Silk-Soy Alloy Materials: Influence of Silk Types (Mori, Thai, Muga, Tussah, and Eri) on the Structure, Properties, and Functionality of Insect–Plant Protein Blends (II)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
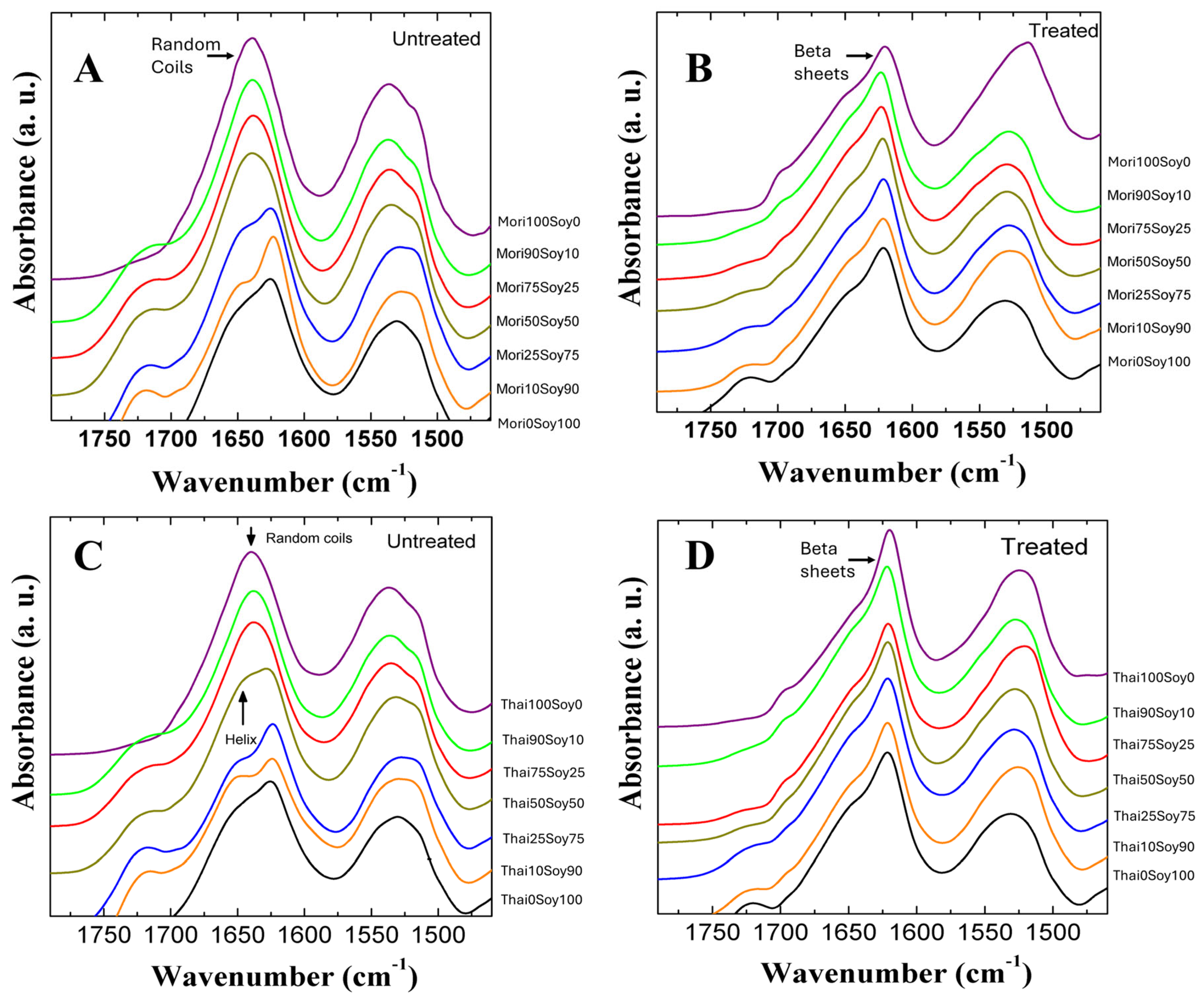
2.1. Structural Analysis
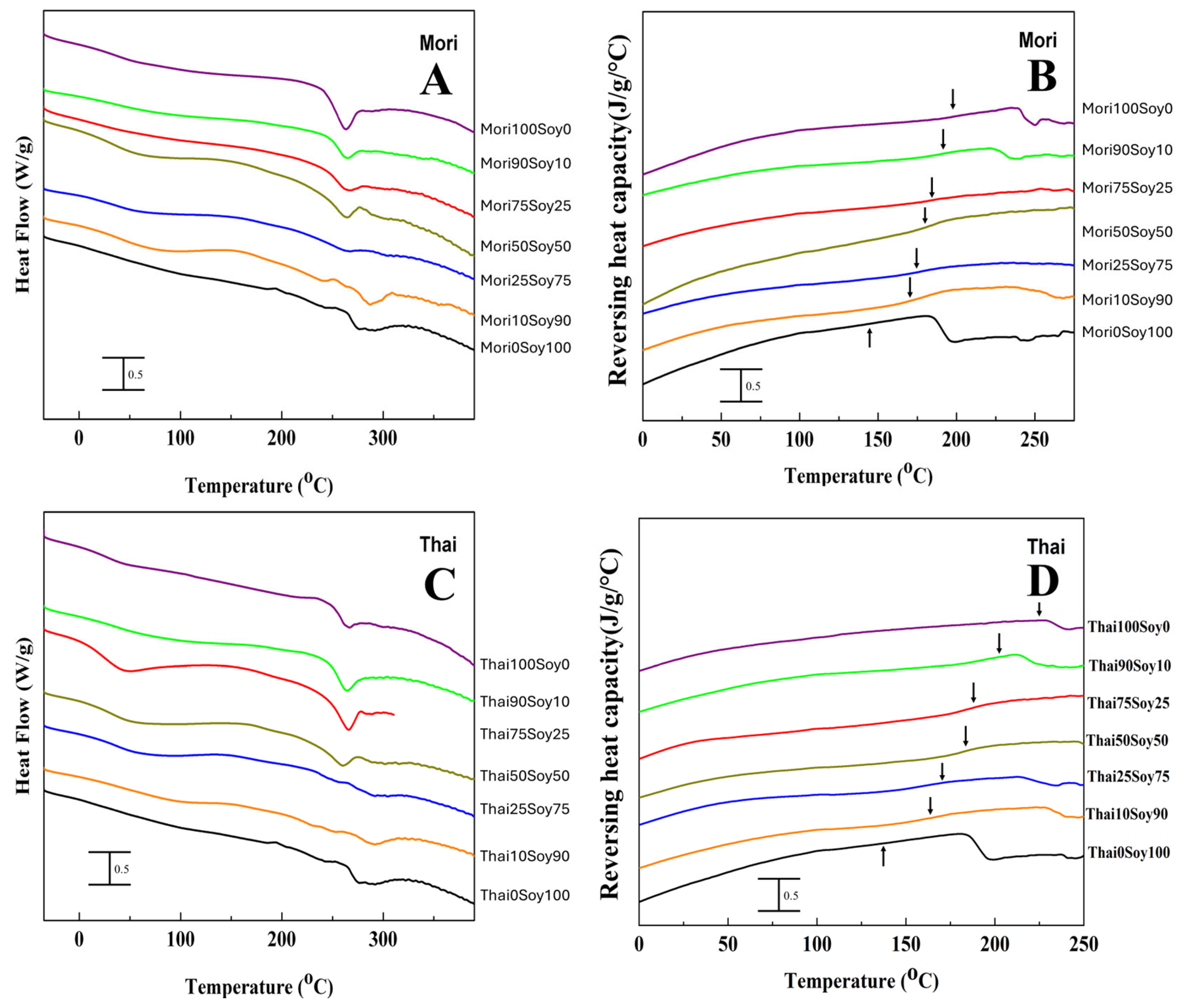
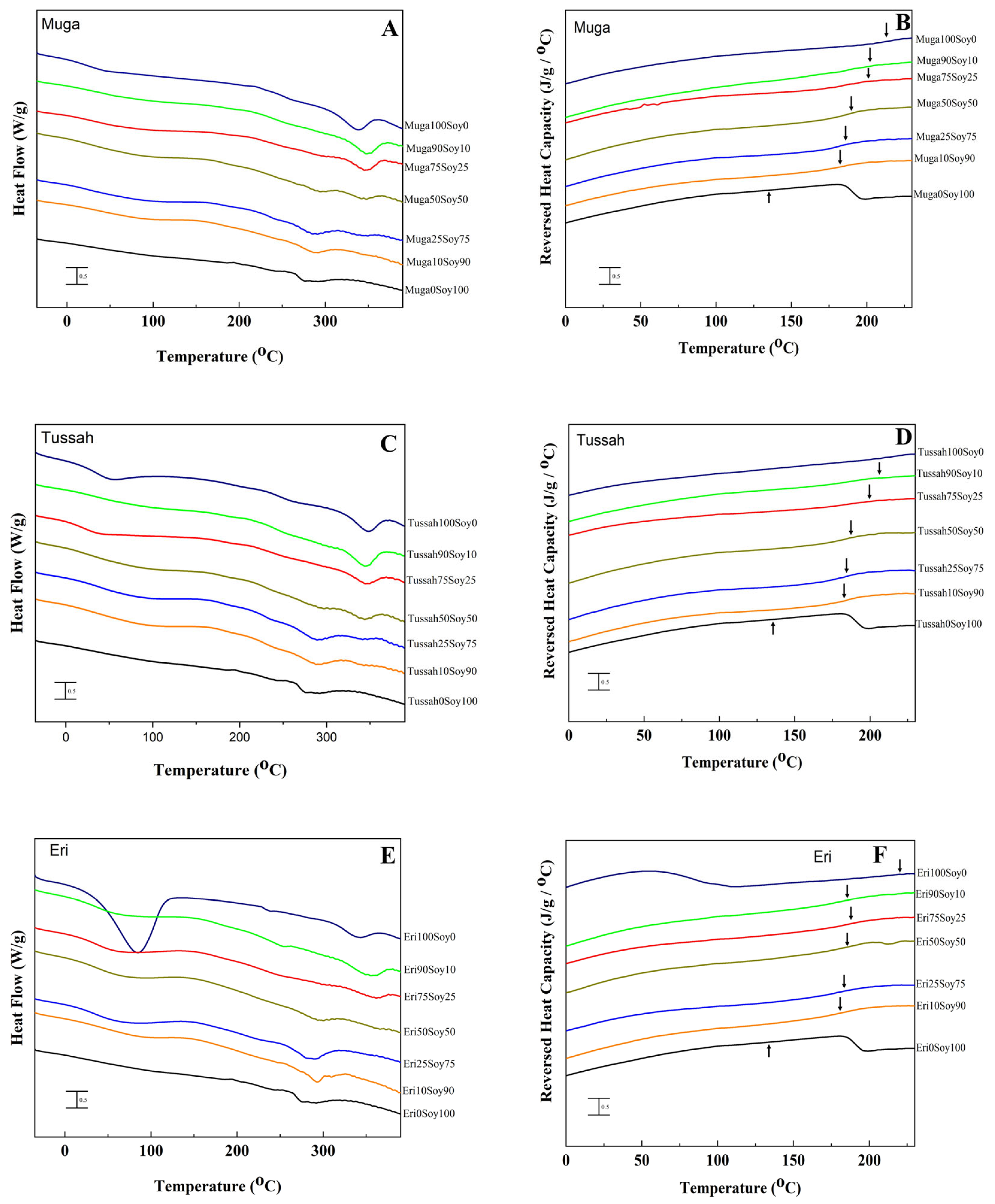
2.2. Thermal Analysis
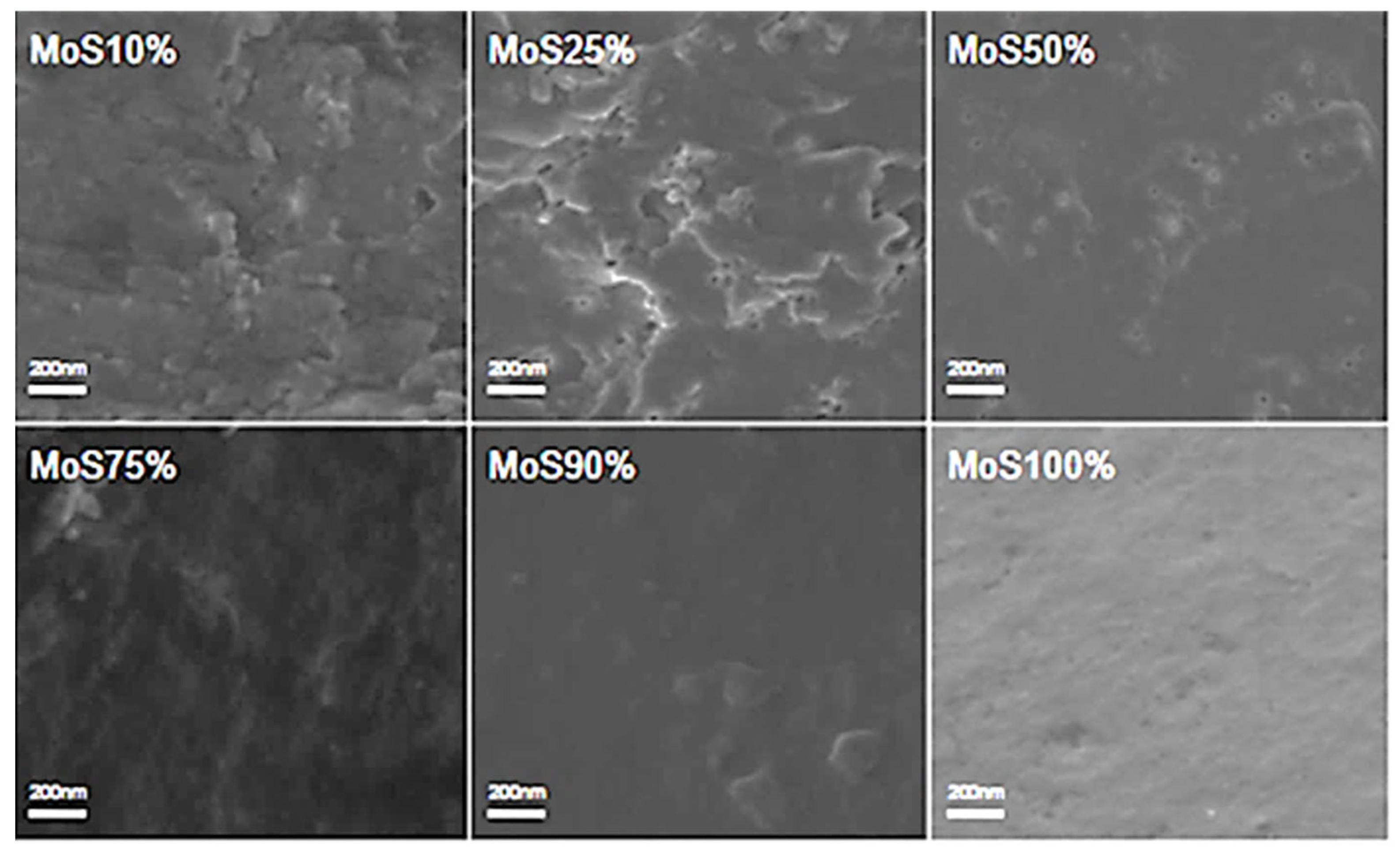
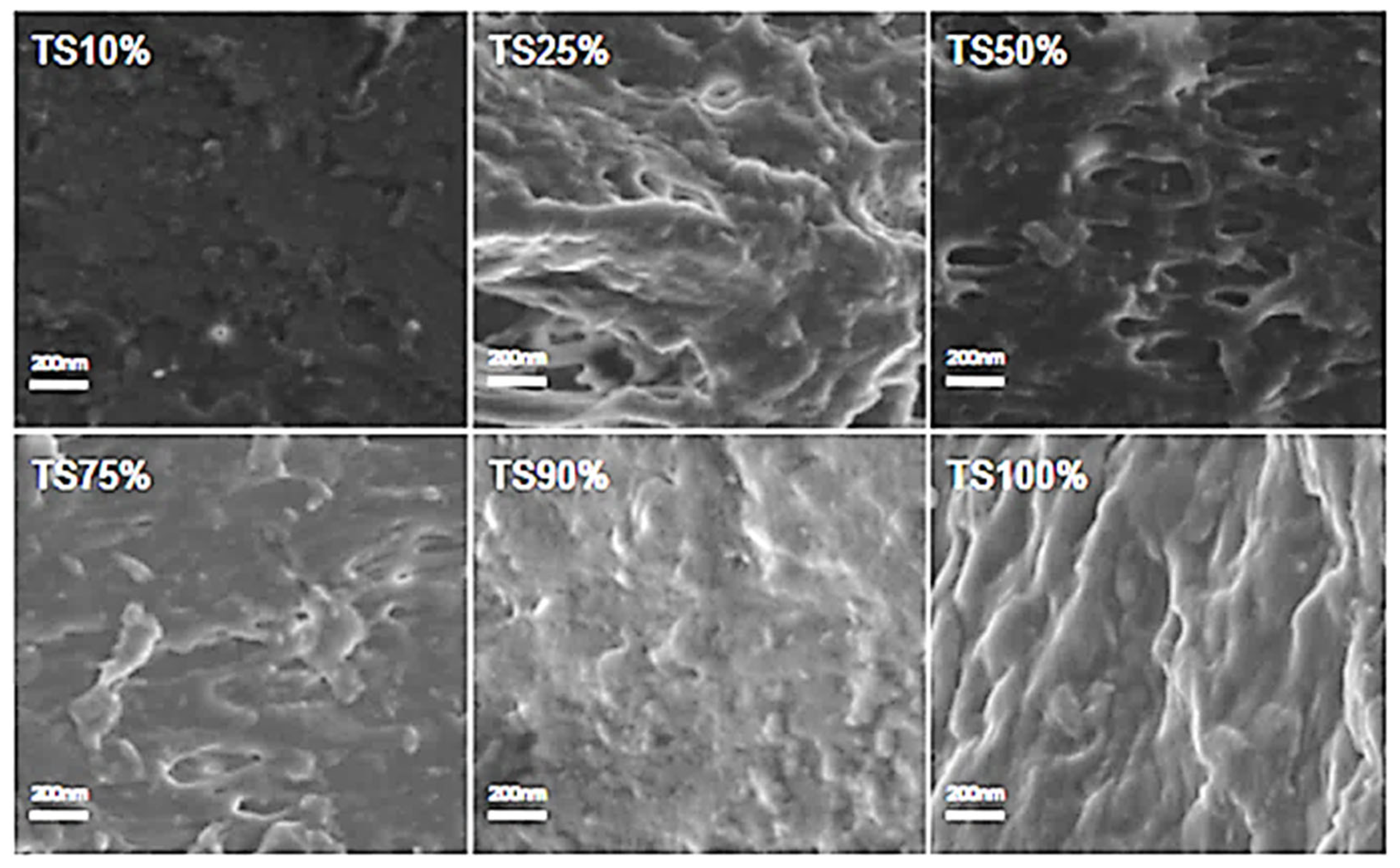
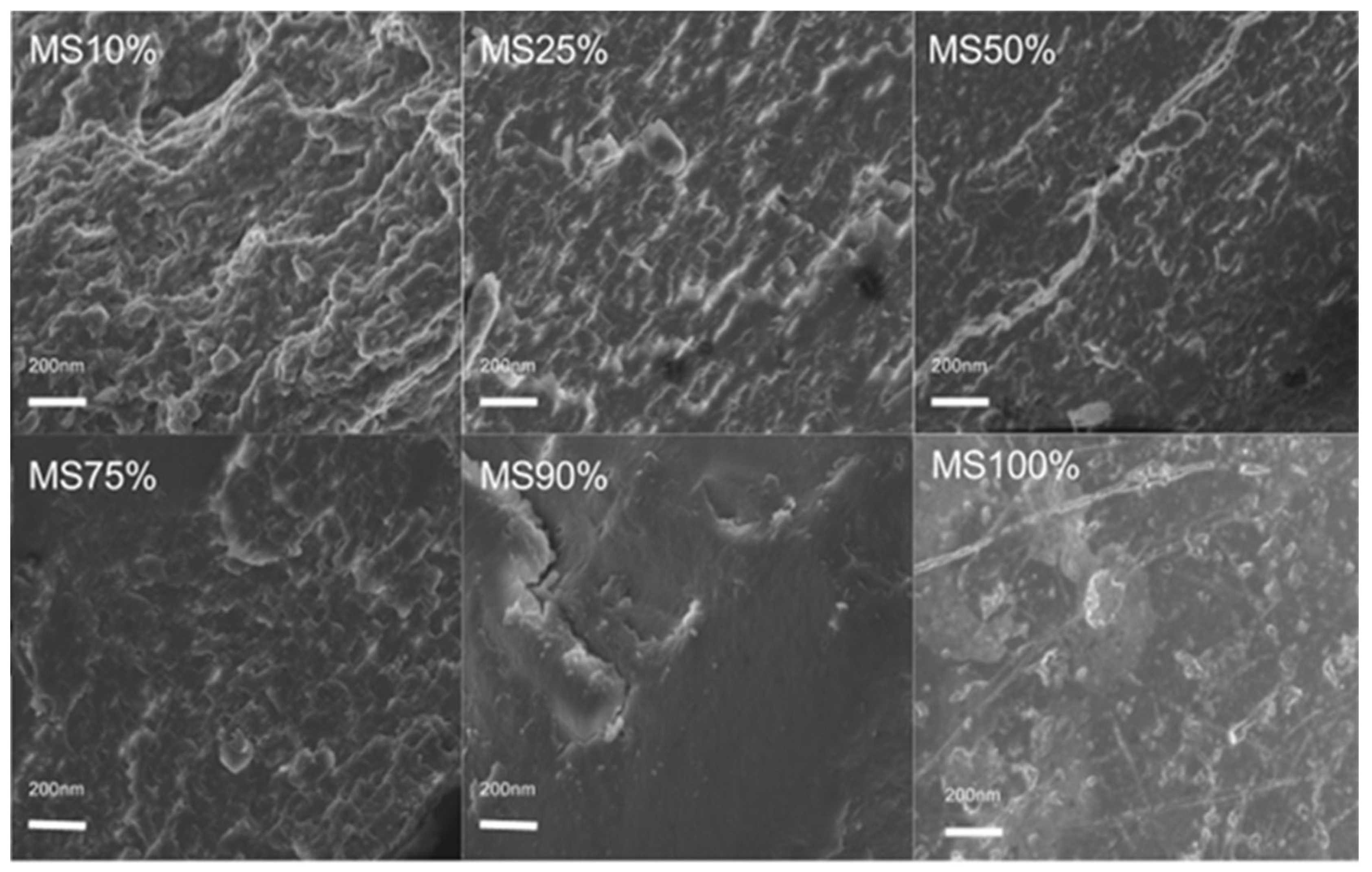
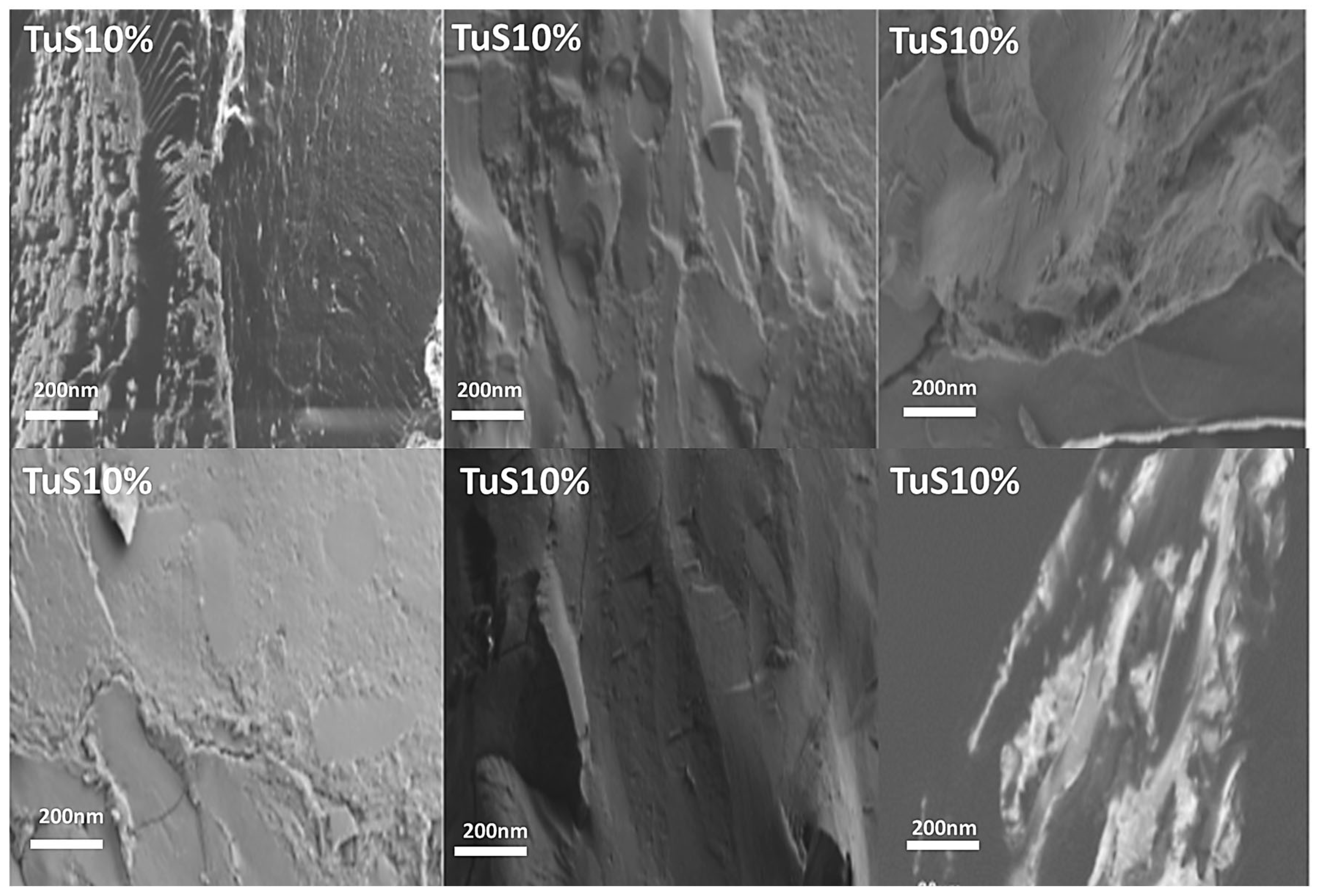
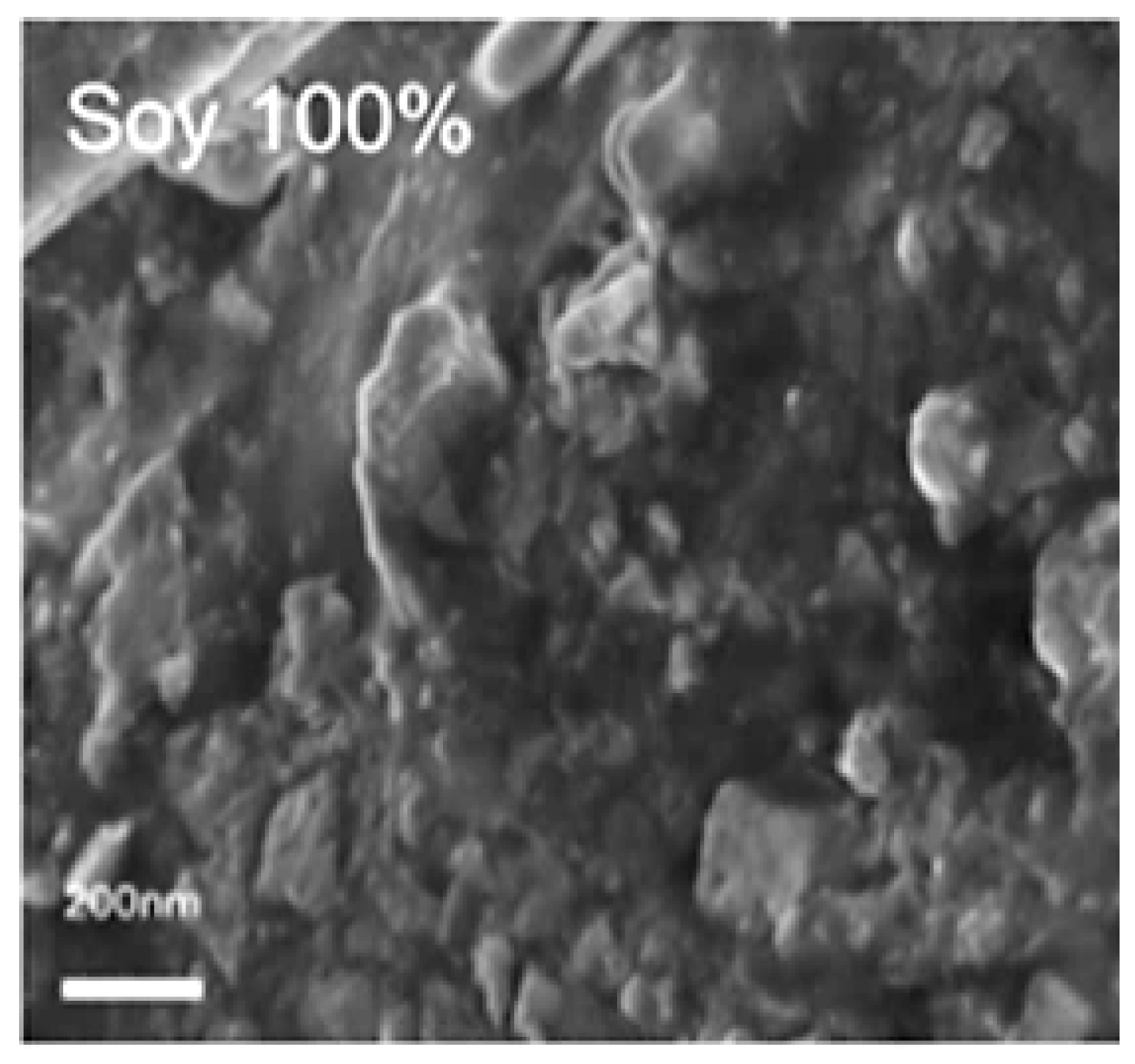
2.3. Morphology Analysis
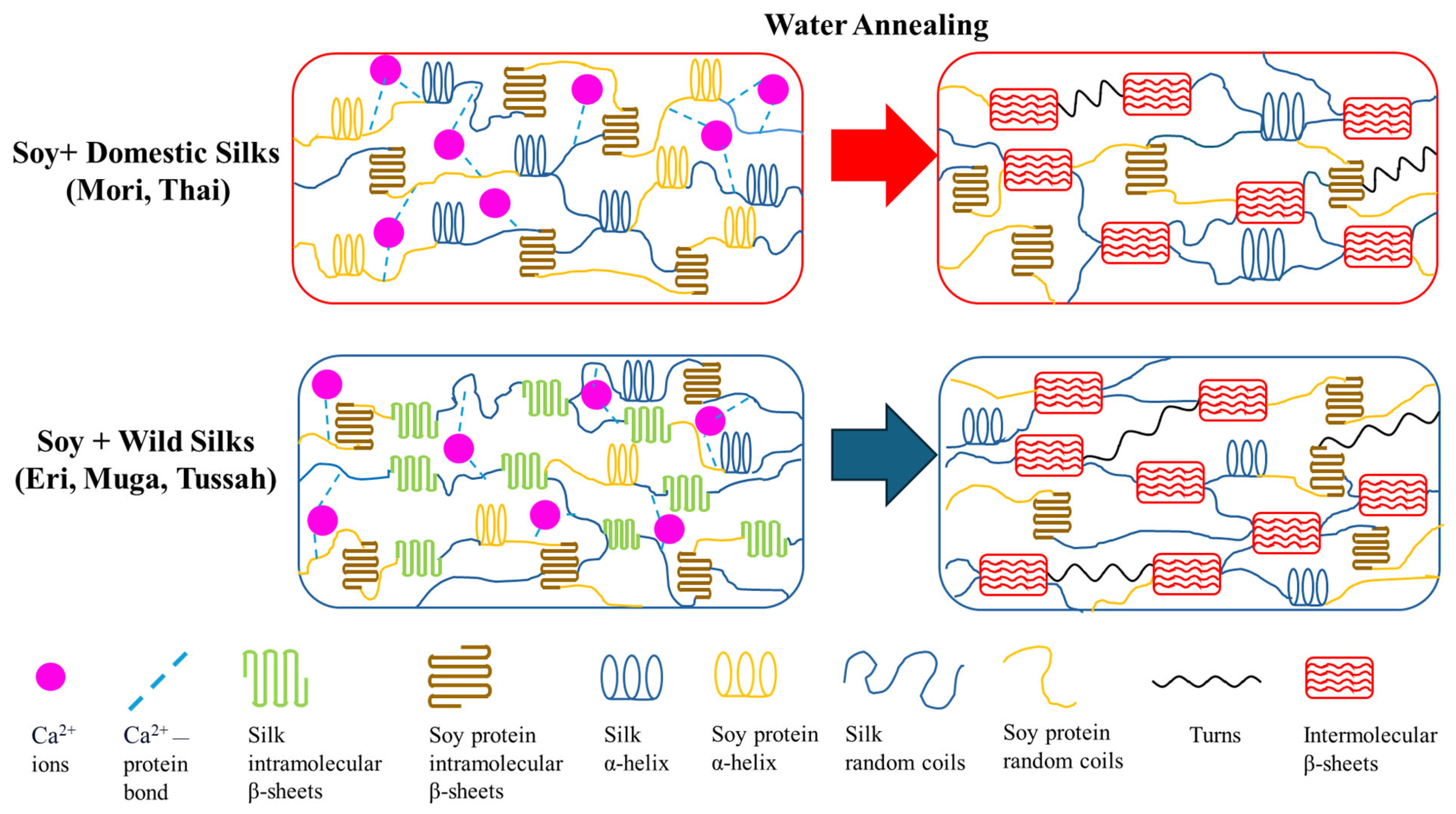
2.4. Mechanism
3. Materials and Methods
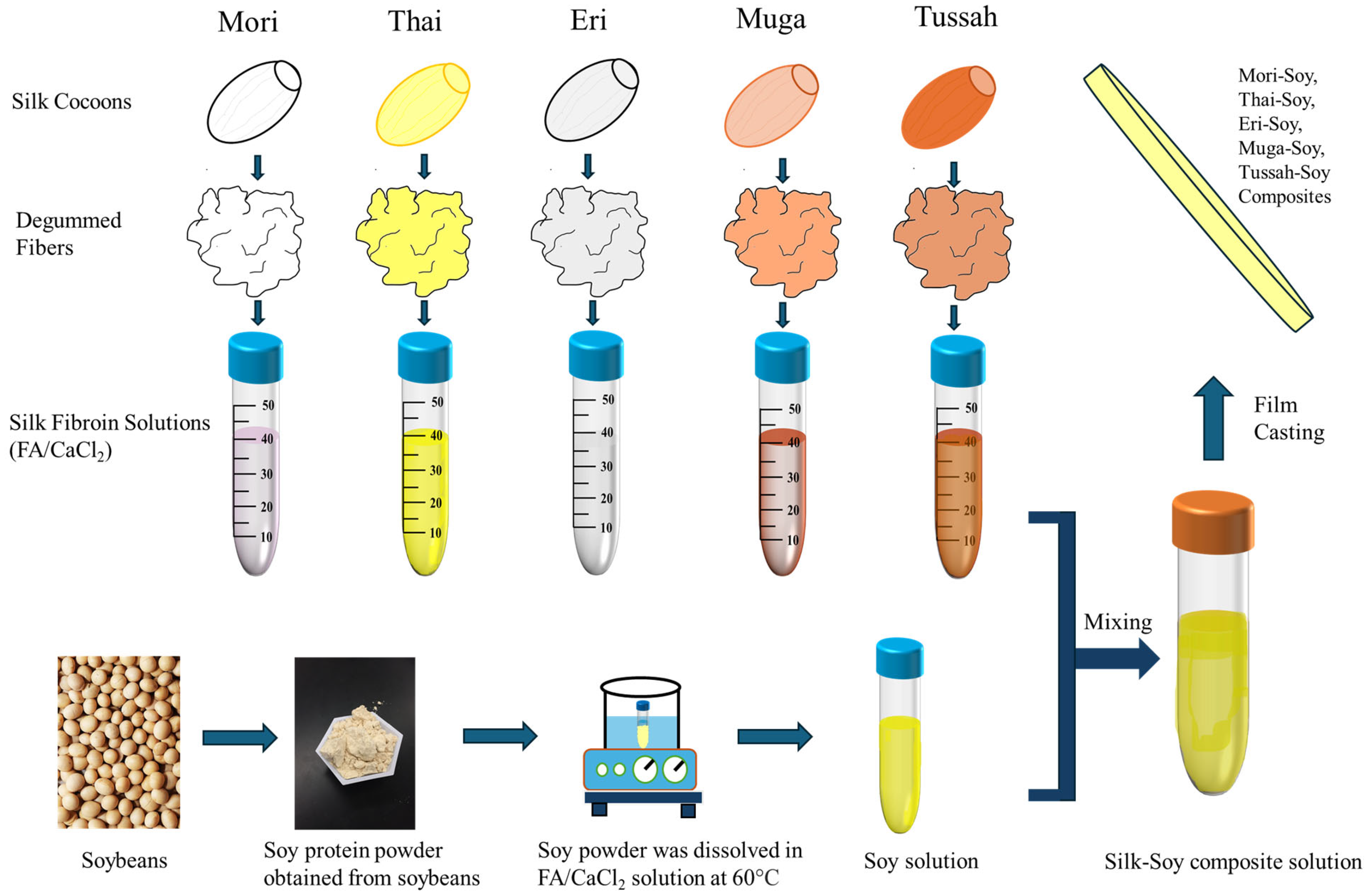
3.1. Preparation of Materials
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrometry (FTIR)
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, X.; Cebe, P.; Weiss, A.S.; Omenetto, F.; Kaplan, D.L. Protein-based composite materials. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Duki, S.; Forys, J.; Hettinger, J.; Buchicchio, J.; Dobbins, T.; Yang, C. Designing Silk-silk Protein Alloy Materials for Biomedical Applications. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, 13, e50891. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, D.; McGrath, K. Protein-Based Materials; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.-J.; Kaplan, D.L. Mechanism of silk processing in insects and spiders. Nature 2003, 424, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, A.; Fambri, L.; Migliaresi, C. Regenerated silk fibroin films: Thermal and dynamic mechanical analysis. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2002, 203, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huemmerich, D.; Slotta, U.; Scheibel, T. Processing and modification of films made from recombinant spider silk proteins. Appl. Phys. A 2006, 82, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shao, Z.; Marinkovic, N.S.; Miller, L.M.; Zhou, P.; Chance, M.R. Conformation transition kinetics of regenerated Bombyx mori silk fibroin membrane monitored by time-resolved FTIR spectroscopy. Biophys. Chem. 2001, 89, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyde, A.J.; Wippler, C. Molecular weight of silk fibroin. J. Polym. Sci. 1962, 58, 1083–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wool, R.; Sun, X.S. Bio-Based Polymers and Composites; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A.; Xu, J. Effect of ionic strength and pH on the thermal and rheological properties of soy protein–amylopectin blend. Food Chem. 2003, 83, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuysinuan, P.; Pengsuk, C.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Techasakul, S.; Svasti, J.; Nooeaid, P. Enhanced Structural Stability and Controlled Drug Release of Hydrophilic Antibiotic-Loaded Alginate/Soy Protein Isolate Core-Sheath Fibers for Tissue Engineering Applications. Fibers Polym. 2019, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peles, Z.; Binderman, I.; Berdicevsky, I.; Zilberman, M. Soy protein films for wound-healing applications: Antibiotic release, bacterial inhibition and cellular response. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2013, 7, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Souzandeh, H.; Zheng, Y.; Xie, Y.; Zhong, W.-H.; Wang, C. Soy protein isolate/bacterial cellulose composite membranes for high efficiency particulate air filtration. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2017, 138, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.-J.; Kim, S.-J.; You, Y.-S.; Lacroix, M.; Han, J. Inhibitory effect of soy protein coating formulations on walnut (Juglans regia L.) kernels against lipid oxidation. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 51, 393–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poluri, N.; Gough, C.R.; Sanderlin, S.; Velardo, C.; Barca, A.; Pinto, J.; Perrotta, J.; Cohen, M.; Hu, X. Silk-Corn Zein Alloy Materials: Influence of Silk Types (Mori, Thai, Muga, Tussah, and Eri) on the Structure, Properties, and Functionality of Insect-Plant Protein Blends. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 26, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, S.A.; Popov, E.; Rybacki, K.; Hu, X.; Salas-de la Cruz, D. Facile treatment to fine-tune cellulose crystals in cellulose-silk biocomposites through hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Jian, M.; Wang, C.; Xia, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Liang, X.; et al. Splash-Resistant and Light-Weight Silk-Sheathed Wires for Textile Electronics. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 7085–7091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defrates, K.; Markiewicz, T.; Callaway, K.; Xue, Y.; Stanton, J.; Salas-de La Cruz, D.; Hu, X. Structure–property relationships of Thai silk–microcrystalline cellulose biocomposite materials fabricated from ionic liquid. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 104 (Pt A), 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, Q.; Wen, J.; Chen, X.; Shao, Z. Preparation and characterization of transparent silk fibroin/cellulose blend films. Polymer 2013, 54, 5035–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen-Karni, T.; Jeong, K.J.; Tsui, J.H.; Reznor, G.; Mustata, M.; Wanunu, M.; Graham, A.; Marks, C.; Bell, D.C.; Langer, R.; et al. Nanocomposite gold-silk nanofibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5403–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, X.; Song, T.; Li, Y.; Pu, Y. Biodegradable nanofibrous membrane of zein/silk fibroin by electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2009, 58, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Huang, Y.; Lu, L.; Fan, L.; Mangavel, C.; Lourdin, D. Mechanical Properties of Thermo-moulded Biofilms in Relation to Proteins/Starch Interactions. Food Biophys. 2011, 6, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Huang, Y.; Yu, H.; Lee, T.-C.; Huang, Q. Reducing the brittleness of zein films through chemical modification. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blessing, B.; Trout, C.; Morales, A.; Rybacki, K.; Love, S.A.; Lamoureux, G.; O’Malley, S.M.; Hu, X.; Salas-de la Cruz, D. Morphology and ionic conductivity relationship in silk/cellulose biocomposites. Polym. Int. 2019, 68, 1580–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwerx, C.; Velings, N.; Mestdagh, M.M.; Axelos, M.A.V. Physico-chemical properties and rheology of alginate gel beads formed with various divalent cations. Polym. Gels Netw. 1998, 6, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhyani, V.; Singh, N. Controlling the cell adhesion property of silk films by graft polymerization. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 5005–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-L.; Xu, Q.; Lu, Z.; Wang, J.-Y. Cell adhesion on zein films under shear stress field. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 111, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, A.R.; Demartini, D.G.; Izumi, M.; Sweeney, A.M.; Holt, A.L.; Morse, D.E. The role of protein assembly in dynamically tunable bio-optical tissues. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mithieux, S.M.; Rasko, J.E.J.; Weiss, A.S. Synthetic elastin hydrogels derived from massive elastic assemblies of self-organized human protein monomers. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 4921–4927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulmoli, J. Scaffolds for Neural Stem Cell Tissue Engineering; University of California, Irvine: Irvine, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vu, T.; Xue, Y.; Vuong, T.; Erbe, M.; Bennet, C.; Palazzo, B.; Popielski, L.; Rodriguez, N.; Hu, X. Comparative Study of Ultrasonication-Induced and Naturally Self-Assembled Silk Fibroin-Wool Keratin Hydrogel Biomaterials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, D.O.S.; Carletto, R.A.; Tonetti, C.; Giachet, F.T.; Varesano, A.; Vineis, C. Wool keratin film plasticized by citric acid for food packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2017, 12, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayden, R.S.; Quinn, K.P.; Alonzo, C.A.; Georgakoudi, I.; Kaplan, D.L. Quantitative characterization of mineralized silk film remodeling during long-term osteoblast–osteoclast co-culture. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3794–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Gong, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, P.; Wang, Q.; Qiu, Y. Transglutaminase-modified wool keratin film and its potential application in tissue engineering. Eng. Life Sci. 2013, 13, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Thin-film nanofibrous composite membranes containing cellulose or chitin barrier layers fabricated by ionic liquids. Polymer 2011, 52, 2594–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusiana; Reichl, S.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Keratin film made of human hair as a nail plate model for studying drug permeation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Yun, Y.J.; Cho, H.; Lee, K.S.; Park, M.; Kim, H.Y.; Son, D.I. Environment-friendly, durable, electro-conductive, and highly transparent heaters based on silver nanowire functionalized keratin nanofiber textiles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 7847–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Nguyen, A.; Allen, A.; Zoldan, J.; Huang, Y.; Chen, J.Y. Regenerated cellulose micro-nano fiber matrices for transdermal drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimmelsmann, N.; Grothe, T.; Homburg, S.V.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning and stabilization of chitosan nanofiber mats. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 254, 102006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluigi, A.; Corbellini, A.; Rombaldoni, F.; Mazzuchetti, G. Wool-derived keratin nanofiber membranes for dynamic adsorption of heavy-metal ions from aqueous solutions. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Li, X.; Song, T. Electrospinning and crosslinking of zein nanofiber mats. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Sun, C.; Wang, D.; Gao, Y. The Interaction between Zein and Lecithin in Ethanol-Water Solution and Characterization of Zein-Lecithin Composite Colloidal Nanoparticles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0167172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yu, H.-Y.; Gu, Z.-G.; Si, L.; Liu, Q.-C.; Hu, X. Impact of calcium chloride concentration on structure and thermal property of Thai silk fibroin films. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 851–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, F.; Torculas, M.; Lofland, S.; Hu, X. Formic Acid Regenerated Mori, Tussah, Eri, Thai, and Muga Silk Materials: Mechanism of Self-Assembly. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 6361–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paquet-Mercier, F.; Lefèvre, T.; Auger, M.; Pézolet, M. Evidence by infrared spectroscopy of the presence of two types of β-sheets in major ampullate spider silk and silkworm silk. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, T.; Freddi, G.; Innocenti, R.; Tsukada, M. Biodegradation of Bombyx mori silk fibroin fibers and films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 91, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogale, A.A.; Cunningham, P.; Dawson, P.L.; Acton, J.C. Viscoelastic, Thermal, and Microstructural Characterization of Soy Protein Isolate Films. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 672–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Tg (°C) | Td1 (°C) | Td2 (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mori100Soy0 | 179.1 | 262.7 | N/A | [44] |
| Mori90Soy10 | 177.8 | 264.0 | N/A | |
| Mori75Soy25 | 175.1 | 265.1 | N/A | |
| Mori50Soy50 | 174.1 | 266.9 | 298.6 | |
| Mori25Soy75 | 173.8 | 268.0 | 302.8 | |
| Mori10Soy90 | 168.6 | 287.1 | N/A | |
| Thai100Soy0 | 218.2 | 264.8 | N/A | [44] |
| Thai90Soy10 | 198.1 | 265.5 | N/A | |
| Thai75Soy25 | 186.7 | 265.3 | N/A | |
| Thai50Soy50 | 186.0 | 259.4 | N/A | |
| Thai25Soy75 | 174.7 | 290.2 | N/A | |
| Thai10Soy90 | 167.2 | 292.9 | N/A | |
| Muga100Soy0 | 212.8 | 338.9 | N/A | [44] |
| Muga90Soy10 | 191.2 | 348.0 | N/A | |
| Muga75Soy25 | 190.6 | 346.7 | N/A | |
| Muga50Soy50 | 185.4 | 294.0 | 344.8 | |
| Muga25Soy75 | 181.2 | 287.6 | 342.7 | |
| Muga10Soy90 | 179.8 | 286.4 | 340.8 | |
| Tussah100Soy0 | 231.7 | 348.0 | N/A | [44] |
| Tussah90Soy10 | 201.3 | 345.4 | N/A | |
| Tussah75Soy25 | 198.2 | 343.4 | N/A | |
| Tussah50Soy50 | 181.5 | 294.7 | 341.6 | |
| Tussah25Soy75 | 179.8 | 288.9 | 340.8 | |
| Tussah10Soy90 | 178.4 | 288.3 | 337.6 | |
| Eri100Soy0 | 220.1 | 344.6 | N/A | [44] |
| Eri90Soy10 | 183.7 | 353.1 | N/A | |
| Eri75Soy25 | 185.9 | 308.2 | 358.8 | |
| Eri50Soy50 | 181.5 | 293.9 | 357.5 | |
| Eri25Soy75 | 178.0 | 283.2 | N/A | |
| Eri10Soy90 | 177.7 | 292.9 | N/A | |
| Soy100 | 135.7 | 279.3 | N/A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poluri, N.; Gough, C.R.; Perrotta, J.; Pinto, J.; Cohen, M.; Sanderlin, S.; Velardo, C.; Barca, A.; Hu, X. Silk-Soy Alloy Materials: Influence of Silk Types (Mori, Thai, Muga, Tussah, and Eri) on the Structure, Properties, and Functionality of Insect–Plant Protein Blends (II). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104563
Poluri N, Gough CR, Perrotta J, Pinto J, Cohen M, Sanderlin S, Velardo C, Barca A, Hu X. Silk-Soy Alloy Materials: Influence of Silk Types (Mori, Thai, Muga, Tussah, and Eri) on the Structure, Properties, and Functionality of Insect–Plant Protein Blends (II). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(10):4563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104563
Chicago/Turabian StylePoluri, Nagireddy, Christopher R. Gough, Joseph Perrotta, Joseph Pinto, Maxwell Cohen, Steven Sanderlin, Christopher Velardo, Anthony Barca, and Xiao Hu. 2025. "Silk-Soy Alloy Materials: Influence of Silk Types (Mori, Thai, Muga, Tussah, and Eri) on the Structure, Properties, and Functionality of Insect–Plant Protein Blends (II)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 10: 4563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104563
APA StylePoluri, N., Gough, C. R., Perrotta, J., Pinto, J., Cohen, M., Sanderlin, S., Velardo, C., Barca, A., & Hu, X. (2025). Silk-Soy Alloy Materials: Influence of Silk Types (Mori, Thai, Muga, Tussah, and Eri) on the Structure, Properties, and Functionality of Insect–Plant Protein Blends (II). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(10), 4563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26104563








