Incongruence Between Prerequisite Molecular Testing and Treatment with Personalized Therapies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results-Medicare Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
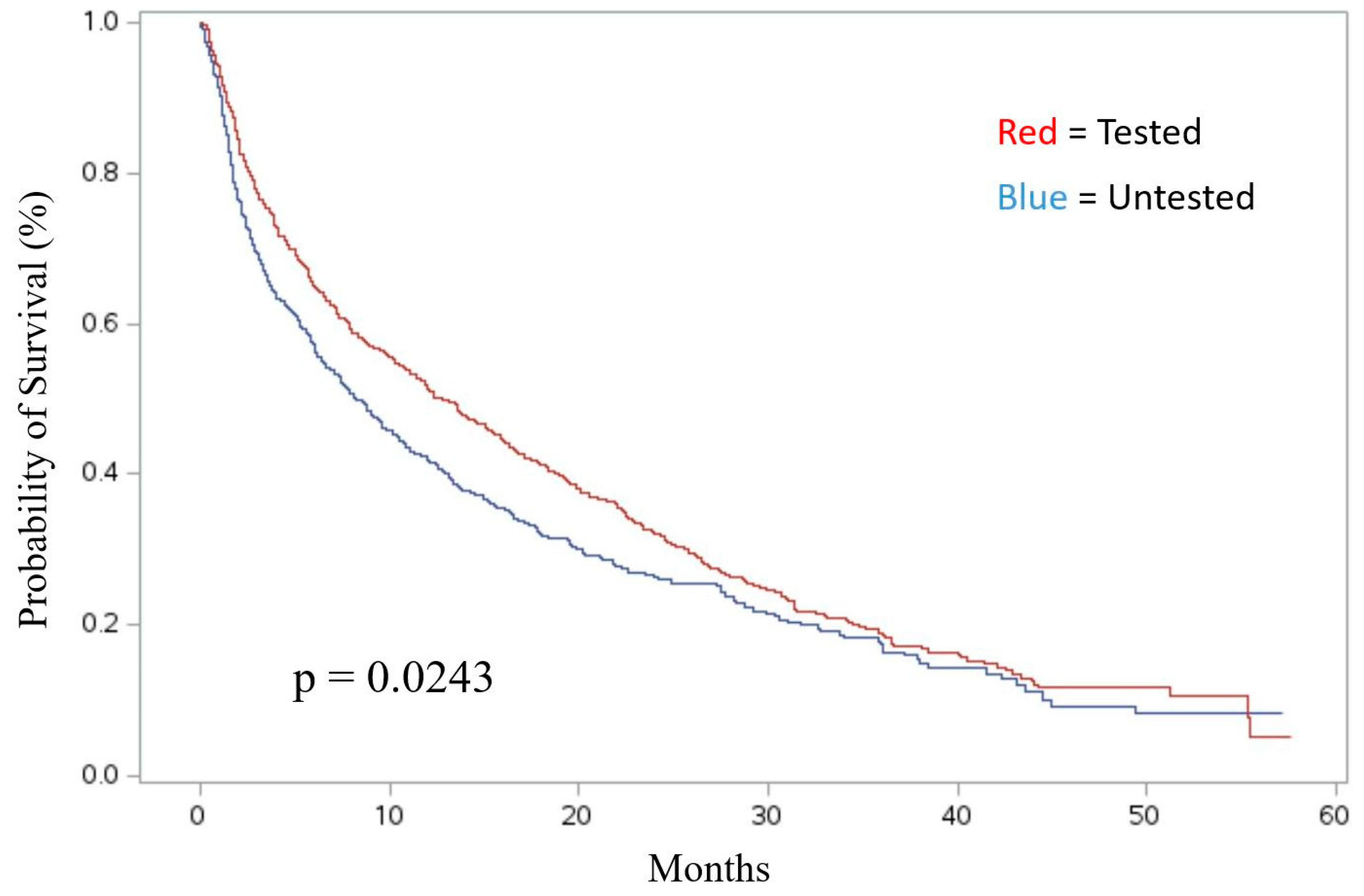
Association of Molecular Testing with Survival
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
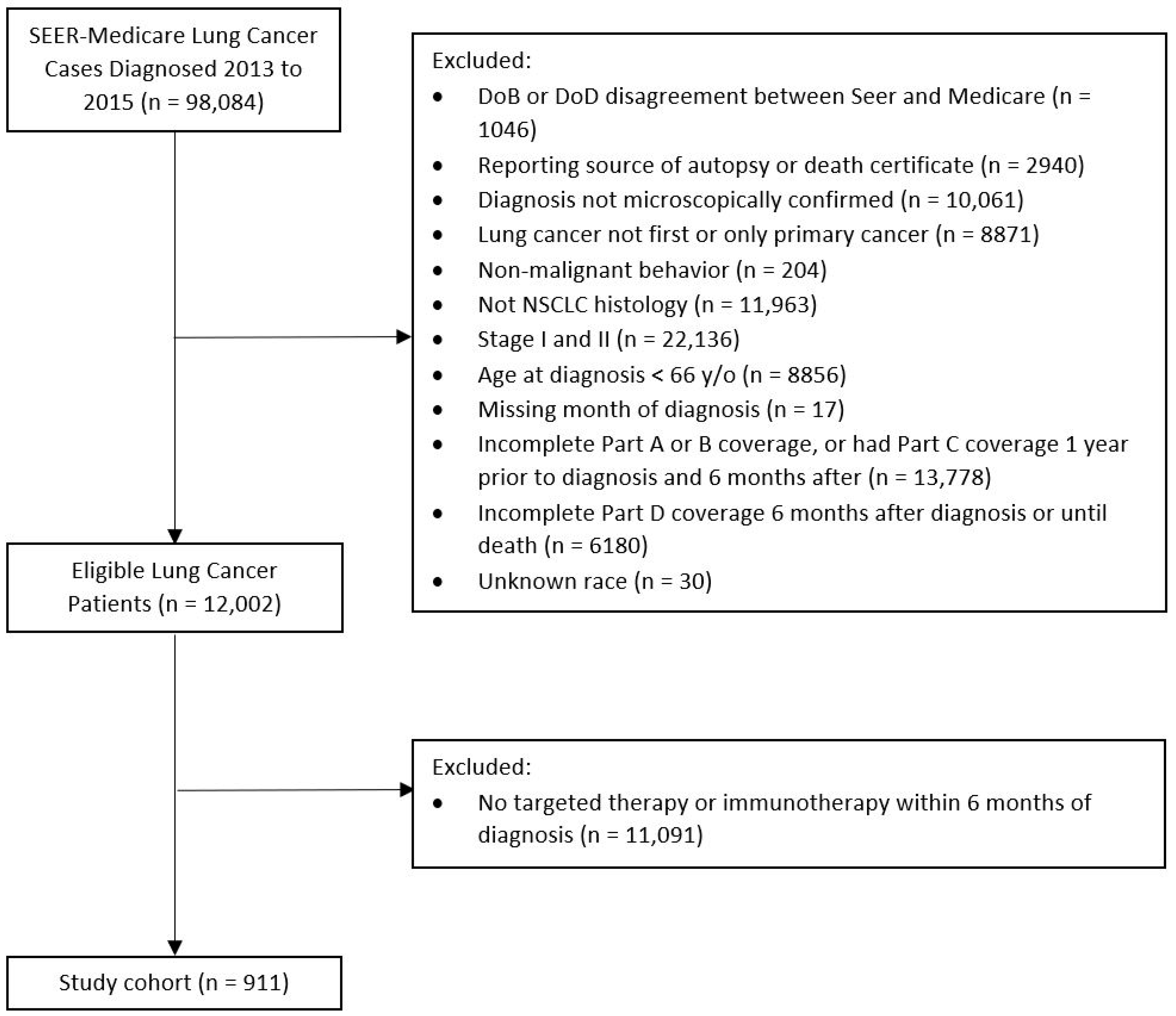
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Main Predictors and Covariates
4.3. Primary Outcome
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cancer of the Lung and Bronchus—Cancer Stat Facts. SEER. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/lungb.html (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Duma, N.; Santana-Davila, R.; Molina, J.R. Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and treatment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2019, 94, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Forjaz, G.; Mooradian, M.J.; Meza, R.; Kong, C.Y.; Cronin, K.A.; Mariotto, A.B.; Lowy, D.R.; Feuer, E.J. The Effect of Advances in Lung-Cancer Treatment on Population Mortality. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 640–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamgeer, M.; Ganju, V.; Watkins, D.N. Novel therapeutic targets in non-small cell lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2013, 13, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, B.A.; Hughes, B.G. Targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: Current standards and the promise of the future. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midha, A.; Dearden, S.; McCormack, R. EGFR mutation incidence in non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology: A systematic review and global map by ethnicity (mutMapII). Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 2892–2911. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, P.L.; Mitchell, P.; Dobrovic, A.; John, T. Prevalence and natural history of ALK positive non-small-cell lung cancer and the clinical impact of targeted therapy with ALK inhibitors. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 6, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways: Similarities, Differences, and Implications of Their Inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacher, A.G.; Gandhi, L. Biomarkers for the Clinical Use of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitors in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1217–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Liu, X.; Ma, T.; Lv, D.; Sun, G. Predictive value of tumor mutational burden for immunotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0263629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.; Ben-Shachar, R.; Gao, Y.; Hyun, S.W.; Rivers, Z.; Epstein, C.; Kaneva, K.; Sangli, C.; Nimeiri, H.; Patel, J. Assessment of Tumor Mutational Burden and Outcomes in Patients With Diverse Advanced Cancers Treated With Immunotherapy. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2311181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.J.; Kehl, K.L.; Brooks, G.A.; Sholl, L.; Wright, A.A.; Landrum, M.B.; Keating, N.L. Practice-Level Variation in Molecular Testing and Use of Targeted Therapy for Patients With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Colorectal Cancer. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2310809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindeman, N.I.; Cagle, P.T.; Aisner, D.L.; Arcila, M.E.; Beasley, M.B.; Bernicker, E.H.; Colasacco, C.; Dacic, S.; Hirsch, F.R.; Kerr, K.; et al. Updated Molecular Testing Guideline for the Selection of Lung Cancer Patients for Treatment With Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Guideline From the College of American Pathologists, the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and the Association for Molecular Pathology. J. Mol. Diagn. 2018, 20, 129–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, J.P.; Li, T.; Yoneda, K.Y. Molecular testing strategies in non-small cell lung cancer: Optimizing the diagnostic journey. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 286–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakelee, H.; Liberman, M.; Kato, T.; Tsuboi, M.; Lee, S.-H.; Gao, S.; Chen, K.-N.; Dooms, C.; Majem, M.; Eigendorff, E.; et al. KEYNOTE-671 Investigators. Perioperative pembrolizumab for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 491–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spicer, J.D.; Gao, S.; Liberman, M.; Kato, T.; Tsuboi, M.; Lee, S.-H.; Chen, K.-N.; Dooms, C.; Majem, M.; Eigendorff, E.; et al. LBA56 Overall survival in the KEYNOTE-671 study of perioperative pembrolizumab for early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34 (Suppl. 2), S1297–S1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorin, M.; Prosty, C.; Ghaleb, L.; Nie, K.; Katergi, K.; Shahzad, M.H.; Dubé, L.-R.; Atallah, A.; Swaby, A.; Dankner, M.; et al. Neoadjuvant Chemoimmunotherapy for NSCLC: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Oncol. 2024, 10, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, L.L.; Sheehan, D.F.; Tramontano, A.C.; Kong, C.Y. Disparities and Trends in Genetic Testing and Erlotinib Treatment Among Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. Publ. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. Cosponsored Am. Soc. Prev. Oncol. 2019, 28, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.; Flores, R.M.; Taioli, E. Unequal racial distribution of immunotherapy for late-stage non-small cell lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2023, 115, 1224–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.; Vallurupalli, M.; McVeigh, Q.; Huang, F.W.; Rebbeck, T.R. Understanding inequities in precision oncology diagnostics. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Brown, C.; Gralla, R.J.; Hirsh, V.; Thongprasert, S.; Tsai, C.-M.; Tan, E.H.; Ho, J.C.-M.; Chu, D.T.; Zaatar, A.; et al. Impact of EGFR inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer on progression-free and overall survival: A meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enewold, L.; Thomas, A. Real-World Patterns of EGFR Testing and Treatment with Erlotinib for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer in the United States. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.; Tsao, M.S.; Le, L.W.; Shepherd, F.A.; Feld, R.; Burkes, R.L.; Liu, G.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Hwang, D.; Tanguay, J.; et al. Biomarker testing and time to treatment decision in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.E.; Choi, K.; Lanman, R.B.; Licitra, E.J.; Skrzypczak, S.M.; Benito, R.P.; Wu, T.; Arunajadai, S.; Kaur, S.; Harper, H.; et al. Genomic profiling of advanced non-small cell lung cancer in community settings: Gaps and opportunities. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarinshenas, R.; Amini, A.; Mambetsariev, I.; Abuali, T.; Fricke, J.; Ladbury, C.; Salgia, R. Assessment of Barriers and Challenges to Screening, Diagnosis, and Biomarker Testing in Early-Stage Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafham, G.K.; Craddock, K.J.; Huang, W.Y.; Louie, A.V.; Zhang, L.; Hwang, D.M.; Parmar, A. Referred molecular testing as a barrier to optimal treatment decision making in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: Experience at a tertiary academic institution in Canada. Cancer Med. 2024, 13, e6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.R.; Wu, X.L.; Sun, Y.L. Therapeutic targets and biomarkers of tumor immunotherapy: Response versus non-response. Sig Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cone, E.B.; Marchese, M.; Paciotti, M.; Nguyen, D.-D.; Nabi, J.; Cole, A.P.; Molina, G.; Molina, R.L.; Minami, C.A.; Mucci, L.A.; et al. Assessment of Time-to-Treatment Initiation and Survival in a Cohort of Patients With Common Cancers. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2030072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wang, L.; Shang, B.; Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Liang, B.; Su, L.; You, W.; Jiang, S. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated toxicity in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: An updated understanding of risk factors. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1094414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitinger, M.; Varosanec, M.V.; Pikija, S.; Wass, R.E.; Bandke, D.; Weis, S.; Studnicka, M.; Grinzinger, S.; McCoy, M.R.; Hauer, L.; et al. Fatal Necrotizing Encephalopathy after Treatment with Nivolumab for Squamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camidge, D.R.; Doebele, R.C.; Kerr, K.M. Comparing and contrasting predictive biomarkers for immunotherapy and targeted therapy of NSCLC. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 16, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Number of Persons by Race and Hispanic Ethnicity for SEER Participants—SEER Registries. SEER. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/registries/data.html (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Shi, Y.; Au, J.S.; Thongprasert, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Tsai, C.-M.; Khoa, M.T.; Heeroma, K.; Itoh, Y.; Cornelio, G.; Yang, P.-C. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2014, 9, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Illinois Cancer Collaborative. Improving Guideline-Based Molecular Profiling for Lung Cancer Patients in Illinois. ILCC. Available online: https://ilcc.lunaroja.org/ (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- SEER Program & Data—SEER-Medicare. Available online: https://healthcaredelivery.cancer.gov/seermedicare/aboutdata/program.html (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Wu, J.; Lin, Z. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Targeted Therapy: Drugs and Mechanisms of Drug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USDA ERS—Rural-Urban Continuum Codes. Available online: https://www.ers.usda.gov/data-products/rural-urban-continuum-codes/ (accessed on 26 December 2024).
- Travis, W.D.; Brambilla, E.; Burke, A.P.; Marx, A.; Nicholson, A.G. Introduction to The 2015 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus, and Heart. J. Thorac. Oncol. Off. Publ. Int. Assoc. Study Lung Cancer 2015, 10, 1240–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comorbidity SAS Macro (2014 version). Available online: https://healthcaredelivery.cancer.gov/seermedicare/considerations/macro-2014.html (accessed on 26 December 2024).
| Molecular Diagnostic Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| No n = 398 (43.7%) | Yes n = 513 (56.3%) | p-value | |
| Race | <0.001 | ||
| Black | 28 (7.0%) | 239 (3.1%) | |
| White | 270 (67.8%) | 403 (78.6%) | |
| Other | 100 (25.1%) | 94 (18.3%) | |
| Census Tract Poverty Indicator (% in poverty) | 0.183 | ||
| <10% in poverty | 205 (51.5%) | 287 (56.0%) | |
| >=10% in poverty | 193 (48.5%) | 226 (44.1%) | |
| Residence b | 0.018 | ||
| Metro (>20k) | 360 (91.1%) | 450 (88.4%) | |
| Urban/Rural (<20k) | 35 (8.9%) | 59 (11.5%) | |
| Sex | 0.252 | ||
| Male | 120 (30.2%) | 173 (33.7%) | |
| Female | 278 (69.9%) | 340 (66.3%) | |
| Age at diagnosis (years) | 0.800 | ||
| 65–69 | 72 (18.1%) | 101 (19.7%) | |
| 70–74 | 99 (24.9%) | 127 (24.8%) | |
| 75–79 | 85 (21.4%) | 109 (21.3%) | |
| 80–84 | 67 (16.8%) | 94 (18.3%) | |
| 85+ | 75 (18.8%) | 82 (16.0%) | |
| Marital Status | 0.393 | ||
| Single | 183 (46.0%) | 213 (41.5%) | |
| Married | 201 (50.5%) | 282 (55.0%) | |
| Unknown | 14 (3.5%) | 18 (3.5%) | |
| Charlson comorbidity score (mean, sd a) | 1.3 (1.6) | 1.0 (1.3) | <0.001 |
| Histology | 0.004 | ||
| Squamous | 35 (8.8%) | 42 (8.2%) | |
| Adenocarcinoma | 316 (79.4%) | 444 (86.6%) | |
| Large cell/Other | 47 (11.8%) | 27 (5.2%) | |
| Primary Tumor Sites | 0.037 | ||
| Upper lobe | 202 (50.8%) | 246 (48.0%) | |
| Middle lobe | 12 (3.0%) | 21 (4.1%) | |
| Lower lobe | 92 (23.1%) | 155 (30.2%) | |
| Other | 92 (23.1%) | 91 (17.7%) | |
| Stage | 0.026 | ||
| III | 109 (27.4%) | 108 (21.1%) | |
| IV | 289 (72.6%) | 405 (78.9%) | |
| Year of Diagnosis | 0.033 | ||
| 2013 | 128 (32.2%) | 159 (31.0%) | |
| 2014 | 134 (33.7%) | 139 (27.1%) | |
| 2015 | 136 (34.2%) | 215 (41.9%) | |
| EGFR Test | ||
|---|---|---|
| No n = 316 (61.6%) | Yes n = 197 (38.4%) | |
| EGFR Treatment | ||
| No | 66 (20.9%) | 31 (15.7%) |
| Yes | 250 (79.1%) | 166 (84.3%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Turner, W.M.; Tuminello, S.; Untalan, M.; Flores, R.; Taioli, E. Incongruence Between Prerequisite Molecular Testing and Treatment with Personalized Therapies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results-Medicare Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104581
Turner WM, Tuminello S, Untalan M, Flores R, Taioli E. Incongruence Between Prerequisite Molecular Testing and Treatment with Personalized Therapies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results-Medicare Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104581
Chicago/Turabian StyleTurner, Wiley M., Stephanie Tuminello, Matthew Untalan, Raja Flores, and Emanuela Taioli. 2025. "Incongruence Between Prerequisite Molecular Testing and Treatment with Personalized Therapies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results-Medicare Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104581
APA StyleTurner, W. M., Tuminello, S., Untalan, M., Flores, R., & Taioli, E. (2025). Incongruence Between Prerequisite Molecular Testing and Treatment with Personalized Therapies for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results-Medicare Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104581







