Effects of Combination Treatment with Leptin and Liraglutide on Glucose Metabolism in Insulin-Dependent Diabetic Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
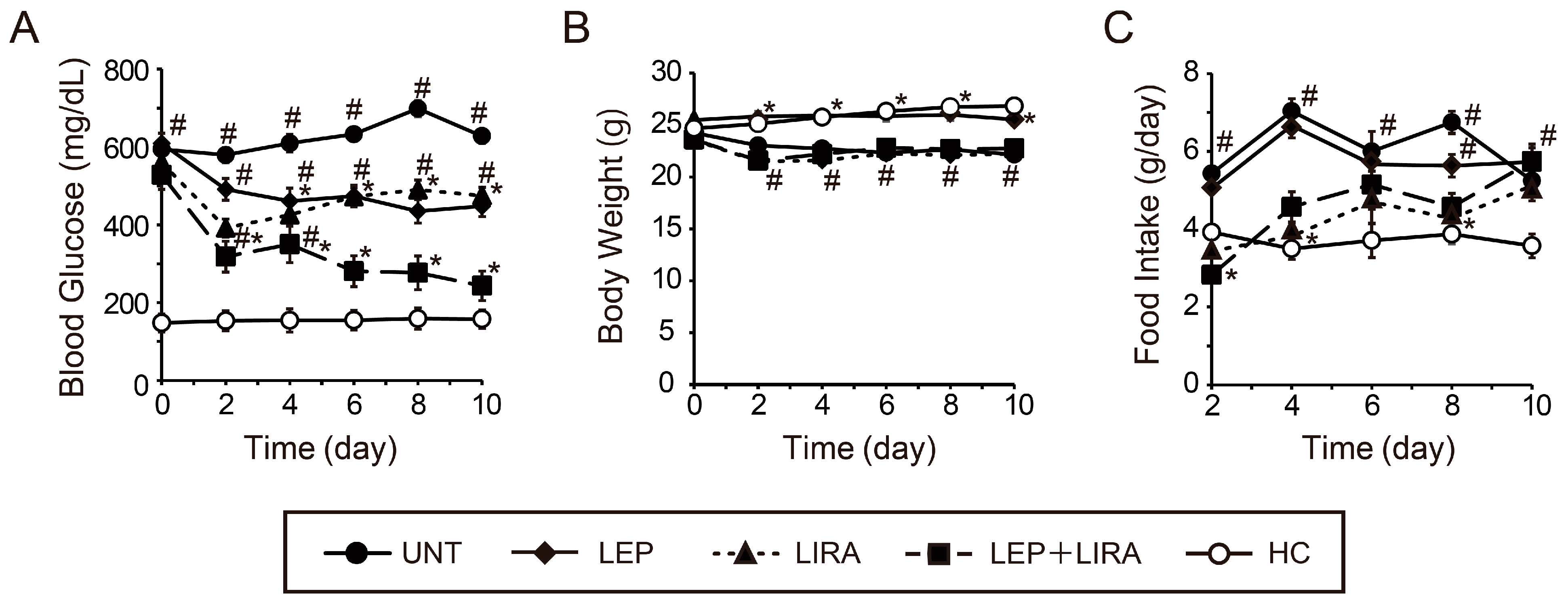
2.1. The Peripheral Co-Administration of Leptin and Liraglutide Improved Hyperglycemia in Mice with IDDM
2.2. Peripheral Co-Administration of Leptin and Liraglutide Improved Glucose Tolerance in Mice with IDDM
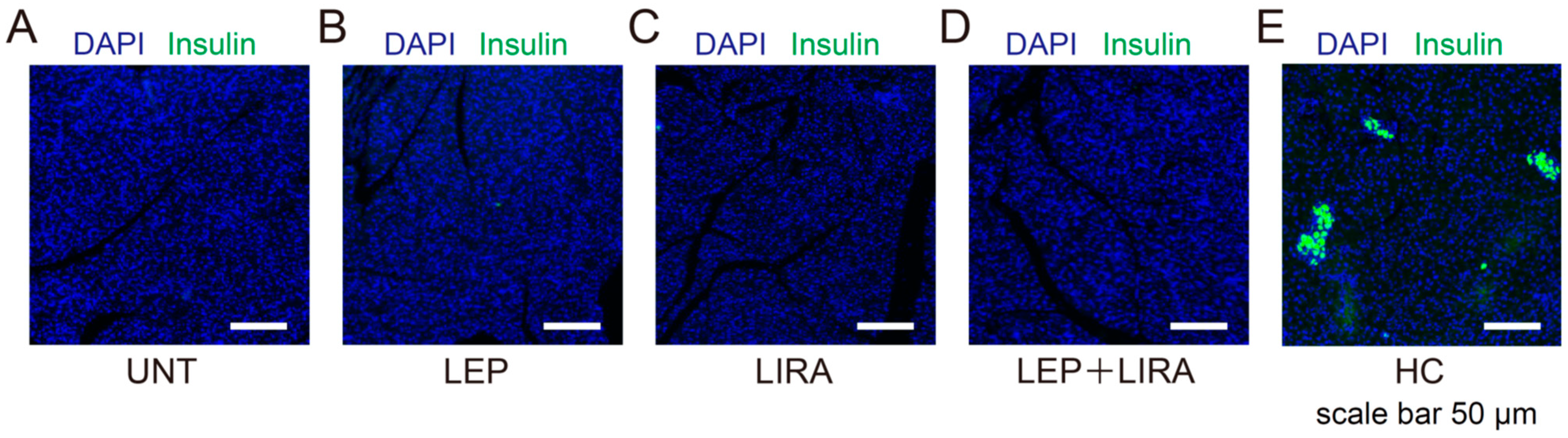
2.3. Liraglutide Treatment Failed to Restore Pancreatic β Cell Area in Mice with IDDM
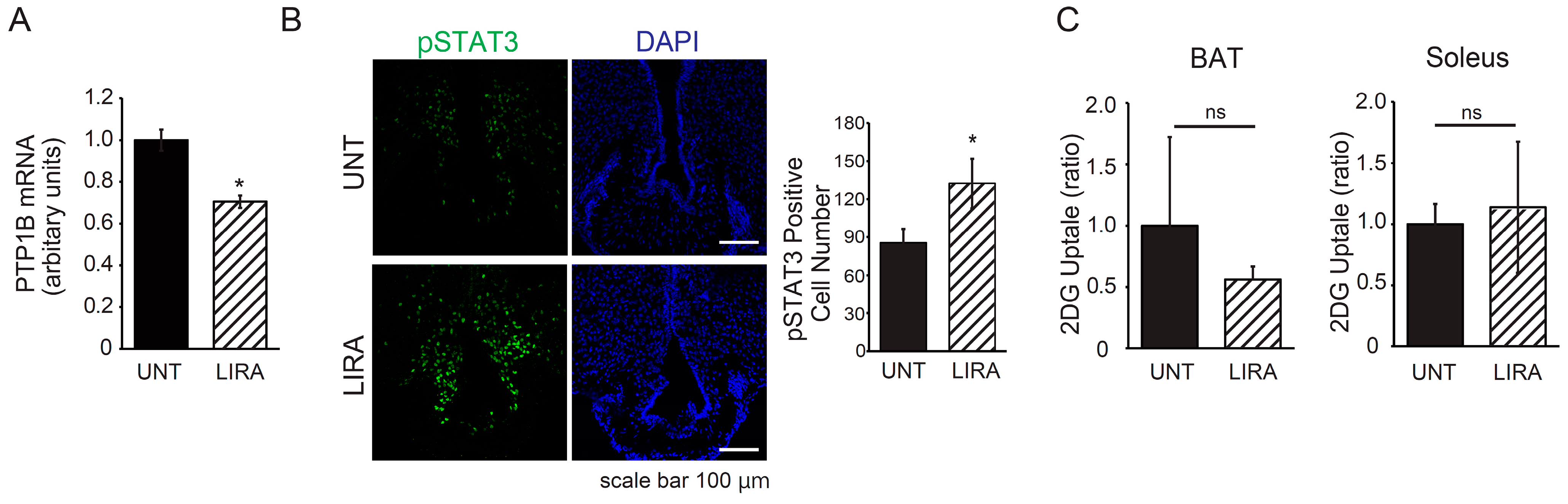
2.4. Liraglutide Treatment Resulted in Decreased PTP1B Expression in the Hypothalamic Arcuate Nucleus and Enhanced Leptin Receptor Signaling in Mice with IDDM
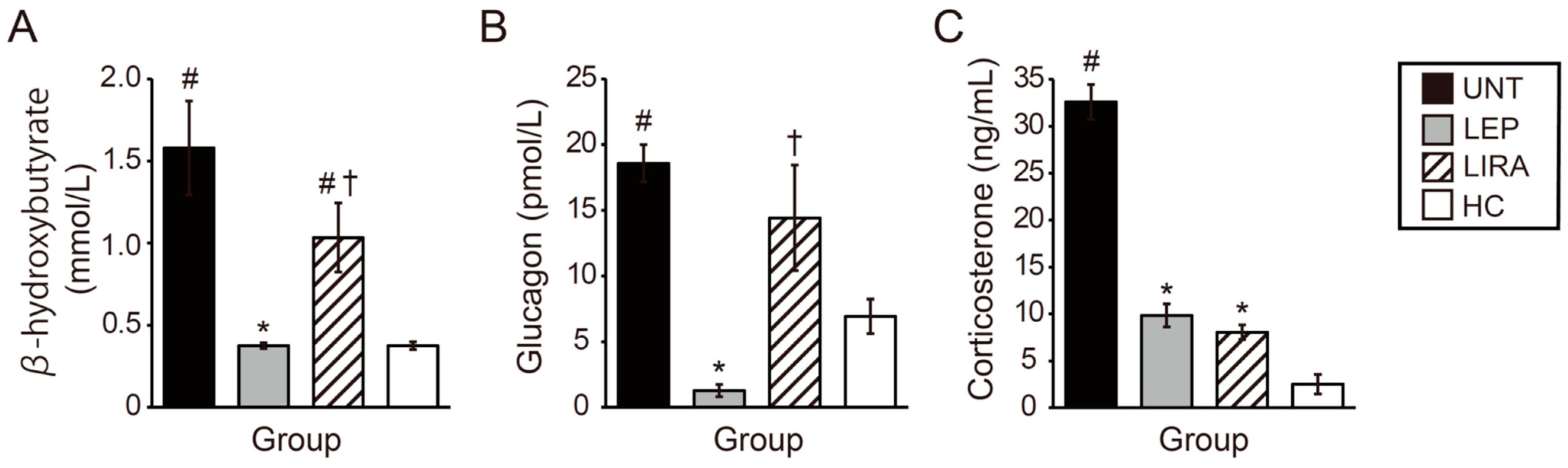
2.5. Leptin and Liraglutide Improved Hypercorticosteronemia, but Only Leptin Improved Hyperketonemia and Hyperglucagonemia in Mice with IDDM
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Model and Experimental Design
4.2. In Vivo Glucose Homeostasis
4.3. Blood and Tissue Samples
4.4. Measurement of Serum Glucagon and Corticosterone Levels
4.5. Measurement of 2-Deoxyglucose Uptake
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. Gene Expression Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IDDM | Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus |
| BG | Blood glucose |
| GTT | Glucose tolerance test |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| PTP1B | Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| ARC | Arcuate nucleus |
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
| BW | Body weight |
| AUC | Area under the curve |
| 2DG | 2-deoxyglucose |
| BAT | Brown adipose tissue |
| BH | β-hydroxybutyrate |
References
- Mathis, D.; Vence, L.; Benoist, C. beta-Cell death during progression to diabetes. Nature 2001, 414, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMeglio, L.A.; Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2018, 391, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cryer, P.E. Mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure and its component syndromes in diabetes. Diabetes 2005, 54, 3592–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, J.; Brekke, M.; Sandvik, L.; Arnesen, H.; Hanssen, K.F.; Dahl-Jorgensen, K. Silent coronary atheromatosis in type 1 diabetic patients and its relation to long-term glycemic control. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2637–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orchard, T.J.; Olson, J.C.; Erbey, J.R.; Williams, K.; Forrest, K.Y.; Smithline Kinder, L.; Ellis, D.; Becker, D.J. Insulin resistance-related factors, but not glycemia, predict coronary artery disease in type 1 diabetes: 10-year follow-up data from the Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications Study. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1374–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachin, J.M.; Nathan, D.M. Understanding metabolic memory: The prolonged influence of glycemia during the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT) on future risks of complications during the study of the Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (EDIC). Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 2216–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachin, J.M.; Bebu, I.; Nathan, D.M. The beneficial effects of earlier versus later implementation of intensive therapy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 2225–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, D.M.; Genuth, S.; Lachin, J.; Cleary, P.; Crofford, O.; Davis, M.; Rand, L.; Siebert, C. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 329, 977–986. [Google Scholar]
- Borchers, A.T.; Uibo, R.; Gershwin, M.E. The geoepidemiology of type 1 diabetes. Autoimmun. Rev. 2010, 9, A355–A3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmquist, J.K.; Elias, C.F.; Saper, C.B. From lesions to leptin: Hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron 1999, 22, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meek, T.H.; Morton, G.J. The role of leptin in diabetes: Metabolic effects. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, J.P.; Thaler, J.P.; Wisse, B.E.; Oh, I.S.; Sarruf, D.A.; Matsen, M.E.; Fischer, J.D.; Taborsky, G.J., Jr.; Schwartz, M.W.; Morton, G.J. Leptin activates a novel CNS mechanism for insulin-independent normalization of severe diabetic hyperglycemia. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 394–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Bartolome, C.L.; Low, C.S.; Yi, X.; Chien, C.H.; Wang, P.; Kong, D. Genetic identification of leptin neural circuits in energy and glucose homeostases. Nature 2018, 556, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, T.; Berglund, E.D.; Patel, V.R.; Ramadori, G.; Vianna, C.R.; Vong, L.; Thorel, F.; Chera, S.; Herrera, P.L.; Lowell, B.B.; et al. Leptin engages a hypothalamic neurocircuitry to permit survival in the absence of insulin. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.Y.; Chen, L.; Clark, G.O.; Lee, Y.; Stevens, R.D.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; Wenner, B.R.; Bain, J.R.; Charron, M.J.; Newgard, C.B.; et al. Leptin therapy in insulin-deficient type I diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4813–4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, C.; Muse, E.D.; Cheng, A.; Chen, L.; Scherer, T.; Pocai, A.; Su, K.; Cheng, B.; Li, X.; Harvey-White, J.; et al. Leptin controls adipose tissue lipogenesis via central, STAT3-independent mechanisms. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 667–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denroche, H.C.; Levi, J.; Wideman, R.D.; Sequeira, R.M.; Huynh, F.K.; Covey, S.D.; Kieffer, T.J. Leptin therapy reverses hyperglycemia in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes, independent of hepatic leptin signaling. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1414–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.J.; Peng, L.; Abulizi, A.; Kennedy, L.; Cline, G.W.; Shulman, G.I. Mechanism for leptin’s acute insulin-independent effect to reverse diabetic ketoacidosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasandani, C.; Clark, G.O.; Adams-Huet, B.; Quittner, C.; Garg, A. Efficacy and safety of metreleptin therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes: A pilot study. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Sun, R.; Yagimuma, H.; Taki, K.; Mizoguchi, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Onoue, T.; Tsunekawa, T.; Takagi, H.; et al. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency improves glucose homeostasis in type 1 diabetes treated with leptin. Diabetes 2022, 71, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonks, N.K.; Diltz, C.D.; Fischer, E.H. Purification of the major protein-tyrosine-phosphatases of human placenta. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 6722–6730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakke, J.; Haj, F.G. Protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B substrates and metabolic regulation. Semin. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2015, 37, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brautigan, D.L.; Pinault, F.M. Serine phosphorylation of protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP1B) in HeLa cells in response to analogues of cAMP or diacylglycerol plus okadaic acid. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1993, 127–128, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, R.C.; Bence, K.K. Central regulation of metabolism by protein tyrosine phosphatases. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabolotny, J.M.; Bence-Hanulec, K.K.; Stricker-Krongrad, A.; Haj, F.; Wang, Y.; Minokoshi, Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Elmquist, J.K.; Tartaglia, L.A.; Kahn, B.B.; et al. PTP1B regulates leptin signal transduction in vivo. Dev. Cell 2002, 2, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunekawa, T.; Banno, R.; Mizoguchi, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Tominaga, T.; Onoue, T.; Hagiwara, D.; Ito, Y.; Iwama, S.; Goto, M.; et al. Deficiency of PTP1B attenuates hypothalamic inflammation via activation of the JAK2-STAT3 Pathway in microglia. EBioMedicine 2017, 16, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bence, K.K.; Delibegovic, M.; Xue, B.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Neel, B.G.; Kahn, B.B. Neuronal PTP1B regulates body weight, adiposity and leptin action. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banno, R.; Zimmer, D.; De Jonghe, B.C.; Atienza, M.; Rak, K.; Yang, W.; Bence, K.K. PTP1B and SHP2 in POMC neurons reciprocally regulate energy balance in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 720–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balland, E.; Chen, W.; Dodd, G.T.; Conductier, G.; Coppari, R.; Tiganis, T.; Cowley, M.A. Leptin signaling in the arcuate nucleus reduces insulin’s capacity to suppress hepatic glucose production in obese mice. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 346–355.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren, S.; Fantus, I.G. Inhibition of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP1B: Potential therapy for obesity, insulin resistance and type-2 diabetes mellitus. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 21, 621–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoski, S.E.; Ong, Z.Y.; Fortin, S.M.; Schlessinger, E.S.; Grill, H.J. Liraglutide, leptin and their combined effects on feeding: Additive intake reduction through common intracellular signalling mechanisms. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; van Baar, M.J.B.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Hoorn, E.J.; Joles, J.A.; van Raalte, D.H. GLP-1 and the kidney: From physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 605–628. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, U.H.; Denroche, H.C.; Mojibian, M.; Covey, S.D.; Kieffer, T.J. Insulin knockout mice have extended survival but volatile blood glucose levels on leptin therapy. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa, T.; Chuang, J.C.; Sakata, I.; Ramadori, G.; Coppari, R. Leptin therapy improves insulin-deficient type 1 diabetes by CNS-dependent mechanisms in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17391–17396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaginuma, H.; Banno, R.; Sun, R.; Taki, K.; Mizoguchi, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Sugiyama, M.; Tsunekawa, T.; Onoue, T.; Takagi, H.; et al. Peripheral combination treatment of leptin and an SGLT2 inhibitor improved glucose metabolism in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 147, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.S.; Minokoshi, Y.; Hamai, M.; Iwai, M.; Horiuchi, M.; Shimazu, T. Role of the sympathetic nervous system and insulin in enhancing glucose uptake in peripheral tissues after intrahypothalamic injection of leptin in rats. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1706–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Shiuchi, T.; Toda, C.; Okamoto, S.; Coutinho, E.A.; Saito, K.; Miura, S.; Ezaki, O.; Minokoshi, Y. Induction of glucose uptake in skeletal muscle by central leptin is mediated by muscle β(2)-adrenergic receptor but not by AMPK. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.J.; Petersen, K.F.; Shulman, G.I. Pleotropic effects of leptin to reverse insulin resistance and diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 933–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, R.J.; Zhang, X.M.; Zhang, D.; Kumashiro, N.; Camporez, J.P.; Cline, G.W.; Rothman, D.L.; Shulman, G.I. Leptin reverses diabetes by suppression of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 759–763. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Kleine, N.; Orskov, C.; Holst, J.J.; Willms, B.; Creutzfeldt, W. Normalization of fasting hyperglycaemia by exogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36 amide) in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hare, K.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Asmar, M.; Deacon, C.F.; Knop, F.K.; Holst, J.J. The glucagonostatic and insulinotropic effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 contribute equally to its glucose-lowering action. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyton, J.; Jeon, M.; Brooks, A. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2019, 76, 1739–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Considine, R.V.; Sinha, M.K.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Nyce, M.R.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Marco, C.C.; McKee, L.J.; Bauer, T.L.; et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, M.; Halaas, J.; Ravussin, E.; Pratley, R.E.; Lee, G.H.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, H.; Kim, S.; Lallone, R.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. Leptin levels in human and rodent: Measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frederich, R.C.; Hamann, A.; Anderson, S.; Löllmann, B.; Lowell, B.B.; Flier, J.S. Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: Evidence for diet-induced resistance to leptin action. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1311–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, B.W.; Garg, S.K. The emerging role of adjunctive noninsulin antihyperglycemic therapy in the management of type 1 diabetes. Endocr. Pract. 2016, 22, 220–230. [Google Scholar]
- Heinzerling, L.; Raile, K.; Rochlitz, H.; Zuberbier, T.; Worm, M. Insulin allergy: Clinical manifestations and management strategies. Allergy 2008, 63, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Tobe, K.; Uchigata, Y.; Nakazono, M.; Yasuda, K.; Terauchi, Y.; Iwamoto, Y.; Akanuma, Y.; Kimura, S.; Kadowaki, T. Antibody-mediated insulin resistance treated by cessation of insulin administration. Intern. Med. 2000, 39, 143–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, K.M.; Foster, N.C.; Beck, R.W.; Bergenstal, R.M.; DuBose, S.N.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Maahs, D.M.; Tamborlane, W.V. Current state of type 1 diabetes treatment in the U.S.: Updated data from the T1D Exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 971–978. [Google Scholar]
- Withaar, C.; Meems, L.M.G.; Markousis-Mavrogenis, G.; Boogerd, C.J.; Silljé, H.H.W.; Schouten, E.M.; Dokter, M.M.; Voors, A.A.; Westenbrink, B.D.; Lam, C.S.P.; et al. The effects of liraglutide and dapagliflozin on cardiac function and structure in a multi-hit mouse model of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 2108–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakipovski, G.; Rolin, B.; Nøhr, J.; Klewe, I.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Augustin, R.; Hecksher-Sørensen, J.; Ingvorsen, C.; Polex-Wolf, J.; Knudsen, L.B. The GLP-1 analogs liraglutide and semaglutide reduce atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− and LDLr−/− mice by a mechanism that includes inflammatory pathways. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2018, 3, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjørnholm, K.D.; Skovsted, G.F.; Mitgaard-Thomsen, A.; Rakipovski, G.; Tveden-Nyborg, P.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Povlsen, G.K. Liraglutide treatment improves endothelial function in the Ldlr−/− mouse model of atherosclerosis and affects genes involved in vascular remodelling and inflammation. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 128, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 5th ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019; p. 103. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, L.; Sugiyama, M.; Kamal, S.; Ide, T.; Takeda, T.; Kuno, M.; Takagi, H.; Koike, T.; Arima, H.; Banno, R. Effects of Combination Treatment with Leptin and Liraglutide on Glucose Metabolism in Insulin-Dependent Diabetic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104595
Fu L, Sugiyama M, Kamal S, Ide T, Takeda T, Kuno M, Takagi H, Koike T, Arima H, Banno R. Effects of Combination Treatment with Leptin and Liraglutide on Glucose Metabolism in Insulin-Dependent Diabetic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104595
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Linlin, Mariko Sugiyama, Shahriar Kamal, Tsubasa Ide, Tadashi Takeda, Mitsuhiro Kuno, Hiroshi Takagi, Teruhiko Koike, Hiroshi Arima, and Ryoichi Banno. 2025. "Effects of Combination Treatment with Leptin and Liraglutide on Glucose Metabolism in Insulin-Dependent Diabetic Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104595
APA StyleFu, L., Sugiyama, M., Kamal, S., Ide, T., Takeda, T., Kuno, M., Takagi, H., Koike, T., Arima, H., & Banno, R. (2025). Effects of Combination Treatment with Leptin and Liraglutide on Glucose Metabolism in Insulin-Dependent Diabetic Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104595





