Cao, Y.; Nordlund, P. Monitoring drug target engagement in cells and tissues using the cellular thermal shift assay. Science 2013, 341, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalli, M.; Di Magno, L.; Wen, Y.; Liu, X.; D’Ambrosio, M.; Puxeddu, M.; Parisi, A.; Sebastiani, J.; Sorato, A.; Coluccia, A.; et al. Novel N-(Heterocyclylphenyl) benzensulfonamide Sharing an Unreported Binding Site with T-Cell Factor 4 at the β-Catenin Armadillo Repeats Domain as an Anticancer Agent. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2023, 6, 1087–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Kiperman, T.; Li, W.; Dhawan, S.; Lee, J.; Yechoor, V.; Ma, K. The Clock-modulatory Activity of Nobiletin Suppresses Adipogenesis Via Wnt Signaling. Endocrinology 2023, 164, bqad096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Yan, J.; Duan, R.; Zhu, Y.; Hua, Y.; Liao, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, W.; Ji, S. E3 ligase Cul2 mediates Drosophila early germ cell differentiation through targeting Bam. Dev. Biol. 2023, 493, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Q.; Yu, S.P.; Yang, Y.T.; Zhao, Y.S.; Wang, F.Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.H.; Tian, P.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.G.; et al. Muscone derivative ZM-32 inhibits breast tumor angiogenesis by suppressing HuR-mediated VEGF and MMP9 expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 136, 111265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Lin, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y. Eltrombopag Inhibits Metastasis in Breast Carcinoma by Targeting HuR Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, C.; Chen, G.; Li, R.; Peng, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Yu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J. Juglone suppresses vasculogenic mimicry in glioma through inhibition of HuR-mediated VEGF-A expression. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2024, 227, 116458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Ye, H.; Yang, B.; Ao, M.; Yu, X.; Wu, Y.; Xi, M.; Hou, M. m6A-modified circNFIX promotes ovarian cancer progression and immune escape via activating IL-6R/JAK1/STAT3 signaling by sponging miR-647. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 124, 110879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Primer | Sequence |
|---|---|
| β-catenin forward (human) | 5′-AAAGCGGCTGTTAGTCACTGG-3′ |
| β-catenin reverse (human) | 5′-CGAGTCATTGCATACTGTCCAT-3′ |
| Snail forward (human) | 5′-CTGGGTGCCCTCAAGATGCA-3′ |
| Snail reverse (human) | 5′-CCGGACATGGCCTTGTAGCA-3′ |
| Slug forward (human) | 5′-GTTTCATCCAGGATCGAGCAG-3′ |
| Slug reverse (human) | 5′-CATCTTCTTCCAGATGGTGA-3′ |
| ZEB1 forward (human) | 5′-ACTGTTTGTAGCGACTGGATT-3′ |
| ZEB1 reverse (human) | 5′-TAAAGTGGCGGTAGATGGTA-3′ |
| Twist forward (human) | 5′-CGGCCTAGCGAGTGGTTCTT-3′ |
| Twist reverse (human) | 5′-AGGAAAGAGCGCGGCATAGT-3′ |
| Gapdh forward (human) | 5′-CAGGAGGCATTGCTGATGAT-3′ |
| Gapdh reverse (human) | 5′-GAAGGCTGGGGCTCATTT-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chai, Y.; Yu, S.; Lin, G.; Luo, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, R.; Peng, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J. Polyphyllin I Inhibits the Metastasis of Cervical Cancer Through the Regulation of the β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104630
Chai Y, Yu S, Lin G, Luo C, Wang X, Zhang R, Peng J, Zhu Y, Zhang J. Polyphyllin I Inhibits the Metastasis of Cervical Cancer Through the Regulation of the β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104630
Chicago/Turabian StyleChai, Yingbin, Shaopeng Yu, Guoqiang Lin, Chunying Luo, Xu Wang, Rui Zhang, Jiawen Peng, Yuying Zhu, and Jiange Zhang. 2025. "Polyphyllin I Inhibits the Metastasis of Cervical Cancer Through the Regulation of the β-Catenin Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104630
APA StyleChai, Y., Yu, S., Lin, G., Luo, C., Wang, X., Zhang, R., Peng, J., Zhu, Y., & Zhang, J. (2025). Polyphyllin I Inhibits the Metastasis of Cervical Cancer Through the Regulation of the β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4630. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104630





